Homogenization of Endosymbiont Communities Hosted by Equatorial Corals during the 2016 Mass Bleaching Event
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
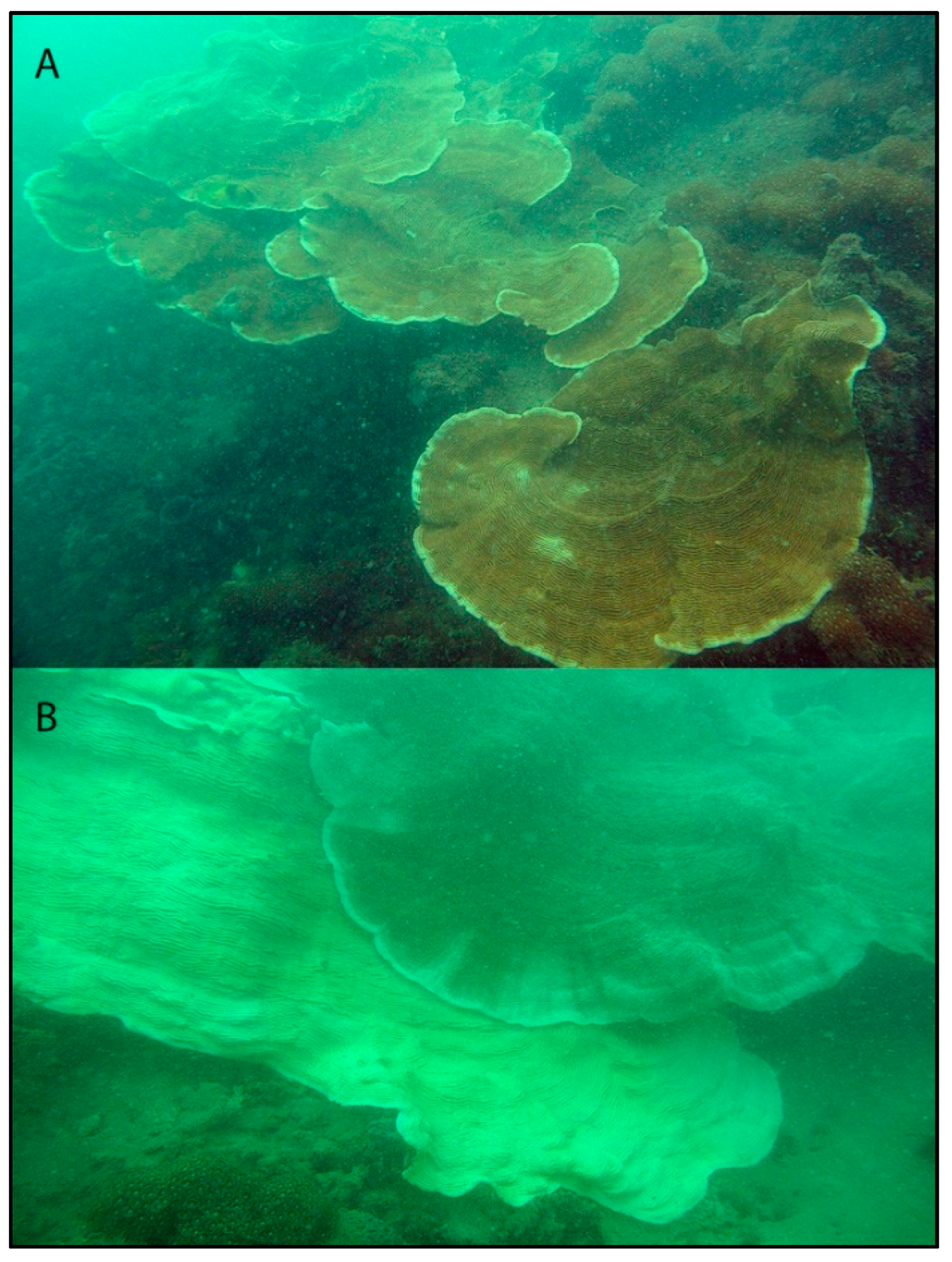
2.1. Field Collections
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.4. Illumina Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
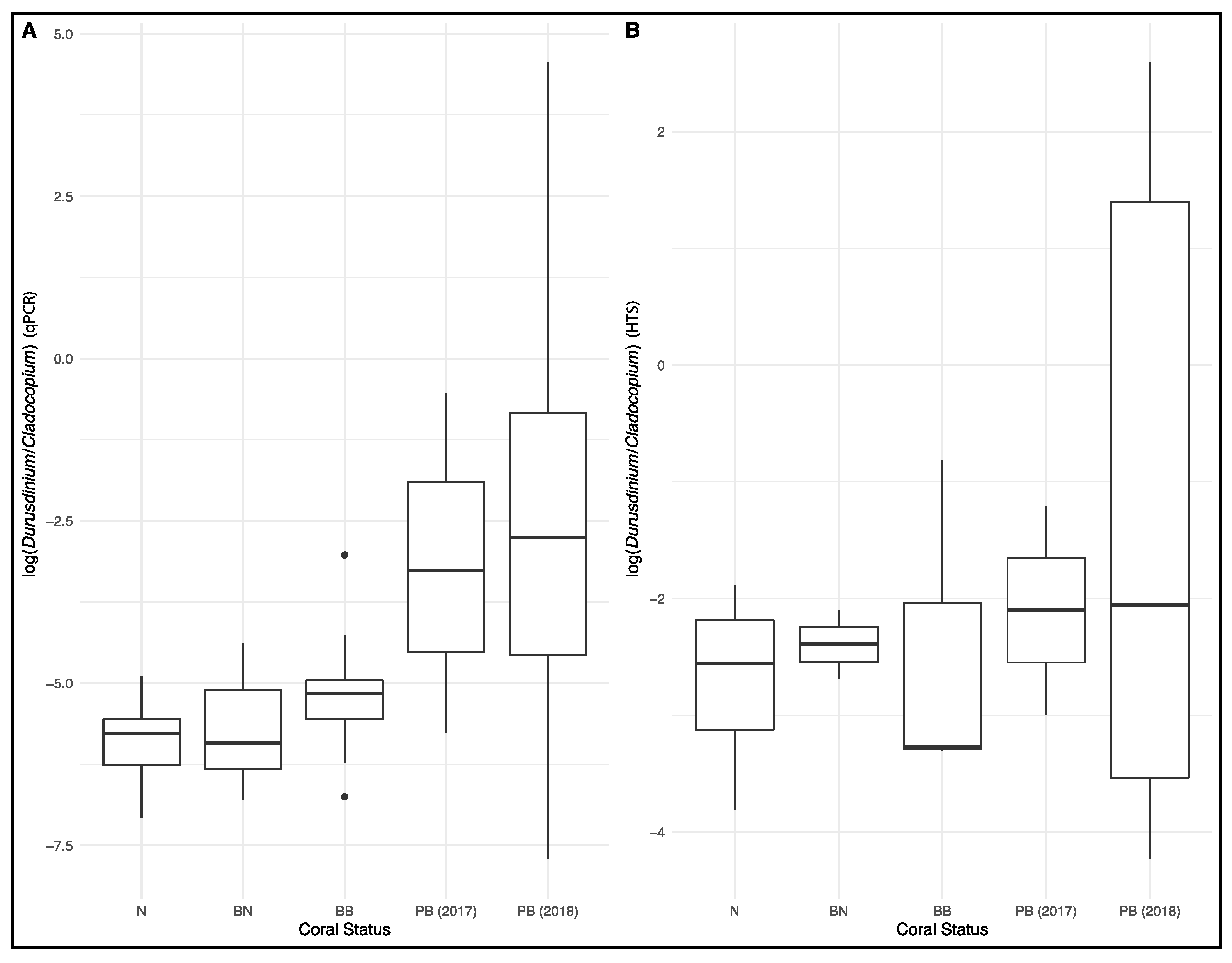
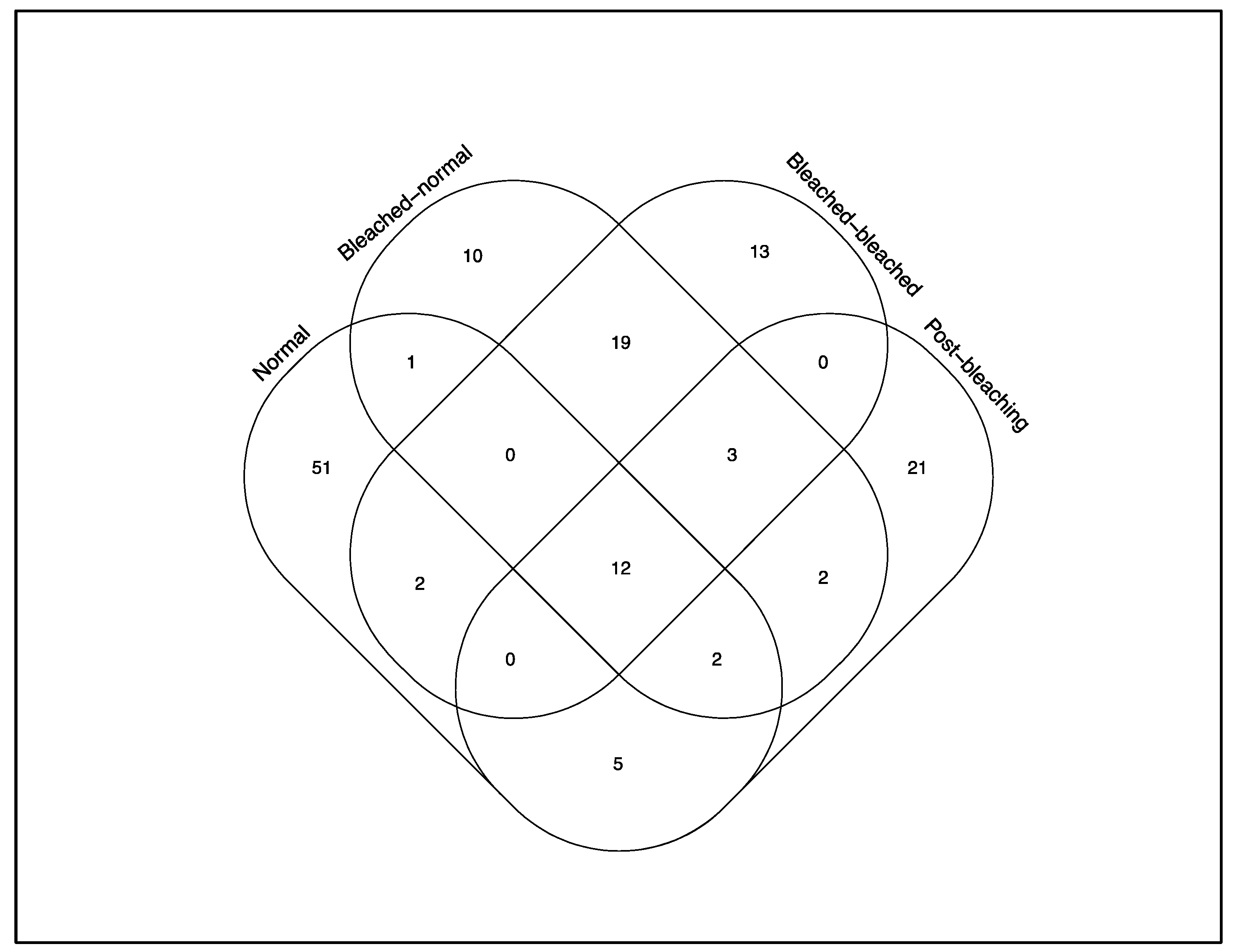
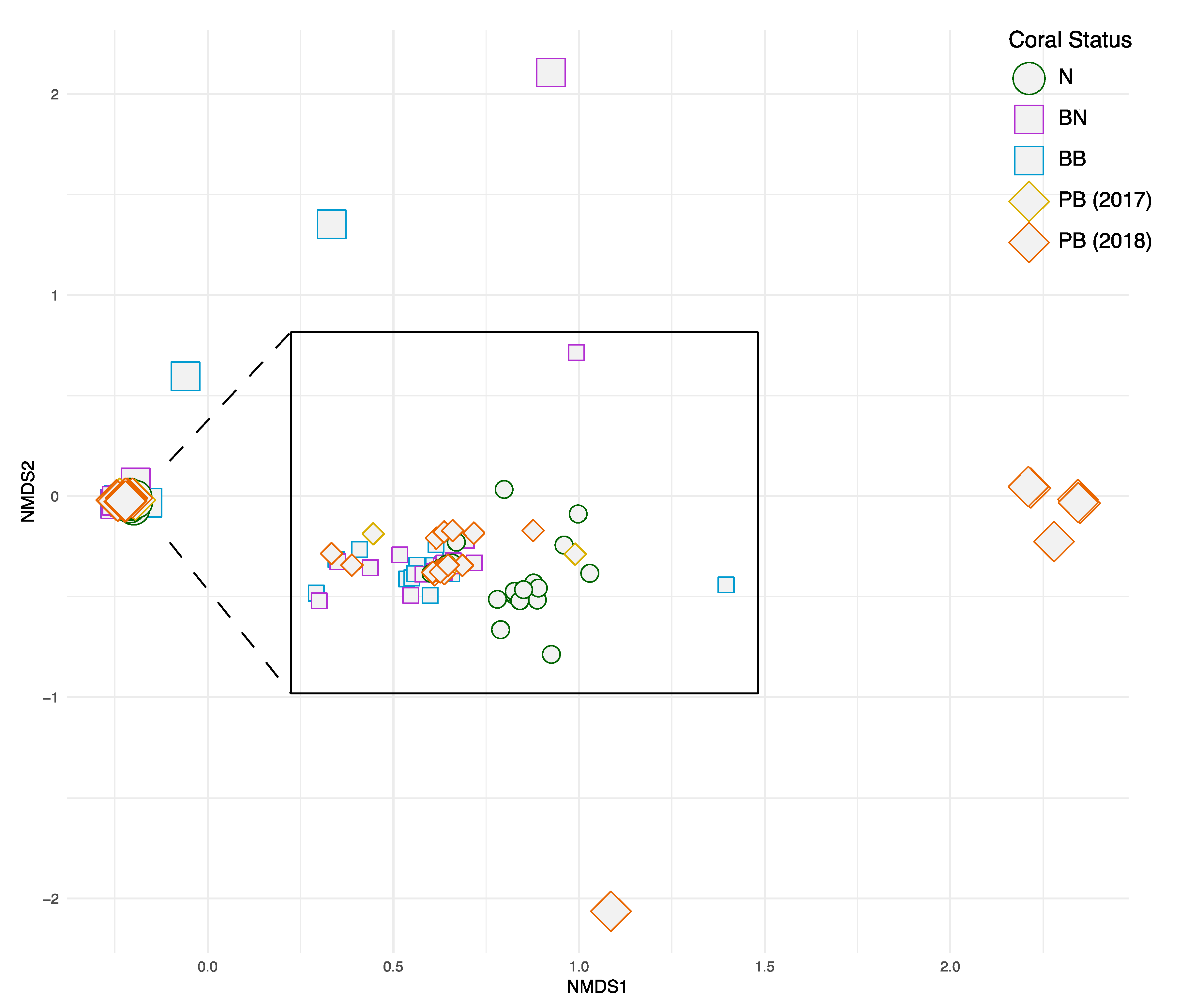
3. Results
4. Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kitahara, M.V.; Fukami, H.; Benzoni, F.; Huang, D. The New Systematics of Scleractinia: Integrating Molecular and Morphological Evidence. In The Cnidaria, Past, Present and Future; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 41–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, S.D.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Van der Land, J. Appendix: List of extant stony corals. Atoll Res. Bull. 1999, 459, 13–46. [Google Scholar]
- LaJeunesse, T.C.; Parkinson, J.E.; Gabrielson, P.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Reimer, J.D.; Voolstra, C.R.; Santos, S.R. Systematic Revision of Symbiodiniaceae Highlights the Antiquity and Diversity of Coral Endosymbionts. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2570–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, P.W. Coral reef bleaching: Facts, hypotheses and implications. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1996, 2, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.E. Coral bleaching: Causes and consequences. Coral Reefs 1997, 16, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscatine, L.; McCloskey, L.R.; Marian, R.E. Estimating the daily contribution of carbon from zooxanthellae to coral animal respiration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.S. The role of zooxanthellae in the nutritional energy requirements of Pocillopora eydouxi. Coral Reefs 1984, 2, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Stat, M.; Morris, E.; Gates, R.D. Functional diversity in coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9256–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, C.; Daniels, C.; Bayer, T.; Banguera-Hinestroza, E.; Barbrook, A.; Howe, C.J.; Lajeunesse, T.C.; Voolstra, C.R. Assessing Symbiodinium diversity in scleractinian corals via next-generation sequencing-based genotyping of the ITS2 rDNA region. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4418–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzil, J.T.I.; Ng, A.P.K.; Tey, Y.Q.; Tan, B.H.Y.; Yun, E.Y.; Huang, D. A Preliminary Characterisation of Symbiodinium Diversity in Some Common Corals From Singapore. Cosmos 2016, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochon, X.; Gates, R.D. A new Symbiodinium clade (Dinophyceae) from soritid foraminifera in Hawai’i. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzé, H.; Lecellier, G.J.; Saulnier, D.; Planes, S.; Gueguen, Y.; Wirshing, H.H.; Berteaux-Lecellier, V. An updated assessment of symbiodinium spp. that associate with common scleractinian corals from moorea (French Polynesia) reveals high diversity among background symbionts and a novel finding of clade B. PeerJ 2017, 2017, e2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunning, R.; Baker, A.C. Excess algal symbionts increase the susceptibility of reef corals to bleaching. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzé, H.; Lecellier, G.; Saulnier, D.; Berteaux-Lecellier, V. Symbiodinium clades A and D differentially predispose Acropora cytherea to disease and Vibrio spp. colonization. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.C. Flexibility and Specificity in Coral-Algal Symbiosis: Diversity, Ecology, and Biogeography of Symbiodinium. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 34, 661–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.E.; Mieog, J.C.; Colin, P.L.; Idip, D.; Van Oppen, M.J.H. Identity and diversity of coral endosymbionts (zooxanthellae) from three Palauan reefs with contrasting bleaching, temperature and shading histories. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieog, J.C.; Van Oppen, M.J.H.; Cantin, N.E.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. Real-time PCR reveals a high incidence of Symbiodinium clade D at low levels in four scleractinian corals across the Great Barrier Reef: Implications for symbiont shuffling. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claar, D.C.; McDevitt-Irwin, J.M.; Garren, M.; Vega Thurber, R.; Gates, R.D.; Baum, J.K. Increased diversity and concordant shifts in community structure of coral-associated Symbiodiniaceae and bacteria subjected to chronic human disturbance. Mol. Ecol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggat, W.; Seneca, F.; Wasmund, K.; Ukani, L.; Yellowlees, D.; Ainsworth, T.D. Differential responses of the coral host and their algal symbiont to thermal stress. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Baird, A.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Card, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Folke, C.; Grosberg, R.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; et al. Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science 2003, 301, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, P.W.; Maté, J.L.; Baker, A.C.; Calderón, M.O. Coral bleaching and mortality in Panama and Ecuador during the 1997–1998 El Niño-Southern Oscillation event: Spatial/temporal patterns and comparisons with the 1982–1983 event. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2001, 69, 79–109. [Google Scholar]
- Berkelmans, R.; Van Oppen, M.J.H. The role of zooxanthellae in the thermal tolerance of corals: A “nugget of hope” for coral reefs in an era of climate change. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oppen, M.J.H.; Lough, J.M. Coral Bleaching: Patterns, Processes, Causes and Consequences, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, M.W.; Strong, A.E. Applying MCSST to coral reef bleaching. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 16, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claar, D.C.; Szostek, L.; McDevitt-Irwin, J.M.; Schanze, J.J.; Baum, J.K. Global patterns and impacts of El Niño events on coral reefs: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, P.W. Extensive ‘Bleaching’ and Death of Reef Corals on the Pacific Coast of Panamá. Environ. Conserv. 1983, 10, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Barnes, M.L.; Bellwood, D.R.; Cinner, J.E.; Cumming, G.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; Van De Leemput, I.A.; Lough, J.M.; Morrison, T.H.; et al. Coral reefs in the Anthropocene. Nature 2017, 546, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Baird, A.H.; Connolly, S.R.; Dietzel, A.; Eakin, C.M.; Heron, S.F.; Hoey, A.S.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Liu, G.; et al. Global warming transforms coral reef assemblages. Nature 2018, 556, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eakin, C.M.; Morgan, J.A.; Heron, S.F.; Smith, T.B.; Liu, G.; Alvarez-Filip, L.; Baca, B.; Bartels, E.; Bastidas, C.; Bouchon, C.; et al. Caribbean corals in crisis: Record thermal stress, bleaching, and mortality in 2005. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.W.; Hernandez-Pech, X.; Iglesias-Prieto, R.; Fitt, W.K.; Schmidt, G.W. Community dynamics and physiology of Symbiodinium spp. before, during, and after a coral bleaching event. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levas, S.; Schoepf, V.; Warner, M.E.; Aschaffenburg, M.; Baumann, J.; Grottoli, A.G. Long-term recovery of Caribbean corals from bleaching. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2018, 506, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, A.A.; Ziegler, M.; Roik, A.; Röthig, T.; Hardenstine, R.S.; Emms, M.A.; Jensen, T.; Voolstra, C.R.; Berumen, M.L. In situ observations of coral bleaching in the central Saudi Arabian Red Sea during the 2015/2016 global coral bleaching event. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, E.O.; Smith, D.J.; Ziegler, M.; Kürten, B.; Conrad, C.; El-Haddad, K.M.; Voolstra, C.R.; Suggett, D.J. Thermal refugia against coral bleaching throughout the northern Red Sea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, e474–e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantin, N.E.; Cohen, A.L.; Karnauskas, K.B.; Tarrant, A.M.; McCorkle, D.C. Ocean Warming Slows Coral Growth in the Central Red Sea. Science 2010, 329, 322–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.E.; Dunne, R.P.; Chansang, H. Coral bleaching relative to elevated seawater temperature in the Andaman sea (Indian ocean) over the last 50 years. Coral Reefs 1996, 15, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, T.; Teleki, K.A.; Bradshaw, C.; Spalding, M.D. Coral bleaching in the Southern Seychelles during the 1997-1998 Indian Ocean warm event. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, J.M.B.; Burt, A.J.; Haupt, P.; Bunbury, N.; Mumby, P.J.; Schaepman-Strub, G. Impacts of the 2014–2017 global bleaching event on a protected remote atoll in the Western Indian Ocean. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClanahan, T.R.; Baird, A.H.; Marshall, P.A.; Toscano, M.A. Comparing bleaching and mortality responses of hard corals between southern Kenya and the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, P.A.; Baird, A.H. Bleaching of corals on the Great Barrier Reef: Differential susceptibilities among taxa. Coral Reefs 2000, 19, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkelmans, R.; De’ath, G.; Kininmonth, S.; Skirving, W.J. A comparison of the 1998 and 2002 coral bleaching events on the Great Barrier Reef: Spatial correlation, patterns, and predictions. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulstrup, K.E.; Berkelmans, R.; Ralph, P.J.; Van Oppen, M.J.H. Variation in bleaching sensitivity of two coral species across a latitudinal gradient on the Great Barrier Reef: The role of zooxanthellae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 314, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.F.; Selig, E.R. Regional decline of coral cover in the Indo-Pacific: Timing, extent, and subregional comparisons. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.S.L.; Huang, D.; Toh, K.B.; Sam, S.Q.; Kikuzawa, Y.P.; Toh, T.C.; Taira, D.; Chan, Y.K.S.; Hung, L.Z.T.; Sim, W.T.; et al. Responses of urban reef corals during the 2016 mass bleaching event. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Carballo-Bolaños, R.; Kuo, C.Y.; Keshavmurthy, S.; Chen, C.A. Leptoria phrygia in Southern Taiwan shuffles and switches symbionts to resist thermal-induced bleaching. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.J.; Knapp, I.S.; Maragos, J.E.; Davy, S.K. Modeling patterns of coral bleaching at a remote Central Pacific atoll. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, H.C.; Cohen, A.L.; Mollica, N.R.; Brainard, R.E.; Rivera, H.E.; DeCarlo, T.M.; Lohmann, G.P.; Drenkard, E.J.; Alpert, A.E.; Young, C.W.; et al. Repeat bleaching of a central Pacific coral reef over the past six decades (1960–2016). Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.L.; Lobel, P.S.; Tomasky, G.L. Coral Bleaching on Johnston Atoll, Central Pacific Ocean. Biol. Bull. 1997, 193, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, P.W. Coral Mortality and Disturbances to Coral Reefs in the Tropical Eastern Pacific. Elsevier Oceanogr. Ser. 1990, 52, 55–126. [Google Scholar]
- LaJeunesse, T.C.; Reyes-Bonilla, H.; Warner, M.E. Spring “bleaching” among Pocillopora in the Sea of Cortez, Eastern Pacific. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Cortés, J.; León, A.; Eleazar, R. Coral Bleaching and Mortality Associated with the 1997-98 El Niño in an Upwelling Environment in the Eastern Pacific (Gulf of Papagayo, Costa Rica). Bull. Mar. Sci. 2001, 69, 151–169. [Google Scholar]
- Eakin, C.M.; Sweatman, H.P.A.; Brainard, R.E. The 2014–2017 global-scale coral bleaching event: Insights and impacts. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClanahan, T.R.; Darling, E.S.; Maina, J.M.; Muthiga, N.A.; D’agata, S.D.; Jupiter, S.D.; Arthur, R.; Wilson, S.K.; Mangubhai, S.; Nand, Y.; et al. Temperature patterns and mechanisms influencing coral bleaching during the 2016 El Niño. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devotta, D.; De La Cour, J.; Geiger, E.; Gomez, A.; Heron, S.F.; Liu, G.; Marsh, B.; Skirving, W.J.; Eakin, C.M. Overview of the third global coral bleaching event (2014–2017). In Status of Coral Reefs in East Asian Seas Region: 2018, Ministry of the Environment of Japan and Japan Wildlife Research Center, Tokyo, Japan (2018); Kimura, T., Tun, K., Chou, L.M., Eds.; Ministry of the Environment: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, K.; Singh, T.; Iguchi, A. Bleaching and post-bleaching mortality of Acropora corals on a heat-susceptible reef in 2016. PeerJ 2019, 2019, e8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayanne, H.; Suzuki, R.; Liu, G. Bleaching in the Ryukyu Islands in 2016 and associated Degree Heating Week threshold. Galaxea J. Coral Reef Stud. 2017, 19, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siau, M.E. Warmer Seas Causing Mass Coral Bleaching in Singapore Waters. Today Online 2016. Available online: https://www.todayonline.com/singapore/warmer-seas-causing-mass-coral-bleaching-singapore-waters (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Tan, A. Warming Seas Cause Longest Coral Bleaching in Singapore. Straits Times 2016. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/environment/warming-seas-cause-longest-coral-bleaching-in-spore (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Toh, T.C.; Huang, D.; Tun, K.; Chou, L.M. Summary of Coral Bleaching from 2014 to 2017 in Singapore. In Status of Coral Reefs in East Asian Seas Region: 2018, Ministry of the Environment of Japan and Japan Wildlife Research Center, Tokyo, Japan (2018); Kimura, T., Tun, K., Chou, L.M., Eds.; Ministry of the Environment: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, A.C. Symbiont Diversity on Coral Reefs and Its Relationship to Bleaching Resistance and Resilience. Coral Heal. Dis. 2004, 177–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sampayo, E.M.; Ridgway, T.; Bongaerts, P.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Bleaching susceptibility and mortality of corals are determined by fine-scale differences in symbiont type. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10444–10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulotte, N.M.; Dalton, S.J.; Carroll, A.G.; Harrison, P.L.; Putnam, H.M.; Peplow, L.M.; Van Oppen, M.J.H. Exploring the Symbiodinium rare biosphere provides evidence for symbiont switching in reef-building corals. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.M.; Freeman, C.J.; Wong, J.C.Y.; Fogel, M.L.; Knowlton, N. Climate change promotes parasitism in a coral symbiosis. ISME J. 2018, 12, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunning, R.; Baker, A.C. Not just who, but how many: The importance of partner abundance in reef coral symbioses. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.R.; Low, J.; Tun, K.; Wilson, B.; Ng, C.; Raingeard, D.; Ulstrup, K.E.; Tanzil, J.T.I.; Todd, P.A.; Toh, T.C.; et al. Coral community response to bleaching on a highly disturbed reef. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.S.Y.; Chan, Y.K.S.; Ng, C.S.L.; Tun, K.P.P.; Darling, E.S.; Huang, D. Comparing patterns of taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity in reef coral communities. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, G.S.E.; Chan, Y.K.S.; Jain, S.S.; Huang, D. Light limitation selects for depth generalists in urbanised reef coral communities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 147, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, L.M.; Toh, T.C.; Toh, K.B.; Ng, C.S.L.; Cabaitan, P.; Tun, K.; Goh, E.; Afiq-Rosli, L.; Taira, D.; Du, R.C.P.; et al. Differential response of coral assemblages to thermal stress underscores the complexity in predicting bleaching susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.G.; Gurskaya, A.; Hume, B.C.C.; Voolstra, C.R.; Todd, P.A.; Bauman, A.G.; Burt, J.A. Low Symbiodiniaceae diversity in a turbid marginal reef environment. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulstrup, K.E.; Van Oppen, M.J.H. Geographic and habitat partitioning of genetically distinct zooxanthellae (Symbiodinium) in Acropora corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, A.M.S.; McDonald, M.D.; Baker, A.C. Development of clade-specific Symbiodinium primers for quantitative PCR (qPCR) and their application to detecting clade D symbionts in Caribbean corals. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; Tseng, C.H.; Chen, C.A.; Tang, S.L. The dynamics of microbial partnerships in the coral Isopora palifera. ISME J. 2011, 5, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavmurthy, S.; Hsu, C.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Meng, P.J.; Wang, J.T.; Chen, C.A. Symbiont communities and host genetic structure of the brain coral Platygyra verweyi, at the outlet of a nuclear power plant and adjacent areas. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 4393–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.G.; Ketchum, R.N.; Burt, J.A. Host specificity of Symbiodinium variants revealed by an ITS2 metahaplotype approach. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, M.; Arif, C.; Burt, J.A.; Dobretsov, S.; Roder, C.; LaJeunesse, T.C.; Voolstra, C.R. Biogeography and molecular diversity of coral symbionts in the genus Symbiodinium around the Arabian Peninsula. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Chai, G.J.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, K.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Liao, B.; et al. Flexible symbiotic associations of Symbiodinium with five typical coral species in tropical and subtropical reef regions of the northern South China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, O.S.; Lin, X.; Ng, T.Y.; Li, L.; Ang, P.; Lin, S. Genome Size, rDNA Copy, and qPCR Assays for Symbiodiniaceae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Library Preparation. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Hume, B.C.C.; D’Angelo, C.; Smith, E.G.; Stevens, J.R.; Burt, J.; Wiedenmann, J. Symbiodinium thermophilum sp. nov., a thermotolerant symbiotic alga prevalent in corals of the world’s hottest sea, the Persian/Arabian Gulf. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, B.; D’Angelo, C.; Burt, J.; Baker, A.C.; Riegl, B.; Wiedenmann, J. Corals from the Persian/Arabian Gulf as models for thermotolerant reef-builders: Prevalence of clade C3 Symbiodinium, host fluorescence and ex situ temperature tolerance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, B.C.C.; Smith, E.G.; Ziegler, M.; Warrington, H.J.M.; Burt, J.A.; LaJeunesse, T.C.; Wiedenmann, J.; Voolstra, C.R. SymPortal: A novel analytical framework and platform for coral algal symbiont next-generation sequencing ITS2 profiling. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1063–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, A.M.; Morrison, H.G.; Lescault, P.J.; Reveillaud, J.; Vineis, J.H.; Sogin, M.L. Minimum entropy decomposition: Unsupervised oligotyping for sensitive partitioning of high-throughput marker gene sequences. ISME J. 2015, 9, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Mcglinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Package “vegan”: Community Ecology Package. Community Ecol. Packag. 2019, 2, 1–296. [Google Scholar]
- Lajeunesse, T.C.; Bhagooli, R.; Hidaka, M.; deVantier, L.; Done, T.; Schmidt, G.; Fitt, W.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Closely related Symbiodinium spp. differ in relative dominance in coral reef host communities across. Mar. Ecol. Ser. 2004, 284, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, T.F.; Ulstrup, K.E.; Dandan, S.S.; Heyward, A.J.; Kühl, M.; Muirhead, A.; O’Leary, R.A.; Ziersen, B.E.F.; van Oppen, M.J.H. Niche specialization of reef-building corals in the mesophotic zone: Metabolic trade-offs between divergent Symbiodinium types. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaerts, P.; Sampayo, E.M.; Bridge, T.C.L.; Ridgway, T.; Vermeulen, F.; Englebert, N.; Webster, J.M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Symbiodinium diversity in mesophotic coral communities on the Great Barrier Reef: A first assessment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 439, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, J.W.; Jordan, F.L.; Maier, R.M. Analysis of artifacts suggests DGGE should not be used for quantitative diversity analysis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.; Acolado, P.; Cala, Y.; Cobi Án, D.; Coelho, V.; Hernández, A.; Jones, R.J.; Mallela, J.; Manfrino, C. The Effects of Coral Bleaching in the Northern Caribbean and Western Atlantic. Faculty Authored Books and Books Contributions 2008, 108. Available online: https://scholar.dominican.edu/books/108 (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Buddemeier, R.W.; Fautin, D.G. Coral Bleaching as an Adaptive Mechanism. Bioscience 1993, 43, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.C. Reef corals bleach to survive change. Nature 2001, 411, 765–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, N.; Rohwer, F. Multispecies Microbial Mutualisms on Coral Reefs: The Host as a Habitat. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, S51–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunning, R.; Silverstein, R.N.; Baker, A.C. Investigating the causes and consequences of symbiont shuffling in a multi-partner reef coral symbiosis under environmental change. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.N.; Cunning, R.; Baker, A.C. Change in algal symbiont communities after bleaching, not prior heat exposure, increases heat tolerance of reef corals. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.W.; Spies, N.; Richmond, R. Conservation of Symbiodinium spp. clade in the coral Pocillopora damicornis during the 2014 mass-bleaching event. PeerJ Prepr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.E.; Ward, J.O.; Eggleston, E.M.; Fedorov, E.; Parkinson, J.E.; Dahlgren, C.P.; Cunning, R. Characterization of a thermally tolerant Orbicella faveolata reef in Abaco, The Bahamas. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavmurthy, S.; Tee, H.S.; Kao, K.W.; Wang, J.T.; Chen, C.A. Specificity trumps flexibility—location-based stable associations between Symbiodiniaceae genera and Platygyra verweyi (Scleractinia; Merulinidae). PeerJ 2020, 2020, e8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Hume, B.C.C.; Burt, J.; Smith, E.G.; Achterberg, E.P.; Wiedenmann, J. Local adaptation constrains the distribution potential of heat-tolerant Symbiodinium from the Persian/Arabian Gulf. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gates, R.D.; Eomund, P.J. The physiological mechanisms of acclimatization in tropical reef corals. Am. Zool. 1999, 39, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Van Woesik, R. Water-flow rates and passive diffusion partially explain differential survival of corals during the 1998 bleaching event. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 212, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, H.M.; Stat, M.; Pochon, X.; Gates, R.D. Endosymbiotic flexibility associates with environmental sensitivity in scleractinian corals. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4352–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Suzuki, G.; Hayashibara, T.; Koike, K. Acropora recruits harbor “rare” Symbiodinium in the environmental pool. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meistertzheim, A.L.; Pochon, X.; Wood, S.A.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Hédouin, L. Development of a quantitative PCR–high-resolution melting assay for absolute measurement of coral-Symbiodiniaceae associations and its application to investigating variability at three spatial scales. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornhill, D.J.; Lajeunesse, T.C.; Santos, S.R. Measuring rDNA diversity in eukaryotic microbial systems: How intragenomic variation, pseudogenes, and PCR artifacts confound biodiversity estimates. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 5326–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, K.M.; Davies, S.W.; Kenkel, C.D.; Willis, B.L.; Matz, M.V.; Bay, L.K. Deep-sequencing method for quantifying background abundances of Symbiodinium types: Exploring the rare Symbiodinium biosphere in reef-building corals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunning, R.; Gates, R.D.; Edmunds, P.J. Using high-throughput sequencing of ITS2 to describe Symbiodinium metacommunities in St. John, US Virgin Islands. PeerJ 2017, 2017, e3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terraneo, T.I.; Fusi, M.; Hume, B.C.C.; Arrigoni, R.; Voolstra, C.R.; Benzoni, F.; Forsman, Z.H.; Berumen, M.L. Environmental latitudinal gradients and host-specificity shape Symbiodiniaceae distribution in Red Sea Porites corals. J. Biogeogr. 2019, 46, 2323–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howells, E.J.; Bauman, A.G.; Vaughan, G.O.; Hume, B.C.C.; Voolstra, C.R.; Burt, J.A. Corals in the hottest reefs in the world exhibit symbiont fidelity not flexibility. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokell, J.R.; Hamp, T.J.; Steck, T.R. Examining changes in bacterial abundance in complex communities using next-generation sequencing is enhanced with quantitative PCR. Antonie Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 109, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Luukkonen, P.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Salonen, A.; Korpela, K. Quantitative PCR provides a simple and accessible method for quantitative microbiota profiling. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obura, D.O.; Aeby, G.; Amornthammarong, N.; Appeltans, W.; Bax, N.; Bishop, J.; Brainard, R.E.; Chan, S.; Fletcher, P.; Gordon, T.A.C.; et al. Coral reef monitoring, reef assessment technologies, and ecosystem-based management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, W.K.; Gates, R.D.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bythell, J.C.; Jatkar, A.; Grottoli, A.G.; Gomez, M.; Fisher, P.; Lajuenesse, T.C.; Pantos, O.; et al. Response of two species of Indo-Pacific corals, Porites cylindrica and Stylophora pistillata, to short-term thermal stress: The host does matter in determining the tolerance of corals to bleaching. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2009, 373, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loya, Y.; Sakai, K.; Yamazato, K.; Nakano, Y.; Sambali, H.; Van Woesik, R. Coral bleaching: The winners and the losers. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Woesik, R.; Sakai, K.; Ganase, A.; Loya, Y. Revisiting the winners and the losers a decade after coral bleaching. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 434, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.L.; Raina, J.B.; Kahlke, T.; Seymour, J.R.; van Oppen, M.J.H.; Suggett, D.J. Symbiodiniaceae-bacteria interactions: Rethinking metabolite exchange in reef-building corals as multi-partner metabolic networks. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, S.S.; Afiq-Rosli, L.; Feldman, B.; Levy, O.; Phua, J.W.; Wainwright, B.J.; Huang, D. Homogenization of Endosymbiont Communities Hosted by Equatorial Corals during the 2016 Mass Bleaching Event. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091370
Jain SS, Afiq-Rosli L, Feldman B, Levy O, Phua JW, Wainwright BJ, Huang D. Homogenization of Endosymbiont Communities Hosted by Equatorial Corals during the 2016 Mass Bleaching Event. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091370
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Sudhanshi S., Lutfi Afiq-Rosli, Bar Feldman, Oren Levy, Jun Wei Phua, Benjamin J. Wainwright, and Danwei Huang. 2020. "Homogenization of Endosymbiont Communities Hosted by Equatorial Corals during the 2016 Mass Bleaching Event" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091370
APA StyleJain, S. S., Afiq-Rosli, L., Feldman, B., Levy, O., Phua, J. W., Wainwright, B. J., & Huang, D. (2020). Homogenization of Endosymbiont Communities Hosted by Equatorial Corals during the 2016 Mass Bleaching Event. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091370





