Abstract
In this study, the specific amplifications of six denitrification-associated genes using PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer sets were compared. Thereafter, the PCR primer sets that were determined to be suitable for each denitrification-associated gene were used to test samples from sixteen aqueous environments (three from groundwater, three from stream water, and ten from hyporheic zone water). The specific amplification was determined using PCR primer sets for denitrification-associated genes and nucleic acids from eleven types of strains. NosZ was the most frequently amplified gene from the nucleic acid of type, with a specific band seen in all eleven strains. The specific band amplification and PCR time of the strains were analyzed to select one PCR primer set for each gene. The selected PCR primer sets were used to analyze sixteen samples from the aqueous environments in which denitrifying microorganisms were expected to be present. Specific bands of narG, nirS, and nosZ were most frequently observed in the hyporheic water samples. The results showed that microorganisms containing nirG (involved in the reduction of nitrate to nitrite), nirS (involved in the reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide), and nosZ (involved in the reduction of nitrous oxide to nitrogen gas) were the most abundant in the hyporheic zone samples used in this study.
1. Introduction
The nitrogen cycle is one of the most important nutrient cycles in terrestrial ecosystems and is carried out via nitrogen fixation, mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification [1]. The nitrogen cycle involves biological and non-biological processes, where the biological processes usually involve microorganisms [2]. Denitrification is the last step of the nitrogen cycle, in which the nitrogen in fixed forms, such as nitrates, returns to the atmosphere in the form of nitrogen gas. This process can prevent nitrate contamination of groundwater and surface water that arises from the overuse of nitrogen fertilizers [3].
Microorganisms involved in the nitrogen cycle are labeled as either nitrogen-fixing, nitrifying, or denitrifying microorganisms according to their characteristics [2]. Of these, denitrifying microorganisms are typically found in the soil, mud, sewage, sea, and wetland, and are phylogenetically diverse, belonging to Firmicutes [4], Actinobacteria [5], Proteobacteria [6], Archaebacteria [7], and fungi [8,9]. In genetic and biochemical studies, six genes, including nirK, nirS, and nosZ, have been reported to be involved in the denitrification process (Figure 1, [9,10]).
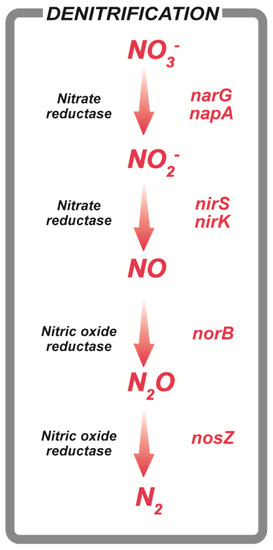
Figure 1.
Genes related to denitrification in the nitrogen cycle.
It has been reported that non-culture-based methods are generally used to analyze denitrifying microorganisms in soil and water environments [11,12,13,14]. Methods used to analyze the diversity of microorganisms include denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE), cloning, and pyrosequencing [15,16,17,18]. The analysis of denitrifying communities typically uses a molecular approach [19,20,21,22].
The hyporheic zone is an environment where the mixing of groundwater and surface water occurs and it is critical for denitrification. Hyporheic exchanges are of great interest because they make the hyporheic zone highly productive and complex environments. In particular, the exchange patterns play an important role in removing contaminants or attenuating contamination under certain conditions with indigenous microbes when contaminants or polluted water pass-through the hyporheic zone. It has been consistently shown that when surface water with a high nitrate concentration is passed through the hyporheic zone, the nitrate-nitrogen concentration of the surface water is decreased by indigenous microorganisms living in hyporheic zones. Therefore, this study aimed to perform comparative analyses and sample testing of PCR primer sets for each denitrification-associated gene for the analysis of denitrifying microorganisms in environmental samples extracted from hyporheic zones.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
The study area is situated in the Haean basin located in the northeast part of Yanggu County, Kangwon province, northeastern South Korea, along the demilitarized zone (DMZ) between South and North Korea (Figure 2a) [23,24]. Geologically, the “punchbowl” shaped basin is composed of Precambrian gneiss at the higher elevations, with a Jurassic biotite granite intrusion that was subsequently eroded in the central portion of the catchment. The basin consists of highly weathered biotite granite at the basin’s bottom, surrounded by metamorphic rocks forming mountain ridges. [24]. The average annual precipitation in the Haean basin is 1520 mm, with approximately 70% of the rainfall occurring during the monsoon period in June and July [23,24].
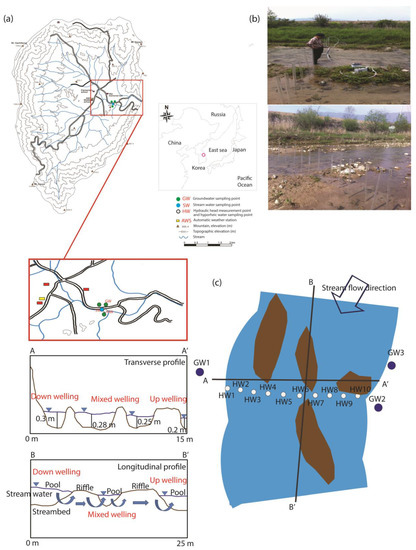
Figure 2.
A map showing the sampling locations. (a) Location of study area and sampling points (b) Installed piezometers (c) Points of monitoring wells and piezometers
The entire basin has an area of 64 km2 and is a major agricultural area. Rice paddies cover 11.4% of the arable land, whereas the four most important dryland crops (radish, bean, potato, and cabbage) account for approximately 30% of the cropped area [25]. The use of total fertilizer for crops was 181–259 kg·N·ha−1·yr−1 in 2010, 248 kg·N·ha−1·yr−1 in 2011, and 279 kg·N·ha−1·yr−1 in 2012 [24]. Tributaries draining this area flow into Lake Soyang and ultimately the Han River, providing a major drinking water source to the metropolitan city of Seoul [24]. Groundwater exists throughout the top of the weathered rock and the bottom of the fractured bedrock. The aquifer thickness of this study area was 10 m and the water table ranged from 1.1–8.0 m below the surface in the dry season and from 0.8–5.5 m below the surface in the wet season [24]. The Darcian velocity of the groundwater was estimated to be 2.1 × 10−5–3.0 × 10−5 cm·s−1. The experimental investigation focused on the stream Mandae, a tributary of Soyang. The study site was approximately 25 m long and 15 m wide. The streambed was highly permeable. The investigated stream’s reach was characterized by longitudinal sequences of pools and riffles (Figure 2a). The stream was well connected to the aquifer. Therefore, the stream was chosen based on its representativeness regarding characteristic hydro-geomorphic streambed conditions, such as groundwater upwelling and stream water downwelling (Figure 2b). The calculated hyporheic zone depths of the site using heat transfer analysis ranged from 9.2 to 15 cm [22,23]. Moreover, ten hyporheic water samples, three stream water samples, and three groundwater samples were collected in December 2018. At the transect (Figure 2b,c), a total of 10 piezometers were inserted at a 0.1 m depth [23] beneath the streambed adjacent to each seepage meter installation point at regular intervals (Figure 2c). Before water sampling took place, hyporheic water extraction was performed using a peristaltic pump (Precise peristaltic pump BT100-2J, Logger precision pump Co., Ltd., West Yorkshire, UK) until a specific volume had been extracted and the physicochemical parameters had stabilized (Figure 2c). Water samples were collected in acid-washed, 2000 mL polypropylene bottles for microbial analysis after filtration through 0.20 µm membrane filters.
2.2. Type Strain Collection and Nucleic Acid Extraction
Eleven type strains of denitrifying bacteria were obtained from the Korean Agricultural Culture Collection (KACC) and cultured according to the culture conditions provided by the KACC (Table 1). One inoculation loop of cultured strains was mixed in a 1.5 mL tube that contained 500 µL of sterilized distilled water and the mixture was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 min to collect cells. Nucleic acid was extracted using a FastDNA® SPIN Kit (MP Biomedicals, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and quantified using a NanoDropTM 2000C (Thermo Fisher, MA, USA).

Table 1.
Information regarding the collected denitrification microorganisms.
2.3. Comparison of the PCR Primers for Denitrification-Associated Genes
For the denitrification-associated genes, narG, napA, nirS, nirK, norB (cnorB and qnorB), and nosZ were selected. For the amplification of each gene, five primer sets for narG, two primer sets for napA, five primer sets for nirS, five primer sets for nirK, five primer sets for norB (three sets for cnorB and two sets for qnorB), and five primer sets for nosZ were analyzed. For the PCR, 10 ng/µL of nucleic acid extracted from 11 type strains was used as the template DNA. The PCR mixture had a total volume of 20 µL and contained AccuPower® HotStart PCR PreMix (Bioneer, Seoul, Korea), 1 µL of template nucleic acid, 2 µL of primers (1 µL of forward, 1 µL of reverse; concentrations were based on the conditions used in the references (Table S1)), and 17 µL of nucleic-acid-free water. The PCR was performed according to the thermal conditions described in the references listed (Table S1). The amplification of specific bands of each denitrification-associated gene (number of type strains detected) and detection time was compared and analyzed. For each gene, the PCR primer sets that detected the highest number of type strains were selected.
2.4. PCR Amplification Testing of Denitrification-Associated Genes
To test whether denitrification-associated genes were amplified from the samples using a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany), where the nucleic acid was extracted from sixteen aqueous environmental samples (three groundwater, three stream water, and ten hyporheic water samples) taken from areas where denitrifying microorganisms were expected to be present. The extracted nucleic acid was quantified using a NanoDropTM 2000C and used as template DNA for the sample testing. The PCR primer sets selected for each denitrification-associated gene were applied to analyze the amplification of specific bands. The PCR mixture had a total volume of 20 µL and contained AccuPower® HotStart PCR PreMix (Bioneer, Seoul, Korea), 1 µL of template nucleic acid, 2 µL of primers (1 µL of forward, 1 µL of reverse), and 17 µL of nucleic-acid-free water. The PCR was performed according to the conditions described in the references listed (Supplementary Table S1).
3. Results
3.1. Type Strain Collection and Nucleic Acid Extraction
All 11 type strains were cultured and activated according to the conditions provided by the KACC and the concentration range of the extracted nucleic acid was determined to be approximately 10.5–88.9 ng/µL.
3.2. Comparison of PCR Primers for Denitrification Associated Genes
The specific amplification of six denitrification-associated genes (narG, napA, nirS, nirK, norB (cnorB and qnorB), and nosZ) from 11 type strains was determined using PCR primer sets. For denitrification-associated narG, primer sets 2, 5, and 3 formed a specific band in six type strains, two type strains, and one type strain, respectively, whereas only non-specific bands in some of the type strains were observed for primer sets 1 and 4. For napA, only primer set 1 formed a specific band in three strains and no reaction was observed for primer set 2. For nirS, primer set 1 formed a specific band in five strains but multiple non-specific bands were formed, making differentiation difficult. Although specific reactions were observed for primer sets 2 and 5 in four strains, several non-specific bands were observed with primer set 5. For nirK, sets 1 and 2, sets 3 and 5, and set 4 formed a specific band in four strains, three strains, and two strains, respectively, and multiple non-specific bands of strong intensity were observed for primer sets 1, 3, 4, and 5. For norB, primer sets 2 and 3 and primer set 1 formed a specific band in four strains and three strains for cnorB, respectively, whereas primer sets 4 and 5 formed a specific band in three strains and two strains, respectively, for qnorB. Additionally, multiple bands and non-specific bands were observed for five sets. For nosZ, primer sets 4, 1, 2, and primer sets 3 and 5 formed a specific band in eleven strains, ten strains, seven strains, and three strains, respectively. Multiple bands were observed for primer set 1 and non-specific bands were observed in several reactions for primer set 4 (Table 2). In addition, the PCR time for each denitrification-associated gene was approximately 60–140 min (see the Supplementary Materials).

Table 2.
Comparison of denitrification-associated gene PCR primer sets using eleven denitrifying bacteria type strains.
3.3. PCR Amplification Testing of Denitrification-Associated Genes
Efficient PCR primer sets for each denitrification-associated gene were selected based on the formation of specific bands and the number of type strains detected. The PCR amplification experiments for six denitrification-associated genes from sixteen aqueous environmental samples showed the amplification of denitrification-associated genes in fifteen samples. Of the six denitrification-associated genes, a specific band for narG was most frequently observed (fourteen samples), followed by nosZ (13 samples), nirS (13 samples), and napA (11 samples). Specific bands for nirK and cnorB were observed in fewer samples (Table 3).

Table 3.
PCR primer set validation of denitrification-associated genes using sixteen aqueous environmental samples.
NosZ has been reported to be more related to nirS than to nirK [26]. In this study, fifteen samples were observed to have a denitrification-associated gene that might be negatively correlated with nitrous oxide emission, which might allow for a reduction in the levels of nitrous oxide and nitrogen dioxide.
4. Discussion
The nitrogen cycle is a microorganism-mediated process that occurs in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and is linked between these systems. If nitrogen transported to aquatic ecosystems from terrestrial ecosystems is not cycled, it leads to environmental issues, including eutrophication and an excess of dissolved oxygen [27]. The process of nitrogen removal from wastewater from livestock sheds and chicken houses takes place in aerobic and anaerobic environments. In an aerobic environment, ammonia is oxidized to nitric acid by autotrophic nitrifying microorganisms, and in an anaerobic environment, nitric acid is reduced to nitrogen gas by heterotrophic denitrifying microorganisms [28]. Of the genes identified by the amplification of specific bands from a large number of samples, nosZ is known to code for nitrous oxide reductase, which reduces nitrous oxide to nitrogen gas; nirS has been reported to code for nitrite reductase, which reduces nitrogen dioxide to nitric oxide [9]. It has been reported that nirK is positively correlated [29] and nirS is negatively correlated [30] with nitrous oxide emission.
Key denitrifying microbial communities mainly consist of microorganisms that belong to the α, β, and γ subclasses of Proteobacteria [31], where the key denitrifying microorganism genera are Agrobacteria, Campylobacter, Morococcus, Oligella, and Sphingobacterium [32]. Although denitrification by microorganisms generally occurs under anaerobic conditions, it has been reported to also occur in microaerophilic and aerobic conditions by various bacteria and fungi [33].
Functional gene-based approaches for studying microorganismal communities may be useful for the advancement of ecological theory and predictions regarding how microorganisms respond to environmental change [34]. Although DGGE, temperature gradient gel electrophoresis, and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism allow for seasonal and regional analysis of a large number of samples, these techniques have drawbacks as only a small number of genes may be cloned and sequence analysis needs to be performed. It has been reported that the use of microarrays (DNA/RNA chips) for the analysis of denitrifying microorganism diversity allows for the analysis of specific microbial communities in nitrogen cycle processes [15].
5. Conclusions
The hydrogeological patterns in hyporheic zones affect all microbial communities, including denitrifiers. In this study, we performed comparative analyses and sample testing of PCR primer sets for each denitrification-associated gene for the analysis of denitrifying microorganisms in environmental samples extracted from hyporheic zones. The specific amplification of six denitrification-associated genes using PCR primer sets was compared.
Thereafter, the PCR primer sets that were determined to be suitable were selected for each denitrification-associated gene and tested using sixteen environmental samples (three groundwater, three surface water, and ten hyporheic water samples). The specific amplification was determined using PCR primer sets for denitrification-associated genes and nucleic acid from eleven type strains. NosZ was found to be the most frequently amplified gene from the nucleic acid of type strains, with a specific band formed in all eleven type strains. The specific band amplification and PCR time of the type strains were analyzed to select one PCR primer set for each gene. The selected PCR primer sets were used to analyze 16 aqueous environmental samples in which denitrifying microorganisms were expected to be present, and the results showed that specific bands of narG, nirS, and nosZ were most frequently observed. Therefore, we believe that microorganisms with narG, which is involved in the reduction of nitrate to nitrite; nirS, which is involved in the reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide; and nosZ, which is involved in the reduction of nitrous oxide to nitrogen gas were the most abundant in the aqueous environmental samples used in this study.
NosZ was the most frequently amplified gene from the nucleic acid of type strains, with a specific band formed in all eleven type strains. The specific band amplification and PCR time of the type strains were analyzed to select one PCR primer set for each gene. However, this case report showed that for the samples from different water environments, even the best-performing primer pair for each gene failed to amplify more than about 50% of a selection of denitrifying strains, except that for nosZ. Further studies on denitrification genes related to water environment samples, such as hyporheic zones, are needed.
The selected PCR primer sets were used to analyze three groundwater, three stream water, and ten hyporheic water samples in which denitrifying microorganisms were expected to be present, and the results showed that specific bands of narG, napA, nirS, and nosZ were most frequently observed in the hyporheic zone water samples. We expect that the PCR primer sets selected for the denitrification-associated genes in this study may be used to evaluate denitrification by denitrifying microorganisms in response to seasonal and regional changes.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/12/4172/s1, Table S1: PCR primer information of denitrification-associated genes.
Funding
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (grant numbers 2019R1A6A1A03033167, 2019R1I1A2A01057002).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Hayatsu, M.; Tago, K.; Saito, M. Various players in the nitrogen cycle: Diversity and functions of the microorganisms involved in nitrification and denitrification. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.Y.; Kiotz, M.G. The nitrogen cycle. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, R.D. Nitrogen fertilizer effects in nitrogen cycle processes. In Terrestrial Nitrogen Cycles; Clark, F.E., Rosswall, T., Eds.; Swedish Natural Science Research Council: Stockholm, Sweden, 1981; pp. 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty, F.; Garcia, J.L.; Job, C.; Durand, M. Denitrification by Bacillus licheniformis. Can. J. Microbiol. 1978, 24, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoun, H.; Kano, M.; Baba, I.; Takaya, N. Denitrification by actinomycetes and purification of dissimilatory nitrite reductase and azurin from Streptomyces thioluteus. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4413–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, T.N.; Betlach, H.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Numerically dominant denitrifying bacteria from world soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancinelli, R.L.; Hochstein, L.I. The occurrence of denitrification in extremely halophilic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1986, 35, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Takimoto, A.; Suzuki, S.; Maruo, F.; Shoun, H. Denitrification, a novel type of respiratory metabolism in fungal denitrification. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 5, 16263–16267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippot, L.; Hallin, S. Molecular analyses of soil denitrifying bacteria. In Molecular Techniqeus for Soil, Rhizosphere; Cooper, J.E., Rao, J.R., Eds.; CAB International: Willingford, UK, 2006; pp. 146–165. [Google Scholar]
- van Spanning, R.J.M.; Richardson, D.J.; Ferguson, S.J. Introduction to the biochemistry and molecular biology of denitrification. In Biology of the Nitrogen Cycle; Bothe, H., Ferguson, S.J., Newton, W.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Braker, G.; Tiedje, J.M. Nitric oxide reductase (norB) genes from pure cultures and environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3476–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, C.; Braker, G.; Matthies, D.; Reuter, A.; Engels, C.; Conrad, R. Impact of plant functional group, plant species, and sampling time on the composition of nirK-type denitrifier communities in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, M.; Braker, G.; Dippner, J.; Jürgens, K. Linking denitrifier community structure and prevalent biogeochemical parameters in the pelagial of the central Baltic Proper (Baltic Sea). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 57, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kandeler, E.; Deiglmayr, K.; Tscherko, D.; Bru, D.; Philippor, L. Abundance of narG, nirS, nirK, and nosZ genes of denitrifying bacteria during primary successions of a glacier foreland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5957–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bothe, H.; Jost, G.; Schloter, M.; Ward, B.B.; Witzel, K.P. Molecular analysis of ammonia oxidation and denitrification in natural environments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enwall, K.; Hallin, S. Comparison of T-RFLP and DGGE techniques to assess denitrifier community composition in soil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Pan, G. Abundance, composition and activity of denitrifier communities in metal polluted paddy soils. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Yi, N.; Wang, C.; Di, P.; Yan, S. Variations in abundance and community composition of denitrifying bacteria during a cyanobacterial bloom in a eutrophic shallow lake in China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2017, 32, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.L.; Byrnes, J.E.; Weisman, D.; Colaneri, C. Functional gene pyrosequencing and network analysis: An approach to examine the response of denitrifying bacteria to increased nitrogen supply in salt marsh sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.M.; Salganik, M.; Vega, L.; Pickering, K.D.; Kerkhof, L.J. Replicability of bacterial communities in denitrifying bioreactors as measured by PCR/T-RFLP analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, N.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S. Response of spatial patterns of denitrifying bacteria communities to water properties in the stream inlets at Dianchi Lake, China. Int. J. Genom. 2015, 2015, 572121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kaown, D.; Mayer, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, K.K. Combining pyrosequencing and isotopic approaches to assess denitrification in a hyporheic zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.K.; Lee, J.Y. Numerical verification of hyporheic zone depth estimation using streambed temperature. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kaown, D.; Mayer, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Hyun, Y.; Lee, K.K. Identifying the sources of nitrate contamination of groundwater in an agricultural area (Haean basin, Korea) using isotope and microbial community analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, S.P.; Peiffer, S.; Gebauer, G. Origin and fate of nitrate runoff in an agricultural catchment: Haean, South Korea–Comparison of two extremely different monsoon seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Shimomura, Y.; Akiyama, H.; Hayatsu, M. Responses of denitrifying bacterial communities to short-term waterlogging of soils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, S.E.G.; Gregory, S.V.; Grimm, N.B.; Johnson, S.L.; McDowell, W.H.; Meyer, J.L.; Valett, H.M.; Webster, J.R.; Arango, C.P.; Beaulieu, J.J.; et al. Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 2008, 452, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, H.S.; Hirai, M.; Shoda, M. Characteristics of ammonium removal by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification by Alcaligenes faecalis No. 4. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.M.; Buchkina, N.; Jhurreea, D.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Hirsch, P.R. Impacts of nitrogen application rates on the activity and diversity of denitrifying bacteria in the Broadbalk Wheat Experiment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuhel, J.; Simek, M.; Laughlin, R.J.; Bru, D.; Cheneby, D.; Watson, C.J.; Philippot, L. Insights into the effect of soil pH on N2O and N2 emissions and denitrifier community size and activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovski, S. Structure and Function of Microbial Communities in Constructed Wetlands—Influence of Environmental Parameters and Pesticides on Denitrifying Bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2009; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Coyne, M.S.; Lal, R.; Stewart, B.A. Soil Nitrogen Uses and Environmental Impacts; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 95–139. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek, A.; Kozarek, J.L.; Hondzo, M.; Lurndahl, N.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Wang, P.; Staley, C. Environmental drivers of denitrification rates and denitrifying gene abundances in channels and riparian areas. Water Res. Res. 2017, 53, 6523–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.L.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Whitaker, R.J. Microbial biogeography: From taxonomy to traits. Science 2008, 320, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).