Connecting the Dots: From Teachers’ Perceived Ability to Teach Reading and Their Knowledge of Language and Literacy Concepts to Students’ Reading Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Teachers’ Knowledge of Language and Literacy Concepts
1.2. Teachers’ Perceived Ability to Teach Reading
1.3. The Joint Effects of Teachers’ Knowledge and Perceived Ability to Teach Reading on Students’ Reading Performance
1.4. The Present Study
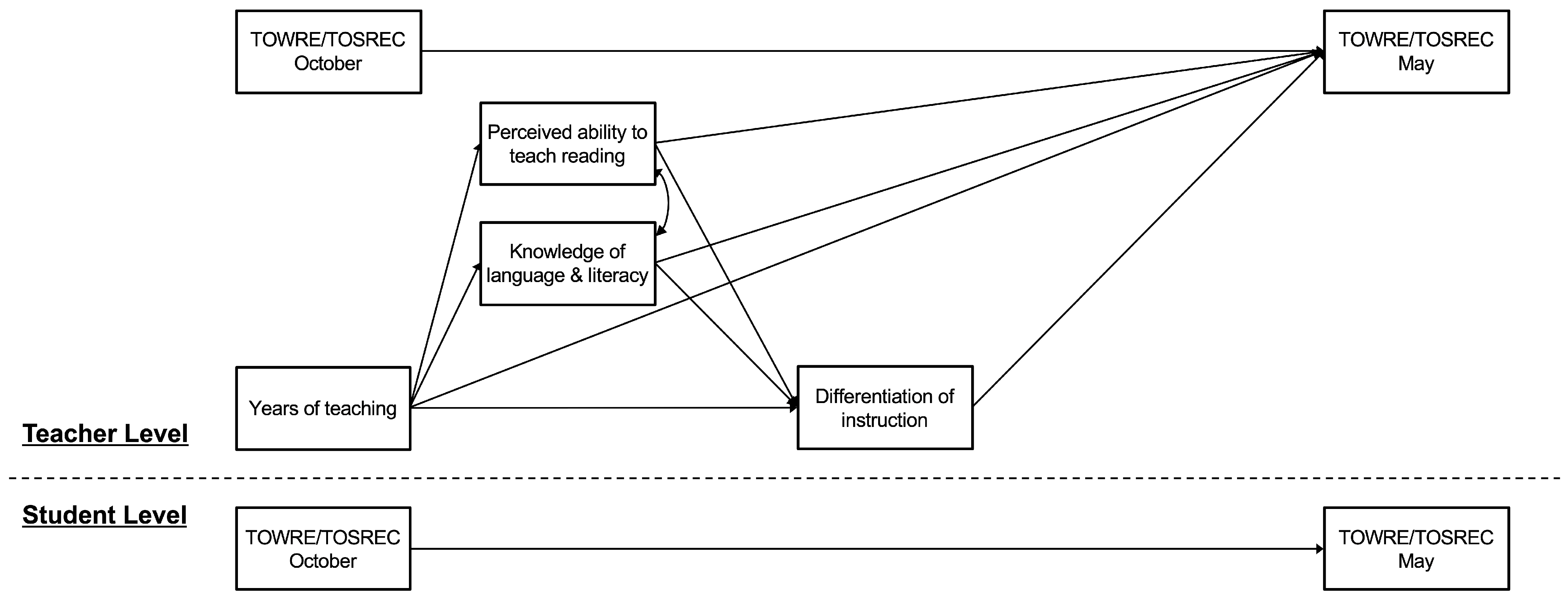
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
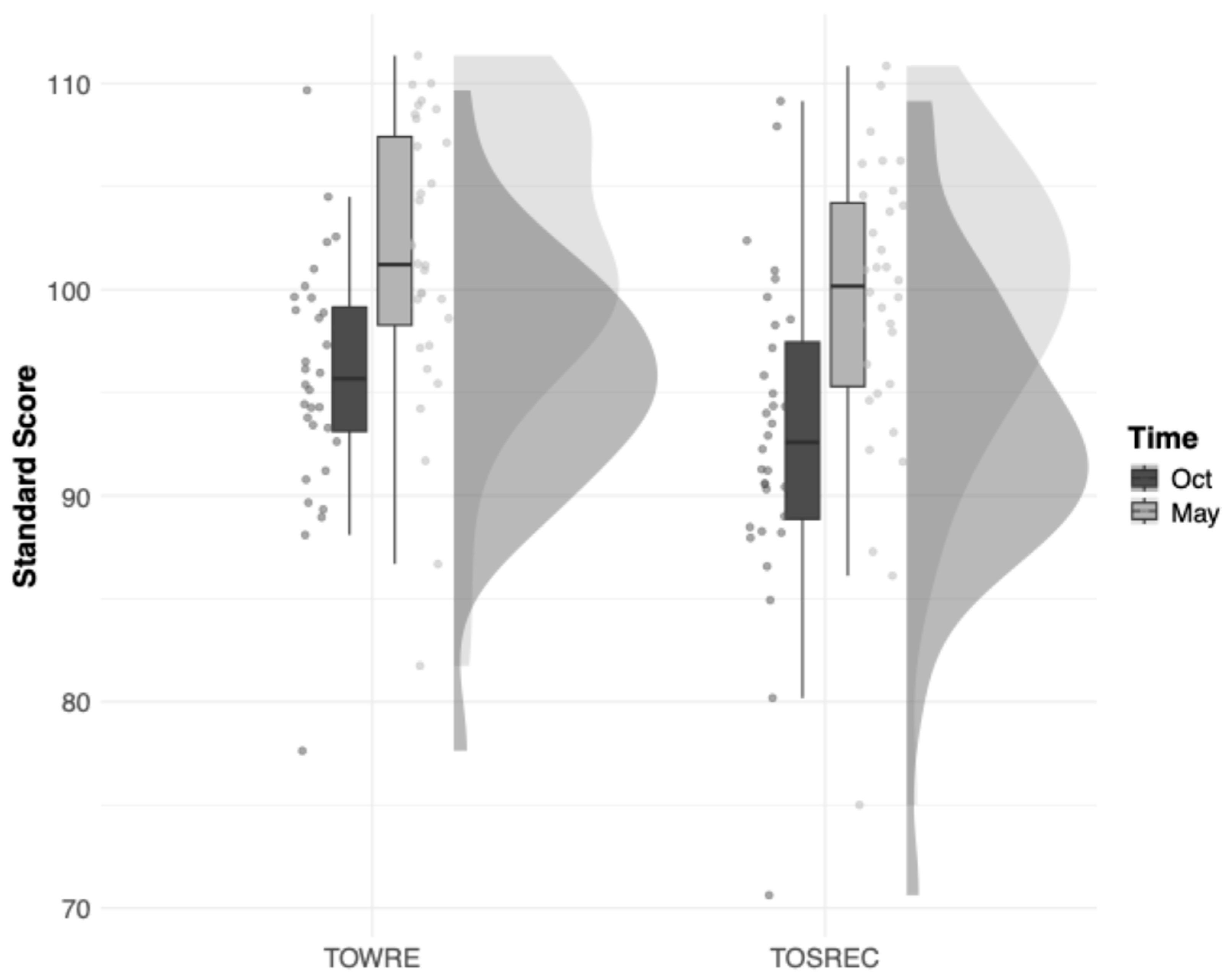
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
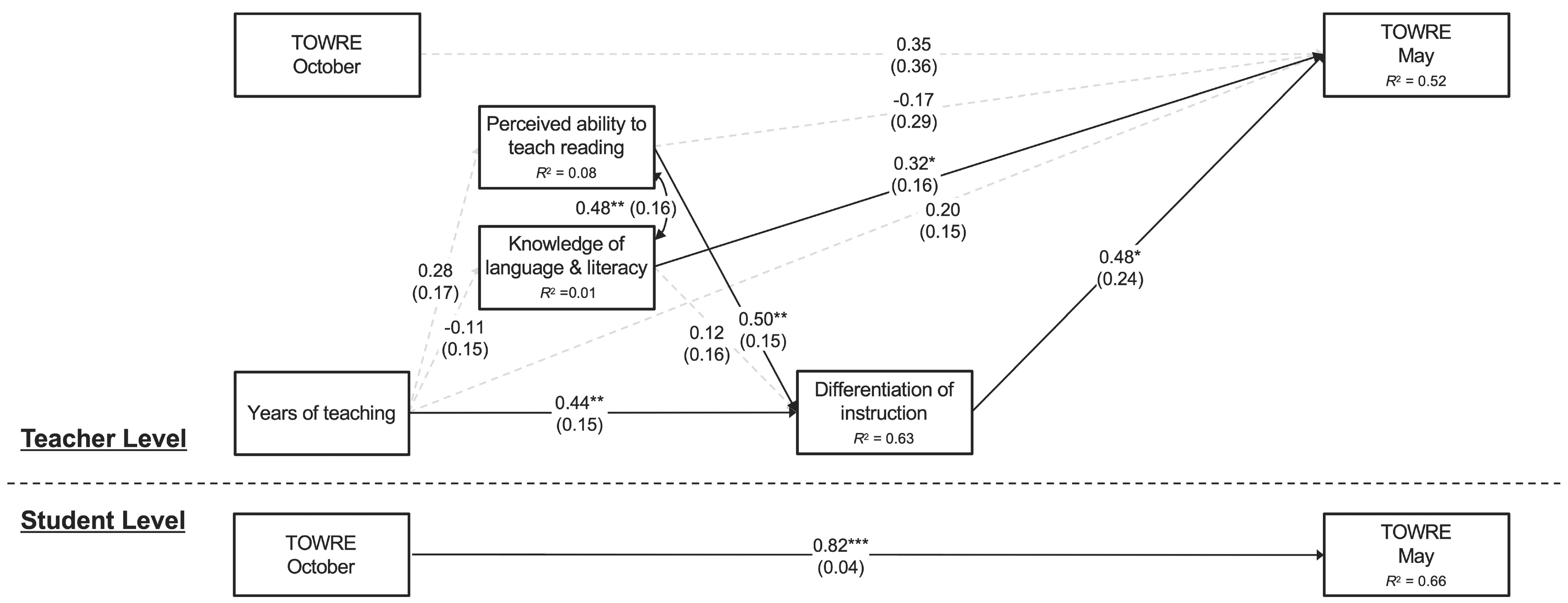
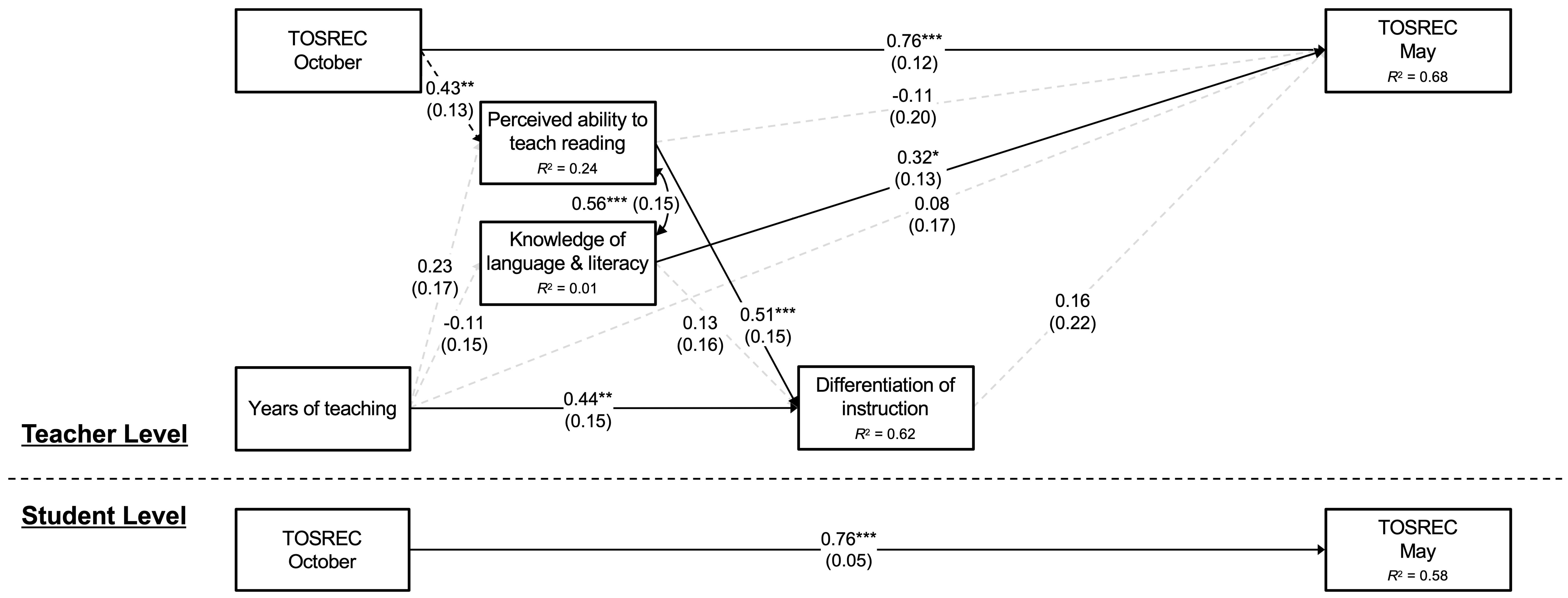
3.2. Multilevel Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Practice
4.2. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aro, M., & Björn, P. M. (2016). Preservice and inservice teachers’ knowledge of language constructs in Finland. Annals of Dyslexia, 66(1), 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Prentice-Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, C., Mather, N., Dickson, S., Podhajski, B., & Chard, D. (2001). Perceptions and knowledge of preservice and inservice educators about early reading instruction. Annals of Dyslexia, 51(1), 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowey, J. A. (2005). Predicting individual differences in learning to read. In M. J. Snowling, & C. Hulme (Eds.), The science of reading: A handbook (pp. 155–172). Blackwell Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S., Gillis, M., Smith, T., Lavalette, M., Liss-Bronstein, L., Lowe, E., North, W., Russo, E., & Wilder, T. D. (2009). First grade teachers’ knowledge of phonological awareness and code concepts: Examining gains from an intensive form of professional development and corresponding teacher attitudes. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 22(4), 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, G. V., Barbaranelli, C., Steca, P., & Malone, P. S. (2006). Teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs as determinants of job satisfaction and students’ academic achievement: A study at the school level. Journal of School Psychology, 44(6), 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J. F., Correnti, R., Phelps, G., & Zeng, J. (2009). Exploration of the contribution of teachers’ knowledge about reading to their students’ improvement in reading. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 22, 457–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J. F., Kelcey, B., Rowan, B., & Phelps, G. (2011). Teachers’ knowledge about early reading: Effects on students’ gains in reading achievement. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 4(4), 289–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castles, A., Rastle, K., & Nation, K. (2018). Ending the reading wars: Reading acquisition from novice to expert. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 19(1), 5–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, C. M., Piasta, S. B., Fishman, B., Glasney, S., Schatschneider, C., Crowe, E., Underwood, P., & Morrison, F. J. (2009). Individualizing student instruction precisely: Effects of child x instruction interactions on first graders’ literacy development. Child Development, 80(1), 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A. E., Firestone, A. R., & Zegers, M. (2023). Measuring and improving teachers’ knowledge in early literacy. In S. Q. Cabell, S. B. Neuman, & N. P. Terry (Eds.), Handbook on the science of early literacy (pp. 211–223). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, A. E., Perry, K. E., Stanovich, K. E., & Stanovich, P. J. (2004). Disciplinary knowledge of K-3 teachers and their knowledge calibration in the domain of early literacy. Annals of Dyslexia, 54(1), 139–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl-Leonard, K., Hall, C., DeCoster, J., & Solari, E. (2025). Elementary educator self-efficacy and knowledge to teach reading. Teachers and Teaching, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimone, L. M. (2009). Improving impact studies of teachers’ professional development: Toward better conceptualizations and measures. Educational Researcher, 38(3), 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimone, L. M., & Garet, M. S. (2015). Best practices in teachers’ professional development in the United States. Psychology, Society & Education, 7(3), 252–263. [Google Scholar]
- Fielding-Barnsley, R. (2010). Australian pre-service teachers’ knowledge of phonemic awareness and phonics in the process of learning to read. Australian Journal of Learning Difficulties, 15(1), 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J. M., & Vaughn, S. (2009). Response to intervention: Preventing and remediating academic difficulties. Child Development Perspectives, 3(1), 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgie, J. C., Hu, J., & Boccalon, M. (2022). Pre-service and in-service early childhood educators’ self-efficacy and knowledge for early literacy instruction. Cogent Education, 9(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, G., Peyton, A., Antoniuk, A., Beach, P., Fraser, A., Kirby, J. R., Klein, P., Li, G., Metsala, J., Mousavi, A., Nickel, J., Savage, R., & Joshi, R. M. (2025). Pre-service teachers’ knowledge of language and literacy concepts: The skeleton in Canada’s closet? Annals of Dyslexia. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, G. K., Inoue, T., Papadopoulos, T. C., & Parrila, R. (2021). Examining the growth trajectories and cognitive predictors of reading in a consistent orthography: Evidence from a 10-year longitudinal study. Applied Psycholinguistics, 42(5), 1287–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, G. K., Kushnir, G., & Parrila, R. (2020). Moving the needle on literacy: Lessons learned from a school where literacy rates have improved over time. Alberta Journal of Educational Research, 66(3), 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., Connor, C. M., Yang, Y., Roehrig, A. D., & Morrison, F. J. (2012). The effects of teacher qualification, teacher self-efficacy, and classroom practices on fifth graders’ literacy outcomes. The Elementary School Journal, 113(1), 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J. (2023). Visible learning: The sequel: A synthesis of over 2100 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Taylor and Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, A. F. (2022). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach (3rd ed.). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, R. H., & Thomas, S. L. (2009). An introduction to multilevel modeling techniques (2nd ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, A. K. (2022). Upper elementary teachers’ knowledge of reading comprehension, classroom practice, and student’s performance in reading comprehension. Reading Research Quarterly, 58, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R. M., Binks, E., Hougen, M., Dahlgren, M. E., Ocker-Dean, E., & Smith, D. L. (2009). Why elementary teachers might be inadequately prepared to teach reading. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 42(5), 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H. S., Cha, J., & Ha, B.-W. (2013). What should we consider in teachers’ professional development impact studies? Based on the conceptual framework of Desimone. Creative Education, 4(4A), 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanolainen, D., Psyridou, M., Eklund, K., Aro, T., & Torppa, M. (2024). Predicting reading fluency growth from grade 2 to age 23 with parental and child factors. Scientific Studies of Reading, 28(5), 485–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierstead, M., Georgiou, G., Poth, C., & Mack, E. (2023). Effective school literacy culture and learning outcomes: The multifaceted leadership role of the principal. Alberta Journal of Educational Research, 69(4), 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, R. M., Tze, V. M., Betts, S. M., & Gordon, K. A. (2011). Teacher efficacy research 1998–2009: Signs of progress or unfulfilled promise? Educational Psychology Review, 23(1), 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R. B. (2023). Principles and practice of structural equation modelling (5th ed.). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, H. B., Hudson, R. F., Leite, W. L., Kosanovich, M. L., Strout, M. T., Fenty, N. S., & Wright, T. L. (2008). Teachers’ knowledge about reading fluency and indicators of students’ fluency growth in reading first schools. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 25(1), 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leino, K., Nissinen, K., & Sirén, M. (2022). Associations between teacher quality, instructional quality and student reading outcomes in Nordic PIRLS 2016 data. Large-Scale Assessments in Education, 10(1), 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, N., Bos, C., & Babur, N. (2001). Perceptions and knowledge of preservice and inservice teachers about early literacy instruction. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 34(5), 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutchen, D., Abbott, R. D., Green, L. B., Beretvas, S. N., Cox, S., Potter, N. S., Quiroga, T., & Gray, A. L. (2002). Beginning literacy: Links among teacher knowledge, teacher practice, and student learning. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutchen, D., Green, L., Abbott, R. D., & Sanders, E. A. (2009). Further evidence for teacher knowledge: Supporting struggling readers in grades three through five. Reading and Writing, 22(4), 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, K. M., Oslund, E. L., & Odegard, T. N. (2019). Characterizing the knowledge of educators receiving training in systematic literacy instruction. Annals of Dyslexia, 69, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moats, L. C. (1994). The missing foundation in teacher education: Knowledge of the structure of spoken and written language. Annals of Dyslexia, 44(1), 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moats, L. C., & Foorman, B. R. (2003). Measuring teachers’ content knowledge of language and reading. Annals of Dyslexia, 53(1), 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (1998–2017). Mplus user’s guide (8th ed.). Muthén & Muthén. [Google Scholar]
- Nippold, M. A. (2018). The literate lexicon in adolescents: Monitoring the use and understanding of morphologically complex words. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups, 3(1), 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, M., & Harris, J. (2019, June 8–12). Effectiveness of reflective practice in a TA peer-mentorship program. Canadian Engineering Education Association (CEEA), Ottawa, ON, Canada. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrila, R., Inoue, T., Dunn, K., Savage, R., & Georgiou, G. (2024). Connecting teachers’ language knowledge, perceived ability and instructional practices to Grade 1 students’ literacy outcomes. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 37(5), 1153–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrila, R., Kirby, J. R., & McQuarrie, L. (2004). Articulation rate, naming speed, verbal short-term memory, and phonological awareness: Longitudinal predictors of early reading development? Scientific Studies of Reading, 8(1), 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasta, S. B., Connor, C. M., Fishman, B. J., & Morrison, F. J. (2009). Teachers’ knowledge of literacy concepts, classroom practices, and student reading growth. Scientific Studies of Reading, 13(3), 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasta, S. B., Park, S., Farley, K. S., Justice, L. M., & O’Connell, A. A. (2020). Early childhood educators’ knowledge about language and literacy: Associations with practice and children’s learning. Dyslexia, 26(2), 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittman, R. T., Zhang, S., Binks-Cantrell, E., Hudson, A., & Joshi, R. M. (2020). Teachers’ knowledge about language constructs related to literacy skills and student achievement in low socio-economic status schools. Dyslexia, 26(2), 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhajski, B., Mather, N., Nathan, J., & Sammons, J. (2009). Professional development in scientifically based reading instruction: Teacher knowledge and reading outcomes. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 42(5), 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S. B., Odegard, T. N., Farris, E. A., & Oslund, E. L. (2024). Effects of teacher knowledge of early reading on students’ gains in reading foundational skills and comprehension. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 37(8), 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S. B., Odegard, T. N., McMahan, M., & Farris, E. A. (2022). Characterizing the knowledge of educators across the tiers of instructional support. Annals of Dyslexia, 72(1), 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. (2025). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Spear-Swerling, L., & Brucker, P. O. (2004). Preparing novice teachers to develop basic reading and spelling skills in children. Annals of Dyslexia, 54(2), 332–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Canada. (2016). Just the facts: A portrait of the school-age population and measures of student achievement. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/89-28-0001/2018001/article/00014-eng.htm (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Torgesen, J. K., Wagner, R. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (2012). Test of word reading efficiency—Second edition (TOWRE-2). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Tschannen-Moran, M., & Hoy, A. W. (2001). Teacher efficacy: Capturing an elusive construct. Teaching and Teacher Education, 17(7), 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschannen-Moran, M., & McMaster, P. (2009). Sources of self-efficacy: Four professional development formats and their relationship to self-efficacy and implementation of a new teaching strategy. The Elementary School Journal, 110(2), 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R. K., Torgesen, J. K., Rashotte, C. A., Hecht, S. A., Barker, T. A., Burgess, S. R., Donahue, J., & Garon, T. (1997). Changing relations between phonological processing abilities and word-level reading as children develop from beginning to skilled readers: A 5-year longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 33(3), 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R. K., Torgesen, J. K., Rashotte, C. A., & Pearson, N. A. (2010). Test of silent reading efficiency and comprehension (TOSREC). Pro-Ed. [Google Scholar]
- Washburn, E. K., Joshi, R. M., & Binks-Cantrell, E. S. (2011). Teacher knowledge of basic language concepts and dyslexia. Dyslexia, 17(2), 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | n | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Skew | Kurtosis | ICC [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teacher-level variables | ||||||||
| Years of teaching | 30 | 16.58 | 12.30 | 1 | 38 | 0.07 | −1.61 | – |
| Ability to teach typically developing readers | 32 | 2.62 | 0.55 | 1 | 3 | −1.04 | −0.03 | – |
| Ability to teach struggling readers | 32 | 2.44 | 0.76 | 1 | 4 | −0.44 | −0.65 | – |
| Ability to teach phonemic awareness | 32 | 2.53 | 0.76 | 1 | 4 | −0.31 | −0.45 | – |
| Ability to teach phonics | 32 | 2.62 | 0.61 | 2 | 4 | 0.36 | −0.82 | – |
| Ability to teach morphological awareness | 32 | 2.47 | 0.72 | 1 | 4 | −0.40 | −0.49 | – |
| Ability to differentiate instruction for students | 32 | 2.50 | 0.67 | 1 | 4 | −0.31 | −0.40 | – |
| Knowledge of phonological awareness | 32 | 75.42 | 17.80 | 13.33 | 100 | −1.45 | 2.44 | – |
| Knowledge of phonics | 32 | 85.94 | 14.11 | 56.25 | 100 | −0.56 | −1.09 | – |
| Knowledge of morphology | 32 | 60.94 | 17.39 | 25 | 93.75 | −0.15 | −0.75 | – |
| Student-level variables | ||||||||
| TOWRE-2 October | 582 | 95.80 | 16.50 | 53 | 139 | −0.27 | 0.03 | 0.042 [0.007, 0.108] |
| TOWRE-2 May | 579 | 102.05 | 17.14 | 53 | 147 | −0.15 | −0.08 | 0.091 [0.041, 0.182] |
| TOSREC October | 569 | 93.79 | 17.13 | 54 | 143 | −0.11 | −0.15 | 0.123 [0.063, 0.227] |
| TOSREC May | 580 | 100.09 | 16.83 | 54 | 146 | −0.03 | 0.07 | 0.103 [0.049, 0.199] |
| Variables | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Years of teaching | |||||||
| 2. Perceived ability to teach reading | 0.28 | ||||||
| 3. Differentiation of instruction | 0.57 ** | 0.67 ** | |||||
| 4. Knowledge of language and literacy | −0.11 | 0.41 * | 0.28 | ||||
| 5. TOWRE-2 October | 0.08 | 0.24 | −0.01 | 0.04 | |||
| 6. TOWRE-2 May | 0.34 | 0.42 * | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.62 ** | ||
| 7. TOSREC October | 0.13 | 0.38 * | 0.14 | −0.06 | 0.60 ** | 0.62 ** | |
| 8. TOSREC May | 0.19 | 0.41 * | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.66 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.73 ** |
| Variables | 1. | 2. | 3. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. TOWRE-2 October | |||
| 2. TOWRE-2 May | 0.78 ** | ||
| 3. TOSREC October | 0.58 ** | 0.58 ** | |
| 4. TOSREC May | 0.67 ** | 0.68 ** | 0.78 ** |
| Indirect Effect | Estimate | SE | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived ability → Differentiation → TOWRE | 0.073 | 0.046 | 0.118 |
| Perceived ability → Differentiation → TOSREC | 0.161 | 0.233 | 0.489 |
| Knowledge → Differentiation → TOWRE | 0.019 | 0.029 | 0.504 |
| Knowledge → Differentiation → TOSREC | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.409 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guilbault, P.; Georgiou, G.K.; Huynh, J.; Inoue, T. Connecting the Dots: From Teachers’ Perceived Ability to Teach Reading and Their Knowledge of Language and Literacy Concepts to Students’ Reading Growth. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101408
Guilbault P, Georgiou GK, Huynh J, Inoue T. Connecting the Dots: From Teachers’ Perceived Ability to Teach Reading and Their Knowledge of Language and Literacy Concepts to Students’ Reading Growth. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101408
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuilbault, Pamela, George K. Georgiou, Joanna Huynh, and Tomohiro Inoue. 2025. "Connecting the Dots: From Teachers’ Perceived Ability to Teach Reading and Their Knowledge of Language and Literacy Concepts to Students’ Reading Growth" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 10: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101408
APA StyleGuilbault, P., Georgiou, G. K., Huynh, J., & Inoue, T. (2025). Connecting the Dots: From Teachers’ Perceived Ability to Teach Reading and Their Knowledge of Language and Literacy Concepts to Students’ Reading Growth. Behavioral Sciences, 15(10), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101408







