A Comprehensive Investigation of Potential Bacterial Pathogens in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Bacteria
2.3. DNA Sequencing
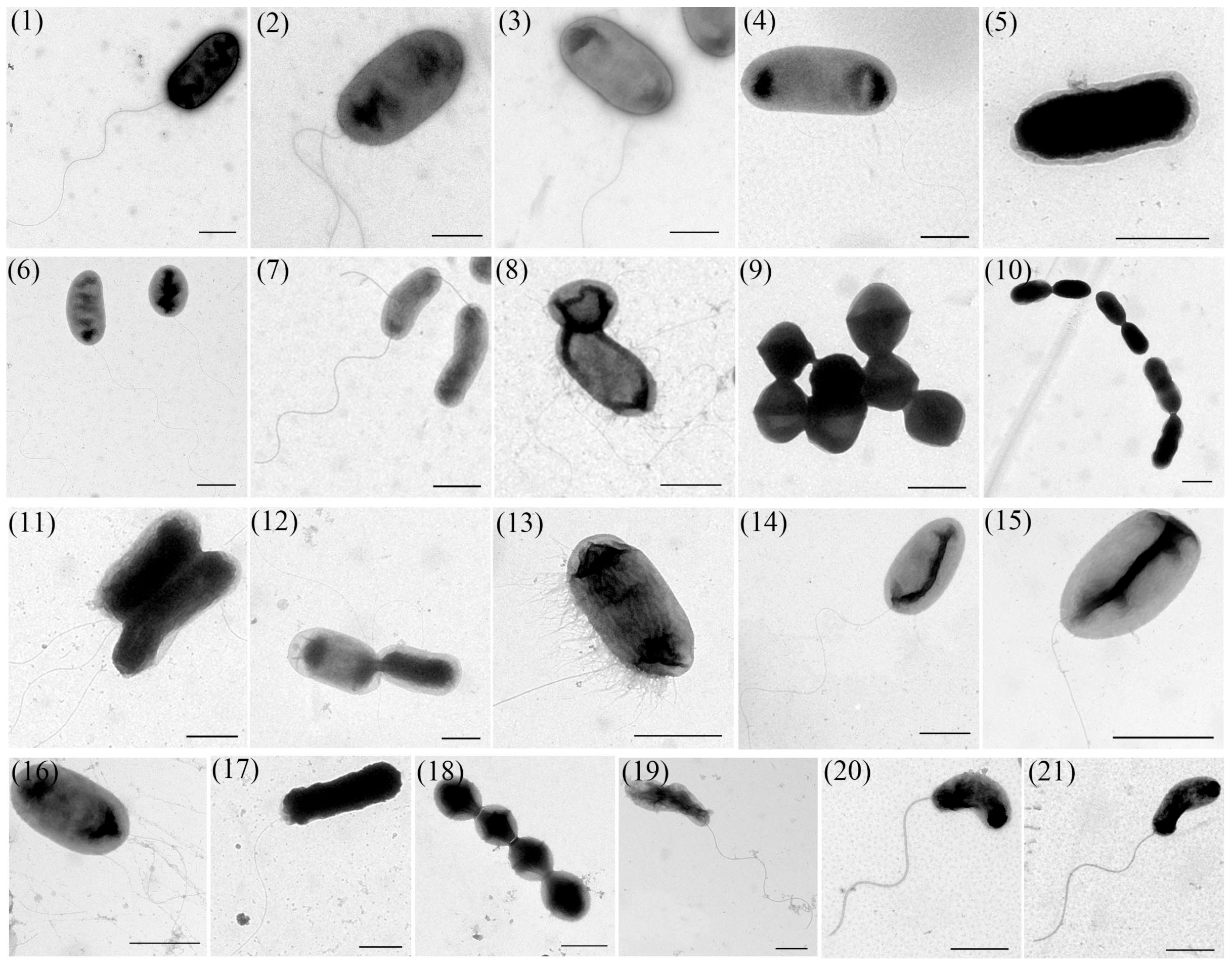
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Observation
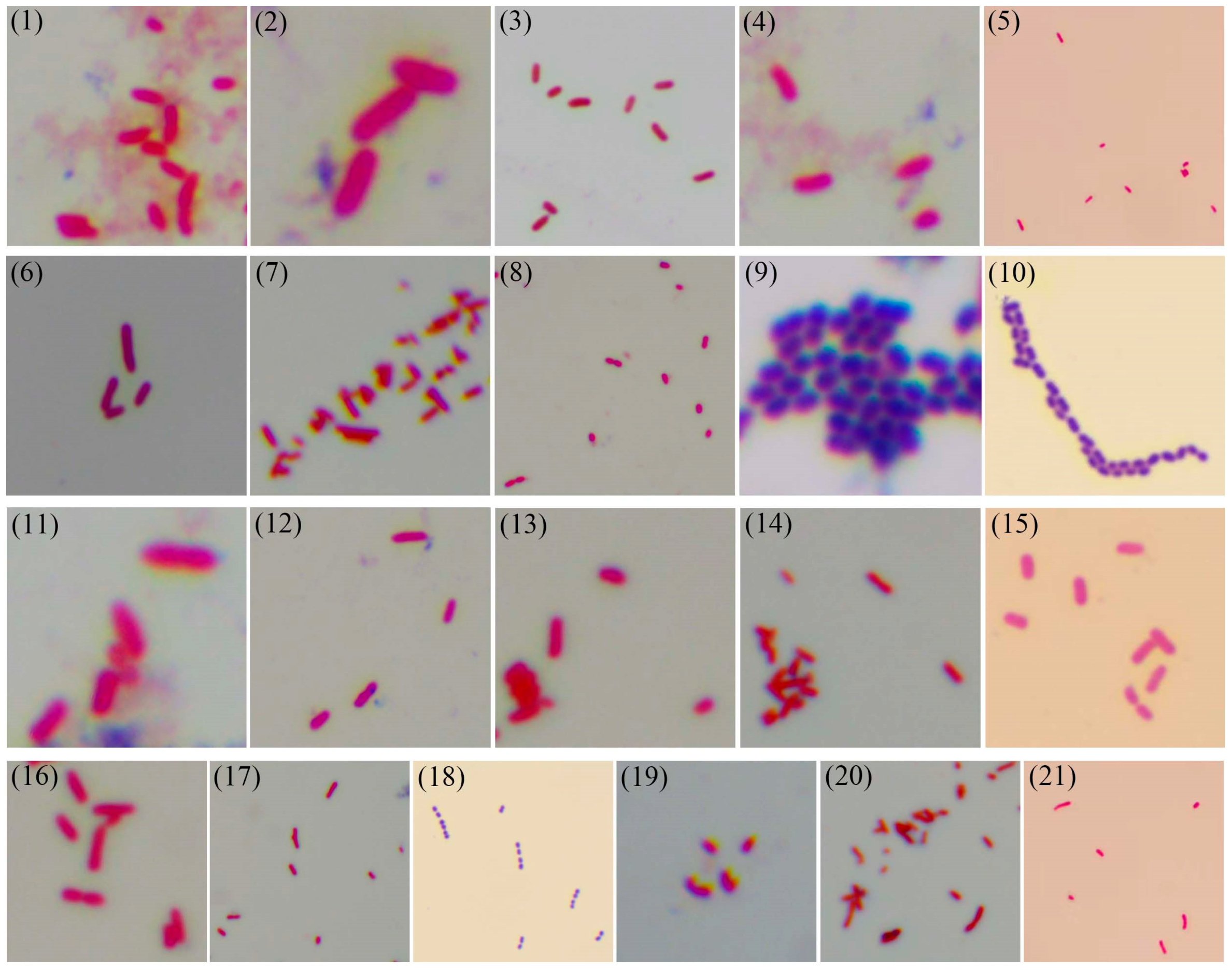
2.5. Gram Staining
2.6. Capsule Staining
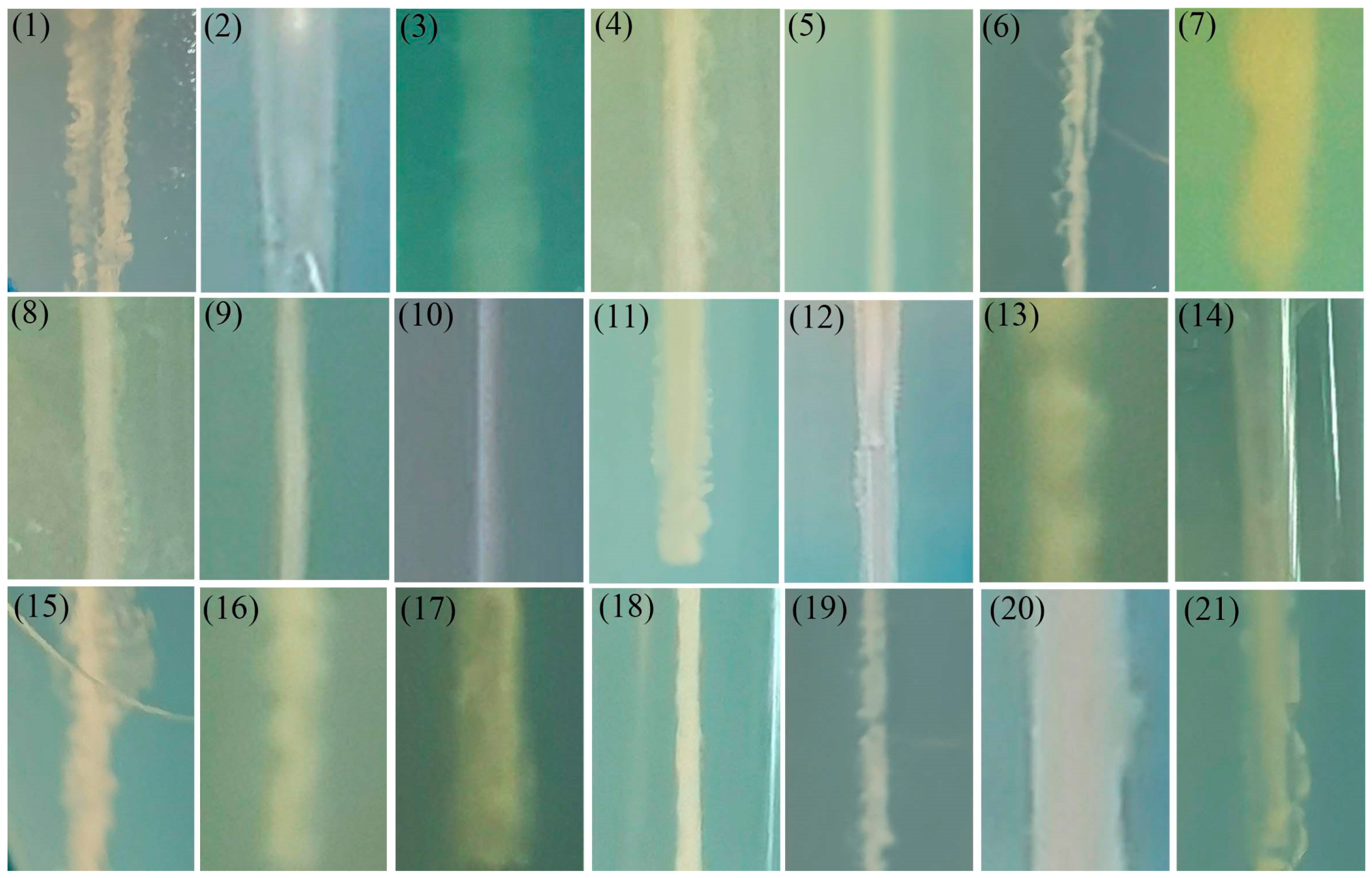
2.7. Motility Detection
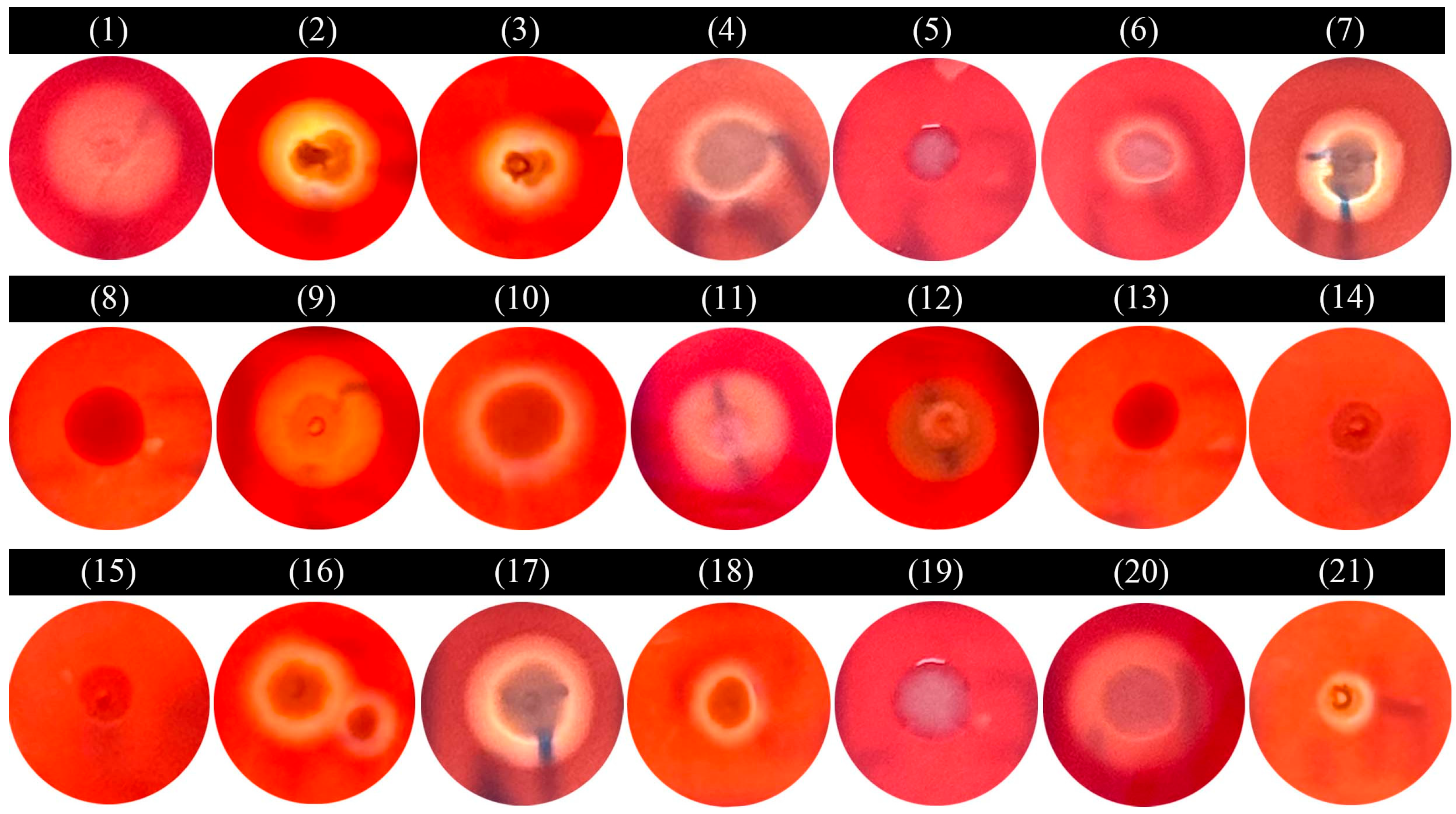
2.8. Hemolytic Test
2.9. Biochemical Identification
2.10. Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
3. Results and Discussion
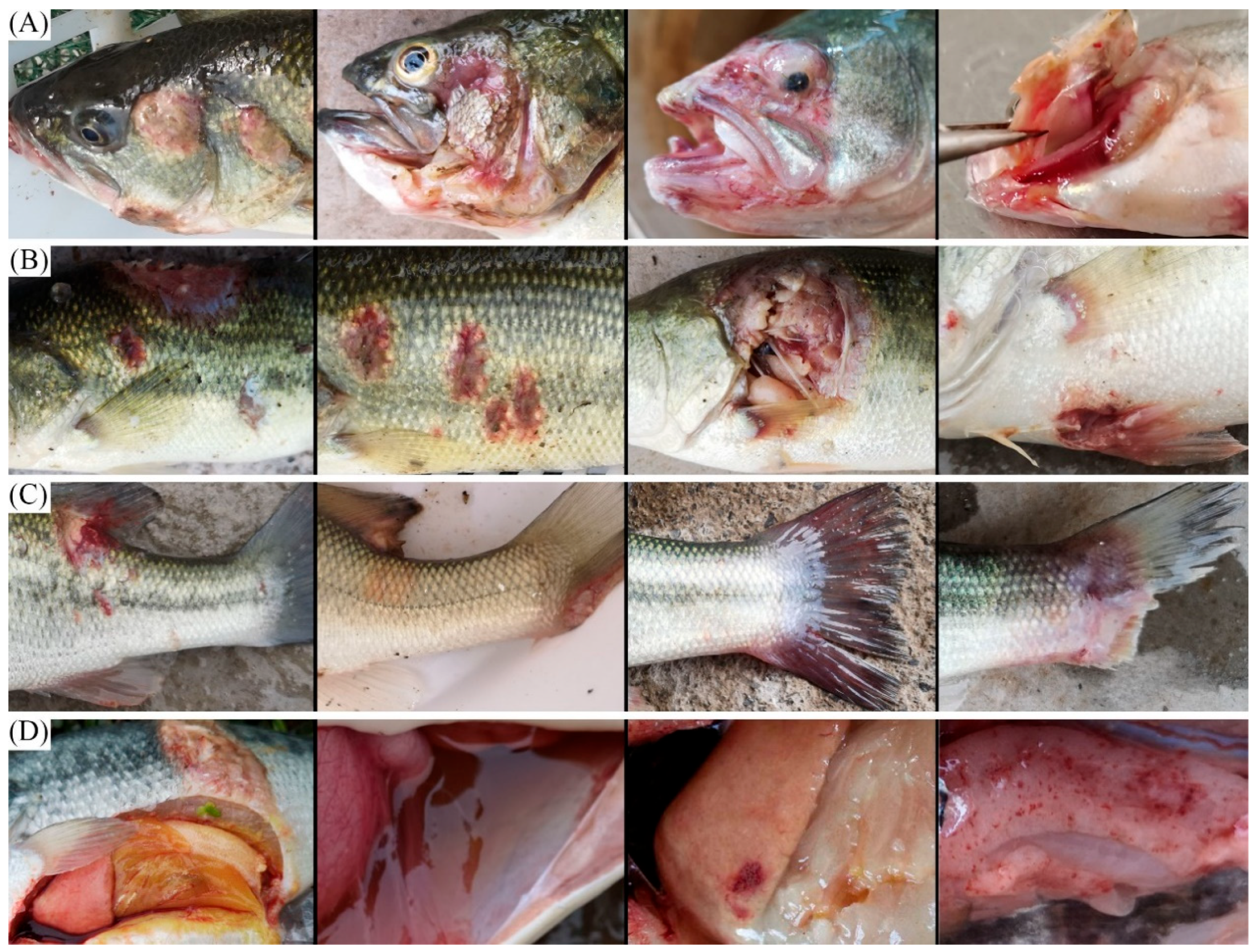
3.1. Clinical Signs of the Diseased Largemouth Bass
3.2. Species Identification
3.3. TEM Observation
3.4. Gram Staining
3.5. Capsule Staining
3.6. Motility Detection
3.7. Hemolytic Test
3.8. Biochemical Identification
3.9. Antibiotic Sensitivity of the Isolated Strains
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Jia, Z.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals growth-related mutations and candidate genes at early growth stages in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2025, 599, 742184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Wen, C.Y.; Jiang, B.; Su, Y.L. Analysis of the prevalence of bacterial pathogens and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Edwardsiella piscicida in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) from Guangdong, China. Pathogens 2024, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Zhao, R.; Geng, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, P.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Zuo, Z.; He, C.; Chen, Z.; et al. Nocardia seriolae: A serious threat to the largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) industry in Southwest China. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2021, 145, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Qian, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X. Pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii causing mass mortality of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and its induced host immune response. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, J.; Geng, Y.; Ou, Y.; Chen, D.; Yin, L.; Li, L.; et al. Comparative pathological description of nocardiosis in largemouth bass (Micropterus almoides) and other Perciformes. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Dong, J.J.; Ke, X.L.; Yi, M.M.; Cao, J.M.; Gao, F.Y.; Wang, M.; Ye, X.; Lu, M.-X. Isolation, identification, and pathogenic characteristics of Nocardia seriolae in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2022, 149, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, A.; Griffin, M.; Armwood, A.; Soto, E. A spontaneous outbreak of systemic Edwardsiella piscicida infection in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) (Lacepede, 1802) in California, USA. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogelson, S.B.; Petty, B.D.; Reichley, S.R.; Ware, C.; Bowser, P.R.; Crim, M.J.; Getchell, R.G.; Sams, K.L.; Marquis, H.; Griffin, M.J. Histologic and molecular characterization of Edwardsiella piscicida infection in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2016, 28, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tu, Y.Y.; Zhang, N.; Miao, B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Deng, X.T.; He, T.; Su, S.Q.; Lin, L.Y.; Zhu, S. Co-infections of Aeromonas dhakensis and Chryseobacterium indologenes in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, B.; Shokrak, N.M.; Abozahra, N.A.; Elshamy, Y.M.; Kadira, H.I.; Mohamed, R.A. Aquaculture and Aeromonas hydrophila: A complex interplay of environmental factors and virulence. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 7671–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Jin, W.; Quan, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Bacterial capsules: Occurrence, mechanism, and function. Nat. Partn. J. Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, S.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. Comparative study of immune reaction against bacterial infection from transcriptome analysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; An, N.; Li, D.C.; Huang, M.M.; Fei, H. Updates on infectious diseases of largemouth bass: A major review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N.; Liu, W.; Meng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y. Isolation, identification and characteristics of Aeromonas caviae from diseased largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes 2022, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.C.; Philipp, P.D.; Inendino, K.R.; Goldberg, T.L. Effects of temperature on the susceptibility of largemouth bass to largemouth bass virus. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2003, 15, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, Z.; Chen, S.; Song, G.; Hu, H.; Lin, S.; Long, Y. Biochemical, histological and transcriptomic analyses for the immunological organs provide insights into heat stress-induced disease susceptibility in largemouth bass. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Z.; Bai, J.; Hu, X.; Lu, A.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Song, Y. Detection and characterization of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. Salmonicida infection in crucian carp Carassius auratus. Vet. Res. Commun. 2020, 44, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.B.; Li, E.C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.F.; Ren, Z.L.; Li, Q.M.; Guo, W.L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.C. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity characterization of Vibrio ponticus from the golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2018, 496, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. Pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides causing mass mortalities of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and its induced host immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 132, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.S.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Hong, B.Y.; Petersen, L.M.; Demkowicz, P.; Chen, L.; Leopold, S.R.; Hanson, B.M.; Agresta, H.O.; Gerstein, M.; et al. Evaluation of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for species and strain-level microbiome analysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Gao, X.; Cui, Z. Application of gyrB in the identification of closely related bacteria—A review. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2008, 48, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Pei, X.; Wu, Y.; Yan, L.; Yan, Y.; Song, Y.; Coyle, N.M.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Quince, C.; Hu, Q.; et al. Recent mixing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus populations. Int. Soc. Microb. Ecol. J. 2019, 13, 2578–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Ewiss, M.; Khalefa, H.S.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Elgendy, M.Y.; Abdel-Moneam, D.A. Coinfections of Aeromonas spp., Enterococcus faecalis, and Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from farmed Nile tilapia and African catfish in Egypt, with an emphasis on poor water quality. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 160, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.; Yazdi, Z.; Littman, E.; Shahin, K.; Heckman, T.I.; Quijano Cardé, E.M.; Nguyen, D.T.; Hu, R.; Adkison, M.; Veek, T.; et al. Detection and virulence of Lactococcus garvieae and L. petauri from four lakes in southern California. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2023, 35, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.D.; Blazer, V.S.; Walsh, H.L.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Starliper, C.E.; Sperry, A. The effects of disease-related mortality of young-of-year smallmouth bass on population characteristics in the Susquehanna River Basin, Pennsylvania and potential implications to conservation of black bass diversity. In Black Bass Diversity: Multidisciplinary Science for Conservation, 82nd ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015; pp. 319–332. [Google Scholar]
- Santucci, P. Intracellular pathogens, membrane damage and cytosolic access. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preenanka, R.; Safeena, M.P. Morphological, biological and genomic characterization of lytic phages against Streptococcus agalactiae causing streptococcosis in tilapia. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; San, L.; Hou, J. Isolation, identification and the pathogenicity characterization of Pseudomonas putida 1C3 and its activation on immune responses in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 160, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhiya, A.V.; Dinesh, H.R. Identification of Vibrio related bacterial pathogens in aquaculture by molecular techniques: A review. J. Exp. Zool. India 2015, 18, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquina-Lemonche, L.; Burns, J.; Turner, R.D.; Kumar, S.; Hobbs, J.K. The architecture of the gram-positive bacterial cell wall. Nature 2020, 582, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhu, P.; Liu, H.M.; Zhang, H.T.; Liu, L. Ethanol induced mitochondria injury and permeability transition pore opening: Role of mitochondria in alcoholic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro, K.C.F.; Inzana, T.J. The Francisella tularensis polysaccharides: What is the real capsule? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, e00065-19. [Google Scholar]
- Balhuizen, M.D.; Dijk, A.V.; Jansen, J.W.A.; Lest, C.H.A.V.D.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Haagsman, H.P. Outer membrane vesicles protect gram-negative bacteria against host defense peptides. mSphere 2021, 6, e0052321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Zhang, L.; Ji, R.L. Isolation and identification of a manganese oxidizing bacteria in mining area. J. Nanchang Hangkong Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 36, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, G.M. The Role of bacterial biofilm in antibiotic resistance and food contamination. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 281, 1705814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Redondo, M.; Ardá, A.; Gimeno, A.; Jiménez-Barbero, J. Bacterial polysaccharides: Conformation, dynamics and molecular recognition by antibodies. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2020, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, T.S.; Kazmierczak, B.I. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits sliding motility in the absence of type IV pili and flagella. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.S. Population Dependent Regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Under Conditions of Stress, Starvation and Biofilm Development. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of New South Wales Sydney, Kensington, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. The role of motility as a virulence factor in bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 291, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottemann, K.M.; Lowenthal, A.C. Helicobacter pylori uses motility for initial colonization and to attain robust infection. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Kolter, R. Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginos biofilm development. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakioti, M.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Bacterial biofilms: Development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a010306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, K.; Zhou, R.; Li, M. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk in Hunan Province. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, P.; Wang, M.; Li, A.; Miao, M.; Xie, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Identification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains with an incomplete hemolytic phenotype. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.A. The Escherichia coli hemolysin. Environ. Ecol. Sci. Collect. Plus 2005, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakdi, S.; Tranum-Jensen, J. Alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.J.; Dalziel, C.E. The biology of pneumolysin. Subcell. Biochem. 2014, 80, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, L.E.; Price-Whelan, A.; Petersen, A.; Whiteley, M.; Newman, D.K. The phenazine pyocyanin is a terminal signalling factor in the quorum sensing network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumru, S.; Balta, Z.D.; Aliu, H.; Balta, F. Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from commercial fish feeds and infected fish specimens. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2024, 75, 7523–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdi, S.; DaSilva, L.V.; Parveen, S. Antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in various countries: A review. Food Microbiol. 2016, 57, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Deb, S.C.; Alam, M.S.; Alam, M.J.; Islam, M.T. Molecular identification of multiple antibiotic resistant fish pathogenic Enterococcus faecalis and their control by medicinal herbs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xing, Y.; Lei, Y.; Tong, G.; Lin, X.; He, P.; Tang, S.; Zheng, F.; Zeng, H.; Wei, X.; et al. Genetic diversity, antibiotic resistance, and pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii isolated from farmed largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) in the main aquaculture regions of China. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.; Kannimuthu, D. Comparative resistome analysis of Aeromonas species in aquaculture reveals antibiotic resistance patterns and phylogeographic distribution. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.X.; Feng, J.; Geng, Y.J.; Xu, L.W.; Wang, J.Y. Studies on the drug resistance of aquatic bacteria. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 770–776. [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, C.G.; Yang, J.; Yuan, M.; Bai, X.N.; Jin, D.; Liang, J.R.; Cui, Z.G.; Li, J. Genetic diversity, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence genes of Aeromonas isolates from clinical patients, tap water systems, and food. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 385–395. [Google Scholar]


| S. No. | Species | Frequency (%) | Mean Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THI | FLO | FLU | ENR | DOH | NES | SUS | VcMP-CiH | Sud-Tri | Sum-Tri | Suo-Tri | |||
| 1 | Aeromonas caviae | 3.76 | - | 12 | 34 | 32 | 12 | 16 | - | 24 | - | - | - |
| 2 | Aeromonas dhakensis | 4.63 | - | 8 | 38 | 36 | 12 | 22 | - | 30 | - | - | - |
| 3 | Aeromonas hydrophila | 20.98 | - | 9 | 32 | 34 | 8 | 21 | - | 24 | - | - | - |
| 4 | Aeromonas jandaei | 4.05 | 38 | 32 | 38 | 40 | 36 | 22 | 14 | 42 | 28 | 28 | 26 |
| 5 | Aeromonas salmonicida | 9.12 | 26 | 32 | 24 | 22 | 12 | 15 | - | 27 | 22 | 23 | 22 |
| 6 | Aeromonas veronii | 24.60 | - | 12 | 18 | 22 | 14 | 16 | - | 28 | - | - | - |
| 7 | Chryseobacterium indologenes | 1.88 | 14 | 26 | 30 | 25 | 24 | 10 | - | 20 | 22 | 24 | 28 |
| 8 | Edwardsiella piscicida | 6.51 | - | - | 26 | 22 | - | 12 | - | 30 | - | - | - |
| 9 | Enterococcus faecalis | 0.87 | - | 26 | - | 18 | - | - | - | 22 | 33 | 26 | 24 |
| 10 | Lactococcus garvieae | 1.01 | 16 | 19 | 9 | 16 | 9 | 9 | - | 15 | - | - | - |
| 11 | Photobacterium damselae | 2.75 | - | 40 | - | 22 | - | 16 | - | 22 | 33 | 32 | 32 |
| 12 | Plesiomonas shigelloides | 3.47 | - | 14 | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | Proteus vulgaris | 1.59 | 9 | 20 | 28 | 26 | 14 | 16 | - | 34 | 24 | 20 | 22 |
| 14 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 2.75 | 11 | 10 | 14 | 22 | 9 | 8 | - | 30 | 13 | - | 10 |
| 15 | Pseudomonas parafulva | 0.72 | 11 | 22 | 14 | 19 | 14 | 17 | - | 25 | - | - | - |
| 16 | Pseudomonas putida | 1.74 | - | 8 | - | - | - | 18 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 17 | Shewanella xiamenensis | 0.72 | 30 | 41 | 11 | 9 | 19 | 22 | - | - | 29 | 28 | 28 |
| 18 | Streptococcus agalactiae | 3.04 | 22 | 32 | - | 22 | 22 | - | - | 21 | 24 | 14 | - |
| 19 | Vibrio alginolyticus | 2.03 | 26 | 32 | 25 | 26 | 14 | 16 | - | 24 | 18 | 14 | 18 |
| 20 | Vibrio cholerae | 1.30 | 26 | 25 | 28 | 24 | 16 | 14 | - | 28 | 25 | 23 | 24 |
| 21 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | 2.46 | 25 | 32 | 24 | 22 | 12 | 16 | - | 24 | 21 | 18 | 24 |
| S. No. | Mor | Fla | Cap | GR | Hem | MR-VP | ONPG | Ur | GH | AD | OD | LD | Ox | NaCl Tryptone Water | 1% NaCl | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 3% | 6% | 8% | 10% | Mal | Mae | La | Ce | Ar | Su | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 4 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | + |
| 5 | R | N | Y | − | γ | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 7 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| 8 | R | Y | N | − | γ | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 9 | C | N | N | + | β | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| 10 | C | N | N | + | β | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + |
| 11 | R | Y | Y | − | β | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| 12 | R | Y | N | − | α | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| 13 | R | Y | N | − | γ | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| 14 | R | Y | N | − | γ | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| 15 | R | Y | N | − | γ | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 16 | R | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 17 | R | Y | N | − | β | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + |
| 18 | C | N | Y | + | β | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | + | − |
| 19 | CR | Y | N | − | γ | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + |
| 20 | CR | Y | N | − | β | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | + |
| 21 | CR | Y | N | − | β | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, Y.-Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Leng, J.; Yang, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhu, C.-K.; He, T.; Hu, J.-Y.; Lv, M.-J.; et al. A Comprehensive Investigation of Potential Bacterial Pathogens in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061413
Tu Y-Y, Lu Q, Zhang N, Leng J, Yang Q, Yu J, Zhu C-K, He T, Hu J-Y, Lv M-J, et al. A Comprehensive Investigation of Potential Bacterial Pathogens in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061413
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Yun-Yao, Qun Lu, Na Zhang, Jie Leng, Qin Yang, Jie Yu, Cheng-Ke Zhu, Tao He, Jian-Yong Hu, Ming-Ji Lv, and et al. 2025. "A Comprehensive Investigation of Potential Bacterial Pathogens in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061413
APA StyleTu, Y.-Y., Lu, Q., Zhang, N., Leng, J., Yang, Q., Yu, J., Zhu, C.-K., He, T., Hu, J.-Y., Lv, M.-J., & Zhu, S. (2025). A Comprehensive Investigation of Potential Bacterial Pathogens in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microorganisms, 13(6), 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061413






