Myocarditis in an FIP-Diseased Cat with FCoV M1058L Mutation: Clinical and Pathological Changes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
2.1. Clinical Exam at the VTH
2.2. Blood Analysis
2.3. Ultrasound Investigation and Effusion Analysis
2.4. Therapy
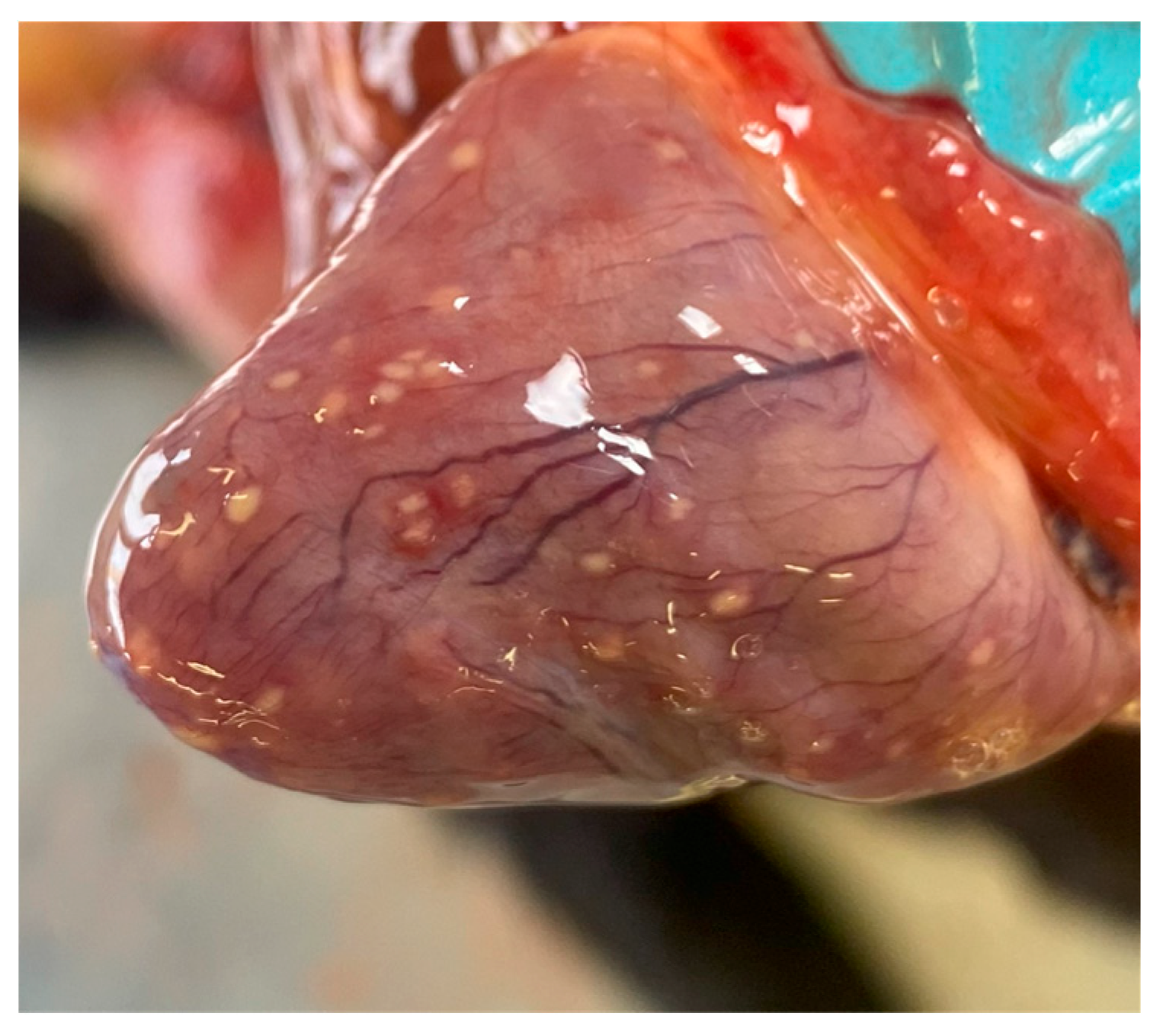
2.5. Euthanasia, Post-Mortem Examination, and Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Investigations
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felten, S.; Hartmann, K. Diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis: A review of the current literature. Viruses 2019, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.D.; Belak, S.; Bourcraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffyd-Jones, T.; Hartman, K.; Hosie, M.J.; Lloret, A.; Lutz, H.; et al. Feline Infectious peritonitis. ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Mari, V.; Lanave, G.; Lorusso, E.; Lucente, M.S.; Desario, C.; Colaianni, M.L.; Elia, G.; Ferrigno, F.; Alfano, F.; et al. Mutation analysis of the spike protein in Italian feline infectious peritonitis virus and feline enteric coronavirus sequences Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.I.; Baptiste, K.E.; Bowker, L.J.; Lutz, H. Sites of feline coronavirus persistence in healthy cats. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, D.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.B.; Wang, K.; Hu, G.X.; Gao, F.S. An updated review of feline coronavirus: Mind the two biotypes. Virus Res. 2023, 326, 199059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.; Kipar, A.; Muller, C.; Jenal, K.; Gonczi, E.; Borel, N.; Gunn-Moore, D.; Chalmers, S.; Lin, F.; Reinacher, M.; et al. High viral loads despite absence of clinical and pathological findings in cats infected with feline coronavirus (FCoV) type I and naturally FCoV infected cats J. Feline Med. Surg. 2004, 6, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewerchin, H.L.; Cornelissen, E.; Nauwynck, H.J. Replication of feline coronavirus in peripheral blood monocytes Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 2483–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Dodd, K.A.; Pesavento, P.A. Significance of coronavirus mutants in feces and diseased tissues of cats suffering from feline infectious peritonitis. Viruses 2009, 1, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Gandolfi, B.; Lyons, L.A. The influence of age and genetics on natural resistance to experimentally induced feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 162, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Troyer, J.L.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Roelke, M.E.; O’Brien, S.J. Genetics and pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, L.G.; Grisemer, R.A. Feline infectious peritonitis. Pathol. Vet. 1966, 3, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Boyle, J.F.; Floyd, K.; Fudge, A.; Baker, J. An enteric coronavirus infection of cats and its relationship with feline infectious peritonitis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1981, 42, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ernandes, M.A.; Cantoni, A.M.; Armando, F.; Corradi, A.; Ressel, L.; Tamborini, A. Feline coronavirus-associated myocarditis in domestic longhair cat. JFMS Open Rep. 2019, 5, 2055116919879256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Ichikawa, N.; Koike, M.; Hirokawa, T.; Sasaoka, K.; Machida, N.; Taguchi, M. Two feline cases of dilated cardiomyopathy-like disease caused by feline infectious peritonitis virus. J. Anim. Clin. Med. 2016, 25, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bank-Wolf, B.R.; Stalikamp, I.; Wiese, S.; Moritz, A.; Teske, G.; Thiel, H.J. Mutation of 3c and spike protein genes correlate with the occurrence of feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 117–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline coronavirus: Insight into viral pathogenesis based on the spike protein structure and function. Virology 2018, 517, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Liu, J.; Yin, Y.; Cao, S.; Yan, R.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Liao, X.; et al. Epidemiology and comparative analysis of the S gene on feline coronavirus in central China. Pathogens 2022, 11, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, K.; Chang, H.W.; Rottier, P.J.M. Differential susceptibility of macrophages to serotype II feline coronaviruses correlates with differences in the viral spike protein. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangl, L.; Matiasek, K.; Felten, S.; Gründl, S.; Bergmann, M.; Balzer, H.J.; Pantchev, N.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hartmann, K. Detection of feline coronavirus mutations in paraffin-embedded tissues in cats with feline infectious peritonitis and controls. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVMA Panel on Euthanasia. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-882691-09-8. Version 2020.0.1. [Google Scholar]
- Tasker, S. Diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis: Update on evidence supporting available tests. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, K. Feline coronavirus and feline infectious peritonitis. In Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 8th ed.; Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2017; pp. 983–989. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, J.V.; Poma, R. Neurology diagnosis and clinical signs of feline infectious peritonitis in the central nervous system. Can. Vet. J. 2019, 50, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Cave, T.A.; Thompson, H.; Reid, S.W.; Hodgson, D.R.; Addie, D.D. Kitten mortality in the United Kingdom: A retrospective analysis of 274 histopathological examinations (1986 to 2000). Vet. Rec. 2002, 151, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbach, B.W.; Legendre, A.M.; Baldwin, C.A.; Lein, D.H.; Reed, W.M.; Wilson, R.B. Epidemiology of feline infectious peritonitis among cats examined at veterinary medical teaching hospitals. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, K. Feline infectious peritonitis – new developments in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Thai J. Vet. Med. Suppl. 2017, 47, S97–S100. [Google Scholar]
- Stranieri, A.; Scavone, D.; Paltrinieri, S.; Giordano, A.; Bonsembiante, S.; Ferro, S.; Gelan, M.E.; Meazzi, S.; Lauzi, S. Concordance between histology, immunohistochemistry, and RT-PCR in the diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 852–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.Y.; Jo, J.G.; Song, K.H.; Seo, K.W. Recurrent pericardial effusion with feline infectious peritonitis in a cat. J. Vet. Clin. 2017, 34, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Xiaoya, L.; Ouyang, H.; Ji, W.; Jiahao, L.; Xueyu, L.; Junyi, L.; Changmin, H. A retrospective study of clinical and laboratory features and treatment on cats highly suspected of feline infectious peritonitis in Wuhan, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5208–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, A.N.; Andre, N.M.; Stout, A.E.; Licitra, B.N.; Whittaker, G.R. Clinical and molecular relationships between COVID-19 and feline infectious peritonitis (FIP). Viruses 2022, 14, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, F.; Kuehner, K.A.; Ritz, S.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Clinical and laboratory features of cats with feline infectious peritonitis—A retrospective study of 231 confirmed cases (2000–2010). J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; O’Brien, R.T. Abdominal ultrasonographic findings associated with feline infectious peritonitis: A retrospective review of 16 cases. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2010, 46, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, D.; Kwok, W.; Graham, E.; Armitage, A.; Irvine, R.; Johnston, P.; McDonald, M.; Montgomery, D.; Nicolson, L.; Robertson, E.; et al. Diagnosis of non-effusive feline infectious peritonitis by reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR from mesenteric lymph node fine-needle aspirates. J. Feline. Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziolkowska, N.; Pazdzior-Czapula, K.; Lewczuk, B.; Mikulska-Skupien, E.; Przybylska-Gornowicz, B.; Kwiecinska, K.; Ziolkowski, H. Feline infectious peritonitis: Immunohistochemical features of ocular inflammation and the distribution of viral antigens in structures of the eye. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 54, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, K.L.; Joseph, R.J.; Averdill, D.R. Feline infectious peritonitis with neurologic involvement: Clinical and pathological findings in 24 cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1994, 30, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Olarte-Castillo, X.A.; Licitra, B.N.; Abdré, N.M.; Sierra, M.A.; Mason, C.E.; Goodman, L.B.; Whittaker, G.R. Intra-host variation in the spike S1/S2 region of feline coronavirus type-1 in a cat with persistent infection. bioRxiv 2023, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Lenehan, P.J.; Nielsen, M.; Yoo, U.; Patwardhan, D.; Montorzi, M.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Soundararajan, V. Genetic alteration of human MYH6 is mimicked by SARS-CoV2 polyprotein: Mapping viral variants of cardiac interest. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 124–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltrinieri, S.; Giordano, A.; Stranieri, A.; Lauzi, S. Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) and coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19): Are they similar? Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value | Reference Interval (RI) |
|---|---|---|
| RBCs | 7.43 | 5–10 × 106/μL |
| Hemoglobin | 9 | 8–14 g/dL |
| Hematocrit | 26.3 | 24–45% |
| MCV | 35.4 | 41.3–52.6 |
| MCHC | 34.2 | 30–36 |
| Leucocytes | 28,300 | 5000–19,000/mm3 |
| Neutrophils | 24,340 | 2000–125,000/μL |
| Lymphocytes | 2480 | 1500–7000/μL |
| Monocytes | 1200 | 100–850/μL |
| Eosinophils | 60 | 0–750/μL |
| Basophils | 20 | 0/μL |
| Platelets | 20 | 156–624 × 103/μL |
| Parameter | Value | Reference Interval (RI) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 5437 | 91–326 U/L |
| LDH | 1973 | 63–193 U/L |
| AST | 1226 | 14–41 U/L |
| ALT | 335 | 5–45 U/L |
| SAP | 31 | 19–70 U/L |
| GGT | 1 | 0–8 U/L |
| Bilirubin | 3.49 | 0–0.7 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol | 144 | 64–229 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides | 154 | 19–81 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 0.54 | 0.8–1.80 mg/dL |
| Urea | 99 | 15–60 mg/dL |
| Glucose | 41 | 75–160 mg/dL |
| Total proteins | 7.66 | 6.0–8.0 g/dL |
| Albumin | 1.88 | 2.10–3.30 g/dL |
| Phosphorus | 7.92 | 2.9–8.3 mg/dL |
| Calcium | 5.6 | 7.3–10.5 mg/dL |
| Sodium | 129 | 141–156 mEq/L |
| Potassium | 3.9 | 3.6–4.5 mEq/L |
| Chlorine | 112 | 112–119 mEq/L |
| Magnesium | 3 | 1.8–2.5 mg/dL |
| Iron | 95 | 50–118 μg/dL |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| TNCC | 6420 cells/mm3 |
| Bilirubin | 3.02 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 0.75 mg/mL |
| Triglycerides | 59 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol | 96 mg/dL |
| Potassium | 3.80 mEq/L |
| Total proteins | 5.7 g/dL |
| Albumin | 1.4 g/dL |
| A/G | 0.3 |
| Test | Result |
|---|---|
| Feline coronavirus RNA (real-time PCR) | Positive |
| Mutation M1058L single-nucleotide variations (SNVs) S-RT-rtPCR | Positive |
| Mutation S1060A single-nucleotide variations (SNVs) S-RT-rtPCR | Negative |
| Biotype | FIPV |
| Antibody | Supplier and Code | Clonality | Retrieval | Dilution | Incubation | Labeling System | Visualization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIPV (feline coronavirus) | BioRad, clone FIPV3-70 (MCA2194) | mouse monoclonal | Buffer H, pH 9.0, in 100 °C water bath | 1:2000 | 1 h 30 min at RT | ABC-peroxidase | DAB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarnieri, C.; Bertola, L.; Ferrari, L.; Quintavalla, C.; Corradi, A.; Di Lecce, R. Myocarditis in an FIP-Diseased Cat with FCoV M1058L Mutation: Clinical and Pathological Changes. Animals 2024, 14, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111673
Guarnieri C, Bertola L, Ferrari L, Quintavalla C, Corradi A, Di Lecce R. Myocarditis in an FIP-Diseased Cat with FCoV M1058L Mutation: Clinical and Pathological Changes. Animals. 2024; 14(11):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111673
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarnieri, Chiara, Luca Bertola, Luca Ferrari, Cecilia Quintavalla, Attilio Corradi, and Rosanna Di Lecce. 2024. "Myocarditis in an FIP-Diseased Cat with FCoV M1058L Mutation: Clinical and Pathological Changes" Animals 14, no. 11: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111673
APA StyleGuarnieri, C., Bertola, L., Ferrari, L., Quintavalla, C., Corradi, A., & Di Lecce, R. (2024). Myocarditis in an FIP-Diseased Cat with FCoV M1058L Mutation: Clinical and Pathological Changes. Animals, 14(11), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111673








