Quantum Approximation for Wireless Scheduling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Bra–Ket Notation
2.2. Basic Quantum Gates
2.3. Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA)
3. Wireless Scheduling Modeling Using Maximum Weight Independent Set (MWIS)
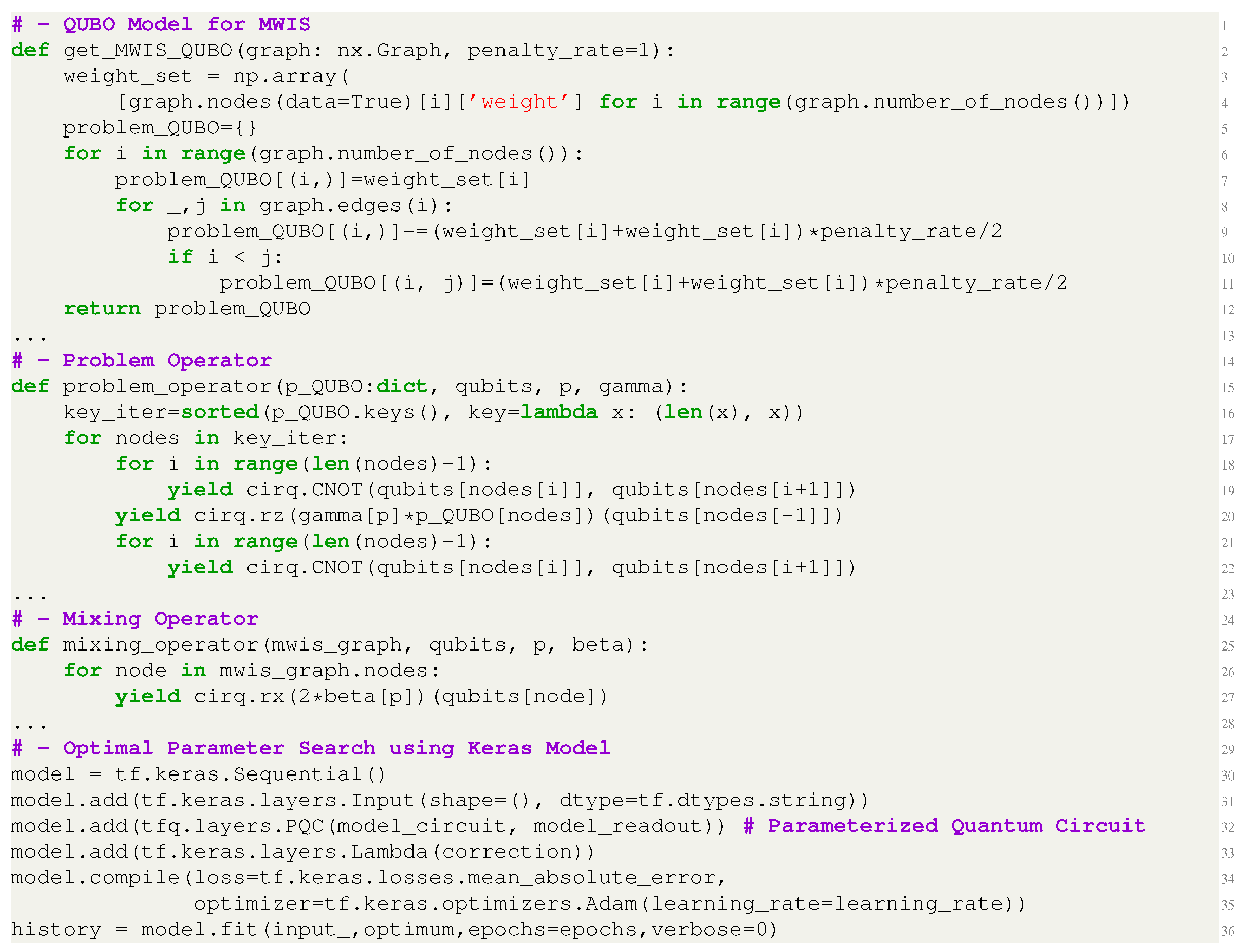
4. Quantum Approximate Optimization for Scheduling (QAOS)
4.1. Design of the Problem Hamiltonian
4.1.1. Design of the Objective Hamiltonian
4.1.2. Design of the Constraint Hamiltonian
4.2. Design of the Mixing Hamiltonian
4.3. Apply to QAOA Sequence
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Software Implementation
5.2. Experiments
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arute, F.; Arya, K.; Babbush, R.; Bacon, D.; Bardin, J.C.; Barends, R.; Biswas, R.; Boixo, S.; Brandao, F.G.; Buell, D.A.; et al. Quantum Supremacy using a Programmable Superconducting Processor. Nature 2019, 574, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhi, E.; Goldstone, J.; Gutmann, S.; Lapan, J.; Lundgren, A.; Preda, D. A Quantum Adiabatic Evolution Algorithm Applied to Random Instances of an NP-Complete Problem. Science 2001, 292, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandala, A.; Mezzacapo, A.; Temme, K.; Takita, M.; Brink, M.; Chow, J.M.; Gambetta, J.M. Hardware-Efficient Variational Quantum Eigensolver for Small Molecules and Quantum Magnets. Nature 2017, 549, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyer, M.; Wiese, U.J. Computational Complexity and Fundamental Limitations to Fermionic Quantum Monte Carlo Simulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 170201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, E.; Goldstone, J.; Gutmann, S. A Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.4028. [Google Scholar]
- Preskill, J. Quantum Computing in the NISQ Era and Beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, J. The Useful Quantum Computing Techniques for Artificial Intelligence Engineers. In Proceedings of the 34th IEEE ICOIN, Barcelona, Spain, 7–10 January 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, S.T.; Choi, S.; Pichler, H.; Lukin, M.D. Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm: Performance, Mechanism, and Implementation on Near-Term Devices. Phys. Rev. X 2020, 10, 021067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, J. A Tutorial on Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA): Fundamentals and Applications. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE ICTC, Jeju Island, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, S.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Wyne, S.; Patwary, M.N.; Asaduzzaman, M. Quantum Machine Learning for 6G Communication Networks: State-of-the-Art and Vision for the Future. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 46317–46350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, F.; Khandaker, M.R.; Wong, K.K.; Imran, M.A.; Bennis, M.; Debbah, M. A Speculative Study on 6G. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, H.; Mogensen, P.E. Communications in the 6G Era. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 57063–57074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Kawamoto, Y.; Kato, N.; Liu, J. Future Intelligent and Secure Vehicular Network Toward 6G: Machine-Learning Approaches. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Caire, G.; Molisch, A.F. Quality-Aware Streaming and Scheduling for Device-to-Device Video Delivery. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 24, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basagni, S. Finding a Maximal Weighted Independent Set in Wireless Networks. Telecommun. Syst. 2001, 18, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalidis, I.C.; Huang, F.; Lai, W. A Message-Passing Algorithm for Wireless Network Scheduling. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2015, 23, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, S.; Shah, D.; Willsky, A.S. Message Passing for Maximum Weight Independent Set. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2009, 55, 4822–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapp, H.P. The Copenhagen Interpretation. Am. J. Phys. 1972, 40, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.J.; Taylor, T.S.; Slaten, J.C. On the Probability Amplitude of Quantum Entanglement and the Pauli Matrices. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, S.; Wang, Z.; O’Gorman, B.; Rieffel, E.G.; Venturelli, D.; Biswas, R. From the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm to a Quantum Alternating Operator Ansatz. Algorithms 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkevich, M.; Weimer, M.; Li, L.; Smola, A.J. Parallelized Stochastic Gradient Descent. In Proceedings of the 24th NIPS, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–9 December 2010; pp. 2595–2603. [Google Scholar]
- Nawi, N.M.; Ransing, M.R.; Ransing, R.S. An Improved Learning Algorithm Based on the Broyden-Fletcher- Goldfarb-Shanno (BFGS) Method for Back Propagation Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE ISDA, Jinan, China, 16–18 October 2006; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Streif, M.; Leib, M. Training the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm without Access to a Quantum Processing Unit. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hadfield, S.; Jiang, Z.; Rieffel, E.G. Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm for MaxCut: A Fermionic View. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 022304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, S. On the Representation of Boolean and Real Functions as Hamiltonians for Quantum Computing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.09130. [Google Scholar]
- Broughton, M.; Verdon, G.; McCourt, T.; Martinez, A.; Yoo, J.; Isakov, S.V.; Massey, P.; Niu, M.Y.; Halavati, R.; Peters, E.; et al. TensorFlow Quantum: A Software Framework for Quantum Machine Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.02989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Improved Adam Optimizer for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 26th IEEE/ACM IWQoS, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–6 June 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Feo, T.A.; Resende, M.G. Greedy Randomized Adaptive Search Procedures. J. Glob. Optim. 1995, 6, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Togasaki, M.; Yamazaki, K. A Note on Greedy Algorithms for the Maximum Weighted Independent Set Problem. Discret. Appl. Math. 2003, 126, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, E.; Harrow, A.W. Quantum Supremacy through the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07674. [Google Scholar]
- Bravyi, S.; Gosset, D.; König, R. Quantum Advantage with Shallow Circuits. Science 2018, 362, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| QAOS, | QAOS, | QAOS, | Greedy | Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69.50% | 49.67% | 42.83% | 33.83% | 15.17% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, J. Quantum Approximation for Wireless Scheduling. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207116
Choi J, Oh S, Kim J. Quantum Approximation for Wireless Scheduling. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(20):7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207116
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jaeho, Seunghyeok Oh, and Joongheon Kim. 2020. "Quantum Approximation for Wireless Scheduling" Applied Sciences 10, no. 20: 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207116
APA StyleChoi, J., Oh, S., & Kim, J. (2020). Quantum Approximation for Wireless Scheduling. Applied Sciences, 10(20), 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207116






