Abstract
Gut microbiota is composed of different microorganisms that play an important role in the host. New research shows that bidirectional communications happen between intestinal microbiota and the brain, which is known as the gut–brain axis. This communication is significant and could have a negative or positive effect depending on the state of the gut microbiota. Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a mental illness associated with metabolic, immunologic, biochemical, sensory abnormalities, and extremely low body weight. Different studies have shown a dysbiosis in patients with AN. Due to the gut–brain axis, it was observed that some of the symptoms could be improved in these patients by boosting their gut microbiota. This paper highlights some evidence connecting the role of microbiota in the AN onset and disease progress. Finally, a proposal is done to include the microbiota analysis as part of the recovery protocol used to treat AN patients. When conducting clinical studies of gut microbiota in AN patients, dysbiosis is expected to be found. Then the prescription of a personalized treatment rich in prebiotics and probiotics could be proposed to reverse the dysbiosis.
1. Introduction
The intestine hosts a large community of microorganisms, called microbiota, which live in symbiosis with the host. Microbiota is composed of: archaea, protozoa, viruses and, above all, bacteria that exceed the number of human cells. The microbiota composition is like a fingerprint, unique and specific for each human [1]. The microbiota changes in number and type of species along the intestine, and its density and composition are affected by chemical, nutritional and immunological factors. For example, the small intestine contains elevated levels of acids and oxygen and the transit time is fast due to peristaltic movements. These factors limit bacterial growth, thus only those fast-growing bacteria will be able to adhere to the mucosal epithelium. In the colon, the environmental conditions are different, and therefore it can be inhabited by larger communities of bacteria, especially anaerobes. In fact, the majority of these bacterial communities are found precisely in the colon [2].
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a mental illness that endangers the life of those who suffer from it. According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V) criteria, patients who maintain a diet restriction in relation to their energy needs, present a significantly lower weight than expected (according to their age, gender, development, and health status), or an intense fear for gaining weight are diagnosed with AN and can be classified as restrictive (self-induced vomiting, laxative abuse, diuretics or enemas during the last three months) or compulsive (binge-eating/ purging) [3]. Furthermore, AN is associated with metabolic, immunological, biochemical, sensory abnormalities, and an extremely low body weight [4,5,6]. Patients present alterations in the perception of their weight or their corporal silhouette, exaggeration of feeding importance or denial of the danger that the low weight implies. Weight recovery in patients with AN is essential for the prevention of somatic and psychological sequelae as osteoporosis, infertility or depression [7].
2. The Brain–Gut Axis and Possible Implications for Anorexia Nervosa
The Brain–Gut axis is the bidirectional communication system between the gut and the host brain that is regulated by neural, endocrine, and immunological systems and in which microbiota plays a key role [8,9]. The brain–microbiota communication is complex and carried out in several ways. One of these is the communication to the nervous system through the enteric nervous system (ENS). These connections coordinate and control the secretions, motility, mucosal transport and blood flow of the gastrointestinal tract that directly influence gut microbiota composition. The system works by means of motor neurons located in their ganglia, which act as effector cells of the gastrointestinal tract [10]. The ENS is connected to the central nervous system (CNS) by means of the vagus nerve, thus creating direct neurochemical signals from the gut microbiota to the brain [11], and from the nervous system to the gut microbiota [12].
There is a plethora of molecules that connect the brain and the gut microbiota. In animal studies, it has been observed that the absence of microbiota provokes an abnormal development of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis), that controls the release of cortisol which is the stress induced hormone [13]. The gut microbiota also impacts on endocrine glands that produce sexual and thyroid hormones and is implicated in the regulation of the peptides and hormones release, involved in the body mass energy balance and feeding behavior [14]. It has been proposed that certain microbiota microorganisms can induce an effect (positive or negative) on the host food habits and emotional behavior through the secretion of molecules [15]. On the other side, bacteria have receptors for these hormones, so they can communicate with the host’s brain [16]. For example, Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria are capable of synthesizing the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that reduces anxiety and stress, while Escherichia, Bacillus, and Saccharomyces produce norepinephrine [17]. Serotonin has been isolated from Candida, Streptococcus, Escherichia, and Enterococcus, and dopamine, the major disruptor of the CNS [18], is one of the final products of the metabolism of Bacillus and Serratia [19]. Moreover, the gut microbiota also produces butyrate acid that can exert numerous beneficial effects in brain [20], but also release the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to the bloodstream that crosses the blood-brain barrier and can induce neuroinflammation with an implication of the microglia [21,22]. Thus, microorganisms that composed the microbiota seem to be the recruiters for the bidirectional communication between the gut and the nervous system (Figure 1), and to modulate brain development, function, and behavior [23]. It has even been suggested that gut microbiota control our appetite and the preference for foods that serve them as a substrate [24].
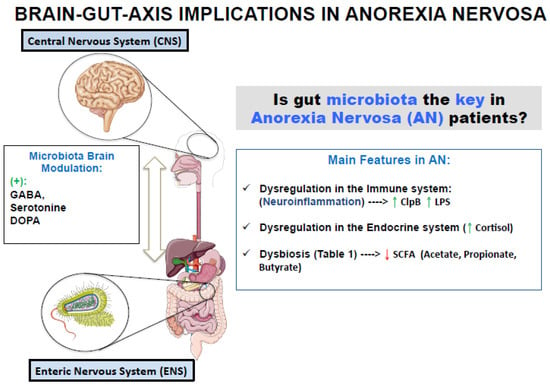
Figure 1.
Microbiota as a recruiter of bidirectional communication between the brain and the gut and changes in microbiota composition observed in Anorexia Nervosa patients [15,17,19].
The immune system also connects the brain and the microbiota [12]. Concerning the connections to the immune response and its relationship with the microbiota, we can classify the relationship in three terms: (1) when the brain–blood barrier (BBB) is damaged and allows molecules produced, direct or indirectly, by the microbiota, as LPS or the inflammatory interleukin IL-6, to cross the barrier producing neuroinflammation (“leaky gut” theory); (2) the microglia involvement in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation; and (3) the immune cells, as maturation and function of both, T and B-cells (and also its Ig production) are under the microbiota control [25]. As described by Liang et al. all the mentioned factors can have an impact on AN [26].
Although the pathophysiological mechanisms behind the AN are still to be elucidated, a neuropeptide and neuroendocrine dysregulation is usually found in eating disorders [27]. In AN there is a dysregulation of the endocrine system including the hypothalamic–pituitary axis hormones, adipokines, and appetite-regulating hormones [28]. Emerging data point to a dysregulation of serotonin pathways in cortical and limbic structures that may be related to anxiety, behavioral inhibition, and body image distortions that happen in patients diagnosed of AN [29]. The anxiety and stress associated with AN disorder can be relevant factors altering the microbiota, since prolonged psychological stress induce changes in gut microbiota and in their associated metabolites [30]. It has been demonstrated an inverse relationship between stress and the abundance of Lactobacillus [31] and a positive relationship between Campylobacter and stress [32]. It seems that stress-induced dysbiosis is the key between chronic psychological stressors and systemic inflammation in humans [33].
3. Dysbiosis in Anorexia Nervosa Patients
Gut microbiota may play a vital role in eating disorders. Diet is the most influential external factor for gut microbiota composition and the starvation and emotional imbalance that occurs in AN can induce several changes in gut microbiota. Data available on microbiota in AN population show marked differences in the AN patient’s microbiota when compared with the one of the normal weight individuals. The gut microbiota of patients with anorexia nervosa has lower microbial diversity, affecting all taxonomic levels [34], and there is an overgrowth of some families such as Enterobacteriaceae and the archaeon Methanobrevibacter smithii (M. smithii) [35,36,37]. In addition, it has been observed that there are differences in the microbiota between restrictive anorexia and compulsive anorexia [38]. Some of the taxa underrepresented in the gut microbiota of AN patients are short chain fatty acid (SCFA) producers and it has been observed a negative correlation between the butyrate production and the anxiety levels [36]. Diversity and composition of gut microbiota have been also associated with the depression, anxiety and eating disorder psychopathology symptoms [30]. Current research supports that a decrease of Firmicutes with respect to the Bacteroidetes together with an increase of the archaea M. smithii and Proteobacteria could be the microbiota signature associated to AN [38,39]. This archaeon plays an important role removing hydrogen excess from bacterial fermentation in the gut. Its presence seems to be related to the optimization of energy use in the hypocaloric diets followed by AN patients. The presence of M. smithii has been correlated with 22 bacterial taxa, mainly clostridiales, establishing a niche of bacterial partners with a syntrophic relationship [40]. Borgo et al. reported increases levels of M. smithii, a decrease of Roseburia, Ruminococcus, and Clostridium, followed by a reduction in the butyrate production, possibly due to the decrease of Roseburia and Clostridium, butyrate producers. They also observed an increase of Enterobacteriaceae, which is normally associated with intestinal inflammation and can produce the bacterial peptide caseinolytic protease b (ClpB), an antigen mimeting the a-MSH that suppress appetite through the activation of anorexigenic neurons [36]. Female patients with eating disorders had elevated levels of ClpB that positively correlated with the eating disorder inventory 2 score (EDI-2) [41]. This work would indicate that bacterial peptides could have a role in eating disorders. On the other hand, the secretion of antibacterial peptides such as defensins or immunoglobulin A (IgA), which play an important role in the health of the host by maintaining symbiosis and avoiding colonization by pathogens, could be altered by the AN intestinal dysbiosis [42]. Nowadays, there is no work in the literature that addresses changes in the secretion of antibacterial peptides with the intestinal dysbiosis that occurs in patients with AN.
Diet shapes the composition of gut microbiota, defining which microorganisms colonize, growth, persist, or become extinguished, and therefore also influences the health of the host [43,44]. The lack of food intake in AN could significantly modify the host-gut microbiota. In fact, the microbiota of undernourished children has an immature profile and could be implied in their stunted growth [45,46]. The lack of food can affect the Lactobacillus population that usually live in nutrient rich environments and that enter the stationary phase of growth when there are not enough nutrients [47]. There are several populations of bacteria (Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides and Verrucomicrobia) that feed on diet non-digestible carbohydrates and that in the absence of them can use the host-derived glycans, in particular, the mucins that constitute the protective layer of the intestine [48,49,50]. Due to their proximity to the immune system, mucins-degrading bacteria are in a prime location to influence the immune host response and could explain the increase risk of opportunistic infections that suffer AN patients [51]. Bacteroides synthesize their membrane exopolysaccharides (EPS) from host glycans. These EPS make them more resistant and in turn reinforce the host’s immune system [49]. If in periods of starvation, such as AN, there is a co-association or competition and exclusion of species that feed on mucins (as Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides and Verrucomicrobia) is something that is still unknown today. Mack et al. [38] have found elevated levels of Verrucomicrobia phylum and a lower abundance of the Bacteroides genus in patients with AN. When patients gain weight, bacterial diversity increases, but many of the disturbances that have arisen, are maintained [38,52]. (Figure 1; Table 1).

Table 1.
Differences of gut microbiota when comparing AN patients and controls.
4. The Role of Lifestyle in Microbiota Patterns
The etiology of AN is complex. The microbiota dynamics depends on complex interactions between genetics and environmental factors and the microbiome is needed to keep a healthy state. Data suggest that environmental and psychological factors can fire the expression of the associated genetic risk to cause the eating disorder [53]. Concerning the environment, the impact of dietary and non-dietary lifestyle factors on the gut microbiota is well known but not many data are available for AN patients. It seems to be a direct consequence of the disordered feeding behaviors such as vomiting or laxative practices as a part of an unhealthy lifestyle. The discussion about if some cases of AN could be considered a consequence of an inappropriate lifestyle or feeding behaviors is always in the air, for example, the study of Pro-Ana movements, groups of people discussing about anorexia in the social media define the maintenance of certain lifestyle patterns that keep the obsessive idea of getting a very low weight [54]. Indeed, it is common for patients with AN to avoid carbohydrates in the diet and increase the consumption of protein of animal origin. By obtaining a smaller amount of fiber, a smaller amount of short-chain fatty acids is formed, and the production of branched-chain fatty acids increases changing the microbiota composition. This change in the type of fatty acids may be relevant in eating disorders for metabolic dysfunctions and in insulin resistance [55].
Individuals with AN commonly present a comorbid anxiety disorder [56]. Animal studies in anx−/anx+ mice have generated new theories that make a point for this comorbidity in inflammation. Moreover, some microbiota patterns in inflammatory situations are related to the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis response to stressors [13]. Some stressors may promote microbial translocation boosting gut inflammation which eventually has been considered the link between microbiota changes in AN and its onset [57]. In fact, although, the analysis of many inflammation biomarkers in blood reported no changes in patients with severe AN symptoms [58], the commensal microbiota related to inflammation suffers changes in AN patients [55]. In addition, diets that are used for recovery, based on animal products, could lead to the development of microbiota with an inflammatory profile [7].
The microbiota patterns in AN, and its changes from the onset to the first stages, could probably give us information about the individual cases and the implications of the different actors in the eating disorder development. It has been reported that early life perturbations can impact neurodevelopment and being responsible of mental problems suffered later in life as both seems to evolve in parallel. This is a point where a lifestyle-based therapeutic intervention should to be consider to combat future brain disorders [59].
5. Managing Microbiota in Anorexia Nervosa
There are two ways to manipulate microbiota: By manipulating content after the administration of pro/prebiotics or by direct transfer of gut microbiota from another organism. The treatment for eating disorders consists of psychological/psychiatric therapy and nutritional rehabilitation tailored to the patient. However, the biological part of the AN pattern is not usually considered for the treatment, as there are not biological biomarkers that can be used as predictors for the onset and development of AN. Up to date, it is still not clear if the gut microbiota plays a role in the onset and evolution of the disorder but the therapeutic potential of a diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics or the complementation with some probiotic strain look promising [60].
The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) defines probiotics as living microorganisms that, when administered in adequate quantities, confer benefits for host health [61]. The ISAPP panel supports the general benefits of probiotics for gut microbiota, confirming that they help to have a healthy digestive tract. It mentions, as well, the growing research concerning its use in improving the reproductive tract, oral cavity, lungs, skin, and the microbiota–gut–brain axis [61]. Some probiotics were reported as supplements that improve emotions [62] and certain Lactobacillus strains improved behavioral abnormalities [63]. Moreover, the use of the probiotic strain Bacteroides fragilis has been proposed in order to correct gastrointestinal function, and it seems to be implicated in the serotonin production restoration [64]. Some other examples of strains studied for the general health benefits mentioned above are Bifidobacteria (B. adolescentis, B. animalis, B. bifidum, B. brevis, and B. longum) and Lactobacillus (L. acidophilus, L. casei, L. fermentum, L. gasseri, L. johnsonii, L. paracasei, L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, and L. salivarius). Recently, it has been suggested that the supplementation with the probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum P8 alleviates stress and anxiety patterns that could be related to AN as we stated above [65].
These treatments must be in consonance with the nutritional rehabilitation, with the aim to restore physiological functions by reversing malnutrition. It has to be underlined that patients can respond to them in an unusual way [66]. The use of probiotics strain in AN must be managed carefully due to the risk of bacterial infections. Although these infections are not common, opportunistic microorganisms can take the advantage of infecting immunosuppressed patients like those with malnutrition habits [51]. There are some data on gut microbiota patients with AN suggesting that refeeding increases gut microbial diversity [30]. For this reason, the characterization of the bacterial population through the alpha and beta diversities of patients should be also considered.
Furthermore, the metabolites from prebiotic fermentation, especially those of SCFA as acetate, propionate, butyrate, and lactate are reported to be beneficial for health, [67]. Concerning the prebiotics, studies in mice show that the use of fructans as prebiotics, reduces obesity, diabetes, hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and insulin resistance and, at the same time, promotes the secretion of peptide YY and GLP1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) [66]. A debate has been opened regarding fiber classification as a prebiotic: not all fibers can be classified as such and the only ones that fit in this category are the fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) and the galacto-oligosacáridos (GOS) [68]. Inulin is the most well-known type of FOS. It has been shown that inulin can inhibit the intestine colonization from pathogens, providing a protective effect against acute or chronic gut disturbances [67].
Considering other way to manipulate microbiota, the transfer of microbiota between organisms can be done using fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). For mental disorders, transplantation of fecal samples from patients with depression into germ-free mice result in depressive patterns [69]. Upcoming studies will tell us if this is the approximation to restore the microbiota diversity in patients with an impaired microbiota.
Then, taking into consideration the information managed, a protocol including the microbiota study and a possible intervention to replace the damaged microbiota in dysbiosis could be considered. Some of the interesting parameters for studying the microbiota are summarized in three aspects that may be included in the protocol: (1) check nutritional status, dietary patterns and fiber consumption; (2) microbiota analysis focusing in the study of bacterial diversity, the estimation of the Firmicutes-Bacteroidetes ratio and the total count of Proteobacteria and M. smithii, through metagenomic studies; and (3) in case of inadequate feeding habits, correct the diet, increasing the fiber intake and consider the supplementation with probiotics strains or food rich in probiotics.
6. Conclusions
The intestinal microbiota changes depend on the feeding habits. M. smithii, have been found incremented in patients with AN and could be considered a marker for the disease onset and progression. Also, the loss of diversity and changes in the bacterial community composition due to a dysbiosis and the presence of inadequate feeding habits could be a signature to start with the microbiota handling in patients with AN. The intervention could include the restoration of impaired microbiota with different tools as pro/prebiotics intake or a FMT.
Thus, considering the available data, and, in the absence of good biomarkers for the study of AN, microbiota could be a good point of intervention in the management of AN patients. This protocol must be in consonance with a controlled refeeding, increasing the levels of dietary fiber and the use of certain pro/prebiotics that could provide us one step ahead in the knowledge of the complex scenario found in AN patients.
Author Contributions
V.M.-F., M.B., M.L. and R.G.-S. performed the bibliography search and designed the article. R.B.M., J.M.B. and A.B.-F. designed and review the clinical intervention. R.G.-S. wrote the article. C.B., M.L. and M.B. carefully reviewed and gave some inputs about the paper.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ramón y Cajal grant 2012_11910 and the AGL2016-77288-R project from the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, Spain, the “Cátedra ASISA” project 2015/UEM46, and Universidad Europea projects: 2017/UEM15 and 2018/UEM4.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Milner, M.R.; McAnarney, E.R.; Klish, W.J. Metabolic abnormalities in adolescent patients with anorexia nervosa. J. Adolesc. Heal. Care 1985, 6, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.; Stewart, P.M.; Vizzard, J.; Abraham, S. Biochemical abnormalities in anorexia nervosa and bulimia. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1987, 24, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nova, E.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Morandé, G.; Marcos, A. Cytokine production by blood mononuclear cells from in-patients with anorexia nervosa. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J.; Baines, J. Food matters: How the microbiome and gut–brain interaction might impact the development and course of anorexia nervosa. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacias, M.; Gaspari, S.; Santos, P.M.G.; Tamburini, S.; Andrade, M.; Zhang, F.; Shen, N.; Tolstikov, V.; Kiebish, M.A.; Dupree, J.L.; et al. Microbiota-driven transcriptional changes in prefrontal cortex override genetic differences in social behavior. Elife 2016, 5, e13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omran, Y.; Aziz, Q. The brain-gut axis in health and disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T.R.; Mazmanian, S.K. Control of brain development, function, and behavior by the microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, N. Microbiome, HPA axis and production of endocrine hormones in the gut. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, H.; Debelius, J.W.; Knight, R.; Koren, O. Microbial endocrinology: The interplay between the microbiota and the endocrine system. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, C.; Tsuji, H.; Hata, T.; Gondo, M.; Takakura, S.; Kawai, K.; Yoshihara, K.; Ogata, K.; Nomoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.T. Influence of Stressor-Induced Nervous System Activation on the Intestinal Microbiota and the Importance for Immunomodulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehhaghi, M.; Kazemi Shariat Panahi, H.; Guillemin, G.J. Microorganisms’ Footprint in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrensel, A.; Ceylan, M.E. The gut-brain axis: The missing link in depression. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2015, 13, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C. How gut microbes talk to organs: The role of endocrine and nervous routes. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.W.; Alim, I.; Bultman, S.J.; Ratan, R.R. Butyrate, neuroepigenetics and the gut microbiome: Can a high fiber diet improve brain health? Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 625, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzki, L.; Szulc, A. “Immune Gate” of psychopathology-The role of gut derived immune activation in major psychiatric disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; De Angelis, A.L.H.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut instincts: Microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, ageing and neurodegeneration. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, J.; Maley, C.C.; Aktipis, C.A. Is eating behavior manipulated by the gastrointestinal microbiota? Evolutionary pressures and potential mechanisms. BioEssays 2014, 36, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoop, K.A.; Gustafsson, J.K.; McDonald, K.G.; Kulkarni, D.H.; Coughlin, P.E.; McCrate, S.; Kim, D.; Hsieh, C.S.; Hogan, S.P.; Elson, C.O.; et al. Microbial antigen encounter during a preweaning interval is critical for tolerance to gut bacteria. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaao1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wu, X.; Jin, F. Gut-Brain Psychology: Rethinking Psychology From the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailer, U.; Kaye, W. A Review of Neuropeptide and Neuroendocrine Dysregulation in Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2003, 2, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schorr, M.; Miller, K.K. The endocrine manifestations of anorexia nervosa: Mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailer, U.F.; Kaye, W.H. Serotonin: Imaging findings in eating disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 6, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Watson, H.J.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tarantino, L.M.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. The Intestinal Microbiota in Acute Anorexia Nervosa and during Renourishment: Relationship to Depression, Anxiety, and Eating Disorder Psychopathology. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Nelson, M.C.; Yu, Z.; Dowd, S.E.; Walter, J.; Kumar, P.S.; Lyte, M.; Bailey, M.T. Exposure to a social stressor disrupts the community structure of the colonic mucosa-associated microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indikova, I.; Humphrey, T.J.; Hilbert, F. Survival with a helping hand: Campylobacter and microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mörkl, S.; Lackner, S.; Müller, W.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Kashofer, K.; Oberascher, A.; Painold, A.; Holl, A.; Holzer, P.; Meinitzer, A.; et al. Gut microbiota and body composition in anorexia nervosa inpatients in comparison to athletes, overweight, obese, and normal weight controls. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armougom, F.; Henry, M.; Vialettes, B.; Raccah, D.; Raoult, D. Monitoring Bacterial Community of Human Gut Microbiota Reveals an Increase in Lactobacillus in Obese Patients and Methanogens in Anorexic Patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgo, F.; Riva, A.; Benetti, A.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Bertelli, S.; Garbossa, S.; Anselmetti, S.; Scarone, S.; Pontiroli, A.E.; Morace, G.; et al. Microbiota in anorexia nervosa: The triangle between bacterial species, metabolites and psychological tests. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Million, M.; Angelakis, E.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Giorgi, R.; Valero, R.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium animalis, Methanobrevibacter smithii and Escherichia coli. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, I.; Cuntz, U.; Grmer, C.; Niedermaier, S.; Pohl, C.; Schwiertz, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Zipfel, S.; Enck, P.; Penders, J. Weight gain in anorexia nervosa does not ameliorate the faecal microbiota, branched chain fatty acid profiles, and gastrointestinal complaints. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurigemma, N.C.; Koltun, K.J.; VanEvery, H.; Rogers, C.J.; De Souza, M.J. Linking the Gut Microbiota to Bone Health in Anorexia Nervosa. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.E.; Lozupone, C.A.; Rey, F.E.; Wu, M.; Guruge, J.L.; Narra, A.; Goodfellow, J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; McDonald, D.T.; Goodrich, J.A.; et al. Pan-genome of the dominant human gut-associated archaeon, Methanobrevibacter smithii, studied in twins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4599–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Akkermann, K.; Järv, A.; Harro, J.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Elevated plasma concentrations of bacterial ClpB protein in patients with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, N.H. Paneth cell defensins and the regulation of the microbiome. Gut Microbes. 2010, 1, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, F.; van Sinderen, D.; O’Toole, P.W.; Stanton, C. Feeding the microbiota: Transducer of nutrient signals for the host. Gut 2017, 66, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanton, L.V.; Charbonneau, M.R.; Salih, T.; Barratt, M.J.; Venkatesh, S.; Ilkaveya, O.; Subramanian, S.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Jorgensen, J.M.; et al. Gut bacteria that prevent growth impairments transmitted by microbiota from malnourished children. Science 2016, 351, aad3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, M.; Makki, K.; Storelli, G.; Machuca-Gayet, I.; Srutkova, D.; Hermanova, P.; Martino, M.E.; Balmand, S.; Hudcovic, T.; Heddi, A.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum strain maintains growth of infant mice during chronic undernutrition. Science 2016, 351, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Alegría, Á.; Bron, P.A.; de Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; Lemos, J.A.; Linares, D.M.; Ross, P.; Stanton, C.; et al. Stress Physiology of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 837–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottacini, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Omics of bifidobacteria: Research and insights into their health-promoting activities. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 4137–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comstock, L.E. Importance of glycans to the host-bacteroides mutualism in the mammalian intestine. Cell Host Microbe. 2009, 5, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Plugge, C.M.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanachi, M.; Bohem, V.; Bemer, P.; Kayser, N.; de Truchis, P.; Melchior, J.-C. Negative role of malnutrition in cell-mediated immune response: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in a severely malnourished, HIV-negative patient with anorexia nervosa. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 25, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Glenny, E.M.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tsilimigras, M.C.B.; Fodor, A.A.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. Daily Changes in Composition and Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Series of Three Cases. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2017, 25, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culbert, K.M.; Racine, S.E.; Klump, K.L. Research Review: What we have learned about the causes of eating disorders—A synthesis of sociocultural, psychological, and biological research. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2015, 56, 1141–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lladó, G.; González-Soltero, R.; Blanco Fernández de Valderrama, M.J.; Lladó, G.; González-Soltero, R.; Blanco, M.J. Anorexia y bulimia nerviosas: Difusión virtual de la enfermedad como estilo de vida. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Maguire, S.; Palacios, T.; Caterson, I.D. Are the gut bacteria telling us to eat or not to eat? Reviewing the role of gut microbiota in the etiology, disease progression and treatment of eating disorders. Nutrients 2017, 9, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, W.H.; Bulik, C.M.; Thornton, L.; Barbarich, N.; Masters, K. Comorbidity of Anxiety Disorders With Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieder, R.; Wisniewski, P.J.; Alderman, B.L.; Campbell, S.C. Microbes and mental health: A review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.; Campbell, I.; Chung, R.; Breen, G.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H. Inflammatory Markers in Anorexia Nervosa: An Exploratory Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borre, Y.E.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: Implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larroya-García, A.; Navas-Carrillo, D.; Orenes-Piñero, E. Impact of gut microbiota on neurological diseases: Diet composition and novel treatments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; van Hemert, S.; Bosch, J.A.; Colzato, L.S. A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, C.J.K.; Milev, R. The effects of probiotics on depressive symptoms in humans: A systematic review. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2017, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous Bacteria from the Gut Microbiota Regulate Host Serotonin Biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, L.-C.; Hor, Y.-Y.; Yusoff, N.A.A.; Choi, S.-B.; Yusoff, M.S.B.; Roslan, N.S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohammad, J.A.M.; Abdullah, M.F.I.L.; Zakaria, N.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum P8 alleviated stress and anxiety while enhancing memory and cognition in stressed adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti del Moral, A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Martínez Hernández, J.A. Efecto de los prebióticos sobre el metabolismo lipídico. Nutr. Hosp. 2003, 18, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delcour, J.A.; Aman, P.; Courtin, C.M.; Hamaker, B.R.; Verbeke, K. Prebiotics, Fermentable Dietary Fiber, and Health Claims. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenny, E.M.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Tang, Q.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. Eating Disorders and the Intestinal Microbiota: Mechanisms of Energy Homeostasis and Behavioral Influence. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).