Simultaneous Removal of Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from High-Strength Swine Wastewater Using a Novel Integrated Treatment Process
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Swine Wastewater
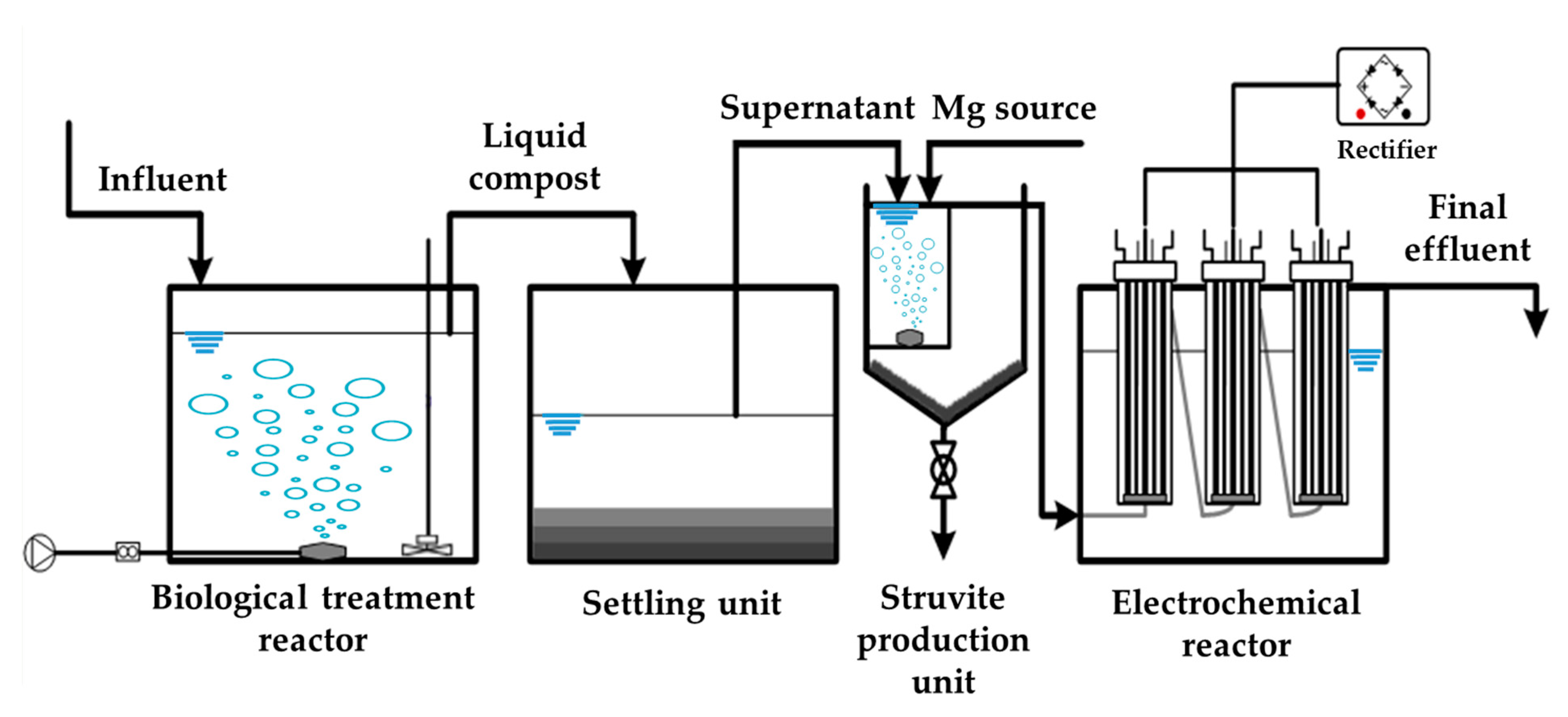
2.2. Configuration of the Treatment Sequence and Operational Methods
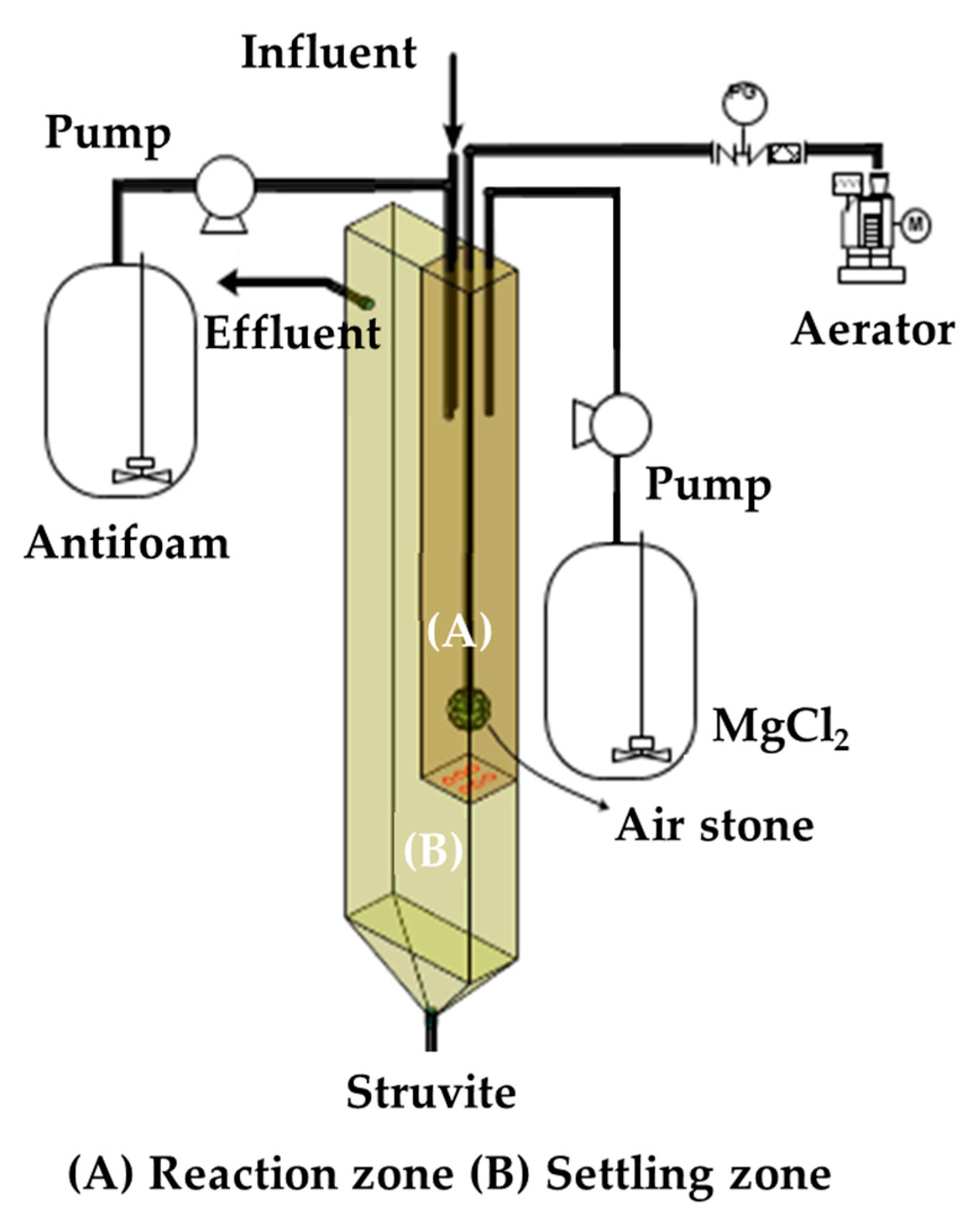
2.2.1. Lab-Scale Treatment Process
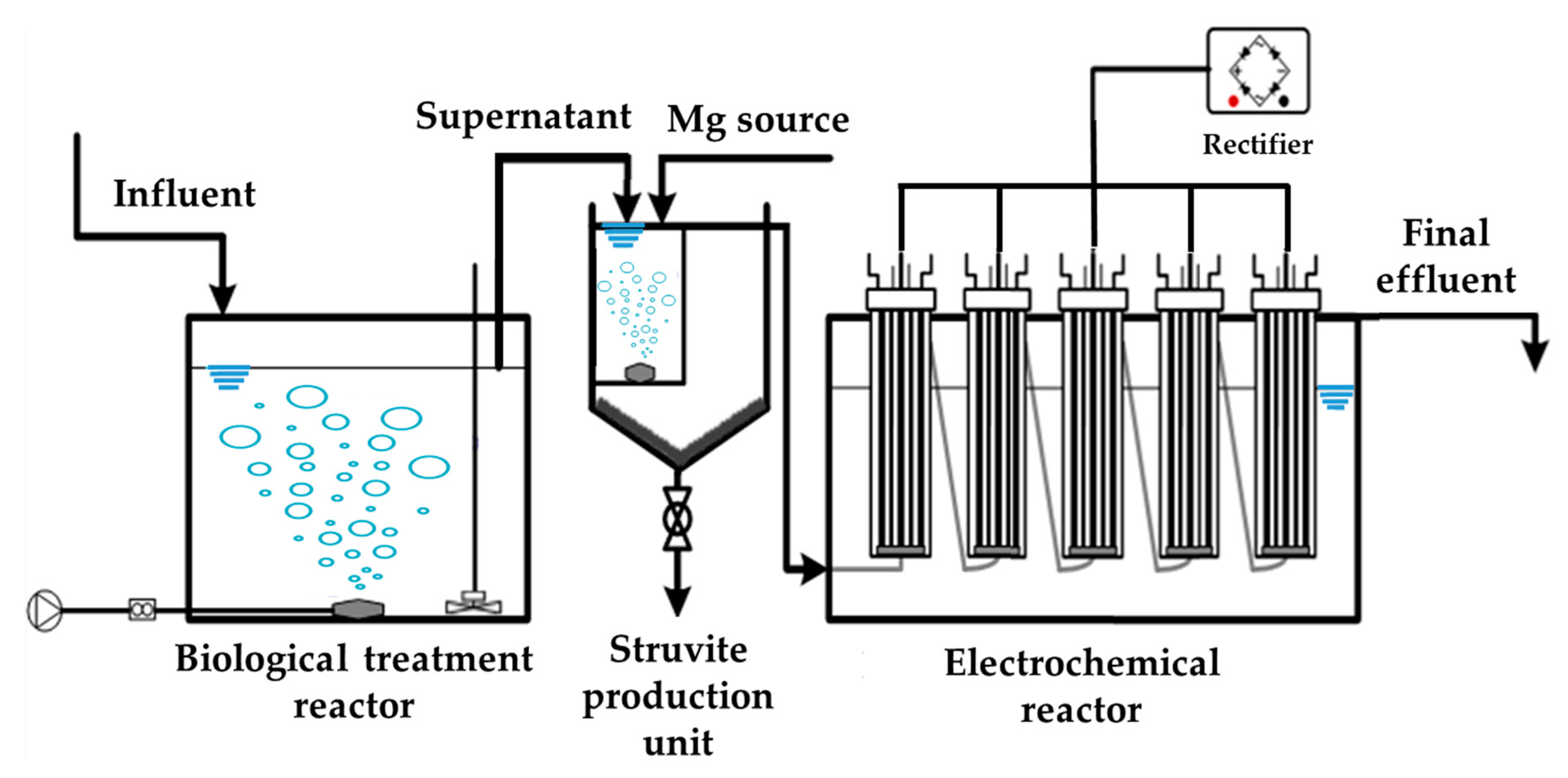
2.2.2. Farm-Scale Treatment Process
2.3. Sampling and Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of the Lab-Scale Treatment Process
3.1.1. Biological Treatment Unit
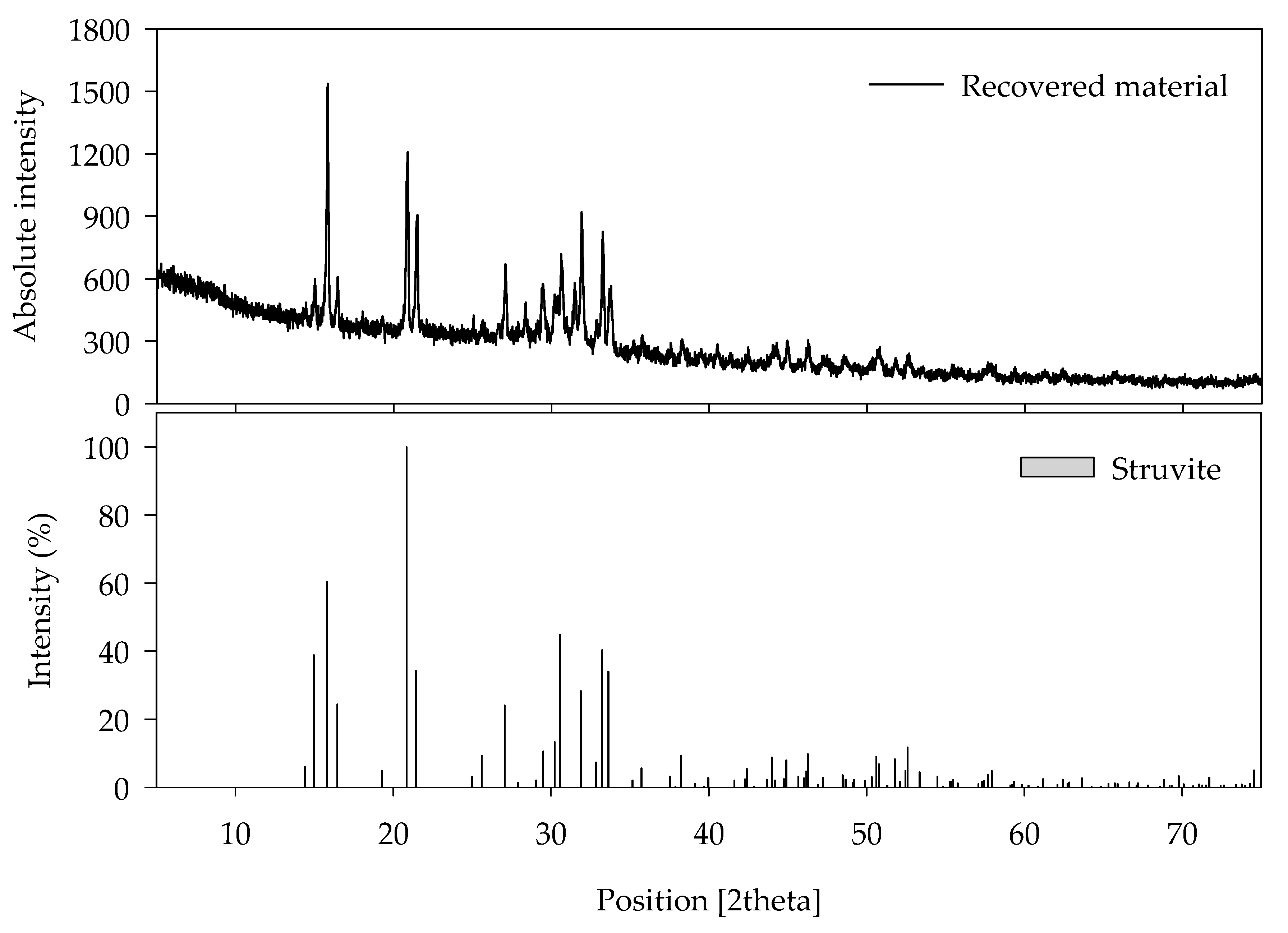
3.1.2. Struvite Production Unit
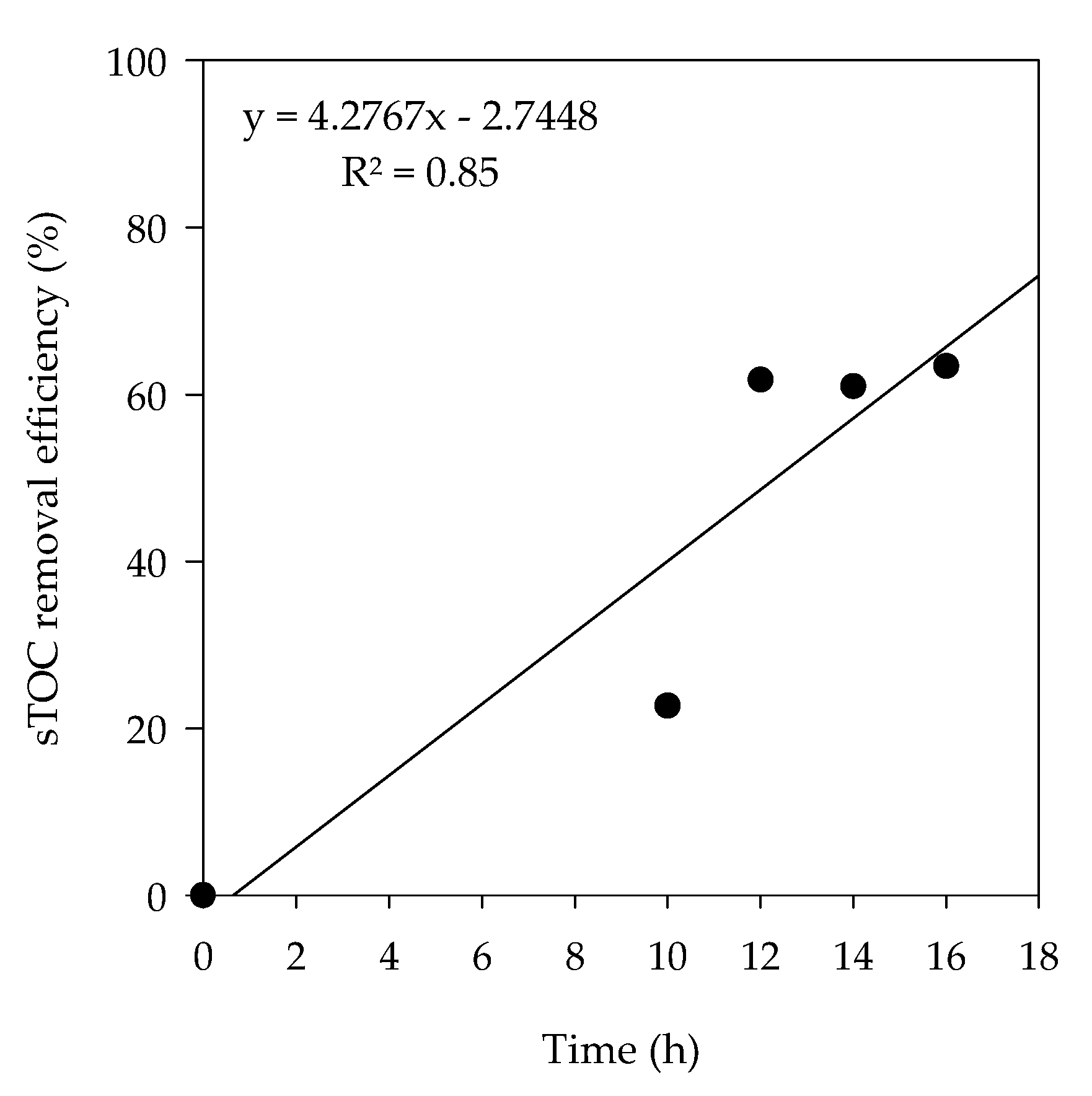
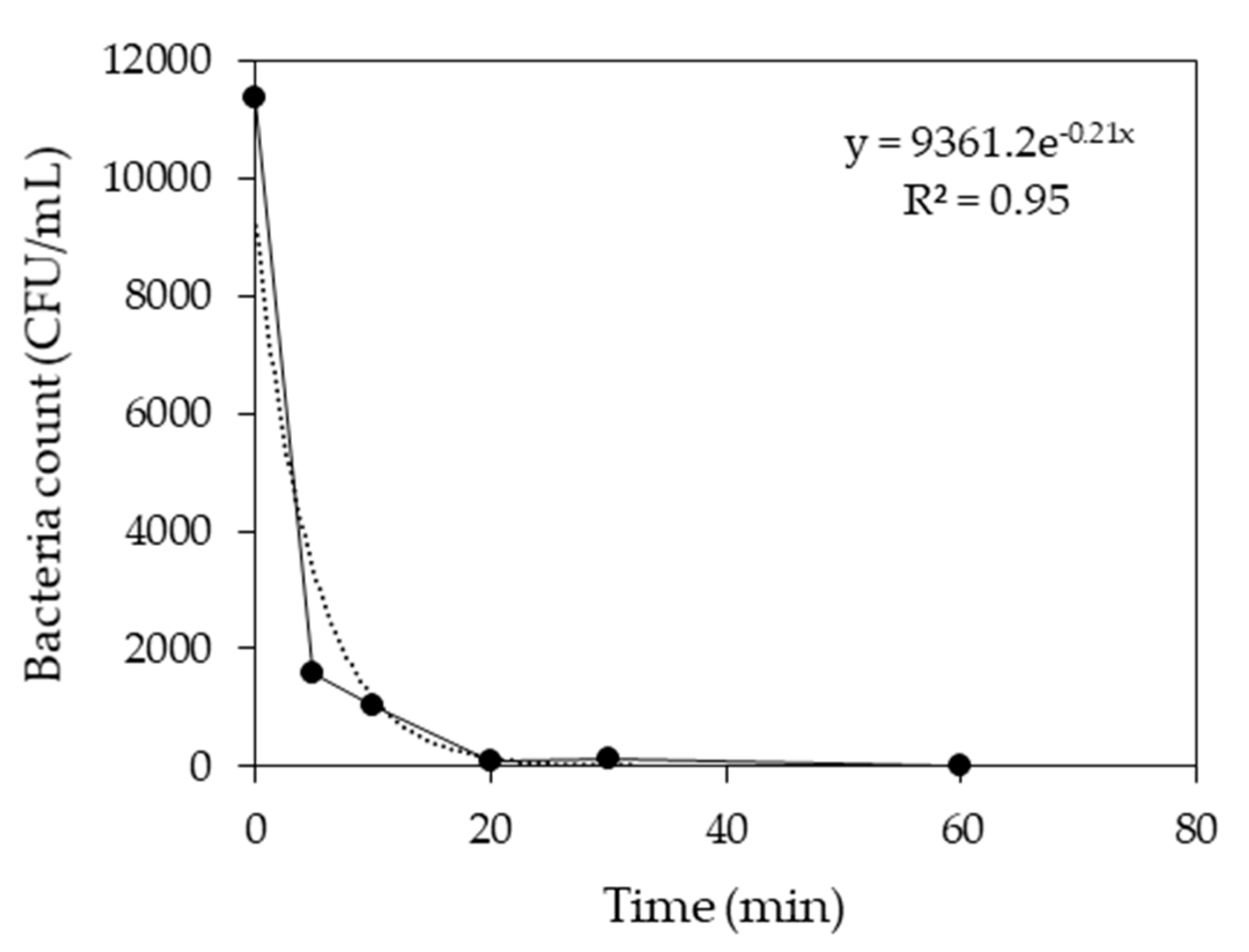
3.1.3. Electrochemical Reactor
3.2. Performance of the Farm-Scale Treatment Process
3.3. Overall Performance of the Novel Intregated Treatment Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, S.J.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.; Shin, I.H.; Kwak, H.S. Enhanced treatment of swine wastewater by electron beam irradiation and ion-exchange biological reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Global Number of Pigs 2012–2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/263963/number-of-pigs-worldwide-since-1990/ (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Osada, T.; Haga, K.; Harada, Y. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from swine wastewater by the activated sludge units with the intermittent aeration process. Water Res. 1991, 25, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.; Shim, S.; Kim, S.; Ahmed, N.; Won, S.; Ra, C. Nutrient Leaching Loss of Pre-Treated Struvite and Its Application in Sudan Grass Cultivation as an Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Fertilizer Source. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Lin, C.; Duan, N.; Peng, Y.; Ye, Z. Application of aerobic biological filter for treating swine farms wastewater. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.; Kok, R. Nitrogen transformation in swine manure in an oxidation ditch under aerobic conditions. Trans. ASAE 1986, 29, 799–0806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, B. Swine wastewater treatment in anaerobic digesters with floating medium. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapcho, C. Biological anoxic/aerobic treatment of swine waste for reduction of organic carbon, nitrogen, and odor. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Mahmood, Q. Improvement in post-treatment of digested swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3136–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Zhu, J.; Ndegwa, P.M. Removal of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in pig manure by continuous and intermittent aeration at low redox potentials. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 82, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, S.M. Phosphate Rock, USGS Mineral Commodities Summary. Available online: http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/phosphate_rock/ (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- Rahman, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Kwag, J.; Ra, C. Recovery of struvite from animal wastewater and its nutrient leaching loss in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 2026–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Rashid, U.; Ahsan, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Ra, C. Production of slow release crystal fertilizer from wastewaters through struvite crystallization–A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Shim, S.; Won, S.; Ra, C. Struvite recovered from various types of wastewaters: Characteristics, soil leaching behaviour, and plant growth. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2864–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Shim, S.; Reza, A.; Kim, S.; Won, S.; Jung, B.; Kim, J.; Ra, C. Evaluation of Struvite Recovered from Swine Wastewater as an Alternative Phosphorus Source in Broiler Feed. Agriculture 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Won, S.; Reza, A.; Kim, S.; Ahn, S.; Jung, B.; Yoon, B.; Ra, C. In Vivo Toxicity and In Vitro Solubility Assessment of Pre-Treated Struvite as a Potential Alternative Phosphorus Source in Animal Feed. Animals 2019, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouropoulos, N.C.; Koutsoukos, P.G. Spontaneous precipitation of struvite from aqueous solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 213, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kwag, J.; Kim, J.; Ra, C. Recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus by struvite crystallization from swine wastewater. Desalination 2011, 277, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Weon, S.; Lee, C.; Koopman, B. Removal of nitrogen and phosphate from wastewater by addition of bittern. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikaar, I.; Rozendal, R.A.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J.; Rabaey, K. Electrochemical sulfide oxidation from domestic wastewater using mixed metal-coated titanium electrodes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5381–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maljaei, A.; Arami, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Decolorization and aromatic ring degradation of colored textile wastewater using indirect electrochemical oxidation method. Desalination 2009, 249, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.R.; Olivi, P. Effect of chloride concentration on the electrochemical treatment of a synthetic tannery wastewater. Electrochimica Acta 2009, 54, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Jeon, D.; Rahman, M.; Kwag, J.; Ra, C. Optimization of electrochemical reaction for nitrogen removal from biological secondary-treated milking centre wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikaar, I.; Rozendal, R.A.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J.; Rabaey, K. Electrochemical sulfide removal from synthetic and real domestic wastewater at high current densities. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, L.C.; Chang, J.E.; Tseng, S.C. Electrochemical oxidation pretreatment of refractory organic pollutants. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Huitle, C.A.; Ferro, S. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: Direct and indirect processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1324–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOSIS. Livestock Farms According to Manure Treatment Method in 2109. Available online: http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1EA1032&conn_path=I2 (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Cho, J.; Lee, J.; Ra, C. Effects of electric voltage and sodium chloride level on electrolysis of swine wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF; WPCF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, T. Agricultural Fertilizers as a Source of Pollution. In Pollution Science; Pepper, I.L., Gerba, C.P., Brusseau, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Vigil, M.; Kissel, D. Equations for estimating the amount of nitrogen mineralized from crop residues. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, B. Nitrification/denitrification in intermittent aeration process for swine wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Eng. 2001, 127, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.L.; Wang, C.T.; Hsu, C.W.; Huang, K.Y.; Liu, T.C. Removal of total organic carbon from aqueous solution containing polyvinyl alcohol by electrocoagulation technology. Desalination 2010, 259, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, K.M.; Honda, Y.; Sakugawa, H. Dynamics and optical nature of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in river waters in Hiroshima prefecture, Japan. Geochem. J. 2005, 39, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.; Jørgensen, B.; Fossing, H.; Glud, R.; Gundersen, J.; Ramsing, N.; Thamdrup, B.; Hansen, J.; Nielsen, L.; Hall, P. Marine sediments, burial, pore water chemistry, microbiology and diagenesis pathways of organic carbon oxidation in three continental margin sediments. Mar. Geol. 1993, 113, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Oldring, K.; Churchley, J.; Price, C.; Parsons, S.A. Chemical control of struvite precipitation. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAFRA. Limit and Standard of the Harmful Compounds in Fertilizer and Feed. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/admRulBylInfoPLinkR.do?admRulSeq=2100000052530&admRulNm=%EC%82%AC%EB%A3%8C%20%EB%93%B1%EC%9D%98%20%EA%B8%B0%EC%A4%80%20%EB%B0%8F%20%EA%B7%9C%EA%B2%A9&bylNo=0016&bylBrNo=00&bylCls=BE&bylClsCd=BE&joEfYd=&bylEfYd= (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- Lei, X.; Maekawa, T. Electrochemical treatment of anaerobic digestion effluent using a Ti/Pt–IrO2 electrode. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3521–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfatti, F.; Ferro, S.; Lavezzo, F.; Malacarne, M.; Lodi, G.; De Battisti, A. Electrochemical incineration of glucose as a model organic substrate. II. Role of active chlorine mediation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y. Ammonia removal in electrochemical oxidation: Mechanism and pseudo-kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, M.N.; Esakku, S.; Palanivelu, K. Electrochemical treatment of landfill leachate. Indian Chem. Eng. 2005, 47, 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Szpyrkowicz, L.; Naumczyk, J.; Zilio-Grandi, F. Electrochemical treatment of tannery wastewater using TiPt and Ti/Pt/Ir electrodes. Water Res. 1995, 29, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Nakasono, S.; Takamuku, T.; Burgess, J.G.; Nakamura, N.; Sode, K. Disinfection of drinking water by using a novel electrochemical reactor employing carbon-cloth electrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okochi, M.; Matsunaga, T. Electrochemical sterilization of bacteria using a graphite electrode modified with adsorbed ferrocene. Electrochimica Acta 1997, 42, 3247–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoE. Water Quality Standard for Swine Wastewater Effluent Discharge According to Locations and Treatment Facilities; Ministry of Environment: Sejong City, Korea, 2015.
- González, C.; Garcia, P.; Muñoz, R. Effect of feed characteristics on the organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus removal in an activated sludge system treating piggery slurry. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Nieto-Diez, P.P.; León-Cofreces, C.; García-Encina, P.A. Solids and nutrients removals from the liquid fraction of swine slurry through screening and flocculation treatment and influence of these processes on anaerobic biodegradability. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6233–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanotti, M.; Rashash, D.; Hunt, P. Solid-liquid separation of flushed swine manure with PAM: Effect of wastewater strength. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, C.; Lo, K.; Shin, J.; Oh, J.; Hong, B.J. Biological nutrient removal with an internal organic carbon source in piggery wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chen, M.; Kishida, N.; Sudo, R. Integrated real-time control strategy for nitrogen removal in swine wastewater treatment using sequencing batch reactors. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3340–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernet, N.; Delgenes, N.; Akunna, J.C.; Delgenes, J.P.; Moletta, R. Combined anaerobic–aerobic SBR for the treatment of piggery wastewater. Water Res. 2000, 34, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Ra, C. Biological nitrogen removal with a real-time control strategy using moving slope changes of pH(mV)- and ORP-time profiles. Water Res. 2011, 45, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.O.; Mikkelsen, R.L.; Hesterberg, D.L. Struvite precipitation in anaerobic swine lagoon liquid: Effect of pH and Mg:P ratio and determination of rate constant. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, L.; Mangin, D.; Barat, R.; Seco, A. A pilot-scale study of struvite precipitation in a stirred tank reactor: Conditions influencing the process. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6285–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Qiu, G.L.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.Y.; Peng, J.F.; Zeng, P.; Zeng, P.; Duan, L.; Xiang, L.C.; Qian, F. Nutrients removal and recovery from anaerobically digested swine wastewater by struvite crystallization without chemical additions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.M.; Chen, Y.X.; Jilani, G.; Wu, W.X.; Liu, W.L.; Han, Z.Y. Optimization of struvite crystallization protocol for pretreating the swine wastewater and its impact on subsequent anaerobic biodegradation of pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 16, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Kwag, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Ra, C. Recycle of electrolytically dissolved struvite as an alternative to enhance phosphate and nitrogen recovery from swine wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Won, S.; Reza, A.; Kim, S.; Ahmed, N.; Ra, C. Design and Optimization of Fluidized Bed Reactor Operating Conditions for Struvite Recovery Process from Swine Wastewater. Processes 2020, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihashi, O.; Hirooka, K. Removal and recovery of phosphorus as struvite from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera-Díaz, C.; Ureña-Nuñez, F.; Campos, E.; Palomar-Pardavé, M.; Romero-Romo, M. A combined electrochemical-irradiation treatment of highly colored and polluted industrial wastewater. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2003, 67, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetilmezsoy, K.; Ilhan, F.; Sapci-Zengin, Z.; Sakar, S.; Gonullu, M.T. Decolorization and COD reduction of UASB pretreated poultry manure wastewater by electrocoagulation process: A post-treatment study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters (mg/L) | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| (A) Lab-Scale | (B) Farm-Scale | |
| TS 1 (g/L) | 28.52 ± 8.24 | 16.58 ± 1.66 |
| SS 2 (g/L) | 11.20 ± 2.02 | 12.89 ± 2.55 |
| NH4-N 3 | 3453.92 ± 67.19 | 1662.28 ± 181.34 |
| O-P 4 | 141.19 ± 13.64 | 49.2 ± 23.92 |
| TN 5 | 11362.1 ± 0.64 | 4139.32 ± 438.84 |
| TP 6 | 172.13 ± 11.03 | 65.59 ± 13.76 |
| sTOC 7 | 16,769.17 ± 439.12 | 2096.33 ± 385.04 |
| Color (color units) | 44216.39 | 56,056.57 |
| pH | 7.53 ± 0.11 | 7.53 ± 0.11 |
| Parameters (mg/L) | Influent | Biological Treatment | Struvite Production Unit | Electrochemical Treatment | Removal (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) | (E) | (F) | (G) | (A-B) | (B-C) | (C-E) | (A-E) | (A-G) | |
| 10 h | 12 h | 14 h | 16 h | |||||||||
| TS 1 (g/L) | 28.52 | 13.52 | 6.84 | 7.42 | 6.38 | 6.28 | 5.88 | 52.7 | 49.4 | 6.7 | 77.6 | 79.4 |
| ±8.24 | ±0.54 | ±0.31 | ||||||||||
| SS 2 (g/L) | 11.20 | 2.51 | 0.91 | 0.5 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.14 | 77.6 | 63.7 | 71.4 | 97.7 | 98.8 |
| ±2.02 | ±0.57 | ±0.07 | ||||||||||
| NH4-N 3 | 3453.92 | 988.96 | 548.84 | 191.87 | 138.37 | 89.99 | 43.33 | 71.4 | 44.5 | 74.8 | 96.0 | 98.7 |
| ±67.19 | ±96.95 | ±49.36 | ±0.16 | ±0.47 | ±0.14 | ±0.02 | ||||||
| O-P 4 | 141.19 | 15.44 | 5.96 | 6.54 | 6.57 | 6.12 | 7.48 | 89.1 | 61.4 | - | 95.3 | 94.7 |
| ±13.64 | ±2.93 | ±0.59 | ±0.07 | ±0.07 | ±0.07 | ±0.14 | ||||||
| TN 5 | 11362.1 | 7891.34 | 4357.32 | 1429.34 | 1355.14 | 884.8 | 691.28 | 30.5 | 44.8 | 68.9 | 88.1 | 93.9 |
| ±0.64 | ±0.59 | ±0.06 | ||||||||||
| TP 6 | 172.13 | 51.23 | 31.72 | 21.51 | 14.07 | 13.9 | 11.98 | 70.2 | 38.1 | 55.6 | 91.8 | 93.0 |
| ±11.03 | ±2.31 | ±0.17 | ||||||||||
| sTOC 7 | 16,769.17 | 5571.93 | 2725.61 | 2107.65 | 1043.1 | 1065.4 | 998.93 | 66.8 | 51.1 | 61.7 | 93.8 | 94.0 |
| ±439.12 | ±648.10 | ±378.50 | ±4.03 | ±77.22 | ±38.32 | ±49.50 | ||||||
| Color (color units) | 44216.39 | 23481.28 | 12737.64 | 7434.85 | 3654.57 | 2700.6 | 1001.79 | 46.9 | 45.8 | 71.3 | 91.7 | 97.7 |
| pH | 7.53 | 8.68 | 8.66 | 8.27 | 8.53 | 8.02 | 7.81 | - | - | - | - | - |
| ±0.11 | ±0.10 | ±0.07 | ||||||||||
| Parameters | Recovered Material (mg/kg) | Standard Limits (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer | Feedstock | ||
| As | 0 | 45 | 2 |
| Cd | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| Cr | 0 | 200 | 100 |
| Cu | 17.86 | 360 | − |
| Pb | 0 | 130 | 10 |
| Hg | ND 1 | 2 | 0.4 |
| Ni | 0 | 45 | − |
| Se | ND 1 | − | 2 |
| Zn | 95.54 | 900 | − |
| Parameters (mg/L) | Influent | Biological Treatment | Struvite Production Unit | Electrochemical Treatment | Removal (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) | (A-B) | (B-C) | (C-D) | (A-D) | |
| 10 h | ||||||||
| TS 1 (g/L) | 16.58 | 2.97 | 2.21 | 1.41 | 82.1 | 25.6 | 36.2 | 91.5 |
| ±1.66 | ±0.04 | ±0.04 | ±0.03 | |||||
| SS 2 (g/L) | 12.89 | 1.58 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 87.7 | 67.1 | 90.4 | 99.6 |
| ±2.55 | ±0.07 | ±0.02 | ±0.00 | |||||
| NH4-N 3 | 1662.28 | 24.7 | 25.12 | 23.06 | 98.5 | - | 6.5 | 98.6 |
| ±181.34 | ±10.69 | ±7.57 | ±14.49 | |||||
| O-P 4 | 49.2 | 43.83 | 7.9 | 3.99 | 10.9 | 82.0 | 49.5 | 91.9 |
| ±23.92 | ±12.78 | ±3.71 | ±1.47 | |||||
| TN 5 | 4139.32 | 375.86 | 310.43 | 226.97 | 90.9 | 17.3 | 39.6 | 94.5 |
| ±438.84 | ±94.33 | ±88.47 | ±30.65 | |||||
| TP 6 | 65.59 | 72.2 | 17.89 | 21.65 | −10.1 | 75.2 | - | 67 |
| ±13.76 | ±9.09 | ±5.49 | ±4.46 | |||||
| sTOC 7 | 2096.33 | 212.78 | 140.98 | 82.46 | 89.8 | 33.7 | 41.8 | 96.1 |
| ±385.04 | ±57.30 | ±42.43 | ±25.24 | |||||
| Color (color units) | 56,056.57 | 7811.57 | 1180.34 | 603.59 | 86.1 | 84.9 | 48.9 | 98.9 |
| pH | 7.53 | 7.31 | 7.56 | 7.24 | - | - | - | - |
| ±0.11 | ±0.10 | ±0.07 | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shim, S.; Reza, A.; Kim, S.; Ahmed, N.; Won, S.; Ra, C. Simultaneous Removal of Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from High-Strength Swine Wastewater Using a Novel Integrated Treatment Process. Animals 2020, 10, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050835
Shim S, Reza A, Kim S, Ahmed N, Won S, Ra C. Simultaneous Removal of Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from High-Strength Swine Wastewater Using a Novel Integrated Treatment Process. Animals. 2020; 10(5):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050835
Chicago/Turabian StyleShim, Soomin, Arif Reza, Seungsoo Kim, Naveed Ahmed, Seunggun Won, and Changsix Ra. 2020. "Simultaneous Removal of Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from High-Strength Swine Wastewater Using a Novel Integrated Treatment Process" Animals 10, no. 5: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050835
APA StyleShim, S., Reza, A., Kim, S., Ahmed, N., Won, S., & Ra, C. (2020). Simultaneous Removal of Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from High-Strength Swine Wastewater Using a Novel Integrated Treatment Process. Animals, 10(5), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050835







