Study on the Selective Behavior of Brachymystax tsinlingensis Li, 1966 (Order: Saloniformes, Family: Salmonidae) on Substrate Color and Type
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Animals
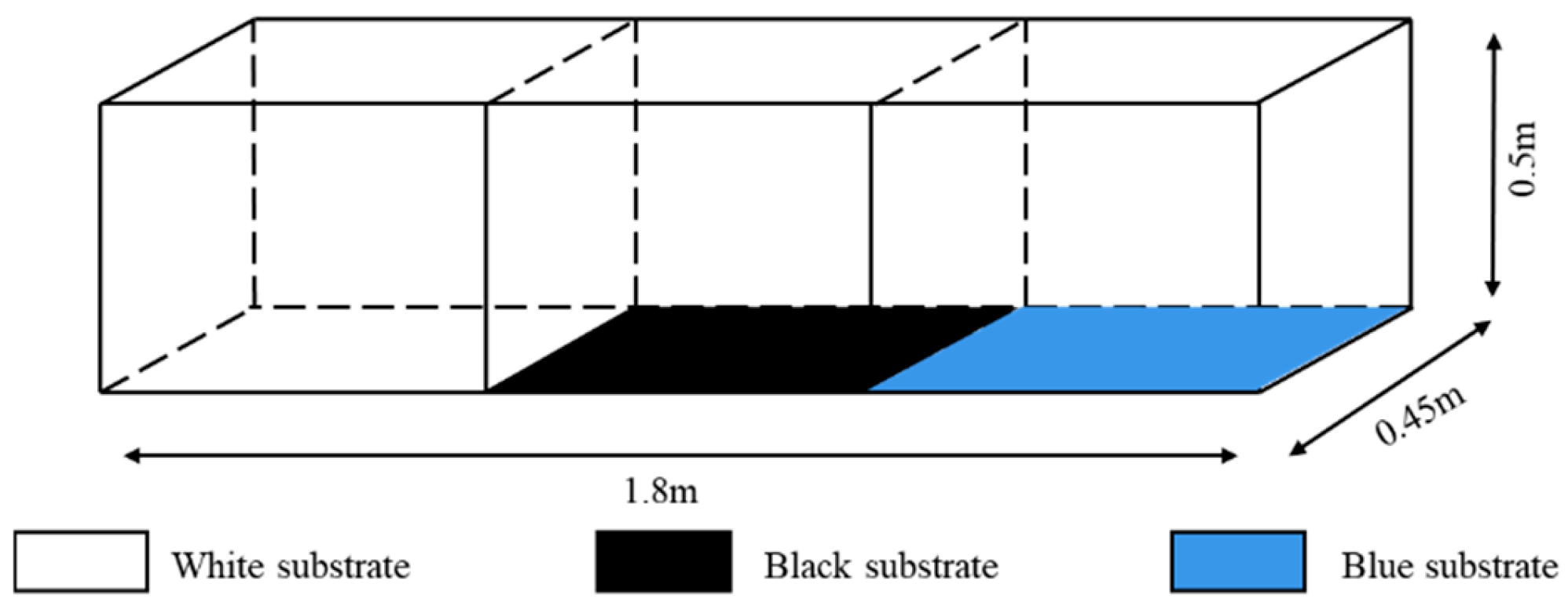
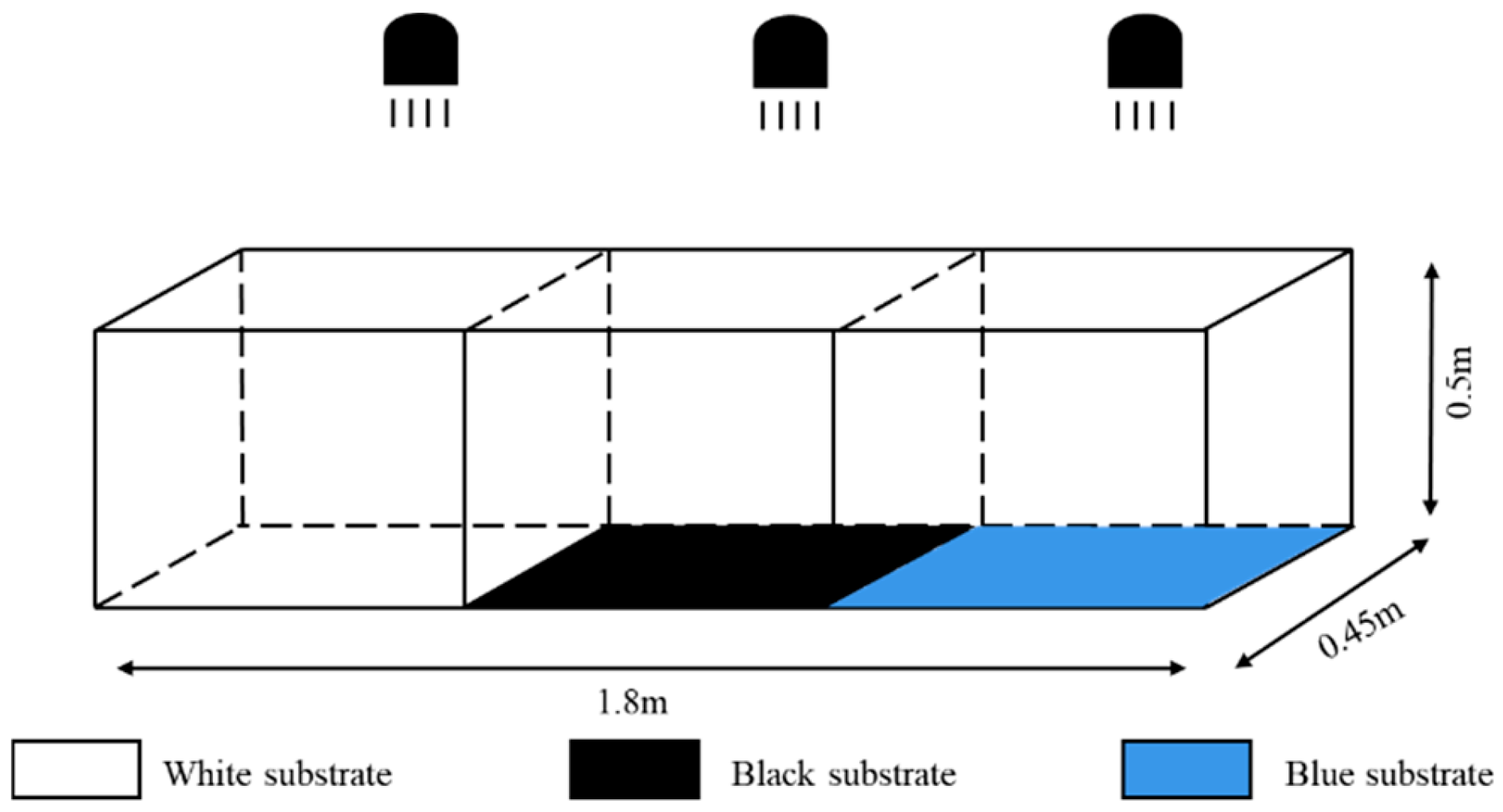
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.2.1. Experimental Setup for Substrate Color
2.2.2. Substrate Type Experimental Setup
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
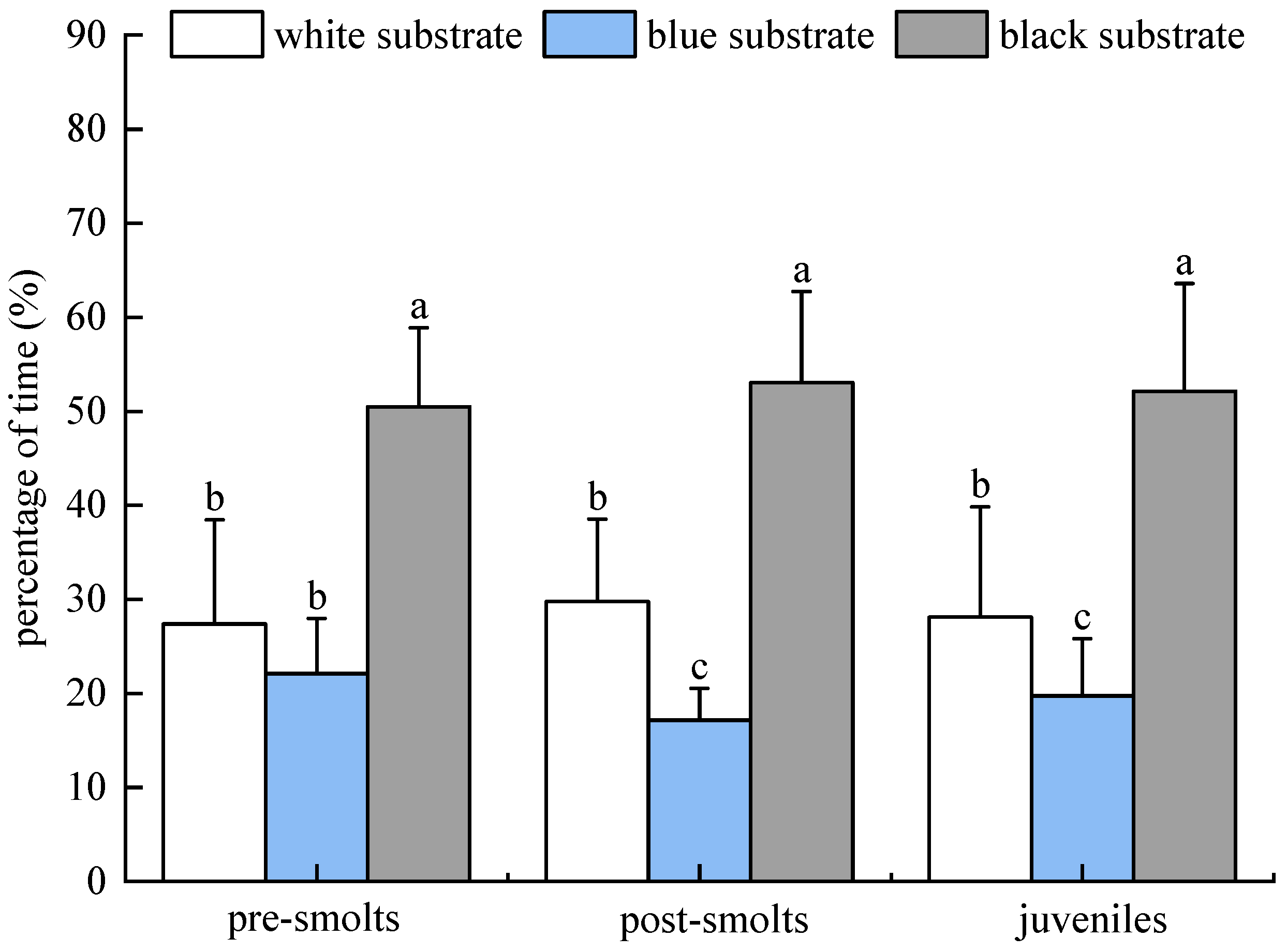
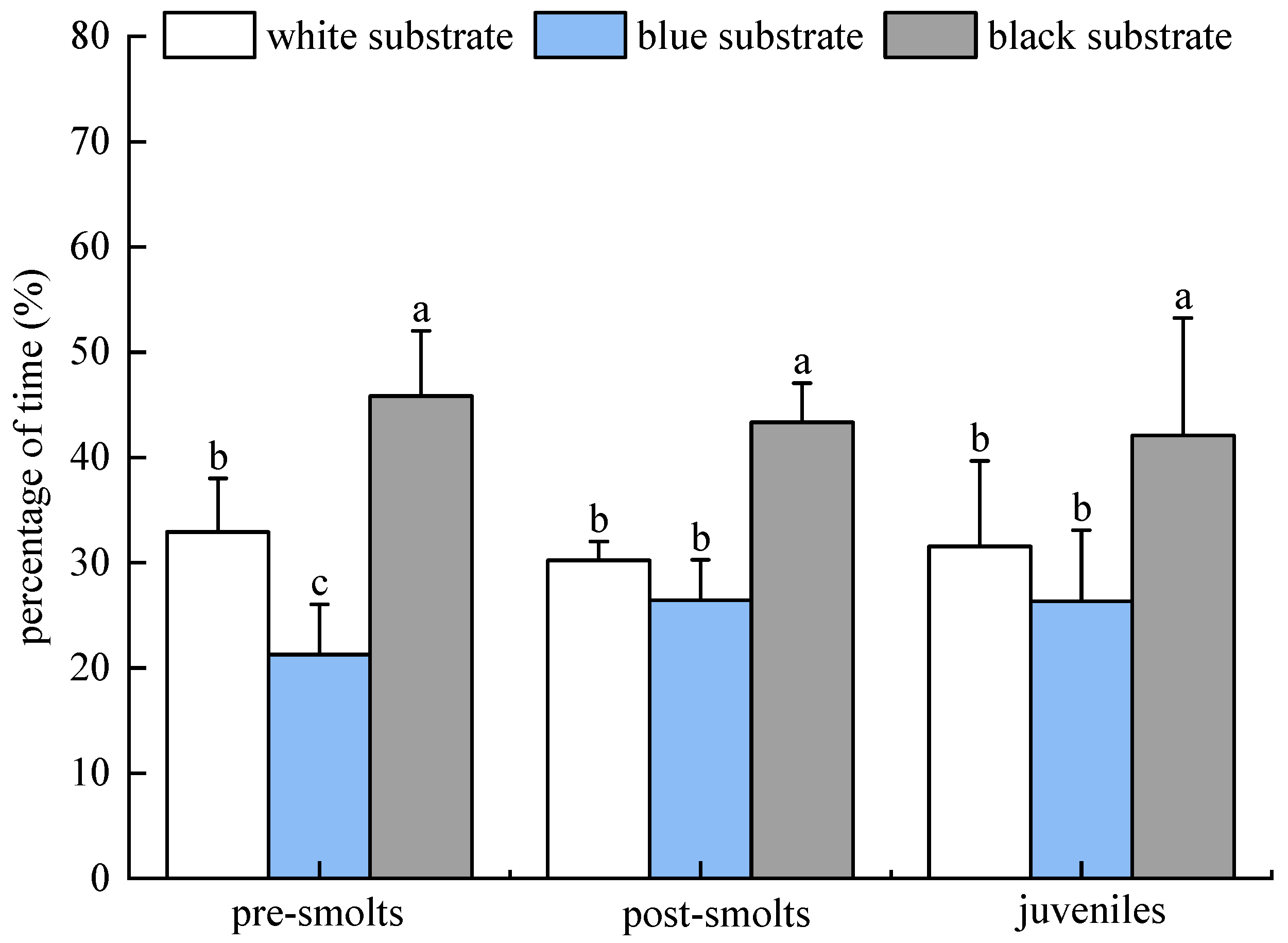
3.1. Substrate Color Selection Experiment
3.1.1. Results of Individual Experiments in Light Environment
3.1.2. Results of Individual Experiments in Dark Environment
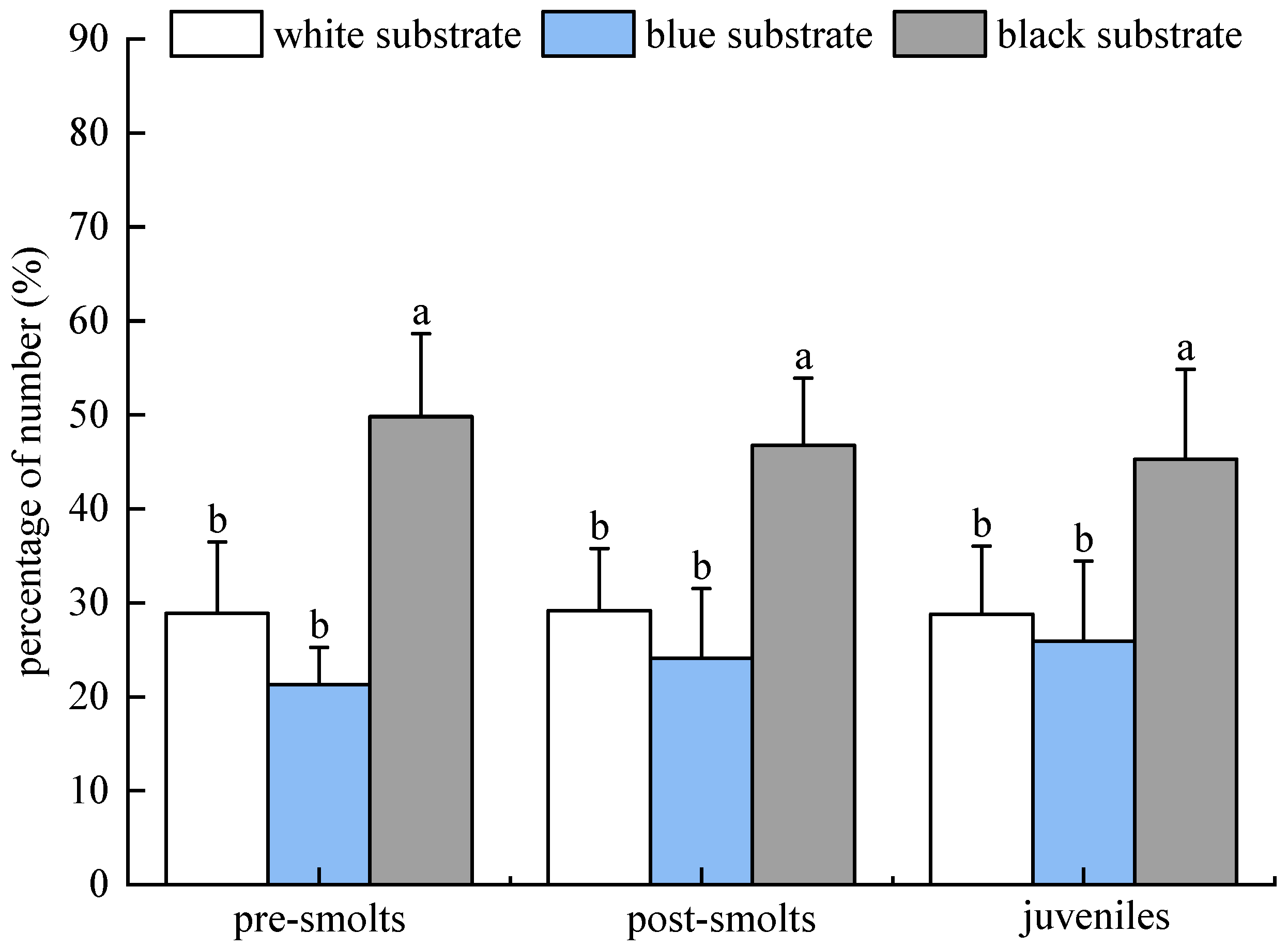
3.1.3. Results of Population Experiments in Light Environment
3.1.4. Results of Population Experiments in Dark Environment
3.2. Substrate Type Selection Experiment
3.2.1. Results of Individual Experiments in Light Environment
3.2.2. Results of Individual Experiments in Dark Environment
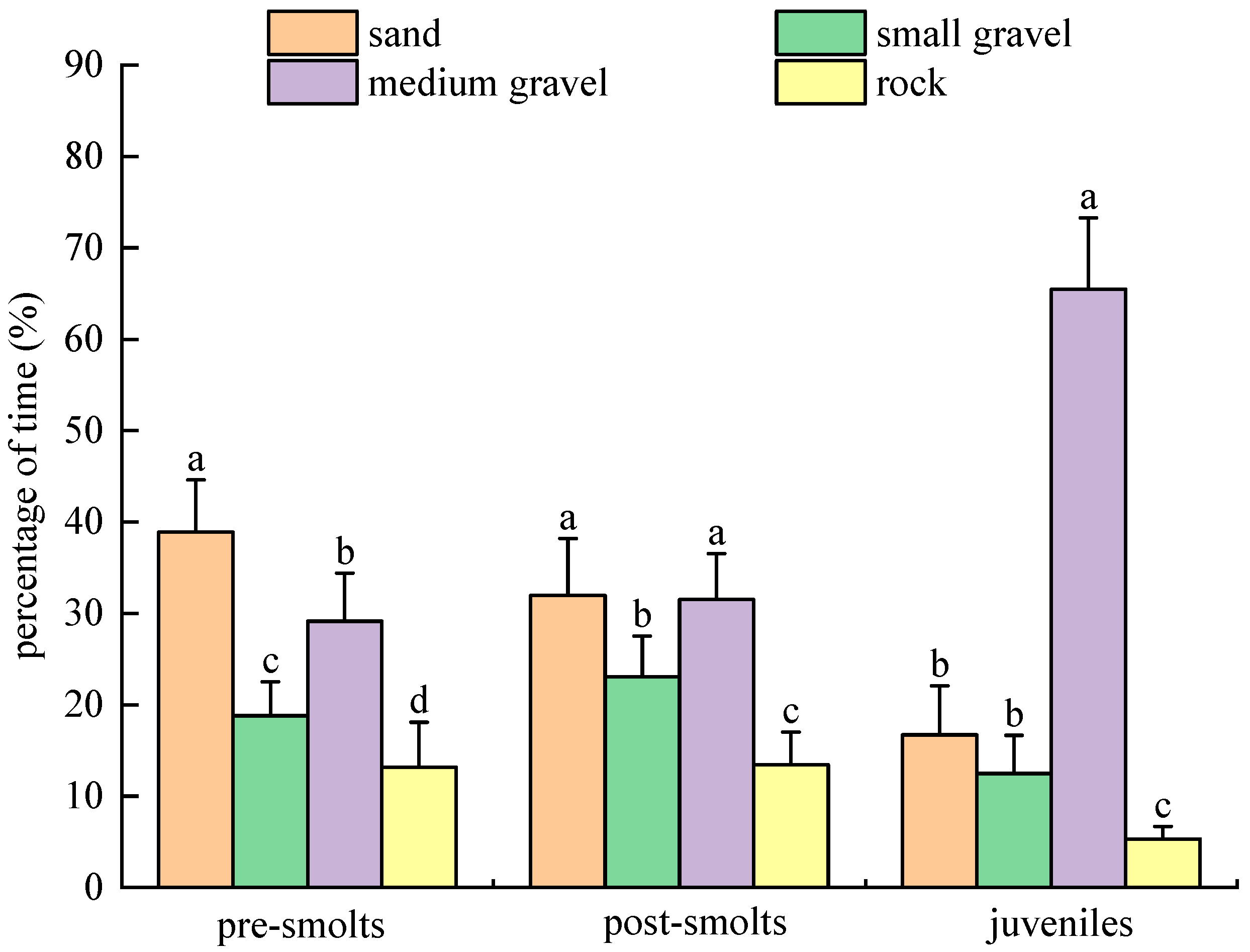
3.2.3. Results of Population Experiments in Light Environment
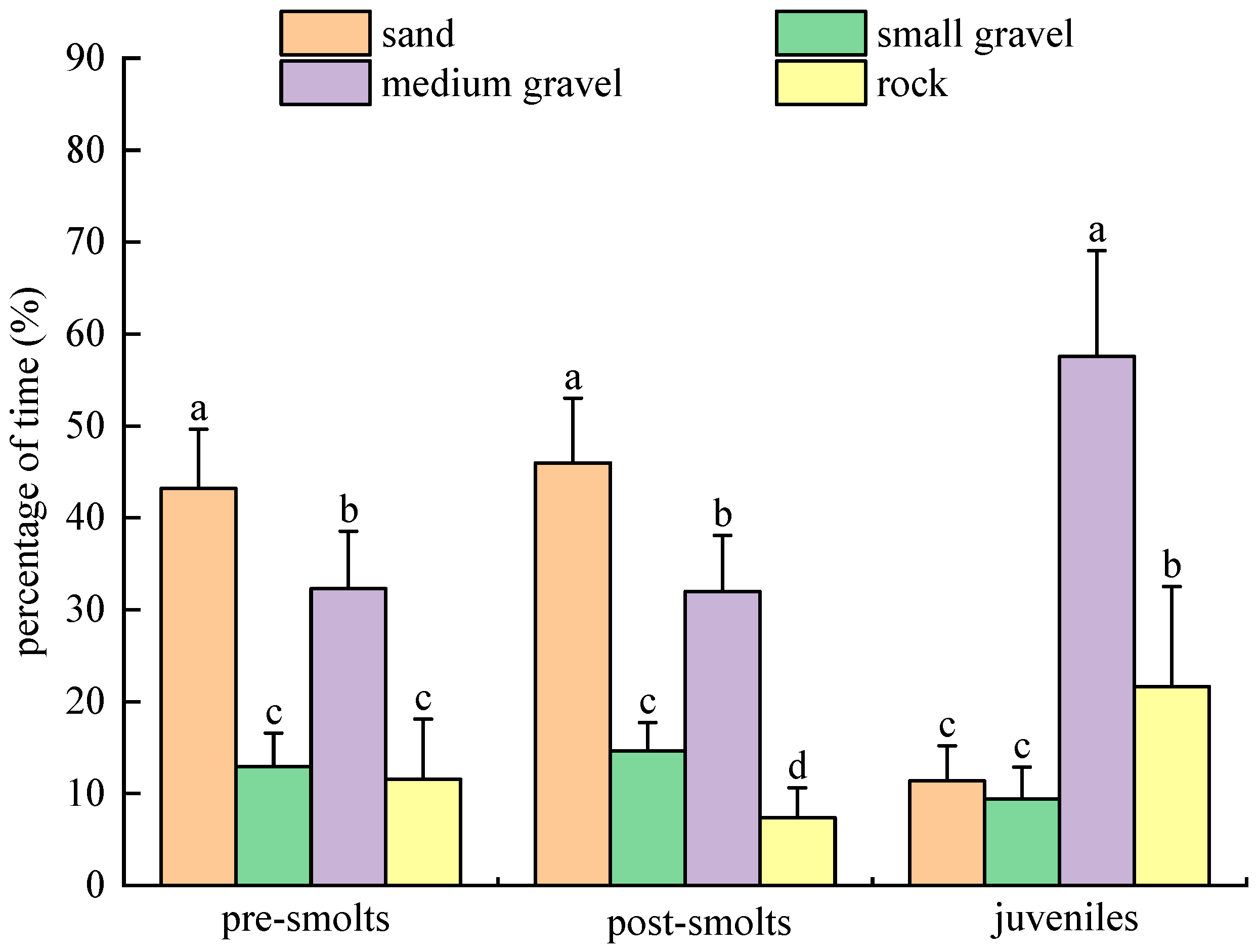
3.2.4. Results of Population Experiments in Dark Environment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Cruze, N. The impact of human activities on the habitat selection of sloth bears (Melursus ursinus) in India. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00545. [Google Scholar]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Foss, A.; Vikingstad, E.; Elvegård, T.A. The use of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) to control sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis Krøyer) infestations in intensively farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2014, 424–425, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, K.; Duan, J.; Shi, W. Zooplankton community characteristics and ecological assessment of water quality in eriocheir sinensis, siniperca chuatsi national aquatic germ plasm resources protected areas. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2014, 36, 833–840. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Huang, X.; Feng, G.; Zuang, P.; Geng, Z.; Wu, Y. Preference for substrate in different developmental stagesof Eriocheir sinensis. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 888–895. [Google Scholar]
- Kynard, B.; Parker, E. Ontogenetic behavior and dispersal of Sacramento River white sturgeon, Acipenser transmon-tanus, with a notebody color. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2005, 74, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, J.; Plath, M. Divergent evolution of feeding substrate preferences in a phylogenetically young species flock of pupfish (Cyprinodon spp.). Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galhardo, L.; Almeida, O.; Oliveira, R.F. Preference for the presence of substrate in male cichlid fish: Effects of social dominance and context. Appl. Anim. Haviour Sci. 2009, 120, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snickars, M.; Sundblad, G.O.R.; Sandstr, O.M.A. Habitats electivity of substrate-spawning fish: Modelling requirements for the Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 398, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.L.; Purser, J.G. Substrate-attachment Preferences of Cultured Newborn Pot- bellied Seahorses, Hippocampus abdominalis (Lesson, 1827). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2012, 43, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Hou, J.; Zunag, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Selective behavior of Anguilla japonica glass eel on substrate color and light intensity in the Yangtze Estuary. Mar. Fish. 2015, 37, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Kynard, B.; Horgan, M. Ontogenetic behavior and migration of Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus, andshortnose sturgeon, A. brevirostrum, with notes on social behavior. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 63, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasteur, G. A Classificatory Review of Mimicry Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1982, 13, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Gonzales, J.L.; Loew, E.R.; Uy, J.A. Variation in the visual habitat may mediate the maintenance of color polymorphism in a poeciliid fish. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, N.; Humphries, N.E.; Mucientes, G.; Hammerschlag, N.; Lima, F.P.; Scales, K.L.; Miller, P.I.; Sousa, L.L.; Seabra, R.; Sims, D.W. Ocean-wide tracking of pelagic sharks reveals extent of overlap with longline fishing hotspots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhuang, P.; Yan, A.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L. The influences of illumination, water current and stocking density on feeding, behavior and growth in juveniles Acipeniles schrenckii. J. Fish. China 2004, 28, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Breder, C.M., Jr. On the phenomenon of locomotor disorganization induced by strong light in small plectognath fishes. Am. Soc. Ichthyol. Herpetol. (ASIH) 1942, 1942, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhen, Z.; Mu, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y. Study on the hiding behavior of the Glyptosternum maculatum larvae and juveniles. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. On new subspecies of fresh-water trout, Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis, from taipaishan, shensi, China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sin. 1966, 3, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Chu, Z.; Lu, B.; Wei, Q.; Wang, F. Effects of different baits on the growth and survival of Chinook salmon fry in the Brachymystax tsinlingensis. Sci. Fish Farming 2018, 8, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.; Chen, Y. China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals; Pisces; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Wei, Q.; Sun, Q.; Li, L.; Du, H. Early ontogenesis of Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis. J. Fish. Sci. China 2012, 19, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Wei, Q.; Sun, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, L. Age and growth of Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis. J. Fish. Sci. China 2013, 20, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Luo, W.; Wei, Q.W. Assignment of parentage by microsatellite analysis in the endangered brachymystax Lenok Tsinlingensis (Salmonidae). Aquat. Biol. 2017, 26, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Cai, H. Fish Behavior; Xiamen University Press: Xiamen, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P.; Boyd, K.; Zhang, L.Z. Comparative ontogenetic behavior and migration of Kaluga, Huso Dauricus, and Amur Sturgeon, Acipenser schrenckii, from the Amur River. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2003, 66, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P. Individual Developmental Behavior of Sturgeon Fishes and Its Implications for Evolution and Practice; Institute of Aquatic Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Wuhan, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek, P.; Iwamoto, T.; Murakami, N. Differences in aggression between wild-type and domesticated fighting fish are context dependent. Anim. Behav. 2008, 73, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korner, K.E.; Schlupp, I.; Plath, M.; Loew, E.R. Spectral sensitivity of mollies: Comparing surface- and cave-dwelling Poecilia mexicana. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosakowski, T.; Wagner, E.J. Assessment of fin erosion by comparison of relative fin length in hatchery and wild trout in Utah. Canadian J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 51, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhuang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Shi, X.; Zhao, F.; Liu, J. Substrate preference of juvenile Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis captured from Yang gtze River estuary. Chin. J. Ecol. 2008, 27, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, Y. On the feeding habits and growth for larval of Clarias lazera under pond nursery. J. Fish. China 1990, 14, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Shi, X.; Liu, D.; Luo, J.; Bai, Y. White and Black Substrate Preference and Hiding Behavior of Pelteobagrus vachelli. J. Hydroecology 2012, 33, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P.; Boyd, K.; Zhang, L.Z. Ontogenetic behavior and migration of Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 65, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Species characteristics and protective counter measures of Qinling Lenok. Acta Ecol. Anim. Domastici 2008, 29, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Shao, J.; Du, H.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q. Habitat environmental characteristics of Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2017, 41, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, M. Feeding and growth of the larva stage of fish. J. Fish. China 1995, 19, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; He, X.; Deng, M.; Wu, C.; Qin, Y. Hiding behavior and swimming aqueous layers of yellow catfish larvae and juveniles. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2017, 36, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, R.P.; Theilacker, G.H.; Lon, C.H. Causes of mortality in young Mackerel. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1985, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. On the feeding, growth and survival of larval mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris). J. Fish. China 2014, 12, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Cejas, R.J.; Almansa, E.; Jerez, S. Changes in lipid class and fatty acid composition during development in white seabream (Diplodus sargus) eggs and larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 2004, 139, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J.; Ma, W. Effects of salinity and pH on the embryonic development and larval activity of kelp bass Epinephelus moara. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2013, 34, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonca, F.Z.; Volpato, G.L.; Costa-Ferreira, R.S. Substratum choice for nesting in male Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Lu, J.; Ke, S.; Li, D.; Ji, H.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, H.; Gao, S.; Tu, Z. Differences in habitat substrate preferences between male and female individuals and groups of Gymnocypris przewal skii during their breeding and migration period. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2024, 48, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Cause analysis of resources change and reconstruction strategy of Larimichthys crocea Daiqu group in the East China Sea. J. Fish. China 2022, 46, 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Du, H.; Wu, J.; Cheng, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Q. Effect of illumination on the hatching of Sichuan taimen (Hucho bleekeri Kimura) eggs. Freshw. Fish. 2019, 49, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, T.; Yang, D.; Wu, X. Prelimininary study on substrate preference of Schizothorax wangchiachii larvae fish. Freshw. Fish. 2019, 49, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Liu, W.; Xu, F.; Ma, B.; Huo, T.; Jiang, Z. Analysis on the variation of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) population homing to Amur River system in China. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2010, 19, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Oppedal, F.; Taranger, G.L.; Juell, E.J. Light intensity affects growth and sexual maturation of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) postsmolts in sea cages. Aquat. Living Resour. 1997, 10, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, H.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Ni, Z. Distribution and habitat character of Hucho bleekeri in the Dadu river basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Shi, Y. Attractive effect of fish reef model on black porgy (Sparus macrocephalus). J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1995, 34, 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, D. Habitat suitability index model and minimum habitat area estimation of young Procypris rabaudi (Tchang): A simulation experiment in laboratory. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 227–234. [Google Scholar]





| Fish | Length Range/cm | Length/cm | Weight Range/g | Weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-smolts | 1.82~2.07 | 1.94 ± 0.12 | 0.04~0.07 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| Post-smolts | 2.12~2.20 | 2.17 ± 0.03 | 0.06~0.09 | 0.07± 0.01 |
| Juveniles | 3.54~3.62 | 3.59 ± 0.03 | 0.37~0.42 | 0.39 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Song, R.; Shao, J. Study on the Selective Behavior of Brachymystax tsinlingensis Li, 1966 (Order: Saloniformes, Family: Salmonidae) on Substrate Color and Type. Animals 2025, 15, 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142089
Zhang L, Song R, Shao J. Study on the Selective Behavior of Brachymystax tsinlingensis Li, 1966 (Order: Saloniformes, Family: Salmonidae) on Substrate Color and Type. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lin, Rongqun Song, and Jian Shao. 2025. "Study on the Selective Behavior of Brachymystax tsinlingensis Li, 1966 (Order: Saloniformes, Family: Salmonidae) on Substrate Color and Type" Animals 15, no. 14: 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142089
APA StyleZhang, L., Song, R., & Shao, J. (2025). Study on the Selective Behavior of Brachymystax tsinlingensis Li, 1966 (Order: Saloniformes, Family: Salmonidae) on Substrate Color and Type. Animals, 15(14), 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142089




