The Impact of Biofilms upon Surfaces Relevant to an Intermediate Level Radioactive Waste Geological Disposal Facility under Simulated Near-Field Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
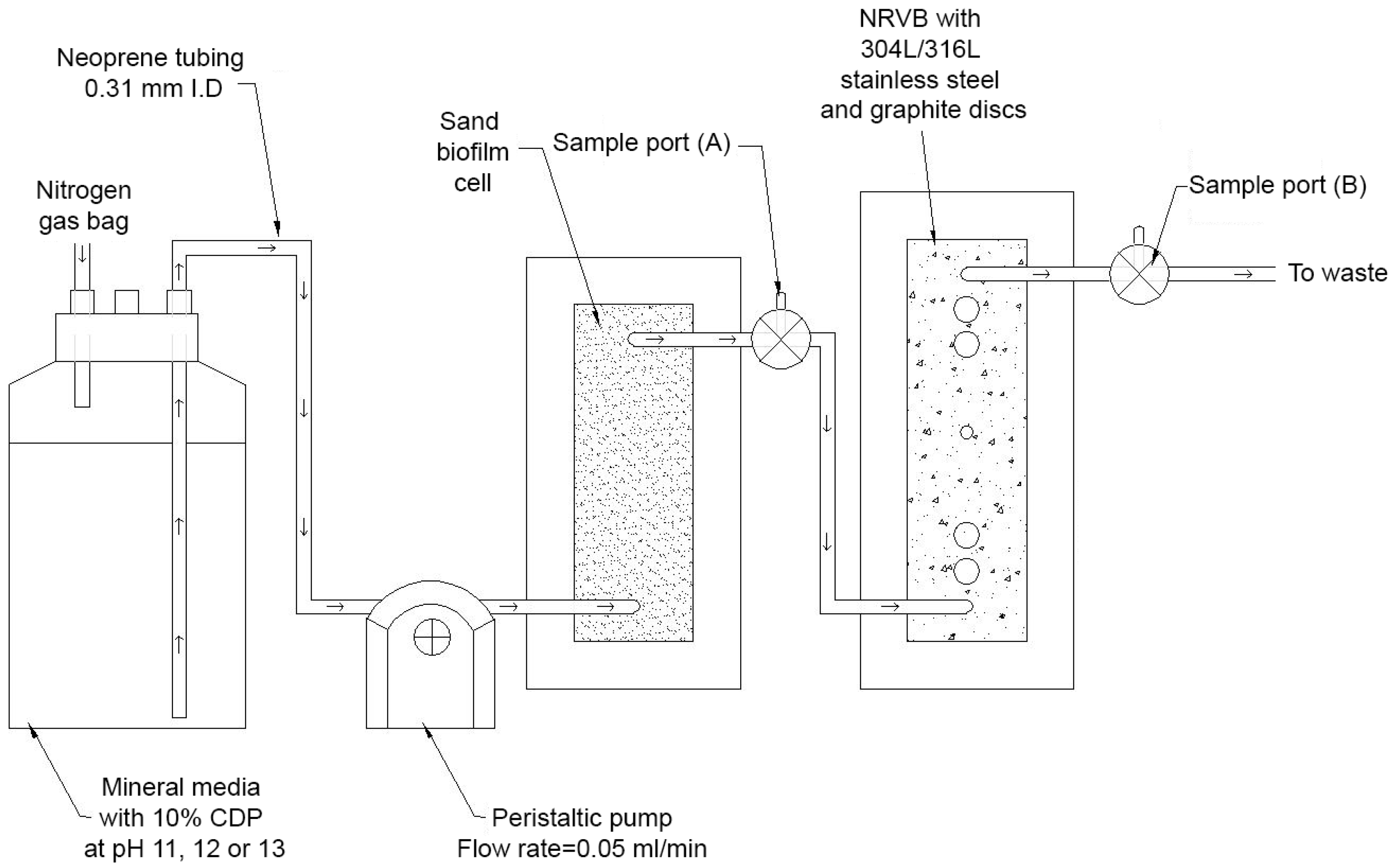
2. Materials and Methods
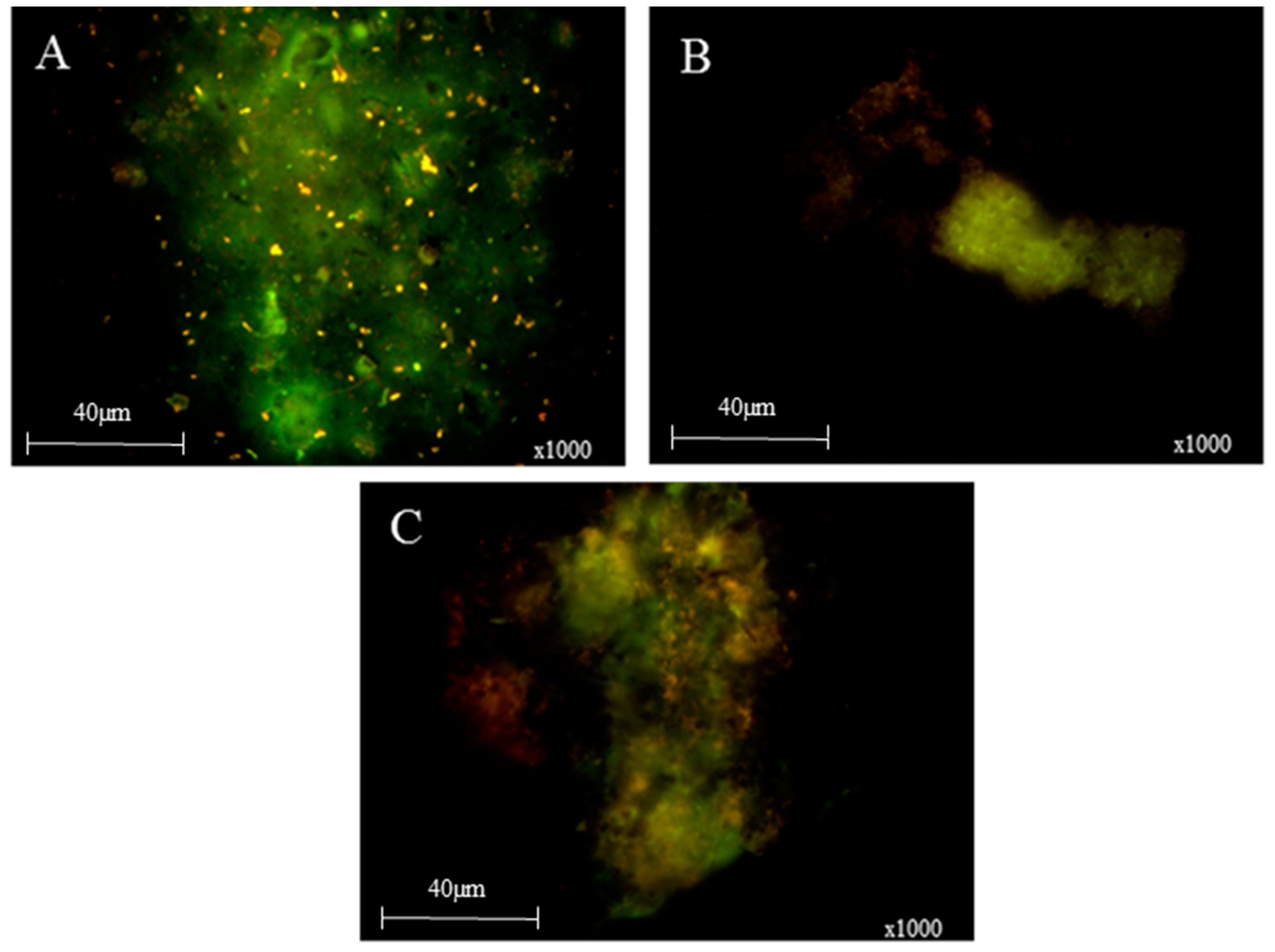
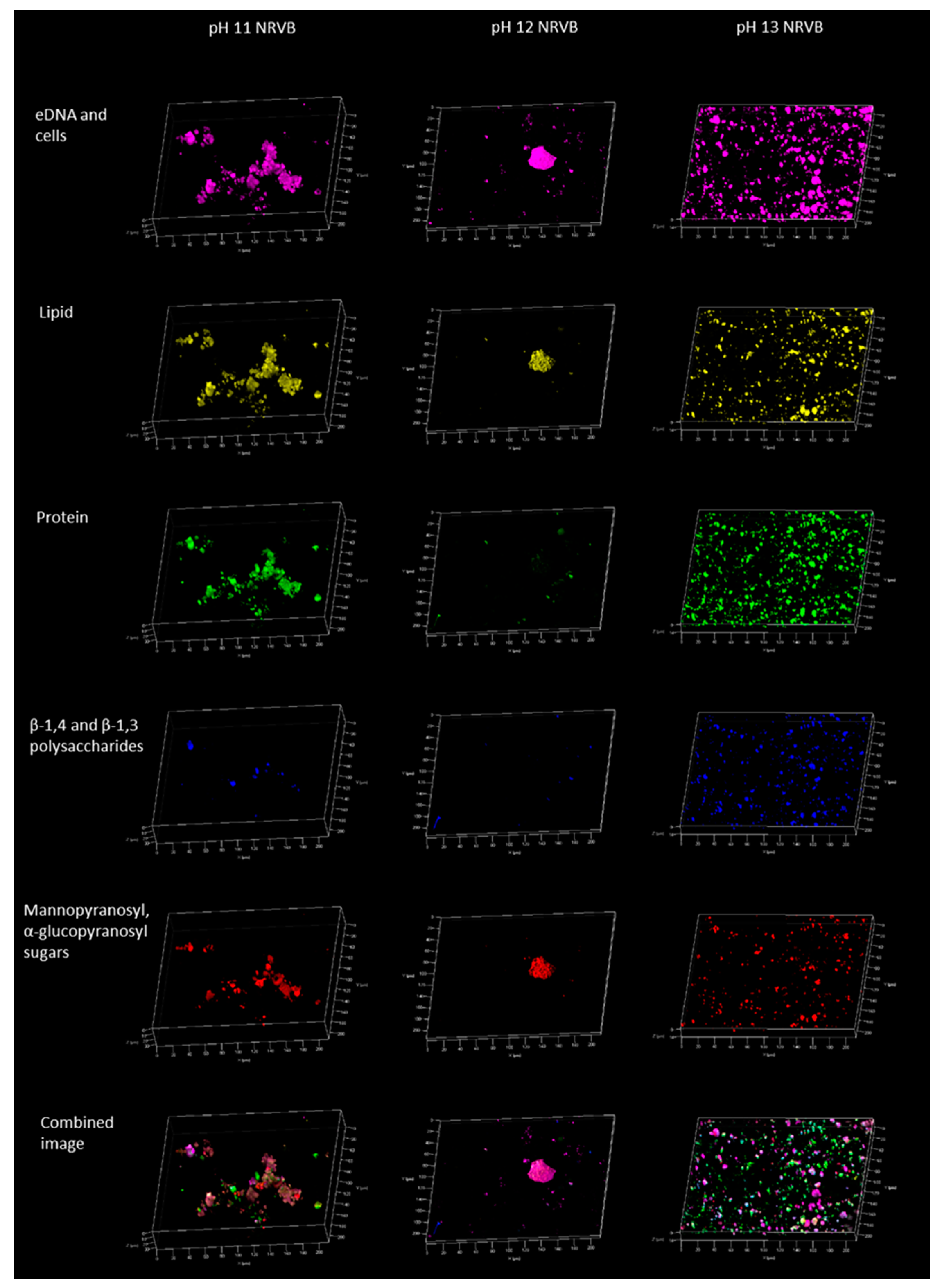
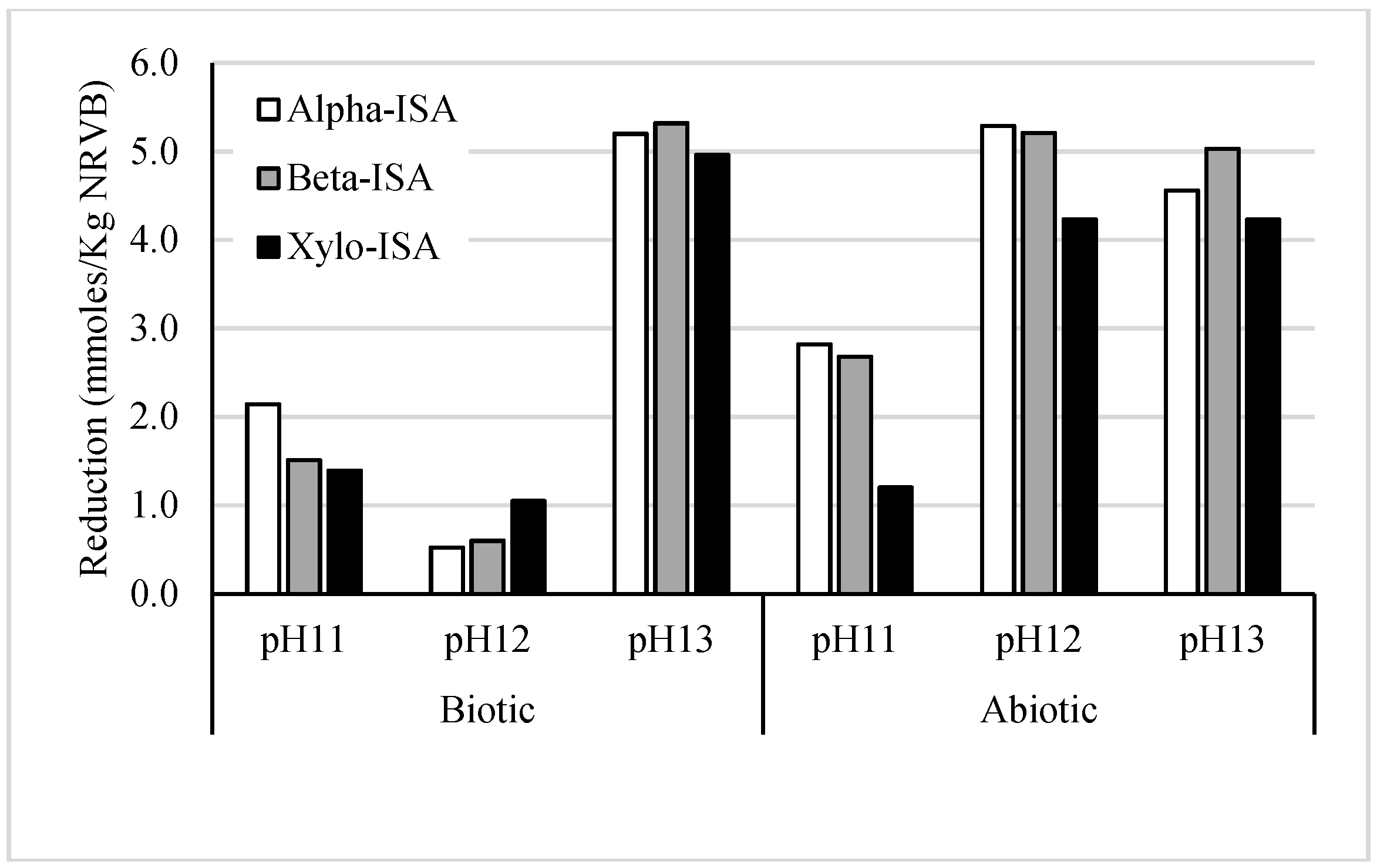
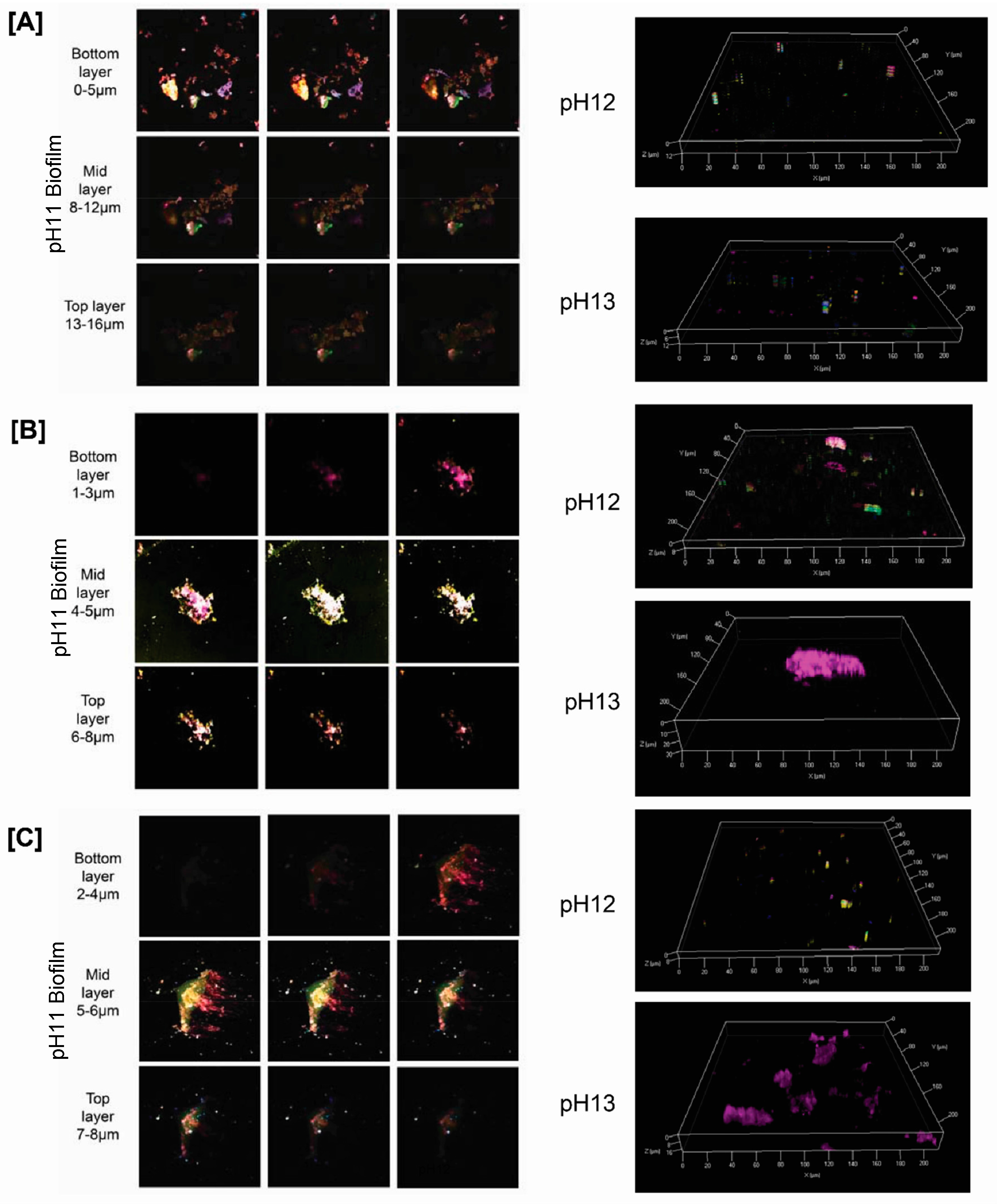
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- N.D.A. Geological Disposal: An Introduction to the Generic Disposal System Safety Case; NDA/RWMD/010; Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (Radioactive Waste Management Directorate): Didcot, UK, 2010.
- N.D.A. Geological Disposal: Near-Field Evolution Status Report; NDA/RWMD/033; Nuclear Decommissioning Agency (Radioactive Waste Management Directorate): Didcot, UK, 2010.
- N.D.A. Geological Disposal: Package Evolution Status Report; NDA/RWMD/031; Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (Radioactive Waste Management Directorate): Didcot, UK, 2010.
- Butcher, E.J.; Borwick, J.; Collier, N.; Williams, S.J. Long term leachate evolution during flow-through leaching of a vault backfill (NRVB). Mineral. Mag. 2012, 76, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N.D.A. Geological Disposal: Geosphere Status Report; NDA/RWMD/035; Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (Radioactive Waste Management Directorate): Didcot, UK, 2010.
- Humphreys, P.; Laws, A.; Dawson, J. A Review of Cellulose Degradation and the Fate of Degradation Products under Repository Conditions; SERCO/TAS/002274/001 Serco Contractors Report for the Nuclear Decommisisioning Authority; Serco: Didcot, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Knill, C.J.; Kennedy, J.F. Degradation of cellulose under alkaline conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 51, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, L.R.; Glaus, M.A.; Stallone, S.; Laube, A. Sorption of isosaccharinic acid, a cellulose degradation product, on cement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1243–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, P.N.; West, J.M.; Metcalfe, R. Microbial Effects on Repository Performance; QRS-1378Q-1, Version 3.0; University of Huddersfield Repository: Didcot, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bassil, N.M.; Bewsher, A.D.; Thompson, O.R.; Lloyd, J.R. Microbial degradation of cellulosic material under intermediate-level waste simulated conditions. Mineral. Mag. 2015, 79, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeremeh, I.A.; Charles, C.J.; Rout, S.P.; Laws, A.P.; Humphreys, P.N. Microbial community evolution is significantly impacted by the use of calcium isosaccharinic acid as an analogue for the products of alkaline cellulose degradation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, A.; Behra, R.; Kaegi, R.; Sigg, L. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of freshwater biofilms stabilize and modify CeO2 and Ag nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Muynck, W.; Debrouwer, D.; De Belie, N.; Verstraete, W. Bacterial carbonate precipitation improves the durability of cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Rout, S.; Garratt, E.; Patel, K.; Laws, A.; Humphreys, P. The enrichment of an alkaliphilic biofilm consortia capable of the anaerobic degradation of isosaccharinic acid from cellulosic materials incubated within an anthropogenic, hyperalkaline environment. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, S.P.; Charles, C.J.; Garratt, E.J.; Laws, A.P.; Gunn, J.; Humphreys, P.N. Evidence of the generation of isosaccharinic acids and their subsequent degradation by local microbial consortia within hyper-alkaline contaminated soils, with relevance to intermediate level radioactive waste disposal. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, C.; Rout, S.; Patel, K.; Akbar, S.; Laws, A.; Jackson, B.; Boxall, S.; Humphreys, P. Floc formation reduces the pH stress experienced by microorganisms living in alkaline environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 02985–03016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, S.P.; Radford, J.; Laws, A.P.; Sweeney, F.; Elmekawy, A.; Gillie, L.J.; Humphreys, P.N. Biodegradation of the alkaline cellulose degradation products generated during radioactive waste disposal. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- B.S.I. Plastics—Determination of the Ultimate Anaerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials in an Aqueous System—Method by Measurement of Biogas Production; BS ISO 14853:2005; British Standards Institute: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-F.; Chen, J.-W. The experimental investigation of concrete carbonation depth. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H.; Show, K.-Y. Staining of extracellular polymeric substances and cells in bioaggregates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, W.D.; Holtom, G.J.; Kelly, N.O.; Malpass, J.; Rosevear, A.; Watkiss, P.; Widdowson, D. Microbial Degradation of Cellulose Derived Complexants under Repository Conditions; AEAT/ERRA-0301; AEA Technology: Didcot, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, W.M. Bacterial adhesion: Seen any good biofilms lately? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Dittrich, M. Carbonate precipitation through microbial activities in natural environment, and their potential in biotechnology: A review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, T.D.T.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Zhang, X.V.; McNamara, C.J.; Polz, M.F.; Martin, S.T.; Berke, N.; Mitchell, R. Binding of harvested bacterial exopolymers to the surface of calcite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8770–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N.N.L. Demonstration of Carbonation of the NRVB; NNL(14)13296; National Nuclear Labs: Harwell, UK, 2015.
- B.G.S. Results of Laboratory Carbonation Experiments on NRVB Cement: Minerals and Waste Programme; OR/14/048 Energy science programme; British Geological Survey: Keyworth, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Almond, M.; Shaw, P.B.; Humphreys, P.N.; Chadha, M.J.; Niemela, K.; Laws, A.P. Behaviour of xyloisosaccharinic acid and xyloisosaccharino-1,4-lactone in aqueous solutions at varying pHs. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 363, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okshevsky, M.; Meyer, R.L. The role of extracellular DNA in the establishment, maintenance and perpetuation of bacterial biofilms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Sehar, S.; Manefield, M. The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Schramm, A.; Neu, T.R.; Revsbech, N.P.; Meyer, R.L. Extracellular DNA in adhesion and biofilm formation of four environmental isolates: A quantitative study. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 86, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Sasaki, K.; Nakashimada, Y.; Kakizono, T.; Noparatnaraporn, N.; Nishio, N. Growth and flocculation of a marine photosynthetic bacterium Rhodovulum sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Sehar, S.; Koop, L.; Wong, Y.K.; Ahmed, S.; Siddiqui, K.S.; Manefield, M. Influence of calcium in extracellular DNA mediated bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.L.; Hanman, K.; Reuter, M.; Betts, R.P.; van Vliet, A.H.M. Campylobacter jejuni biofilms contain extracellular DNA and are sensitive to dnase i treatment. Front Microbiol. 2015, 6, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Component | Mass (g) |
|---|---|
| Lime | 300 |
| Limestone flour | 990 |
| Portland cement | 900 |
| Water | 1230 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charles, C.J.; Rout, S.P.; Laws, A.P.; Jackson, B.R.; Boxall, S.A.; Humphreys, P.N. The Impact of Biofilms upon Surfaces Relevant to an Intermediate Level Radioactive Waste Geological Disposal Facility under Simulated Near-Field Conditions. Geosciences 2017, 7, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030057
Charles CJ, Rout SP, Laws AP, Jackson BR, Boxall SA, Humphreys PN. The Impact of Biofilms upon Surfaces Relevant to an Intermediate Level Radioactive Waste Geological Disposal Facility under Simulated Near-Field Conditions. Geosciences. 2017; 7(3):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharles, Christopher J., Simon P. Rout, Andrew P. Laws, Brian R. Jackson, Sally A. Boxall, and Paul N. Humphreys. 2017. "The Impact of Biofilms upon Surfaces Relevant to an Intermediate Level Radioactive Waste Geological Disposal Facility under Simulated Near-Field Conditions" Geosciences 7, no. 3: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030057
APA StyleCharles, C. J., Rout, S. P., Laws, A. P., Jackson, B. R., Boxall, S. A., & Humphreys, P. N. (2017). The Impact of Biofilms upon Surfaces Relevant to an Intermediate Level Radioactive Waste Geological Disposal Facility under Simulated Near-Field Conditions. Geosciences, 7(3), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030057





