Abstract
Atmospheric particulate matter (PM) contains numerous constituents, including organic molecules, inorganic ions, and metals, with some of them possessing hazardous properties. Although mainly associated with air pollution, PM can rapidly be transferred from air and land to aquatic ecosystems, and consequently poses a risk to marine biota. The aim of this work was to evaluate how urban atmospheric PM (a standard reference mixture of urban PM, known to contain various organic and inorganic contaminants), suspended in seawater, may cause toxicity in marine organisms. To this purpose, mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) were exposed to two concentrations of suspended PM: 5.7 and 11.4 mg/L. After 7, 14, and 21 days, the animals were collected and the gills and digestive gland were analysed for stress biomarkers (CAT, SOD, GPX, GST, MDA, and Ubi). In general, the results show that exposure to different concentrations of PM caused an increase in GST, UBI, and GPx activities compared to their respective controls. The average activities of GST (87.65 ± 30.23 nmol/min/mg of total protein) in the gills of the animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L of PM increased after 21 days of exposure, and the activity of GPx (8.04 ± 3.09 nmol/min/mg of total protein) in the gills increased after 14 days in the animals exposed to 5.7 mg/L of PM. MDA results also provided information on cellular damage, with the most pronounced effects being found in the gills of exposed mussels. This study confirms that mussels are useful as “early warning” indicators of environmental contamination and provides important information on the effects of PM on marine biota.
1. Introduction
Increased urbanization and industrialization have led atmospheric particulate matter (PM) to reach high levels within densely populated regions [1]. In fact, PM can be particularly dangerous, since it can contain harmful substances such as PAHs, N-heterocyclic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated pesticides, toxic metals, and other persistent compounds that can rapidly enter and accumulate in living organisms and potentially lead to biomagnification [2,3,4,5]. These types of contaminants, especially atmospheric fine particulates (PM1 or PM2.5), are linked to several risks to human health, such as damage to the respiratory tract and cardiopulmonary disorders [6,7]. Thus, PM is often associated with several adverse effects, including the risk of lung cancer and pro-inflammatory effects leading to numerous health issues in humans [8,9,10,11,12]. Therefore, their concentration must be controlled to meet the EU Directive 2008/50/EC limits.
However, despite several studies on exposure to atmospheric PM, mainly in cell lines, terrestrial models or epidemiological studies, existing information on the effects on marine biota of PM deposited and suspended in the ocean surface is still very scarce. This is particularly relevant since PM, which may contain a mixture of pollutants, can be rapidly transferred to the marine environment through natural processes such as dry and wet deposition during nutrient renewal [13]. In addition, they may also reach the marine environment through rivers.
Worldwide, the distribution of suspended PM in aquatic systems shows a high variability. For example, Wei et al. [14] reports that European coasts show 0.7 to 73 g/m3 (above surface water), while the Yangtze estuary (China) showed 0.7 to 2.1 g/m3 (above surface water). Moreover, Artic/Alaska values ranged from 0.15 to 100 g/m3 (in water) and California/San Francisco suspended PM levels ranged from 2.3 to 134 g/m3 (in water), according to the same author. Additionally, data from the Copernicus monitoring program shows that the Northwest Shelf Region of the Atlantic has variable concentrations of suspended PM, ranging between <0.01 to >100 g/m3, depending on the season and geographic area [15]. Despite this great variability, and the fact that in most cases the concentration of the suspended PM is low, in some locations the marine biota may be at risk, as they can be exposed to high concentrations of suspended PM, such as 100 g/m3. Therefore, it is of great importance to assess the toxic effects of exposure to suspended PM on marine organisms, including those belonging to different trophic levels, for understanding whether there is a trophic transfer of this material.
Mussels, as sessile filter-feeders, have been used as sentinels, indicating environmental pollution [16,17,18], which has led to an extensive monitoring program by the US EPA that is known as the Mussel Watch program [19]. This has also inspired other national and international monitoring programs worldwide. Thus, mussels (Mytilus sp.) are considered a suitable bioindicator for exposure to xenobiotics, mainly due to their high tolerance to diverse variations in physical and chemical parameters (e.g., salinity, pH, temperature), good bio-accumulation capacity, and low mobility [20,21,22].
Additionally, biomarkers are commonly used in these monitoring programs to assess the effects of exposure to contaminants and often provide early warning of harmful effects on organisms [23]. In fact, despite having some limitations, biomarkers (e.g., oxidative stress enzymes, metallothionein, among others) have been useful for this purpose. Moreover, animals exposed to contaminants often experience an increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative stress and the potential damage of cellular components or even death. However, the amount of oxidative stress experienced by these organisms will depend on the level and type of xenobiotics, the period of exposure and the organism’s innate ability to detoxify [24,25]. Several biomarkers can indicate damage after exposure to contaminants (e.g., inflammatory markers). However, the most used in toxicity studies are oxidative stress enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). Thus, altered levels of these enzymes may indicate oxidative stress in animals exposed to xenobiotics [26,27]. On the other hand, excessive ROS production can also damage cellular components, such as lipids, proteins, and DNA, which are often used as indicators of injury [28,29].
The current study explores the hypothesis that exposure to atmospheric PM deposited on the ocean surface and suspended in the water column may affect marine organisms. Therefore, this work aimed to evaluate, for the first time, the effects of a standard reference urban atmospheric PM, suspended in seawater, on a marine model organism, the mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis), exposed for 7, 14, and 21 days to two different concentrations of PM (5.7 and 11.4 mg/L); and the analysis of specific stress biomarkers (CAT, SOD, GPx, GST, MDA, and ubiquitin levels) in two key tissues, the digestive gland and gills.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PM Stock Solution
The PM stock solutions used in the exposure tests were prepared in artificial seawater from Standard Reference PM (NIST, SRM® 1648a—Urban Particulate Matter, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) to obtain final concentrations of 5.7 mg/L and 11.4 mg/L in the test aquaria. According to information provided by NIST, PM is mainly composed of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), nitro-substituted (nitro-PAH), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), chlorinated pesticides and toxic metals [30]. PM stock solutions were then sonicated for 10 min at 25 °C in an ultrasonic bath (J-P Selecta Ultrasounds HD, Barcelona, Spain). Artificial seawater was prepared by diluting artificial sea salt (Red Sea salt, Eilat, Israel) in distilled water until it reached the desired salinity (33–34‰).
2.2. Biological Model
Mussels (M. galloprovincialis) were selected as a biological model for exposure trials. They were gathered manually in the rocky shore at Cabo Raso (N 38 42.569′, W 009 29.150′) near Guincho (Portugal) during Spring 2022 and then transported to the laboratory facilities in a refrigerated thermal container. Upon arrival, the organisms were immediately placed in tanks containing seawater from the same sampling site (33‰, pH = 8.0), which is considered a pristine site. Afterwards, an acclimatization period (4–5 days) was carried out with filtered recirculating seawater, continuous aeration (>6 mg/L dissolved oxygen), and a 12 h light–dark photoperiod.
2.3. Exposure Assays
Before the beginning of the trials, the animals’ shells were washed and cleaned, to remove impurities, sand, and attached algae, and placed in four tanks (in duplicate) with seawater collected at Guincho, Cascais (N 38.73247°, W 9.47248°).
For the exposure trials, 48 organisms (shell length 3.6 ± 0.39 cm) were randomly distributed through three 15 L volume tanks (16 individuals each). The assay consisted of a control group (clean seawater without PM) and two exposure concentrations (5.7 mg/L and 11.4 mg/L of PM).
Exposure concentrations were selected based on data retrieved from the Copernicus monitoring program (data.marine.copernicus.eu). Daily, the animals were fed by supplying 1.5 mg/L of Chlorella sp. (Shine superfood, Portugal) previously dissolved in seawater. Some physical and chemical parameters were also monitored in the test tanks: pH (8.06 ± 0.07), salinity (35.10 ± 0.17 ppm), temperature (17.60 ± 0.40 °C), total dissolved solids (TDS: 35.10 ± 0.17 ppm), and electric conductivity (59.26 ± 0.99 mS/cm). Every 48 h, the seawater in each tank was changed and contaminated with PM.
After 7, 14, and 21 days, mussels were sampled and sacrificed to remove gills and digestive glands. Each organ was then homogenized (Tissue Master 125, Omni, Kennesaw, GA, USA) in 2 mL of phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS: 140 mM NaCl (Panreac, Barcelona, Spain); 10 mM Na2HPO4, (Sigma–Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA); 3 mM KCl (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany); 2.0 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.40, (Sigma–Aldrich)) and centrifuged for 10 min at 15,000× g (VWR, model CT 15RE from Hitachi Koki, Tokyo, Japan) to obtain the cytosolic fraction. Then, the supernatants were collected in 1.5 mL microtubes and stored at −45 °C until further analysis.
2.4. Total Protein Determination
The amount of protein in the samples was quantified following the Bradford method, as described in Coelho et al. [31].
A standard curve was constructed by preparing different concentrations of bovine serum albumin (BSA, Nzytech, Lisboa, Portugal), ranging from 0 to 4 mg/L. The phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution was used as a blank. Then, after placing 20 µL of each sample or standard in the wells of a 96-well microplate (Greiner, BioOne GmbH, Frickenhausen, Germany), 180 µL of the Bradford reagent was added to the microplate wells. Finally, the samples’ and standards’ absorbance were measured at 595 nm using a microplate reader (Synergy HTX; Biotek, Multi-Mode Reader, Winooski, VT, USA).
2.5. Antioxidant Enzyme Biomarkers
2.5.1. Catalase (CAT)
Catalase was determined following the method described in Cid et al. [32]. A calibration curve (0 to 75 mM), using formaldehyde as a standard, was prepared from a stock solution (4.25 mM; Sigma-Aldrich). Subsequently, in a 96-well microplate (Greiner, BioOne GmbH), 20 µL of the sample or blank solution (PBS) was placed in duplicate, together with 100 µL of assay buffer (100 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.0), and 30 µL of methanol (~99.8%; Honeywell; Seelze, Germany). The reaction was initiated by adding 20 µL of hydrogen peroxide (0.035 M; H2O2 35% Pure; PanReac). After a 20 min incubation period at room temperature, with the plate covered with aluminum foil and under constant agitation in an orbital shaker (Optic Ivymen System, Comecta, Barcelona, Spain), 30 µL of potassium hydroxide (KOH 10 M) and 30 µL of 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (purpald; ≥99%; Sigma–Aldrich; dissolved at 34.2 mM in 0.5 M HCl, and distilled water) were added to the wells followed by a new 10 min incubation period. Finally, 10 µL of potassium periodate (KIO4; 65.2 mM in 0.5 M KOH) was added to stop the reaction, followed by an additional 5 min incubation period under agitation. Then, the microplate was read at 540 nm (SynergyHTX, Biotek, Multi-Mode Reader). The activity results were normalized to the total protein concentration.
2.5.2. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
The superoxide dismutase (SOD) assay was performed as described by Matos et al. [33]. First, 200 µL of potassium phosphate buffer (50 mM; pH 8.0), 10 µL of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA; 3mM; Honeywell Riedel-de Haen GmbH), 10 µL of xanthine (3 mM; Sigma–Aldrich), and 10 µL of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT; 0.75 mM; Sigma–Aldrich) were added to each well of the microplate (Greiner, BioOne GmbH). Then, 10 µL of each sample (in duplicate) and PBS as a blank (in quadruplicate) were placed in the wells, followed by 10 µL of xanthine oxidase XOD (0.4 U/mg of protein; Sigma–Aldrich) to start the reaction. The microplate was read at 560 nm every minute for 26 min in a microplate reader (Synergy HTX, BioTek), and results were normalized to the total protein concentration.
2.5.3. Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx)
The glutathione peroxidase (GPx) assay was performed as described in Coelho et al. [31]. Thus, 20 µL of the sample (in duplicate) and blanks (PBS in quadruplicate) were placed in the microplate wells (Greiner BioOne GmbH). The assay was carried out by mixing phosphate buffer (50 mM; pH 7.4) with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA; 5 mM; Riedel-Haën; Seelze, Germany) and adding 120 µL of this mixture to each well. Then, 50 µL of a co-substrate solution, consisting of NADPH (~98%; Sigma–Aldrich), reduced glutathione (GSH; 200 mM; Sigma–Aldrich), sodium azide (4 mM NaN3; Sigma-Aldrich), and 5 µL of glutathione reductase (GSSH reductase from S. cerevisiae; Sigma–Aldrich) was also added into the microplate wells. Afterward, 20 µL of 15 mM cumene hydroperoxide (80%; Sigma–Aldrich) was added to the wells. The absorbances were read using a microplate reader (Synergy HTX, BioTek) at 340 nm every minute for 6 min, and enzyme activities were calculated using an extinction coefficient for NADPH of 0.00373 µM−1. Total protein was used to normalize the results.
2.5.4. Glutathione S-Transferase (GST)
Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) activities were determined based on a protocol described in Larguinho et al. [34]. First, a reaction mixture composed of 9.6 mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS 7.3), 0.1 mL reduced glutathione (GSH) at 200 mM (Sigma–Aldrich), and 0.1 mL 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) at 100 mM was prepared (Sigma–Aldrich). Then, 180 µL of this reaction mixture and 20 µL of the samples (in duplicate) or blank (PBS in duplicate) were added to each well of a 96-well microplate (Greiner, BioOne GmbH). Then, a microplate reader was used to monitor the reaction for 6 min (Synergy HTX, BioTek). GST activities were determined using the CDNB extinction coefficient of 5.3 mM−1, and total protein content was used to normalize the results.
2.6. Lipid Peroxidation (LPO)
Lipid peroxidation (LPO) followed the thiobarbituric acid assay, as previously described in Diniz et al. [35]. A calibration curve was constructed by preparing malondialdehyde (MDA) standards at different concentrations (0 to 0.100 mM). Then, a solution containing 2.29 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS: 140 mM NaCl (Panreac), 10 mM Na2HPO4, (Sigma–Aldrich), 3 mM KCl, (Merck), 2.0 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.40, (Sigma–Aldrich)), 0.64 mL sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS; 8.1% (w/v)), 4.75 mL trichloroacetic acid (122 mM TCA, pH 3.5; PanReac), 4.75 mL 4,6-dihydroxy-2-mercapto pyrimidine, 4,6-dihydroxy pyrimidine-2-thiol (69 mM TBA, Sigma–Aldrich), and 2.57 mL ultrapure water was prepared.
Then, 295 µL of the reaction mixture was previously prepared and 5 µL of samples or standards were added into microtubes (1.5 mL) and mixed for one minute; then, the microtubes (with perforated caps) were placed in a dry bath (Digital Thermoblock, Labnet, Woodbridge, NJ, USA) at 100 °C. After 10 min, each microtube was placed on ice to cool, and 62.5 µL of ultrapure water was added to each microtube and subsequently mixed. Finally, 150 µL of each sample was added to the microplate wells in duplicate (Greiner, BioOne GmbH). The results were obtained by measuring the absorbance at 530 nm using a microplate reader (Synergy HTX, BioTek) and then normalized to total protein content.
2.7. Ubiquitin (Ubi) Assay
The total ubiquitin was determined following the method described in Coelho et al. [31]. A calibration curve was constructed using various concentrations of a standard ubiquitin (UbpBio, E-1100, Dallas, TX, USA), ranging from 0 to 0.8 µgmL−1.
To perform the assay, 50 µL of samples or standards, in duplicate, were added to a 96-well microplate (Microlon 600, Greiner Bio-One GmbH) and incubated overnight at 4 °C. On the following day, after washing the microplate three times with PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20 (PanReac), 100 µL of a blocking solution (1% BSA in PBS) was added and then incubated (2 h, at room temperature). After a new washing step with PBS (0.05% Tween-20), 50 µL of the primary antibody in PBS with 1% BSA (Ub (P4D1) Sc-8017, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) was added to the microplate wells and left to incubate overnight (covered in aluminum foil at 4 °C). On the next day, after washing the microplate as described before, 50 µL of secondary antibody (Anti-Mouse Ig-Fc specific-Alkaline Phosphatase conjugated; Sigma–Aldrich), diluted to 1:1000, was added to the microplate wells and left to incubate overnight (at 4 °C). After the incubation period, the microplate was rewashed, and 50 µL of the substrate solution (10 mg of 4-Nitrophenyl phosphate disodium salt hexahydrate (PnPP ≥ 99%; Sigma–Aldrich), 157 mg trizma hydrochloride (Tris HCl; Sigma–Aldrich), 58.4 mg NaCl, and 50 µL magnesium chloride hexahydrate at 5 mM (Fluka, BioChemika, Buchs, Switzerland), pH: 8.5) was added to the microplate wells followed by a 30 min incubation period at room temperature. Finally, to stop the reaction, 50 µL of STOP solution (3M NaOH) was added to each well, and the absorbance was read at 405 nm using a microplate reader (Synergy HTX, BioTek). Results were normalized to the total protein content.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Prism 9: GraphPad (version 9.5.1). Multiple comparison tests were performed using Brown–Forsythe and Welch’s ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test to assess significant differences (p < 0.05) between assayed organisms. Pearson’s r correlation coefficient was used to measure the correlation between variables and build a correlation heat-map.
2.9. Ethics
In this study, all relevant policies regarding animal experimentation and welfare were followed (e.g., Directive 2010/63/EU) [36]. Results were also reported following the ARRIVE guidelines (e.g., the 3 Rs principle of animal welfare) [37]. Additionally, the researchers who conducted the experiments with clams are certified with level C by the Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science (FELASA) and have long expertise in animal experimentation.
3. Results
3.1. Mortality
During the exposure trials, no mortality was recorded.
3.2. Enzymatic Biomarkers
3.2.1. Catalase (CAT)
The results of CAT activities determined in the gills and digestive glands are presented in Figure 1. In the gills (Figure 1a), the highest average activity (0.06 ± 0.02 nmol/min/mg total protein) was recorded in the control group collected after 7 days of exposure. In contrast, the lowest average activity (0.03 ± 0.01 nmol/min/mg total protein) was determined in animals exposed to 5.7 mg/L PM, after 14 days of exposure. On the other hand, the highest CAT average activities (0.10 ± 0.03 nmol/min/mg of total protein) were determined in the digestive glands of mussels exposed to 5.7 mg/L of PM for 14 days (Figure 1b). Meanwhile, the lowest average activity (0.04 ± 0.04 nmol/min/mg of total protein) was observed in the control group sampled after 7 days of exposure.
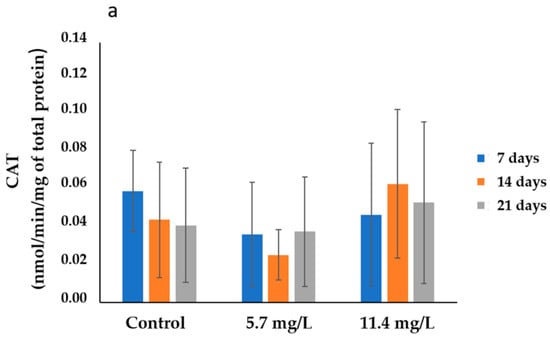
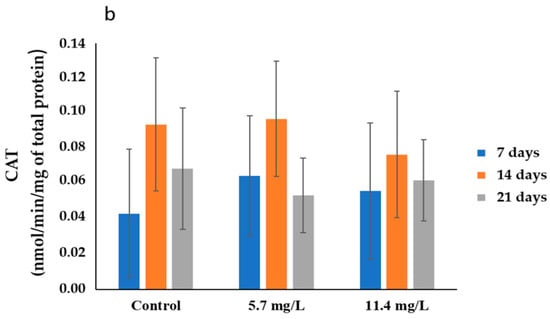
Figure 1.
CAT activities (mean ± SD) in mussels’ (a) gills and (b) digestive glands after 7, 14, and 21 days of exposure to different concentrations of PM.
Regarding statistics, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were found, in both organs, between the organisms exposed to the different concentrations and their respective controls or between treatments throughout the exposure period.
3.2.2. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
The results of SOD activities are shown in Figure 2. The highest average activity (13.58 ± 2.99 U/mg of total protein) was observed in the gills of mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L of PM for 21 days. On the other hand, the lowest average value (3.74 ± 1.32 U/mg of total protein) was observed in the digestive gland of mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L of PM for 7 days.
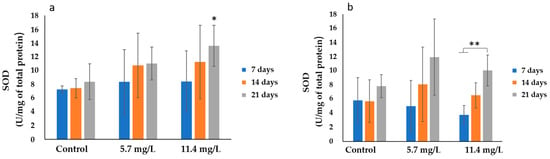
Figure 2.
SOD activities (mean ± SD) in mussels’ (a) gills and (b) digestive glands after 7, 14, and 21 days of exposure to different concentrations of PM. Significant differences (p < 0.05) compared to controls (*) and between exposure periods (**).
There was a general trend towards increasing SOD activities in both organs of the exposed animals. Statistics showed a significant (p < 0.05) increase in the gills of animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM after 21 days (Figure 2a). Regarding the digestive glands, no significant differences were found between controls and treatments. However, significant differences (p < 0.05) were found over time (Figure 2b) in animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM.
3.2.3. Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx)
GPx results are shown in Figure 3. The highest average activity (8.04 ± 3.09 nmol/min/mg of total protein) was found in the gills of mussels exposed to 5.7 mg/L PM for 14 days. On the other hand, the lowest average activity (3.49 ± 2.44 nmol/min/mg of total protein) was observed in the digestive gland of individuals exposed to 5.7 mg/L PM and sampled after 7 days.
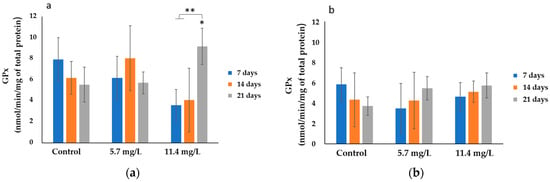
Figure 3.
GPx activities (mean ± SD) in mussels’ (a) gills and (b) digestive Glands after 7, 14, and 21 days of exposure to different concentrations of PM. Significant differences (p < 0.05) compared to controls (*) and between exposure periods (**).
Regarding gills (Figure 3a), a slight increase in GPx activity is evident in mussels exposed to 5.7 mg/L PM after 14 days compared to their respective controls, while a significant increase (p < 0.05) was observed in animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM, compared to respective controls. Besides, a significant increase (p < 0.05) of GPx activity was found from 7 and 14 to 21 days in animals exposed to the highest concentration.
Additionally, significant differences (p < 0.05) were also found between animals exposed to 5.7 and those exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM, after 21 days.
With respect to digestive glands (Figure 3b), a slight increase in GPx activity was observed in animals exposed for 14 and 21 days to both tested concentrations (5.7 mg/L and 11.4 mg/L PM) according to the exposure times; however, no significant changes (p > 0.05) were detected.
3.2.4. Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST)
The results of GST activity are presented in Figure 4. The highest GST average activity (87.65 ± 30.23 nmol/min/mg of total protein) was found in the gills of mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM for 21 days (Figure 4a). While the lowest average activity (29.21 ± 10.87 nmol/min/mg of total protein) was observed in the digestive glands of mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM for 7 days (Figure 4b).
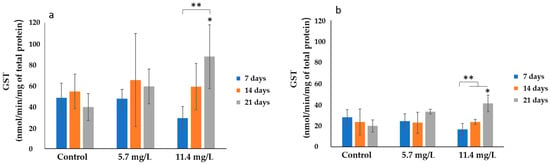
Figure 4.
GST activities (mean ± SD) in mussels’ (a) gills and (b) digestive glands after 7, 14, and 21 days of exposure to different concentrations of PM. Significant differences (p < 0.05) compared to controls (*) and between exposure periods (**).
Statistical analysis revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) in the gills of mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM compared to their respective controls after 21 days (Figure 4a). Concerning GST activities measured in the digestive gland (Figure 4b), significant differences (p < 0.05) were found in mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM, compared to their respective controls after 21 days. Significant changes were also observed in both organs of the mussels exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM throughout the exposure time.
3.3. Lipid Peroxidation (LPO)
Lipid Peroxidation was assessed by measuring the MDA concentration in the gills and digestive glands, as shown in Figure 5a,b, respectively. In both organs, MDA levels rise with increasing PM concentrations and exposure time. In the gills, the highest average MDA levels (0.11 ± 0.008 nmol/mg of total protein) was found in animals exposed to the highest PM concentration (11.4 mg/L) after 7 days, while the lowest average value (0.041 ± 0.013 nmol/mg of total protein) was observed in mussels exposed to 5.7 mg/L after 21 days. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were found between the gills of animals exposed to 5.7 and those exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM after 21 days.
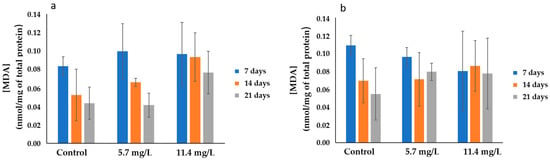
Figure 5.
MDA concentration (mean ± SD) in mussels’ (a) gills and (b) digestive glands after 7, 14, and 21 days of exposure to different concentrations of PM.
In the digestive glands, the highest average MDA value (0.11 ± 0.01 nmol/mg of total protein) was determined in controls after 7 days of exposure. Meanwhile, the lowest average values (0.055 ± 0.029 nmol/mg of total protein) were measured in controls after 21 days. An increasing trend can be observed in animals exposed to the highest concentration of 11.4 mg/L PM compared to respective controls; however, no significant changes were found between tested concentrations and controls or over the exposure periods.
3.4. Total Ubiquitin
Total ubiquitin levels determined in the gills and digestive glands are presented in Figure 6a,b, respectively. The highest average level of total ubiquitin (0.87 ± 0.27 µg/mg of total protein) was observed in gills exposed to a PM concentration of 11.4 mg/L after 21 days. Meanwhile, the lowest average level (0.27 ± 0.06 µg/mg of total protein) was observed in the digestive glands of animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L of PM after 7 days.
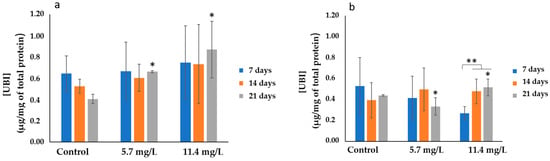
Figure 6.
Ubiquitin concentrations (mean ± SD) in mussels’ (a) gills’ and (b) digestive glands after 7, 14, and 21 days of exposure to different concentrations of PM. Significant differences (p < 0.05) compared to controls (*) and between exposure periods (**).
A significant increase (p < 0.05) in total ubiquitin levels was observed in both organs of the animals exposed to the highest PM concentration (11.4 mg/L) compared to respective controls after 21 days. Additionally, statistical analysis revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) in the gills between mussels exposed to a PM concentration of 5.7 mg/L and respective controls after 21 days of exposure. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were also found in the digestive glands of animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM throughout the exposure periods.
3.5. Correlation Analyses
Figure 7a,b show the results of the correlation analysis (Pearson r) in gills and digestive glands. Regarding the digestive glands, results show significant low to moderate positive correlations between GST and UBI (p = 0.003; r = 0.45), GST and SOD (p < 0.0001; r = 0.64), and SOD and UBI (p < 0.0001; r = 0.58); and significant but low positive correlation between GPX and LPO (p = 0.008; r = 0.43). In gills, significant low to moderate positive correlations were found between GST and SOD (p < 0.0001; r = 0.56), GST and GPX (p = 0.001; r = 0.47), UBI and CAT (p = 0.007; r = 0.45), UBI and LPO (p = 0.011; r = 0.39) and UBI and SOD (p < 0.0001; r = 0.66).
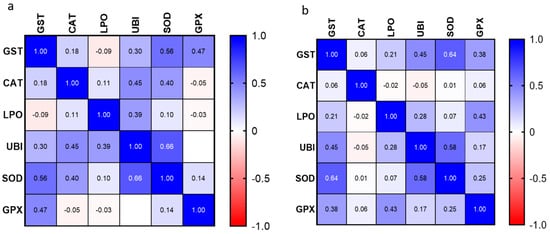
Figure 7.
Correlation analyses (Pearson r) performed in mussels’ (a) gills and (b) digestive glands.
4. Discussion
The increasing perception of the risk to human health resulting from exposure to PM, coupled with the dispersion and movement in the atmosphere of air masses carrying PM, implies that the effects on humans and animals, in many areas, including marine organisms, are often unknown. Therefore, Smoot et al. [38] suggested that, in addition to traditional in vivo models using mammals, other models (e.g., Danio rerio, Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster) should be used to obtain information on PM toxicity. In the present study, we selected the mussel as a biological model to study the effects of PM on marine biota. In fact, aquatic ecosystems, especially estuaries, are constantly threatened by the entry of pollutants, mainly from anthropic sources [39]. Moreover, the effects following exposure to PM on marine biota are poorly studied, leading to a lack of knowledge about the associated risks to aquatic ecosystems.
PM toxicity is often attributed to contaminants (e.g., toxic metals, PAHs, and other organic compounds) present in the particulate material. Furthermore, in addition to composition, particulate size is a significant factor affecting its toxicity. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) has been particularly well-documented, and according to the European Environmental Agency (EEA), is responsible for several premature human deaths [40,41] due to its high environmental prevalence and ability to penetrate deeper into tissues [42,43,44].
Although most of the studies have been carried out in mammals or cell lines, very few studies have been carried out with aquatic organisms. For example, in a study involving the embryonic stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio), evidence suggests that PM2.5 triggered toxicity in various fish organs, with the cardiovascular, hepatic, and neurological systems being the most affected, leading to the death of the organisms [45].
Other studies performed in zebrafish embryos and larvae exposed to 100 and 200 µg/mL PM10 reported harmful effects on the nervous system, various morphological abnormalities, and increased mortality [46]. Cen at al. [47] also showed that PM10 exposure caused developmental disorders and induced cardiovascular toxicity, which was attributed to increased ROS levels. In addition, Ren et al. [48] also showed an elevation of ROS in zebrafish embryos exposed to PM2.5, causing cardiac harm, DNA damage, and apoptosis. Moreover, medaka (Oryzias melastigma) exposed to PM2.5, simulating atmospheric wet precipitation, showed decreased growth, disturbances in the gut microbiome, and affected the lipid metabolism [49].
A study by Hartono et al. [50] revealed that freshwater snails (Parafossarulus striatulus), exposed to 7.75 mg/L PM2.5, led to a significant decrease in animals’ movement behavior. Whereas, a low concentration of PM2.5 (3.88 mg/L) did not significantly affect the snails’ behavior, suggesting that, despite not being lethal, the higher concentration of PM2.5 still has an impact on organism’s normal behavior. This is in accordance with the present study, where no mortality was observed, although some biomarkers were altered. The low mortality could be due to the innate resistance of mussels to external contaminants [51,52], but also to its filter-feeding capabilities [53].
In the present study, the mussel responses to PM exposure were assessed by determining some markers of oxidative stress (CAT, SOD, GPx, and GST), which are enzymes linked to the fight against ROS and oxidative stress [54]. SOD and GPX activities increased, showing a similar pattern of response in the gills of animals exposed to the highest concentration of PM tested (11.4 mg/L) and suggesting a more pronounced effect in this organ. Interestingly, significant moderate to strong positive correlations were found between SOD and GST and between SOD and UBI, for both organs, which may suggest a link between increasing SOD, detoxification, and/or antioxidant processes and increased protein damage. In addition, the activities of most oxidative stress enzymes increased over the exposure time (7 to 21 days), mainly in animals exposed to 11.4 mg/L PM, suggesting that this concentration may lead to oxidative stress in mussels.
On the contrary, despite showing a general trend to rise with increasing concentrations and exposure periods, CAT activities did not show significant differences in both organs evaluated, possibly because other defense mechanisms are acting to protect cells.
Adorno et al. [55] exposed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) for 96 h to 1.0 g/L of settleable particulate matter (SePM), causing oxidative stress in fish blood. The fish showed increased CAT and GPx activities and LPO, but no changes in GST were observed. On the other hand, the results showed the inhibition of SOD and Glutathione reductase (GR). Although the elevation of GPx and LPO is in line with our study, CAT activities were not altered. However, the differences found between the two studies can be explained by the duration of the assay, the concentrations tested, the different type of PM employed and the use of a different species.
In a study developed by Duarte et al. [56], brown mussels (Perna perna) were exposed for one month to SePM from a metallurgical area in Brazil, close to an estuary. They found that the mussels bioaccumulated several metals that were correlated with cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in a dose and exposure time-dependent manner. In addition, no changes in LPO were found, suggesting an effective antioxidant system to protect the animals. However, it should be noted that the PM concentrations tested ranged from 0.01 to 1 g/L, and, at the lowest concentration, no significant changes were observed. In another study, Monteiro et al. [57] exposed the juvenile fat snook fish (Centropomus parallelus) to different concentrations of SePM (0 to 1.0 g/L), for 96 h. They found a reduction in SOD activity in the gills; an increase in SOD, CAT, and GPx in the hepatopancreas; an increase in CAT, GST, and GSH in the kidneys; but no alterations were found in LPO and oxidized proteins, suggesting that antioxidant defenses were enough to prevent oxidative stress.
In mussels, the digestive glands play a role in metabolism like that of the liver in other animals. Thus, this organ is expected to have higher GST activity, associated with the ability to metabolize xenobiotics [58,59,60]. However, this fact is only noticeable in the present study for the gills and digestive glands after 21 days of exposure, where a significant increase was observed. Furthermore, GST activities, determined in both organs, increased over the exposure time (7 to 21 days), especially in organisms exposed to the highest PM concentration (11.4 mg/L), which suggests a detoxifying response, as this enzyme is involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics. In addition, GST may help fight oxidative stress, thus an increase in its activity may also occur [61,62].
Han et al. [63] showed that exposure of the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus to PM2.5 led to oxidative stress. Indeed, the authors exposed copepods to 4.7, 9.5, and 18.9 mg/L PM2.5 and first found an intracellular reduction of ROS in animals exposed to 4.7 and 18.9 PM2.5, but no changes were detected in animals exposed to 9.5 mg/L PM2.5. Furthermore, they observed an upregulation of several CYP and GST genes which are involved in detoxification processes.
Exposure to PM has been associated with DNA damage, lipid peroxidation, and protein damage [26,60,61]. Thus, the increase in total ubiquitin levels found in this study suggests protein damage, mainly in the gills of animals exposed to the highest PM concentration (11.4 mg/L) after 21 days. In addition, an increase in MDA concentrations was also observed, mostly in animals exposed to the highest PM concentration (11.4 mg/L), suggesting cell membrane damage. Moreover, both MDA and ubiquitin results suggest that the antioxidant defense system was not capable of efficiently removing the excess of ROS produced, leading to some cellular damage after 21 days of exposure.
5. Conclusions
Although there is little information about the effects of atmospheric PM on marine biota, which is deposited and suspended in the ocean, the present study shows that environmentally relevant concentrations of PM found in various regions of the ocean (mainly in coastal zones) can lead to oxidative stress in exposed mussels, as demonstrated by the elevation of some antioxidant enzymes at the highest exposure concentration (11.4 mg/L PM). These findings are also supported by the results of total ubiquitin and, to some extent, MDA levels. Furthermore, the results suggest that mussels have some resilience, as no mortality was recorded during the trial, and thus can be used as an “early warning” indicator of environmental contamination. Finally, due to the paucity of information to compare our results, in the same species and with similar PM exposure concentrations, further studies are imperative to fully understand the effects of PM on marine biota.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D. and R.M.B.O.D.; methodology, M.D., I.J.F. and I.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D., I.J.F. and I.R.; writing—review and editing, supervision, M.D., I.J.F. and R.M.B.O.D.; project administration, R.M.B.O.D.; funding acquisition, R.M.B.O.D. and M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded to CESAM by FCT/MCTES (UIDP/50017/2020+UIDB/50017/2020+LA/P/0094/2020), and to UCIBIO (Applied Molecular Biosciences Unit) funded by FCT/MCTES (04378 2020 and UIDB/04378 2020) through national funds. This work was also supported by project AMBIEnCE (PTDC/CTA AMB/28582 2017) funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
This paper contributes to the science plan of the Surface Ocean Lower Atmosphere Study (SOLAS) which is supported by the U S National Science Foundation via the Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research (SCOR), which have given their consent to this acknowledgement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Buis, A. Getting to the Heart of the Particulate Matter. Earth Science Communications Team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory|California Institute of Technology. Available online: https://climate.nasa.gov/news/3027/getting-to-the-heart-of-the-particulate-matter/ (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- He, M.; Sun, Y.L.X.; Yang, Z. Distribution patterns of nitrobenzenes and polychlorinated biphenyls in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from mid- and downstream of the Yellow River (China). Chemosphere 2006, 65, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovljević, I.; Pehnec, G.; Vađić, V.; Čačković, M.; Tomašić, V.; Jelin, J.D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 particle fractions in an urban area. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Bandara, P.C.; Novo, L.A.B.; Kumar, A.; Ambade, B.; Naveendrakumar, G.; Ranagalage, M.; Magana-Arachchi, D.N. Deposition of trace metals associated with atmospheric particulate matter: Environmental fate and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świsłowski, P.; Hrabák, P.; Wacławek, S.; Liskova, K.; Antos, V.; Rajfur, M.; Ząbkowska-Wacławek, M. The Application of Active Biomonitoring with the Use of Mosses to Identify Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in an Atmospheric Aerosol. Molecules 2021, 26, 7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, R.; Duarte, A. Urban Atmospheric Aerosols: Sources, Analysis, and Effects. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.M.B.O.; Duarte, A.C. Health Effects of Urban Atmospheric Aerosols. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Badran, G.; Verdin, A.; Ledoux, F.; Roumié, M.; Courcot, D.; Garçon, G. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives in airborne particulate matter: Sources, analysis and toxicity. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 439–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M.; Dumanoglu, Y.; Efstathiou, C.; Kukučka, P.; Matejovičová, J.; Maurer, C.; Přibylová, P.; Prokeš, R.; Sofuoglu, A.; Sofuoglu, S.C.; et al. Fast formation of Nitro-PAHs in the Marine Atmosphere Constrained in a Regional Scale Lagragian Field Experiment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8914–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Cui, B.; Ding, R.; Shi, X.; He, P. Association between particulate matter air pollution and lung cancer. Thorax 2020, 5, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood-Garibay, J.A.; Angulo-Molina, A.; Mendez-Rojas, M.A. Particulate matter and ultrafine particles in urban air pollution and their effect on the nervous system. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2023, 25, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.S.; Ferreira, R.M.P.; Silva, A.M.S.; Duarte, A.C.; Neves, B.M.; Duarte, R.M.B.O. Structural Features and Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Water-Soluble Organic Matter in Inhalable Fine Urban Air Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara, M. Emissions of Airborne Particulate Matter. In Issues in Environmental Science and Technology Nº42, Airborne Particulate Matter: Sources, Atmospheric Processes and Health, 1st ed.; Edited by Hester, R.E., Harrison, R.M., Querol, X., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–22. Available online: https://api.pageplace.de/preview/DT0400.9781782626589_A28401559/preview-9781782626589_A28401559.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L.; Yu, X.; Mikelsons, K.; Shen, F. Global estimation of suspended particulate matter from satellite ocean color imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E.U. Copernicus Marine Service Information (CMEMS). Marine Data Store (MDS). 2023. Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/OCEANCOLOUR_NWS_BGC_HR_L3_NRT_009_203/contacts (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Ruus, A.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis spp.) as sentinel organisms in coastal pollution monitoring: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Lise, I.; Bråte, N.; Sun, C.; Hossain, M.S.; Li, Q.; et al. Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekhoroshkov, P.; Bezuidenhout, J.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Vergel, K.; Frontasyeva, M. Levels of Elements in Typical Mussels from the Southern Coast of Africa (Namibia, South Africa, Mozambique): Safety Aspect. Water 2021, 13, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrington, J.W.; Tripp, B.W.; Tanabe, S.; Subramanian, A.; Sericano, J.L.; Wade, T.L.; Knap, A.H.; Edward, D. Goldberg’s proposal of “the Mussel Watch”: Reflections after 40 years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailov, A.T.; Torrado, M.; Méndez, J. Mussel Mytilus as model organisms in marine biotechnology: Polypeptide markers of development and sexual differentiation of the reproductive system. In New Development in Marine Biotechnology; Le Gal, Y., Halvorson, H.O., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Costa, M.; Leite, C.; Borges, C.; Coppola, F.; Henriques, B.; Monteiro, R.; Russo, T.; Di Cosmo, A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; et al. Ecotoxicological effects of lanthanum in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Biochemical and histopathological impacts. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 211, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curpan, A.S.; Impellitteri, F.; Plavan, G.; Ciobica, A.; Faggio, C. Review: Mytilus galloprovincialis: An essential, low-cost model organism for the impact of xenobiotics on oxidative stress and public health. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 256, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.K.S.; Gray, J.S. The use of biomarkers in environmental monitoring programmes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borković, S.; Saponjić, J.; Pavlović, S.; Blagojević, D.; Milosević, S.; Kovacević, T.; Radojičić, R.M.; Spasić, M.B.; Žikić, R.V.; Saicić, Z. The activity of antioxidant defence enzymes in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Adriatic Sea. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Munari, M.; Masiero, L. Ecotoxicological hazard of a mixture of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid to the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlahogianni, T.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regoli, F.; Giuliani, M.E. Oxidative pathways of chemical toxicity and oxidative stress biomarkers in marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 93, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chora, S.; McDonagh, B.; Sheehan, D.; Starita-Geribaldi, M.; Roméo, M.; Bebianno, M. Ubiquitination and carbonylation as markers of oxidative-stress in Ruditapes decussatus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Umeno, A.; Shichiri, M. Lipid peroxidation biomarkers for evaluating oxidative stress and assessing antioxidant capacity in vivo. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2013, 52, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIST Office of Reference Materials. Standard Reference Material® 1648a-Urban Particulate Matter, USA. National Institute of Standards & Technology-Certificate of Analysis. Available online: https://tsapps.nist.gov/srmext/certificates/1648a.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- Coelho, J.; Court, M.; Otjacques, E.; Lopes, V.; Paula, J.; Repolho, T.; Diniz, M.; Rosa, R. Effects of tidal emersion and marine heatwaves on cuttlefish early ontogeny. Mar. Biol. 2022, 170, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, A.; Picado, A.; Correia, J.; Chaves, R.; Silva, H.; Caldeira, J.; Matos, A.P.A.; Diniz, M. Oxidative stress and histological changes following exposure to diamond nanoparticles in the freshwater Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774). J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 284, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, B.; Martins, M.; Samamed, A.; Sousa, D.; Ferreira, I.; Diniz, M. Toxicity Evaluation of Quantum Dots (ZnS and CdS) Singly and Combined in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larguinho, M.; Correia, D.; Diniz, M.; Batista, P. Evidence of one-way flow bioaccumulation of gold nanoparticles across two trophic levels. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.; Matos, A.; Lourenço, J.; Castro, L.; Peres, I.; Mendonça, E.; Picado, A. Liver Alterations in Two Freshwater Fish Species (Carassius auratus and Danio rerio) Following Exposure to Different TiO2 Nanoparticle Concentrations. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Animal Research Association. EU Regulations on Animal Research. Available online: https://www.eara.eu/animal-research-law (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- NSW Department of Primary Industries and Animal Research Review Panel. Three Rs. Available online: https://www.animalethics.org.au/three-rs (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Smoot, J.; Padilla, S.; Farraj, A.K. The utility of alternative models in particulate matter air pollution toxicology. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 3, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Kong, F.; Li, M.; Xi, M.; Yu, Z. How do trophic magnification factors (TMFs) and biomagnification factors (BMFs) perform on toxic pollutant bioaccumulation estimation in coastal and marine food webs. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostro, B.; Hu, J.; Goldberg, D.; Reynolds, P.; Hertz, A.; Bernstein, L.; Kleeman, M. Associations of Mortality with Long-Term Exposures to Fine and Ultrafine Particles, Species and Sources: Results from the California Teachers Study Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEA. Premature Deaths Due to Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter in Europe. European Environmental Agency. December 2022. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/ims/health-impacts-of-exposure-to (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Kim, J.; Son, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Jeong, S.; Park, T.; Son, S.W.; Ryu, H. Particulate matter (PM)2.5 affects keratinocytes via endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress- mediated suppression of apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Forsberg, B. Epidemiological evidence of effects of coarse airborne particles on health. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, B.; Alam, K.; Sorooshian, A.; Blaschke, T.; Ahmad, I.; Shahid, I. On the Morphology and Composition of Particulate Matter in an Urban Environment. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1431–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, L.; Shi, Y.; Miller, M.; Sun, Z. Multi-organ toxicity induced by fine particulate matter PM2.5 in zebrafish (Danio rerio) model. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Rajendran, R.S.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Cen, J. Exposure of particulate matter (PM10) induces neurodevelopmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Neurotoxicology 2021, 87, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, J.; Jia, Z.-L.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Zhang, F.; Chen, W.-Y.; Liu, K.-C.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhang, Y. Particulate matter (PM10) induces cardiovascular developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos and larvae via the ERS, Nrf2 and wnt pathways. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Ji, C.; Huang, Y.; Aniagu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T. AHR-mediated ROS production contributes to the cardiac developmental toxicity of PM2.5 in zebrafish embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 135097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, W.; Hong, Y.; Chena, J.; Dong, S.; Huang, Q. Long-term wet precipitation of PM2.5 disturbed the gut microbiome and inhibited the growth of marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, D.; Lioe, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, J. Impacts of particulate matter (PM2.5) on the behavior of freshwater snail Parafossarulus striatulus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurelec, B.; Pivčević, B. Evidence for a multixenobiotic resistance mechanism in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 1991, 19, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzellitti, S.; Capolupo, M.; Wathsala, R.; Valbonesi, P.; Fabbri, E. The Multixenobiotic resistance system as a possible protective response triggered by microplastic ingestion in Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis): Larvae and adult stages. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 219, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimany, E.; Ramón, M.; Ibarrola, I. Feeding behavior of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (L.) in a Mediterranean estuary: A field study. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.A.; Bainy, A.C.D.; Loureiro, A.P.M.; Martinez, G.R.; Miyamoto, S.; Onuki, J.; Barbosa, L.F.; Garcia, C.C.M.; Prado, F.M.; Ronsein, G.E.; et al. Oxidative stress in Perna perna and other bivalves as indicators of environmental stress in the Brazilian marine environment: Antioxidants, lipid peroxidation and DNA damage. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2007, 146, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorno, H.; Souza, I.; Monferrán, M.; Wunderlin, D.; Fernandes, M.; Monteiro, D. A multi-biomarker approach to assess the sublethal effects of settleable atmospheric particulate matter from an industrial area on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.F.A.; Ortega, A.D.S.B.; Paço, M.S.; Sadauskas-Henrique, H.; Cesar-Ribeiro, C.; Souza, I.C.; Monteiro, R.; Monferrán, M.V.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Fernandes, M.N.; et al. Settleable atmospheric particulate matter harms a marine invertebrate: Integrating chemical and biological damage in a bivalve model. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Souza, I.C.; Morozesk, M.; Pereira Soares, M.; De Angelis, C.F.; Vieira, N.S.; Bendhack, F.; Monferran, M.V.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Fernandes, M.N. Metalliferous atmospheric settleable particulate matter action on the fat snook fish (Centropomus parallelus): Metal bioaccumulation, antioxidant responses and histological changes in gills, hepatopancreas and kidneys. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moron, M.; Depierre, J.; Mannervik, B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 582, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Lagarde, F.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Bruneau, M.; Akcha, F.; Sussarellu, R.; Rouxel, J.; Costil, K.; Decottignies, P.; Cognie, B.; et al. Tissue-Specific Biomarker Responses in the Blue Mussel Mytilus spp. Exposed to a Mixture of Microplastics at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobal, V.; Suárez, P.; Ruiz, Y.; García-Martín, O.; Juan, F. Activity of antioxidant enzymes in Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to tar: Integrated response of different organs as pollution biomarker in aquaculture areas. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczek, G.; Kramarz, P.; Babczyńska, A. Activity of carboxylesterase and glutathione S-transferase in different life-stages of carabid beetle (Poecilus cupreus) exposed to toxic metal concentrations. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 134, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Yang, D.; Cheng, B.; Wang, Q. The role of GST omega in metabolism and detoxification of arsenic in clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 204, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Park, Y.; Jeong, H.; Park, C.J. Effects of particulate matter (PM2.5) on life history traits, oxidative stress, and defensome system in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).