Abstract
The production of ethanol from sugarcane or molasses generates vinasse, a residue rich in organic matter and minerals. Vinasse is often used in fertilization and irrigation practices, which may be linked to negative environmental outcomes if excess is applied. Herein, we introduce a novel alternative to the treatment of vinasse promoting the reduction in Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) levels, phenolic compounds, and its mineral content through the coupling of ozone treatment, anaerobic digestion, and the aerobic growth of fungi. The ozone treatment is able to remove about 30% of the total COD, and deplete the concentration of phenolic compounds, while anaerobic digestion produces biogas and generates vinasse digestate, which is less biorecalcitrant than raw vinasse. The aerobic fungal growth generates oleaginous fungal biomass and promotes over 80% of Kjeldahl-Nitrogen in the vinasse. If vinasse were treated following the sequence of anaerobic digestion, aerobic fungal growth, and ozone treatment, the effluent would have about 95% of the COD decreased, complete removal of phenolic compounds, and over 80% of Kjeldahl-Nitrogen.
1. Introduction
The production of ethanol through the Melle-Boinot process represents a well-established industry in Brazil, having contributed significantly to the energy security of the country over the past decades [1]. Among the residues generated within the process, vinasse is often regarded as a by-product with extensive environmental implications [2]. Vinasse is generated as one the bottom fractions of the distillation columns within an ethanol plant [3], and it is composed by the non-volatile compounds present in the ethanol fermentation tank, as yeast and sugarcane proteins, cell debris, phenolic structures, and other complex molecules [4]. The major concerns regarding the environmental implications of vinasse are directly related to its utilization as a fertirrigation agent [2]. Fertirrigation, i.e., fertilization coupled with irrigation, is a common practice in sugarcane fields located nearby ethanol distilleries, as the nutrients present in vinasse contribute to lowering the costs of chemical fertilizers and water applied to the sugarcane cultures [5]. The conditions in which vinasse is applied to sugarcane fields, however, have been reported to increase Chemical Oxygen Demands (COD) levels in groundwater reservoirs and to leaching effects of vinasse-derived ions to water bodies in Brazil [5].
There have been numerous attempts to the development of alternatives to the use of vinasse [3]. Considering its composition rich in organic matter, a number of biological processes to convert the nutrients present in vinasse to microbial biomass have been developed. Different species of filamentous fungi have been cultured with vinasse-based media, mostly aiming towards the production of single-cell protein. A Generally-Regarded-as-Safe (GRAS) strain of Rhizopus oligosporus was successfully cultured in vinasse-rich media, generating a protein-rich biomass, with approximately 50% of dry weight being composed by feed-grade protein, promoting a removal of about 80% of COD levels in the vinasse medium utilized in the assays [6,7]. Aspergillus oryzae and Neurospora intermedia have also been successfully cultured in vinasse, producing fungal biomass with protein contents reaching around 45% [8]. Anaerobic treatment of vinasse has also been widely studied for decades, being responsible, for example, for the implementation of an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) as a demonstration unit since mid-1980’s in Brazil [9]. Anaerobic Digestion practices of sugarcane vinasse in Brazil are relatively scarce to date, but may represent significant economic gains to ethanol plants, given the biogas produced and the reduction of organic load in vinasse after the AD treatment. Common concerns related to AD of vinasse regard the production of H2S-rich biogas, and the imbalance of nutrients, which often require supplementation for optimal performance. The economics of anaerobic digestion operations in vinasse, however, have been linked to potential extensive energy generation within a distillery, being able to replace up to 12% of the bagasse used in combined power and heat operations [5].
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP) represent a wide array of wastewater treatment alternatives. The principle of most AOP techniques is involved with the high reactivity of radicals generated, which promotes oxidation of all sorts of pollutants and recalcitrant components in wastewater [10]. Multiple AOP have been described in the literature aiming to degrade molecules that present are little to no biodegradable, including those based in ultraviolet irradiation (UV), Fenton reaction, and the oxidizing power of peroxides [11]. The main oxidizing agent present in AOP treatments is the hydroxyl radical (HO•), which act as a powerful and non-selective oxidizing agent that is able to cleave biorecalcitrant bonds and structures [12]. Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive, and are produced in situ, usually through the combination of strong oxidizing agents, visible or ultraviolet radiations, as well as through the utilization of metal ions [13]. Among the wide array of AOP techniques available in the market, ozone often stands as one of the most used and studied, due to the low-capital and operating costs, as well as to the low volume of hazardous waste generated [14].
In this sense, this article aims to evaluate the possibility of serialization of ozone treatment of sugarcane vinasse considering the possibilities of aerobic growth using a filamentous fungal species, Mucor circinelloides, and AD. We evaluate a few possibilities of sequential treatment: (i) anaerobic digestate as a substrate for aerobic fungal growth followed by ozonization; (ii) anaerobic digestate as a substrate for fungal growth; and (iii) ozone treatment of vinasse followed by aerobic fungal growth. In this sense, we try to provide feasible alternatives to the sugarcane ethanol industry to reduce its water usage, providing a potential partial recirculation of water to the system, and simultaneously the generation of biogas and fungal biomass.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vinasse and Microorganism
Vinasse was gently donated by the São Martinho Iracema plant (Iracemápolis, Brazil). The same plant, which operates a pilot-size UASB (Upflow-Anaerobic Sludge Blanket), also donated the vinasse digestate used in this study. The samples were maintained at −20 °C prior to use. The vinasse provided was obtained from an early to mid-season sugarcane batch from a plant operating on an adapted Melle-Boinot process using residual sugar molasses as feedstock for the ethanol production. Vinasse and vinasse digestate present the composition described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characterization of Vinasse and Vinasse Digestate used in the study.
Mucor circinelloides URM 4182 strain was used as fungal species for aerobic fermentation assays. The strain was obtained from the Mycology Bank at the Federal University of Pernambuco (Recife, Brazil). The URM 4182 is maintained at the Biocatalysis Laboratory at the Engineering School of Lorena at the University of São Paulo with periodic conservation and propagation using Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium.
2.2. Ozone Assays and Pre-Treatment of Vinasse
The ozone treatment assays were conducted using an adaptation from Cortez et al. [15] using operational volumes of 250 mL, with a magnetic stirrer and ozone pumping through a silicone tube coupled to the bottom of the flask. Ozone was generated via the conversion of O2 to O3 through an electric discharge using double discharge barrier with an Ozone Generator (OzoneLife 3.0 RM, São José dos Campos, Brazil). The assays were conducted with an output of 80 W with an oxygen flow of 1 L min−1, producing O3 at a range of 25 to 30 mg L−1.
Raw vinasse samples were processed at room temperature for 1 h, unless specified differently. Residual ozone in vinasse samples was removed via aeration using an air pump for 1 h. As ozone-treatment of organic-rich substrates promotes the generation of peroxides dissolved in the aqueous phase of the medium [16], and considering the fact that peroxide is toxic to the growth of fungi, peroxide was removed from the treated-vinasse medium using an adaptation to the methodology described by Wu et al. [17], using a Na2CO3 dosage at 20 g L−1 following heating at 90 °C and magnetic stirring for 14 h. The pH of the medium after the carbonate addition reached values around 8.0 to 8.5, which was adjusted to pH 4.5 with HCl 1.0 mol L−1.
2.3. Aerobic Fungal Growth
M. circinelloides URM 4182 was cultured using four different vinasse-based substrates: (i) raw vinasse; (ii) raw vinasse diluted with water in concentrations ranging from 10 vol. % up to 90 vol. %; (iii) vinasse digestate; and (iv) vinasse treated with ozone. As the main goal of the study focuses on the recycling potential of vinasse within the sugarcane-industry, and considering that vinasse alone presents a complex and rich mineral composition, there was no addition of exogenous nutrients to the vinasse samples which could fortify it as a fungal culture medium. All the experiments were carried in an orbital shaker using 250-mL Erlenmeyer flasks with 50 mL of medium operating at 26 °C and 250 rpm for 5 days (120 h), except for the experiments using solely raw vinasse as substrate, in which the factor of cultivation time (ranging from 5 days to 15 days) was tested. In order to avoid microbial contamination, all the flasks, media, and inoculation materials were sterilized using an autoclave at 121 °C for 20 min.
Vinasse digestate was used as obtained, and the vinasse treated with ozone was used in its condition after the treatment described in Section 2.2. Fungal cells were harvested via filtration and were tested for their moisture and lipid contents. Moisture content was determined using a precision balance coupled with infrared (Shimadzu MOC63u) and the content of lipids in the cells was calculated based on the weight of the total lipids extracted and the corresponding cell dry weight. Lipids were extracted following the methodology described by Carvalho et al. [18].
2.4. Analytical Methods
Relevant anions and cations were determined via Ion Chromatography using a Metrohm 940 Professional IC Vario system equipped with a Metrohm A Supp 7 for anions and C4 column for cations, followed by the respective guard columns. Carbonate (5.5 mmol L−1) was used as mobile phase for anions, and Tartaric Acid (600 mg L−1) and Pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (125 mg L−1) were used for cations. Samples were injected via a direct auto-sampling device, model 858 Professional Sample Processor. Data analysis was performed by Metrohm software. The measurement of total solids followed the standard method APHA [19]. Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen was measured via back acid titrimetric quantification of NH4B(OH)4 formed after acid digestion and distillation of the sample following the standard methodology [19]. The measurement of COD proceeded using a spectrophotometric reading at a wavelength of 620 nm of the digested sample following the standard procedure [19]. The concentration of peroxides and ozone was estimated via classical titrimetry using thiosulfate and permanganate as titrants, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Ozone Treatment of Raw Vinasse
The treatment of ozone on raw vinasse promotes the cleavage of complex molecular structures to smaller and less complex structures. Figure 1 summarizes the data on a sequence of treatment following (i) 120 min of ozonation, followed by (ii) aeration of the medium, and (iii) removal of peroxides. Firstly, (i) ozonation promotes the adsorption of ozone into the liquid phase, and the simultaneous rapid disappearance of total phenolic compounds. There is a simultaneous formation of peroxides in the liquid phase observed in correlation with the ozone adsorbed in the liquid phase. The profile of ozone adsorbed into the medium follows common typical curves described in the literature [20]. Aeration of the medium (ii) was applied in order to decrease the concentration of ozone adsorbed into the liquid phase. The 1-h treatment, applied on the second stage of the treatment, does not change significantly the concentration of peroxide nor promotes observable changes in the pH of the medium.
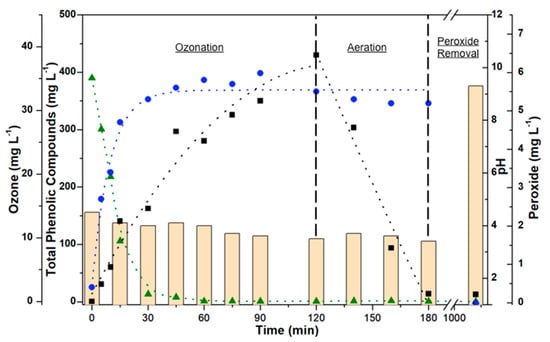
Figure 1.
Curves of ozone adsorption, disappearance of total phenolic compounds, formation of peroxides, and change of pH in the ozone-assisted treatment of vinasse. Dotted lines represent an approximate fit of each curve. Bar: pH value; Green Triangle: Total Phenolic Compounds (mg L−1); Black Square: Adsorbed Ozone (mg L−1); Blue Circle: Peroxide (mg L−1).
The removal of peroxide from the medium (iii) is assisted by a 14-h reaction with carbonate, represented on the right-handside part of Figure 1, in which a substantial increase of the pH is observed until a pH value around 9. The methodology of peroxide removal using Na2CO3 promotes the release of CO2 derived from the decomposition of H2O2 [17].
In addition to the partially recalcitrant COD present in vinasse, the moderately high concentrations of phenolic compounds in vinasse is linked to lower biomass accumulation rates. The ozone treatment is known to degrade phenolic compounds at a fast rate. The initial analysis on the required time for degradation of phenolic compounds promoted the fully degradation of phenolic compounds within 45 min to 1 h of treatment. An increase in the treatment time of the batch ozone systems also promoted higher decolorization of vinasse. Figure 2 demonstrates the color disappearance of vinasse due to ozone treatment ranging from 0 to 240 min.

Figure 2.
Color profile of vinasse subjected to ozone treatment at pH 4.5 with a feed rate of oxygen of 1 L min−1 producing O3 within the concentration range of 25 to 30 mg L−1.
Considering that the concentration of phenolic compounds approaches zero in less than 60 min of treatment, the treatment time of 1 h was selected for subsequent assays. In order to evaluate the effect of pH on the degradation profile of COD and the formation of peroxides, vinasse had its pH adjusted to values of 6.0, 7.5, 9.0, and 10.5. Figure 3 shows the levels of COD and peroxides formed compared to the control (raw vinasse, pH 4.5) and the different pH values. It can be clearly observed higher degradation of COD at higher pH values, with a correlated increase in peroxides formed during the degradation. Martín Santos et al. [12] described the ozone concentration profile on the degradation of an undisclosed vinasse source. The concentration profile of ozone in the liquid phase is given as asymptotic, similar to the one observed herein, demonstrating that it is likely that ozone degrades at a similar rate as the feed rate or it achieves a solid-liquid equilibrium state in which no further ozone can be adsorbed into the liquid phase. Martín Santos et al. [12] described ozone as an efficient method for degrading phenolic compounds in vinasse. Considering that the selectivity of ozone towards phenolic structures is directly related to its molecular forms instead of its free radicals, radical promoters to the medium should be, thus, attenuated. Alkaline conditions are directly linked to the formation of hydroxyl radicals in ozone-bearing conditions. In this sense, in order to selectively degrade phenolic structures via ozone processes, the reaction conditions that provide the highest selectivities should occur in acid media. The pH of vinasse is naturally acid, thus the selected conditions for ozonation of vinasse occurred at its original pH value of 4.5. As depicted in Figure 3, an increase in pH provides higher degradation of COD, however, the operation of the ozone treatment at the natural pH of vinasse provides the desirable complete degradation of the phenolic compounds, while it does not degrade as much of the organic matter that could be utilized to support fungal growth as higher pH values would. In addition, another positive effect of operating the ozone treatment at the natural pH of vinasse is linked to avoid using exogenous alkali to increase the pH to an improved ozone degradation of COD, which would need to be lowered to slightly acid values to support the fungal cell growth.
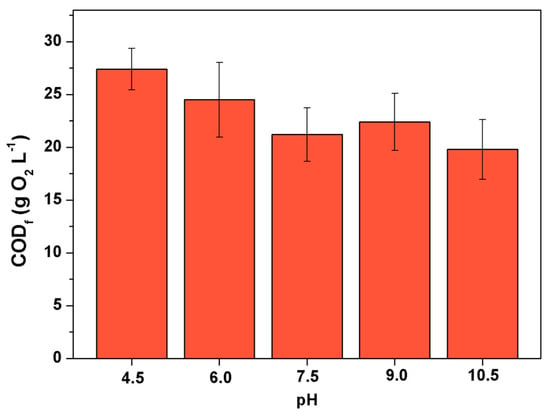
Figure 3.
Effect of pH on ozone-assisted removal of COD. Fixed time of 1 h. CODf: COD level at the end of the treatment.
3.2. Fungal Growth in Raw Vinasse, Vinasse Digestate and Vinasse Pre-Treated by Ozone
The profile of fungal growth in raw vinasse depicts a maximum reduction of approximately 54% of COD in vinasse, while a slightly constant biomass concentration is observed after 5 days of growth, near 3.5 to 4.0 g L−1 of cell dry weight. Though it is not the main focus of this study, it is still interesting to acknowledge the abundance of lipids in the fungal biomass. A maximum concentration of approximately 24% was observed at 15 days of growth. Therefore, while longer times may promote higher degradation and consumption of COD, shorter cultivation times provides fungal biomass with similar properties in regards to cell density and lipid content when compared to the longer times. As from an operational point of view longer cultivation times may become unfeasible if no clear benefit is obtained, the cultivation time of 5 days (120 h) was selected as the time for all the fungal culture assays. Results are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Effect of time on the culture of M. circinelloides URM 4182 on raw vinasse.
An initial assumption of vinasse being an inadequate culture medium for the M. circinelloides URM 4182 strain due to its excess minerals was tested by evaluating the dilution of vinasse from 10 vol. % to 90 vol. %. The results are depicted in Table 3, demonstrating that the dilution of vinasse promotes a correlated decrease of biomass accumulation proportionally with the dilution of vinasse applied. Thus, under the studied condition, vinasse does not impose significant effects on the fungal biomass accumulation that could be attenuated by the dilution of vinasse with water or even by promoting a longer cultivation time.

Table 3.
Effect of dilution of raw vinasse on the culture of M. circinelloides URM 4182.
The use of vinasse digestate as a culture medium for M. circinelloides provided lower biomass accumulation when compared to raw vinasse. Such observation is expected due to the low values of COD present in vinasse digestate. Nevertheless, the use of raw vinasse digestate still demonstrated to be a feasible culture medium for M. circinelloides, with an observable decrease in the lipid accumulation results when compared to raw vinasse. It is possible to correlate the decrease in lipid concentration in regards to the biomass content is due to the lower carbon to nitrogen ratio in digestate, estimated herein through the COD over TKN ratio. As the concentration of COD is decreased in the anaerobic digestion process and the concentration of nitrogen is slightly increased, the COD:TKN ratio is decreased from values within the range of 80 to a culture medium based on raw vinasse to approximately 10 in a digestate-based medium. Considering that nitrogen deficiency is an important factor for inducing the lipogenesis pathway in oleaginous microorganisms, it is expected that decreases in the C:N ratio, herein estimated via the COD:TKN ratio, are linked to lower lipid accumulation in oleaginous microorganisms [21].
The pre-treatment of vinasse using ozone promoted slightly an increase in biomass and lipid accumulation when compared to the control experiment of 5 days. Biomass accumulation was increased by about 20%, and the concentration of lipids in regards to the biomass was also increased by about 25%. A possible explanation for the observed increase in biomass was due to the cleavage of complex substances that contributes to the COD of vinasse, decreasing the biorecalcitrance of the material [22], which promotes better assimilation of the organic matter by the fungus. The visual comparison of results comparing the growth in raw vinasse, vinasse digestate, and on pre-treated vinasse is found in Figure 4.
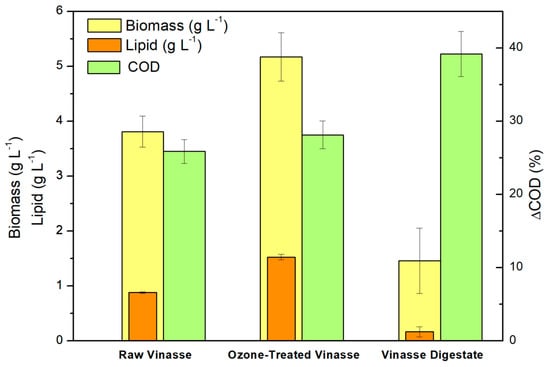
Figure 4.
Comparison of the biomass composition of M. circinelloides URM 4182 using the three tested substrates on 120-h growth, and the removal of COD from the feedstock material promoted by the fungal treatment.
The aforementioned results corroborate with conclusions raised by Nair et al. [8], which described vinasse as a complex and rich medium for fungal growth. Nair et al. [8] tested the use of diluted vinasse on the growth of Neurospora intermedia and Aspergillus oryzae and noticed that exogenous addition of nitrogen or phosphorus to the growth medium did not provided significant improvements in biomass accumulation. It is, however, hard to contrast and compare different vinasse studies, as the composition varies greatly among different batches and particularly among different plants. It is, however, interesting to notice that the diluted vinasse evaluated by Nair et al. [8] served as an efficient growth medium for fungi, similarly to the results observed herein.
3.3. Characterization of Culture Broth
The culture broth for all the tested conditions after cell harvesting presents significantly lower concentrations of COD and minerals. As the organic matter present in vinasse is consumed as carbon source by the fungi, the COD levels decrease in the culture broth. Considering the feasibility of water recirculation within the ethanol industry, the goal of removing the most nutrients as possible from vinasse in order to reutilize it as process water in the fermentation process should, thus, be approachable. In addition to the removal of COD, the high osmotic pressure of vinasse would likely increase cellular stress on the fermenting yeast in case vinasse would be recirculated as process water.
Similarly to the factors above, special attention should be given to the phenolic compounds present in vinasse, as ideally the effluent could be reused in the ethanol fermentation process. Phenolic substances significantly decrease the fermenting capacity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under natural conditions [23]. The removal of phenolic compounds via fungal cultivation, however, has demonstrated to be an unfeasible operation under the studied conditions. Therefore, if only a treatment of vinasse would be based on the growth of M. circinelloides in order to provide culture broth in conditions to be used as recirculation water, such liquid would certainly contain moderately concentrations of phenolic compounds. The literature regarding the utilization of phenolic compounds by Mucorales fungi, as M. circinelloides, is scarce. Nonetheless, it has been reported that a few forms of phenolic compounds, as hydroquinone, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, do not support the cell growth of M. circinelloides CBS 108.16 strain [24].
Though there are studies describing one and two-step anaerobic digestion of vinasse [25,26], the industrial examples integrated to sugarcane-ethanol plants in Brazil is only of one-step digestion. Anaerobic digestion occurs as the biodegradation of part of the organic load of vinasse to produce biogas and biodigested vinasse, i.e., digestate. The hydrolysis and acidogenic stages of anaerobic digestion are responsible for the bacteria-assisted cleavage of complex carbohydrate, proteins, and lipids to lower-size chain molecules. This initial hydrolysis is followed by the biological oxidation of the lower-size carbon chains to volatile fatty acids, particularly acetic and propionic acids [27]. The highest rates of reduction of COD values are usually observed in these phases. Acetogenesis, in which short-chain compounds, as H2, CO2, NH3/NH4+, and H2S, and methanogenesis, responsible for the production of CO2 and CH4, follows as the completing stages of the one-stage anaerobic digestion [28]. Vinasse digestate, thus, is presented as a partially degraded substrate, with potentially lower inhibition to microbial growth [29]. The concentration of phenolic compounds is also decreased in the digestate when compared to the raw vinasse. Phenolic compounds are known to decrease the rate of anaerobic digestion. For instance, Borja et al. [30] evaluated the anaerobic digestion of olive mill wastewater using the raw feedstock bearing a number of phenolic substances and concludes that while some species are partially degraded by the anaerobic digestion process (e.g. apigenin, thyrosol, oleuropein, and caffeic and p-coumaric acids), other are recalcitrant to the treatment, particularly luteolin, quercetin, caffeylglucose, and hydroxythyrosol monoglucoside. Vinasse digestate has a concentration of phenolic compounds decreased by approximately half when compared to raw vinasse. Though the distribution of phenolic compounds was not performed in this study, it is likely that some of the biorecalcitrant forms of phenols are linked to those described by Borja et al. [30].
Finally, if a sequence of vinasse treatment would follow (i) anaerobic digestion, which is known to decrease the concentration of phenolic compounds and COD, (ii) aerobic fungal growth with further removal of COD, minerals, and anions, as phosphate and sulfate, and (iii) ozonation, which drives the concentration of phenolic compounds to null values and decreases further COD, the effluent would have the characteristics described in Figure 5. Ozone treatment of anaerobic digestion alone has been considered and described in the literature for a few kinds of materials, with a particular focus on lignocellulosic matrices, as rice straw [31]. The coupling of ozone as a post-treatment strategy with fungal processes based on anaerobic digestate is, to our knowledge, not been reported to the scientific community so far.
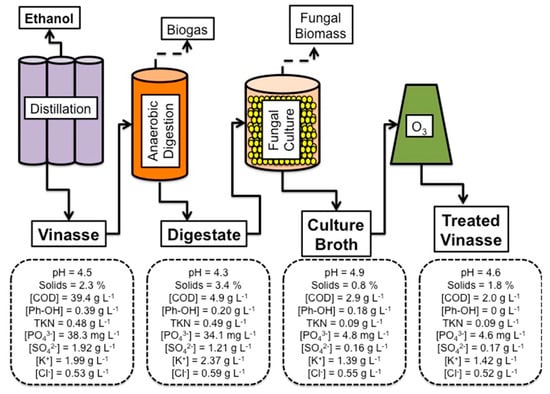
Figure 5.
Comparison of the sequence following the growth of M. circinelloides on vinasse digestate and ozonation of culture broth. Ph-OH: Total Phenolic Compounds.
4. Integration of Combined Ozone, Aerobic Fungal Growth and Anaerobic Digestion into a Sugarcane-Ethanol Industry: Economic and Technical Prospects
Efforts in the value addition of vinasse have been of particular interest from research and industrial groups for over half a century [2,32]. Significant progress has been made over the past decades on the utilization of chemical and biological treatments [3]. The range of potential economic investment to the feasibility of vinasse treatment varies considerably, including techniques using ion exchange processes to remove target compounds to the addition of moderately low-cost chemicals with oxidative processes, as hydrogen peroxide and ferrous ions [3]. Biological treatment of vinasse, particularly through anaerobic digestion, has been given some attention by ethanol plants in Brazil when the first Upflow-Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) pilot reactor entered into operation in a large-scale facility in the state of São Paulo about 30 years to date. UASB have been claimed to be one of the most appropriate designs for anaerobic digestion of vinasse due to its composition [33]. UASB reactors operate by a vertical upflow feeding strategy, in which the bottom of the reactor is responsible for adsorbing most of the organic matter, while biogas is produced in the reactor, moving upwards, where gas bubbles are removed [34]. Since the development of the first pilot operation in Brazil, considerable advances on the particularities of processing vinasse through anaerobic digestion have been achieved, in a way that biogas is generated and vinasse is treated [35]. A significant challenge, however, in the utilization of vinasse as feedstock for anaerobic digestion prevails as the high concentrations of sulfur compounds that are partially reduced to hydrogen sulfide (H2S) through the last steps of the anaerobic digestion processes [36]. Despite most sugarcane-to-ethanol plants being completely energy independent, mainly to the burning operations of bagasse and co-generation of heat and power, anaerobic digestion of vinasse provides an alternative to the treatment of vinasse and to the production of another product that could inherently provide another revenue source to plants, as the biogas produced has similar calorific value, once purified, when compared to natural gas [37].
The interest in coupling diverse treatment technologies with valuable co-products generated, particularly in this case the production of lipid-bearing fungal biomass generated through the aerobic growth of M. circinelloides, and the production of natural gas through the anaerobic digestion process of vinasse may provide a favorable outlook in regards to the process economics. Considering the points discussed in the sections above, the optimal conditions that would likely provide the highest removal of organic matter, minerals, and phenolic compounds of vinasse would be the fungal growth promoted by the utilization of vinasse digestate coupled with a post-ozone treatment of the culture broth. It is important to highlight that these conditions and the organization of the sequential treatment may be modified in order to also generate more fungal biomass and lipids on a volumetric aspect, i.e., to generate to the highest volumetric production ratio of M. circinelloides biomass per volume of vinasse utilized. In case the fungal biomass would be preferable when compared to the water treatment aspect of the operations, ozone would need to be applied firstly to raw vinasse under the naturally occurring acid pH of vinasse, which would need to be followed by the aerobic fungal growth. Nonetheless, under all the studied conditions, the presence of ozone deemed to be an important aspect in coupling the aspects of aerobic growth of fungi on vinasse as well on the recycling of vinasse as process water.
The integration of ozone units in ethanol plants would require capital expenditures regarding the ozone generation equipment as well as oxygen generators and gas pumps, with additional operation costs regarding the costs of electricity and eventual repairs to the unit. A rough estimation of the process economics could be initially based on the numbers raised by Lucas et al. [38], who promoted an analysis on the operating costs of different ozone-based treatments of winery wastewater, and estimated that a treatment under the pH of 4 and with peroxide and UV-assisted ozone, a cost of 1.31 € m−3 g−1 of Total Organic Carbon mineralized. Lucas et al. [38] also highlights that the dilution of the effluent should not be carried, as it increases significantly the treatment costs.
In addition to the treatment aspect of vinasse, an important look should be given to the co-products generated in the process. Though it not the focus of this study to evaluate alternatives for the use of the lipids produced by the fungi, recent efforts have been given to address the production of biodiesel-grade esters from the modification of such lipids. A common criticism given to the culture of microorganisms and their integration to high-volume production chains, as is the case of biofuels, is the usual high production costs involved primarily in the preparation of culture media, maintenance of bioreactors, and cell harvesting. Hoarau et al. [39] addressed the evaluation of 28 strains of filamentous fungi and yeasts on vinasse samples obtained from a plant in France and described the growth and lipid accumulation of such microorganisms. Though still at early stages of research, the integration of microbial lipids to ethanol plants as a low-cost feedstock for biodiesel production may partially yield technical solutions to the numerous issues involved in vinasse management. The fungal strain addressed in this study, M. circinelloides URM 4182, has been previously described as being oleaginous and having been tested as feedstock for Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters of fuel grade using chemical [34] and biochemical [40] catalysts, through different processing routes, as one- and two-step transesterification [41,42].
5. Conclusions
A novel water reclamation process is disclosed herein, in which aerobic and anaerobic microbial treatments are coupled with ozonation. The microorganism selected as model for the aerobic growth, M. circinelloides, is able to have its growth supported by raw vinasse, promoting accumulation of biomass within the range of 3.8 g L−1, promoting COD removal ranging from values between the range 20 to 50%.
If ozone is used as a pre-treatment to support the cell growth of M. circinelloides, the concentration of biomass and lipids accumulated by the fungi is increased by about 30%. In addition, the use of vinasse digestate as culture medium also promoted efficient conversion of COD to fungal biomass, albeit lower values of lipid accumulation were observed. A serialization of anaerobic digestion of vinasse with subsequent use of the digestate as culture medium for the fungi, with a post-treatment step of ozonation promotes a complete removal of the phenolic compounds, significant decrease in minerals and anions, and over 90% of COD, indicating the possibility of a water reclamation process in which vinasse could be recycled within an ethanol plant, with valuable fungal biomass and biogas generated as coproducts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.E.R.R. and H.F.D.C.; funding acquisition, C.E.R.R. and H.F.D.C.; investigation, C.E.R.R., H.B.S.B., T.M.A., A.K.F.C. and H.F.D.C.; methodology, C.E.R.R., A.K.F.C. and H.F.D.C.; resources, H.F.D.C.; supervision, H.F.D.C.; validation, H.F.D.C.; writing—original draft, C.E.R.R., H.B.S.B., T.M.A., A.K.F.C. and H.F.D.C.; writing—review and editing, C.E.R.R., H.B.S.B., T.M.A., A.K.F.C. and H.F.D.C.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, FAPESP, grant numbers 2016/10636-8, 2017/12907-9 and 2018/05060-5. This study also was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—razil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful for the samples provided by Usina Iracema from the São Martinho group.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goldemberg, J.; Coelho, S.T.; Guardabassi, P. The sustainability of ethanol production from sugarcane. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 2086–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofoletti, C.A.; Escher, J.P.; Correia, J.E.; Marinho, J.F.U.; Fontanetti, C.S. Sugarcane vinasse: Environmental implications of its use. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues Reis, C.E.; Hu, B. Vinasse from sugarcane ethanol production: Better treatment or better utilization? Front. Energy Res. 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- España-Gamboa, E.; Vicent, T.; Font, X.; Dominguez-Maldonado, J.; Canto-Canché, B.; Alzate-Gaviria, L. Pretreatment of vinasse from the sugar refinery industry under non-sterile conditions by Trametes versicolor in a fluidized bed bioreactor and its effect when coupled to an UASB reactor. J. Biol. Eng. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, B.S.; Junqueira, T.L.; Pavanello, L.G.; Cavalett, O.; Mantelatto, P.E.; Bonomi, A.; Zaiat, M. Anaerobic digestion of vinasse from sugarcane biorefineries in Brazil from energy, environmental, and economic perspectives: Profit or expense? Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitayavardhana, S.; Issarapayup, K.; Pavasant, P.; Khanal, S.K. Production of protein-rich fungal biomass in an airlift bioreactor using vinasse as substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitayavardhana, S.; Khanal, S.K. Innovative biorefinery concept for sugar-based ethanol industries: Production of protein-rich fungal biomass on vinasse as an aquaculture feed ingredient. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9078–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.B.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Valorization of sugar-to-ethanol process waste vinasse: A novel biorefinery approach using edible ascomycetes filamentous fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Júnior, A.D.N.F.; Koyama, M.H.; de Araújo Júnior, M.M.; Zaiat, M. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of raw sugarcane vinasse. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Insola, A.; Marotta, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.P.A.; Carneiro, L.M.; Roberto, I.C. Treatment of rice straw hemicellulosic hydrolysates with advanced oxidative processes: A new and promising detoxification method to improve the bioconversion process. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Santos, M.A.; Bonilla Venceslada, J.L.; Martín Martín, A.; García García, I. Estimating the selectivity of ozone in the removal of polyphenols from vinasse. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 2005, 80, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.A.T.; Frimmel, F.H. A simple simulation of the degradation of natural organic matter in homogeneous and heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.J.; Rey, A. Free radical and direct ozone reaction competition to remove priority and pharmaceutical water contaminants with single and hydrogen peroxide ozonation systems. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Evaluation of fenton and ozone-based advanced oxidation processes as mature landfill leachate pre-treatments. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, W.H.; Kang, J.-W.; Chapin, D.H. The chemistry of water treatment processes involving ozone, hydrogen peroxide and ultraviolet radiation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1987, 9, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Englehardt, J.D. A new method for removal of hydrogen peroxide interference in the analysis of chemical oxygen demand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.K.F.; Rivaldi, J.D.; Barbosa, J.C.; de Castro, H.F. Biosynthesis, characterization and enzymatic transesterification of single cell oil of Mucor circinelloides–a sustainable pathway for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rischbieter, E.; Stein, H.; Schumpe, A. Ozone solubilities in water and aqueous salt solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.T.; Ratledge, C. Effect of nitrogen source on lipid accumulation in oleaginous yeasts. Microbiology 1984, 130, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje-Ramirez, I.; De Velasquez, M.T.O. Removal and transformation of recalcitrant organic matter from stabilized saline landfill leachates by coagulation–ozonation coupling processes. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.; Cassland, P.; Jönsson, L.J. Development of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with enhanced resistance to phenolic fermentation inhibitors in lignocellulose hydrolysates by heterologous expression of laccase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botha, A.; Kock, J.L.F.; Coetzee, D.J.; Botes, P.J. Physiological properties and fatty acid composition in Mucor circinelloides f. circinelloides. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1997, 71, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuess, L.T.; Kiyuna, L.S.M.; Júnior, A.D.N.F.; Persinoti, G.F.; Squina, F.M.; Garcia, M.L.; Zaiat, M. Thermophilic two-phase anaerobic digestion using an innovative fixed-bed reactor for enhanced organic matter removal and bioenergy recovery from sugarcane vinasse. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, B.S.; Petersen, S.O.; Zaiat, M.; Sommer, S.G.; Triolo, J.M. Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from vinasse through anaerobic digestion. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwari, K.V.; Balakrishnan, M.; Kansal, A.; Lata, K.; Kishore, V.V.N. State-of-the-art of anaerobic digestion technology for industrial wastewater treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.I.; Sales, D.; Cantero, D.; Galan, M.A. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of winery waste (vinasses): Kinetics and process optimization. Process Biochem. 1988, 23, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, S.S.I.; Nascimento, I.A.; de Almeida, P.F.; Chinalia, F.A. Growth of Chlorella vulgaris on sugarcane vinasse: The effect of anaerobic digestion pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, R.; Martin, A.; Maestro, R.; Alba, J.; Fiestas, J.A. Enhancement of the anaerobic digestion of olive mill wastewater by the removal of phenolic inhibitors. Process Biochem. 1992, 27, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xi, J.; Ai, P.; Yu, L.; Zhai, H.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing ethanol production from thermophilic and mesophilic solid digestate using ozone combined with aqueous ammonia pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanghe, H. Production of mushroom mycelium as a protein and fat source in submerged culture in medium of vinasse. Appl. Microbiol. 1962, 10, 572–576. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, M.E.; Fuzaro, G.; Polegato, A.R. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of vinasse in pilot plant uasb reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettinga, G.; Hulshoff Pol, L.W. Uasb-process design for various types of wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 24, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuess, L.T.; Klein, B.C.; Chagas, M.F.; Rezende, M.C.A.F.; Garcia, M.L.; Bonomi, A.; Zaiat, M. Diversifying the technological strategies for recovering bioenergy from the two-phase anaerobic digestion of sugarcane vinasse: An integrated techno-economic and environmental approach. Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, E.L.; Spanjers, H.; Dewulf, J.; Romero, O.; Rosa, E. The sulfur chain in biogas production from sulfate-rich liquid substrates: A review on dynamic modeling with vinasse as model substrate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, K.R.; Lora, E.E.S. Estimate of the electric energy generating potential for different sources of biogas in brazil. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A.; Puma, G.L. Treatment of winery wastewater by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes (O3, O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2) in a pilot-scale bubble column reactor and process economics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, J.; Grondin, I.; Caro, Y.; Petit, T. Sugarcane distillery spent wash, a new resource for third-generation biodiesel production. Water 2018, 10, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.K.F.; da Conceição, L.R.V.; Silva, J.P.V.; Perez, V.H.; de Castro, H.F. Biodiesel production from Mucor circinelloides using ethanol and heteropolyacid in one and two-step transesterification. Fuel 2017, 202, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.K.F.; Bento, H.B.S.; Izário Filho, H.J.; de Castro, H.F. Approaches to convert Mucor circinelloides lipid into biodiesel by enzymatic synthesis assisted by microwave irradiations. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, H.B.S.; Carvalho, A.K.F.; Reis, C.E.R.; De Castro, H.F. Microbial biodiesel production: From sucrose-based carbon sources to alkyl esters via enzymatic transesterification. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 121, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).