Isolation of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Food of Animal and Plant Origin: Genomic Analysis and Implications for Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Bacterial Strain Isolation
2.3. ESBL-Producing Screening
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Contamination Rate of Food Samples with ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae
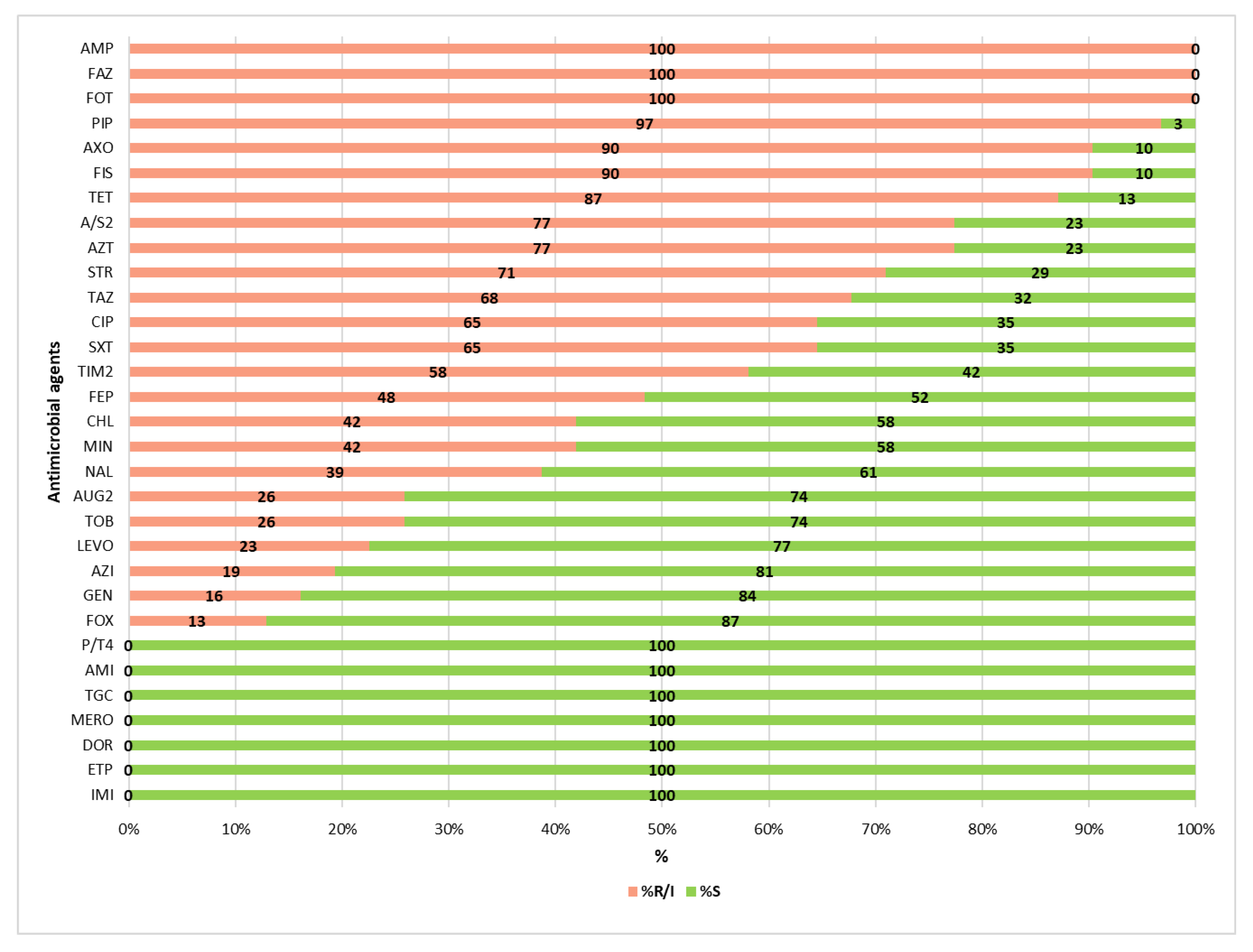
3.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of the ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Isolates
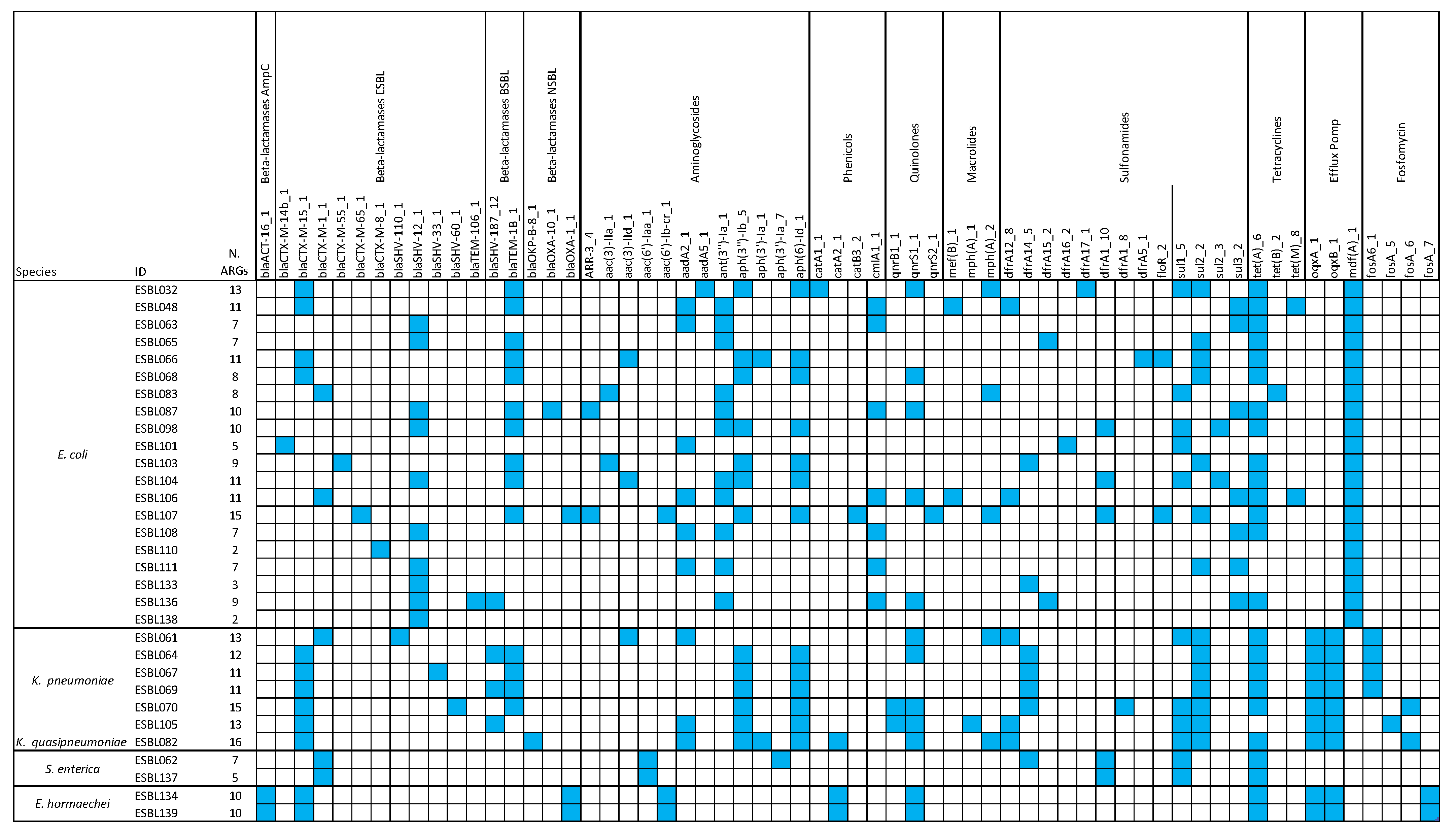
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants
3.4. Correlation Between the Presence of ARGs and Phenotypic Resistance
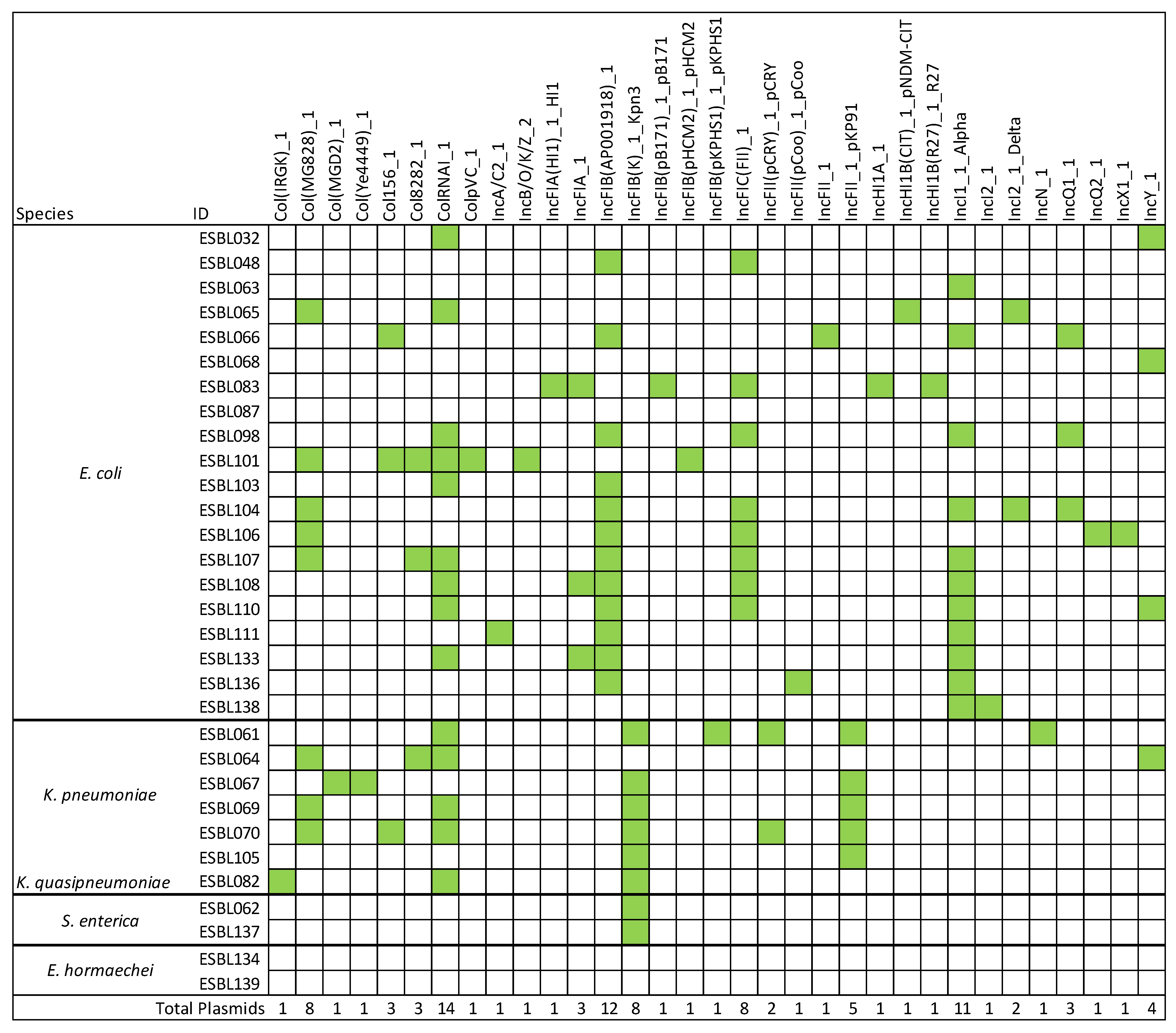
3.5. Detection of Plasmid Genes
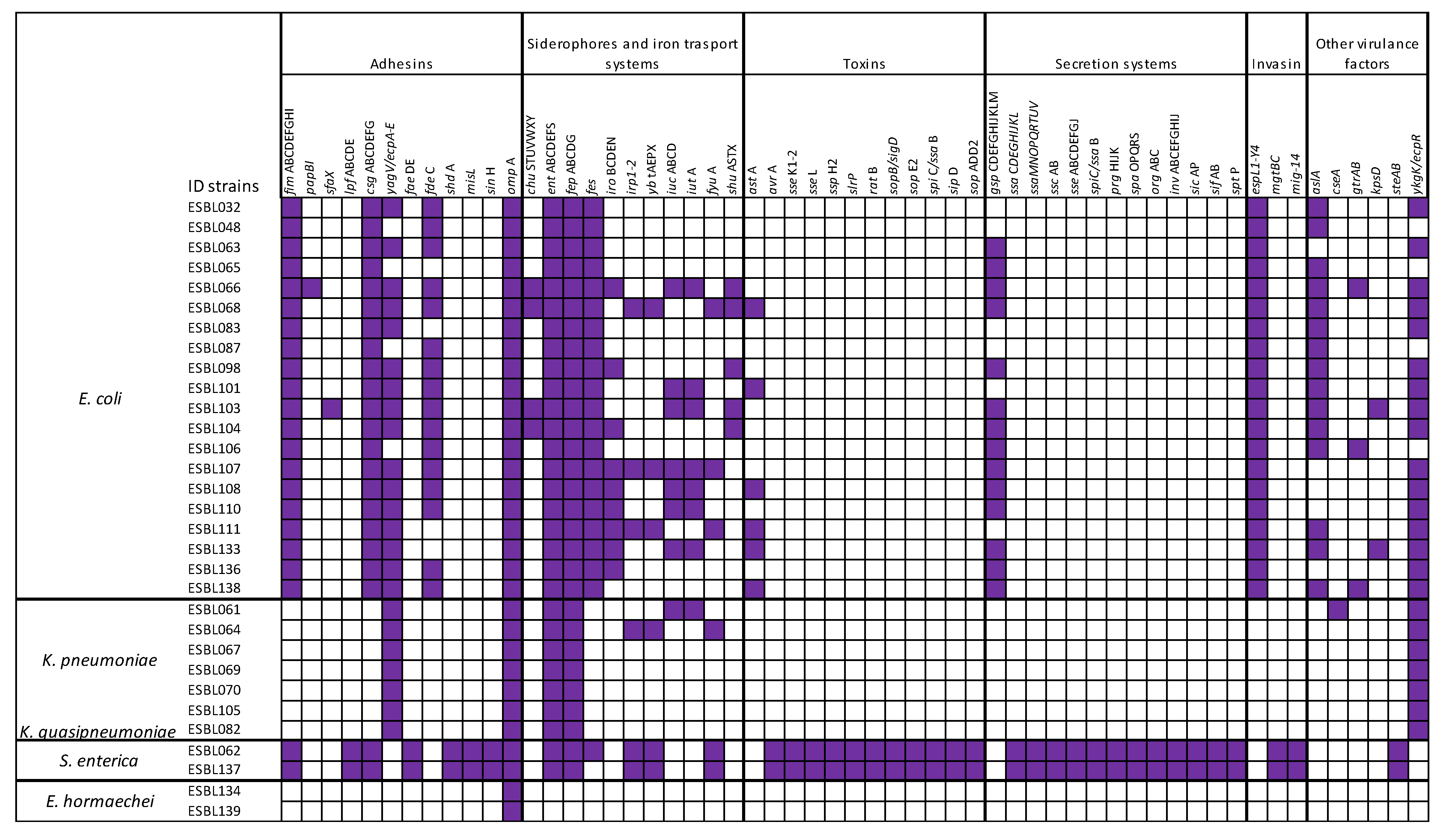
3.6. Detection of Virulence Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | antimicrobial resistance |
| ARGs | antimicrobial resistance genes |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| ESBL | Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase |
| ESBL-PE | Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| RTE | Ready-to-eat |
| VG | Virulence gene |
| WGS | Whole-Genome Sequencing |
References
- Lay, K.K.; Jeamsripong, S.; Sunn, K.P.; Angkititrakul, S.; Prathan, R.; Srisanga, S.; Chuanchuen, R. Colistin Resistance and ESBL Production in Salmonella and Escherichia coli from Pigs and Pork in the Thailand, Cambodia, Lao PDR, and Myanmar Border Area. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Jacoby, G.A. Updated Functional Classification of β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Fatima, J.; Shakil, S.; Danish Rizvi, S.M.; Kamal, M.A. Antibiotic resistance and extended spectrum beta-lactamases: Types, epidemiology and treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawz, S.M.; Bonomo, R.A. Three Decades of β-Lactamase Inhibitors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 160–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M.; Canton, R.; Gniadkowski, M.; Nordmann, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Arlet, G.; Ayala, J.; Coque, T.M.; Kern-Zdanowicz, I.; Luzzaro, F.; et al. CTX-M: Changing the Face of ESBLs in Europe. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 59, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, D.L.; Bonomo, R.A. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases: A Clinical Update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 657–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelia, A.; Nugroho, A.; Harijanto, P.N. Diagnosis and Management of Infections Caused by Enterobacteriaceae Producing Extended-Spectrum b-Lactamase. Acta Medica Indones. 2016, 48, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kiratisin, P.; Chattammanat, S.; Sa-Nguansai, S.; Dansubutra, B.; Nangpatharapornthawee, P.; Patthamalai, P.; Tirachaimongkol, N.; Nunthanasup, T. A 2-Year Trend of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Thailand: An Alert for Infection Control. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrgang, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Falgenhauer, L.; Guiral, E.; Schmoger, S.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Fischer, J.; Guerra, B.; Chakraborty, T.; Käsbohrer, A. Diversity of CTX-M-1-Producing E. coli from German Food Samples and Genetic Diversity of the Bla CTX-M-1 Region on IncI1 ST3 Plasmids. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 221, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karisik, E.; Ellington, M.J.; Pike, R.; Warren, R.E.; Livermore, D.M.; Woodford, N. Molecular Characterization of Plasmids Encoding CTX-M-15-Lactamases from Escherichia coli Strains in the United Kingdom. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, A.A.; Hotzel, H.; Neubauer, H.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Tomaso, H.; Hafez, H.M.; Roesler, U.; El-Adawy, H. Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from Healthy Broilers in Egypt: Emergence of Colistin-Resistant and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraccalvieri, R.; Bianco, A.; Difato, L.M.; Capozzi, L.; Del Sambro, L.; Castellana, S.; Donatiello, A.; Serrecchia, L.; Pace, L.; Farina, D.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Colistin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae from Foods in Two Italian Regions in the South of Italy. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.P. (Ed.) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-68440-104-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, A.; Capozzi, L.; Monno, M.R.; Del Sambro, L.; Manzulli, V.; Pesole, G.; Loconsole, D.; Parisi, A. Characterization of Bacillus cereus Group Isolates From Human Bacteremia by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 599524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laukkanen-Ninios, R.; Didelot, X.; Jolley, K.A.; Morelli, G.; Sangal, V.; Kristo, P.; Brehony, C.; Imori, P.F.M.; Fukushima, H.; Siitonen, A.; et al. Population Structure of the Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis Complex According to Multilocus Sequence Typing. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 3114–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibach, D.; Dekker, D.; Gyau Boahen, K.; Wiafe Akenten, C.; Sarpong, N.; Belmar Campos, C.; Berneking, L.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Krumkamp, R.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; et al. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Local and Imported Poultry Meat in Ghana. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 217, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Bagutti, C.; García-Martín, A.B.; Roth, J.A.; Alt Hug, M.; Maurer Pekerman, L.; Schindler, R.; Furger, R.; Eichenberger, L.; Steffen, I.; et al. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales in Diverse Foodstuffs: A Prospective, Longitudinal Study in the City of Basel, Switzerland. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1295037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdevest, I.; Willemsen, I.; Rijnsburger, M.; Eustace, A.; Xu, L.; Hawkey, P.; Heck, M.; Savelkoul, P.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.; van der Zwaluw, K.; et al. Extended-Spectrum B-Lactamase Genes of Escherichia coli in Chicken Meat and Humans, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, P.; López-Cerero, L.; Torres, E.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Serrano, L.; Navarro Sánchez-Ortiz, M.D.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Pascual, A. Increased Raw Poultry Meat Colonization by Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in the South of Spain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 159, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plain Language Summary of the European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2021–2022. EFSA J. 2024, 22, 220202. [CrossRef]
- Kaesbohrer, A.; Bakran-Lebl, K.; Irrgang, A.; Fischer, J.; Kämpf, P.; Schiffmann, A.; Werckenthin, C.; Busch, M.; Kreienbrock, L.; Hille, K. Diversity in Prevalence and Characteristics of ESBL/pAmpC Producing E. coli in Food in Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 233, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damianos, A.; Tsitsos, A.; Economou, V.; Gioula, G.; Haidich, A.-B. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Occurrence of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. in Foods of Animal Origin in Europe. Food Control 2025, 171, 111127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, E.A.; Abdul Aziz, S.; Bitrus, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L. Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Milk, and Farm Environments in Peninsular Malaysia. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batabyal, K.; Banerjee, A.; Pal, S.; Dey, S.; Joardar, S.N.; Samanta, I.; Isore, D.P.; Singh, A.D. Detection, Characterization, and Antibiogram of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Escherichia coli Isolated from Bovine Milk Samples in West Bengal, India. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.P.; Lodge, M.P.; Elviss, N.C.; Lemma, F.L.; Hopkins, K.L.; Teale, C.J.; Woodford, N. Evaluation of Meat, Fruit and Vegetables from Retail Stores in Five United Kingdom Regions as Sources of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 241, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenouf, N.S.; Carvalho, I.; Messaï, C.R.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Mama, O.M.; Titouche, Y.; Zitouni, A.; Hakem, A.; Torres, C. Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from Broiler Liver in the Center of Algeria, with Detection of CTX-M-55 and B2/ST131-CTX-M-15 in Escherichia coli. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizinga, P.; Kluytmans-van Den Bergh, M.; Rossen, J.W.; Willemsen, I.; Verhulst, C.; Savelkoul, P.H.M.; Friedrich, A.W.; García-Cobos, S.; Kluytmans, J. Decreasing Prevalence of Contamination with Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-E) in Retail Chicken Meat in the Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, M.; Hamze, M.; Bonnet, R.; Saras, E.; Madec, J.-Y.; Haenni, M. OXA-48 and CTX-M-15 Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases in Raw Milk in Lebanon: Epidemic Spread of Dominant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, G.K.; Sudha, S.; Muneeb, K.H.; Shome, B.; Holmes, M.; Cole, J. Molecular Assessment of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Multi Drug Resistant ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from Food Fishes, Assam, India. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pławińska-Czarnak, J.; Wódz, K.; Kizerwetter-Świda, M.; Bogdan, J.; Kwieciński, P.; Nowak, T.; Strzałkowska, Z.; Anusz, K. Multi-Drug Resistance to Salmonella spp. When Isolated from Raw Meat Products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, D.; Gargano, V.; Butera, G.; Sciortino, S.; Pizzo, M.; Oliveri, G.; Cardamone, C.; Piraino, C.; Cassata, G.; Vicari, D.; et al. Food Is Reservoir of MDR Salmonella: Prevalence of ESBLs Profiles and Resistance Genes in Strains Isolated from Food. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primeau, C.A.; Bharat, A.; Janecko, N.; Carson, C.A.; Mulvey, M.; Reid-Smith, R.; McEwen, S.; McWhirter, J.E.; Parmley, E.J. Integrated Surveillance of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Salmonella and Escherichia coli from Humans and Animal Species Raised for Human Consumption in Canada from 2012 to 2017. Epidemiol. Infect. 2023, 151, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Chen, M. Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae From Retail Food in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, W.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hegazy, Y.; Torky, H.A.; Shimamoto, T. High Prevalence of ESBL and Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica Isolated from Retail Meats and Slaughterhouses in Egypt. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-K.; Lin, H.-J.; Liu, P.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R. Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacter hormaechei. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 60, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) Lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00135-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteo, J.; Diestra, K.; Juan, C.; Bautista, V.; Novais, Â.; Pérez-Vázquez, M.; Moyá, B.; Miró, E.; Coque, T.M.; Oliver, A.; et al. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Spain Belong to a Large Variety of Multilocus Sequence Typing Types, Including ST10 Complex/A, ST23 Complex/A and ST131/B2. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumith, M.; Day, M.; Ciesielczuk, H.; Hope, R.; Underwood, A.; Reynolds, R.; Wain, J.; Livermore, D.M.; Woodford, N. Rapid Identification of Major Escherichia coli Sequence Types Causing Urinary Tract and Bloodstream Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworh, M.K.; Kwaga, J.K.P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Okolocha, E.C.; Thakur, S. Genetic Relatedness of Multidrug Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Humans, Chickens and Poultry Environments. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluta, R.P.; Logue, C.M.; Casas, M.R.T.; Meng, T.; Guastalli, E.A.L.; Rojas, T.C.G.; Montelli, A.C.; Sadatsune, T.; De Carvalho Ramos, M.; Nolan, L.K.; et al. Overlapped Sequence Types (STs) and Serogroups of Avian Pathogenic (APEC) and Human Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic (ExPEC) Escherichia coli Isolated in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, T.H.; Aslam, B.; Arshad, M.I.; Alvi, R.F.; Muzammil, S.; Yasmeen, N.; Aslam, M.A.; Khurshid, M.; Rasool, M.H.; Baloch, Z. Emergence of BlaNDM-1 Harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae ST29 and ST11 in Veterinary Settings and Waste of Pakistan. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.-S.; Oh, J.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Lee, D.-Y.; Jeong, O.-M.; Choi, B.-K.; Youn, S.-Y.; Jeon, B.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, H.-S. Public Health Significance of Major Genotypes of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Present in Both Human and Chicken Isolates in Korea. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 112, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Davies, R.H.; Threlfall, E.J. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Recent developments. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnning, A.; Kristiansson, E.; Fick, J.; Weijdegård Band Larsson, D.G.J. Resistance Mutations in gyrA andpar Care Common in Escherichia Communities of both Fluoroquinolone-Polluted and Uncontaminated Aquatic Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcusson, L.L.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Hughes, D. Interplay in the selection of fluoroquinolone resistance and bacterial fitness. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machuca, J.; Briales, A.; Labrador, G.; Díaz-De-Alba, P.; López-Rojas, R.; Docobo-Pérez, F.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Pachón, M.E.; Pascual, Á.; et al. Interplay between plasmid-mediated and chromosomal-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance and bacterial fitness in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 3203–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgrave, L.S.; Sutton, S.B.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J. Fluoroquinolone resistance: Mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialvaei, A.Z.; Kafil, H.S.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Aghazadeh, M.; Yousefi, M. CTX-M Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella spp, Salmonella spp, Shigella spp and Escherichia coli Isolates in Iranian Hospitals. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulitsch-Fuchs, A.H.; Melchior, N.; Haitzmann, T.; Fingerhut, T.; Feierl, G.; Baumert, R.; Kittinger, C.; Zarfel, G. Analysis of Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase (ESBL) Genes of Non-Invasive ESBL Enterobacterales in Southeast Austria in 2017. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolund, A. Overview of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae from a Nordic Perspective. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2014, 4, 24555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valentin, L.; Sharp, H.; Hille, K.; Seibt, U.; Fischer, J.; Pfeifer, Y.; Michael, G.B.; Nickel, S.; Schmiedel, J.; Falgenhauer, L.; et al. Subgrouping of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli from Animal and Human Sources: An Approach to Quantify the Distribution of ESBL Types between Different Reservoirs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boolchandani, M.; D’Souza, A.W.; Dantas, G. Sequencing-Based Methods and Resources to Study Antimicrobial Resistance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Chang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Xiao, X.; Xia, X.; Lin, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, G.; Van Tyne, D. Escherichia fergusonii, an Underrated Repository for Antimicrobial Resistance in Food Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01617-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujňáková, D.; Puvača, N.; Ćirković, I. Virulence Factors and Antibiotic Resistance of Enterobacterales. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, D.; Twittenhoff, C.; Becker, F.; Holler, M.; Narberhaus, F. OmpA, a Common Virulence Factor, Is Under RNA Thermometer Control in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 687260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, O.M.; Rukh, S.; Dos Santos Pereira, S.; Saran, A.; Chandran, V.I.; Muneeb, A.; Banderas Echeverry, W.M.; Shoyoye, M.; Akintunde, D.M.; Hassan, D.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Role of Virulence Factors in Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Injury. Cureus 2025, 17, e83475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouma, F.F.; Sina, H.; Adjobimey, T.; Noumavo, A.D.P.; Socohou, A.; Boya, B.; Dossou, A.D.; Akpovo, L.; Konmy, B.B.S.; Mavoungou, J.F.; et al. Susceptibility and Virulence of Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Benin. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Rossen, J.W.A. Virulence Factors of Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva De Sousa, C.; Dubreuil, J.D. Distribution and Expression of the astA Gene (EAST1 Toxin) in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 291, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozwandowicz, M.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Fischer, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Guerra, B.; Mevius, D.J.; Hordijk, J. Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance Plasmid Families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuga, B.; Sellera, F.P.; Cerdeira, L.; Esposito, F.; Cardoso, B.; Fontana, H.; Moura, Q.; Cardenas-Arias, A.; Sano, E.; Ribas, R.M.; et al. WHO Critical Priority Escherichia coli as One Health Challenge for a Post-Pandemic Scenario: Genomic Surveillance and Analysis of Current Trends in Brazil. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01256-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
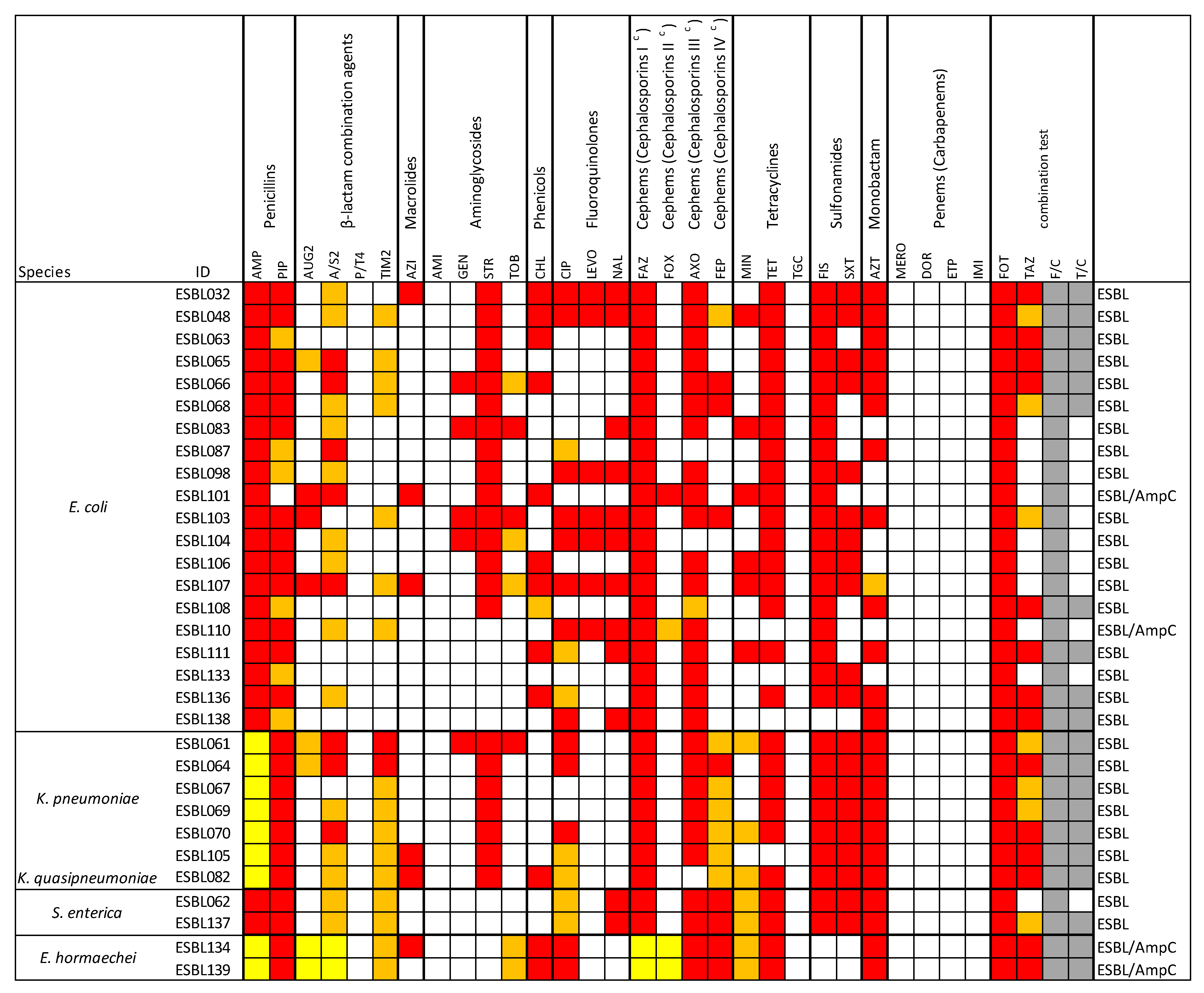
| Antimicrobial Class (Subclass) | Agent | Range µg/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | AMP—Ampicillin | 1–32 |
| PIP—Piperacillin | 16–64 | |
| β-lactam combination agents | AUG2—Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid | 1/0.5–32/16 |
| A/S2—Ampicillin/Sulbactam | 4/2–16/8 | |
| P/T4—Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 8/4–128/4 | |
| TIM2—Ticarcillin/Clavulanic acid | 8/2–64/2 | |
| Macrolides | AZI—Azithromycin | 0.25–32 |
| Aminoglycosides | AMI—Amikacin | 2–8 |
| GEN—Gentamicin | 0.25–16 | |
| STR—Streptomycin | 2–64 | |
| TOB—Tobramycin | 2–8 | |
| Phenicols | CHL—Chloramphenicol | 2–32 |
| Quinolones (Fluoroquinolones) | CIP—Ciprofloxacin | 0.015–4 |
| LEVO—Levofloxacin | 1–8 | |
| Quinolones | NAL—Nalidixic Acid | 0.5–32 |
| Cephems (Cephalosporins I c) | FAZ—Cefazolin | 1–16 |
| Cephems (Cephalosporins II c) | FOX—Cefoxitin | 0.5–64 |
| Cephems (Cephalosporins III c) | AXO—Ceftriaxone | 0.25–64 |
| Cephems (Cephalosporins IV c) | FEP—Cefepim | 0.06–32 |
| Tetracyclines | MIN—Minocycline | 1–8 |
| TET—Tetracycline | 4–32 | |
| Tetracycline (Glycylcycline) | TGC—Tigecyline | 1–8 |
| Sulfonamides | FIS—Sulfisoxazole | 16–256 |
| SXT—Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 0.12/2.38–4/76 | |
| Monobactam | AZT—Aztreonam | 1–16 |
| Penems (Carbapenems) | MERO—Meropenem | 0.03–16 |
| DOR—Doripenem | 4–8 | |
| ETP—Ertapenem | 0.25–8 | |
| IMI—Imipenem | 0.12–16 | |
| ESBL-producing screening combination test method | FOT—Cefotaxime | 0.25–64 |
| TAZ—Ceftazidime | 0.25–128 | |
| F/C—Cefotaxime/Clavulanic acid | 0.06/4–64/4 | |
| T/C—Ceftazidime/Clavulanic acid | 0.12/4–128/4 |
| Raw Food Samples | Isolates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | N. Analyzed Samples | N. ESBL Positive (Type of Food) | ESBL Positive (%) | N. ESBL Positive | rMLST Species | Sequence Type (ST) | ID Strain |
| Raw Milk | 52 | 2 (raw milk from vending machine) | 4 | 2 | E. coli | ST744 | ESBL032 |
| E. coli | ST10 | ESBL048 | |||||
| Raw Meat | 207 | 10 (poultry meat) | 9 | E. coli | ST223 | ESBL063 | |
| E. coli | ST1011 | ESBL098 | |||||
| E. coli | ST457 | ESBL103 | |||||
| E. coli | ST1011 | ESBL104 | |||||
| E. coli | ST155 | ESBL108 | |||||
| E. coli | ST88 | ESBL110 | |||||
| E. coli | ST8132 | ESBL111 | |||||
| E. coli | ST93 | ESBL133 | |||||
| E. coli * | ST4162 | ESBL136 | |||||
| 2 | S. enterica * | ST32 | ESBL137 | ||||
| S. enterica | ST32 | ESBL062 | |||||
| 2 (turkey meat) | 2 | K. pneumoniae | ST3069 | ESBL070 | |||
| K. pneumoniae | ST187 | ESBL105 | |||||
| 1 (minced turkey meat) | 2 | E. coli ** | ST2705 | ESBL065 | |||
| K. pneumoniae ** | ST29 | ESBL064 | |||||
| 1 (minced horse meat) | 1 | E. coli | ST69 | ESBL068 | |||
| 2 (minced beef and pork) | 2 | E. coli | ST69 | ESBL066 | |||
| K. pneumoniae | ST35 | ESBL067 | |||||
| 1 (pork meat) | 1 | K. pneumoniae | ST29 | ESBL069 | |||
| 2 (fresh pork sausage) | 2 | K. pneumoniae | ST25 | ESBL061 | |||
| E. coli | ST2179 | ESBL107 | |||||
| 1 (hamburger) | 1 | E. coli | ST218 | ESBL106 | |||
| Subtotal | 20 | 10 | 22 | ||||
| Seafood products | 133 | 1 (mussel) | 2 | E. coli | ST10 | ESBL101 | |
| 1 (frozen squid rings) | E. hormaechei | ST109 | ESBL134 | ||||
| Subtotal | 2 | 1.5 | 2 | ||||
| Bakery and pastry products, fresh pasta | 28 | 1 (fresh egg pasta) | 3.6 | 1 | E. coli | ST515 | ESBL087 |
| Vegetables | 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | / | |
| TOT | 500 | 25 | 5 | 27 | |||
| Ready-To-Eat Food Samples | Isolates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | N. Analyzed Samples | N. ESBL Positive (Type of Food) | ESBL Positive (%) | N. ESBL Positive | rMLST Species | Sequence Type (ST) | ID Strain |
| Milk and Cheese | 240 | 1 (canestrello cheese) | 0.5 | 1 | E. coli | ST10 | ESBL083 |
| Dried or cooked Sausages | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | / | |
| Ready meals | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | / | |
| Bakery and pastry products, fresh pasta | 27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | / | |
| Ice cream | 66 | 1 (packaged ice cream) | 1.5 | 2 | E. coli | ST2223 | ESBL138 |
| E. hormaechei | ST109 | ESBL139 | |||||
| Vegetables | 32 | 1 (mixed salad) | 3.0 | 1 | K. quasipneumoniae | ND | ESBL082 |
| TOT | 500 | 3 | 0.6 | 4 | |||
| gyr A | parC | parE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate ID | S83L | D87N | A56T | S80I | S80R | L416F | S458A |
| ESBL032 | |||||||
| ESBL048 | |||||||
| ESBL061 | |||||||
| ESBL062 | |||||||
| ESBL063 | |||||||
| ESBL064 | |||||||
| ESBL065 | |||||||
| ESBL066 | |||||||
| ESBL067 | |||||||
| ESBL068 | |||||||
| ESBL069 | |||||||
| ESBL070 | |||||||
| ESBL083 | |||||||
| ESBL087 | |||||||
| ESBL098 | |||||||
| ESBL101 | |||||||
| ESBL103 | |||||||
| ESBL104 | |||||||
| ESBL105 | |||||||
| ESBL106 | |||||||
| ESBL107 | |||||||
| ESBL108 | |||||||
| ESBL110 | |||||||
| ESBL111 | |||||||
| ESBL133 | |||||||
| ESBL134 | |||||||
| ESBL136 | |||||||
| ESBL137 | |||||||
| ESBL138 | |||||||
| ESBL139 | |||||||
| ESBL82 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fraccalvieri, R.; Castellana, S.; Bianco, A.; Difato, L.M.; Capozzi, L.; Del Sambro, L.; Donatiello, A.; Pugliese, D.; Tempesta, M.; Parisi, A.; et al. Isolation of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Food of Animal and Plant Origin: Genomic Analysis and Implications for Food Safety. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081770
Fraccalvieri R, Castellana S, Bianco A, Difato LM, Capozzi L, Del Sambro L, Donatiello A, Pugliese D, Tempesta M, Parisi A, et al. Isolation of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Food of Animal and Plant Origin: Genomic Analysis and Implications for Food Safety. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081770
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraccalvieri, Rosa, Stefano Castellana, Angelica Bianco, Laura Maria Difato, Loredana Capozzi, Laura Del Sambro, Adelia Donatiello, Domenico Pugliese, Maria Tempesta, Antonio Parisi, and et al. 2025. "Isolation of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Food of Animal and Plant Origin: Genomic Analysis and Implications for Food Safety" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081770
APA StyleFraccalvieri, R., Castellana, S., Bianco, A., Difato, L. M., Capozzi, L., Del Sambro, L., Donatiello, A., Pugliese, D., Tempesta, M., Parisi, A., & Caruso, M. (2025). Isolation of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Food of Animal and Plant Origin: Genomic Analysis and Implications for Food Safety. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081770








