Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, and Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Raw Fish in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus aureus
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.4. Identification of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Sequence Analysis
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.8. In Silico Characterization of Whole-Genome Sequences
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Raw Fish Samples
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Confirmation of MRSA
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of MRSA
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
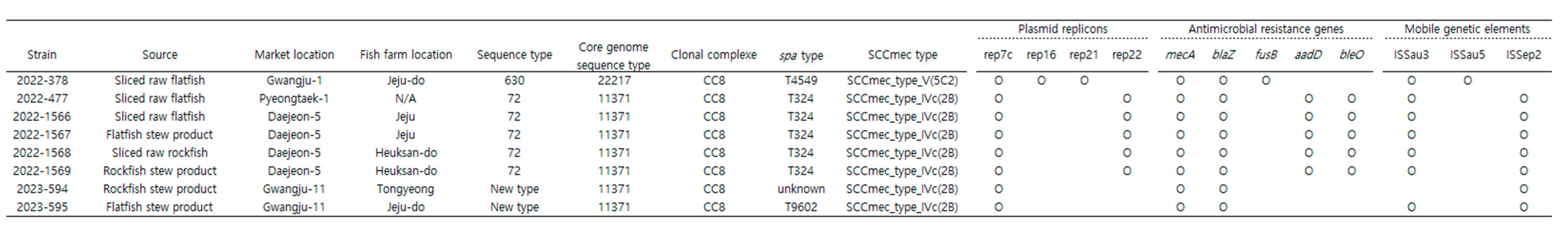
3.5. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Plasmid Replicons
3.6. Detection of Point Mutation AMD Virulence Factors
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Statistical Information Service. Available online: https://www.index.go.kr/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- National Fishery Products Quality Management Service. Available online: https://www.nfqs.go.kr (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Ogur, S.; Silva, M. Pathogenic bacteria load and safety of retail marine fish. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staphylococcus aureus Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/staphylococcus-aureus/about/index.html (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mrsa/about/index.html (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Vaiyapuri, M.; Joseph, T.C.; Rao, B.M.; Lalitha, K.V.; Prasad, M.M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in seafood: Prevalence, laboratory detection, clonal nature, and control in seafood chain. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Ming, T.; Zhou, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, R.; Su, X. The response and survival mechanisms of Staphylococcus aureus under high salinity stress in salted foods. Foods 2022, 11, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Machado, C.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Different Food Groups and Drinking Water. Foods 2024, 13, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, L.; Chen, T.; Chen, W.; Ge, Y.; Bi, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, M. Prevalence and WGS-based characteristics of MRSA isolates in hospitals in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1002691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, T.-M.; Kim, T.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, J.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, I.-S.; Lee, S.-W. Whole-genome analysis of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enteritidis strains isolated from poultry sources in Korea. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Food Code. Available online: https://various.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/fsd/#/ (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- CLSI. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twentieth Informational Supplement, CLSI Document m100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clinical breakpoints (v 13.0). Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Rey, J.; Gil, M.; de Mendoza, J.H.; García, A.; Gaitskell-Phillips, G.; Bastidas-Caldes, C.; Zalama, L. Clonality and persistence of multiresistant methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from the staff of a university veterinary hospital. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Kwak, H.S. Prevalence and characteristics of antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from retail meat in Korea. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Li, X.; Li, B. Deciphering of microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge reactors under high selective pressure of different antibiotics. Water Res. 2019, 151, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Chang, E.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.-O.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, S. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of ST72 methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus: Comparison with ST72 methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Infect. Chemother. 2024, 56, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Chang, E.; Bae, S.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, Y.S. The origin of sequence type 72 community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and fusidic acid (FA) resistant sequence type 5 MRSA: Analysis of FA resistance and spa type in a single center in South Korea. J. Infect. Chemother. 2024, 30, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, G.R.; Quinto, V.P.; Machado, D.C.; Lipnharski, C.; Weber, M.B.; Bonamigo, R.R.; D’Azevedo, P.A. Staphylococcus aureus resistance to topical antimicrobials in atopic dermatitis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2016, 91, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouiten, A.; Mehri, I.; Beltifa, A.; Ghorbel, A.; Sire, O.; Van Loco, J.; Abdenaceur, H.; Reyns, T.; Ben Mansour, H. Designation of pathogenic resistant bacteria in the Sparusaurata sea collected in Tunisia coastlines: Correlation with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of antibiotics. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Type | Prevalence of Isolates (%; No. of Isolate-Positive Samples/No. of Tested Samples) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | Cefoxitin Resistance S. aureus | MecA-Positive MRSA | |
| Sliced raw flatfish | 11.0 (36/327) | 1.5 (5/327) | 0.9 (3/327) |
| Flatfish stew product | 7.2 (8/111) | 1.8 (2/111) | 1.8 (2/111) |
| Sliced raw rockfish | 9.4 (8/85) | 1.2 (1/85) | 1.2 (1/85) |
| Rockfish stew product | 18.2 (2/11) | 18.2 (2/11) | 18.2 (2/11) |
| Antimicrobial Agent | % (Number of Resistant Strains) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sliced Raw Flatfish (n = 36) | Flatfish Stew Product (n = 8) | Sliced Raw Rockfish (n = 8) | Rockfish Stew Product (n = 2) | Total | |
| Cefoxitin | 14.3 (5) | 25.0 (2) | 11.1 (1) | 100 (2) | 18.5 (10) |
| Chloramphenicol | 2.9 (1) | 25.0 (2) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 5.6 (3) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 25.7 (9) | 12.5 (1) | 11.1 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 20.4 (11) |
| Clindamycin | 2.9 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 1.9 (1) |
| Erythromycin | 20.0 (7) | 12.5 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 14.8 (8) |
| Fusidate | 48.6 (17) | 37.5 (3) | 44.4 (4) | 0.0 (0) | 44.4 (24) |
| Gentamicin | 2.9 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 1.9 (1) |
| Kanamycin | 8.6 (3) | 0.0 (0) | 11.1 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 7.4 (4) |
| Linezolid | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) |
| Mupirocin | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) |
| Penicillin | 60.0 (21) | 100 (8) | 88.9 (8) | 100 (2) | 72.2 (39) |
| Quinupristin/Dalfopristin | 2.9 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 1.9 (1) |
| Rifampin | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 5.7 (2) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 3.7 (2) |
| Tetracycline | 14.3 (5) | 12.5 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 11.1 (6) |
| Trimethoprim | 8.6 (3) | 12.5 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 7.4 (4) |
| Vancomycin | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) |
| Antimicrobial Resistance | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Strain | Source | Cefoxitin | Chloramphenicol | Ciprofloxacin | Clindamycin | Erythromycin | Fusidate | Gentamicin | Kanamycin | Linezolid | Mupirocin | Penicillin | Quinupristin/Dalfopristin | Rifampin | Sulfamethoxazole | Tetracycline | Trimethoprim | Vancomycin |
| 2022 | 378 | Sliced raw flatfish | O | O | O | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 477 | Sliced raw flatfish | O | O | O | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 1566 | Sliced raw flatfish | O | O | O | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 1567 | Flatfish stew product | O | O | |||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 1568 | Sliced raw rockfish | O | O | O | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 1569 | rockfish stew product | O | O | |||||||||||||||
| 2023 | 594 | rockfish stew product | O | O | |||||||||||||||
| 2023 | 595 | Flatfish stew product | O | O | |||||||||||||||
| VF Class | Virulence Factor | Related Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Adherence | Elastin binding protein | ebp |
| Fibrinogen binding protein | efb | |
| Fibronectin binding proteins | fnbA, fnbB | |
| Intercellular adhesin | icaA, icaB, icaC, icaR | |
| Staphylococcal protein A | spa | |
| Enzyme | Cysteine protease | sspB, sspC |
| Hyaluronate lyase | hysA | |
| Lipase | Geh, lip | |
| Serine V8 protease | sspA | |
| Staphylocoagulase | coa | |
| Thermonuclease | nuc | |
| Immune evasion | Sbi | sbi |
| Secretion system | Type VII secretion system | esaA, esaD, esaE, esaG, essA, essB, essC, esxA, esxB, esxC, esxD |
| Toxin | Alpha hemolysin | hly/hla |
| Delta hemolysin | hld | |
| Exotoxin | set18, set30, set31, set37 | |
| Gamma hemolysin | hlgA, hlgB, hlgC |
| Virulence Factor Class | Virulence Factors | Related Genes | 2022_378 | 2022_477 | 2022_1566 | 2022_1567 | 2022_1568 | 2022_1569 | 2023_594 | 2023_595 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adherence | Autolysin | atl | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| Cell wall associated fibronectin binding protein | ebh | O | ||||||||
| Clumping factor A | clfA | O | ||||||||
| Intercellular adhesin | icaD | O | O | O | ||||||
| Ser-Asp rich fibrinogen-binding proteins | sdrC | O | O | O | O | O | ||||
| sdrD | O | O | O | O | ||||||
| sdrE | O | O | O | O | O | |||||
| Enzyme | Serine protease | splA | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| splB | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| splC | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| splD | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| Staphylokinase | sak | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Immune evasion | AdsA | adsA | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| CHIPS | chp | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| SCIN | scn | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Secretion system | Type VII secretion system | esaB | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Toxin | Enterotoxin G | seg | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| Enterotoxin Yent2 | yent2 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Enterotoxin-like K | selk | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Enterotoxin-like M | selm | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Enterotoxin-like N | seln | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Enterotoxin-like O | selo | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | ||
| Exotoxin | set10 | O | ||||||||
| set15 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| set21 | O | |||||||||
| set22 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| set24 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| set25 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| set33 | O | |||||||||
| set34 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
| set36 | O | |||||||||
| set38 | O | |||||||||
| set39 | O | |||||||||
| set40 | O | |||||||||
| Leukotoxin D | lukD | O | O | O | O | O | O | O |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.M.; Kim, Y.h.; Joo, I.; Kim, H. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, and Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Raw Fish in South Korea. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061415
Kang H, Lee J, Han JM, Kim Yh, Joo I, Kim H. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, and Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Raw Fish in South Korea. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061415
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Haiseong, Jonghoon Lee, Ji Min Han, Yong hoon Kim, Insun Joo, and Hyochin Kim. 2025. "Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, and Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Raw Fish in South Korea" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061415
APA StyleKang, H., Lee, J., Han, J. M., Kim, Y. h., Joo, I., & Kim, H. (2025). Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, and Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Raw Fish in South Korea. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061415





