The Relationships between Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
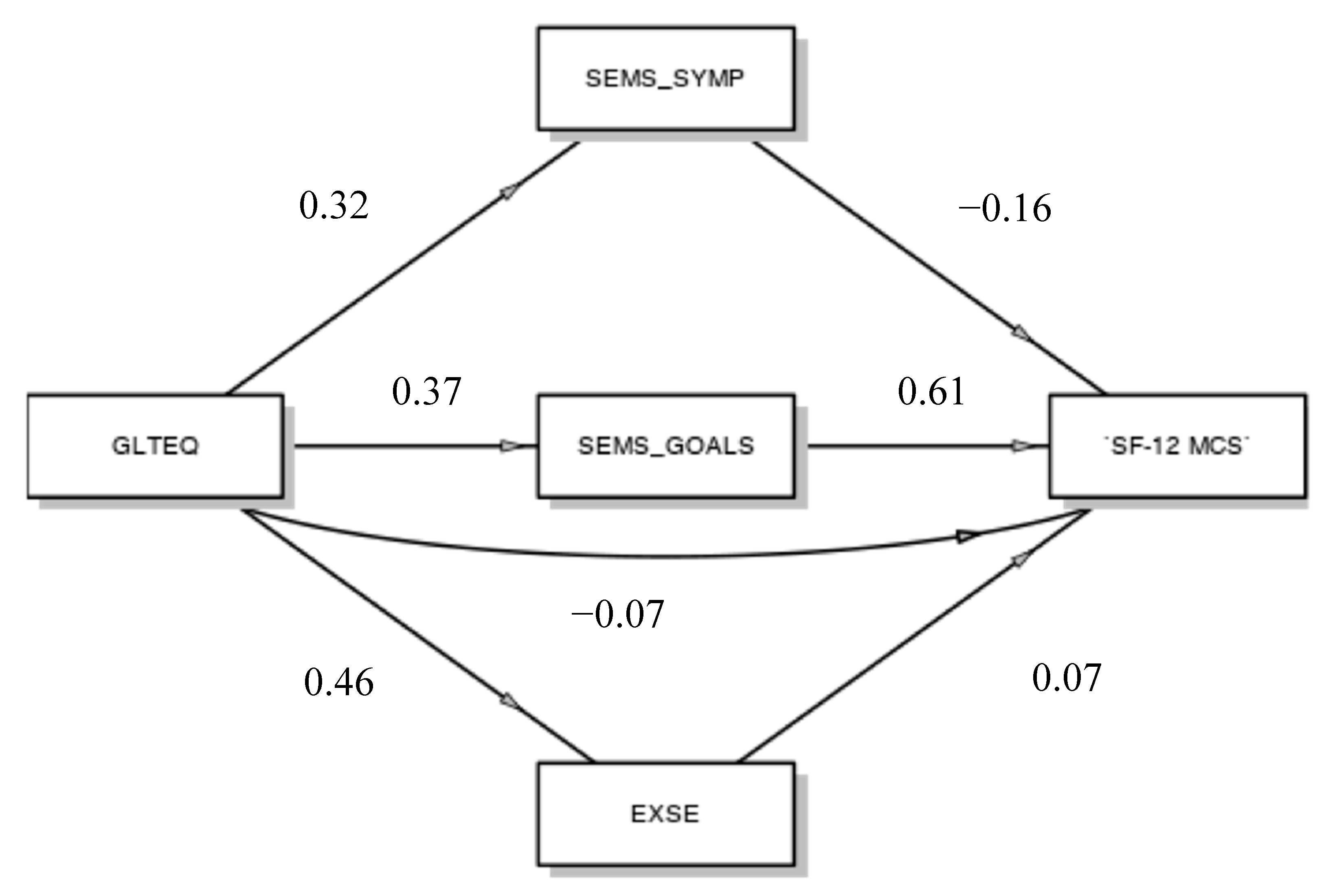
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Høglund, R.A.; Maghazachi, A.A. Multiple sclerosis and the role of immune cells. World J. Exp. Med. 2014, 4, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Multiple Sclerosis Society. Available online: https://www.nationalmssociety.org (accessed on 14 September 2018).
- Motl, R.W.; Sandroff, B.M.; Kwakkel, G.; Thompson, A. Exercise in patients with multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, T.L.; Benedict, R.; Bennett, S.; Motl, R.W.; White, A.T.; Bombardier, C.H.; Hebert, J.R. Exercise as prescriptive therapy in multiple sclerosis: A consensus conference white paper. Int. J. MS Care 2012, 14, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabchi, F.; Alizadeh, Z.; Sahraian, M.A.; Abolhasani, M. Exercise prescription for patients with multiple sclerosis: Potential benefits and practical recommendations. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geidl, W.; Gobster, C.; Streber, R.; Pfeifer, K. A systematic critical review of physical activity aspects in clinical guidelines for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 25, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnett-Hopkins, D.; Adamson, B.; Rougeau, K.; Motl, R.W. People with MS are less physically active than healthy controls but as active as those with other chronic diseases: An updated meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 13, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W.; McAuley, E.; Snook, E.M. Physical activity and multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. 2005, 11, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Horwitz, R.; Cutter, G.; Tyry, T.; Campagnolo, D.; Vollmer, T. Comorbidity delays diagnosis and increases disability at diagnosis in MS. Neurology 2009, 72, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaren, R.E.; Sebastiao, E.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Kinnett-Hopkins, D.; McAuley, E.; Motl, R.W. Levels and rates of physical activity in older adults with multiple sclerosis. Aging Dis. 2016, 7, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulick, E.E.; Goodman, S. Physical activity among people with multiple sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2006, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, W.L.; Lee, I.M.; Pate, R.R.; Powell, K.E.; Blair, S.N.; Franklin, B.A.; Bauman, A. Physical activity and public health: Updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007, 116, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riet-berg, M.B.; van Wegen, E.E.H.; Kollen, B.J.; Kwakkel, G. Do patients with multiple sclerosis show different daily physical activity patterns from healthy individuals? Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J.S.; Banasik, J.L. Exercise self-efficacy. Clin Excel. Nurse Pract. 2001, 5, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guicciardi, M.; Lecis, R.; Anziani, C.; Corgiolu, L.; Porru, A.; Pusceddu, M.; Spanu, F. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, and body satisfaction. An application of the transtheoretical model in older adults. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2014, 2, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knittle, K.P.; Warner, L.M.; Ziegelmann, J.P.; Schuez, B.E.C.; Wurm, S. Sources of self-efficacy for physical activity in older adults with multiple chronic conditions. In Proceedings of the 24th Conference of the European Health Psychology Society, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 1–4 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Knittle, K.P.; De Gucht, V.; Hurkmans, E.J.; Vieland, T.P.; Peeters, A.J.; Ronday, H.K.; Maes, S. Effect of self-efficacy and physical activity goal achievement on arthritis pain and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorig, K.R.; Holman, H.R. Self-Management education: History, definition, outcomes, and mechanisms. Ann. Behav. Med. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig, K.R. Self-Management education: More than a nice extra. Med. Care 2003, 41, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, E.; Blissmer, B. Self-Efficacy determinants and consequences of physical activity. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2000, 28, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier, S.; Dunlop, N.; Blanchard, C. The role of outcome expectations and self-efficacy in explaining physical activity behaviours of individuals with multiple sclerosis. Behav. Med. 2010, 36, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, D.; Spink, K.; Andersen, M.; Knox, K. Attributions and self-efficacy for physical activity in multiple sclerosis. Psychol. Health Med. 2014, 19, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; McAuley, E.; Snook, E.M.; Scott, J.A. Validity of physical activity measures in ambulatory individuals with multiple sclerosis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W.; Snook, E.M.; McAuley, E.; Gliottoni, R.C. Symptoms, self-efficacy, and physical activity among individuals with multiple sclerosis. Res. Nurs. Health 2006, 29, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W.; McAuley, E.; Snook, E.M. Physical activity and quality of life in multiple sclerosis: Possible roles of social support, self-efficacy, and functional limitations. Rehabil. Psychol. 2007, 52, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; Snook, E.M. Physical activity, self-efficacy, and quality of life in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Behav. Med. 2008, 35, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W.; McAuley, A.; Snook, M.; Gliottoni, R.C. Physical activity and quality of life in multiple sclerosis: Intermediary roles of disability, fatigue, mood, pain, self-efficacy and social support. Psychol. Health Med. 2009, 14, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W.; McAuley, E.; Wynn, D.; Sandroff, B.; Suh, Y. Physical activity, self-efficacy, and health-related quality of life in persons with multiple sclerosis: Analysis of associations between individual-level changes over one year. Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.S.; McAuley, E.; Motl, R.W. Self-Efficacy and environmental correlates of physical activity among older women and women with multiple sclerosis. Health Educ. Res. 2008, 23, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anens, E.; Zetterberg, L.; Urell, C.; Emtner, M.; Hellström, K. Self-Reported physical activity correlates in Swedish adults with multiple sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonino, S.; Graziano, F.; Borghi, M.; Marengo, D.; Molinengo, G.; Calandri, E. The self-efficacy in multiple sclerosis (SEMS) scale: Development and validation with Rasch analysis. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2018, 34, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankhorst, G.J.; Jelles, F.; Smits, R.C.; Polman, C.H.; Kuik, D.J.; Pfennings, L.E.; Cohen, L.; van der Ploeg, H.; Ketelaer, P.; Vleugels, L. Quality of life in multiple sclerosis: The disability and impact profile (DIP). J. Neurol. 1996, 243, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudick, R.A.; Miller, D.; Clough, J.D.; Gragg, L.A.; Farmer, R.G. Quality of life in multiple sclerosis: Comparison with inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naess, H.; Beiske, A.G.; Myhr, K. Quality of life among young patients with ischaemic stroke compared with patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2008, 117, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilutti, L.; Dlugonski, D.; Sandroff, B.; Klaren, R.; Motl, R. Randomized controlled trial of a behavioral intervention targeting symptoms and physical activity in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W. Lifestyle physical activity in persons with multiple sclerosis: The new kid on the MS block. Mult. Scler. 2014, 20, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandri, E.; Graziano, F.; Borghi, M.; Bonino, S. Depression, positive and negative affect, optimism and health-related quality of life in recently diagnosed multiple sclerosis patients: The role of identity, sense of coherence, and self-efficacy. J. Happiness Stud. 2018, 19, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojano, M.; Lucchese, G.; Graziano, G.; Taylor, B.V.; Simpson, S.; Lepore, V.; Grand’Maison, F.; Duquette, P.; Izquierdo, G.; Grammond, P.; et al. Geographical variations in sex ratio trends over time in multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, G.; Shephard, R.J. A simple method to assess exercise behavior in the community. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1985, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sikes, E.M.; Richardson, E.V.; Cederberg, K.J.; Sasaki, J.E.; Sandroff, B.M.; Motl, R.W. Use of the Godin leisure-time exercise questionnaire in multiple sclerosis research: A comprehensive narrative review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 1243–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learmonth, Y.C.; Adamson, B.C.; Kinnett-Hopkins, D.; Bohri, M.; Motl, R.W. Results of a feasibility randomised controlled study of the guidelines for exercise in multiple sclerosis project. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2017, 54, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; Pekmezi, D.; Wingo, B.C. Promotion of physical activity and exercise in multiple sclerosis: Importance of behavioral science and theory. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalron, A.; Menascu, S.; Frid, L.; Aloni, R.; Achiron, A. Physical activity in mild multiple sclerosis: Contribution of perceived fatigue, energy cost, and speed of walking. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.A.; Sawicki, C.P.; Kinnett-Hopkins, D.; Finlayson, M.; Schneiderman, J.E.; Banwell, B.; Till, C.; Motl, R.W.; Yeh, A. Physical activity and its correlates in youth with multiple sclerosis. J. Pediatr. 2016, 179, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, E. Self-Efficacy and the maintenance of exercise participation in older adults. J. Behav. Med. 1993, 16, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolone, G.; Mosconi, P.; Quattrociocchi, L.; Gianicolo, E.A.L.; Groth, N.; Ware, J.E., Jr. Questionario sullo Stato di Salute SF-12; Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research (IRFMN): Milano, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ottoboni, G.; Cherici, A.; Marzocchi, M.; Chattat, R. Algoritimi di Calcolo per gli Indici PCS e MSC del Questinario SF-12. Technical Report for AMS Acta. 2017, Volume 3, pp. 1–2. Available online: http://amsacta.unibo.it/id/eprint/5751 (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- Rosseel, Y. lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi (Version 1.0.5) 2019, [Computer Software]. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org/about.html (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Fjeldstad, C.; Pardo, G. Self-Efficacy, physical activity and QOL in people with MS. Neurol. Neurophysiol. 2014, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, T.; Anderson, C.; Carmack, C. Mediating variable framework in physical activity interventions: How are we doing? How might we do better? Am. J. Prev. Med. 1998, 15, 266–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guicciardi, M.; Lecis, R.; Anziani, C.; Corgiolu, L.; Porru, A.; Pusceddu, M.; Spanu, F. Type 2 diabetes: Negative thoughts to physical activity. Sport Sci. Health 2014, 10, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settineri, S.; Frisone, F.; Merlo, E.M.; Geraci, D.; Martino, G. Compliance, adherence, concordance, empowerment, and self-management: Five words to manifest a relational maladjustment in diabetes. J. Multidiscipl. Healthc. 2019, 12, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taal, E.; Rasker, J.J.; Seydel, E.R.; Wiegman, O. Health status, adherence with health recommendations, self-efficacy and social support in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Patient Educ. Couns. 1993, 20, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, B.; Coote, S.; Galvin, R.; Donnelly, A. Objective physical activity levels in people with multiple sclerosis: Meta-analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Measure | Mean Score | Standard Deviation | Range of Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLTEQ | 17.96 | 19.11 | 0–78 |
| SEMS SYMP | 24.14 | 4.66 | 14–30 |
| SEMS GOALS | 33.79 | 7.04 | 13–44 |
| EXSE | 67.44 | 33.86 | 0–100 |
| SF-12 PCS | 41.11 | 11.74 | 17.35–57.51 |
| SF-12 MCS | 53.28 | 10.35 | 27.70–70.36 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. GLTEQ | 0.259 | 0.255 | 0.519 ** | 0.310 | 0.010 |
| 2. SEMS SYMP | 0.764 *** | 0.435 * | 0.191 | 0.472 * | |
| 3. SEMS GOALS | 0.338 | 0.141 | 0.533 ** | ||
| 4. EXSE | 0.315 | 0.239 | |||
| 5. SF-12 PCS | −0.255 | ||||
| 6. SF-12 MCS |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guicciardi, M.; Carta, M.; Pau, M.; Cocco, E. The Relationships between Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9120121
Guicciardi M, Carta M, Pau M, Cocco E. The Relationships between Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis. Behavioral Sciences. 2019; 9(12):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9120121
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuicciardi, Marco, Maria Carta, Massimiliano Pau, and Eleonora Cocco. 2019. "The Relationships between Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis" Behavioral Sciences 9, no. 12: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9120121
APA StyleGuicciardi, M., Carta, M., Pau, M., & Cocco, E. (2019). The Relationships between Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis. Behavioral Sciences, 9(12), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9120121







