Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Concentrate Supplementation Alleviates Body Weight Loss by Regulating Rumen Function in Lactating Tibetan Sheep During the Cold Season
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal and Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Histomorphology Analysis
2.4. Determination of Rumen Rermentation
2.5. Measurement of Digestive Enzymes
2.6. 16s rDNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.7. RNA Isolation, Transcriptomic Sequencing, and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance of Lactating Tibetan Sheep
3.2. Histomorphological Analysis of Rumen
3.3. Rumen Fermentation Parameters
3.4. Ruminal Digestive Enzyme of Lactating Tibetan Sheep
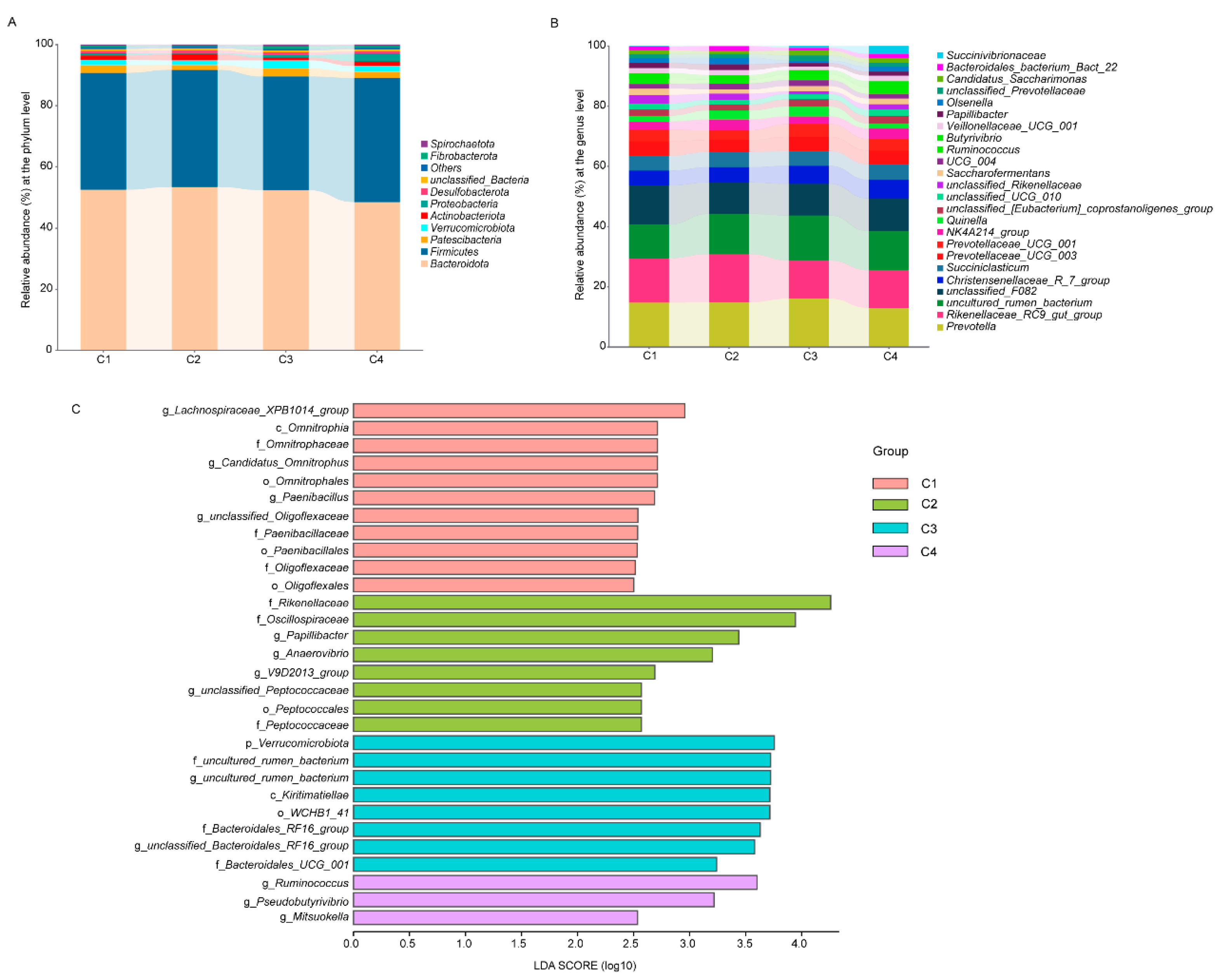
3.5. Microbial Composition of Rumen in Lactating Tibetan Sheep
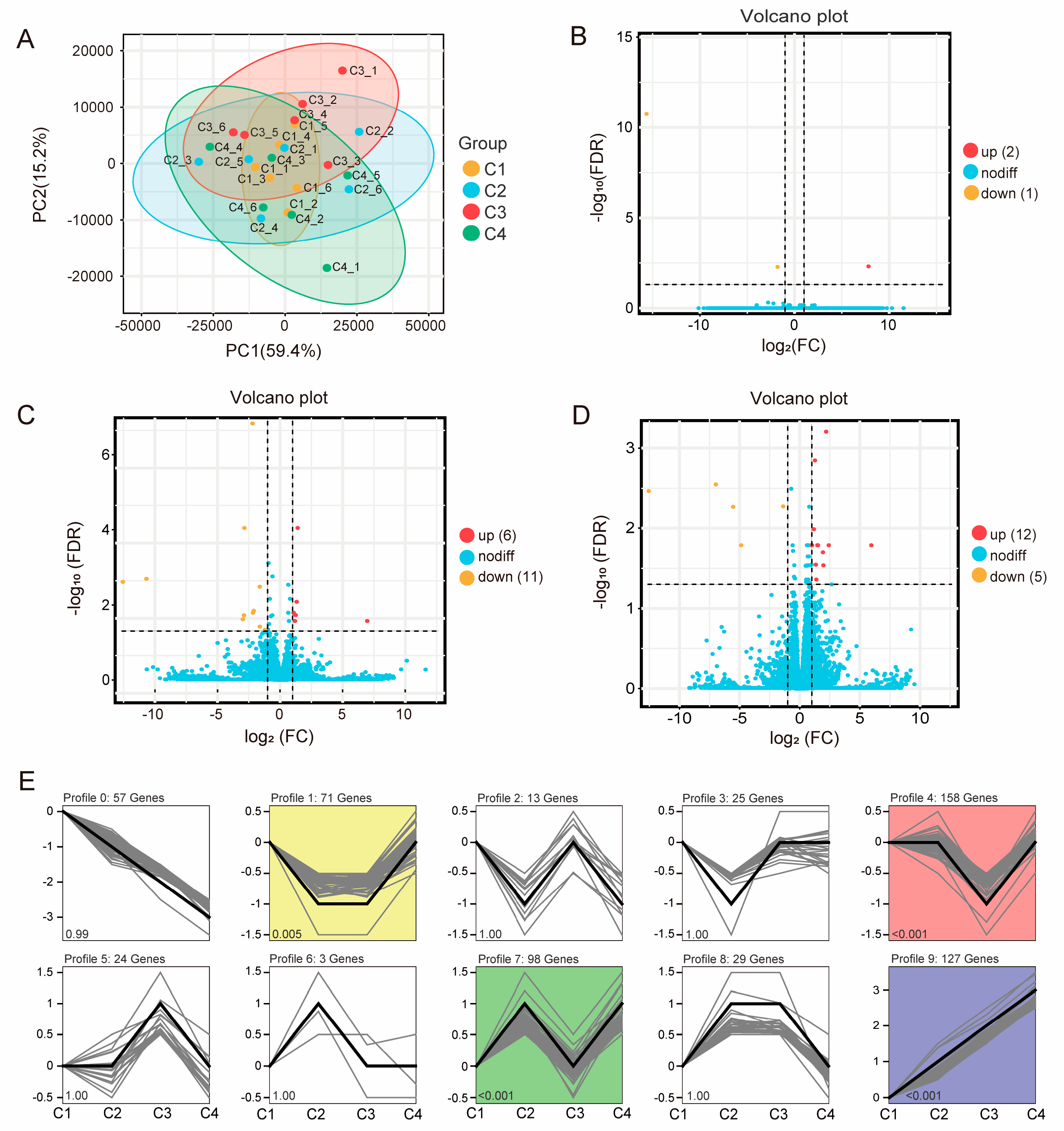
3.6. Transcriptomic Profile of Rumen in Lactating Tibetan Sheep
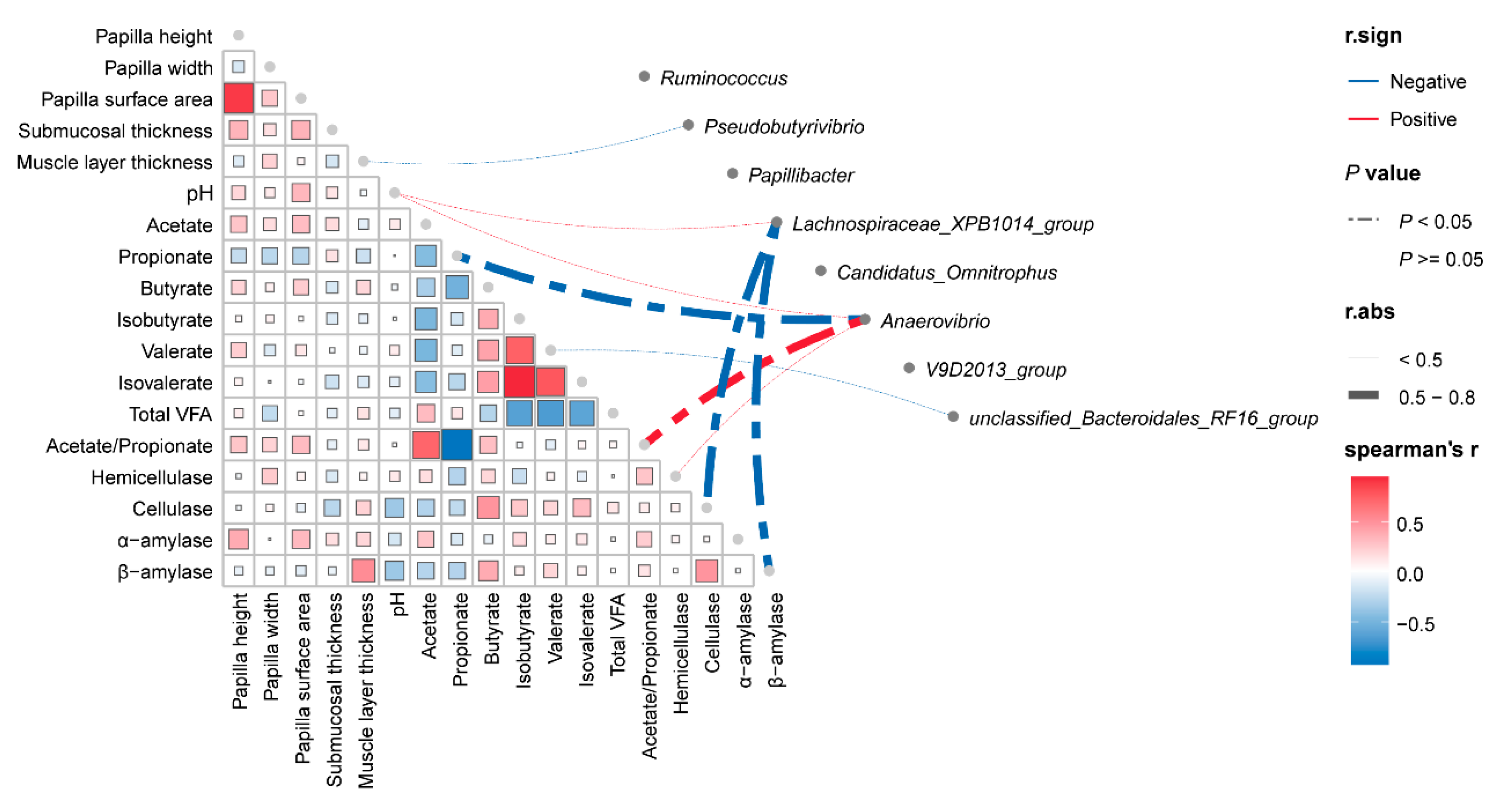
3.7. Correlation Analysis Between Phenotype and Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, N.; Hu, L.; Xu, S. Comparative Analysis of the Composition of Fatty Acids and Metabolites between Black Tibetan and Chaka Sheep on the Qinghai—Tibet Plateau. Animals 2022, 12, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yuan, C.; An, X.; Guo, T.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J. Genome-Wide Selection Signals Reveal Candidate Genes Associated with Plateau Adaptation in Tibetan Sheep. Animals 2024, 14, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Ge, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Nie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Ren, Y. Effects of soil ingestion on nutrient digestibility and rumen bacterial diversity of Tibetan sheep. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Gibb, M.; Leiber, F.; Ismail, M.; Ding, L.; Guo, X.; Long, R. The sustainable development of grassland-livestock systems on the Tibetan plateau: Problems, strategies and prospects. Rangel. J. 2014, 36, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Research on the Value-Added Process of the Value Chain of Tibetan Sheep Based on the Rotational Grazing. J. Adv. Agric. Technol. 2023, 10, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, P.J. Degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose by ruminal microorganisms. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Alimon, A.R.; Yaakub, H.; Samsudin, A.A.; Candyrine, S.C.L.; Wan Mohamed, W.N.; Md Noh, A.; Fuat, M.A.; Mookiah, S. Effects of vegetable oil supplementation on rumen fermentation and microbial population in ruminant: A review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B.; Muck, R.E.; Weimer, P.J. Quantitative analysis of cellulose degradation and growth of cellulolytic bacteria in the rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, G.; Cox, F.; Ganesh, S.; Jonker, A.; Young, W.; Janssen, P.H. Rumen microbial community composition varies with diet and host, but a core microbiome is found across a wide geographical range. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sha, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Huang, W.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Gao, X. A Study on the Differences in Rumen Microbiota–Liver Gluconeogenesis–Mitochondrial Interaction Between Tibetan Sheep and Hu Sheep in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Animals 2025, 15, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Nonaka, I.; Higuchi, K.; Takusari, N.; Kurihara, M.; Takenaka, A.; Mitsumori, M.; Kajikawa, H.; Aminov, R.I. Influence of high temperature and humidity on rumen bacterial diversity in Holstein heifers. Anaerobe 2007, 13, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Cong, H.; Yang, G.; Liu, G. Rumen microbiota helps Tibetan sheep obtain energy more efficiently to survive in the extreme environment of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1431063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Effect of Seasonal Dynamics on Feed Intake, Blood Parameters, Rumen Microbiota and Metabolites in Grazing Tibetan Sheep. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yang, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Yao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, F. Effects of dietary effective fiber to rumen degradable starch ratios on the risk of sub-acute ruminal acidosis and rumen content fatty acids composition in dairy goat. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 189, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, Q.; Gui, L.; Gebeyew, K.; Hou, S.; Wang, Z.; Han, L.; Yang, C. The influence of resveratrol and β-Hydroxy-β-methyl butyric acid supplementation alone or in combination on the development and health of the duodenum in Tibetan sheep. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1612102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Marc, L.; Bjoern, U. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; et al. KOBAS-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, J.; Bar-Joseph, Z. STEM: A tool for the analysis of short time series gene expression data. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Downing, M.M.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Harrigan, T.; Woznicki, S.A. Climate change and livestock: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 16, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Cui, X.; Wang, Z.; Chang, S.; Wanapat, M.; Yan, T.; Hou, F. Rumen microbiota of Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) adaptation to extremely cold season on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 673822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Geng, Y.; Kang, S.; Xu, S. Effects of dietary protein levels on growth performance, carcass traits, serum metabolites, and meat composition of Tibetan sheep during the cold season on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Animals 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Ou, J.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Ren, C.; Chen, J. Effect of dietary concentrate-to-forage ratios during the cold season on slaughter performance, meat quality, rumen fermentation and gut microbiota of tibetan sheep. Animals 2024, 14, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xu, S.; Hu, L.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X. Effect of dietary types on feed intakes, growth performance and economic benefit in Tibetan sheep and yaks on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during cold season. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169187. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelraheem, N.; Li, F.; Guo, P.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, F. Oat hay as winter feed improves digestibility, nitrogen balance and energy utilization of Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) in the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Livest. Sci. 2019, 230, 103854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.-S.; Raza, S.H.A.; Allam, F.A.E.A.; Zhou, L.; Hou, S.; Khan, I.; Kakar, I.U.; Abd El-Aziz, A.H.; Jia, J.; Sun, Y. Altered milk yield and rumen microbial abundance in response to concentrate supplementation during the cold season in Tibetan sheep. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 53, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.; Simmons, N.L. Functional organization of the bovine rumen epithelium. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R173–R181. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Sha, Y.; Lv, W.; Cao, G.; Guo, X.; Pu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Luo, Y. Multi-omics reveals that the rumen transcriptome, microbiome, and its metabolome co-regulate cold season adaptability of Tibetan sheep. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 859601. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, M.A.; Penner, G.B.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Guan, L.L. Development and physiology of the rumen and the lower gut: Targets for improving gut health. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4955–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, I.R.; Yin, G.; Borovok, I.; Miller, M.E.B.; Yeoman, C.J.; Dassa, B.; Yu, Z.; Mizrahi, I.; Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A. Functional phylotyping approach for assessing intraspecific diversity of Ruminococcus albus within the rumen microbiome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; Dingkao, R.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X. Supplementary feeding of cattle-yak in the cold season alters rumen microbes, volatile fatty acids, and expression of SGLT1 in the rumen epithelium. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Xu, S.; Ma, L.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Zhao, N.; Chen, Y. Effect of dietary concentrate to forage ratio on growth performance, rumen fermentation and bacterial diversity of Tibetan sheep under barn feeding on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhuang, S.; Dong, W.; Chang, G.; Yan, R.; Wang, T. Effects of different dietary concentrate to forage ratios on rumen fluid pH and VFA levels and blood VFA levels in dairy goats. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2013, 4, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Peng, C.; Jing, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Lachnospira is a signature of antihistamine efficacy in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Zhu, W. Impact of subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) adaptation on rumen microbiota in dairy cattle using pyrosequencing. Anaerobe 2013, 24, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Lin, L.; Hu, F.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. Disruption of ruminal homeostasis by malnutrition involved in systemic ruminal microbiota-host interactions in a pregnant sheep model. Microbiome 2020, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Zhou, M. The impact of diet on the composition and relative abundance of rumen microbes in goat. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 30, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Shen, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yu, D.; Liu, T.; Luo, D.; Xing, G.; Tang, J. Increase dietary fiber intake ameliorates cecal morphology and drives cecal species-specific of short-chain fatty acids in white pekin ducks. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 853797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Hu, F.; Guo, C.; Mei, S.; Xie, F.; Zeng, H.; Mao, S. Undernutrition shifted colonic fermentation and digest-associated bacterial communities in pregnant ewes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5973–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopherson, M.R.; Dawson, J.A.; Stevenson, D.M.; Cunningham, A.C.; Bramhacharya, S.; Weimer, P.J.; Kendziorski, C.; Suen, G. Unique aspects of fiber degradation by the ruminal ethanologen Ruminococcus albus 7 revealed by physiological and transcriptomic analysis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crost, E.H.; Le Gall, G.; Laverde-Gomez, J.A.; Mukhopadhya, I.; Flint, H.J.; Juge, N. Mechanistic insights into the cross-feeding of Ruminococcus gnavus and Ruminococcus bromii on host and dietary carbohydrates. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Ho, Y.; Abdullah, N. Mitsuokella jalaludinii sp. nov., from the rumens of cattle in Malaysia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gelsinger, S.; Edwards, A.; Riehle, C.; Koch, D. Transcriptome analysis of rumen epithelium and meta-transcriptome analysis of rumen epimural microbial community in young calves with feed induced acidosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sha, Y.; Pu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Coevolution of rumen epithelial circRNAs with their microbiota and metabolites in response to cold-season nutritional stress in Tibetan sheep. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Content |
|---|---|
| Ingredient, % DM basis | |
| Corn | 32.00 |
| Wheat | 7.00 |
| Palm meal | 30.00 |
| Soybean meal | 4.00 |
| Rapeseed meal | 18.00 |
| Cottonseed meal | 2.00 |
| Glucose | 2.00 |
| Medical stone | 1.20 |
| Sodium chloride | 1.10 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.35 |
| CaHPO4 | 0.35 |
| Premix 1 | 2.00 |
| Total | 100 |
| Nutritional level 2 | |
| Dry matter, % | 88.00 |
| Digestible energy, MJ/kg | 10.44 |
| Crude protein, % | 14.63 |
| Ether extract, % | 2.97 |
| Neutral detergent fiber, % | 26.66 |
| Acid detergent fiber, % | 13.53 |
| Calcium, % | 0.95 |
| Phosphorus, % | 0.55 |
| Item | Group | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |||
| Initial BW, kg | 45.75 a | 45.26 a | 44.95 b | 43.92 b | 5.542 | 0.013 |
| D34 BW, kg | 41.57 | 44.78 | 44.86 | 44.68 | 4.641 | 0.543 |
| D68 BW, kg | 37.39 | 44.30 | 44.81 | 45.25 | 4.457 | 0.381 |
| Average BW loss, kg | −0.123 b | −0.014 a | −0.002 a | 0.020 a | 0.083 | <0.001 |
| Average dry matter intake, kg | 1.19 d | 1.37 c | 1.56 b | 1.72 a | 0.164 | <0.001 |
| Items | Group | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |||
| Papilla height, μm | 930.01 | 947.49 | 1065.39 | 1054.08 | 461.70 | 0.612 |
| Papilla width, μm | 456.26 b | 510.35 b | 530.53 ab | 646.35 a | 226.09 | 0.008 |
| Papilla surface area, mm2 | 423.26 | 520.76 | 574.66 | 569.71 | 353.64 | 0.339 |
| Submucosal thickness, μm | 423.37 a | 355.92 b | 354.44 b | 365.25 b | 113.19 | 0.027 |
| Muscle layer thickness, μm | 1193.13 c | 1219.41 bc | 1398.37 ab | 1579.55 a | 435.72 | <0.001 |
| Item | Group | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |||
| pH | 7.12 | 7.22 | 6.95 | 7.12 | 0.048 | 0.254 |
| Acetate, % | 68.80 | 68.30 | 66.70 | 65.99 | 0.505 | 0.158 |
| Propionate, % | 17.19 | 17.04 | 19.17 | 16.72 | 0.364 | 0.060 |
| Butyrate, % | 8.62 | 9.27 | 9.13 | 11.48 | 0.486 | 0.163 |
| Isobutyrate, % | 2.15 | 2.18 | 1.99 | 2.24 | 0.080 | 0.747 |
| Valerate, % | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 0.026 | 0.341 |
| Isovalerate, % | 2.38 | 2.39 | 2.23 | 2.62 | 0.094 | 0.569 |
| Total VFA, mmol/L | 33.87 | 44.75 | 46.79 | 40.08 | 1.932 | 0.074 |
| Acetate/Propionate | 4.01 | 4.04 | 3.52 | 3.97 | 0.411 | 0.087 |
| Item | Group | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |||
| Cellulase, μg/h/mL | 4.19 b | 8.66 a | 7.39 ab | 7.78 ab | 0.613 | 0.042 |
| Hemicellulase, nmol/min/mL | 60.38 | 78.36 | 55.24 | 59.69 | 3.634 | 0.107 |
| α-amylase, μg/min/mL | 316.26 | 328.17 | 349.96 | 336.29 | 9.278 | 0.655 |
| β-amylase, mg/min/mL | 2.16 | 2.70 | 4.19 | 5.96 | 0.602 | 0.101 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hou, S. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Concentrate Supplementation Alleviates Body Weight Loss by Regulating Rumen Function in Lactating Tibetan Sheep During the Cold Season. Animals 2025, 15, 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192791
Yang C, Ma Q, Wang J, Wang Z, Hou S. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Concentrate Supplementation Alleviates Body Weight Loss by Regulating Rumen Function in Lactating Tibetan Sheep During the Cold Season. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192791
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chao, Qingling Ma, Jiancui Wang, Zhiyou Wang, and Shengzhen Hou. 2025. "Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Concentrate Supplementation Alleviates Body Weight Loss by Regulating Rumen Function in Lactating Tibetan Sheep During the Cold Season" Animals 15, no. 19: 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192791
APA StyleYang, C., Ma, Q., Wang, J., Wang, Z., & Hou, S. (2025). Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Concentrate Supplementation Alleviates Body Weight Loss by Regulating Rumen Function in Lactating Tibetan Sheep During the Cold Season. Animals, 15(19), 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192791





