Genome-Wide Association Studies of Somatic Cell Count in the Assaf Breed
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Genotyping
2.2.1. GWAS
2.2.2. SNP Genotyping in GWAS Validation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Corrected Phenotype Values for the Somatic Cell Score (SCS) Data
2.3.2. Quality Control (QC)
2.3.3. Stratification Analysis
2.3.4. Genome-Wide Association Analyses (GWAS)
2.3.5. Gene Association Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotype and SNP Data of GWAS
3.2. Genome-Wide Association Analyses (GWAS)
3.3. Validation Studies in the ASSAF Total Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schukken, Y.H.; Gunther, J.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Fontaine, M.C.; Goetze, L.; Holst, O.; Leigh, J.; Petzl, W.; Schuberth, H.J.; Sipka, A.; et al. Host-response patterns of inframammary infections in dairy cows. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 144, 270–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte, E.; Ruiz, R.; Gabiña, D.; Beltrán de Heredia, I. Impact of high-yielding foreign breeds on the Spanish dairy sheep industry. Lives. Prod. Sci. 2001, 71, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oget, C.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; Rupp, R. Genetic and genomic studies in ovine mastitis. Small Rum. Res. 2019, 176, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.C.; Axford, R.F.E.; Nicholas, F.W.; Owen, J.B. Mastitis. In Breeding for Disease Resistance in Farm Animals, 3rd ed.; CABI publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jurado, J.J.; Jiménez, M. Genetic parameter estimation of milk yield, udder conformation and somatic cell counts traits in Assaf sheep breed. In Proceedings of the XVII Jornadas sobre Producción Animal, Zaragoza, España, 30–31 May 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 519–521. [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen, T.H.E.; Goddard, M.E. The use of marker haplotypes in animal breeding schemes. Genet. Sel. Evol. 1996, 28, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, H.A.; Calus, M.P.L.; Veerkamp, R.F. Prediction of haplotypes with missing genotypes and its effect on accuracy of marker-assisted breeding value estimation. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2010, 42, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, J.C.M. Prediction of response to marker-assisted and genomic selection using selection index theory. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2007, 124, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari-Mahyari, S.; Sørensen, A.C.; Lund, M.S.; Thomsen, H.; Berg, P. Across-family marker-assisted selection using selective genotyping strategies in dairy cattle breeding schemes. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, T.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Genetic effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms in JAK2 and STAT5A genes on susceptibility of Chinese Holsteins to mastitis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 8293–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiezzi, F.; Parker-Gaddis, K.L.; Cole, J.B.; Clay, J.S.; Maltecca, C. A genome-wide association study for clinical mastitis in first parity us Holstein cows using single-step approach and genomic matrix re-weighting procedure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Jiang, l.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; et al. Genome wide association study in chinese Holstein cows reveal two candidate genes for somatic cell score as an indicator for mastitis susceptibility. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijas, J.W.; Townley, D.; Dalrymple, B.P.; Heaton, M.P.; Maddox, J.F.; McGrath, A.; Wilson, P.; Ingersoll, R.G.; McCulloch, R.; McWilliam, S.; et al. A genome widesurvey of SNP variation reveals the genetic structure of sheepbreeds. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sechi, S.; Casu, S.; Casula, M.; Congiu, G.B.; Miari, S.; Mulas, G.; Salaris, S.; Sechi, T.; Usai, M.G.; Ligios, C.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of resistance to paratuberculosis and mastitis in dairy sheep. In Proceedings of the Book of Abstracts of the 64th Annual Meeting of the European Federation of Animal Science, Nantes, France, 26–30 August 2013; p. 597. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Gil, B. Detection of QTL influencing somatic cell score in churra sheep employing the OvineSNP50 beadchip. In Proceedings of the Book of Abstracts of the 64th Annual Meeting of the European Federation of Animal Science, Nantes, France, 26–30 August 2013; p. 601. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, R.; Senin, P.; Sarry, J.; Allain, C.; Tasca, C.; Ligat, L.; Portes, D.; Woloszyn, F.; Bouchez, O.; Tabouret, G.; et al. A point mutation in suppressor of cytokine signalling 2 (Socs2) increases the susceptibility to inflammation of the mammary gland while associated with higher body weight and size and higher milk production in a sheep model. PLoS Genet 2015, 11, e1005629. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Gil, B.; Esteban-Blanco, C.; Suarez-Vega, A.; Arranz, J.J. Detection of quantitative trait loci and putative causal variants affecting somatic cell score in dairy sheep by using a 50K SNP-Chip and whole genome sequencing. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9072–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banos, G.; Bramis, G.; Bush, S.J.; Clark, E.L.; McCulloch, M.E.B.; Smith, J.; Schulze, G.; Arsenos, G.; Hume, D.A.; Psifidi, A. The genomic architecture of mastitis resistance in dairy sheep. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oget, C.; Allain, C.; Portes, D.; Foucras, G.; Stella, A.; Astruc, J.M.; Sarry, J.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; Rupp, R. A validation study of loci associated with mastitis resistance in two French dairy sheep breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2019b, 51, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.K.A.; Shook, G.E. An optimum transformation for somatic cell concentration in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijas, J.W.; Porto-Neto, L.; Dominik, S.; Reverter, A.; Bunch, R.; McCulloch, R.; Hayes, B.J.; Brauning, R.; McEven, C.; International Sheep Genomics Consortium. Linkage disequilibrium over short physical distances measured in sheep using a high-density SNP chip. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for Genome-wide Complex Trait Analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dvorkin, D.; Da, Y. SNPEVG: A graphical tool for GWAS graphing with mouse clicks. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominakis, A.; Saridaki, A.; Antonakos, G. Novel Candidate Genes for Somatic Cell Count in Frizarta Dairy Sheep. Int. J. Genet. Genom. 2019, 7(4), 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banos, G.; Clark, E.L.; Bush, S.J.; Dutta, P.; Bramis, G.; Arsenos, G.; Hume, D.A.; Psifidi, A. Genetic and genomic analyses underpin the feasibility of concomitant genetic improvement of milk yield and mastitis resistance in dairy sheep. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Gil, B.; El-Zarei, M.F.; Bayón, Y.; Álvarez, L.; de la Fuente, L.F.; Primitivo, F.S.; Arranz, J.J. Detection of quantitative trait loci influencing somatic cell score in Spanish Churra sheep. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Jauhari, A.; Rizvi, S.A.M. WDR88, CCDC11, and ARPP21 genes indulge profoundly in the desmoplastic retort to prostate and breast cancer metastasis. BioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavati, M.; Bush, S.; Palma-Vera, S.; McCulloch, M.; Hume, D.; Clark, E. Elimination of reference mapping bias reveals robust immune related allele-specific expression in cross-bred sheep. Front Genet. 2019, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lan, X.; Guo, W.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.; Lei, C.; Fang, X.; Chen, H. Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Dairy Goat MicroRNAs from Dry Period and Peak Lactation Mammary Gland Tissues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigli, I.; Maizon, D.O. MicroRNAs and the mammary gland: A new understanding of gene expression. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2013, 36, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, N.; Foroushani, A.B.K.; McCabe, M.S.; O’Farrelly, C.; Lynn, D.J. Next generation sequencing reveals the expression of a unique miRNA profile in response to a Gram positive bacterial infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobuchon, L.; Marthey, S.; Boussaha, M.; Le Guillou, S.; Leroux, C.; Le Provost, F. Annotation of the goat genome using next generation sequencing of microRNA expressed by the lactating mammary gland: Comparison of three approaches. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, T.; Sun, Y. MicroRNA-128 inhibits the inflammatory responses by targeting TAB2 in miiuy croaker, Miichthysmiiuy. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 117, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, K.P.; Senger, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lima, R.; Patel, S.; Ingano, L.; Flavahan, W.A.; Kumar, D.K.V.; Fraser, C.M.; Faherty, C.S.; et al. Salmonella typhi colonization provokes extensive transcriptional changes aimed at evading host mucosal immune defense during early infection of human intestinal tissue. Ebiomedicine 2018, 31, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehfeld, F.; Maticzka, D.; Grosser, S.; Knauff, P.; Eravci, M.; Vida, I.; Backofen, R.; Wulczyn, R.G. The RNA-binding protein ARPP21 controls dendritic branching by functionally opposing the miRNA it hosts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbach, M.; Schwanhäusser, B.; Thierfelder, N.; Fang, Z.; Khanin, R.; Rajewsky, N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008, 455, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.H.; Allis, C.D. Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. Bioessays 1998, 20, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xia, C.; Duan, G. Dual-target inhibitors BASED on HDACs: Novel antitumor agents for cancer therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8977–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beneden, K.; Geers, C.; Pauwels, M.; Mannaerts, I.; Wissing, K.M.; Van den Branden, C.; van Grunsven, L.A. Comparison of trichostatin A and valproic acid treatment regimens in a mouse model of kidney fibrosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 271, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakespear, M.R.; Halili, M.A.; Irvine, K.M.; Fairlie, D.P.; Sweet, M.J. Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marete, A.; Lund, M.S.; Boichard, D.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y. A system-based analysis of the genetic determinism of udder conformation and health phenotypes across three French dairy cattle breeds. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zebell, S.G.; Liang, Z.; Wang, S.; Kang, B.H.; Dong, X. Nuclear pore permeabilization is a convergent signaling event in effector-triggered immunity. Cell 2016, 166, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlido, J.; Sakuma, S.; Raices, M.; Carrette, F.; Tinoco, R.; Bradley, L.M.; D’Angelo, M.A. Nuclear pore complex-mediated modulation of TCR signaling is required for naïve CD4+ T cell homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzola, M.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Bittante, G.; Cecchinato, A.; Dettori, M.L.; Vacca, G.M. Phenotypic and genetic relationships betweResultsen indicators of the mammary gland health status and milk composition, coagulation, and curd firming in dairy sheep. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3164–3175. [Google Scholar]
- Shennan, D.B.; M. Peaker. Transport of milk constituents by the mammary gland. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 925–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norberg, E. Electrical conductivity of milk as a phenotypic and genetic indicator of bovine mastitis: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 30, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population | LOW SCS | HIGH SCS |
|---|---|---|
| Flock A (n = 64) | −0.77 ± 0.09 | 1.61 ± 0.41 |
| Flock B (n = 64) | −0.91 ± 0.14 | 2.15 ± 0.38 |
| Flock C (n = 64) | −0.72 ± 0.04 | 1.79 ± 0.54 |
| Total (n = 192) | −0.80 ± 0.13 | 1.85 ± 0.50 |
| Chr1 | SNP | Oar3.1 | A1 | A2 | MAF | b | se | p-Val | p-Val_FDR10 | Genes_250Kb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
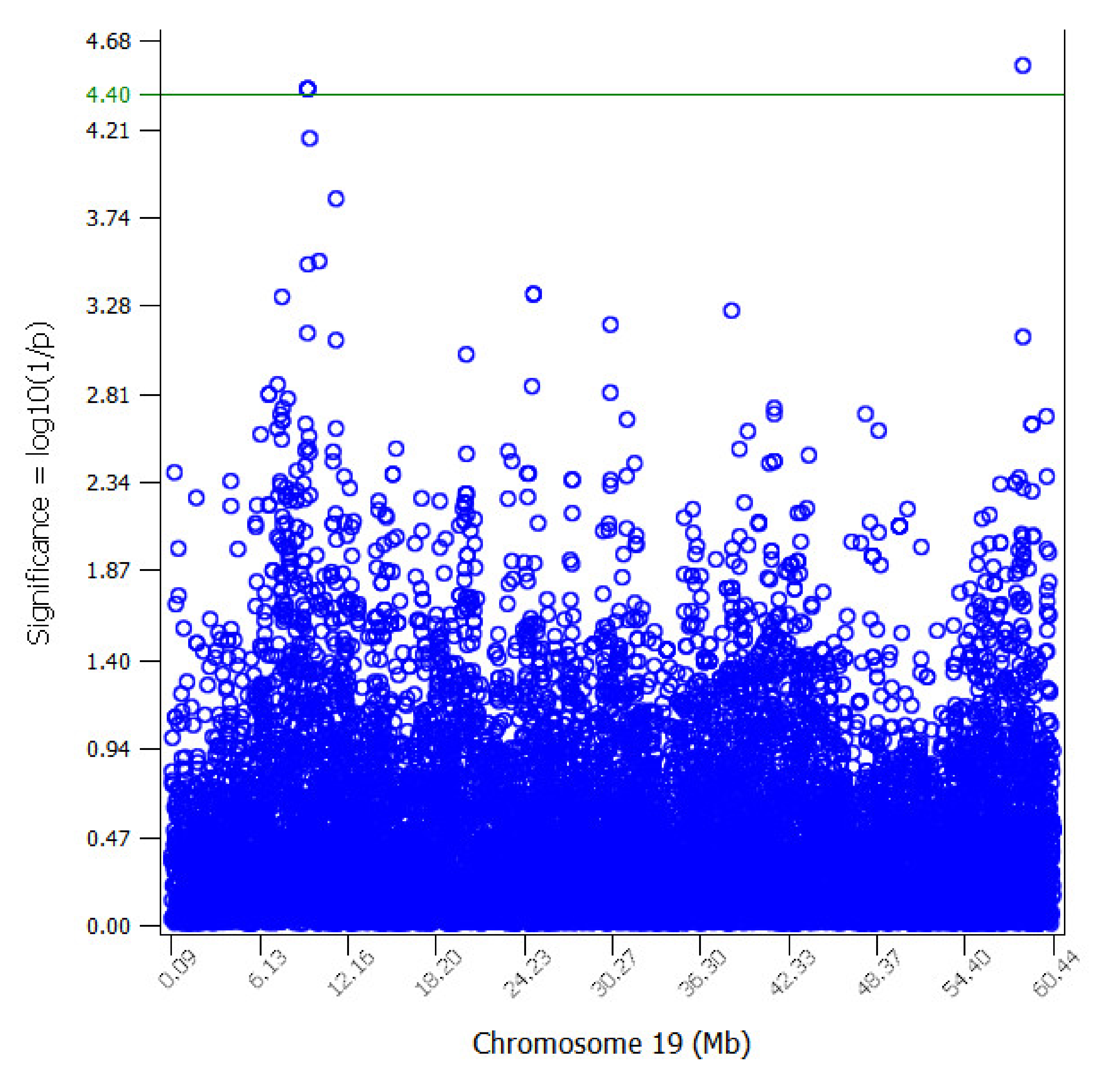
| 19 | rs415580501 | 9401922 | C | A | 0.26 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 3.98 × 10−5 | 4.00 × 10−5 | ARPP21-miR128_2 |
| 19 | rs410336647 | 9407458 | G | A | 0.26 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 3.98 × 10−5 | 4.00 × 10−5 | ARPP21-miR128_2 |
| 19 | rs424642424 | 9410968 | A | G | 0.26 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 3.98 × 10−5 | 4.00 × 10−5 | ARPP21-miR128_2 |
| 19 | rs419096188 | 58334807 | A | G | 0.38 | −0.61 | 0.15 | 2.91 × 10−5 | 4.00 × 10−5 | FBLN2-Ensoarg00000001587-Ensoarg00000026664-HDAC11-NUP210-Ensoarg00000026665- Ensoarg00000026666 |
| SNP | MAF1 | Trait | p -Values | LSmeans Genotype Effect | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Htd2 | DIM | Nlb | A | LN | G | AA | AG | GG | |||
| rs419096188 | 0.40 | SCS | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.549 | 0.252 | 0.071 | 0.003 | 2.70 ± 0.10a,c (n = 282) | 2.91 ± 0.08b (n = 893) | 2.96 + 0.09a,b,d (n = 649) |
| MY | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.884 | <0.001 | 0.337 | 2309.87 ± 74.02 | 2361.59 ± 58.98 | 2284.92 ± 63.53 | ||
| FC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.007 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.204 | 5.43 ± 0.09 | 5.53 ± 0.07 | 5.47 ± 0.08 | ||
| PC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.632 | 0.730 | <0.001 | 0.755 | 5.27 ± 0.04 | 5.28 ± 0.03 | 5.26 ± 0.03 | ||
| LC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.035 | 0.138 | <0.001 | 0.015 | 4.83 ± 0.02a | 4.81 ± 0.02a,b | 4.78 ± 0.02b | ||
| TSC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.528 | 0.317 | 0.546 | 0.075 | 11.03 ± 0.04 | 11.01 ± 0.03 | 10.97 ± 0.04 | ||
| rs424642424 | 0.25 | SCS | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.515 | 0.289 | 0.088 | 0.009 | 2.92 ± 0.13a,b (n = 103) | 2.99 ± 0.09a (n = 689) | 2.82 ± 0.08b (n = 1031) |
| MY | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.787 | <0.001 | 0.144 | 2081.7 ± 135.31 | 2331.85 ± 61.34 | 2336.26 ± 57.33 | ||
| FC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.007 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.158 | 5.59 ± 0.12 | 5.54 ± 0.08 | 5.46 ± 0.07 | ||
| PC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.643 | 0.720 | <0.001 | 0.505 | 5.29 ± 0.05 | 5.28 ± 0.03 | 5.26 ± 0.03 | ||
| LC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.033 | 0.183 | <0.001 | 0.929 | 4.80 ± 0.03 | 4.80 ± 0.02 | 4.80 ± 0.02 | ||
| TSC | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.502 | 0.359 | 0.625 | 0.719 | 11.00 ± 0.05 | 11.01 ± 0.04 | 10.99 ± 0.03 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Öner, Y.; Serrano, M.; Sarto, P.; Iguácel, L.P.; Piquer-Sabanza, M.; Estrada, O.; Juan, T.; Calvo, J.H. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Somatic Cell Count in the Assaf Breed. Animals 2021, 11, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061531
Öner Y, Serrano M, Sarto P, Iguácel LP, Piquer-Sabanza M, Estrada O, Juan T, Calvo JH. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Somatic Cell Count in the Assaf Breed. Animals. 2021; 11(6):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061531
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖner, Yasemin, Malena Serrano, Pilar Sarto, Laura Pilar Iguácel, María Piquer-Sabanza, Olaia Estrada, Teresa Juan, and Jorge Hugo Calvo. 2021. "Genome-Wide Association Studies of Somatic Cell Count in the Assaf Breed" Animals 11, no. 6: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061531
APA StyleÖner, Y., Serrano, M., Sarto, P., Iguácel, L. P., Piquer-Sabanza, M., Estrada, O., Juan, T., & Calvo, J. H. (2021). Genome-Wide Association Studies of Somatic Cell Count in the Assaf Breed. Animals, 11(6), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061531







