Abstract
A numerical mechanism connecting ice algal ecodynamics with the buildup of organic macromolecules is tested within modeled pan-Arctic brine channels. The simulations take place offline in a reduced representation of sea ice geochemistry. Physical driver quantities derive from the global sea ice code CICE, including snow cover, thickness and internal temperature. The framework is averaged over ten boreal biogeographic zones. Computed nutrient-light-salt limited algal growth supports grazing, mortality and carbon flow. Vertical transport is diffusive but responds to pore structure. Simulated bottom layer chlorophyll maxima are reasonable, though delayed by about a month relative to observations due to uncertainties in snow variability. Upper level biota arise intermittently during flooding events. Macromolecular concentrations are tracked as proxy proteins, polysaccharides, lipids and refractory humics. The fresh biopolymers undergo succession and removal by bacteria. Baseline organics enter solely through cell disruption, thus the internal carbon content is initially biased low. By including exudation, agreement with dissolved organic or individual biopolymer data is achieved given strong release coupled to light intensity. Detrital carbon then reaches hundreds of micromolar, sufficient to support structural changes to the ice matrix.
1. Introduction
Sea ice plays a central role in establishing and maintaining the global climate state, acting through a variety of biophysical mechanisms and feedbacks. For example, chlorophyll absorption at the edge of the ice domain can amplify global warming [1] while loss of reflective coverage dramatically alters planetary albedo [2]. Organic chemistry determines key physical features of sea ice, and is now being considered dynamically in the context of global change [3,4,5,6]. Brine drainage, thermodynamics, habitat volume and nutrient retention are all controlled in part by the macromolecular content of the internal channel network [7,8]. Biopolymers are now recognized as leveraging elements of the global marine climate system at multiple levels [9,10,11]. Yet for pack ice, their chemistry has not been simulated at large scales [12]. In the present work, we apply an approach spanning the Arctic environment, and building from several preexisting ecodynamic models developed by our group [13,14]. Emphasis is placed on organic compound production and loss within the brine, as set by ice algal nutrient uptake and traditional carbon cycling [4,15,16,17]. Hence, our scheme is also relevant for more general sea ice biogeochemistry calculations, and it may be extensible to both hemispheres [18].
An offline numerical framework is constructed to provide for testing of the new ice organic mechanism. Light absorption and penetration are computed throughout the pack column, along with diffusive tracer transport and continuity for all major nutrients, biota supported by them and dissolved detritus released as the full complement of byproducts. Results are analyzed based on observed distributions and properties of natural macromolecules in environmental ice systems [3,4,5,6,17,19,20]. In addition, validation is performed against chlorophyll data sets for lower habitat layers and also a selection of Arctic ice organic carbon measurements. We explore the implications of ice algal adaptation for low-temperature high-salt survival, and speculate on trajectories for the organo-ice system under upcoming global change [8,21,22,23]. For the moment, our core mechanism bypasses phase state distinctions among macromolecules [7]. Some steps needed to introduce adsorption, colloids and gelling are therefore mentioned briefly in the discussion section [3,6,7,8,24].
We argue that comparisons between preliminary computations and observational data indicate targeted organic exudation by the pan-hemispheric Arctic brine algae. Direct introduction to the ice internal environment appears sufficient to restructure pores, enhance nutrient retention, and maintain stratification/position in an attenuating light field [7,22,25]. Our results show that selected fresh bioorganic compounds can be injected into the saline network due to growth alone, independent of standard grazing and mortality—in other words, additionally to fundamental cell disruption. We thus identify and explore numerically an alternate ecological flow stream, in simulations for several polar regions. Macromolecular concentrations reach levels cited in the literature for the control of pore morphology and living space [3,8,19]. Although organic emissions are treated here through the idealized biological tracer classes protein, polysaccharide and lipid [7,10,26,27,28], heterogeneous polymeric combinations may be involved as well—glycoproteins, aminosugars, uronic acids, insoluble polysaccharides and short chain humics have all been reported from the saline solution [4,5,6,7,8,17,29]. An ambient brine mix may also include chromophoric groups which are fresh, aromatic and mycosporine-like [30]. Actual molecular configurations may be tailored for cold-hardiness by strong, continual evolutionary pressure [3,17,22,31].
The text is structured as follows: In Section 2, driver simulations from CICE are described [18], along with initial and boundary conditions plus ice algal regulators such as snow and ice thickness. All these quantities and more are averaged over regional subdomains defined in recent biogeographies [13,32]. Assumptions include precipitation, thermodynamic and seawater interfacial constraints provided by the ice dynamics and imposed at the synoptic scale. Our approaches to nutrient-light-salt limited growth, radiation attenuation, ice-internal transport, porosity evolution and organochemical kinetics are described from an historical viewpoint [13,14,25,33,34] with mechanistic ecosystem information organized into two Appendix A and Appendix B. The reduced code effectively constitutes a set of layered, one dimensional population/chemical dynamics calculations. They are resolved vertically at the scale of a few centimeters. The method is developed here to preview more complete CICE biogeochemistry research. We present a mechanism that likely can be applied in other situations. For example, an ocean-ice iron cycle is incorporated [35,36] but not active since trace metals tend to be replete in the Arctic [37,38].
Data collected for validation purposes, discussed mainly in Section 3 and onward, include sea ice chlorophyll, total dissolved organics and most importantly, chemical analyses specific to the proteins, polysaccharides and aged refractory carbon, e.g., [4,7,15,20,39]. For the core ecology (Section 4), optimization has been focused upon the pigment layers of bottom ice because field studies are relatively numerous. In Section 5, our organic release mechanism excludes then introduces the exudates, improving average concentration comparisons with measurement data.
Results from the reduced Arctic organic model are presented as plots of time evolution over a typical year of simulation. The major habitat layers (bottom, interior, freeboard and infiltration) are highlighted. Upper level biota tend to be less ubiquitous in the Arctic than for the Southern Ocean ice domain [40,41,42]. Our exercise predicts that the topmost habitats exist mainly in peripheral ecogeographic zones, and that they remain tenuous—there is a strong sensitivity to snow–ice thickness ratios which determine pack submersion [43]. In a baseline run, organics are supported solely by traditional cell disruption and with the exception of prescribed humics, pack-internal carbon is biased low relative to observations [15,20,29]. A conclusion is that exudation from the brine algae may be required, taking place over and above simple release through mortality and grazing. A scheme specifying threshold light levels near the photophysiological saturation intensity gives improved agreement [44], and is justified on the basis that energy may be required to sustain extra carbon fixation.
Model results are summarized in Section 6, and we conclude with a review of organic molecular behaviors in Arctic sea ice, with attention to forms and concentrations which may be capable of altering channel structure [3,6,17,22]. Pitting, films, gels and a general inhibition of formation are all considered relative to the modeled macromolecular concentrations. The potential is sketched for a full microphysical approach to adsorption and additional phase transitions within the pore network. Our results point strongly toward biological controls on crystal formation, both in bottom ice and during intermediate or upper level blooms in many remote locations. We thus recommend renewed laboratory study and field measurement effort, coordinated with global scale simulations of the processes involved. Development of a bi-hemispheric approach is suggested for the organic chemistry, so that concepts can also be tested in the Antarctic. We expect the most important differences there to revolve around thin ice submersion, upper habitats and the chemistry of chelation [36,40].
2. Model Description
2.1. Simplified Physical Model
Input fields for major physical variables were taken from history files generated by CICE [18] configured in its most recent release (Version 5). The parent code is known for its extended viscous-plastic treatment of rheology, with an elastic wave mechanism allowing for explicit numerics to represent any responses to stress. A thermodynamic model computes local growth rates of snow and ice due to vertical conductive, radiative and turbulent fluxes. Features critical to brine channel biogeochemistry include a mixing length approach to vertical tracer transport, multiphase porous flow (mushy layer theory), incremental remapping advection in the horizontal and a delta-Eddington multiple scattering scheme. Early applications are discussed relative to generalized tracer transport by Jeffery and colleagues [45,46]. For a sample application of bottom layer biogeochemistry to Arctic aerosol production, the reader is referred to Elliott et al. [14]. CICE forms the sea ice component for several climate system models, e.g., [47,48].
In preparation for our offline tests, a standalone CICE run was conducted from 1980 to 2009 using climatological ocean forcing from the Community Earth System Model. The overlying atmosphere is applied through a standard CORE II climatology [49]. The ability of our independent ice model to capture variation in polar coverage has been demonstrated recently in some detail, over multiple decades [50]. Melt ponds are now incorporated into CICE and have been improved with respect to their numerics. In the real polar system surface ponding supports biological activity, but freshwater features will be considered separately and at a later date. We restrict ourselves here to chemistry of the brine.
Using output from the standalone simulation, lower tropospheric, ice and seawater temperatures were averaged temporally at multiple levels along with simulated thicknesses of snow and ice, all over the stated period (predating major climate change-driven losses). The data were then further averaged areally, over the biogeographic zones originally used by Deal et al. [13]. This simplifies the ice algal system to ten one-dimensional problems. The zones encompass the latitude range of all sea ice types in the Northern Hemisphere.
All biogeochemical simulations begin on 1 January. Initial conditions are determined by inserting deep-winter nutrient and organic levels into any pore spaces available. For organics, we make the assumption that only humics are present during polar night. Fresh macromolecular concentrations thus begin at negligible levels. Nutrient and biopolymer cycles below the pack are both specified inside the model’s ocean mixed layer to reflect measurements. Temporal patterns have already been discussed with regard to the Ross Sea [28], and for simplicity these results are phase shifted by six months here for application across the Arctic. Subsurface observations are in close accord [51,52]. Flooding, which is better documented in the Southern Hemisphere [42,53], may also occur in the North and its onset is computed according to Archimedes Law [43]. Sufficient buildup of snow on the pack may cause sinking with infiltration, particularly when/where the ice is thin. Nutrients and organics are spread onto any locally depressed ice surface as dictated by mixed layer concentration data.
2.2. Biogeochemistry
The physical quantities used to force our ice ecosystem model are provided as weekly averages over an annual cycle, for the 10 regions in Figure 1. They are taken as input into a numerical model for vertical ecodynamics, kinetics and transport within sea ice. Biogeochemical continuity equations then represent time evolution for the ecology and organic chemistry. Forms and baseline parameter settings are laid out in detail in the appendices (A and B), and the model system is mapped schematically in Figure 2. A sample list of tracer groups under our notation is:
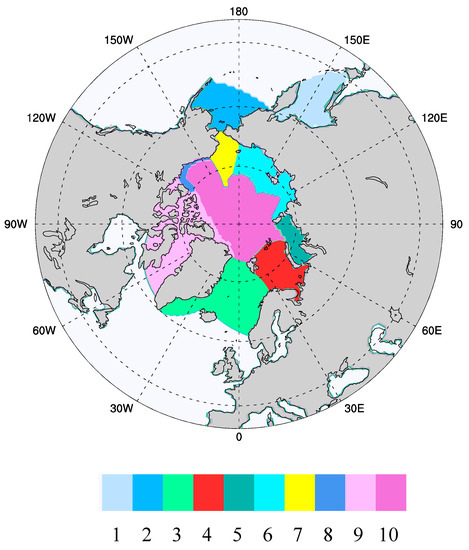
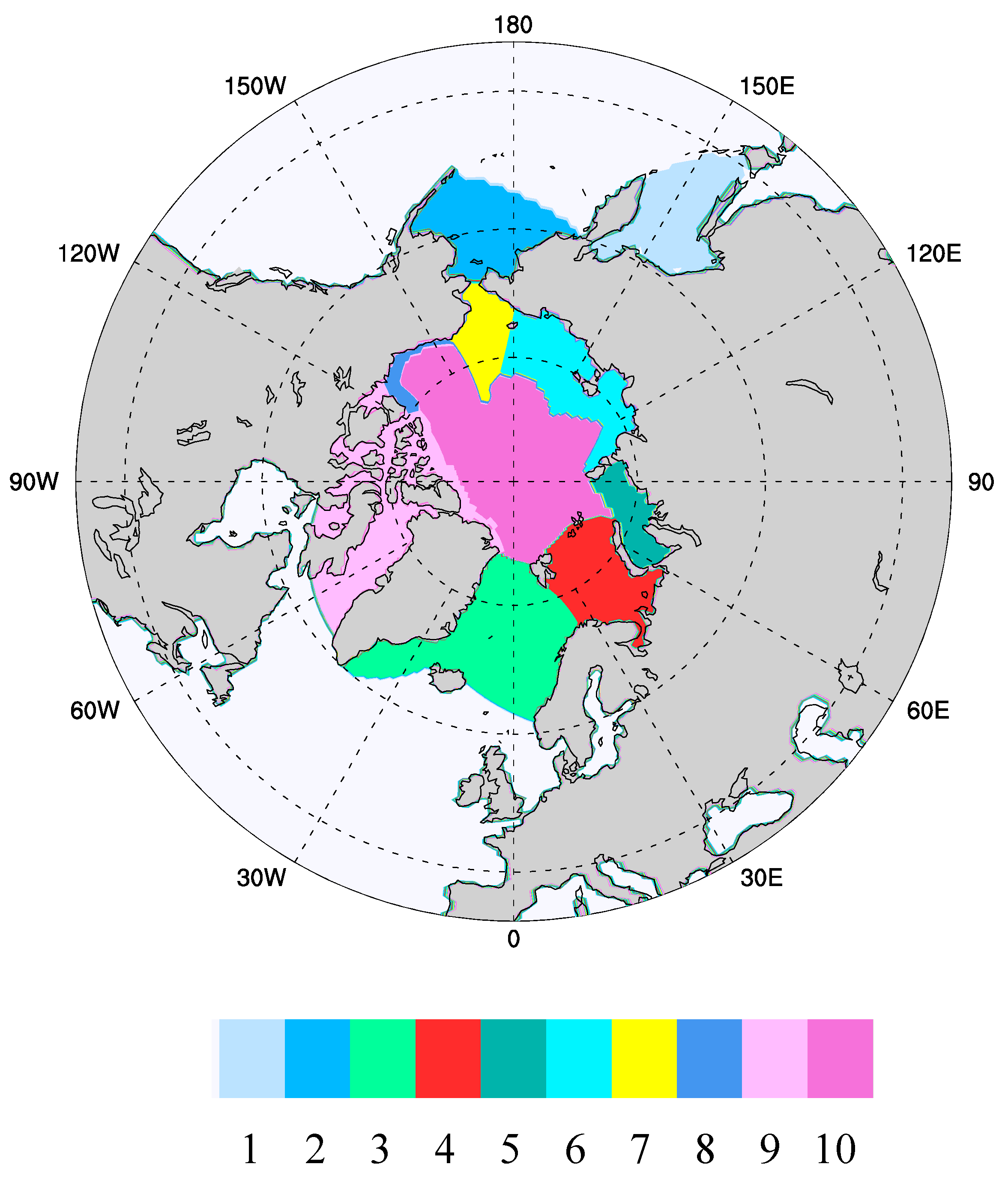
Figure 1.
Ecogeographic zones over which averaging of the CICE results was conducted, and within which the ice algal modeling takes place. (1) Sea of Okhotsk, (2) the Bering Sea, (3) GIN Seas (Greenland, Iceland, Norway), (4) Barents Sea, (5) Kara Sea, (6) Siberian Shelf (combines Laptev and East Siberian), (7) Chukchi Sea, (8) Beaufort Shelf, (9) Canadian Archipelago, (10) Central Arctic. This system is an adaptation of the ecological geography developed originally by Carmack and Wassmann [32] and later extended in the work of Deal et al. [13].
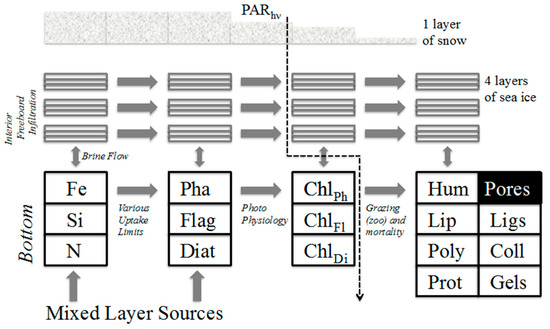
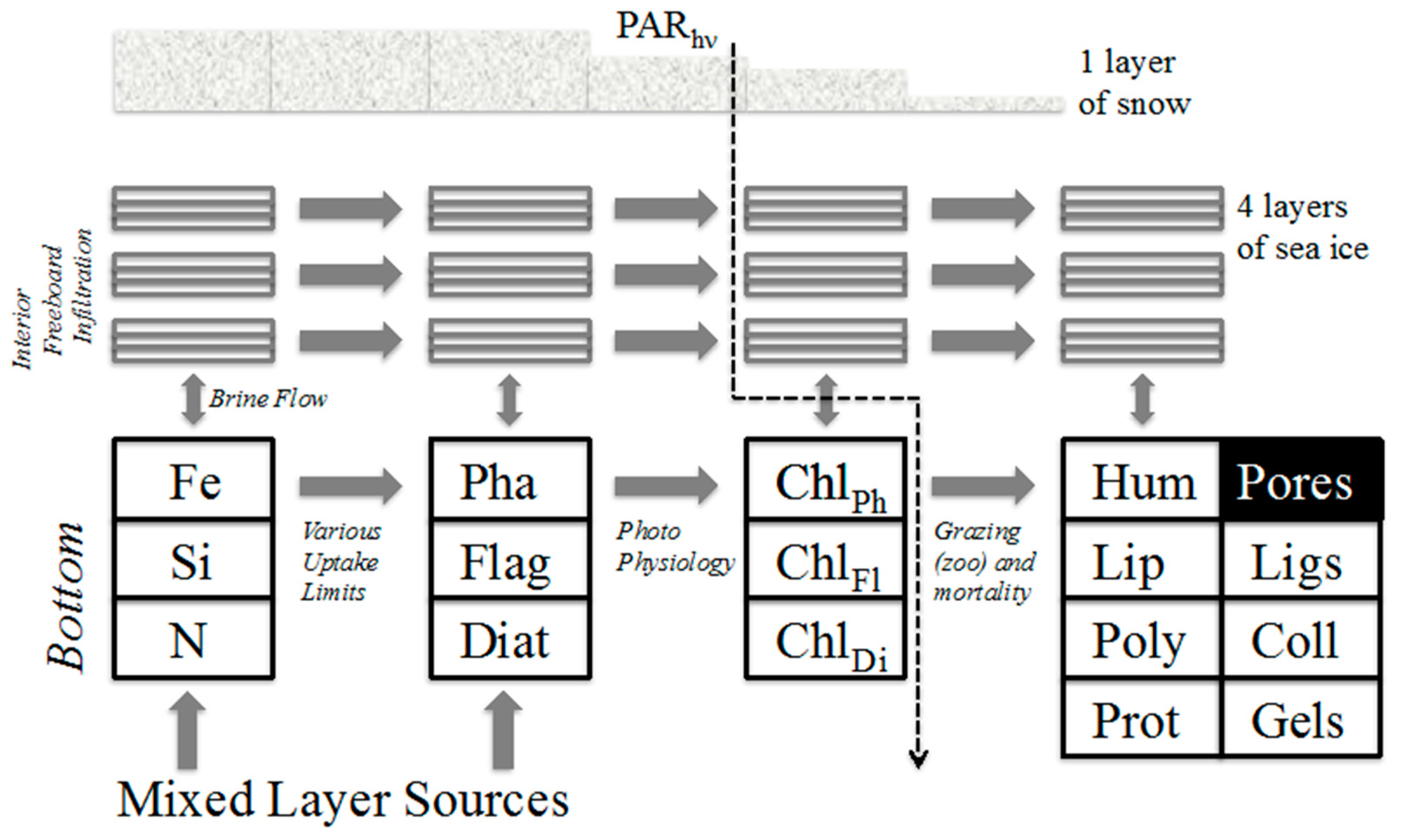
Figure 2.
Schematic of the ice organic biogeochemistry mechanism in the present work. Major ecodynamic channels described anecdotally in the text and as equations in an appendix. Abbreviations: (Diat) generic diatoms, (Flag) microflagellates, (Pha) Phaeocystis, (Chl) chlorophyll content for each class, (Prot) Proteins, (Poly) carbohydrates or polysaccharides, (Lip) the broad class of lipids, (Hum) the heterogeneous polymers humic acid, (Coll) colloids forming from the organics, (Ligs) Ligand effects which can become important under trace metal limitation, (PAR) Photosynthetically Available Radiation.
- auto (autotrophic organisms encompassing phytoplankton and/or ice algae)
- nut (the major inorganic nutrients including redox states plus iron)
- mac (fresh or aged biomacromolecules represented as lipids, oligomers and polymers).
Families of equation are presented in roughly the order
- A1-5 (define the various ice biogeochemical quantities)
- A6-17 (limitations, autotrophic source-sink terms and biological rates of change)
- A18-22 (fixed ecodynamic fractionations and apportionments)
- A23-27 (nutrient uptake and recycling)
- A28-32 (organic processing of biomacromolecular detritus/exudate)
- A33-37 (vertical transport with flushing and continuity)
Relevant constants in the system are listed for the reader’s convenience in a concluding Table A1.
Within each geochemical grouping auto etc., as manipulated in A1-37, elemental ratios can be maintained as desired but overall carbon functions as the primary common currency. Individual nutrients, various inorganic forms, and dissolved macro-carbon content are tracked to deal respectively with alternative sources, resource limitation and successional accumulation. Our scheme is drawn from published ice biogeochemical simulators focused on pigments, biomass and sulfur cycling [14,25,54]. Other ice algal models already treat detrital organics collectively [12], but we choose to emphasize structural resolution (functionality). It has become clear from both the physicochemical and geographic perspectives that carrying macromolecular detail may hold advantages [6,7,8].
Arctic nutrients are fed into the bottom of the lowest sea ice stratum so that they then mix upward through the ice column. Their transport is eddy diffusive, but it adjusts for porosity as a fractional multiplier on flux [34]. A common molecular diffusion coefficient of 10−9 m2/s is adopted for all solutes [25]. The thickness of hypothetical laminae dividing our actual numerical layers can readily be adjusted to reproduce observed ice-internal residence times [25,34,55]. Mixing length and thermodynamic factors are only known to the reduced model secondarily, through the imported CICE output. Snow cover determines buoyancy overall according to Archimedes Principle just as in the main code, with a threshold for submersion (infiltration layer generation) that is tuned post hoc. Porosity is calculated based on the evolving salt content, given standard freezing point depression equilibria [34,44].
Ice algal blooms are triggered in the equation set through relaxation of nutrient or light limitation, subject to salinity restrictions based on laboratory photo-physiological studies [44,54]. A salinity-growth retardation is computed for consistency with the local porosity. Zooplankton are treated in the mechanism as a non-modeled background entity skimming a constant small fraction of primary production [33,54]. This is a typical assumption even in contemporary ice ecodynamic simulations and it will be considered in more detail in the discussion section, since the organics are strongly affected. Grazing and mortality are routed into a complex network of spillage, assimilation and remineralization pathways ([14], appendices). Dissolved carbon of biological origin is present initially as a refractory humic background which predates and underpins the time dependent superposition of fresh macromolecules [28,29]. As will be shown, disruptive releases do not suffice to explain the available analytical chemical observations, and therefore exudation is introduced in several modes to provide additional sourcing. Fixed rates and also analogs varying with relative light level are both tested extensively.
Inorganic tracers include nitrate, ammonia/um, silicate and finally iron, the latter taking a collective bioavailable redox form applicable to open polar waters (grouped from [56]). Autotrophic bins are limited to the ice diatoms (usually pennate), generic microflagellates and an aggregate Phaeocystis. This ensemble of organisms follows the lead of Walsh et al. [57,58], who established an algal vector applicable to both hemispheres. Labile organics are simply the major classes of macromolecule comprising all biological soft tissue [7,27]; proteins, polysaccharides and the lipid family. Mixed polymers naturally also exist and may well be critical to ice structural effects [8,17], but they are treated here as conceptual combinations. All of these appendix biogeochemical quantities are represented in our figure schematic, with details defined by the equation and parameter lists. Our fundamental ice algal reactant and reaction lists derive originally from the pioneering work of Arrigo and company [54]. We have added boreal coastal, archipelagic and ecodynamic adjustments [25,33], Pan-Arctic extensions [13,14], iron in anticipation of Antarctic studies [36,59,60], and now (critically) the suite of macromolecules.
Surfactants are currently given serious consideration in the oceanographic literature along bubble, microlayer, aerosol and other global scale geophysical interfaces [9,10,28]. Amphiphilicity will naturally also figure inside the complex, multiphase medium that is sea ice [22,36,53]. Moreover, certain combinations of organic functionality act as multidentate ligands, retaining metal ions within the matrix [35,36]. Our fresh releases necessarily imply a degree of well-characterized chemistry since we apportion dissolved carbon into several specific forms. A classic marine algal content-spillage ratio of 60, 20 and 20% by moles is adopted throughout for protein, carbohydrate, and lipid [27,28]. Ice structural studies indicate that in some cases heterogeneous material is more important. Mixed polymers can pit brine channel walls [3,19], while hybrids such as the glycoproteins are known to alter tortuosity [8]. For present purposes, mixed monomeric sequences can only be inferred indirectly from the proxy suite.
Time evolution of the baseline organics is driven through ecodynamically disruptive releases associated with grazing-senescence-mortality, while loss control is exerted exclusively by a conceptual heterotrophic (bacterial) population. The same consumer microbes are also called upon for removal during the various direct exudation tests [12,28]. Our overall philosophy is to mimic carbon cycle succession within the pack ice, since waves of activity are often reported in time series [6,7,15,16,17,60]. Although refractory humic acids are treated for the moment as a constant feature of the background water column, like other quantities they are mixed and continually supplied dynamically to sea ice from below. Porosity is thus expected to be a major determinant relative to their bulk concentrations. They are inert but may be squeezed from channels as a solute component during brine rejection.
In earlier, regional ice-biogeochemical modeling, the vertical system has often been decomposed into a virtually continuous series of thin layers [34,54]. For present reduced computing purposes, we simply segregate into four thick, stacked boxes each of roughly centimeter scale. They are identified as follows: the bottom layer which is well known in the Arctic [13,14], the ice interior which may also be ecologically rich [7,41,61] (though low temperatures restrict habitat via desalination), plus freeboard and infiltration strata as defined heuristically during observations [40,62,63]. The latter two levels can be difficult to distinguish in the field, and they are in any case relatively rare in the Northern Hemisphere [64]. Upper level blooms are most often observed and described for the Antarctic and so our intent here is two-fold; to explore their potential for biogeocycing in understudied portions of the boreal environment, and also to prepare for the simulation of Southern Hemisphere ice. Our four vertical sections are given nominal thicknesses of 3, 30, 3 and 3 centimeters (bottom, interior, freeboard and infiltration [25,41,63]), but these fixed choices are varied in sensitivity tests and also temporally in some individual runs.
Attenuation of downwelling radiation through the selected layers is handled by summing contributions from snow, ice and total biopigments, but only in the sense of single scattering and Beer’s Law [14,25,65]. Pigment absorptivities are given in tabular form under the parameter list. Our tracer transport-continuity equations have been discretized and cast primarily into implicit algebraic solution forms. Biological growth is extremely stiff numerically, thus careful consideration had to be given to operator splitting issues. A semi-implicit strategy was eventually settled upon for nutrient uptake, and it is described along with the appendix equations. The organics by contrast are long lived in the brine [4,15], thus in their case, conservation follows regardless of the integration method. The experiments have been designed for the rapid turnover and testing of new features, and ultimately for conceptual handoff to full-scale systems models such as CICE. The software, written in the R statistical programming and analysis package, is available from the authors on request.
3. Observational Data
Several groups have compiled chlorophyll measurements for the different vertical strata of Arctic sea ice [14,39,64]. Observations are much more numerous for the bottom layer than interior or upper habitats. This is partly but not entirely a reflection of lower-level biological dominance. We distill many of the available data in Table 1, categorizing their maxima by month of the year and the Figure 1 map, then internally. Upper ice habitats in the Arctic are probably restricted in time and space due to reduced snow thickness and/or thicker ice. We combine measurements relevant to potential freeboard and infiltration layers since they mainly go unnamed. Among pack ice chemical analyses, the total dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is most often reported, and typical data are included in the table. At perhaps a third of experimental sites, the two quantities chlorophyll and DOC are reported together. The majority of measurements are conducted in the springtime, coinciding with the bloom period. Autumn, however, does not go completely unrepresented.

Table 1.
Selected Arctic sea ice chlorophyll and dissolved organic carbon data, by region as in Figure 1. Measured chlorophyll in italics and mg/m3, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) presented in bold as micromolar carbon. In each cell, the top, middle and bottom rows represent upper ice habitats, the interior and the bottom layer. Abbreviations: (GIN) Greenland Iceland Norway Seas, (NR) not reported, (Beau) Beaufort Sea but mainly coastal, (Arch) Canadian Archipelago. Where bottom layer data are given in the literature as mg/m2, a three-centimeter thickness is adopted for conversion.
Roughly speaking, bottom layer biology appears to maximize at order several hundred standard units of chlorophyll or micromolar of dissolved carbon across the board. A drop in intensity may be discernible moving poleward but the measurements are sparse. DOC in the table may or may not correlate with pigments. We will present and discuss individual organic compound types in Section 5, following the presentation of general biomacromolecular results. While not entirely complete, the selected data in Table 1 are fairly representative (see e.g., [14,39]). Upper level ecosystems are mentioned for the Arctic almost solely anecdotally, for example in the monograph by Melnikov [64]. A working hypothesis is that freeboard and infiltration layers better studied in the Southern Hemisphere [42,66] occur only peripherally and occasionally in the Arctic -although this may be changing as northern ice becomes more seasonal.
4. Model Validation and the Baseline
4.1. Accuracy and Sensitivity
Most simulations are conducted at a time step of order one day, a period which is short relative to decay constants for the organics but long when viewed in the context of intense ice algal doubling rates, e.g., in the bottom layer. In our upper level calculations, growth processes are sometimes artificially delayed by this choice. However, they still result in reasonable maxima since mass limitations control the eventual outcome. Nutrient concentrations below the ice are maintained at observed mixed layer values, even during rapid bloom uptake. In other words, instantaneous mixing is assumed in the water column just underneath the ice, as in most of our previous simulations [13,14,33]. In the bottom layer, concentrations tend to be capped by self-shading. However, due to the long step size and rich resources coming from below, overshoot remains a possibility.
Despite these numerical issues, all major features of the ice algal system are represented realistically. In Table 2, bloom maxima are compared with ice bottom measurements for the ten regional ecozones. Although primary production is phase shifted, peak heights qualitatively correspond. This is true whether results are viewed from the ecogeographic standpoint, across latitude or even for the entire polar regime. In the traditional volumetric chlorophyll units of mg/m3, a typical seasonal buildup is in the hundreds. However, the physical system can prevent biological activity entirely, for example through the accumulation and retention of thick snow cover. Overall quality demonstrated within the table is easily sufficient for present purposes, which are limited to the investigation of ice internal organic chemistry as dictated by background nutrient cycling. Similar comparisons were carried out with interior and upper layer pigment data, with similar though less robust agreement because observations remain sparse.

Table 2.
Comparison of bottom layer chlorophyll maxima from a baseline model run, with the observations of Table 1 (mg/m3), where data are available. A fixed layer thickness of 3 centimeters applies in the model. Geography, abbreviations and references are all defined as in the previous table; NB simply means there was no bloom.
The model was optimized by adjusting multiple variables including the dimension of the bottom layer [14], transfer velocities determined from diffusivities [34] and laminar layer thicknesses [25]. Additionally, dependencies were studied for the main external forcing functions snow depth and surface flooding. The statistical method most often adopted to assess results was as follows: Bulk chlorophyll output was log transformed then converted to Mean Absolute Error relative to the data (MAE as in [67,68]). This calculation allows a quick-scanning assessment against observations when results are distributed in a non-Gaussian manner—over multiple powers of ten in concentration for many cases here. Focusing upon maxima from Table 2 while ignoring the time coordinate, convergence was usually well within an order of magnitude at any given location. In other words, peak sizes were usually adequately represented, supporting our decision to proceed to the simulation of successional carbon chemistry. During the above simulations, zero or decaying concentrations are clamped to a low of 1 mg/m3 to approximate or synthesize the analytical limit of detection.
In further test series, the initial time steps, which could already be considered long, were both lengthened and shortened. Changes in chlorophyll concentration ranged over almost an order of magnitude in each direction. Longer increments led to kinetic instabilities despite conservation constraints. Pigment levels oscillated in several of the layers, due to tradeoffs between excessive shading and ammonia-driven remineralization followed by rebound blooms. Smaller step size experiments yielded a certain amount of variation in the height and timing of the Table 2 maxima, but since mass and light constraints were specifically designed to bracket the measurements these biases are not serious.
4.2. Baseline Results: Inorganics and Biology
Our presentation of time evolution plots begins with nutrients and continues through the primary producers. The Arctic setting of our experiments means that nitrate is most often limiting, and so this is the only chemical driver quantity included. Although silicate restrictions on diatom growth are conceivable [58], such instances have proven to be rare in our simulations. Dissolved iron concentrations were set to high levels reflecting strong boreal shelf and riverine inputs [37,69]. Trace metals were thus never restrictive. Model parameters as listed in Appendix B necessarily dictate the organisms involved, and these are set to match better-known pelagic ecodynamics to facilitate coupling with open water. Choices are typical for the Bering and Pacific Arctic entryway [58]. Detailed observations of cell densities within the pack were called upon for initialization [41,66]. Competitive exclusion dominates in our simulations, but the real situation is generally not so extreme. Microhabitats are thought to enable coexistence [70], but are not included here.
In this section, analysis begins with the Sea of Okhotsk and moves to three further, critical biogeographic zones: the more northerly Chukchi and Beaufort Seas since they are relatively rich in dissolved carbon data (e.g., [20,71,72]) and the polar regime defining an extreme. Bulk concentrations are dealt with exclusively since in most cases measurements are performed on melted core slices (see Appendix A for the conversion to brine-intrinsic levels). We present bulk base 10 logarithms, since the values which must be intercompared and explained range over orders of magnitude. Model output is transformed in this manner then plotted against week number, over the full year of simulation. No attempt has been made to continue into or through a second winter season, which would be better suited to a complete model.
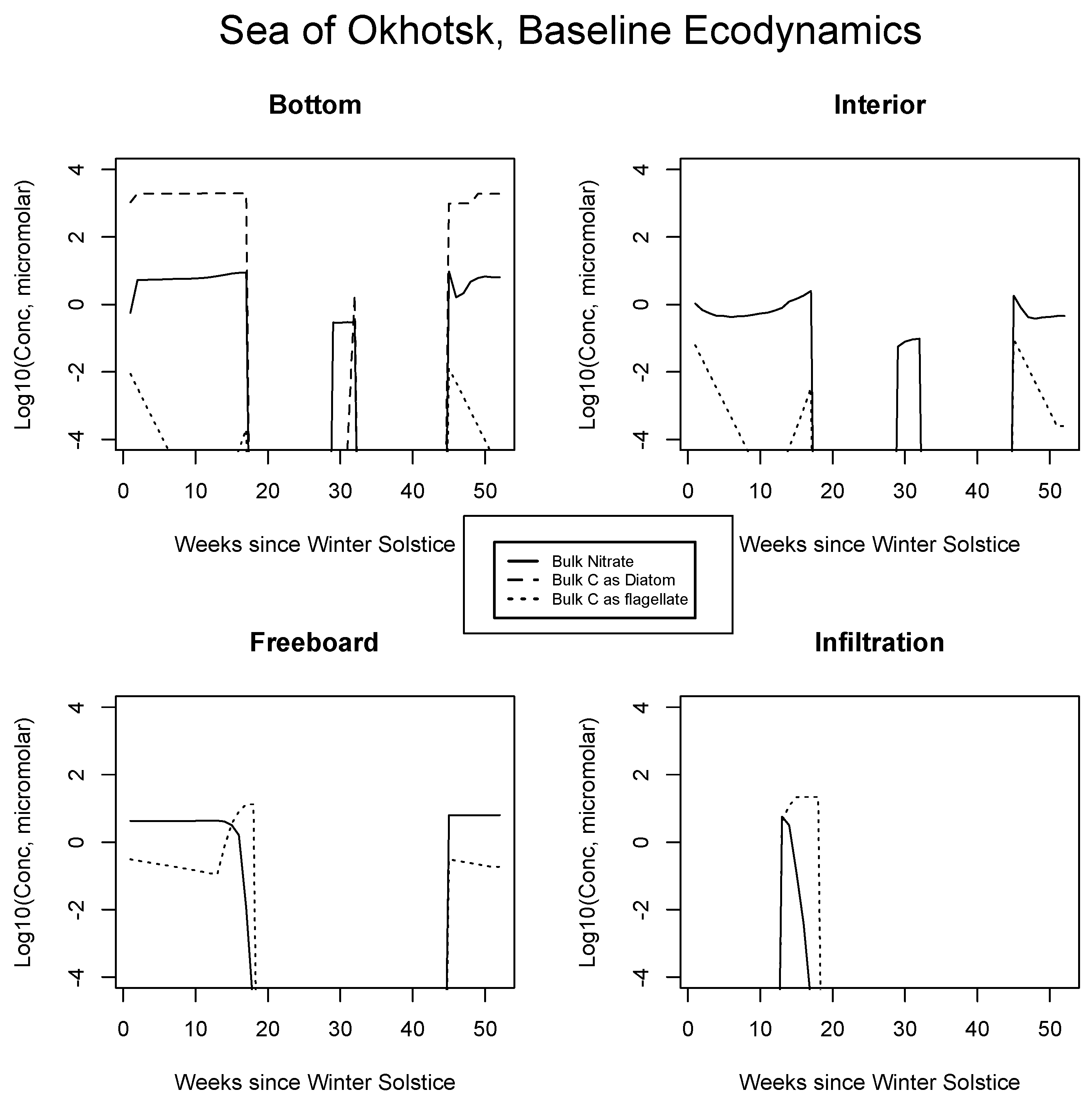
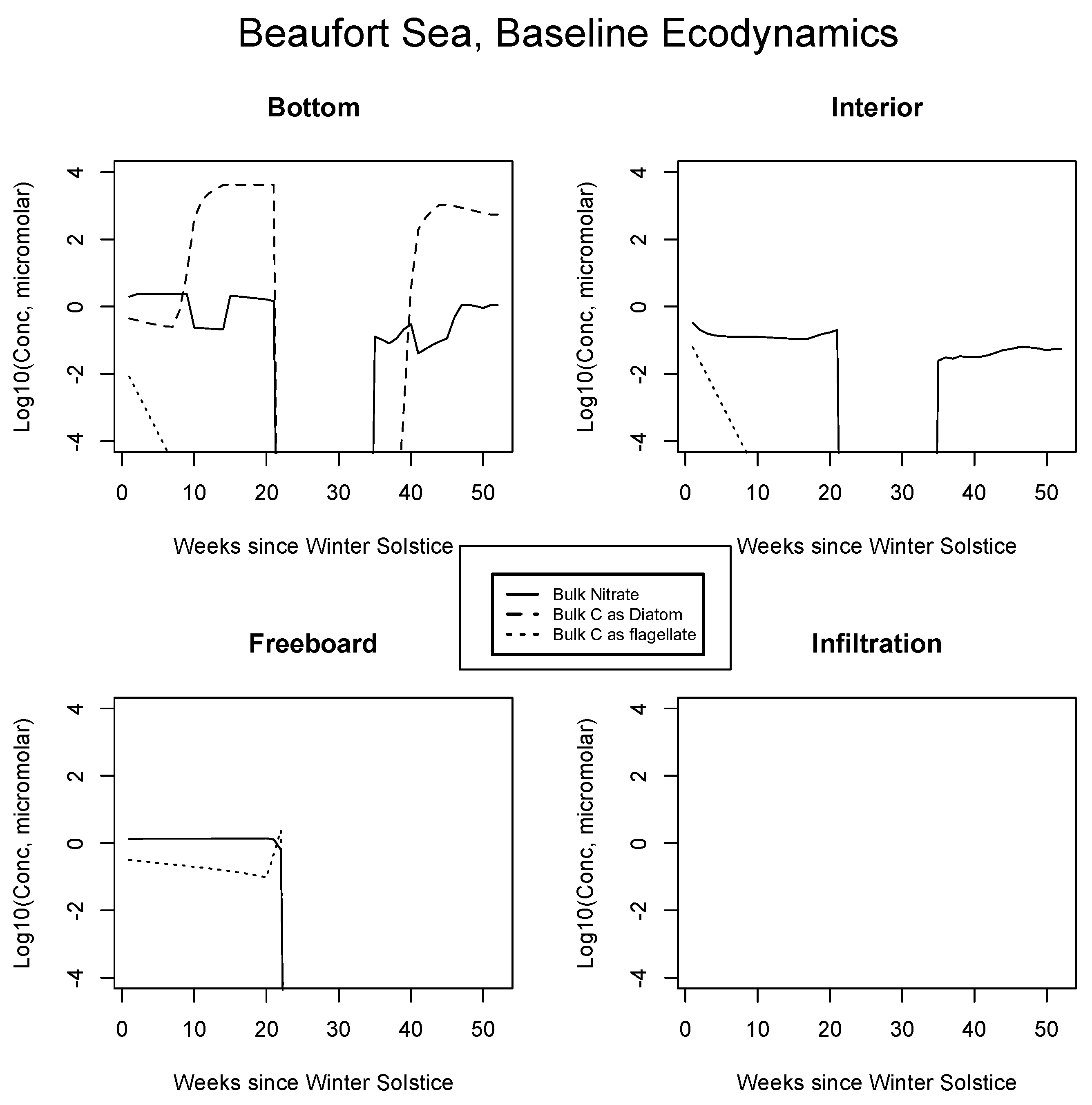
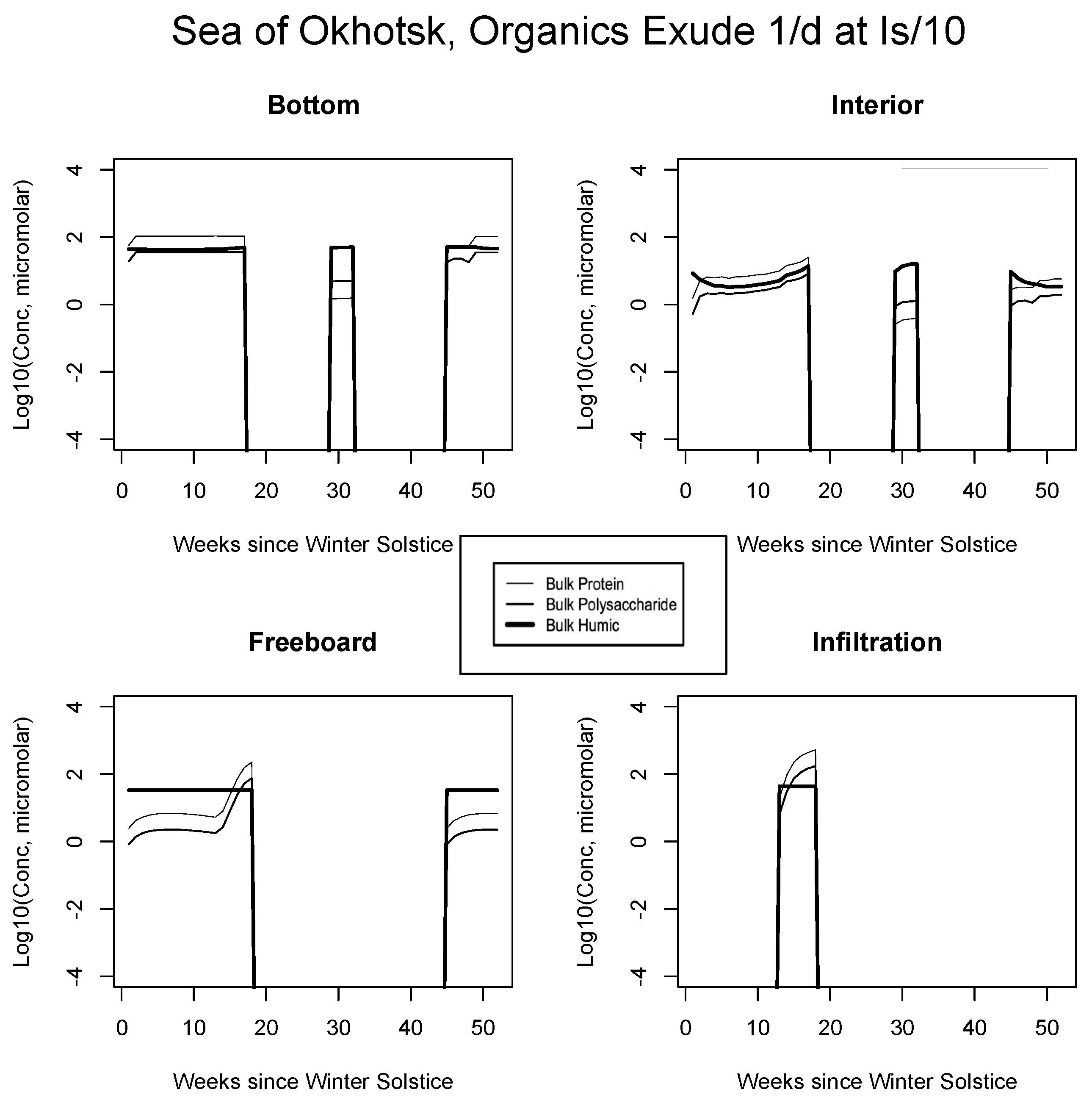
Results from the Okhotsk baseline are presented for certain inorganic or biological quantities in Figure 3. Fast equilibration into bottom ice is expected for mixed layer nitrate. The diatoms bloom rapidly at the relatively low latitudes with sunlight available early in the season, but the rate is nutrient flux limited [14]. Siliceous organisms are ecologically dominant because they go ungrazed and retain their position in the skeletal matrix [25]. (Relative) immobilization strategies probably involve excretion of the organics [7,22]. An initial flagellate population decays due to outbound mixing. Once the diatom bloom tops out, nitrate concentrations are maintained near mixed layer source levels, but with ice porosity at about one half [54].
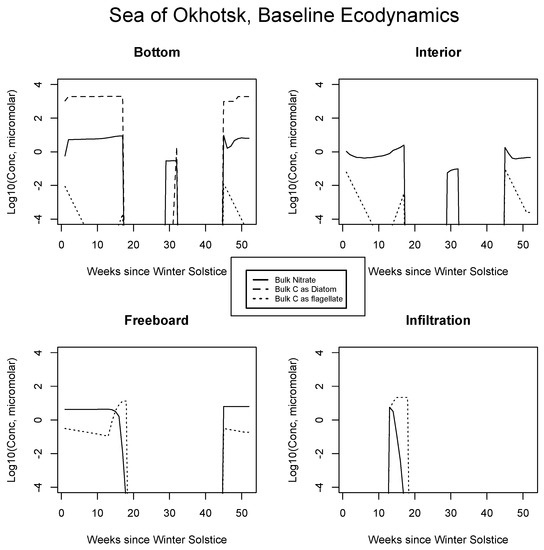
Figure 3.
Sea of Okhotsk, bulk nitrogen and carbon concentrations in the baseline run for the four numerical habitat levels. All values are base 10 logarithms for the major indicator atom types from concentrations computed in micromolar. Silicate is not shown since it is present in excess. Phaeocystis also goes unrepresented in the interest of simplification.
All Sea of Okhotsk concentrations disappear at the point where CICE indicates melting from above, via rapid percolation and flushing (about week 17 [34]; Appendix A). A rebound of both nutrients and the diatoms is supported in the summer since the reduced model allows ice to linger briefly after cessation of the flushing process (weeks 30 to 31). Persistence occurs because the model turns the purge on and off through an adjustable threshold meant to mimic a shift from vertical percolation to floe runoff [73]. It remains to be seen whether this brief seasonal feature can be reproduced in the full code or even whether it represents reality in the environment. We are not aware of biogeochemical observations during the relevant period, and they would no doubt be difficult to obtain on thin ice. Refreezing in the fall re-launches the bottom layer ecology, consistent with observations of autumn bloom activity which can be found in the literature.
Internal ice porosities are low and restrictive of biological activity in Figure 3 [44]; the potential for a bloom is suppressed until spring. Diatoms are not permitted to cross from the bottom matrix to internal channels in our simulations, and so they do not make a contribution to interior carbon. A summer nitrate return peak reflects nutrient transport from the mixed layer, but concentrations are low and no biology ensues. At the freeboard in 3, there is a strong mass limited bloom triggered by increased porosity, but this feature is terminated rapidly by the melt after only a few weeks. Net algal levels are orders of magnitude less than those of the bottom layer and flagellates, which are smaller, dominate [41,66,72]. For simplicity, Phaeocystis populations are not shown alongside those of the flagellates, but since many of the growth parameters are common to both, this class is also competitive [74]. The post-melt bloom recurrence is absent from the freeboard layer because nutrients have been flushed from the upper ice but cannot be resupplied from the ocean below in a timely fashion, due to distance and porosity influences.
In Figure 3 at bottom right, results suggest an infiltration habitat coinciding closely with the spring-centered freeboard bloom. This activity would likely be difficult to segregate from the freeboard itself [40]. Again, concentrations are mass limited, this time by the incoming nitrate content of the local seeped/flooded brine injection, thus levels are very low relative to the early ice bottom. Upper level biology may be more intense in the Antarctic for a deceptively simple reason: mixed layer nitrogen availability is significantly higher there. The Southern Ocean is famously categorized as the largest of all global HNLC zones (High Nutrient Low Chlorophyll [75]). Southern Hemispheric sea ice scavenges iron during frazil stages, thus pelagic trace metal limitations may not apply within the pack [36,76].
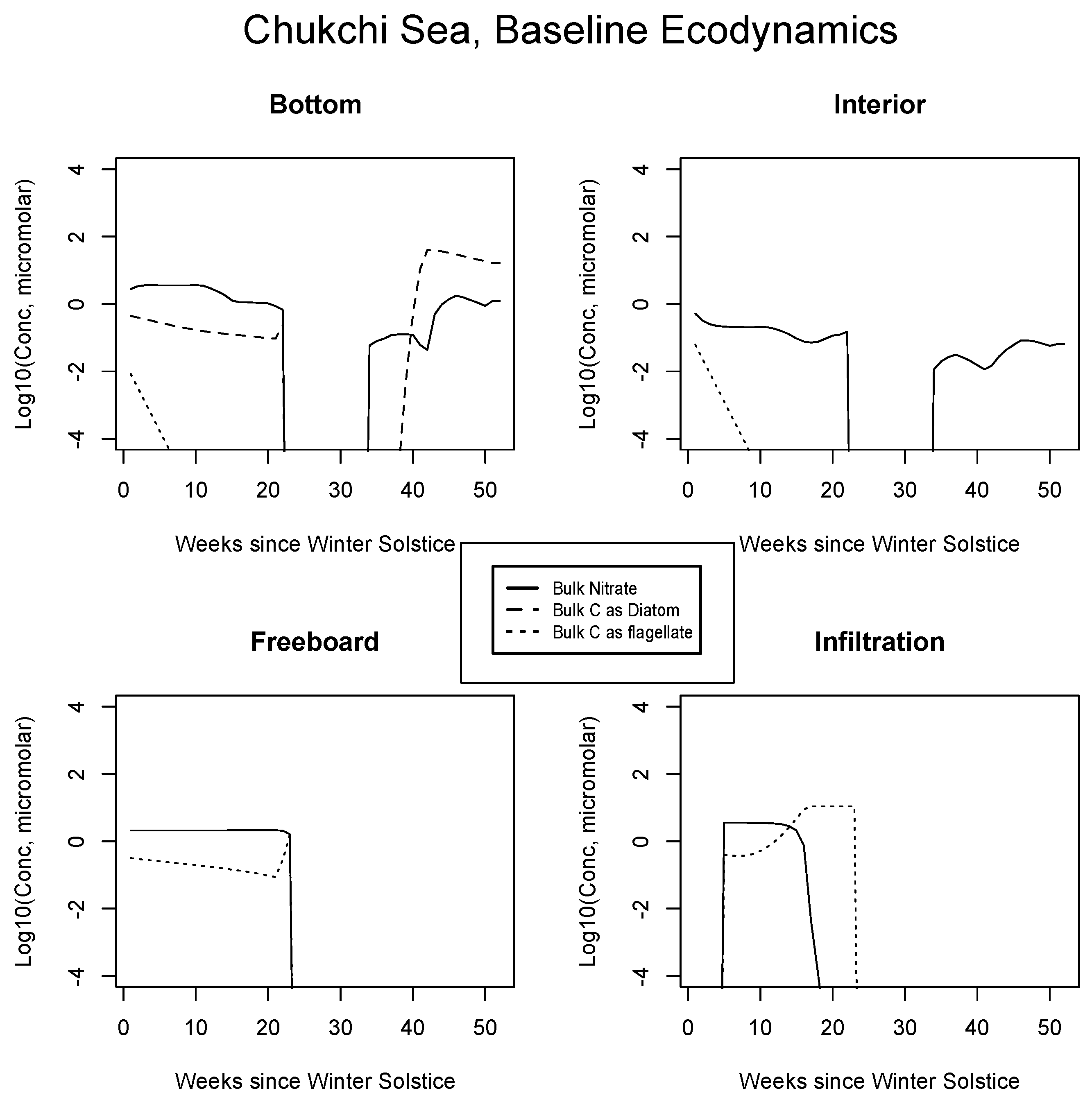
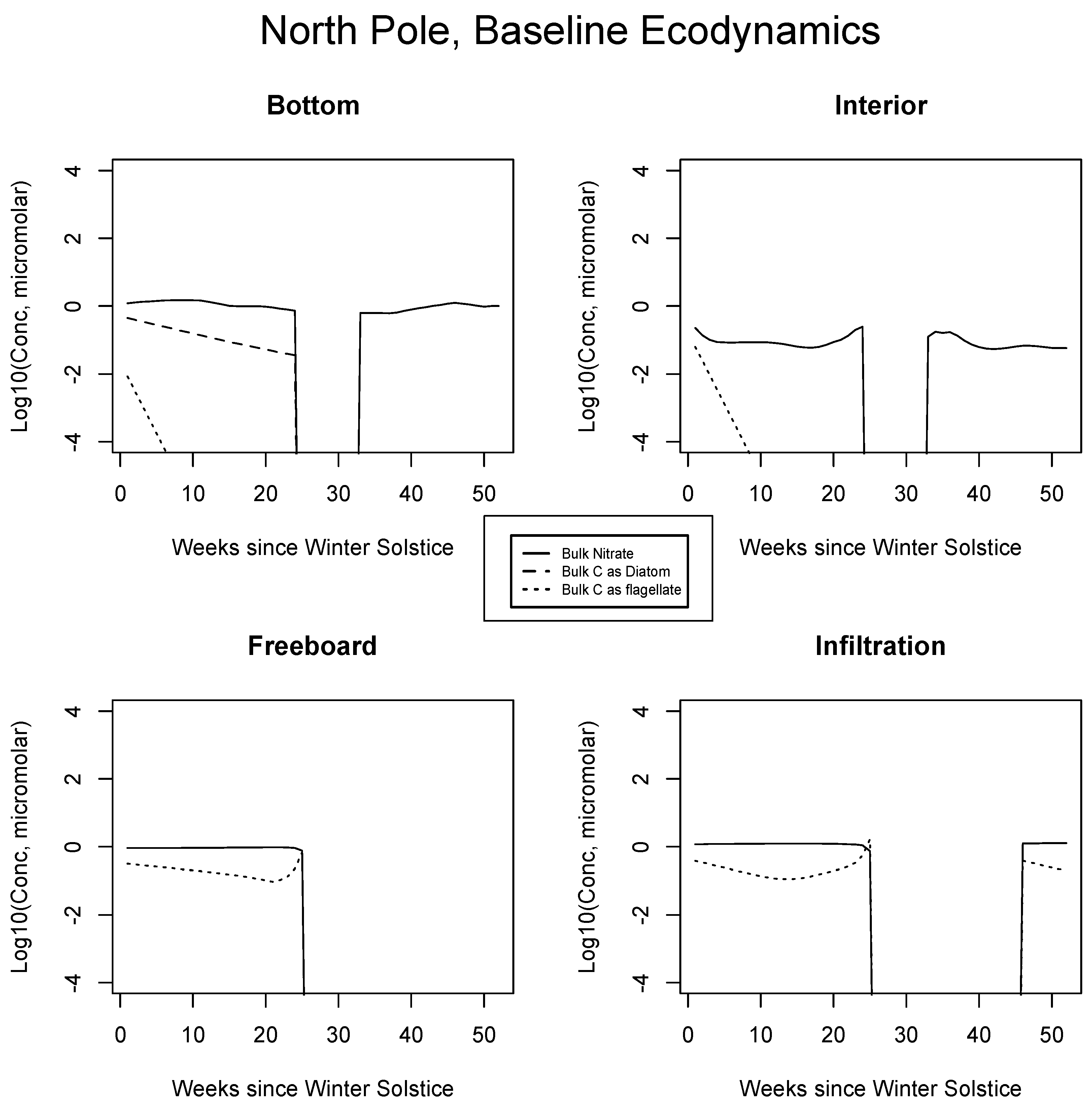
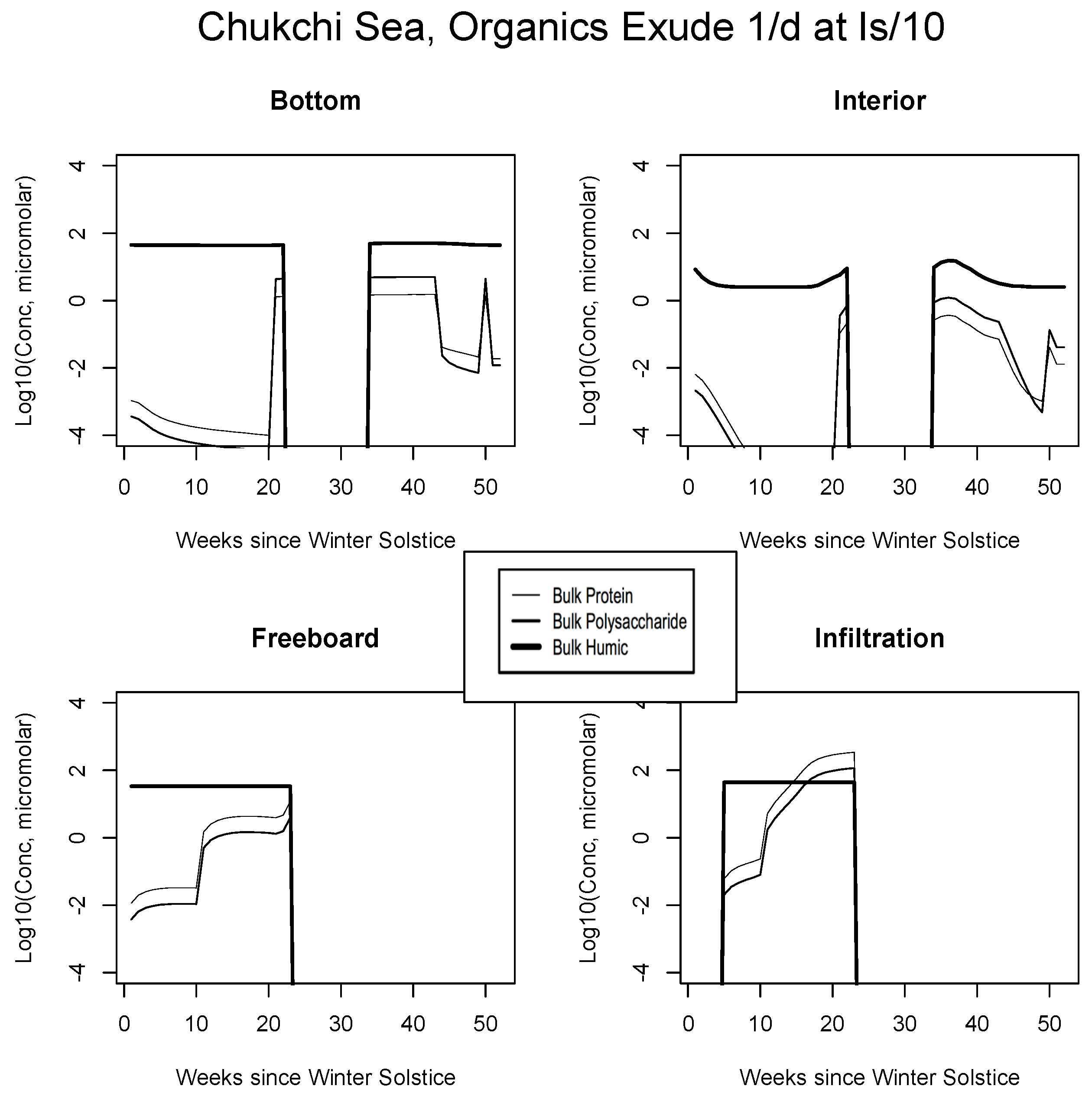
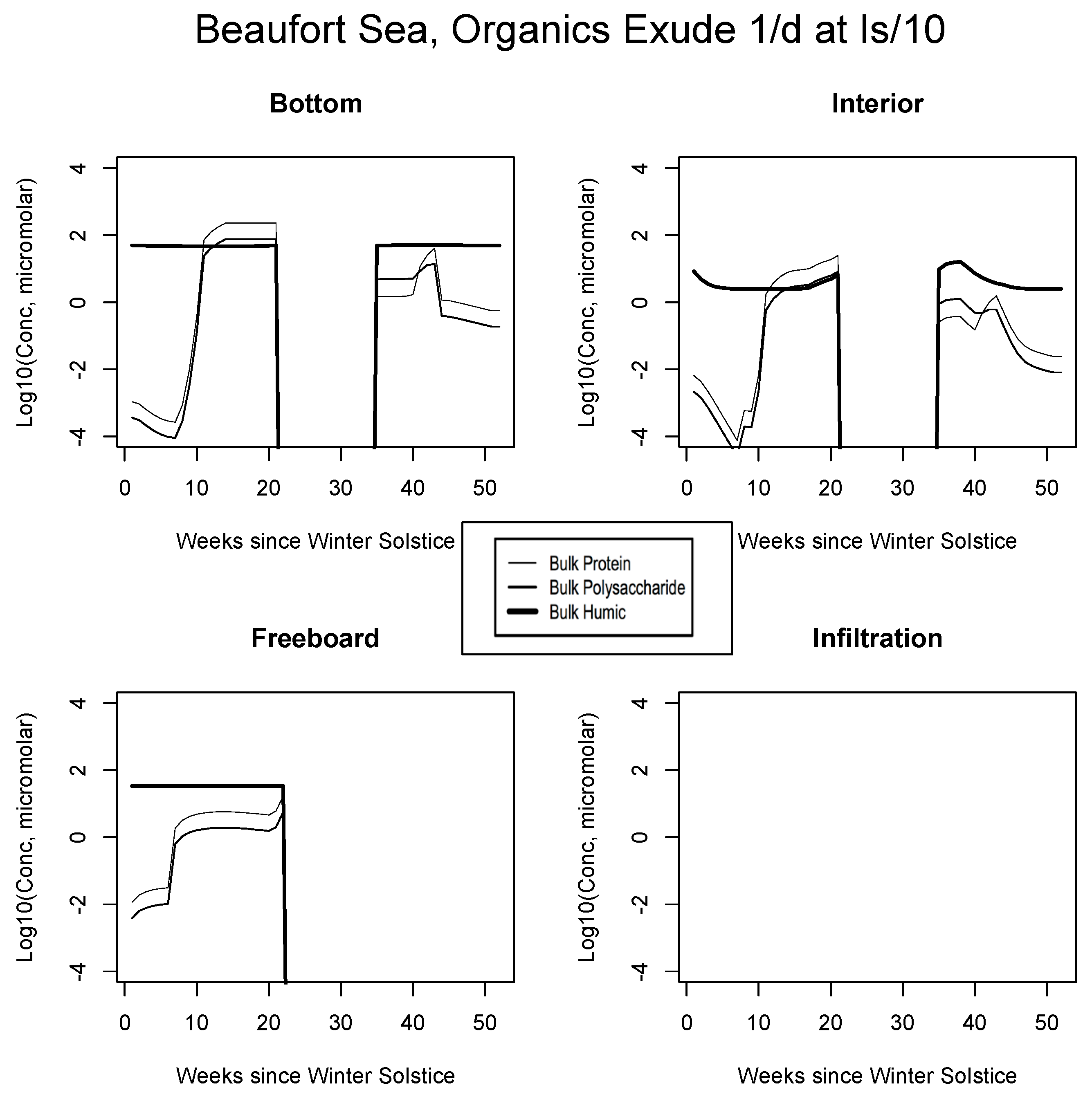
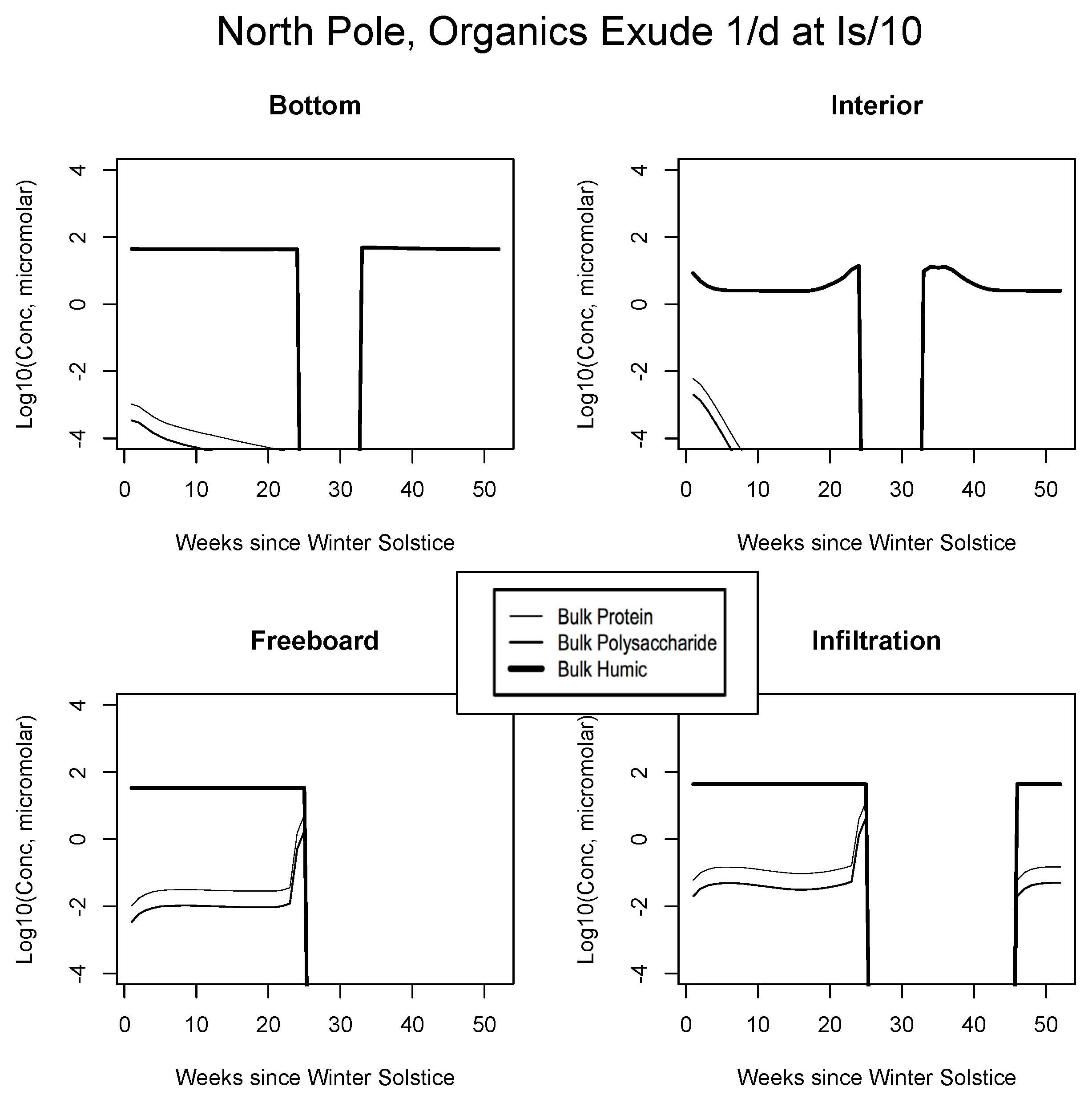
In Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6, analogous results are displayed for more northerly regions, with some similarity to the Okhotsk. In the Chukchi Sea, snow reflectivity delays the diatom bloom, but infiltration sets in early, and light is able to pass at least this far into the system. A mass (mole) constrained flagellate population is therefore established and preserved at the top of the ice column. In the Beaufort, the bottom bloom is even more intense than at lower latitudes, but shifted significantly in time, again due to snow cover. Suppression of supporting nitrate is seen during an especially intense growth period as a “bite” taken out of the evolving profile (weeks 9 to 13). The infiltration layer, however, is completely absent in this sector, since the snow data provided by CICE are insufficient to cause flooding. At the North Pole, biological activity slows but does not shut down entirely (M. Levasseur, unpublished “Polar Sea” cruise data). A modest infiltration layer bloom builds just prior to the melt. This may be a real but unnoticed feature, since the remote central Arctic Ocean is so little observed.
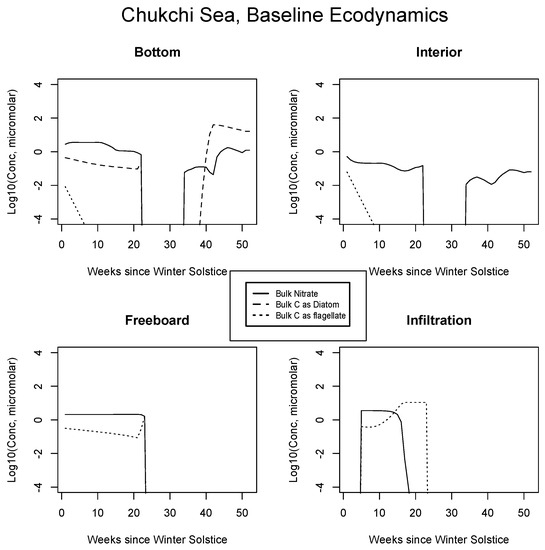
Figure 4.
Chukchi Sea, caption as in Figure 3.
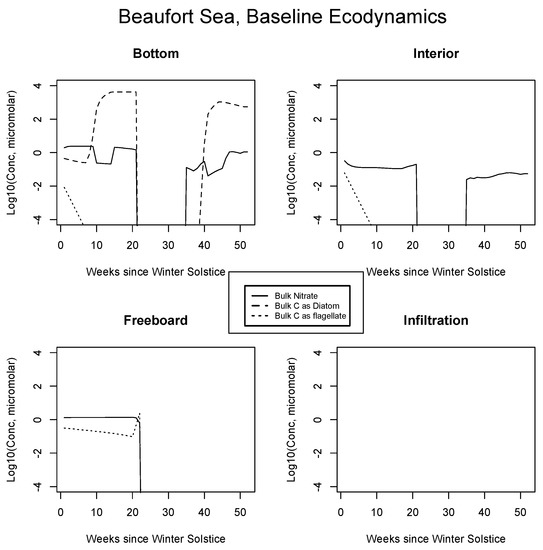
Figure 5.
Beaufort Sea, caption as in Figure 3.
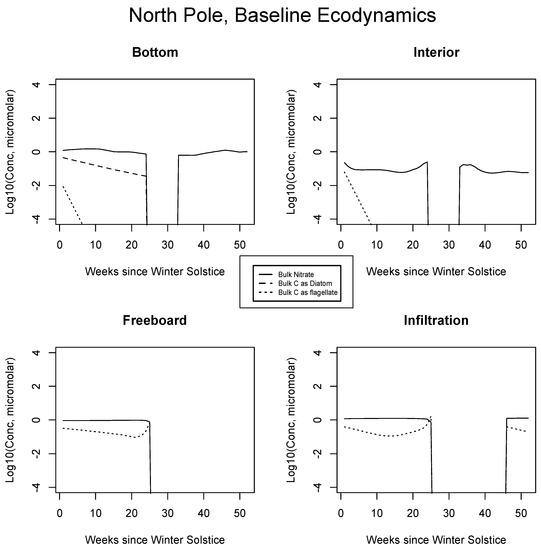
Figure 6.
Central Arctic, caption as in Figure 3.
5. The Organics
5.1. Baseline Results
We display the time evolution of the concentration field for three sample organic tracers. Background humic acid mixes or freezes-in at a constant level reflective of the seawater source, and it is then modulated in bulk by the local porosity. Since this carbon pool is considered refractory [27,28,29,77], inputs and channel tightening are the only factors involved. By contrast, proteins and polysaccharides are injected even at a minimum by grazing or mortality processes, as determined by the network of routings (Appendix A and Appendix B). These compounds are long lived relative to the bloom scale, thus there is a tendency to accumulate during local biological activity [6,31]. Downward transport may exhaust them quickly from bottom ice [14,25] but at other levels month-long decay processes are possible and sometimes apparent. A rich oceanic dissolved organic chemistry may in fact be driven independently by under-ice blooms [78,79]. The effects are parameterized here through variable mixed layer concentrations in springtime, set highest for the longer-lived polysaccharides [28].
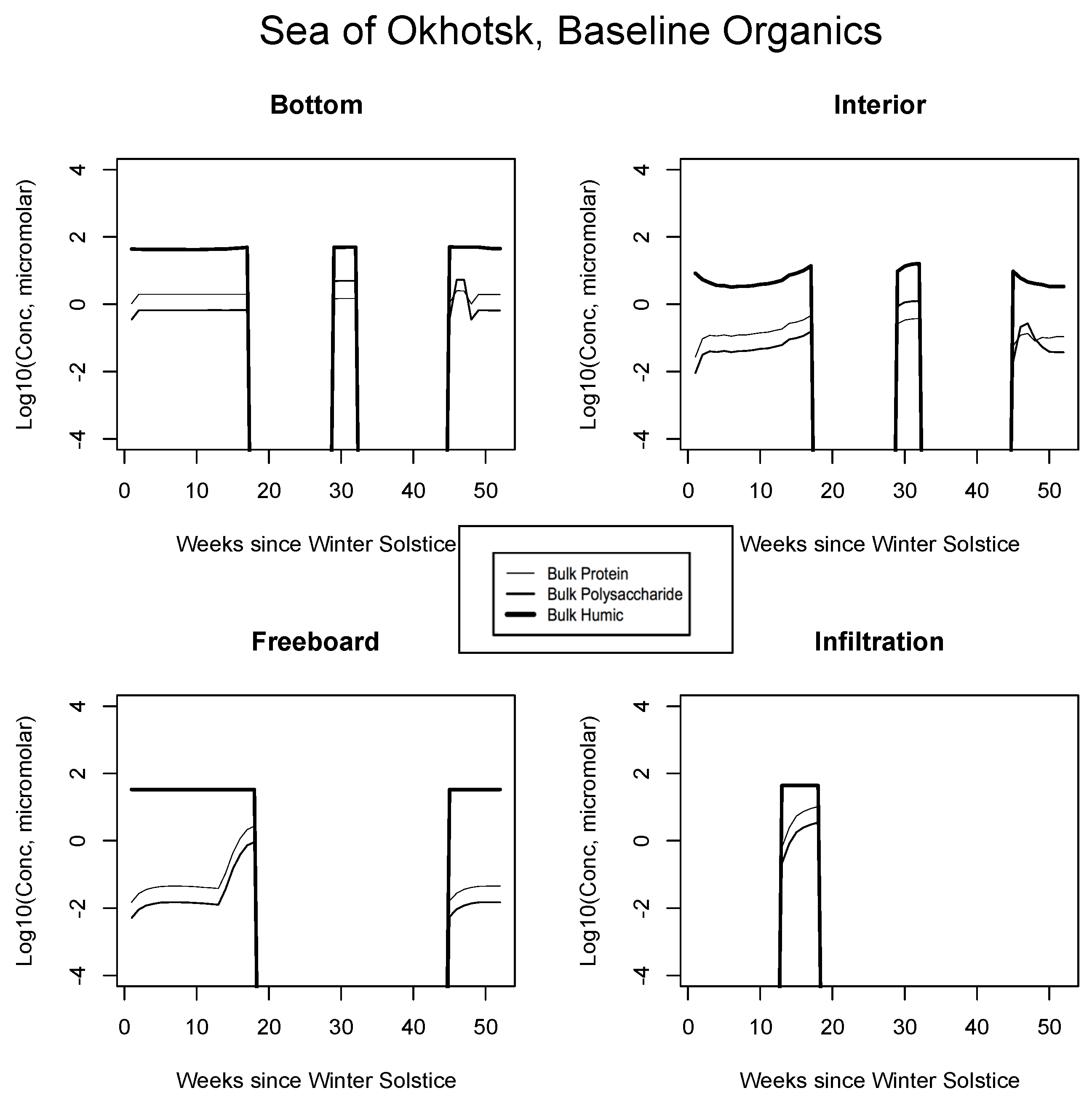
Results for the relatively warm system of the Okhotsk are shown in Figure 7. In the bottom ice layer, concentrations of pure macromolecular forms are maintained at near micromolar, primarily under the control of diatom mortality. Grazing is not permitted in this case and initial flagellates have long since decayed (Figure 3). After a quick ramp-up corresponding to the early bloom, concentrations attain a steady state, balancing the mortality inputs with downward mixing back into the sea. Proteins are in greater abundance since we assume direct release via cell disruption and a typical biochemical composition for autotrophic organisms is fixed at the global average (Appendix B and [26,27,28,80]). Notice that following the melt and prior to disappearance of the pack, the organic source signature is reversed—the thin and intermediate thickness curves have crossed. At this point, carbohydrates are in excess, corresponding with relative oxidation rates below ice. The concentration switch or trade holds for both bottom and interior media, because the two are in fairly close communication with solutes of the mixed layer. At the freeboard level, cold and tight channeling prevents growth while flagellate mortality raises organic concentrations slightly until biological systems open up during spring (roughly week 13). From this stage, grazing emissions greatly bolster the organic cycling. The infiltration layer enters its bloom phase immediately after flooding, since it is proximate to the overhead light source. Here, the biomolecules track their top-level algal producers closely.
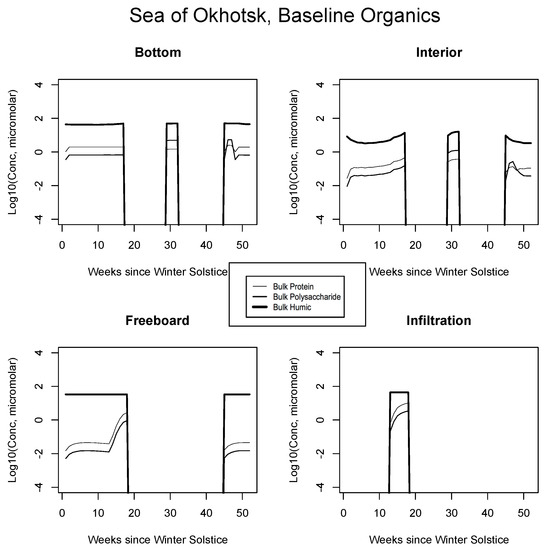
Figure 7.
Sea of Okhotsk. Time evolution for bulk organic concentrations from the baseline run, for the four habitat levels. Values are base 10 logarithms for carbon in micromolar. Lipid profiles closely follow proteins or polysaccharides and for simplicity are not shown.
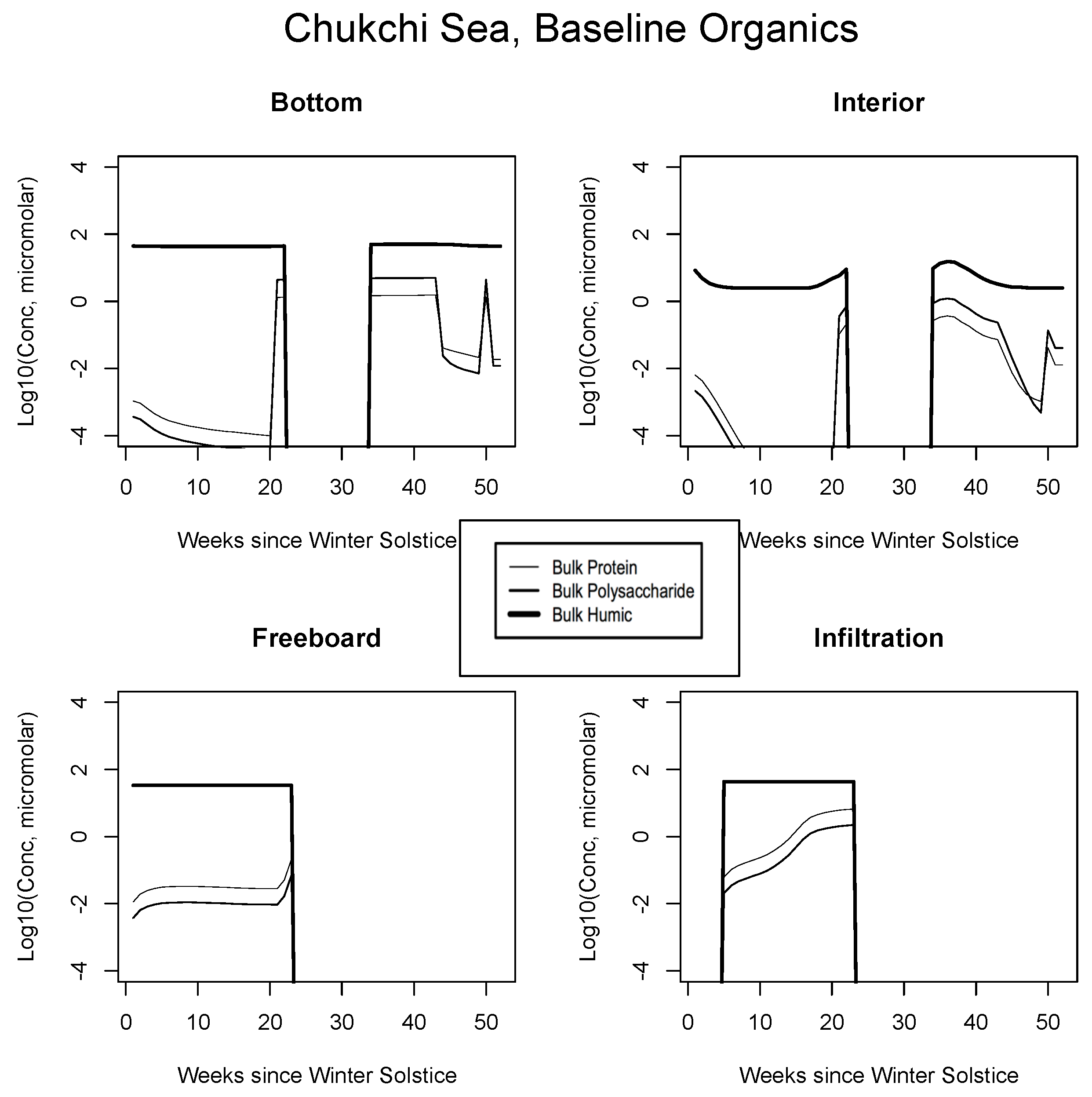
In all Okhotsk cases, fresh organics are generated mainly by mortality until photosynthesis begins. Fractionated grazing and spillage processes then come into play, and the dissolved carbon is always subject to heterotrophic (bacterial) removal on a one month scale (Appendix B). Concentrations supported by baseline ice algal behavior in this region are of order micromolar or less at most times of the year. The summer rebound approaches a value of 10, but it is best attributed to organisms operating independently in the water column. Freeboard and infiltration peaks are brief and corroborative observations are lacking. Results for all other biogeographic zones are consistent with these interpretations. In the Chukchi (Figure 8), snow prevents an early bottom layer rise but the bloom scenario is replayed in autumn. Mixed layer polysaccharides-proteins enter as a virtual step function (week 20) just before the melt takes place. Clearly this situation can be improved/smoothed in coupled ocean-ice calculations. Infiltration layer buildup is substantial, approaching ten micromolar of total fresh biopolymeric carbon. The Beaufort and central scenarios are not displayed; the former resembles the Sea of Okhotsk and the latter exhibits little activity.
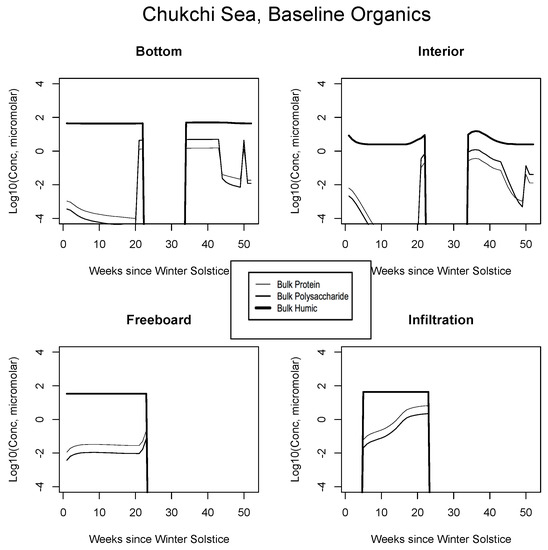
Figure 8.
Chukchi Sea, caption as in Figure 7.
The protein and polysaccharide bins track one another closely in our simulations because they are released and removed in constant ratios. During real-world succession, more complex relationships are naturally observed [16,60]. Furthermore, the full complement of biomacromolecules necessarily includes mixed functionality polymers that are organic combinations of the idealized compound classes represented here [7,8,17,27]. For example, lipids are highly surface active at the water–air interface since they are insoluble [28], and this category is roughly as abundant as the carbohydrates in our calculations. Aliphatic bubble coatings may thus be anticipated in the monolayer sense. Proteins are much more often discussed in the literature for their potential ice-structure altering capabilities [3,6,7,8,19]; we thus elected not to portray lipidic carbon content in our plots, even though the chemistry is just as detailed (Appendix A and Appendix B). Model-generated lipid profiles merely resemble those of our proteins. Generally speaking, the total carbon excluding refractory humics tends to be of order micromolar or much less in our baseline results. Observations and the levels required to match experimental demonstrations of structure change are considerably higher (Table 1; [8,20]). Hence, we turn now to the process of exudation.
5.2. Exudation
To this point in our development, it has been unnecessary to distinguish the physical state of brine organics. We have so far cited only measurements of the DOC (Table 1), components of which must reside in solution as a matter of definition. Typically, filtration is applied in the laboratory and particles exceeding some small number of microns in radius are readily extracted. However, for individual polymer types, viable data are sparse and fragmented. Both pore chemistry and laboratory analyses become much more involved [7,17]. From this point, we will follow the conceptual macromolecular dynamics concepts and definitions provided by Underwood et al. [6,7]. Whether release into the channel network occurs via algal membrane disruption or some alternate means, biomacromolecules are permitted to pass through an initial dissolved state representing a spectrum of molecular weights, although they are sometimes observed only later in aggregate form. The possibility of portraying phase transitions constitutes a future modeling direction, but for the moment we combine filtered material with filtrate in order to obtain a maximum amount of tracer information at the molecular level.
The interactions bypassed under such simplification are likely to prove complex and fascinating. Injected, chained carbon can subsequently be degraded to oligomeric or even monomeric subunits [7,27,60]. Recondensation and hetero-polymerization then come into play [27]. Internal reconstitution of the humics is well documented in the field [29]. Our fundamental goal here is to understand mass redistribution during succession; therefore, a collective approach should be sufficient. The organics are thus lumped by macromolecular class henceforward regardless of their analytical phase state, so that data availability increases. Detailed sorting into colloidal size distributions will be undertaken in later work. Living matter has been classified in the usual way as particulate organic carbon or POC—essential to the logic since structural biochemicals are obviously highly concentrated when they reside within their primary algal sources. Our mechanism, fully described in the appendix, can now be thought of in the following manner: Macromolecules emanating from arbitrary producer cells are often dissolved initially, but since aggregation is not yet considered we remain agnostic toward the evolving physical state.
Several in situ studies of the Northern Hemisphere ice content are summarized under such restrictions in Table 3, and a selection of analogous Antarctic data is appended in the last row for comparison. Total DOC is often present in a laboratory melt at hundreds of micromolar, ignoring its highly variable bonding status [6]. This result is completely consistent with a high refractory background, e.g., as in the porosity-modulated humic acid profiles captured here [29]. However, a strong carbon augmentation is also apparent. More specific measurements are made by means of chemically sensitive techniques such as staining, or liquid chromatography in conjunction with absorption spectroscopy. Comparable levels are often identifiable in the form of protein or as carbohydrate [15].

Table 3.
Summary of composition for measured bulk organic carbon in brine (micromolar carbon), mainly at established research stations. A compilation of analogous Antarctic values is included for comparison. Polymers, oligomers and the associated monomers are considered together for the proteins and carbohydrates. Blanks may carry information down from the set just above. Except for DOC, values are agnostic toward phase state. Abbreviations: (DOC) dissolved organic carbon, (Sacch) Polysaccharide or fresh carbohydrate, (Arch & GIN as in earlier tables).
Since our results underrepresent these features of the polar biogeochemical system by orders of magnitude, we experiment with forced organic release over and above cell disruption. Exudation rate constants are enabled for sensitivity testing. Like more general cellular detritus, exuded species are presumed to enter in their global average ratios to marine biomass [80]. This is clearly an approximation or first guess, and saccharides certainly tend to attract more attention from analysts as a major component of EPS (the collective Extracellular Polymeric Substances [6,7,8]). However, our assumption must be that proteins also participate in the mix, consistent with a general understanding that fresh organics are sometimes present in excess; extra carbon is often observed extending beyond the sum of saccharides and humics [4,7]. Note that by definition, any exudation process differs fundamentally (kinetically) from cell disruption in that it can be decoupled from ice algal grazing, senescence or death.
During initial sensitivity simulations, the fresh biopolymers were injected from all extant primary producers at a fixed rate of one-tenth of their carbon content per day, regardless of local light or nutrient limitation. This pace is likely sustainable for order weeks, since it represents a small proportion of the maximum marine photosynthetic rate [25,44,81]. Next, the emissions were restricted to periods when the light intensity exceeds some set proportion of photophysiological saturation (Is [44,54]) since the carbon fixation could require an external energy source. The radiation threshold was graded downward until significant organic increases could be documented, and the shift took place at a few tenths of the saturation intensity. In this case, the release rate was set to one per day, roughly equivalent to an ice algal growth maximum.
Given constant background emission at the slow rate of one-tenth per day, we found that intermediate intensity ecosystems were only able to sustain up to 10 micromolar of combined protein and polysaccharide, hovering below the background of refractory polymers. This was true for the Sea of Okhotsk and Beaufort at all levels, and in the Chukchi for the infiltration layer. In the central Arctic, fresh organics increased one to two orders of magnitude but were still lower than measurement data and fell well below unit micromolar of carbon. For all ecogeographic zones, profiles resembled those of the organic time evolution figures in Section 5.1 because mortality and grazing releases are proportional under the mechanism. Light-linked results, however, contrasted dramatically both in terms of trajectory and average concentrations. Organic intrusions were strong and dynamic where they were switched on. In all four of our standard scenarios (Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12), dissolved concentrations now fall in line with Table 3 data for many layers and locations.
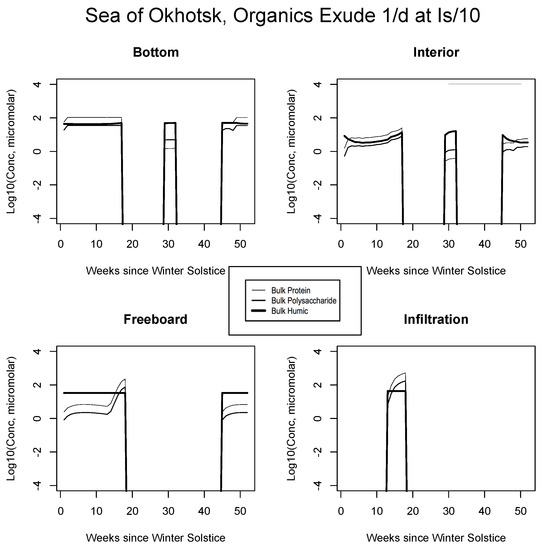
Figure 9.
Sea of Okhotsk. Time evolution for bulk organic concentrations from the light-dependent run, for the four habitat levels. Values are base 10 logarithms for carbon in micromolar. Lipid profiles closely follow proteins or polysaccharides and for simplicity are not shown.
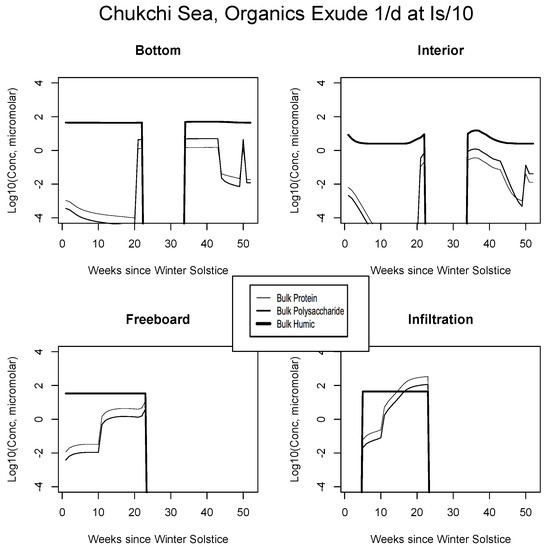
Figure 10.
Chukchi Sea, caption as in Figure 9.
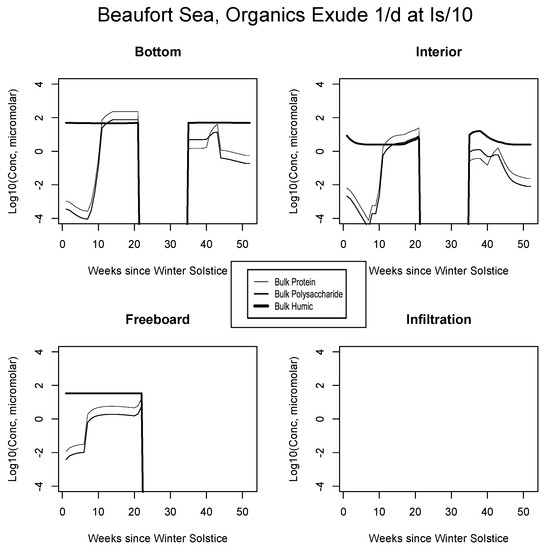
Figure 11.
Beaufort Sea, caption as in Figure 9.
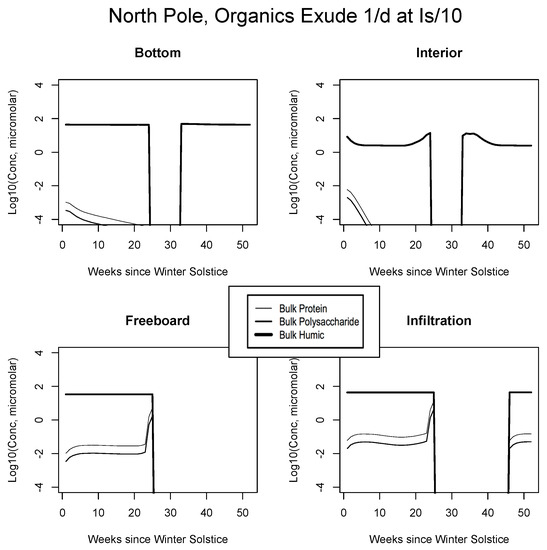
Figure 12.
Central Arctic, caption as in Figure 9.
For example, the resemblance of our enhanced Okhotsk output (Figure 9) is striking relative to Arctic studies such as Krembs et al. [20] or global patterns as collated by Underwood et al. [6]. Taken together, biomacromolecules carried in this final simulation total hundreds of micromolar for ice-internal carbon (add together protein, polysaccharide and humics noting that lipids go unplotted). In fact, the Okhotsk result is reproduced elsewhere among our ecozones but with a phase shift following solar angle, excluding specific systems where snow cover prevents primary production. Order ten to one hundred micromolar of fresh biopolymeric carbon becomes the rule in season, in addition to the humic background. Upper level systems often exceed hundreds of micromolar of the macromolecules. In the Chukchi Sea (Figure 10), snow cover still forestalls both light penetration and photosynthesis in lower ice layers. Near the ocean, physicochemical equilibration thus remains dominant, as indicated by the familiar crossing of protein and polysaccharide contours. However, the transition to one-tenth light saturation is readily discernible, whether at or above the freeboard. Both sea level and the infiltration layer can now support tens to hundreds of organic micromolar. The upper zones bloom in other locations as well. In Figure 11, for example, the Beaufort behaves as a combination of the previous two ecosystems lacking only infiltration biology. Even in the central Arctic, where biological activity is expected to be minimal [82], strong pulses of organic activity are apparent just as the saturation radiation threshold is crossed (beyond week 20 in Figure 12). Model adaptations simulating continuous then light-stimulated exudation ultimately achieve substantial agreement with the data (Table 3).
6. Summary of Results
Macromolecular chemistry occurring in Arctic brine channels, supported by internal algal activity under extreme temperature-salinity conditions, probably influences pack ice structure up to regional scales. Organic polymers exhibit pitting, gelling and salt retention properties which organize vertical nutrient distributions [3,8,17,19,31]. Such features of the physical system allow organisms to maintain their position in the ice column, relative to seawater resources upcoming from below or else the rarified polar light field emanating from above [25,40]. Simultaneously, the trace organics alter thermo-mechanical properties of a high coverage, highly reflective medium countering the greenhouse [1,7,8,53]. In the present work, we have simulated production/distribution of biomacromolecules throughout Arctic sea ice, using a reduced model involving four stacked habitats sorted biogeographically across the boreal environment [32,43,83]. Our mechanism is an extension of earlier research focused on the bottom or skeletal layer [13,14,33], and it is now being implemented for global brine networks in coupled climate codes [18]. Ecological sectors for which ice algal growth and organic inputs have been explored include all those shown in Figure 1. Detailed equation and parameter lists characterizing our approach are provided in the appendices. Validation has been focused of necessity upon the more numerous data available in biologically rich lower habitats (Table 1 [14,39]). For various sun-synchronized chlorophyll peaks occurring at the ocean interface, blooms are represented to well within an order of magnitude (Table 2), and maxima-minima are often accurately portrayed (contrast high biomass with “no bloom” entries).
Communication into the sea ice interior fuels additional growth, but it is restricted in certain key aspects. Lower levels tend to experience light limitation due to attenuation. Pore volumes shrink in the winter, slowing both solute transport and the brine-dependent physiology of photosynthesis [44,54]. In springtime, all ice algal biogeochemical processes are terminated by freshwater flushing [14,25,33]. Thus, the inside of the pack is usually biologically impoverished, despite an abundant potential for nutrient mixing from below. Upper levels carried by our model include both the freeboard and an intermittent infiltration layer. These habitats are better known from the Southern Ocean [40,42,53,63] but nonetheless we include them, since they may be of peripheral importance in the Northern Hemisphere. There will also be a strong need to study their geocycling as we move to Antarctica [83]. At the freeboard, biological activity occurs on expansion of the pore structure, which follows due to rising temperatures and increasing solar radiation. Meanwhile, infiltration depends critically upon snow loading and Archimedes Principle [43,53]. In the latter two strata, blooms are delayed respectively by either porosity/brine constraints or else flood thresholds. They also are truncated early by the melt.
In a set of baseline runs, fresh organic macromolecules identified with intracellular biochemical classes are released exclusively by cell disruption (generic proteins, polysaccharides and lipids [26,27]). Injected carbon chains pass from the algal pool into ice brine channels and accumulate against a background of recalcitrant humics [29,35]. Levels of the recently synthesized biopolymers reach only about one micromolar total (Figure 7 and Figure 8)—likely insufficient to support alterations to the pack crystalline state [4,8,19]. Sensitivity tests include direct exudation processes, represented as targeted release from intact, fully functioning cells. This occurs over and above any carbon flow from mortality or grazing (Appendix A). Constant emissions at a fraction of the maximal growth rate proved to be only partially effective in raising solute concentrations. Given a reasonable light intensity requirement, however, agreement with dissolved organic data is finally obtained. For periods bracketing bottom layer blooms or else the intensification of upper ice biology, hundreds of micromolar bulk organic carbon are generated (Figure 9 and Figure 10). Some notable features of our simulations cannot yet be verified, because most Arctic data are available only for established sites (e.g., offshore Barrow Alaska and the coastal Mackenzie basin [4,8]). Clearly a great deal more field study is required before the organics of sea ice will be completely understood. However, from an empirical standpoint, we cannot currently dismiss the possibility of widespread biological control on structure. Based on the simulated ecogeography, interesting effects are likely associated with spring blooms around the Arctic Ocean rim, with occasional extensions into summer and central ice distributions.
Results presented here in the series of Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 span the conceivable nutrient-biomass sources plus grazing versus light regulated organic inputs. Computed biogeochemical values are consistent across all selected ecozones—given the respective geographical positions of Figure 1. Nitrate enters the pack during periods of vertical brine convection for all cases. Fixed carbon accumulates as sunlight becomes available—blooms follow photon fluxes in the visible but reflect modulation by other factors such as salinity. An expected mode of variability is introduced by regional snow loading from above. The biopolymers lumped together as humic have frozen in by late fall and undergo little net exchange thereafter, since mixed layer concentrations are non-dynamic. Dips in their interior profiles are the rule in all locations, owing to the temperature dependence of porosity. Fresh (unprocessed) macromolecules faithfully track ice biological activity since cell damage is inevitable and always implies at least a background source. Extra-disruption inputs can amplify the injections, and especially during sunlit periods. Specific compound classes are synchronized with one another across the ecogeographic board, since global average carbon ratios are always drawn upon. We do not display time series that may be available from measurement sets for comparison, but several have been consulted and the parallels with our simulations are encouraging, e.g., [4,84]. Most in situ studies actually report only tabled, seasonally averaged concentrations or else correlations [20,29,60,85]. This situation reinforces the extreme need for renewed seagoing investigation.
7. Discussion: Influence on Structure and Future Directions
To the extent that there are macromolecular influences on pack physics, they probably exert themselves through multiphase processing not captured in the current version. High molecular weight material implies interfacial activity for a subset of surfactants, adhesion for some (and this is potentially irreversible), colloid formation, and much more [5,6,7]. Our mechanism deals only with first order, homogenous solid and brine. Natural ice is considered to be a pure crystal, with residual channels and pockets interspersed containing a highly idealized salt solution. Strong simplifications were made in order to handle omitted components. We tacitly assume that all algal biomacromolecules enter our brine quickly and initially in solute form [7,14], and their later interactions along phase boundaries, with each other and with the original producer organisms are duly ignored [19,22,25]. This simple picture serves us well as a startup expedient, but it should be viewed mainly as a convenience. Next generation research could include specific families of proteins, polysaccharides and related re-condensed hybrids known to adsorb during freezing—for which inhibition of phase transition kinetics has sometimes been documented [3,8,86]. Total interfacial areas available for biomacromolecular activity are extreme, with values approaching one square meter per kilogram [87,88,89]. A single monolayer of polymeric adsorbate corresponds to roughly tens of micromolar dissolved carbon, and it could well appear as solute in the laboratory after a typical (analytical) core-slice-melt sequence [60,62,74]. Adhesive macromolecules or clusters thereof may resist outward flushing pressure from drainage, even in the porous low-ice regime. For example, detrital substance exuded by the pennate diatoms is sometimes retained together with its source cells, inside micro-niches of the skeletal layer [17,25].
We confirmed the storage potential of fundamental adsorption processes through sensitivity tests in which proteins were transported by exact analogy with siliceous organisms [14,25]. Their macromolecular mixing was artificially limited in these runs to a single direction, from ocean into the pack. Cell disruption routings were then sufficient to trap concentrations exceeding those of Figure 7 and Figure 8, at least with reference to bottom layers. However, for interior or upper sea ice where vertical interchange is slow, differences were minimal. Hence, the internal chemical boost offered by exudation will likely be required in any case. For simple adsorptive retention to contribute exclusively at the ice bottom, it might be necessary to postulate that exudation is specific to the interior. A medium-term goal will be to evaluate competition between accommodation (at solid walls) versus expulsion (from porous zones). Detailed polymer kinetics will be required over and above the mechanism so far offered [7,90,91]. In order to handle multiphase processes, pack biogeochemistry simulations must soon advance beyond solutes. One strategy will be to incorporate parameterizations for adsorptive, colloidal, gel-forming and other types of interfacial equilibria. Comparisons with micellular data might prove to be advantageous. A general statement is that two-dimensional chemistry must at some point be treated dynamically. Only then can morphological, storage and blockage effects be considered in full [3,6,7,8,19,20].
Our initial approach can also be interpreted from the standpoint of individual species. We begin with humic acid since it forms a stable, overarching organic backdrop. The term “humic” is used here in the usual (natural aqueous chemical) sense to denote mixed detrital biopolymers resistant to enzymatic degradation [77]. We postulated as a condition for startup that such molecules form remotely in surrounding Arctic seawater and are then entrapped during frazil formation [29]. Since the heterogeneous compounds are unreactive by definition, they constitute a steady background level occupying the center of the observed concentration range. Little variation occurs except for dips following temperature and porosity. In fact, however, real humic carbon varies with location in terms of both composition and concentration. It is most abundant where there are riverine or shelf/slope contributions [51,52]. Our lower two numerical boxes merely maintain a constant, transport-driven equilibrium with ocean water, since we do not incorporate the geography of this particular carbon pool. Refractories are usually not discussed in relation to ice structure [4,8,19]. Their hydrogen bonding capabilities are probably too irregular for the matrix to be affected. However, they encompass many of the familiar organic functionalities—heterogeneous polymers are in fact built up from bits and pieces of the pure compounds simulated here, or else from hybrids such as glycoprotein. Recalcitrants may therefore play into ice-iron chelation and net geocycling of carbon in the Southern Ocean [35].
Macromolecular compounds secreted more directly by polar marine organisms include all the classes represented here as textbook constituents. Their physicochemical behavior has been reviewed several times recently relative to Arctic sea ice [6,7,8], but they can further be placed in a general, global biochemical context [26,27,86]. Across the biosphere, microbes release chained carbon in order to form coatings around individual cells for protection, mobility, or else to establish consortia and accumulate in films. Divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium are ubiquitous in seawater, thus electrostatic bridges often form, linking carbohydrate strands into colloids and ultimately gel particles [24,92]. The fundamental forces involved must be included in at least some future modeling work. Ice algae undergo extremes of (seasonal) thermohaline stress [17,31]. Additionally, they experience highly nonstandard pseudo-phase transitions including channel locking and the formation of metastable minerals [5,39,87]. Thus, it is not surprising that ice ecosystems are notable for exopolymer generation. Measurements of our fresh compounds remain sparse and conclusions tentative, but so far the exudation hypothesis is well supported (for example final figures versus Table 3 or [6,7,8]). Total organic carbon in the brine sometimes reaches hundreds of micromolar during the growing season. Saccharides are typically observed as secretions, and several research groups consider them to be a dominant type [4,31,60] with monomers and oligomers sometimes distinguishable [7,93]. However, proteins are regularly measured at high concentrations as well. Along with their polymeric hybrids, they have long been associated with crystal alterations [6,8,19].
Our current model of organic processing closely mimics several higher-level features of this environmental ice chemical system. The mechanism has been specifically designed to superimpose biopolymeric carbon of recent origin upon preexisting humics. All key functional groups are thus represented, from amino acids to carbohydrates and even extending to the family of lipids. We allow only the emission of pure (idealized) macromolecular forms, but the equations listed could be readily adjusted to account for hybridization. For simplicity, we track only carbon as a common currency and set aside any accounting of nitrogen atoms harbored in the proteins. However, Appendix A outlines methods which might be used to conserve multiple elements. Per our baseline parameter settings, the proteins, polysaccharides and lipids are released from marine autotrophic cells in a ratio of 60 to 20 to 20 percent of carbon by moles [26,27,80]. Thus, all compounds will be present in brine channels for any given growth-graze situation. Proteins are more abundant because they serve multiple roles inside the cell. They act as information carriers, catalysts and even in a rigid intracellular-engineering capacity. However, observations in open water tell us that polysaccharide concentrations usually exceed those of the proteins or lipids. The reason is that carbohydrates have a longer residence time; they are less labile when freely dissolved. This is reflected in the midyear cross-over plots (e.g., 7 and 8), as dissolved organics mix upward from below at several of our Figure 1 locations. Sparse Arctic ice data currently seem to point to an excess of the sugars internally (Table 3). The shift may be real and proximity of seawater DOC may offer an explanation, but we elect to maintain the excess protein ratio as an initial, practical expedient.
Several lines of evidence suggest that saccharide dominance is partly an artifact. Amino acids have been observed streaming rapidly from land-fast bottom ice, and at high concentration [94]. Protein–carbohydrate combinations are well known inside marine algal cells [26] and are implicated in the most recent studies of ice salinity alteration [8]. Total dissolved organics are often reported in excess of extracellular carbohydrates taken alone [6,7]. We chose here to maintain proteins at their global average abundance despite the fact that they are less often measured. Where total fresh carbon exceeds micromolar in our simulations, the proteins and polysaccharides can be conceived as a proxy mix. Moreover, they have been given a constant removal rate due to lack of compound-specific kinetic data. Whether taken separately or with carbon concentrations summed, the model biopolymeric profiles indicate that organic macromolecules must often be present at high concentrations. The quantities we have computed closely match those leading to pore geometry reconfigurations in the laboratory or in the field. For example, Krembs et al. [8] reported significant influence on brine volumes and tortuosity from 100 to 1000 micromolar, and point to heat sensitive glycoproteins as the culprits. In future simulations, we intend to refine the chemical composition spectrum, improve decay schemes and couple to critical phase transition thresholds in order to elucidate such issues.
Ecological succession proceeds on a seasonal scale inside of sea ice, and the timing of some organic concentration peaks should be delayed as a consequence. Fresh proteins, polysaccharides and their hybrid compounds flow independently into the channel network and are degraded there by heterotrophic bacteria in order weeks [4,15,20,85]. The heterotrophs then inject extracellular polymers additionally [31]. In our baseline mechanism, only a nominal phase lag could be built into the reaction list relative to primary sources. Production of the biopolymers by cell disruption must for the moment remain fractional and fixed, skimming from the general autotrophy at a constant rate. The organisms themselves are removed with generic time constants set at values similar to those of the macromolecular products (appendices), and therefore delays are difficult to discern in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 where they should perhaps be apparent. In part, this impression can be attributed to weaknesses in the graphics. The plotting step has been set at one week so that an entire year can be conveniently displayed, and brine channel chemical profiles are shown as distinct from the ecology.
The logic of succession, however, suggests two closely related criticisms—both grazing lags and biomass conversions may be intermittently underestimated since our zooplankton are implicit. In other words, cell lysis may be slaved too tightly to the autotrophic source profile. Following a long-standing tradition in ice biogeochemistry modeling, secondary consumption is represented here solely as a fixed proportion of growth [14,25,33,54]. The usual justification is that understanding simply remains inadequate for the higher trophic levels. Additionally, it is sometimes argued that consumption rates are reduced within the brine due to lack of access by larger organisms [25]. Data are not entirely lacking, however, to describe the sea ice microfauna [41,61] and routines imported from open water schemes may well be adaptable to the task [12,95,96,97,98]. Dynamic grazing will be introduced in future experiments, but for the moment we can neither exclude nor explore the potential for competition with exudation. Disruptive macromolecular release could increase locally but significantly when net fractionations are enhanced by realistic zooplankton ecology. By contrast, decoupling is a matter of definition for the light-regulated injections. The few relevant measurement sets are too coarsely resolved to settle the matter (e.g., [4]).
A major result of the current work is that our sea ice organochemical model converges with observations at the Arctic scale, and collectively the evidence suggests crucial geophysical roles for macromolecules of the brine. A diverse suite of biopolymers may exert control over crystal geometries, pore volumes, vertical stratification and nutrient retention. The conclusions apply across multiple sympagic ecosystems surrounding the far northern Pacific and Atlantic, then extending into the central basin. As ice coverage becomes thinner and more seasonal over the next few decades, outcomes which are peripheral in the present simulations could evolve into prominent features of the boreal environment. This statement applies not only to the biologically rich habitats of bottom ice, but also those of the upper column. Pigments generated, trapped and focused near sea level are more likely to attenuate incoming radiation; therefore, amplification becomes an issue [1,2,21,53]. Our simulations in fact suggest that several strata of biological activity will encroach upon the pole, permeating the remaining ice system.
Direct links to inorganic carbon cycling can be identified as well, and these will be especially intricate in the South. Since Antarctic sea ice formation demonstrably strips iron from the water column [36,76], it seems likely that chelating organics function as binding agents during trace metal storage [35,99,100]. Accumulation in the pack may counteract the iron limitation for which Southern Ocean waters are so well known: High (macro-) nutrient conditions described in the acronym HNLC (read as “High Nitrate Low Chlorophyll”) become accessible and exploitable in the uppermost meter or so of the marine system [75,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108] (with last seven as information sources for tables). Flooding onto an iron-replete Antarctic pack could support exceptionally rich blooms, potentially much more intense than those discussed here. Light appropriation by infiltrating organisms has not been obvious in our boreal simulations, but may turn out to be the rule across the austral ice domain, where melting layers are often deeply colored [40,53,83,101]. Iron binding has been attributed to several subclasses of the biopolymers discussed here [35,99,100] and some adsorb tightly to ice interfaces [3,4,5,6,7,86]. Organometallic chemistry will therefore constitute a theme for upcoming global simulations.
Acknowledgments
This work was performed under the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Biological and Environmental Research (OBER) Accelerated Climate Modeling for Energy project. The authors also thank the OBER High-Latitude Regional and Global Climate Modeling (HiLAT) project. Validation sections were funded in parallel by the OBER global biogeochemical program Benchmarking and Feedbacks.
Author Contributions
S.E. functions as the main corresponding author, N.J. and E.H. provided CICE output as the basis for the offline analysis, C.D., S.W. and M.J. acted as experts in polar biogeochemistry, E.E.S. and S.O. assisted with plotting and equation set up.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Equations
Concepts from the main text can be developed into equations representing the sea ice-internal ecodynamics that drive a full dissolved organic chemistry. Although emphasis is placed upon Arctic environments in the present work, our ultimate intent is applicability at both poles. Hence, iron and upper level habitats are included. Until otherwise stated, all expressions are local to the interior of brine channels, thus nonparametric quantities are typically strong functions of vertical location z. For example, nutrient nitrate NO3− = NO3−(z), the internal light intensity Iavg = I(z) and growth limitations Ltype = L(z). Constants in the system are provided in Appendix B. Essentially, we combine approaches from the Fritsen, Lavoie, Jin and Elliott groups [14,25,33,43], while acknowledging the pioneering work of Arrigo and company [44,54,83]. Additional concepts are borrowed from well-known middle to high latitude pelagic ecodynamics models [57,58,96,97,98,109].
In order to manage the inevitable biological and geochemical complexity, notational strategies are hybridized here from matrix algebra, set theory and computer science. Bold font is reserved for ordered lists of related quantities, and these may be thought of as algebraic (nondirectional) vectors, tuples or computational arrays. Sub-superscript pairs are given either an organism-to-property or to-process relationship, or else a kinetic to-from significance. All concentrations except chlorophyll are computed as millimole/m3, which is conveniently identical to micromolar. This is always with reference to an element that is central to a molecule, unit of biomass or polymer chain. In early marine systems simulations, it was possible even at the ocean basin level to focus on a single atom as the primary currency [57,96]. In this tradition, we adopt carbon as a conventional choice to begin. However, our interests extend to both multi-nutrient uptake and macromolecules of varied functional composition. The latter exhibit internal self-affinities as colloids or gels, plus a tendency to bind trace metals [24,110]. Surface, intra- and intermolecular interactions are usually mediated by oxygen- or nitrogen-containing functional groups. Elemental ratios will thus be relevant, whether with regard to biological material or its detritus. Values are indicated by the convention RN/C etc.
Primary producers serve as a suitable initial example. It is anticipated that eventually, bottom layer pennate diatoms, smaller autotrophs inhabiting central ice and even specialists such as Phaeocystis will be numerically segregated [7,61,66,74,100,111,112]. Hence, the subscript i,auto denotes the ith autotroph and our notation can be introduced as
where C indicates net local carbon content of the brine. For the organisms themselves, the ratios R may be thought of as classic Redfield relationships, but sometimes they will be permitted to vary from standard values [12,57,113]. Among macromolecules, the elemental weightings should produce a Redfield average inside of a cell [26]. However, mixing and degradation in the aqueous medium lead rapidly to divergences from the norm [11,27,60]. As usual, chlorophyll is tracked by its weight ratio to the content of the algae, as in Rchl/C [62,95,96,97].
Mechanistic details extend well beyond the primary producers, thus multiple lists of related biogeochemical quantities are required. For example, we organize the nutrients and their central atomic constituents into arrays. This arrangement actually suggests that our informal vectors might be combined into matrices to some advantage. A complete list of nitrogen containing nutrients, for example, might consist of nitrate, ammonium, nitrite, amino acids and other forms. A broader strategy could potentially lead to automation of all the marine biogeochemistry, with compositions for the macromolecules arrayed as stoichiometries across the periodic table. For the moment however, there is a need to reserve the index j for use in overall continuity expressions. In the few instances where a second dimension enters our reasoning, we simply fix the atom type artificially.
Inorganics will be represented by a pseudo-elemental quantity X excluding carbon and bearing the concentration of the central carrier. The dissolved organics by contrast must be simulated as polymers or in some cases chain aliphatics [27,28,110]. Therefore, they are represented by their total carbon content as constituents of the brine. Our scheme maintains the ability to ratio against nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur as a means of counting functional groups (amine, hydroxyl, sulfide etc.). In the next few examples, i,nut signifies one of the several inorganic nutrients and i,mac a particular class of biomacromolecule. Iron is not speciated at this point. In fact, its concentrations are set high to discourage trace metal limitation, which is rare in the Arctic. Ultimately, a goal is to resolve chelation chemistry by taking ligands into account [99,100,114].
Using this array notation, we now address general ice ecodynamics working from the top down, by attenuating incoming solar radiation. The approximation is made that when photons penetrate snow and then interact optically in any way that they have been absorbed. Scattering will be available in the full CICE model. Light limitation is computed avoiding photophysiological factors by noting that chlorophyll absorption depends only weakly on pigment packaging [44]. Spectral resolution is averaged into a traditional broad band spanning the visible wavelengths and referred to as Photosynthetically Available Radiation or PAR [14,25,26]. In what follows, Iavg is the total intensity integrated across the visible portion of the spectrum, in units of W/m2. The italics s and in refer to saturation and inhibition scaling. The saturation reference point is adjusted for acclimation moving downward away from light sources [44,54] through a linearization of culture data. Since step sizes in the offline code approach or exceed environmental adaptation times, the adjustments can be continuous.
where aw is the total attenuation by either snow or ice, with units of reciprocal distance [25]. Nutrient terms are analogous with light limitation Lrad, but we draw on the X to construct Monod factors across the inorganic concentration vector. Fractional apportionments ranging from 0 to 1 begin to appear at this point and they are generically represented as f. Here, in the production calculations they refer mainly to the proportion of growth supported by a given nutrient type inside an elemental class [14]. Only nitrogen possesses two bioavailable forms in our expressions, so the central atom type is fixed in this case to distribute across oxidation states. Deeper and specifically in the carbon growth equation, we include a reduction term for physiological effects of extreme salinity at low brine temperatures [39,44,54].
The factor χ is set to zero in the above excepting nitrate (its vector has the form 1.5 1/µM, 0, 0, 0 [14,33]). The concept is to simulate uptake inhibition by the more useful reduced nitrogen form [95]. Growth is here a shorthand for gross primary production and has the units of a chemical rate (millimole/m3s or per day). In all cases temperature must be expressed in Celsius degrees (°).
We now proceed to the construction of local ecosystem flow terms which rely heavily on fractionation concepts. The abbreviations “resp, mort, spill, zoo, assim, excr and remin” are shortened from the terms respiration, mortality, spillage, zooplankton, assimilation, excretion and remineralization respectively. For more detailed discussion of such routings, see Fasham, Moore or Elliott et al. [14,95,97,98]. One of the main goals of next-generation ice and global ecodynamics simulation will be to render the f below more dynamic and explicit.
In the equations immediately following, the identifier ele is carried implicitly for clarity, e.g., Respele = frespGrowthele.
The factors f ultimately become quite ad hoc, but this is a typical expedient in marine biogeochemistry models [12,54,96,97,98,115]. The advantage is that sensitivity testing is rendered convenient and interpretable. We treat the zooplankton as a single entity, thus no subscripting is required for classes or trophic levels. However, consumer organisms actually go un-modelled. Since grazing has often been treated as a proportion of growth within sea ice, dynamics of the secondary producers are deferred [14,25,33,39]. See a localized study by Tedesco and colleagues [12] for more comprehensive alternatives, discussed in relation to the ecodynamics of a Greenland fjord.
Establishment of autotrophic populations requires uptake of nutrients. The case of silicate is trivial because this solute tends to be fixed and never released from hard parts [14,25,116], consisting mainly of frustules of the ice bottom-dwelling pennate diatoms. Nitrogen inorganics are interrelated by recycling processes. Oxidation states are linked to one another along the overall metabolism then by microbial chemistry [16,66], and routings are once again prominent in the NH4+ case. We model nitrification after reference [33] and all of respiration is presumed to flow through ammonia. No attempt is made to reserve nitrogen atoms for a conservative production of proteins. We view this as a potential application of upcoming atom-balancing approaches. Iron recycling is treated by analogy with ammonia for the simple reason that detailed ice chemical information is lacking [35,36].
We have now dealt with most of the ecodynamic pathways associated with primary and secondary production. Macromolecules in dissolved form or else present as colloids and gels are now added to the scheme. We begin with compound types which have proven useful in studies of global surfactant behavior at the water–air interface [9,27,28]. To this list, one could, and perhaps should, add specific intentional releases including polysaccharides [117], aminosugars [118], siderophores [100] and more. Generic exudation terms are incorporated for purposes of sensitivity testing, with rate constants functionalized as stated in the main text. Since we assume either that leaks are small or light energy may be harvested to support further fixation, exuded carbon need not be accounted during mass conservation. Working from mac and Cmac above then,
The biomass fractionations fi,mac are arranged over i to sum to unity and to reflect standard carbon ratios inside algal cells, which are fairly uniform for the proteins, polysaccharides and lipids [26,27,80]. We assume that high-quality fresh macromolecules and polymers are not excreted by the zooplankton. Removal is mainly bacterial and rates are based on empirical data from real ice systems [4,15,84,85]. Microbial heterotrophs sometimes decouple strongly from the organic cycling within ice at low temperatures [119], and their behaviors are unfamiliar in other ways [120]. Incorporation during frazil stages may require physical attachment to symbiotic algae. Metabolisms can be strongly reduced during frazil/pancake formation, but as congelation proceeds the microbes recover quickly, establishing a growth constant of close to one day and exhibiting relatively low mortality [121]. We assume that bacteria act upon the organic reservoir in a unimolecular fashion. For example, Arrigo et al. discuss exponential vertical protein profiles [94], while Amon and coworkers provide data consistent with a one month oxidative time scale in Arctic ice samples [15].
Local time tendencies can be prepared in this manner for all quantities, and so now we turn our attention to transport. Vertical motions are dealt with exclusively, since over the course of a bloom horizontal advection is slow [122,123]. Outline font now distinguishes a bulk ice quantity from its counterpart in the brine [34]. A vertical continuity equation can be constructed for all our reactive tracers, and they will now be denoted . Thus, the total biogeochemical tuple becomes RT = X, C if we think in terms of central atoms such as silicon or carbon and the bulk (outline) version follows directly. Flux is given separately to emphasize the role of porosity in regulating net mixing. Our approach is based heavily on that of Vancoppenolle [34], but all critical quantities are available in CICE [18] and they can be transported there as well [14,45]. The brine channel system is assumed to be isotropic.
New symbols introduced include bgc identifying the summed biogeochemical tracer list, F for flux, P and L for production/loss, j representing all interactants, superscript bri for a brine specific quantity, K as a generic diffusion coefficient, a flushing velocity driven by upper level melting, and V for brine volume. The purpose for introducing outline font quantities is to combine brine channel kinetics with bulk mixing considerations. The z axis is defined to be positive upward, thus vmelt is negative. Production and loss terms computed as ordinary (time) differentials must be downgraded by the volume fraction for bulk computation.
At this point, we have a representation of column chemistry-transport for global classes of the nutrients, ice algae and detrital macromolecular carbon—all packaged as a vertical scheme for distribution through sea ice. A next challenge will be to develop our equations into a fully dynamic biogeochemistry model [18]. For early testing however, a reduced form is now described which runs entirely offline. It is also applicable to arbitrary output from other groups, thus intercomparisons may be facilitated. Estimated distributions for the ice algae and their by-products are constructed in a convenient post-processing mode.
Certain terms can be handled quickly based on a typical sequence of events as spring unfolds. For example, v is close to zero until snow melt begins. Eventually a nearly instantaneous purge dominates advection [33,73]. The total rate may be modelled as [34]
The delta function is set to unity if the rule of fives allows communication between channels [87]. Here, R is the ratio of densities for snow conversion to liquid, h is a height and finally fperc is the fraction percolating into the network or in other words, not sloughed into cracks or leads [73]. The vmelt may be considered sudden; therefore, ice internal biogeochemical activity shuts down when/where significant surface loss and the delta phase transition coincide. If the time scale h/vmelt is less than one week, we remove all concentrations. The flux equation therefore simplifies to a single diffusion term.
A minimum of four layers is needed to pick up major habitat types: bottom, interior, freeboard and infiltration zones [39,40,63,64]. The latter two may be difficult to separate observationally since they are proximate and measurements tend to be made during spring, when they coincide and are decomposing [40]. However, the freeboard and infiltration ecologies are distinct; we treat them independently. Within our transport framework, the outer partial in depth becomes a thickness while its inner counterpart now represents a thin laminar boundary. The dimension of all layers other than the interior is initialized at 3 centimeters [14,25,55,64,83]. In our reduced framework, the default interior dimension is 30 centimeters [41,61]. The bottom and top of the ice column tend to be more active because they are close to nutrient and light sources respectively, but interior habitats cannot be ignored [39,61]. Ice growth physics is intricate for all the layers [20,25,124] but in our present approach to the kinetics, box heights are kept fixed during each simulation. The bottom layer remains in constant communication with the ocean except during the melt [14,33]. Interior content mixes with our bottom ice volume but all reactions take place independently. Freeboard material is positioned above the porosity cut off, and so blooms typically form under stringent initial mass limitations [40]. A combination of upward percolation and flooding saturates the top of the ice when it is weighted down sufficiently by snow (infiltration [43]). Thresholds for submersion were determined by Archimedes Principle, and the possibility of multiple flooding events was explored. Snow cover, ice thickness and temperature profiles are all extracted as time averages from dynamic model output [18]. By contrast with the chemistry, radiation penetration takes CICE pack height variation into account. The resolution of ingested history files was one week.
Barriers to vertical transport were taken in all cases to be thin, laminar layers segregating boxes well mixed within themselves due to brine convection. For the ocean-to-bottom reservoir transition (o2b), we mimic the Lavoie model [25] and place resistance in the sea, just below the (baseline) three-centimeter thickness of porous material. The laminar dimension is adjusted to a transfer velocity fbriK/Δzo2b = vo2b of 0.3 m/d as a starting point. Geographically, interchange will vary with details of the boundary layer physics, including shear and tidal effects. Crossing from the bottom layer to the interior, tracers must pass through a zone of rapidly falling porosity. The relevant geometry is that of established brine channels, typically one-tenth millimeter across [8,89,125]. Molecular diffusion will define the minimum rate of passage at about 10−9 m2/s for most solutes [25,126]. We treat the vertical extent of the resistance zone as a variable parameter with a starting round figure value of one millimeter. Thus, the calculations begin at fbriK/Δzb2i = vb2i = fbri0.1 m/d. Porosity is averaged from internal CICE data [18,45], thus transfer is initialized at a level significantly slower than for entry into the bottom layer, viewed from the bulk perspective. Roughly speaking, a meter of typical ice thickness fills with biogeochemical activity in order weeks. Upper layers are treated as isolated kinetic boxes because they cap solid material which is sometimes closed to transport due to the rule of fives. The laminar barrier may therefore be conceived of as infinitely thick. This is consistent with the observation that surface chlorophyll bands may be trapped and very intense [53,74].
For each layer and species, a local continuity equation follows and is amenable to discretization then explicit, semi- or implicit integration. If the choice is a forward Euler,
Here, layer signifies the reaction box, lam indicates the dividing barrier and concentrations on either side (e.g., o2b), while n is the current time. The computations are performed working from time averaged CICE output for the main physical drivers, along with over-wintering initializations. We experimented with time steps ranging from 0.1 to 10 days. Light penetration is first mapped downward through the column assuming Beer’s Law and single scattering with snow, ice and preexisting algae all contributing [14,25]. The Ltotal are then constructed, carbon growth and nutrient uptake estimated and finally organisms and organics are distributed through the multiple numerical layers.
Appendix B. Parameters
A biogeochemical baseline simulation is defined here through the parameter list of Table A1, serving as the foundation for sensitivity tests. We adopt a strategy of unifying pack ice autotrophy across the hemispheres, based on strong commonalities which can be drawn from existing polar models. Settings are then diverged slightly in order to simulate fundamental taxonomic differences. This approach is very much like one which has been used to achieve high fidelity in multi-element simulation of basin to global scale pelagic biogeochemistry [97,98,109]. By analogy with bibliographic introductions at the end of the main text, we also now call the last data-oriented references [127,128,129,130] in order to round out our collection of constants in the table.
Since ice algal populations originate in the sea, we adopt a familiar open water tracer combination to deal with internal competition. It has been applied in identical configurations to both Southern Ocean and Arctic food webs [57,58]. A representative model organism is assigned to each of three major high latitude autotroph classes: diatoms, microflagellates and prymnesiophytes. These may be thought of in turn as pennates, cryptophytes plus dino- and other microflagellates, and finally Phaeocystis. The suite is dominant in vertical sections from many sea ice sample cores [41,66,111]. All the classes are notable producers of organics [7,20,113,118]. We will focus our arguments on these few algal types at the expense, for example, of centric diatoms or the coccolithophores since alternate species may not be available or else are incapable of entering the pack [58,111,112]. The selected organisms are seeded into our model ice field at low, equal densities. Subsequent behaviors are then dictated by photo- and nutrient physiological settings according to the parameters in Table A1.
Marine ecodynamics models are normally constructed from a core of historical growth data. We borrow this technique as a means of establishing consistent global brine channel chemistry. Eppley [81] originally reviewed maximum photosynthetic rates measured up to that time, for the entire surface sea. He was able to establish exponential temperature dependence from an envelope of data, arriving at a Q10 of about two. The study was fairly exhaustive and has not required major revision. Arrigo and Sullivan [44] examined the photophysiology of Antarctic ice algae in culture, and provided pack ecosystem values working downward in temperature to account for advancing conditions in the brine. The effects of increased salinity on rate maxima were also reported and are superimposed here. Additionally, a functional form was proposed for photoadaptation and this too is included in our set. Maximum saturation intensities are reduced as a function of attenuated PAR to mimic acclimation [54].
A very similar physiological approach was extended to the full ice column for generic Antarctic situations in both references [43] and [83]. It has also made its way into several Arctic pack ice biology models, including those in CICE [13,14,18,33]. Meanwhile, regional polar ecologists have developed open water ecodynamic mechanisms which are unified across the hemispheres [57,58]. Identical photosynthetic and limitation parameters were adopted to simulate nutrient cycling along both the Palmer Peninsula and coastal Beaufort/Chukchi Seas. Not only are algal seed organisms in these computations appropriate to occupy our brine niches—a single model configuration handles geocycling in the marginal/seasonal ice domain for both boreal and austral environments. We adopt this suite of ecosystems as a coherent conceptual foundation. Common growth, photophysiological and nutrient restriction settings thus apply throughout the total global ice column, allowing a carbon cycle-based study of all polar macromolecules.
The major organism classes diatoms, microflagellates and Phaeocystis map cleanly from open water simulations, and so will transfer conveniently back to our ocean model biogeochemistry during coupled calculations. None are attempted here, but it is worth noting that there is a close correspondence with taxonomies from global models of intermediate complexity. For example, Moore and colleagues originally divided pelagic photosynthesizers into the major classes diatoms and smaller organisms, then segregated Phaeocystis as a unique high latitude contributor [76,97,98,102]. Following the two guiding ice domain mechanisms [57,58], our own selected algal types are given closely related photophysiologies, but empirically it can be shown that they are often dominant respectively in bottom, interior and upper layers [41,74]. Such ecosystem structural differences may eventually play strongly into epontic organic chemistry. We therefore begin to discriminate algal types within the ice matrix in a stepwise manner.
Due to their relative size, ice diatoms are not subject to grazing [57] and further, they are able to use the skeletal layer as a refuge [25,111]. By contrast, our smaller species experience at least some consumption pressure, and in fact this may be necessary to explain certain features of their distributions [41,57,74,113]. The background grazing proportion is increased at the bottom layer as a first order means of achieving diatom dominance there, but dynamic zooplankton treatments will eventually be needed. Higher trophic levels can probably be accommodated simply by transferring algorithms from existing models of water column biology [57,58,97,98]. Diatoms are excluded entirely from the interior here, owing to size effects and their ability to maintain vertical position near the seawater inflow [25]. The latter may in fact be attributable to the use of polysaccharides for gliding [20,22,25]. In more detailed simulations, cell dimension may be compared with pore diameters directly.

Table A1.
Settings used in a baseline simulation of ice biogeochemistry, with emphasis on production of organics. Blank cells carry information down from their neighbor directly above. Abbreviations: NA—not applicable, Chl—chlorophyll, PAR—photosynthetically available radiation, none—dimensionless, poly—polysaccharide. The low reference intensities Is are adjusted moving upward through the column toward higher photon fluxes according to the function in [54]. Photoacclimation is thus assumed identical among species. The growth constant is reduced dependent on salinity per data and forms in [44,54]. Finally, the reader may note that from fresp onward the phyto-class distinctions disappear. Some table columns could be merged from this point. They are maintained for clarity of presentation.
Table A1.
Settings used in a baseline simulation of ice biogeochemistry, with emphasis on production of organics. Blank cells carry information down from their neighbor directly above. Abbreviations: NA—not applicable, Chl—chlorophyll, PAR—photosynthetically available radiation, none—dimensionless, poly—polysaccharide. The low reference intensities Is are adjusted moving upward through the column toward higher photon fluxes according to the function in [54]. Photoacclimation is thus assumed identical among species. The growth constant is reduced dependent on salinity per data and forms in [44,54]. Finally, the reader may note that from fresp onward the phyto-class distinctions disappear. Some table columns could be merged from this point. They are maintained for clarity of presentation.
| Quantity | Diatoms | Flagellates | Phaeocystis | Units | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC/N | 7 | 7 | 7 | mole/mole | 57,58,113 |
| RC/Si | 5 | NA | NA | mole/mole | 25,54 |
| RC/Fe | 2 × 105 | 2 × 105 | 5 × 105 | mole/mole | 56,75,113 |
| RC/Chl | 40 | 40 | 100 | mass/mass | 57,62,113 |
| aChl | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 1/m(mg/m3) | 25,44,57 |
| Is (low PAR) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | W/m2 | 43,54,57,83 |
| Is (high PAR) | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Is (pelagic) | 50 | 30 | 20 | 57,102 | |
| Iin | 100 | 100 | 100 | 33,39,44,127 | |
| KNO3− | 1 | 1 | 1 | μM | 54,57,58,113 |
| KNH4+ | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| KSi(OH4) | 3 | NA | NA | 25,128,129 | |
| KFe | 100 | 100 | 10 | pM | 56,113 |
| gpre | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 1/d | 25,44,57,81 |
| gexp | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 1/Co | 43,44 |
| fsal (50 ppt) | 1 | 1 | 1 | none | 43,44,54 |
| fsal (100 ppt) | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| fgraze (bottom) | 0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | See text | |
| fgraze (other) | NA | 0.1 | 0.1 | 14,25,39,54 | |
| fresp | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 25,54,57 | |
| mpre | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1/d | 14,33,128,130 |
| mexp | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1/Co | |
| fspill | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | none | 14,98 |
| fassim | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1-fspill | |
| fexcr | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 14 | |
| fremin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 14,33,98 | |
| knit | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 1/d | 14,33 |
| fbiomass (protein) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | none | 14,26,27 |
| fbiomass (poly) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||
| fbiomass (lipid) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||
| kexude | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1/d | 27,57,98 |
| kbac | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1/month | 84,85 |
Although many of the limitation terms are intentionally set to similar values for all nondiatoms, flagellates are more often reported from interior core sections and Phaeocystis from layers above [66,74]. In the present computations, no individual group has been given a population-dynamic head start. The Walsh approach entails flagellate-to-Phaeocystis ratios which are skewed toward the former and could eventually be tested for initialization [58]. In the current work however, early algal concentrations are all set to a single low value. Phaeocystis is included because its life history is specialized with regard to the organics—it is known for release of organosulfur compounds, polysaccharides and amino sugars [14,102,118]. Polymer chemistry allows this unique organism to become effectively multicellular by forming colonies. Buoyancy may therefore be regulated, and rising motions are sometimes observed [113]. In future runs, we will simultaneously investigate flagellate population offsets alongside unique Phaeocystis behaviors, and a vigorous competition is expected. Enhanced concentrations of the prymnesiophyte are observable at upper levels and can likely be captured with a proper emphasis on niche adaptation.
In global open water, dissolved organic carbon emanates from autotrophic cells primarily during their eventual disruption [26,27]. Exudation is generally considered a secondary mode. In the high latitude pelagic simulations [57,58], direct emission factors are in agreement with the typical assumptions, because they remain very low (order per cent of overall carbon flow). However, interesting exceptions can readily be cited. The diatoms are thought to release carbohydrates for purposes of aggregation [117], and sugar polymers play into multiple ice surfactant and structural interactions [6,7,8,20,22]. Phaeocystis produces similar substances to form the gel matrix necessary for colony formation [118]. In the Southern Ocean, exudates are known to function as siderophores and also as ligands [99,100]. For present purposes, we fix macromolecular fractions at planetary average values for the biosynthesis of marine proteins, polysaccharides and lipids [26,27,28,80], but the background is supplemented through a set of light modulated exudation terms [7,44,94]. The aim is to reproduce and extend results from those field studies resolving ice organic material into its chemical constituency [6,15,60,93].
Taken together, our parameter settings are designed to provide an ice biogeochemical baseline adequate to either the regional or global (bi-hemispheric) scale, whether in the biogeographic, vertical or chemical dimensions [8,13,14,83]. We introduce a bare minimum of taxonomic resolution [41,66,74], build local ice ecosystems and then focus on tracking succession of organic matter in the brine [16]. Our selected baseline values are collectively summarized in Table A1, with columns organized by algal type. Relative to Appendix A equations, the flagellates now represent all smaller taxa. Our total biological resolution is therefore limited to three algal classes. Constants are offered in roughly their order of appearance in the equation list. We deal with primary production as regulated by light fields plus nutrient uptake, then the numerous fractional routings and finally all production and degradation of organic macromolecules. This sequence serves as an organizing principle throughout the work.
Our parameter table has been constructed based on a close examination of diverse individual reference materials. Uncertainties are naturally large; error bars of a factor of three or more in either direction accompany some of the choices. The situation is typical for modern ecodynamics simulators [12,13,14,25,57,58,95,96,97,98,109]. Formal error quantification lies beyond the scope of the present work, but is definitely warranted considering the importance of sea ice in determining planetary albedo. Sensitivity tests described in the main text revolve around physical thicknesses, transfer velocities and light saturation dependence of the organic release mechanism. However, we do not fail to underscore the network of fractional routings that must someday yield to dynamic channels. These will be explored later in full scale CICE modeling.
References
- Lengaigne, M.; Madec, G.; Bopp, L.; Menkes, C.; Aumont, O.; Cadule, P. Bio-physical Feedbacks in the Arctic Ocean using an Earth system model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.; Simmonds, I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification. Nature 2010, 464, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janech, M.; Krell, A.; Mock, T.; Kang, J.; Raymond, J. Ice-binding proteins from sea ice diatoms (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Michel, C.; Gosselin, M.; LeBlanc, B. Winter-spring dynamics in sea-ice carbon cycling in the coastal Arctic Ocean. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, V.F.; Grannas, A.M.; Abbatt, J.P.D.; Ammann, M.; Ariya, P.; Bartels-Rausch, T.; Domine, F.; Donaldson, D.J.; Guzman, M.I.; Heger, D. Organics in environmental ices: Sources, chemistry and impacts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9653–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, G.; Aslam, S.; Michel, C.; Niemi, A.; Norman, L.; Meiners, K.; Laybourn-Parry, L.; Paterson, H.; Thomas, D. Broad-scale predictability of carbohydrates and exopolymers in Antarctic and Arctic sea ice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15734–15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, G.; Fietz, S.; Papadimitriou, S.; Thomas, D.; Dieckmann, G. Distribution and composition of dissolved extracellular polymeric substances in Antarctic sea ice. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 404, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krembs, C.; Eicken, H.; Deming, J. Exopolymer alteration of physical properties of sea ice and implication for ice habitability and biogeochemistry in a warmer Arctic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, S.; Ogunro, O.; Frossard, A.; Russell, L.; Rasch, P.; Elliott, S. A physically based framework for modeling the organic fractionation of sea spray aerosol from bubble film Langmuir equilibria. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13601–13629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, L.; Nightingale, P. Chemistry and release of gases from the surface ocean. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4015–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letscher, R.; Moore, J.; Teng, Y.; Primeaux, F. Variable C:N:P stoichiometry of dissolved organic matter cycling in the Community Earth System Model. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, L.; Vichi, M.; Thomas, D. Process studies on ecological coupling between sea ice algae and phytoplankton. Ecol. Model. 2012, 226, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, C.; Jin, M.; Elliott, S.; Hunke, E.; Maltrud, M.; Jeffery, N. Large scale modeling of primary production and ice algae within arctic sea ice in 1992. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.; Deal, C.; Humphries, G.; Hunke, E.; Jeffery, N.; Jin, M.; Levasseur, M.; Stefels, J. Pan-Arctic simulations of coupled nutrient-sulfur cycling due to sea ice biology. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, R.; Pitznar, H.; Benner, R. Linkages among the bioreactivity, chemical composition and diagenetic state of marine dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Papadimitriou, S. Biogeochemistry of sea ice. In Sea Ice: An Introduction to its Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Geology; Thomas, D., Dieckmann, G., Eds.; Blackwell Science: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, S.; Cresswell-Maynard, T.; Thomas, D.; Underwood, G. Production and characterization of the intra- and extracellular carbohydrates and polymeric substances (EPS) of three sea-ice diatom species, and evidence for a cryoprotective role for EPS. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1494–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunke, E.; Lipscomb, W.; Turner, A.; Jeffery, N.; Elliott, S. CICE: The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model Documentation and Software User’s Manual Version 5.0; LANL technical report LA-CC-06-012; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2015.
- Raymond, J.; Sullivan, C.; DeVries, A. Release of an ice-active substance by Antarctic sea ice diatoms. Polar Biol. 1994, 14, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krembs, C.; Eicken, H.; Junge, K.; Deming, J. High concentrations of exopolymeric substances in Arctic winter sea ice: Implications for the polar ocean carbon cycle and cryoprotection of diatoms. Deep Sea Res. I 2002, 49, 2163–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreze, M.; Holland, M.; Stroeve, J. Perspectives on the Arctic’s shrinking sea-ice cover. Science 2007, 315, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krembs, C.; Deming, J. The role of exopolymers in microbial adaptations to sea ice. In Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Marx, J.C., Gerday, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Post, E.; Bhatt, U.; Bitz, C.; Brodie, J.; Fulton, T.; Hebblewhite, M.; Kerby, J.; Kutz, S.; Stirling, I.; Walker, D. Ecological consequences of sea-ice decline. Science 2013, 341, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, W.; Orellana, M.; Verdugo, P. Spontaneous assembly of marine dissolved organic matter into polymer gels. Nature 1998, 391, 568–572. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, D.; Denman, K.; Michel, C. Modeling ice algal growth and decline in a seasonally ice-covered region of the Arctic (Resolute Passage, Canadian Archipelago). J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.; Takahashi, M.; Hargrave, B. Biological Oceanographic Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Benner, R. Chemical composition and reactivity. In Biogeochemistry of Dissolved Organic Matter; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 59–90. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, S.; Burrows, S.; Liu, X.; Ogunro, O.; Russell, L.; Wingenter, O. Simulating macromolecular surfactant chemistry of the ocean-atmosphere boundary. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 06412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calace, N.; Castrovinci, D.; Maresca, V.; Petronio, B.; Pietroletti, M.; Scardala, S. Aquatic humic substances in pack ice-seawater-sediment systems. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2001, 79, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.; Thomas, D.; Stedmon, C.; Granskog, M.; Papadimitriou, S.; Krapp, R.; Meiners, K.; Lannuzel, D.; Van der Merwe, P.; Dieckmann, G. The characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Antarctic sea ice. Deep Sea Res. II 2011, 58, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Underwood, G.; Kaartokallio, H.; Norman, L.; Autio, R.; Fischer, M.; Kuosa, H.; Dieckmann, G.; Thomas, D. Dissolved extracellular polymeric substances (dEPS) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmack, E.; Wassmann, P. Food webs and physical-biological coupling on pan-Arctic shelves: Unifying concepts and comprehensive perspectives. Prog. Oceangr. 2006, 71, 446–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Deal, C.; Wang, J.; Shin, K.; Tang, N.; Whitledge, M.; Lee, S.; Gradinger, R. Controls of the landfast ice-ocean ecosystem offshore Barrow Alaska. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 44, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancoppenolle, M.; Goose, H.; Montety, A.; Fichelet, T.; Tremblay, B.; Tison, J. Modeling brine and nutrient dynamics in Antarctic sea ice: The case of dissolved silica. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Merwe, P.; Lannuzel, D.; Mancuso Nichols, C.; Meiners, K.; Heil, P.; Norman, L.; Thomas, D.; Bowie, A. Biogeochemical observations during winter-spring transition in East Antarctic sea ice: Evidence of iron and exopolysaccharide controls. Mar. Chem. 2009, 115, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannuzel, D.; Schoemann, V.; De Jong, J.; Pasquer, B.; Van der Merwe, P.; Masson, F.; Tison, J.; Bowie, A. Distribution of dissolved iron in Antarctic sea ice: Spatial, seasonal and inter-annual variability. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Islas, A.; Hurst, M.; Buck, K.; Sohst, B.; Smith, G.; Lohan, M.; Bruland, K. Micro- and macronutrients in the southeastern Bering Sea: Insight into iron replete versus depleted regimes. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 73, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Islas, A.; Rember, R.; Mordy, C.; Wu, J. Sea ice-derived dissolved iron and its potential influence on the spring algal bloom in the Bering Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K. Primary production in sea ice. In Sea Ice: An Introduction to its Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Geology; Thomas, D., Dieckmann, G., Eds.; Blackwell Science: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ackley, S.; Sullivan, C. Physical controls on the development and characteristics of Antarctic sea ice biological communities—A review and synthesis. Deep Sea Res. I 1994, 10, 1583–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinger, R. Vertical structure of the biomass and composition of algal communities in Arctic pack ice. Mar. Biol. 1999, 133, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiners, K.; Vancoppenolle, M.; Thanassekos, S.; Dieckmann, G.; Thomas, D.; Tison, J.; Arrigo, K.; Garrison, D.; McMinn, A.; Lannuzel, D.; et al. Chlorophyll a in Antarctic sea ice from historical ice core data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsen, C.; Ackley, S.; Kremer, J.; Sullivan, C. Flood-freeze cycles and microalgal dynamics in Antarctic pack ice. In Antarctic Sea Ice: Biological Processes, Interactions and Variability; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 73, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, K.; Sullivan, C. The influence of salinity and temperature covariation on the photophysiological characteristics of antarctic sea ice microalgae. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, N.; Hunke, E.; Elliott, S. Modeling transport of passive tracers in sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, N.; Hunke, E. Modeling the winter-spring transition of first-year ice in the western Weddell Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.; Bitz, C.; Blackmon, M.; Bonan, G.; Bretherton, C.; Carton, J.; Chang, P.; Doney, S.; Hack, J.; Henderson, T.; et al. The Community Climate System Model version 3 (CCSM3). J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2122–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, J.; Hewitt, H.; Keen, A.; Ridley, J.; West, A.; Harris, C.; Hunke, E.; Walters, D. Development of global sea ice 5.0 and 6.0 CICE configurations for the Met Office Global Coupled Model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 2529–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, W.; Yeager, S. The global climatology of an interannually varying air-sea flux data set. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E. Thickness sensitivities in the CICE sea ice model. Ocean Model. 2010, 3–4, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, T.; Kattner, G. Recalcitrant dissolved organic matter in the ocean: Major contribution of small amphiphiles. Mar. Chem. 2003, 82, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, T.; Kattner, G. The biogeochemistry of river and shelf ecosystems of the Arctic Ocean: A review. Mar. Chem. 2003, 83, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, S.; Lewis, M.; Fritsen, C.; Xie, H. Internal melting in Antarctic sea ice: Development of “gap layers”. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.; Kremer, J.; Sullivan, C. A simulated Antarctic fast ice ecosystem. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 6929–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeburgh, W. Fluxes associated with brine motion in growing sea ice. Polar Biol. 1984, 3, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Arrigo, K. Processes governing the supply of iron to phytoplankton in stratified seas. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.; Dieterle, D.; Lenes, J. A numerical analysis of carbon dynamics of the Southern Ocean phytoplankton community: The roles of light and grazing effecting both sequestration of atmospheric CO2 and food availability to larval krill. Deep Sea Res. I 2001, 48, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.; Dieterle, D.; Maslowski, W.; Whitledge, T. Decadal shifts in biophysical forcing of arctic marine food webs: Numerical consequences. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moore, K. Variability of primary production and air-sea CO2 flux in the Southern Ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Kattner, G.; Engbrodt, R.; Gianelli, V.; Kennedy, H.; Haas, C.; Dieckmann, G. Dissolved organic matter in Antarctic sea ice. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 33, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinger, R.; Meiners, K.; Plumley, G.; Zhang, Q.; Bluhm, B. Abundance and composition of the sea-ice meiofauna in pack ice of the Beaufort Gyre in summer 2002/3. Polar Biol. 2005, 28, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, S.; Buck, K.; Taguchi, S. Standing crop of algae in the sea ice of the Weddell Sea region. Deep Sea Res. 1979, 26, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, C.; Thomas, D.; Bareiss, J. Surface properties and processes of perennial Antarctic sea ice in summer. J. Glaciol. 2001, 47, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, I. The Arctic Sea Ice Ecosystem; Overseas Publishers Association: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Flato, G.; Brown, R. Variability and climate sensitivity of landfast Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 26767–26777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsen, C.; Coale, S.; Neenan, D.; Gibson, A.; Garrison, D. Biomass, production and microhabitat characteristics near the freeboard of ice floes in the Ross Sea, Antarctica, during the austral summer. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 33, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Press, W.; Teukolsky, S.; Vetterling, W.; Flannery, B. Numerical Recipes in Fortran 90: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, M. Transport of copper from the Bering Sea to the Northwestern North Pacific. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 42, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G. The paradox of the plankton. Am. Nat. 1961, 95, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuka, N. A time series observation of DMSP production in the fast ice zone near Barrow. Tohoku Geophys. J. 2003, 36, 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Gradinger, R. Sea-ice algae: Major contributors to primary production and algal biomass in the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas during May/June 2002. Deep Sea Res. II 2009, 56, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicken, H.; Krouse, H.; Kadko, D.; Perovich, D. Tracer studies of pathways and rates of meltwater transport through arctic summer sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, J.; Brabant, F.; Dumont, I.; Stefels, J. High resolution dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl sulfoniopropionate time series profiles in decaying summer first-year sea ice at Ice Station Polarstern, western Weddell Sea, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, I.; Meyn, S.; Tegen, I.; Doney, S.; John, J.; Bishop, J. Iron supply and demand in the upper ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bailey, D.; Lindsay, K.; Moore, K.; Holland, M. Impacts of sea ice on the marine iron cycle and phytoplankton productivity. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2014, 11, 2383–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, R. The uniqueness of humic substances in each of soil, stream and marine environments. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 232, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, C.; Gosselin, M.; Ehn, J.; Gratton, Y.; Rossnagel, A.; Barber, D.; Martin, J.; Tremblay, J.; Palmer, M.; Arrigo, K.; et al. Contribution of under-ice primary production to an ice-edge upwelling phytoplankton bloom in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.; Perovich, D.; Pickart, R.; Brown, Z.; Van Kijken, G.; Lowry, K.; Mills, M.; Palmer, M.; Balch, W.; Bahr, F.; et al. Massive phytoplankton blooms under Arctic sea ice. Science 2012, 336, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeham, S.; Lee, C.; Hedges, J.; Hernes, P.; Peterson, M. Molecular indicators of diagenetic status in marine organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 5363–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppley, R. Temperature and phytoplankton growth in the sea. Fish. Bull. 1972, 70, 1068–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Barrie, L.; Plummer, D.; McConnell, J.; Brickell, P.; Levasseur, M.; Gosselin, M. Flux estimation of oceanic dimethyl sulfide around North America. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 21327–21342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.; Worthen, D.; Lizotte, M.; Dixon, P.; Dieckmann, G. Primary production in Antarctic sea ice. Science 1997, 276, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Gosselin, M.; Kudoh, S.; Robineau, B.; Taguchi, S. DOC and its relationship to algae in bottom ice communities. J. Mar. Syst. 1997, 11, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Lara, R.; Eicken, H.; Kattner, G.; Skoog, A. Dissolved organic matter in Arctic multi-year sea ice during winter: Major components and relationship to ice characteristics. Polar Biol. 1995, 15, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P. Physical Chemistry of Foods; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, K.; Ackley, S.; Lytle, V. The percolation phase transition in sea ice. Science 1998, 282, 2238–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krembs, C.; Gradinger, R.; Spindler, M. Implications of brine channel geometry and surface area for the interaction of sympagic organisms in Arctic sea ice. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 243, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, B.; Maykut, G.; Grenfell, T. Effects of temperature on the microstructure of first-year Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Rideal, E. Interfacial Phenomena; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Birdi, K. Lipid and Biopolymer Monolayers at Interfaces; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Verdugo, P.; Alldredge, A.; Azam, F.; Kirchman, D.; Passow, U.; Santschi, P. The oceanic gel phase: A bridge in the DOM-POM continuum. Mar. Chem. 2004, 92, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herborg, L.; Thomas, D.; Kennedy, H.; Haas, C.; Dieckmann, G. Dissolved carbohydrates in Antarctic sea ice. Antarct. Sci. 2001, 13, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.; Dieckmann, G.; Gosselin, M.; Robinson, D.; Fritsen, C.; Sullivan, C. High resolution study of the platelet ice ecosystem in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica: Biomass, nutrient and production profiles within a dense microalgal bloom. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 127, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasham, M.; Sarmiento, J.; Slater, R.; Ducklow, H.; Williams, R. Ecosystem behavior at Bermuda station “S” and ocean weather station “India”: A general circulation model and observational analysis. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 379–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, J.; Slater, R.; Fasham, M.; Ducklow, H.; Toggweiler, J.; Evans, G. A three dimensional ecosystem model of nitrogen cycling in the North Atlantic euphotic zone. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 417–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Doney, S.; Kleypas, J.; Glover, D.; Fung, I. Intermediate complexity marine ecosystem model for the global domain. Deep Sea Res. II 2002, 49, 403–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Lindsay, K.; Doney, S. Upper ocean ecosystem dynamics and iron cycling in a global three dimensional model. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, C.; Schoemann, V. Bioavailability of organically bound Fe to model phytoplankton of the Southern Ocean. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2281–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, C.; Schoemann, V.; Nichols, C.; Butler, E.; Boyd, P. Saccharides enhance iron bioavailability to Southern Ocean phytoplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D. Iron limitation in the Southern Ocean. Science 2003, 302, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Moore, K. Incorporating Phaeocystis into a Southern Ocean ecosystem model. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robineau, B.; Legendre, L.; Kishino, M.; Kudoh, S. Horizontal heterogeneity of microalgal biomass in the first year ice of Saroma-ko Lagoon (Hokkaido, Japan). J. Mar. Syst. 1997, 11, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, H.; Bergmann, M. Seasonal Development of ice algae and its prediction from environmental factors near Resolute, N.W.T. Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Anning, J.; Clement, P.; Cota, G. Abundance and production of ice algae in Resolute Passage, Canadian Arctic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 48, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysgaard, S.; Kuhl, M.; Glud, R.; Hansen, J. Biomass, production and horizontal patchiness of sea ice algae in a high-Arctic fjord (Young Sound, Greenland). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 223, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, M.; Levasseur, M.; Wheeler, P.; Horner, R.; Booth, B. New measurements of phytoplankton and ice algal production in the Arctic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. II 1997, 44, 1623–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, L.; Carrada, G.; Catalano, G.; Dell’Ano, A.; Fabiano, M.; Lazzara, L.; Mangoni, O.; Pusceddu, A.; Saggiomo, V. Structural and functional properties of sympagic communities in the annual sea ice at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctic). Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, W.; Ginoux, P.; Schopf, P.; Casey, N. Phytoplankton and iron: Validation of a global three dimensional ocean biogeochemical model. Deep Sea Res. II 2003, 50, 3143–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M. Marine colloids and trace metals. In Biogeochemistry of Dissolved Organic Matter; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 267–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lizotte, M. Contributions of ice algae to Antarctic marine primary production. Am. Zool. 2001, 41, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, M. The microbiology of sea ice. In Sea Ice: An Introduction to its Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Geology; Thomas, D., Dieckmann, G., Eds.; Blackwell Science: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schoemann, V.; Becquevort, S.; Stefels, J.; Rousseau, V.; Lancelot, C. Phaeocystis blooms in the global ocean and their control mechanisms: A review. J. Sea Res. 2005, 53, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Bopp, L.; Aumont, O.; Arrigo, K. Influence of light and temperature on the marine iron cycle: From theoretical to global modeling. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2009, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, J.; Anderson, T. Modeling DOM Biogeochemistry. In Biogeochemistry of Dissolved Organic Matter; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 717–755. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, D.; Macdonald, R.; Denman, K. Primary productivity and export fluxes on the Canadian shelf of the Beaufort Sea: A modeling study. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 75, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passow, U.; Alldredge, A.; Logan, B. The role of particulate carbohydrates in the flocculation of diatom blooms. Deep Sea Res. I 1994, 2, 335–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijssel, M.; Janse, I.; Noordkamp, D.; Gieskes, W. An inventory of factors that affect saccharide production by Phaeocystis globosa. J. Sea Res. 2000, 43, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.; Wiebe, W. Temperature and substrates as interactive limiting factors for marine heterotrophic bacteria. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 23, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, S.; Gleitz, M. Microbial responses to experimental sea-ice formation: Implications for the establishment of Antarctic sea-ice communities. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1993, 173, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, S.; Dieckmann, G. Bacterial standing stock, activity and carbon production during formation and growth of sea ice in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2746–2753. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nowlin, W.; Klinck, J. The physics of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Rev. Geophys. 1986, 24, 469–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampal, P.; Weiss, J.; Marsan, D.; Bourgoin, M. Arctic sea ice velocity field: General circulation and turbulent-like fluctuations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.; Weeks, W. Brine Drainage and Initial Salt Entrapment in Sodium Chloride Ice; Res. Rep. 345; U.S. Army, Cold Regions Engineering Laboratory: Hanover, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Perovich, D.; Gow, A. A quantitative description of sea ice inclusions. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 18327–18343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J. Aquatic Chemistry: An Introduction Emphasizing Chemical Equilibria in Natural Waters; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kirst, G.; Wiencke, C. Ecophysiology of polar algae. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslinger, D.; Cooney, R.; McRoy, C.; Ward, A.; Kline, T.; Simpson, E.; Allen, J. Plankton dynamics: Observed and modeled responses to physical conditions in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Fish. Oceanogr. 2001, 10, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarthou, G.; Timmermans, K.; Blain, S.; Treguer, P. Growth physiology and fate of diatoms in the ocean: A review. J. Sea Res. 2005, 53, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslinger, D.; Iverson, R. The effects of convective and wind-driven mixing on spring phytoplankton dynamics in the Southeastern Bering Sea middle shelf domain. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 627–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).