Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Compound Soy Protein on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Juvenile American Eels (Anguilla rostrata)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Diet Preparation and Fish Culture
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Growth Performance
2.5. Proximate Composition, Amino Acid Composition, and Antinutritional Factors
2.6. Serum Biochemical Indexes
2.7. Activities of Intestinal Digestive Enzymes
2.8. Intestinal Antioxidant Parameters
2.9. Histological Observation
2.10. Intestinal Microbiota Profiling
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Body Composition
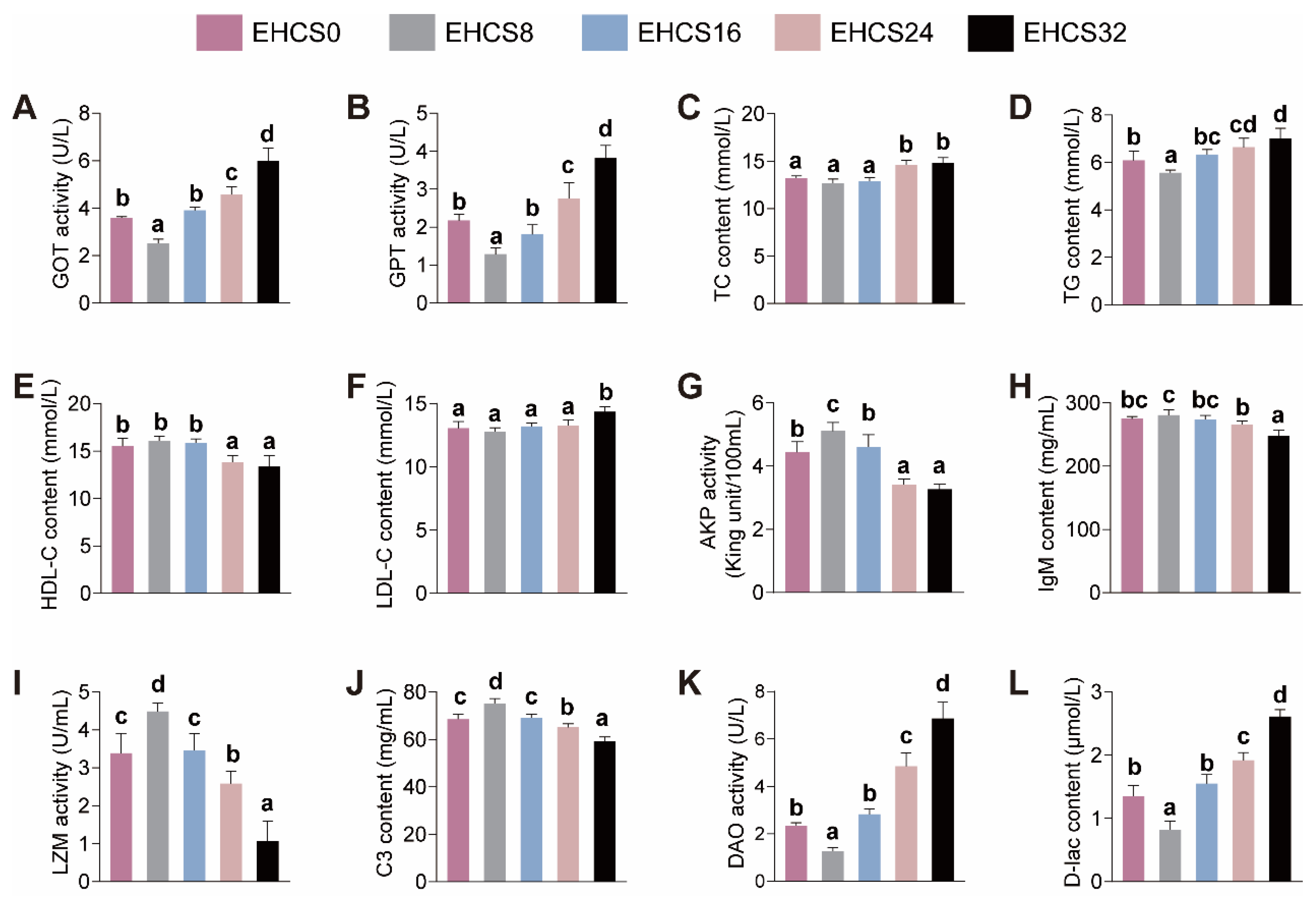
3.3. Serum Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Intestinal Histology
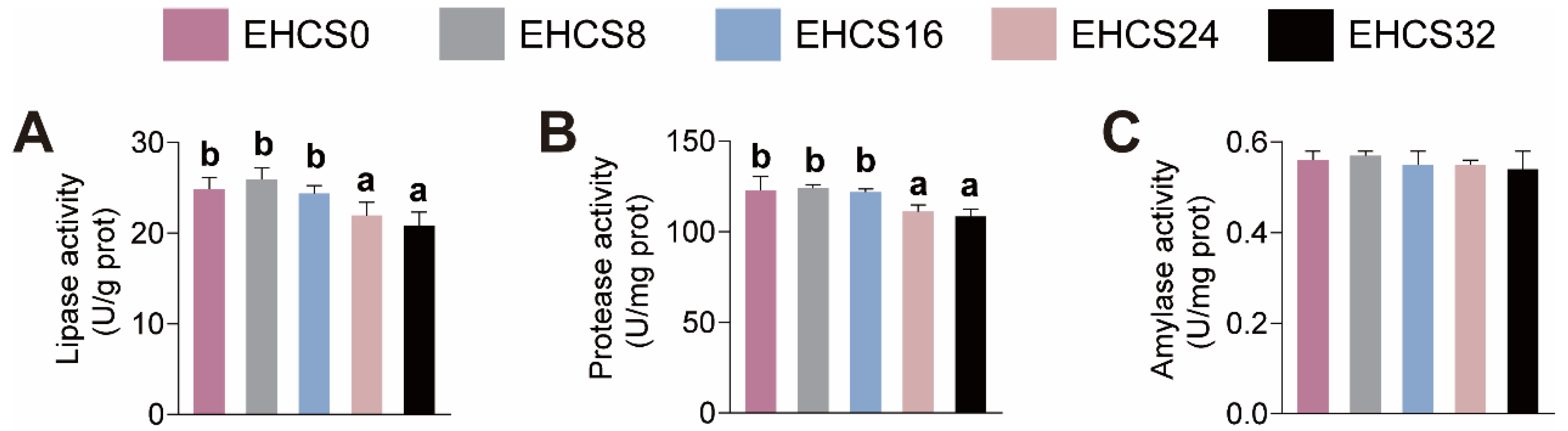
3.5. Intestinal Digestive Enzymes Activities
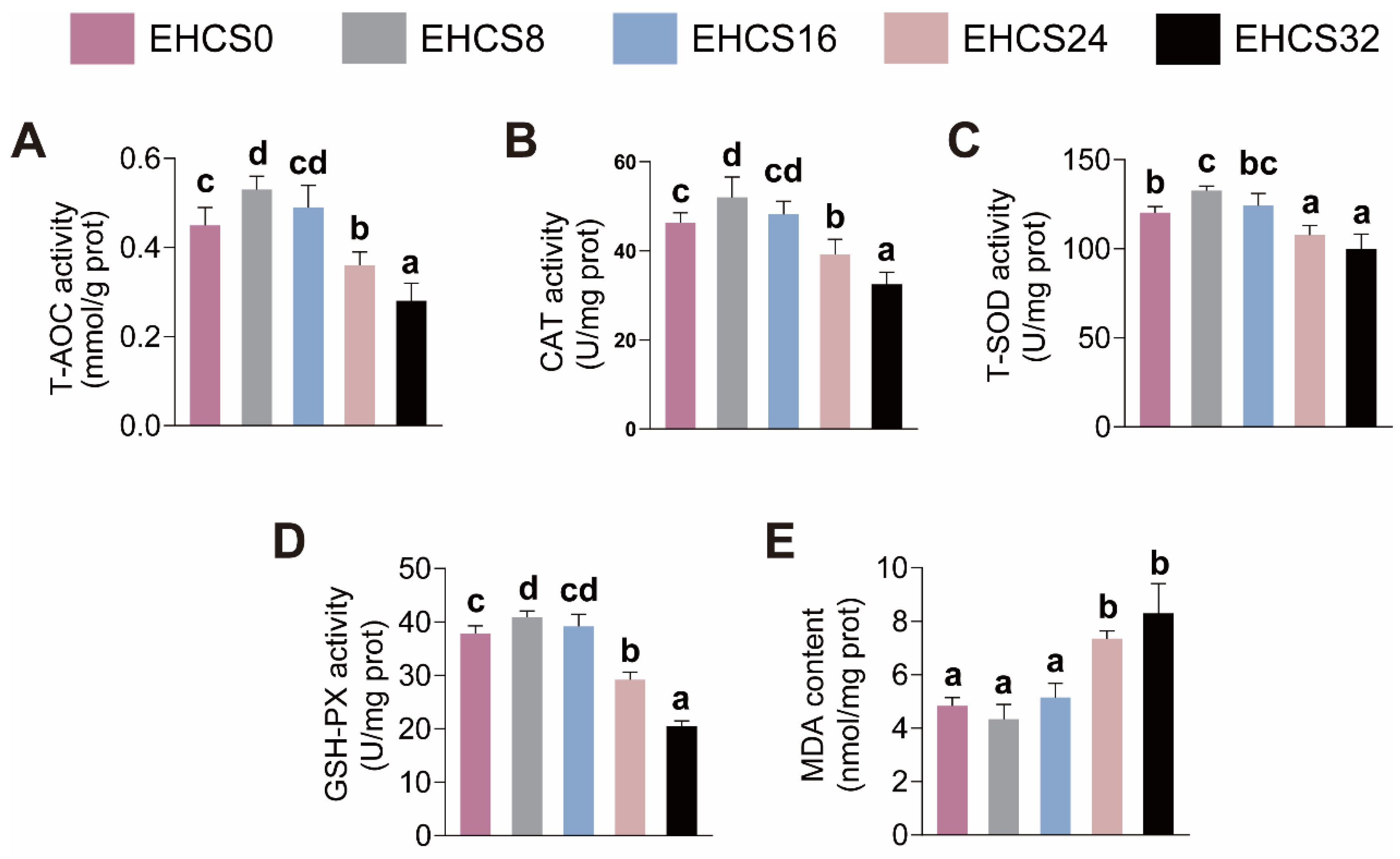
3.6. Intestinal Antioxidant Capacity
3.7. Intestinal Microbiota
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Performance
4.2. Body Composition
4.3. Serum Biochemical Parameters
4.4. Intestinal Health
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Fish meal—Nutritive value. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Bureau, D.P.; Chiu, A.; Elliott, M.; Farrell, A.P.; Forster, I.; Gatlin, D.M.; Goldburg, R.J.; Hua, K.; et al. Feeding aquaculture in an era of finite resources. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15103–15110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulu, S.; Langi, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Missinhoun, D.; Munganga, B.P.; Hampuwo, B.M.; Gabriel, N.N.; Elsabagh, M.; Van Doan, H.; Abdul Kari, Z.; et al. Recent advances in the utilization of insects as an ingredient in aquafeeds: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibaldi, E.; Hakim, Y.; Uni, Z.; Tulli, F.; de Francesco, M.; Luzzana, U.; Harpaz, S. Effects of the partial substitution of dietary fish meal by differently processed soybean meals on growth performance, nutrient digestibility and activity of intestinal brush border enzymes in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 2006, 261, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Li, X.; Cai, X.B.; Zhang, S.X.; Hua, X.M.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, N.Y.; Yao, J.T. Effects of enzymatic hydrolyzed soybean meal on growth performance, liver function and metabolism of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.; Li, E.; Qin, J.; Chen, L. Partial replacement of fish meal by enzymatically hydrolyzed soybean does not adversely impact the growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immunity and intestinal health of the juvenile Eriocheir sinensis. Aquacult. Rep. 2024, 36, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.D.; Bharadwaj, A.S.; Brown, P.B. Soybean lectins and trypsin inhibitors, but not oligosaccharides or the interactions of factors, impact weight gain of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2010, 306, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Do, T.V.; Tran, H.D. Dietary replacement of fish meal by defatted and fermented soybean meals with taurine supplementation for pompano fish: Effects on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and biological parameters in a long-term feeding period. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, F.; Sui, X.; Fang, Y.; Tang, X.; Shen, X. Assessment the flavor of soybean meal hydrolyzed with Alcalase enzyme under different hydrolysis conditions by E-nose, E-tongue and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J. Small peptides isolated from enzymatic hydrolyzate of fermented soybean meal promote endothelium-independent vasorelaxation and ACE inhibition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10844–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Cai, G.; Zhai, S. Effects of dietary supplementation of peanut skin proanthocyanidins on growth performance and lipid metabolism of the juvenile American eel (Anguilla rostrata). Animals 2022, 12, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 18246-2019; Determination of amino acids in feeds, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Guo, J.; Tan, X.; Zhao, T.; Song, Y.F.; Wei, X.; Luo, Z. Effects of different dietary zinc (Zn) sources on growth performance, Zn metabolism, and intestinal health of grass carp. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Yu, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhai, S. Evaluation of methanotroph (Methylococcus capsulatus, bath) bacteria protein as an alternative to fish meal in the diet of juvenile American eel (Anguilla rostrata). Animals 2023, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamauag, R.E.P.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Gao, J.; Nguyen, B.T.; Ragaza, J.A. Soy peptide inclusion levels influence the growth performance, proteolytic enzyme activities, blood biochemical parameters and body composition of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 2011, 321, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.D.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Sun, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.M. Effects of fishmeal replacement with soy protein hydrolysates on growth performance, blood biochemistry, gastrointestinal digestion and muscle composition of juvenile starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Aquaculture 2014, 426, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Gutiérrez, E.; Rodriguez-Armenta, C.; González-Félix, M.L.; Perez-Velazquez, M. Incorporating hydrolyzed soy protein or black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal into feeds for Totoaba macdonaldi. Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Luo, K.; Rao, W.; Chen, P.; Lei, K.; Liu, C.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Effects of replacing dietary fish meal with enzyme-treated soybean meal on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, immunity and mTOR pathway in abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 30, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, A.J.; Williams, K.; Festa, A.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; D’Agostino, R.B., Jr.; Haffner, S.M. Liver markers and development of the metabolic syndrome: The insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3140–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Han, F. Lysozymes in fish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15039–15051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.C.; Lv, J.; He, H.; Huang, W.; Han, Y. Hepatoprotective effects of corn peptides against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. J. Food Biochem. 2012, 36, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.Y.; Xiao, W.W.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, W.D.; Hu, K.; Li, S.H.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Effects of graded levels of dietary methionine hydroxy analogue on immune response and antioxidant status of immune organs in juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcik, M.; Grabowski, S.; Jarosz, Ł.S.; Szymczak, B.; Longo, V.; Della Croce, C.M.; Hejdysz, M.; Cieślak, A.; Gruszczyński, K.; Marek, A. Liver antioxidant capacity and steatosis in laying hens exposed to various quantities of lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) seeds in the diet. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, B.W.; Palmer, M.K.; Nicholls, S.J.; Lundman, P.; Barter, P.J. Doses of rosuvastatin, atorvastatin and simvastatin that induce equal reductions in LDL-C and non-HDL-C: Results from the VOYAGER meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 744–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.C.; Zheng, H.; Hogstrand, C.; Tan, X.Y.; Zhao, T.; Song, Y.F.; Wei, X.L.; Wu, L.X.; Luo, Z. Novel mechanism for zinc inducing hepatic lipolysis via the HDAC3-mediated deacetylation of β-catenin at lysine 311. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 121, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, R.; Fukunaga, K.; Arai, H.; Nishiyama, T.; Yoshida, M. Effects of dietary fish protein on serum and liver lipid concentrations in rats and the expression of hepatic genes involved in lipid metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9256–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Zhou, Y.; Nidhina Haridas, P.A.; Dwivedi, O.P.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Ali, A.; Juuti, A.; Leivonen, M.; Tukiainen, T.; Ahonen, L.; et al. Impaired hepatic lipid synthesis from polyunsaturated fatty acids in TM6SF2 E167K variant carriers with NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Gu, Y.F. Cloning and expression pattern of alkaline phosphatase during the development of Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Ding, L.; Xu, Z. Immunoglobulins, mucosal immunity and vaccination in teleost fish. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 567941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpour, B.; Cardoso, J.C.R.; Canário, A.V.M.; Power, D.M. Specific evolution and gene family expansion of complement 3 and regulatory factor H in fish. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 568631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Bi, H.; Yang, B. Structure identification of soybean peptides and their immunomodulatory activity. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Simpson, B.K.; Sun, H.; Ngadi, M.O.; Ma, Y.; Huang, T. Phaseolus vulgaris lectins: A systematic review of characteristics and health implications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ma, D.; Ma, Z.; Zhai, S. The effects of coated inorganic trace minerals on the growth performance, mineral retention, and intestinal health comparing with inorganic and organic trace minerals for juvenile American eels (Anguilla rostrata). Aquacult. Rep. 2024, 38, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.; Howarth, G.S.; Kitessa, S.M.; Tran, C.D.; Forder, R.E.A.; Hughes, R.J. Intestinal permeability induced by lipopolysaccharide and measured by lactulose, rhamnose and mannitol sugars in chickens. Animal 2017, 11, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Usman, S.; Ding, Z.; Hao, L.; Guo, X. Probiotic effect of ferulic acid esterase-producing Lactobacillus plantarum inoculated alfalfa silage on digestion, antioxidant, and immunity status of lactating dairy goats. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper, D.T.; Rymer, C.; Briens, M. Bioefficacy of hydroxy-selenomethionine as a selenium supplement in pregnant dairy heifers and on the selenium status of their calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7000–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yang, B.; Lv, Y.; Guo, S. Protective and reparative effects of peptides from soybean β-conglycinin on mice intestinal mucosa injury. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tong, X.; Sui, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Antioxidant activity and protective effects of Alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean hydrolysate in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Gong, Y.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Effects of fishmeal substitution by α-galactosidase hydrolytic soybean meal (EhSBM) on growth, antioxidant capacity, inflammatory responses and intestinal health of turbot juveniles (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.D.; Hu, K.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.N.; et al. Soyabean glycinin depresses intestinal growth and function in juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var Jian): Protective effects of glutamine. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, K.; Deng, J.; Huang, R.; Yin, Y. Imbalanced dietary methionine-to-sulfur amino acid ratio can affect amino acid profiles, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal morphology of piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Jiang, W.D.; Duan, X.D.; Feng, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Soybean glycinin caused NADPH-oxidase-regulated ROS overproduction and decreased ROS elimination capacity in the mid and distal intestine of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L.; Vendrell, D.; de Blas, I.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Muzquiz, J.L.; Girones, O. Characterization of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from intestinal microbiota of fish. Aquaculture 2008, 278, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.Z.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, P.W.; Chen, J.X. A review of antibiotics, depression, and the gut microbiome. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 284, 112691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Huang, H.; Nie, Y. Genomic insights from Paraclostridium bifermentans HD0315_2: General features and pathogenic potential. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 928153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaitlina, S.; Bozhokina, E.; Tsaplina, O.; Efremova, T. Bacterial actin-specific endoproteases grimelysin and protealysin as virulence factors contributing to the invasive activities of Serratia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Zuluaga, K.; Hiles, R.; Barua, P.; Caldwell, D.; Iyer-Pascuzzi, A.S. Getting to the root of Ralstonia invasion. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 148–149, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Shoaie, S.; Jacquiod, S.; Sørensen, S.J.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. Comparative genomics analysis of keratin-degrading Chryseobacterium species reveals their keratinolytic potential for secondary metabolite production. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe-Espinoza, P.; Brown, D.M.; Weedon, J.T.; Braster, M.; Brandt, B.W.; Bonte, M.; van Spanning, R.J. Microbial communities associated with landfarming amendments during bioremediation of crude oil in Niger Delta soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Pembroke, J.T. Brevundimonas spp.: Emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Virulence 2018, 9, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ingredients (%) | EHCS0 | EHCS8 | EHCS16 | EHCS24 | EHCS32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHCS | 0.00 | 8.00 | 16.00 | 24.00 | 32.00 |
| White fishmeal | 32.00 | 24.00 | 16.00 | 8.00 | 0.00 |
| Brown fishmeal | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 |
| α-starch | 26.00 | 25.50 | 25.00 | 24.50 | 24.00 |
| Fish oil | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 2.50 |
| Choline chloride | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Mineral premix a | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Vitamin premix b | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Proximate analysis %, dry weight | |||||
| Moisture | 7.24 | 7.47 | 7.68 | 7.95 | 7.84 |
| Crude protein | 48.93 | 48.64 | 48.19 | 48.21 | 47.77 |
| Crude lipid | 6.72 | 6.58 | 6.60 | 6.45 | 6.54 |
| Ash | 11.80 | 10.80 | 9.87 | 8.63 | 7.61 |
| Calcium | 3.08 | 2.70 | 2.30 | 1.86 | 1.39 |
| Phosphorus | 2.04 | 1.91 | 1.71 | 1.50 | 1.28 |
| Total energy | 18.56 | 18.65 | 18.75 | 18.88 | 19.07 |
| EHCS0 | EHCS8 | EHCS16 | EHCS24 | EHCS32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Essential amino acid (EAA) | |||||
| Lysine | 3.71 | 3.63 | 3.55 | 3.47 | 3.38 |
| Methionine | 1.29 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 1.20 | 1.17 |
| Threonine | 2.13 | 2.06 | 1.99 | 1.92 | 1.85 |
| Tryptophan | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.56 |
| Leucine | 3.55 | 3.50 | 3.44 | 3.39 | 3.34 |
| Arginine | 2.72 | 2.72 | 2.71 | 2.71 | 2.71 |
| Histidine | 1.60 | 1.58 | 1.56 | 1.54 | 1.52 |
| Valine | 2.38 | 2.33 | 2.28 | 2.22 | 2.17 |
| Isoleucine | 2.02 | 2.00 | 1.98 | 1.97 | 1.95 |
| Phenylalanine | 1.73 | 1.75 | 1.78 | 1.81 | 1.84 |
| Total EAA | 21.65 | 21.36 | 21.07 | 20.77 | 20.48 |
| Non-essential amino acid (NEAA) | |||||
| Aspartic acid | 4.31 | 4.31 | 4.31 | 4.31 | 4.31 |
| Cysteine | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.50 |
| Tyrosine | 1.72 | 1.66 | 1.59 | 1.52 | 1.46 |
| Serine | 1.93 | 1.92 | 1.90 | 1.89 | 1.87 |
| Glutamate | 6.07 | 6.18 | 6.29 | 6.39 | 6.50 |
| Proline | 1.91 | 1.90 | 1.89 | 1.87 | 1.86 |
| Glycine | 2.96 | 2.81 | 2.66 | 2.52 | 2.37 |
| Alanine | 2.92 | 2.80 | 2.69 | 2.57 | 2.45 |
| Total NEAA | 22.30 | 22.05 | 21.81 | 21.56 | 21.31 |
| Before Enzymatic Hydrolysis | After Enzymatic Hydrolysis | |
|---|---|---|
| Trypsin inhibitor factor | 1.75 | 1.30 |
| Glycinin | 23.60 | <2.00 |
| β-conglycinin | 31.90 | 3.00 |
| EHCS0 | EHCS8 | EHCS16 | EHCS24 | EHCS32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBW (g) | 26.00 ± 0.01 | 25.99 ± 0.02 | 26.01 ± 0.04 | 26.00 ± 0.01 | 26.01 ± 0.02 |
| FBW (g) | 49.90 ± 0.73 c | 52.77 ± 0.83 d | 49.96 ± 0.52 c | 46.61 ± 0.66 b | 42.86 ± 0.81 a |
| WGR (%) | 91.91 ± 2.78 c | 103.06 ± 3.29 d | 92.06 ± 2.04 c | 79.32 ± 2.63 b | 64.76 ± 3.04 a |
| SGR (%/d) | 0.93 ± 0.02 c | 1.01 ± 0.02 d | 0.93 ± 0.02 c | 0.84 ± 0.02 b | 0.71 ± 0.03 a |
| FI (g) | 32.15 ± 0.78 c | 34.32 ± 1.48 d | 31.87 ± 0.63 c | 30.16 ± 0.26 b | 28.08 ± 0.12 a |
| FE (%) | 74.34 ± 0.84 c | 78.07 ± 1.29 d | 75.14 ± 0.42 c | 68.37 ± 2.44 b | 60.01 ± 2.87 a |
| FCR | 1.35 ± 0.02 a | 1.28 ± 0.02 a | 1.33 ± 0.01 a | 1.46 ± 0.05 b | 1.67 ± 0.08 c |
| PER (%) | 154.42 ± 1.74 c | 162.91 ± 2.71 d | 157.49 ± 0.87 cd | 143.94 ± 5.14 b | 126.91 ± 6.08 a |
| SR (%) | 95.00 ± 2.00 b | 96.00 ± 3.27 b | 96.00 ± 3.27 b | 93.00 ± 8.25 ab | 87.00 ± 3.83 a |
| EHCS0 | EHCS8 | EHCS16 | EHCS24 | EHCS32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 68.43 ± 1.05 | 67.99 ± 1.10 | 69.09 ± 0.61 | 70.15 ± 2.40 | 69.24 ± 1.20 |
| Crude protein (%) | 17.95 ± 0.64 | 18.49 ± 0.50 | 18.06 ± 0.60 | 17.71 ± 0.25 | 18.07 ± 0.65 |
| Crude lipid (%) | 9.13 ± 0.34 | 9.04 ± 0.52 | 9.01 ± 0.30 | 8.64 ± 0.36 | 8.68 ± 0.23 |
| Ash (%) | 2.06 ± 0.25 | 1.95 ± 0.13 | 2.03 ± 0.22 | 2.12 ± 0.23 | 2.26 ± 0.07 |
| Calcium (g kg−1) | 4.35 ± 0.15 | 4.33 ± 0.17 | 4.24 ± 0.13 | 4.18 ± 0.11 | 4.36 ± 0.19 |
| Phosphorus (g kg−1) | 3.56 ± 0.50 | 3.49 ± 0.49 | 3.64 ± 0.26 | 3.74 ± 0.43 | 4.05 ± 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, P.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Zhai, S. Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Compound Soy Protein on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Juvenile American Eels (Anguilla rostrata). Animals 2024, 14, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213096
Xu Y, Wu C, Wang P, Han X, Yang J, Zhai S. Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Compound Soy Protein on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Juvenile American Eels (Anguilla rostrata). Animals. 2024; 14(21):3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213096
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yichuang, Chengyao Wu, Pan Wang, Xiaozhao Han, Jinyue Yang, and Shaowei Zhai. 2024. "Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Compound Soy Protein on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Juvenile American Eels (Anguilla rostrata)" Animals 14, no. 21: 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213096
APA StyleXu, Y., Wu, C., Wang, P., Han, X., Yang, J., & Zhai, S. (2024). Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Compound Soy Protein on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Juvenile American Eels (Anguilla rostrata). Animals, 14(21), 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213096







