Abstract
Sewage sludge in natura is rich in nutrients, water, and organic matter and is essential for plant development. However, sewage sludge is diluted with water when composted, which could hamper plant growth. Therefore, supplementation with chemical fertilization may be necessary. This study evaluated the performance of composted sewage sludge (CSS) in producing Peltophorum dubium (Spreng.) Taub. seedlings with and without chemical fertilization via fertigation. The experiment was completely randomized in a 3 × 4 factorial scheme, with four fertigation (Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x: 0.87; (NH4)(H2PO4): 0.21; KCl: 0.47; (NH4)2SO4: 0.11; CH₄N₂O: 0.54; MgSO4: 0.52; Fe (13%): 0.03; B(OH)3: 6.00; CuSO4: 0.60; ZnSO4: 1.40; MnSO4: 6.00; Na2MoO4: 0.16 g L−1) doses: zero, standard, duplicate, and quadruplicate. In addition, three substrates were used: commercial substrate as the control, sewage sludge composted with sugarcane bagasse (LBC), and sewage sludge composted with Eucalyptus bark (LCE). The development of the seedlings was measured through the following variables: height, stem diameter, shoot/root ratio, leaf dry mass, root dry mass, total dry mass, green color index, the Dickson Quality Index, and the accumulation of nutrients in plant tissue. The seedlings produced with LCE that were subjected to the standard dose (1×) and the quadruplicate dose (4×) had the statistically highest mean values for most variables. Nevertheless, supplementation with chemical fertilization was necessary. Composted sewage sludge with eucalyptus bark, at the standard dosage, can be used for the commercial production of P. dubium seedlings, thus preventing the dangerous disposal of waste and strongly decreasing associated environmental hazards.
1. Introduction
Sewage sludge represents the final residue in treating anthropogenic waste, which has no economic value in standard waste stations in some countries. Hence, sewage sludge waste requires a proper discard system to prevent environmental damage. However, the complexity and the high costs of processing sewage sludge have caused anthropogenic waste to be discarded in local landfills [1], causing significant environmental damage due to pathogens and high rates of heavy metals in the sewage sludge [2].
The production quantity of sewage sludge is proportional to population development, raising the environmental impact concern. However, these impacts encourage the prospection of sustainable actions to reuse the organic residue [3].
The high concentrations of nutrients, water, and organic matter in sewage sludge are desirable for producing substrate and fertilizers. Indeed, sewage sludge residue is mainly applied as organic fertilizer and/or substrate for seedlings in forestry and agricultural areas [4].
The CONAMA(Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente, National Environmental Council) Resolution N° 498/2020 [5] regulates the usage of sewage sludge in nature in Brazil due to its high concentration of heavy metals and pathogens [6,7]. For this reason, the residue must be processed at high temperatures and compounded with other structuring materials for use in agricultural and forestry areas [8]. Indeed, composting SS significantly decreases the pathogenic load, and the organic matter content is stabilized, thus reducing heavy metal availability for plants and the entire food chain.
Unfortunately, the nutrient content of sewage sludge is decreased during processing [9], and it needs to be supplemented with chemical fertilizers. The fertigation method consists of the application of a fertilizer via water irrigation [10], which is widely used in the agricultural and forestry sectors to complement the chemical fertilizers in the substrates, which results in the rapid absorption of fertilizers by the roots [11].
However, the development and nutritional requirements of the seedlings of native species via fertigation demand a broad study effort [12]. In addition, the growing concern of native deforestation requires a program of native forestry restoration and the remedying of degraded areas [13]. Culturing forestry species with sewage sludge results in an adequate growth performance of the seedlings since the compound has a high organic matter content, similar to that in forest soils that undergo litter decomposition [14].
Peltophorum dubium (Spreng.) Taub. (P. dubium hereafter) has economic and commercial value [15] and is employed in forest restoration programs due to its rapid growth and robustness [16]. In addition, this species develops in various substrate types. However, the root and aerial growth of P. dubium is higher when produced with a substrate that contains organic matter [17]. Additionally, its growth at the seedling stage using composted sewage sludge compounded with other organic materials as commercial substrate has never been studied, presenting a total novelty.
The objectives of the present work were to (i) evaluate the production of P. dubium seedlings with sewage sludge substrate compounded with sugarcane bagasse and eucalyptus bark with different fertilizer levels and (ii) compare these seedlings with those produced with a peat-based commercial substrate, carbonized rice bark, and vermiculite, which are widely used in forestry nurseries. We hypothesize that the use of composted sewage sludge as a commercial substrate improves and enhances the production of P. dubium seedlings.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiment was conducted in the “Pesquisa em Produção de Mudas Florestais” nursery of the Ciência Florestal Department of the Ciências Agronômicas Faculty, São Paulo State University (Lat. −22.855, Long −48.433), Botucatu municipality (Brazil). The experiment lasted nine months. According to the international classification method of Koppen, the region’s climate is temperate and warm [18,19]. The Sanitation Company of the State of São Paulo (Sabesp) provided the sewage sludge in natura.
The compost types were sewage sludge with sugarcane bagasse (SSB) and sewage sludge with eucalyptus bark (SEB), both in a 1:1 proportion (v:v). The composting lasted 45 days, and the compost was later transferred to the forest nursery. Commercial substrate (CS), which comprised peat (Sphagnum sp.), vermiculite, and carbonized rice bark, was used as the control.
The substrates were physically and chemically characterized (Table 1) to determine the total porosity, macro- and microporosity, water retention, pH, and electric conductivity (EC) [20,21]. The chemical analysis of the substrate followed the “analytical protocol in the chemical characterization of plant substrates” [20].

Table 1.
Substrate physical–chemical analysis before the experiment started. Physical analysis: macro- (Macro) and microporosity (Micro), total porosity (TP), water retention capacity (WRC), pH, electric conductivity (EC). Chemical analysis: macro- and micronutrients.
Each substrate was subjected to four fertigation doses as follows: zero doses (without fertilization); standard dose (1×), which is mainly used by commercial forest nurseries [22]; duplicated dose (2×), with doubled quantity of the standard dose; and quadruplicated dose (4×), with quadruple of the standard dose.
The fertigation was manually applied two times per week, between 16 h and 16:30 h, through the Venturi system, characterized by a closed system and low pressure. The fertigation formulation (Table 2) was the same used by Brazilian commercial nurseries and, for this reason, is at this moment named “standard”.

Table 2.
Fertilizing composition of the standard formulation used in the fertigation forest nurseries.
The experiment was conducted by a factorial arrangement 3 × 4 entirely randomized outline (i.e., three substrate types × four fertigation doses), totaling 12 treatments. Each treatment had three repetitions with 20 seedlings, counting 60 seedlings per treatment. The arboreal native species P. dubium was selected for the present study, which has orthodox seeds with tegmental dormancy. The seed dormancy was broken through thermal shock with 92 °C hot water, and seeds were later transferred to cold water for 24 h [23,24]. After this process, the seeds were planted in tubes with the substrate.
The sewage sludge was sieved through 5.5 mm granulometry to remove larger detritus. Posteriorly, the biosolid was moisturized with water, homogenized through the concrete mixer, and later used to fill the plastic tubes. Each tube received two seeds of P. dubium, posteriorly disposed in trays and stored in a bed with 50% shade for germination. The tubes remained in the bed for approximately 60 days to germinate the seedlings. Posteriorly, the seedlings were separated into beds with transparent plastic to receive each treatment. The irrigation consisted of a 12 mm water blade with a twice-daily frequency [25].
The aerial height and the stem diameter were measured monthly with a centimeter-graded ruler and a digital pachymeter (0.01 mm), respectively. At the end of the experiment, the seedlings’ aerial part (stalk and leaf) and root were separated from drying in a stove at 65 °C for 72 h to obtain the aerial dry mass (MSA), root dry mass, and total dry mass. Posteriorly, the dried material was weighed on an analytical scale (0.001 g precision) for chemical analysis.
Data Analysis
The total dry mass was calculated by adding the aerial dry mass and root dry mass values. Accumulation of each plant nutrient was acquired from the nutrient values content and plant biomass. The Dickson Quality Index (DQI) [26] was calculated to evaluate the seedling quality by the following Equation (1):
The variance analysis (ANOVA) of seedling growth variables was verified using the homogeneity variables and the Shapiro–Wilk normality test, and later the ANOVA and the Scott–Knot (p < 0.05) tests. The levels of one factor within the other were calculated for all variables with interactions between them. The fertigation doses were analyzed by polynomial regressions (quantitative factor) with the rising of measured variables. The statistical analysis was performed using Infostat software v. 2020 [27] and R software 2023.06.1 [28,29].
3. Results
The P. dubium seedlings’ height (Figure 1) was significantly (p < 0.05) correlated with substrate factors and fertigation doses. Thereby, the seedlings’ height growth was higher with zero fertigation dose and sewage sludge composted with eucalyptus bark (SEB). With the standard (1×) and quadruplicated (4×) doses produced with commercial substrate (CS) and SEB, the seedling heights were similar. The growth of seedlings planted with the SEB and duplicated (2×) dose was notable. Nonetheless, the seedling’s height in all the substrates was higher with the 4× and 1× treatments, respectively.
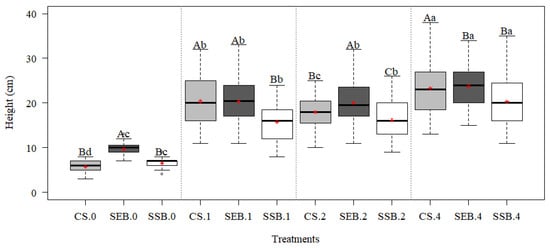
Figure 1.
Interactions of fertigation doses with substrates in P. dubium seedling heights after 150 days of sowing. Mean values in the boxplot (red asterisk) followed by the same lowercase letter (fertigation doses) or uppercase letter (substrate) did not differ according to the Scott–Knot test (p < 0.05). Treatments: commercial substrate (CS); SSB: sewage sludge composted with sugarcane bagasse; SEB: sewage sludge composted with eucalyptus bark. Zero: no fertigation; 1: standard dose; 2: duplicated dose; 4: quadruplicated dose.
The height vs. fertigation dose relationship is better described by a polynomial regressions function. In particular, the seedling height reached by plants growing on the SC (Figure 2a) substrate shows an increasing trend with the increase in fertigation doses. On the SC substrate, the maximum plant height was reached at a 3.3× dose, with seedlings of 24 cm. For SSB (Figure 2b) the same dose (3.3×) showed the maximum plant height (20.5 cm). On the SEB substrate (Figure 2c) the maximum height of 23.5 cm was observed with the 4× dose.
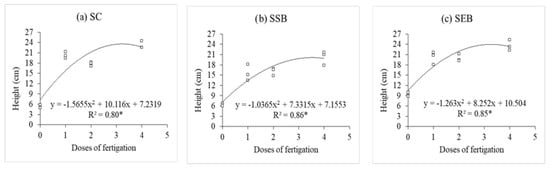
Figure 2.
Polynomial height regression of the P. dubium seedlings with different doses of fertigation and produced with the commercial substrate (a) (SC), sewage sludge with sugarcane bagasse (b) (SSB), and sewage sludge with eucalyptus bark (c) (SEB).
The variations in the stem diameter variable (Figure 3) were influenced by both the fertigation doses and the used substrate. At increasing fertigation doses, we usually observed a statistically significant (p < 0.05) increase passing from 0 to 1, 2, and 4× doses. Looking at the observed differences among investigated substrates, at the 0 dose, the SEB substrate showed a significantly higher stem diameter, as well as at all the other investigated doses (1, 2, 4×), but was similar to CS at 1 and 4× doses. SSB usually showed the worst performances with the relevant exclusion of the 0 dose.
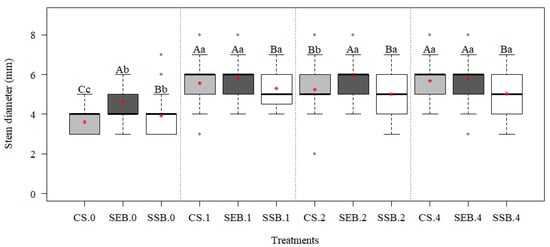
Figure 3.
Interaction between treatments with increasing fertigation doses and the influence on the stem diameter (mm) variable in the production of P. dubium seedlings with 150 days seeding. Boxplot mean values (red asterisk) followed by the same lowercase (fertigation doses) or capital letter (substrates) did not differ according to the Scott–Knott test (p < 0.05). Treatments: CS: commercial substrate; SSB: sewage sludge composted with sugarcane bagasse; SEB: sewage sludge composted with eucalyptus bark. Zero: no fertigation; 1: standard dose; 2: duplicated dose; 4: quadruplicated dose.
By investigating stem diameter performance (Figure 4a–c) through regression analyses, we observed its increase with the increasing fertigation doses. In particular, the stem diameter of the P. dubium seedlings grown in the SC substrate (Figure 4a) reached its maximum value of 6.12 mm at the 3.1× dose. The same dose was responsible for the maximum value (6 mm) reached by P. dubium seedlings in the SEB substrate (Figure 4c). The maximum value (5.2 mm) in the SSB substrate was observed for a dose ranging from 2 to 2.5×.
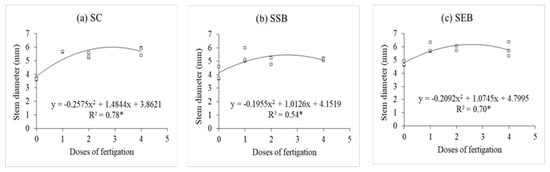
Figure 4.
Polynomial regressions of the stem diameter of P. dubium seedlings in different fertigation doses produced with the commercial substrate (SC), sewage sludge with sugarcane bagasse (SSB), and sewage sludge with eucalyptus bark (SEB).
The height vs. diameter (H/D) ratio varied according to the fertigation doses (Figure 5) and the used substrate. In all investigated cases, i.e., regardless of the used substrate, we clearly observed a significant trend (p < 0.05) as reported: 4× > 2× = 1× > 0. Looking at comparisons among substrates, they usually showed similar performances, with the relevant exception of (i) SEB at the 0 dose, showing a statistically higher (p < 0.05) H/D ratio, and (ii) the 1× dose, where SSB showed the worst performances.
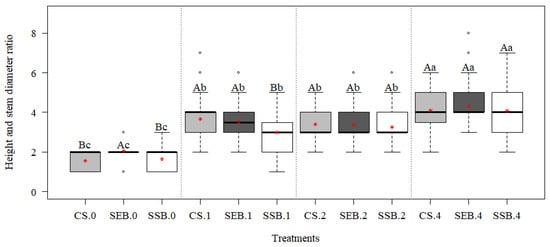
Figure 5.
Height and stem diameter ratio of P. dubium seedlings and interactions of each treatment with increasing fertigation doses with the substrates 150 days after seeding. Boxplot mean values (red asterisk) followed by the same lowercase (fertigation doses) or capital letter (substrates) did not differ according to the Scott–Knott test (p < 0.05). Treatments: CS: commercial substrate; SSB: sewage sludge composted with sugarcane bagasse; SEB: sewage sludge composted with eucalyptus bark. Zero: no fertigation; 1: standard dose; 2: duplicated dose; 4: quadruplicated dose.
The substrates and fertigation dose factors of the aerial dry mass, root dry mass, and total dry mass variables did not present interactions (Figure 6A,B). However, there was an isolated factor influence. The biomass of the seedlings produced with the SEB substrate (Figure 6A) always showed statistically higher values (p < 0.05) compared to CS and SSB. Both the aerial dry mass (ADM) and total dry mass (TDM) showed the significantly highest (p < 0.05) mean values when the 4× fertigation dose was applied (Figure 6B). The root dry mass presented a statistically similar mean value with all fertigation doses except for the zero dose, showing the lowest mean values.
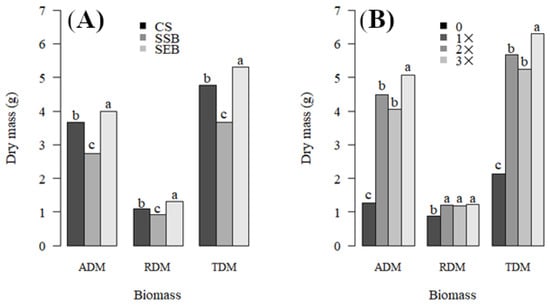
Figure 6.
Interactions between substrates (A) and fertigation doses (B) and the influence on biomass, i.e., aerial dry mass (ADM), root dry mass (RDM), and total dry mass (TDM) (g), of the P. dubium seedlings after 150 days of seeding. Boxplot mean values followed by the same lowercase (fertigation doses) did not differ according to the Scott–Knott test (p < 0.05). Treatments: CS: commercial substrate; SSB: sewage sludge composted with sugarcane bagasse; SEB: sewage sludge composted with eucalyptus bark. Zero: no fertigation; 1: standard dose; 2: duplicated dose; 4: quadruplicated dose.
The polynomial regressions showed that the total dry mass of seedlings produced with SEB and CS increased with the fertigation doses. In particular, at the 3.0× dose, the maximum values were observed for both substrates, by reaching 6.83 g and 6.6 g, respectively (Figure 7a–c). The regression of the SEB substrate showed that the standard (0×) and 4× doses were more favorable in promoting an increase in seedling height, nearing the maximum point of the regression series.
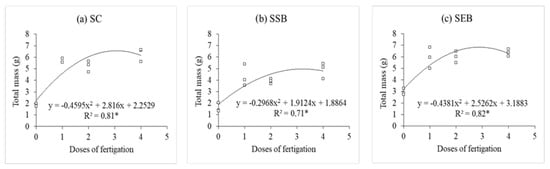
Figure 7.
Polynomial regressions of the total mass of P. dubium seedlings per substrate, showing increasing levels of fertigation with the commercial substrate (SC), sewage sludge with sugarcane bagasse (SSB), and sewage sludge with eucalyptus bark (SEB).
The total dry mass (Table 3) of the seedlings produced in the SEB substrate usually showed higher Ca and S macronutrient contents; SEB together with CS also featured significantly (p < 0.05) higher N, P, K, and Mg content when compared to SSB. The 4× fertigation dose always corresponded with the significantly highest (N, K, and S), or similar to 2× (P, Ca, and Mg), macronutrient dry mass accumulation. Also, for B, Cu, Mn, and Na, the SEB substrate showed the highest or comparable (with CS and SSB for Fe, with SSB for Zn) micronutrient contents. Looking at the fertigation doses, the observed results are quite dependent on the applied dose. Indeed, the highest dose (4.0×) corresponds to the highest B values, while the same dose showed comparable Mn and Zn contents to the 1.0, 2.0×, and 0–2.0× doses, respectively. Copper and Fe reached their highest at the 2.0× applied doses, while Na did so at the 1.0× dose.

Table 3.
Macro- and micronutrient accumulation in total dry mass of the Peltophorum dubium seedlings 150 days after seeding.
4. Discussion
The substrate’s physical analysis showed that the SEB biosolid presented the highest microporosity and water retention. The eucalyptus bark, as it fragmented and decomposed during the composting process, generated fine particles that increased the density of the substrate. This density directly influences water retention, absorption of macronutrients and micronutrients, available water, electrical conductivity, and important physical–chemical features, thus influencing the initial seedlings’ growth [30].
Although CSS, the SSB substrate, presented the highest percentage of macroporosity and the lowest water retention capacity, the low nutritional value and fibers were not altered during the composting process, resulting in a porous substrate with a low water retention capacity, unfavorable for producing P. dubium seedlings.
Except for P, K, and Cu, the amounts of nutrients analyzed in the chemical analysis of the substrates were consistently higher in the SEB substrate. It is expected that sewage-sludge-based biosolids have high macro- and micronutrient concentrations [31]. In contrast, commercial substrates (CSs) tend to be inert [25]. The high P and K amounts observed in CSs are due to the well-known presence of superphosphate added during its development process, mixed with carbonized rice husks, i.e., a potassium-rich material [32].
The eucalyptus bark shows adequate Ca, K, Mg, Na, Mn, and Fe concentrations. Generally, Ca is the element with the highest availability (82–95%), followed by Mg and K (i.e., Ca > K > N > Mg > P), respectively [33]. The high concentrations of Ca in the eucalyptus bark are related to its lower mobility in the phloem and a structural component of the cell membrane [34]. Organic substrates usually contain more nutrients than commercial substrates [35], providing better use of nutrients and mineral fertilization by plants since [36,37] (i) they chemically are in organic form, thus (ii) being gradually released, a feature that (iii) effectively supplies the plant’s nutritional needs during the whole biological cycle. Additionally, due to their high availability, organic substrates are a low-cost commercial alternative [38].
The pH and electrical conductivity are pivotal features of every substrate used in seedling nurseries [39]. The pH of the investigated substrates ranged from 6.1 to 6.8 before fertigation. As expected (Table 2), the pH slightly increased once fertilization was applied, ranging from 6.3 to 7.1. According to Cacini et al. [40], the pH of organic substrates should range from 5.0 to 6.5, a variation favoring both plant growth and nutrient absorption capacity in the substrate. Our results partially disagree with those observed by the previous author. As a matter of fact, the investigated substrates had a pH slightly above that “recommended” by the author before and after fertigation. Despite this, except for zero doses and the SSB substrate, all treatments produced seedlings with satisfactory development. This demonstrates that organic substrates made with the reuse of by-products are less restrictive regarding pH ranges for plant seedling growth, thus being more adaptable for commercial uses.
The electrical conductivity records the concentration of ionized salts in the solution. Saline stress can affect water absorption and nutrients, altering plant metabolism [41]. Yet, high electrical conductivity values are generally observed in sewage-sludge-based substrates due to the high content of nutrients and organic matter [42]. However, in all investigated substrates, an adequate electrical conductivity for the growth of the plant’s seedlings (<1.0 mS cm−1) [43] was observed.
Overall, the SEB substrate shows comparable vegetation growths with CS. More specifically, the height of the seedlings showed higher mean values when produced with SEB. Yet, the SEB and CS substrates showed similar mean values for the seedlings produced with the standard and highest doses (4×). Additionally, all the observed height values are within the range determined by Silva et al. [43], where seedlings of native species showed a height ranging from 20 to 35 cm. As the fertigation dose increased, the height of the P. dubium seedlings also increased, which confirmed its nutritional requirement [44].
Regarding the stem diameters, the seedlings produced in SEB presented the highest growth. With the standard and 4× doses, the CS and the SEB showed similar mean values, while they performed better than SSB. According to Gonçalves et al. (2000) [43], seedlings of native species should present a stem diameter between 5 and 10 mm. Therefore, except for the zero dose, all substrates produced seedlings with adequate stem diameters, although the SEB substrate provided the seedlings with the highest mean values.
The seedlings produced with the SEB substrate presented the highest H/D ratio mean values. The observed H/D ratio values of all treatments gave a mean below 10, regardless of the substrate, including seedlings produced with zero doses, which is considered adequate according to Cargnelutti Filho et al. (2018) [45]. The H/D ratio represents the seedling development capacity. Therefore, lower values characterize superior seedling quality and survival capacity in the field.
The SEB compost presented the highest nutrient concentration from the beginning of the experiment, as reflected by both the chemical analysis and seedlings’ growth in terms of height and diameter. Consequently, this substrate produced a greater biomass of aerial and root parts, presenting superior development compared to the seedlings planted in all the other investigated substrates. The total dry mass is an essential morphological variable to estimate seedlings’ survival and initial growth in the field since a well-developed seedling is more resistant to edaphic adversities [46]. Furthermore, Alonso et al. (2017) [46] also observed that seedlings of three native species (i.e., P. dubium (Springer.) Taub. (Dry flour), Lafoensia pacari A. St.-Hil. (Foxglove) and Ceiba speciosa (A. St.-Hil.) Ravenna (Paineira)) showed a higher amount of aerial and root biomass when produced in sewage sludge composted with clayey soil and sand compared to the control substrate.
The processed sewage sludge, commonly named biosolid, contains high macronutrient, especially N, P, Ca, and Mg, and organic matter contents [25]. However, seedlings produced at zero doses did not reach height and diameter growth within the parameters defined by Gonçalves et al. [43], requiring supplementation with chemical fertilization via fertigation. Although raw sewage sludge contains high amounts of nutrients, the dilution effect may occur during composting [42]. According to Rocha et al. (2013) [47], the accumulation of nutrients in composted sewage sludge is insufficient for initial seedling growth, requiring fertilizers. The height and stem diameter of P. dubium seedlings improved as the fertigation doses gradually increased. With 150 days of seeding, the highest accumulation of nutrients was observed in their aerial part. These results corroborate the data obtained by Gonçalves et al. (1992) [48], where the seedlings of P. dubium at 128 days had higher concentrations of nutrients in the aerial part. Also, at 150 days, the accumulation of macro- and micronutrients in the aerial part of the seedlings was within the suitable standards, according to Malavolta et al. (1997) [49].
The accumulation of N observed in the total mass of seedlings produced with CS and SEB was more significant than in those made with SSB. According to Trigueiro and Guerrini [42], N is usually the most abundant nutrient in sewage sludge. It is the most critical compost required by plants, acting directly in the growth process [50].
Furthermore, the growth of seedlings was reduced with the lower fertigation doses by the omission of P. According to Souza et al. (2013) [51], P. dubium has growth limitations in terms of height and diameter in the absence of N, K, S, Ca, Mg, B, and Zn since the seedlings’ demand for N and P is more significant in the initial seeding stages, which act in the initial growth of height and diameter [32].
The Dickson Quality Index (DQI) [26] is the most reliable parameter for assessing seedling quality, which calculates the main morphological variables. The DQI (Table 4) demonstrated that the seedlings produced with SEB had the best rate compared to those made with CS and SSB. Although the seedlings subjected to the 4× dose stood out in most of the variables analyzed, the DQI proved that the standard and 2× doses formed the best-quality seedlings. Nonetheless, the standard dose is more advantageous regarding the economy of chemical fertilizers for seedling producers.

Table 4.
Dickson Quality Index (DQI) of the seedlings of P. dubium per treatment, 150 days after seeding.
Seedling quality is directly associated with the field’s capacity for development and endurance [51]. Consequently, understanding the nutritional requirements of native forest species would optimize their management and the availability of nutrients [52].
The obtained outcomes show that the sewage sludge composted with eucalyptus bark (SEB) performed best in most investigated parameters. From an environmental perspective, the SEB substrate is the most efficient in P. dubium seedling production, being a promising alternative for the productive and commercial reuse of this residue instead of its landfill disposal. Moreover, SEB substrate would assist in the rising demand for seedlings of native plants to recover degraded areas [53]. As a matter of fact, seedling production represents an essential cost in soil restoration through reforestation programs [4]. One of the costs most affecting the overall commercial balance is represented by the use of commercial substrate [32]. Thus, by using by-products, this significant cost can be strongly reduced, making soil recovery and reforestation programs more feasible.
5. Conclusions
The seedlings produced with SEB presented better performances for most of the investigated parameters. Although seedlings planted in the substrate with the 4.0× fertigation dose showed interesting performances too, the Dickson Quality Index confirmed that the seedlings produced with SEB substrate, supplemented with a 2.0× dose, presented the highest quality. Thus, composted sewage sludge with eucalyptus bark at the standard dose represents the most suitable substrate for P. dubium seedling production. The experiment demonstrated that sewage sludge combined with natural by-products (eucalyptus bark, in this case) represents a highly recommendable substrate in commercial seedling production. More specifically, the seedlings produced with SEB demonstrated similar productivity performance to those produced with commercial fertilizers. This approach could represent an efficient alternative to improve nursery forestry, reducing traditional inputs (chemical fertilizers) and bringing positive socio-economic, environmental, and health effects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.O.C.d.S., A.C.d.F. and M.R.d.S.; methodology, L.O.C.d.S. and A.C.d.F.; software, L.O.C.d.S. and R.L.V.B.; validation, L.O.C.d.S., D.C.L.S. and M.R.d.S.; formal analysis, L.O.C.d.S.; investigation, L.O.C.d.S. and D.C.L.S.; resources, I.A.G.; data curation, A.C.d.F. and R.L.V.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.O.C.d.S., A.C.d.F., M.R.d.S. and G.F.C.; writing—review and editing, L.O.C.d.S., M.R.d.S., G.F.C., A.G. and I.A.G.; visualization, G.F.C. and A.G.; supervision, I.A.G.; project administration, I.A.G.; funding acquisition, I.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by SABESP and FAPESP through the project “Compostagem do Lodo de Esgoto” (SABESP/FAPESP).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to SABESP and FAPESP for the raw material availability. We also thank the project’s team members for their help and the São Paulo State University (FCA/UNESP). L.O.C.S. is thankful to CNPq for the scholarship grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Artuso, F.; Lukiantchuki, J.; Oliveira, J.; Tarazona, S.; Almeida, M.; Benatti, C.T. Investigation on the Feasibility of the Use of Biosolid-Soil Mixtures for Zinc Retention in Waste Landfill Barriers. Soil. Sediment. Contam. Int. J. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, I.A.; Croce, C.G.G.; de Bueno, O.C.; Jacon, C.P.R.P.; Nogueira, T.A.R.; Fernandes, D.M.; Ganga, A.; Capra, G.F. Composted sewage sludge and steel mill slag as potential amendments for urban soils involved in afforestation programs. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2017, 22, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, T.S.; Simões, R.O.; Luque, J.L.F.; Maldonado, A.; Gentile, R. The influence of habitat fragmentation on helminth communities in rodent populations from a Brazilian Mountain Atlantic Forest. J. Helminthol. 2016, 90, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, A.; da Silva, M.R.; Guerrini, I.A.; Fernandes, D.M.; Villas Bôas, R.L.; da Silva, L.C.; da Fonseca, A.C.; Ruggiu, M.C.; Cruz, C.V.; Lozano Sivisaca, D.C.; et al. Composted sewage sludge with sugarcane bagasse as a commercial substrate for Eucalyptus urograndis seedling production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério do Meio Ambiente. CONAMA 498—Define Critérios e Procedimentos para Produção e Aplicação de Biossólido em Solos, e dá Outras Providências; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasilia, Brazil, 2020; pp. 265–269.
- Bittencourt, S.; Serrat, B.M.; Aisse, M.M.; Gomes, D. Sewage Sludge Usage in Agriculture: A Case Study of Its Destination in the Curitiba Metropolitan Region, Paraná, Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistema Nacional de Informações sobre Saneamento—SNIS. Diagnóstico dos Serviços de Água e Esgotos—2014; Ministério das Cidades. Secretaria Nacional de Saneamento Ambiental—SNSA: Brasilia, Brazil, 2016; p. 212.
- Alonso, J.M.; Pereira, R.N.; da Abel, E.L.S.; Ochoski, M.; dos Santos, G.L.; de Abreu, A.H.M. Sewage sludge as substrate in Schinus terebinthifolia raddi seedlings commercial production. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T. Effect of Processing Conditions on Nitrogen Loss of Sewage Sludge Composting. Compos. Sci. Util. 2020, 28, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.M.D.; Coelho, E.F.; Silva, A.C.P.D. Calcium nitrate concentrations in fertigation for ‘terra’ banana production. Eng. Agríc. 2017, 37, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, K.T.O. Quality of seedlings of Moringa oleifera under different levels of nutrients applied via fertigation. Pesqui. Florest. Bras. 2016, 36, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca e Cruz, C.A.; Nogueira de Paiva, H.; da Cunha, M.; Carvalho, A.C.M.; Neves, J.C.L. Macronutrients in production of Peltophorum dubium (Spreng.) Taub. seedlings in red yellow ultisol of the Zona da Mata, MG region. Ciência Florest. 2011, 21, 445–457. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira, M.V.; Delarmelina, W.M.; Peroni, L.; Gonçalves, E.D.; Gomes daSilva, A. Use of sewage sludge and vermiculite for producing Eucalyptus seedlings. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 2013, 43, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabreira, G.V.; dos Leles, P.S.S.; Alonso, J.M.; de Abreu, A.H.M.; Arthur Junior, J.C.; Gusmão, A.V.V.; Lopes, N.F. Fertilization and containers in the seedlings production and post-planting survival of Schizolobium parahyba. Ciênc. Florest. 2019, 29, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, T.R.; Massad, M.D.; Sarmento, M.F.Q. Slow release fertilizer on the growth and seedlings quality of canafístula (Peltophorum dubium (Spreng.) Taub.). Floresta 2016, 46, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gonzaga, L.M.; da Silva, S.S.; de Campos, S.A.; de Ferreira, R.P.; da Campos, A.N.R.; da Cunha, A.C.M.C.M. Evaluation of substrates and amf sporulation in the production of seedlings of native forest species. Rev. Árvore 2016, 40, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silva, O.M.D.C.; Hernández, M.M.; Almeida, R.S.D.; Moreira, R.P.; Leles, P.S.D.S.; Melo, L.A.D. Seedlings of tree species produced in substrates based on organic composts. Floresta 2021, 51, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.B.P.; Francisco Escobedo, J.; Juliana Rossi, T.; dos Santos, C.M.; da Silva, S.H.M.G. Performance of the Angstrom-Prescott Model (A-P) and SVM and ANN techniques to estimate daily global solar irradiation in Botucatu/SP/Brazil. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2017, 160, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.M.; Escobedo, J.F. Temporal variability of atmospheric turbidity and DNI attenuation in the sugarcane region, Botucatu/São Paulo/Brazil. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imprensa Nacional. Instrução Normativa No 17, de 6 de Março de 2020—DOU—Imprensa Nacional. Available online: https://www.in.gov.br/web/dou (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Furlani, A.M.C.; Battaglia, O.C.; Abreu, M.F.; Furlani, P.R.; Quaggio, J.A.; Minami, K. Caracterização, Manejo e Qualidade de Substratos para Produção de Plantas; Instituto Agronômico: Campinas, Brazil, 2002; Documento IAC, 70.
- Gomes da Silva, R.B.; da Silva, M.R. Nursery water management on initial development and quality of Piptadenia gonoacantha seedlings. Sci. For. 2015, 43, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, L.M.; Davide, A.C.; de Carvalho, M.L.M. Evaluation of methods for dormancy breaking and disinfestation of canafistula seeds (Peltophorum dubium (Sprengel) Taubert Caesalpinoideae. Rev. Árvore 2003, 27, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuffo, A.M.; Steiner, F.; Zuffo, J.M.; Bush, A.; da Silva, J.R.M.; Limede, A.C.; da Silva Oliveira, C.E. Non-chemical methods to break seed dormancy of canafistula [Peltophorum dubium (Sprengel) Taubert (Fabaceae)]. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2017, 11, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.O.C.; Da Fonseca, A.C.; Sivisaca, D.C.L.; Da Silva, M.R.; Boas, R.L.V.; Guerrini, I.A. Sewage sludge compost associated to frequency of irrigation for Peltophorum dubium (Sprengel) Taubert seedlings production. Floresta 2020, 50, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.; Leaf, A.L.; Hosner, J.F. Quality appraisal of white spruce and white pine seedling stock in nurseries. For. Chron. 1960, 36, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infostat—Statistical Software. Available online: https://www.infostat.com.ar/?lang=en (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2023; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- De Abreu, A.H.M.; dos Santos Leles, P.S.; Alonso, J.M.; da Silva Abel, E.L.; de Oliveira, R.R. Characterization of sewage sludge generated in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and perspectives for agricultural recycling. Semin. Ciências Agrárias 2017, 38, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, H.Y.; Pan, M. Fertilization Value of Biosolids on Nutrient Accumulation and Environmental Risks to Agricultural Plants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, I.A.; Sampaio, T.F.; Bogiani, J.C.; Backes, C.; Harrison, R.B.; Oliveira, F.C.; Gava, J.L.; Traballi, R.C.; Garuba de Menezes Mota, R.; Roder, L.R.; et al. Sewage sludge as a pedotechnomaterial for the recovery of soils compacted by heavy machinery on Eucalyptus commercial plantation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, M.; Schumacher, M.V.; Bonacina, D.M.; de Oliveira Ramos, L.O.; Rodríguez-Soalleiro, R. Biomass and nutrient allocation to aboveground components in fertilized Eucalyptus saligna and E. urograndis plantations. New For. 2017, 48, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, S.M.; Schumacher, M.V.; Viera, M.; Stahl, J.; Consensa, C.B. Biomass and nutrient stocks in clonal plantations of Eucalyptus saligna Smith. at different ages. Sci. For. 2016, 44, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Higashikawa, F.S.; Silva, C.A.; Nunes, C.A.; Bettiol, W.; Guerreiro, M.C. Physico-Chemical Evaluation of Organic Wastes Compost-Based Substrates for Eucalyptus Seedlings Growth. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, L.E. Chemical Composition of Sewage Sludges and Analysis of Their Potential Use as Fertilizers. J. Environ. Qual. 1977, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.A.; Ceglie, F.; Tuzel, Y.; Koller, M.; Koren, A.; Hitchings, R.; Tittarelli, F. Organic substrate for transplant production in organic nurseries. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, M.; Hänninen, K. Composting of bio-waste, aerobic and anaerobic sludges—Effect of feedstock on the process and quality of compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2842–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacini, S.; Di Lonardo, S.; Orsenigo, S.; Massa, D. Managing pH of Organic Matrices and New Commercial Substrates for Ornamental Plant Production: A Methodological Approach. Agronomy 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, L.F.; Cordeiro, J.C.; Nascimento, J.A.M.; Cavalcante, Í.; Dias, T.J. Sources and levels of salinity of water on seedlings of papaya tree cv. sunrise solo. Semin. Ciências Agrárias 2010, 31, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Trigueiro, R.M.; Guerrini, I.A. Use of biosolids as substrate for Eucalyptus seedlings production. Sci. For. 2003, 64, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.L.D.M.; Santarelli, E.G.; Moraes Neto, S.P.D.; Manara, M.P. Produção de mudas de espécies nativas: Substrato, nutrição, sombreamento e fertilização; IPEF: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2015; Volume 427, p. Il.
- Silva, P.R.D.; Landgraf, M.D.; Zozolotto, T.C.; Rezende, M.O.O. Estudo preliminar do vermicomposto produzido a partir de lodo de esgoto doméstico e solo. São Paulo 2010, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cargnelutti Filho, A.; Araujo, M.M.; Gasparin, E.; Foltz, D.R.B. Sample size for height and diameter evaluation of timbauva plants. Floresta E Ambiente 2018, 25, e00121314. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, J.M.; de Abreu, A.H.M.; de Melo, L.A.; dos Leles, P.S.S.; Cabreira, G.V. Biosolids as substrate for the production of ceiba speciosa seedlings. Cerne 2018, 24, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.H.T.; Backes, C.; Diogo, F.A.; Pascotto, C.B.; Borelli, K. Composto de lodo de esgoto como substrato para mudas de eucalipto. Pesqui. Florest. Bras. 2013, 33, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Kageyama, P.Y.; Freixêdas, V.M.; Gonçalves, J.C.; de Geres, W.L.A. Capacidade de absorção e eficiência nutricional de algumas espécies arbóreas tropicais. Rev. Do Inst. Florest. 1992, 4, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E.; Vitti, G.C.; de Oliveira, S.A. Avaliação do Estado Nutricional das Plantas: Princípios e Aplicações; Piracicaba Associação Brasileira para Pesquisa da Potassa e do Fosfato: Piracicaba, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Leghari, S.J.; Wahocho, N.A.; Laghari, G.M.; HafeezLaghari, A.; MustafaBhabhan, G.; HussainTalpur, K.; Bhutto, T.A.; Wahocho, S.A.; Lashari, A.A. Role of nitrogen for plant growth and development: A review. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, N.H.; Marchetti, M.E.; de Carnevali, T.O.; Ramos, D.D.; Scalon, S.d.P.Q.; da Silva, E.F. Nutrition study of canafístula (I): Initial growth and seedlings quality of peltophorum dubium in response to fertilization with nitrogen and phosphorus. Rev. Árvore 2013, 37, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, N.H.; Marchetti, M.E.; Carnevali, T.; Ramos, D.D.; Quintao Scalon, S.; da Silva, E.F. Nutrition Study of Canafistula (II): Nutritional Efficiency as a Function of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilization. Available online: https://hero.epa.gov/hero/index.cfm/reference/details/reference_id/4490651 (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Siqueira, D.P.; Barroso, D.G.; de Carvalho, G.C.M.W.; Erthal, R.M.; Rodrigues, M.C.C.; Marciano, C.R. Sewage sludge treated in the substrate composition for Plathymenia reticulata Benth seedling production. Ciênc. Florest. 2019, 29, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).