Behavioral Fever in Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectu) Enhances the Immune Response to Vibrio harveyi Infection
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Seahorses
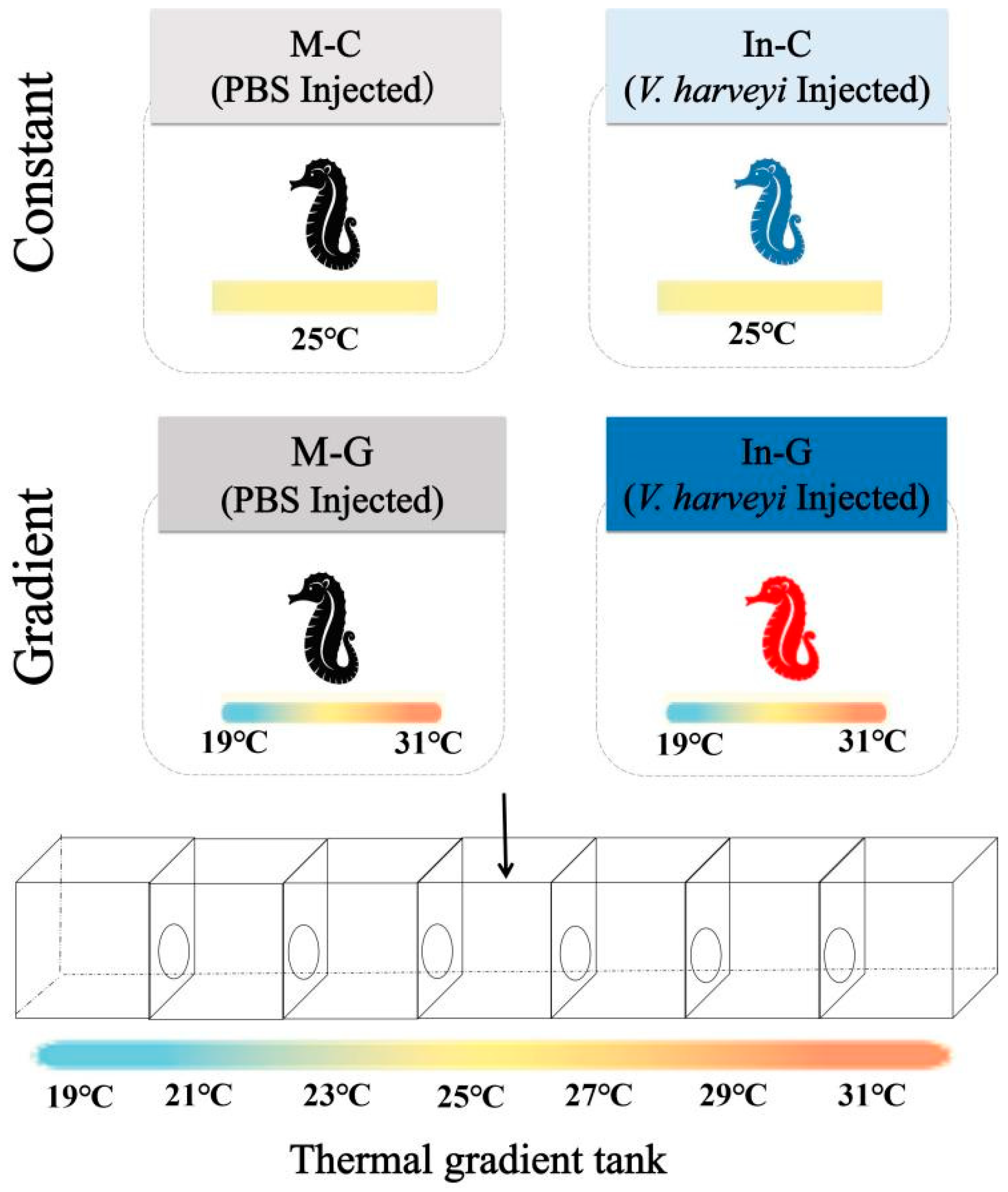
2.2. Thermal Gradient Experiment Setup
2.3. Vibrio Harveyi Challenge and Behavioral Fever Assay
2.4. Behavioral Monitoring and Sample Collection
2.5. Plasma Analysis by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Thermoregulatory Behavior in V. harveyi Challenged Seahorse
3.2. The Onset of Behavioral Fever in Seahorse
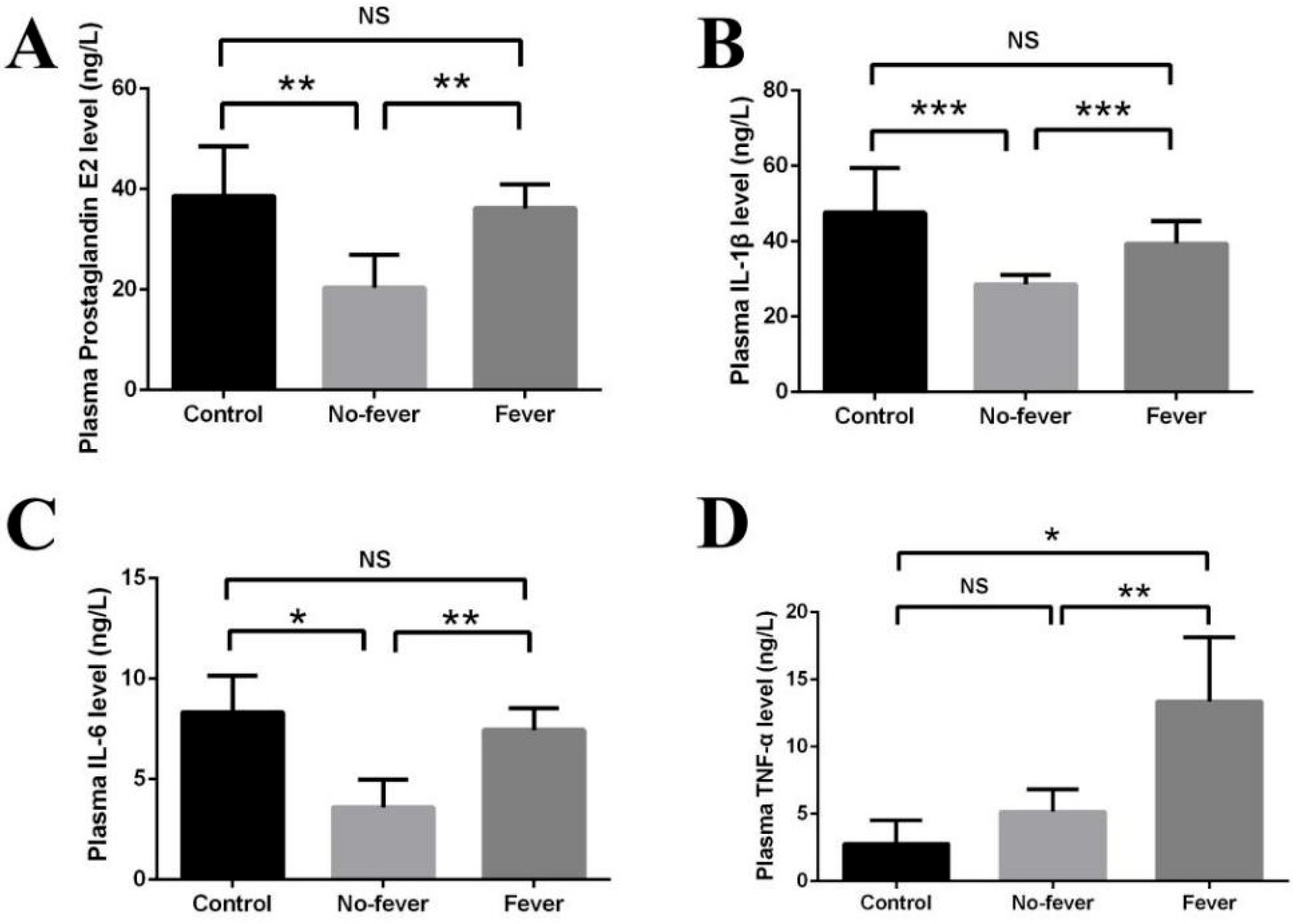
3.3. Effect of Behavioral Fever on Immune Physiology
3.4. Effect of Behavioral Fever on Immune Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, S.S.; Repasky, E.A.; Fisher, D.T. Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: The immune system feels the heat. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Commission for Thermal Physiology of the International Union of Physiological Sciences. Glossary of terms for thermal physiology. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2001, 51, 245–280. [Google Scholar]
- Rakus, K.; Ronsmans, M.; Forlenza, M.; Boutier, M.; Piazzon, M.C.; Jazowiecka-Rakus, J.; Gatherer, D.; Athanasiadis, A.; Farnir, F.; Davison, A.J.; et al. Conserved Fever Pathways across Vertebrates: A Herpesvirus Expressed Decoy TNF-α Receptor Delays Behavioral Fever in Fish. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, W.; Casterlin, M.; Covert, J. Behavioural fever in teleost fishes. Nature 1976, 259, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.Y.; Wei, X.M.; Li, K.; Cao, Y.; Rao, W.Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Wang, D.; Yang, J.L. Cold-blooded vertebrate utilizes behavioral fever to alleviate T cell apoptosis and optimize antimicrobial immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 21, e2408969121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltaña, S.; Aguilar, A.; Sanhueza, N.; Donoso, A.; Mercado, L.; Imarai, M.; Mackenzie, S. Behavioral fever drives epigenetic modulation of the immune response in fish. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltaña, S.; Sanhueza, N.; Donoso, A.; Aguilar, A.; Crespo, D.; Vergara, D.; Arriagada, G.; Morales-Lange, B.; Mercado, L.; Rey, S.; et al. The expression of TRPV channels, prostaglandin E2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines during behavioural fever in fish. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 71, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltaña, S.; Rey, S.; Roher, N.; Vargas, R.; Huerta, M.; Huntingford, F.A.; Goetz, F.W.; Moore, J.; Garcia-Valtanen, P.; Estepa, A.; et al. Behavioural fever is a synergic signal amplifying the innate immune response. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Cytokines as endogenous pyrogens. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Kullberg, B.J.; Van der Meer, J.W.M. Circulating cytokines as mediators of fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, K.; Cao, C.; Ozaki, M.; Morii, H.; Nakadate, K.; Watanabe, Y. Brain endothelial cells express cyclooxygenase-2 during lipopolysaccharide-induced fever: Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical studies. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 6279–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagata, K.; Matsumura, K.; Inoue, W.; Shiraki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yasuda, S.; Sugiura, H.; Cao, C.; Watanabe, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Coexpression of microsomal-type prostaglandin E synthase with cyclooxygenase-2 in brain endothelial cells of rats during endotoxin-induced fever. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, L.; Ruud, J.; Eskilsson, A.; Larsson, A.; Mackerlova, L.; Kugelberg, U.; Qian, H.; Vasilache, A.M.; Larsson, P.; Engblom, D.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced fever depends on prostaglandin E2 production specifically in brain endothelial cells. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, S.; Moiche, V.; Boltaña, S.; Teles, M.; MacKenzie, S. Behavioural fever in zebrafish larvae. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 67, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltaña, S.; Sanhueza, N.; Aguilar, A.; Gallardo-Escarate, C.; Arriagada, G.; Valdes, J.A.; Soto, D.; Quinones, R.A. Influences of thermal environment on fish growth. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6814–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grans, A.; Rosengren, M.; Niklasson, L.; Axelsson, M. Behavioural fever boosts the inflammatory response in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.D.; Blanford, S.; Thomas, M.B. House flies delay fungal infection by fevering: At a cost. Ecol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, A.; Perelberg, A.; Abramovitz, J.; Hutoran, M.; Tinman, S.; Bejerano, I.; Steinitz, M.; Kotler, M. Efficient vaccine against the virus causing a lethal disease in cultured Cyprinus carpio. Vaccine 2003, 21, 4677–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntingford, F.; Rey, S.; Quaggiotto, M.M. Behavioural fever, fish welfare and what farmers and fishers know. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 231, 10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, M.; Chung, K.S.; Manrique, R. Experimental culture of seahorse, Hippocampus erectus. In The Role of Aquaculture in World Fisheries, Proceedings of World Fisheries Congress, Theme 6; Heggberget, T.G., Woiwode, J.G., Wolotira, R.J., Eds.; Science Publishers: New Hampshire, UK, 1989; pp. 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Scarratt, A.M. Techniques for raising lined seahorses (Hippocampus erectus). Aquar. Front. 1998, 3, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Lin, J.D.; Huang, L.M. Effects of substrate color, light intensity and temperature on survival and skin color change of juvenile seahorses, Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810. Aquaculture 2009, 298, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Lin, Q. Growth and survival of juvenile lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus (Perry), at different stocking densities. Aquac. Res. 2010, 42, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Johnson, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Miller, G.; Turingan, R.G.; Guisbert, E.; Lin, Q. Temperature-induced physiological stress and reproductive characteristics of the migratory seahorse Hippocampus erectus during a thermal stress simulation. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio032888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourie, S.A.; Vincent, A.C.J.; Hall, H.J. Seahorse: An Identification Guide to the World’s Species and Their Conservation; Project Seahorse: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.J.; Vincent, A.C.J. Life history and ecology of seahorses: Implications for conservation and management. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, L. Effects of light intensity, stocking density and temperature on the air-bubble disease, survivorship and growth of early juvenile seahorse Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810. Aquac. Res. 2010, 42, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaró, M.; Amaral-Ruiz, M.; Huipe-Zamora, I.; Martınez-Moreno, G.; Simões, N.; Rosas, C. Thermal tolerance and phenotypic plasticity in juvenile Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810: Effect of acute and chronic exposure to contrasting temperatures. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 483, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca-Ruibal, B.; Sainsbury, A.W. Disease of Syngnathidae and their treatment and control. ZooMed. Bull. Br. Vet. Zool. Soc. 2005, 5, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.T.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Xiao, D.X. Variations of immune parameters in the lined seahorse Hippocampus erectus after infection with enteritis pathogen of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldewey, H.J.; Martin-Smith, K.M. A global review of seahorse aquaculture. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.S.; Yan, Z.Z. The administration of Lactobacillus plantarum directly to food: An effective way to improve the survival and growth of juvenile lined seahorses (Hippocampus erectus). Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.T.; Liu, X.; Xiao, D.X.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.S.; Zhu, X.L. Lactobacillus spp. as probiotics for prevention and treatment of enteritis in the lined seahorse (Hippocampus erectus) juveniles. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Liu, X.; Shen, F.Y.; Lin, T.T.; Zhang, D. First insight of the genome-wide association study and genomic prediction into enteritis disease (Vibrio harveyi) resistance trait in the lined seahorse (Hippocampus erectus). Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1474746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.Y.; Tan, A.C.; Nvanti, L.; Sim, S.F.; Grinang, J.; Lee, K.S.P.; Ganval, T. Seasonal variations in water quality of a tropical reservoir: Considerations for cage aquaculture expansion. AACL Bioflux 2018, 11, 333–347. [Google Scholar]
- Cabanac, M.; Gosselin, F. Emotional fever in the lizard Callopistes maculatus (Teiidae). Anim. Behav. 1993, 46, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.; Rey, A.; Silva, T.; Featherstone, Z.; Crumlish, M.; McKenzie, S. Thermal preference predicts animal personality in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordahl, O.; Tibblin, P.; Koch-Schmidt, P.; Berggren, H.; Larsson, P.; Forsman, A. Sun-basking fish benefit from body temperatures that are higher than ambient water. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2018, 285, 0639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalty, K.M.H.; Meek, M.H.; Stephens, M.R.; Rincón, G.; Fangue, N.A.; May, B.P.; Baerwald, M.R. Transcriptional response to acute thermal exposure in Juvenile Chinook salmon determined by RNAseq. G3 2015, 5, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinagre, C.; Madeira, D.; Mendonça, V.; Dias, M.; Roma, J.; Diniz, M.S. Effect of increasing temperature in the differential activity of oxidative stress biomarkers in various tissues of the Rock goby, Gobius paganellus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 97, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.V.; O’Connor, C.M.; Gilmour, K.M.; Cooke, S.J. The glucocorticoid stress response is repeatable between years in a wild teleost fish. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2011, 197, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, J.; Janssen, H.; Kuske, A.; Kurtz, J.; Scharsack, J.P. Heat and immunity: An experimental heat wave alters immune functions in three-spined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Primer 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| tnf-α | F:TGCCAGCACAGCAGTTCG |
| R:TTGCCGCCGTCCGTTT | |
| il-1β | F:CAAGCACAACCCTAACCACA |
| R:GAGACCTCCAGGCTCAATCC | |
| il-6 | F:CTCCTCCAACTTCAGCAAGG |
| R:TGTGACCTCCTCTGGCTTTT | |
| ifn-g | F:CGCCTACTTGTGTCTGTGTC |
| R:GCAGCTCCTCGTACGTCT | |
| il-2 | F:ACTCGCTCCACTGGCTTCC |
| R:CCCTGCTCTGTGCTCCTCA | |
| il-10 | F:GAGGACACGAGGGACTTGAA |
| R:AGCTCGCCCATAGCTTTGTA | |
| tlr5 | F:ACGTTACATATTTGGACATTCGG |
| R:TCAAGGTCAAACTGAGCAAATGG | |
| pis | F:CTGGTCACGCTCTTCCTG |
| R:TGTCGGTTCTCCCAAGC | |
| β-actin | F:ACCATGTACCCTGGCATTG |
| R:TCATACTCCTGCTTGCTGAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, D. Behavioral Fever in Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectu) Enhances the Immune Response to Vibrio harveyi Infection. Animals 2025, 15, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111509
Li S, Liu X, Lin T, Zhang D. Behavioral Fever in Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectu) Enhances the Immune Response to Vibrio harveyi Infection. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Siping, Xin Liu, Tingting Lin, and Dong Zhang. 2025. "Behavioral Fever in Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectu) Enhances the Immune Response to Vibrio harveyi Infection" Animals 15, no. 11: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111509
APA StyleLi, S., Liu, X., Lin, T., & Zhang, D. (2025). Behavioral Fever in Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectu) Enhances the Immune Response to Vibrio harveyi Infection. Animals, 15(11), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111509







