Ecological Effects and Microbial Regulatory Mechanisms of Functional Grass Species Assembly in the Restoration of “Heitutan” Degraded Alpine Grasslands
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Characterize the composition of key functional bacterial groups and their niche differentiation under varying mixed-seeding ratios;
- Decipher the multidimensional interaction mechanisms among vegetation traits, soil environment, and microbial networks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Situation of the Study Area
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Design and Methods
- Vertical stratification pairing of upper-canopy and lower-canopy grasses;
- Synergistic combination of cold-tolerant and stress-resistant types;
- Priority selection of high seed-yielding cultivars developed in Qinghai Province.
2.4. Vegetation Survey and Soil Sampling
2.5. Measurements and Methods
2.6. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Mixed-Seeding Treatments on Soil Physicochemical Properties in Artificial Grassland
3.2. Effects of Different Mixed-Seeding Treatments on Soil Bacterial Community Composition
3.2.1. Quality Assessment of 16S rRNA Sequencing Data and OTU Variation
3.2.2. Taxonomic Composition and Relative Abundance of Soil Bacterial Communities
3.2.3. LEfSe Analysis of Soil Bacterial Community Composition
3.3. Analysis of Soil Bacterial Community Diversity
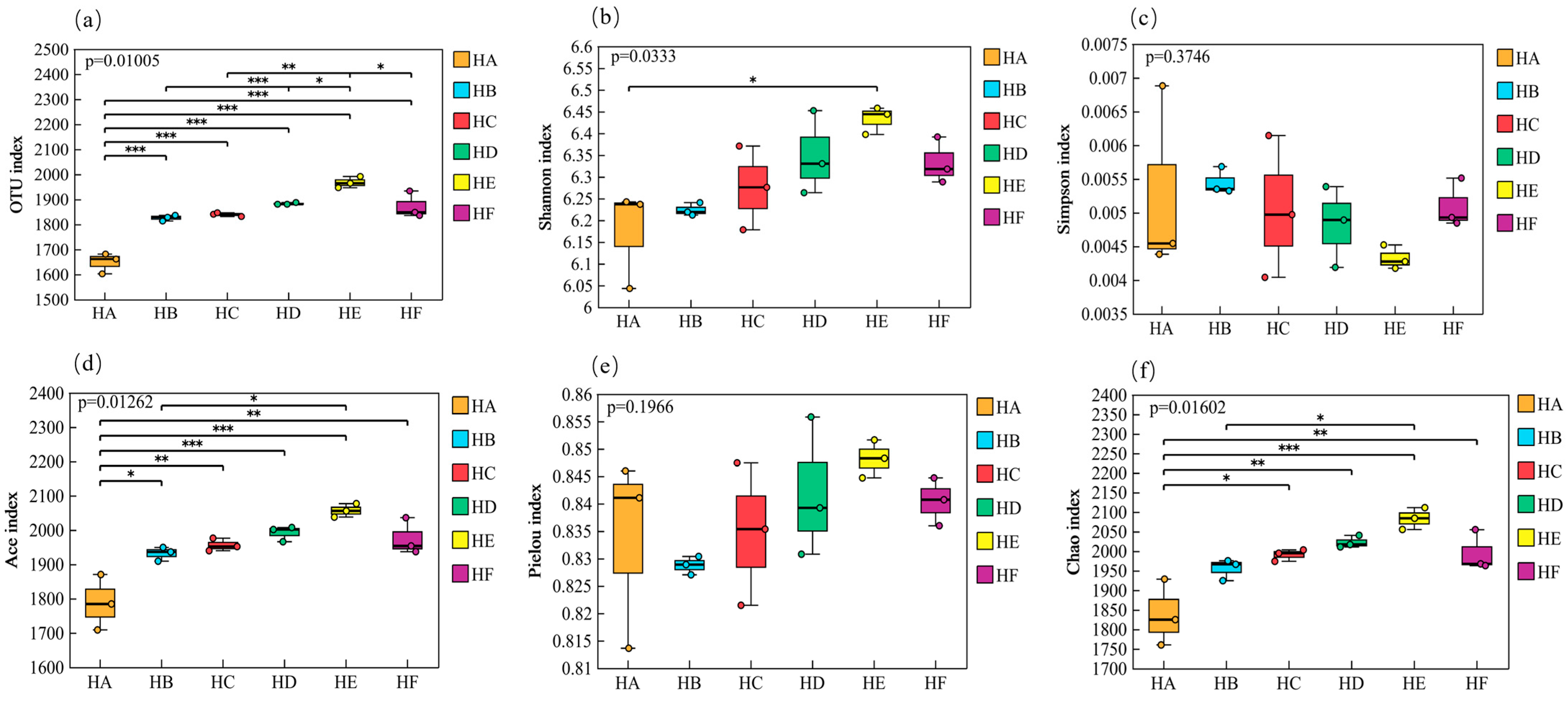
3.3.1. α-Diversity Analysis of Soil Bacterial Communities
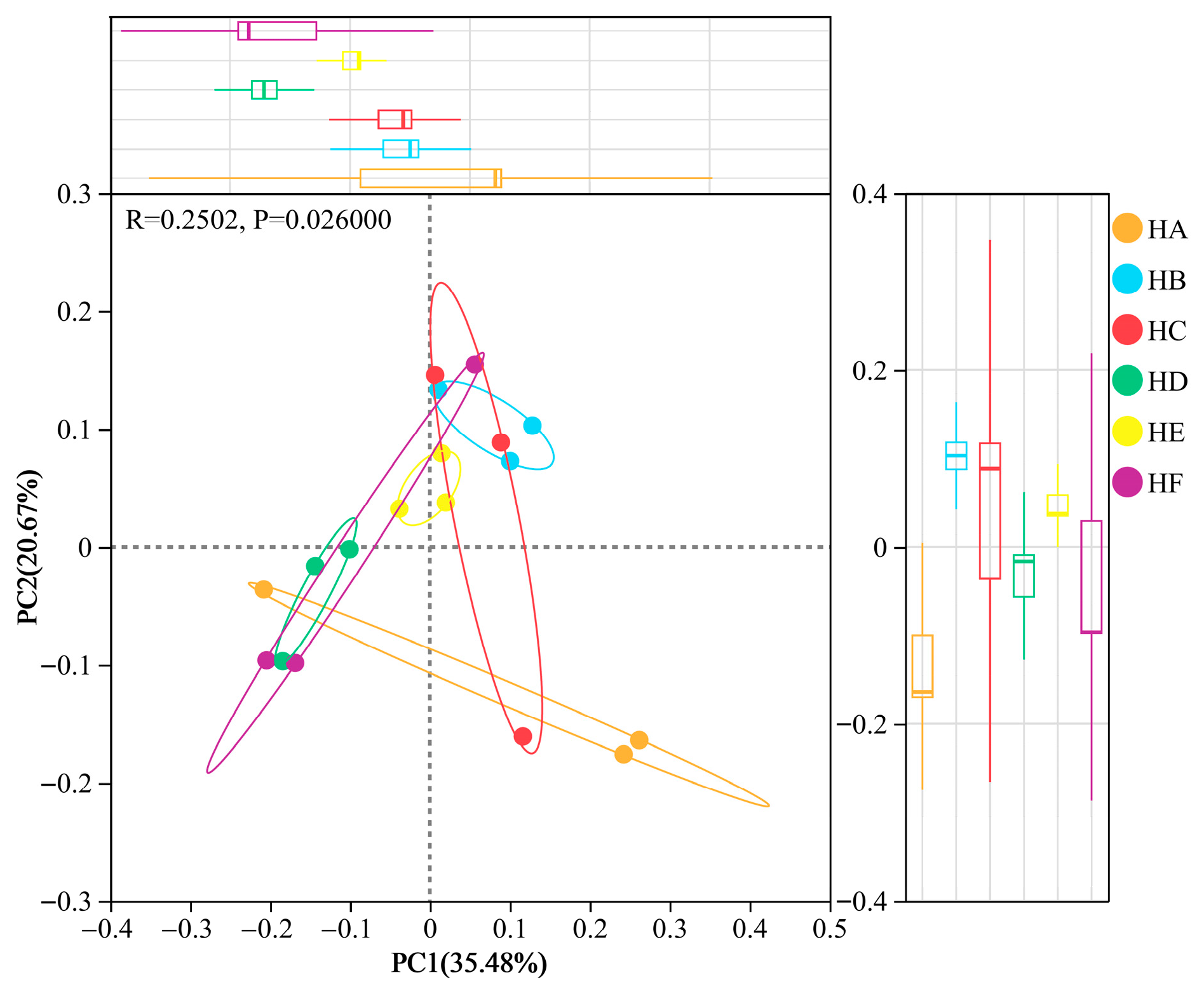
3.3.2. β-Diversity Analysis (PCoA) of Soil Bacterial Communities
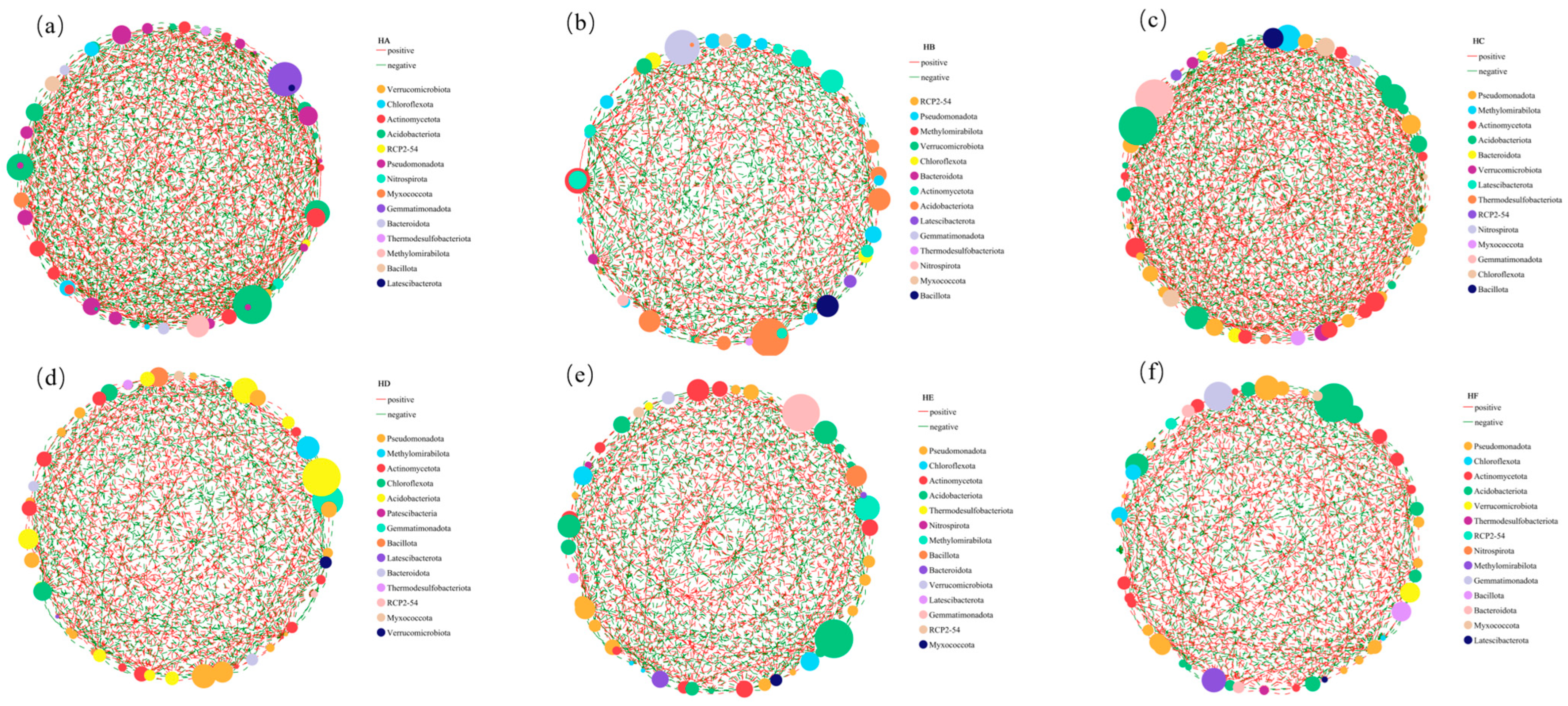
3.4. Univariate Correlation Network Variations in Soil Bacterial Communities
3.5. Functional Prediction of Soil Bacterial Communities
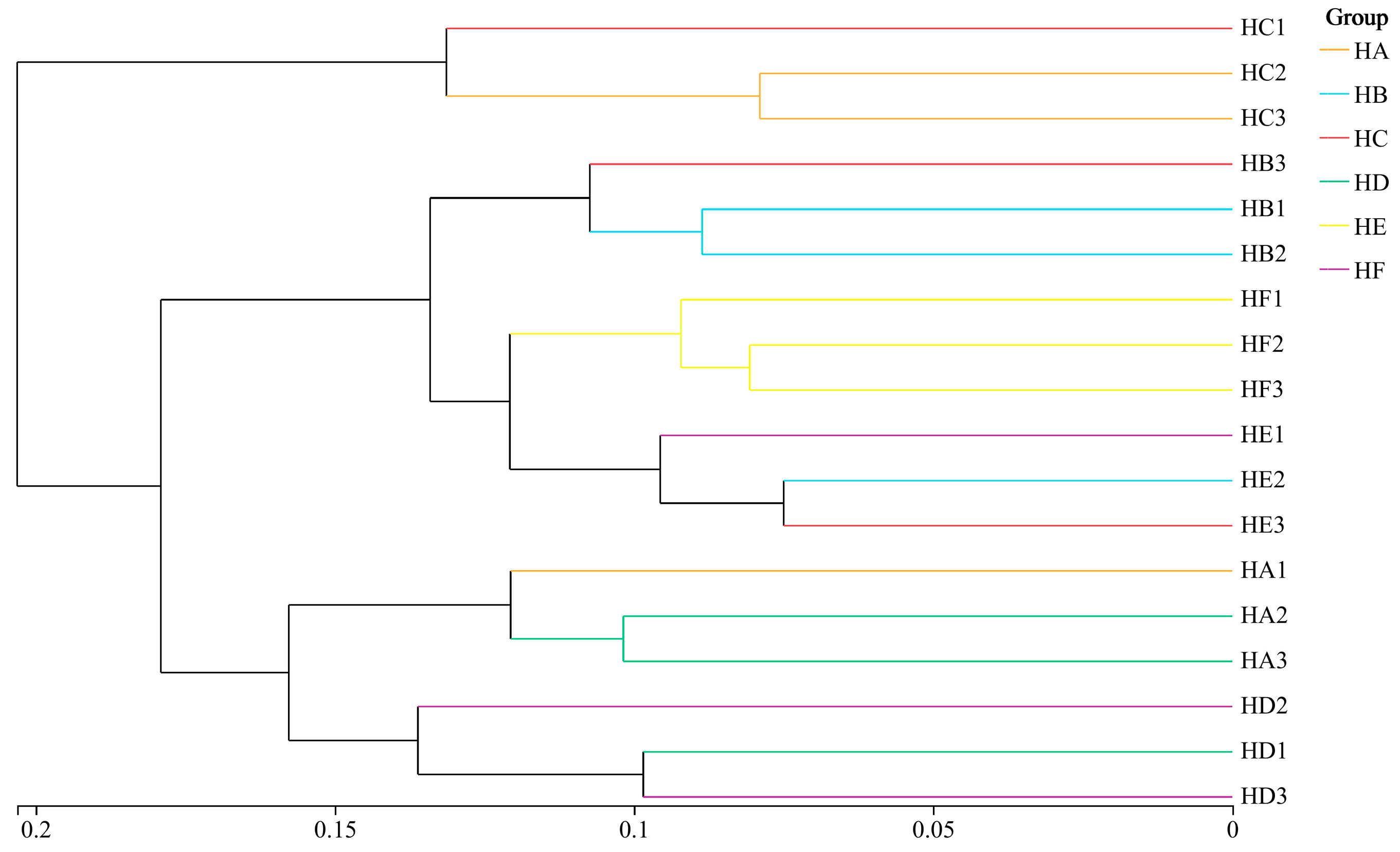
3.6. Cluster Analysis of Soil Bacterial Communities
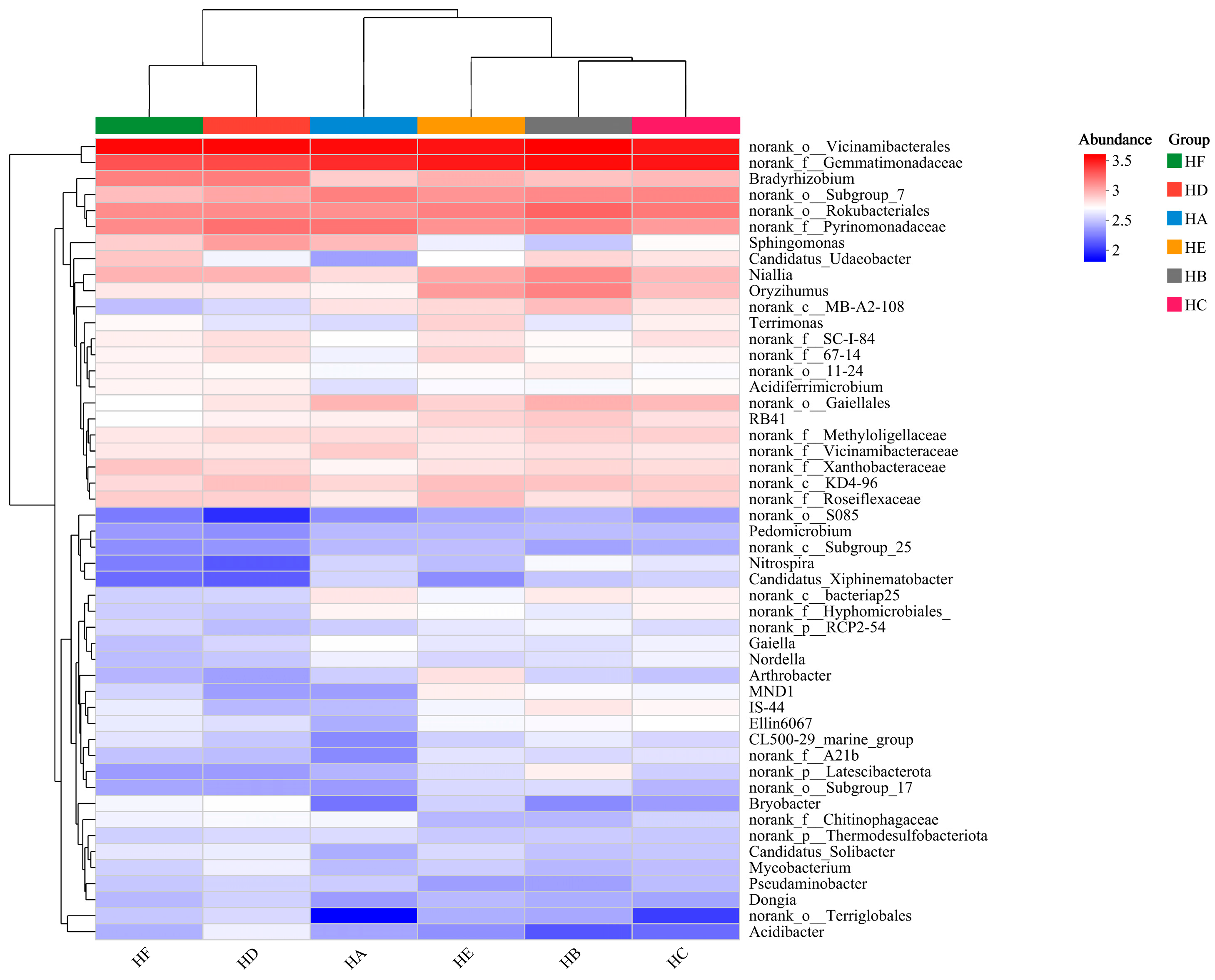
3.7. Heatmap Analysis of Soil Microbial Communities
3.8. Coupling Relationships Among Vegetation Characteristics, Soil Physicochemical Properties, and Soil Bacterial Communities
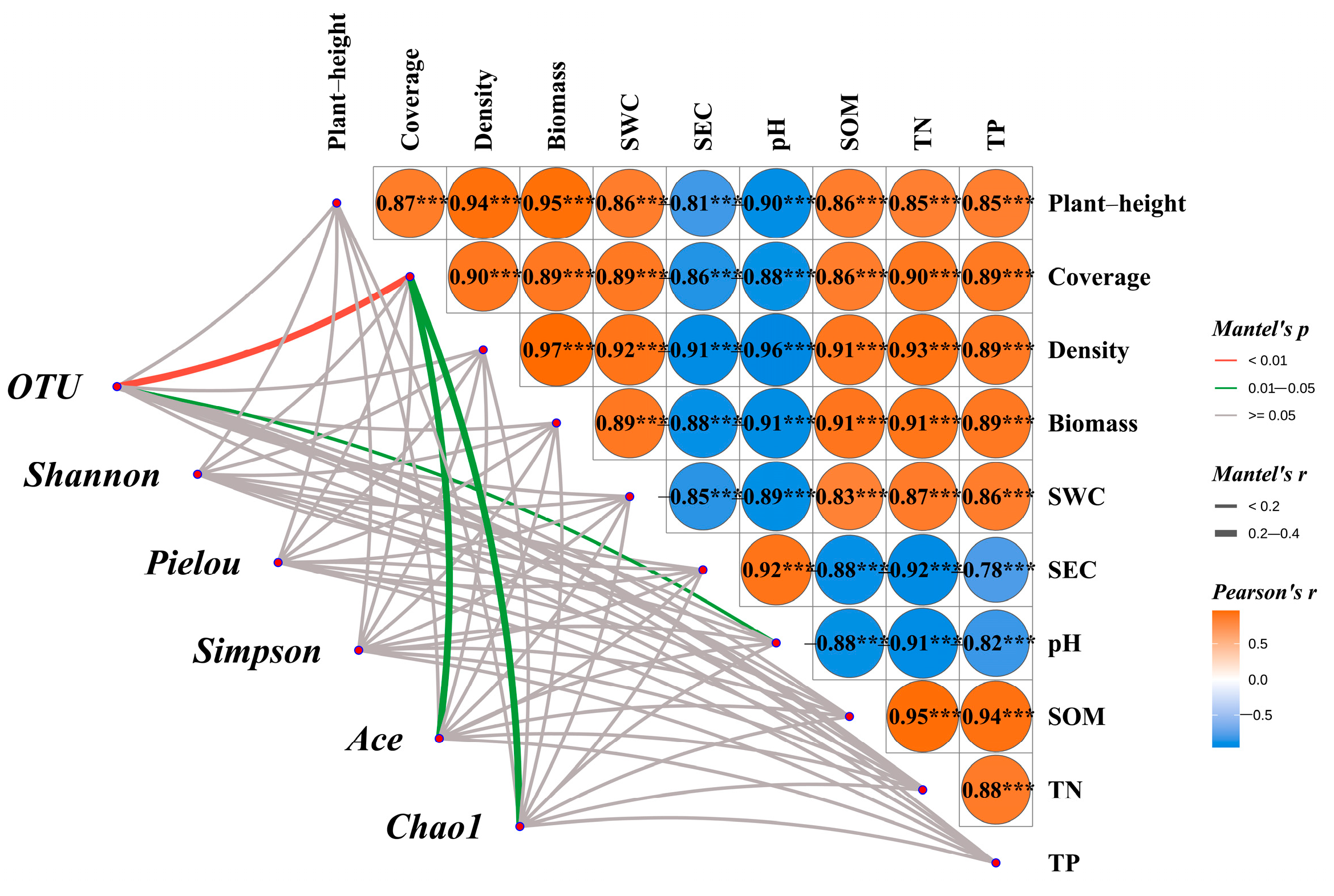
3.8.1. Mantel Test Analysis of Vegetation–Soil–Microbe Interactions
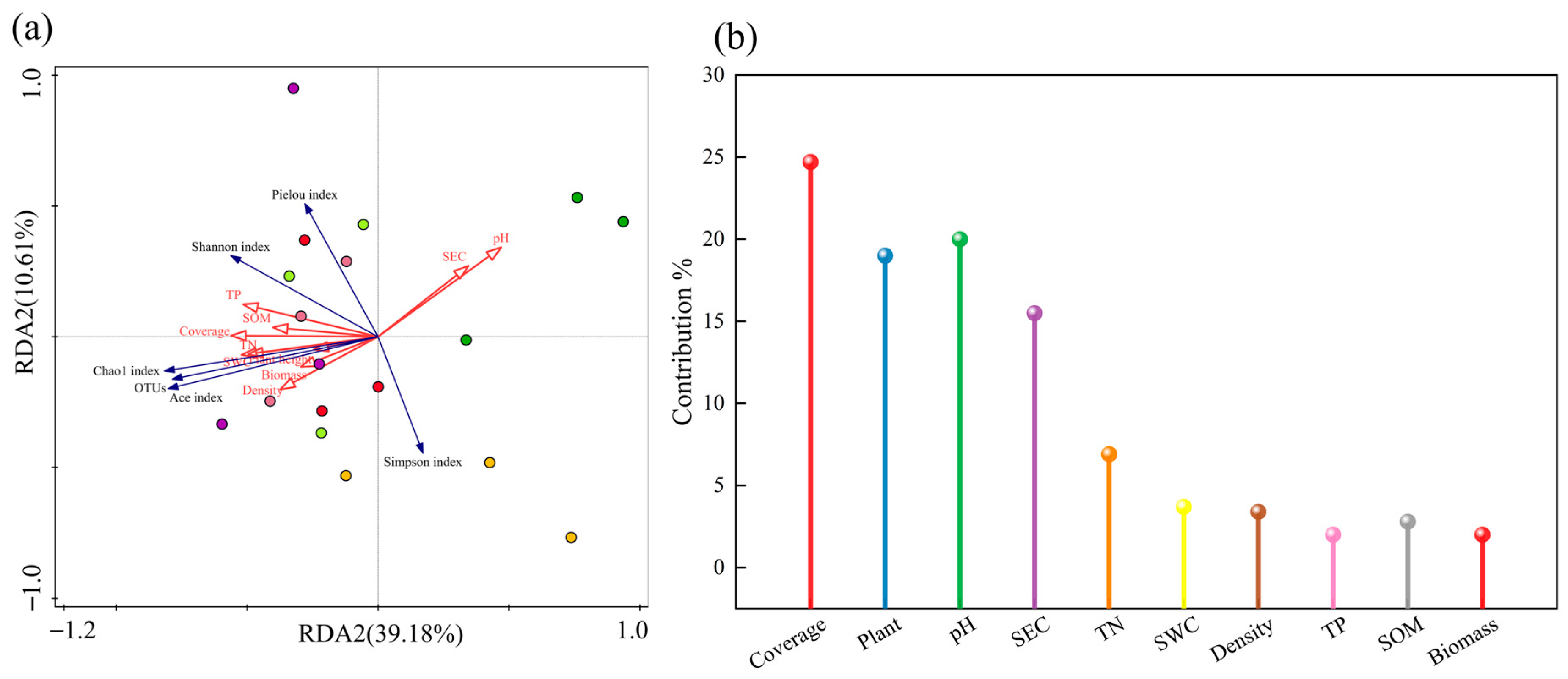
3.8.2. RDA of Vegetation–Soil–Bacteria Relationships
3.8.3. Path Analysis of Vegetation–Soil–Bacteria Relationships
3.8.4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Vegetation–Soil–Bacteria Systems
4. Discussion
4.1. Regulation Effects of Different Mixed-Seeding Treatments on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Vegetation Characteristics in Artificial Grasslands
4.2. Impacts of Different Mixed-Seeding Treatments on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Function in Artificial Grasslands
4.3. Correlation Analysis Between Rhizosphere Microbial Composition and Soil-Vegetation Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.J.; Han, I.L.; Lee, J.; Li, G.Y.; He, P.S.; Baldwin, T.M.; Kao Kniffin, J.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhou, J.Z.; Gu, A.Z. Climate warming enhances biodiversity and stability of grassland soil phosphorus-cycling microbial communities. ISME J. 2025, 19, wraf118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Xu, Y.D.; Li, S.; Shen, H.; Yang, M.Y.; Xiao, J.N. Restoration actions associated with payment for ecosystem services promote the economic returns of alpine grasslands in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.T.; Wang, Z.; Pang, G.W.; Long, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.K.; Song, J.X. Analysis of the distribution pattern and driving factors of bald patches in black soil beach degraded grasslands in the Three-River-Source Region. Land 2025, 14, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.L. Changes in soil bacterial and fungal community composition and functional groups during the artificial restoration of degraded grassland of “Black-Soil Mountain”. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Niu, B.; Wang, Y.L.; Wei, Z.F.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, X.R. Shifts in the vegetation and microbial conditions accelerate soil organic carbon accumulation over a 65-year desert revegetation chronosequence. Catena 2025, 258, 109248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Z.; Chen, X.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Chi, Y.K. Vegetation restoration patterns influence the supply and interrelations of grassland ecosystem services in karst desertification control. Land 2024, 13, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Z.; Sheng, Y.P.; Ren, H.; Gao, F.Y.; Zhang, J. A study on the root competitive pattern of annual pasture in mixed grassland in alpine region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saby, L.; Vidaller, C.; Ramone, H.; Dutoit, T. Nature-based solutions increase sowing success for Mediterranean grassland restoration: A first short-term in situ and ex situ comparison. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 2350–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.C.; Zhao, S.J.; Wang, P. Seasonal variation and key factors influencing evapotranspiration partitioning in alpine ecosystems of the Qinghai Lake Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 177, 113774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ning, Y.M.; Liu, M.R.; Liu, S.T.; Liu, Y.J. Plant interaction modifies effects of soil heterogeneity on seed germination, plant growth, and biomass of plant communities. AoB Plants 2025, 17, plaf013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Dong, Y.; Hai, W.B.; Xue, H.D.; Huo, Z.F.; Li, J.Z.; Wang, H.; Bo, J.H.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, H.B.; et al. Long-term legume cultivation affects the soil bacterial community via altering the soil pore structure in coal mine reclamation agroecosystems. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.W.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhou, Q.P.; Zhang, X.Q.; Hou, F.J. The interplay between plant communities and soil properties response to litter manipulation shape soil bacterial community composition in an alpine meadow. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 213, 106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, F.S.; Xia, C.K.; Wang, F.C.; Wang, S.N.; Liang, C.; Hu, X.F. Interconnections among co-existing soil bacteria taxa drive the home-field advantage of litter decomposition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2025, 61, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yin, Y.L.; Song, J.Q.; Li, S.X. Mixed sowing improves plant and soil bacterial community restoration in the degraded alpine meadow. Plant Soil 2024, 499, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, C.P.; Dong, Q.M.; Cao, Q.; Huo, L.A.; Yang, Z.Z.; Tong, Y.S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, C.D. Differences in rhizosphere soil metabolites and bacterial community structure between mixed cropping and monocropping cultivated grasslands. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2025, 31, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.L.; Huang, Z.Q. Meta-analysis shows positive effects of plant diversity on microbial biomass and respiration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Niu, K.C. Effects of grass mixed-sowing on soil microbial diversity on the Qingzang (Tibetan) Plateau. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Lyu, L.Y.; Liu, Q.Q.; Li, F.Y.; Bao, S.C.; Han, Y.; Shen, C.J.; Shi, J.J. Response of phenotypic characteristics of Anthoxanthum glabrum (Trin.) Veldkamp to heterogeneous soil habitats in the source region of the three rivers. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2025, 43, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscalleda Alvarez, J.; Page, G.F.M.; Zdunic, K.; Prober, S.M. Estimating woody vegetation cover in arid and semi-arid rangelands. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 177, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.B.; Li, S.C.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.P. Reseeding promotes plant biomass by improving microbial community stability and soil fertility in a degraded subalpine grassland. Geoderma 2025, 453, 117160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, R.R.; Liang, Q.W.; Na, R.S.; Li, T.; Yang, X.F.; Bao, Y.H.; Xin, X.P. Study on soil physical and chemical properties and carbon and nitrogen sequestration of grassland under different utilization modes. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2021, 30, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Pan, Q.M.; Xing, Q. Fundamental theories and technologies for optimizing the production functions and ecological functions in grassland ecosystems. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skersiene, A.; Slepetiene, A.; Stukonis, V.; Norkeviciene, E. Contributions of different perennial grass species and their roots’ characteristics to soil organic carbon accumulation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.S.; Zhang, C.P.; Yu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Dong, Q.M.; Yang, Z.Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Huo, L.A.; Li, C.D. Effects of mixed seeding of perennial grasses in the area around Qinghai Lake. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 2203–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Kou, Y.; Wang, J.; Tu, B.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peay, K.G.; Sha, L.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Soil pH is a major driver of soil diazotrophic community assembly in Qinghai-Tibet alpine meadows. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Xiao, Y.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Xu, J.X.; Ma, Y.H.; Li, Q.F.; Zhou, G.Y. Relationship between plant diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality in degraded alpine meadows under multifunctional group species combination models. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2025, 49, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Li, J.W.; Tian, N.X.; Li, G.X.; Sheng, L.X.; He, C.G.; Bian, H.F. Effect of experimental warming on dissolved organic matter and bacterial diversity in a forest swamp soil. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Wang, P.P.; Liu, Q.H.; Luo, R.Y.; Pang, X.Y. Microbial functional groups govern soil multifunctionality during alpine grassland restoration via turf transplantation. Catena 2025, 258, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.W.; Li, J.J.; Li, H.; Du, G.Z. Effects of high-density mixed planting in artificial grassland on microbial community. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Z.; Xiong, K.N.; Chi, Y.K.; He, C.; Fang, J.Z.; He, S.Y. Effect of cultivated pastures on soil bacterial communities in the karst rocky desertification area. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 922989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragelund, C.; Levantesi, C.; Borger, A.; Thelen, K.; Eikelboom, D.; Tandoi, V.; Kong, Y.; van der Waarde, J.; Krooneman, J.; Rossetti, S. Identity, abundance and ecophysiology of filamentous Chloroflexi species present in activated sludge treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, L.L.; Guo, Q.E.; Tan, J.H.; Kang, F.Y. Influence of rotation fallow mode on bacterial community in soil. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2020, 38, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Xie, Z.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, R.J. Research advances in mutualistic symbiotic microbes diversities. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 3899–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyensa, G.; Ashworth, A.J.; Yang, Y.C.; Adhikari, K.; Savin, M.; Owens, P.; Sauer, T.; Pedretti, E.F.; Cocco, S.; Corti, G. Soil bacterial diversity based on management and topography in a silvopastoral system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Lu, G.X.; Yan, H.L.; Wang, Y.C. Effects of the transformation from natural alpine grassland to mixed artificial grassland on the characteristics of soil microbial community. Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 2928–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, A.; Felder, S.; Höver, T.; Kehraus, S.; Neu, E.; Lohr, F.; König, G.M.; Schäberle, T.F. Antibiotics from gliding bacteria. Phytochem. Rev. 2013, 12, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.F.; Jia, C.Z.; Wang, X.P.; Zhao, P.P.; Hu, X.W. Effect of multi-species grouping on restoration of alpine degraded meadows in Gannan, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2025, 49, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Kang, Y.M.; Sakurai, K.; Ohnishi, K. Fixation of carbon dioxide by chemoautotrophic bacteria in grassland soil under dark conditions. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2017, 67, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, K.; Ding, Y.; Struik, P.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, Y.H. The mechanism of plant-soil microbial feedback in grassland succession. Chin. J. Grassl. 2022, 44, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Jing, Y.Y.; Xu, C.L.; Yu, X.J. The effects of spring rest-grazing on soil extracellular enzyme activities and microbial metabolic limitation in alpine meadows of the Eastern Qilian Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 17, 8614–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.J.; Li, H.C.; Fan, Q.R.; Li, J.J. Evolution of soil bacterial community assembly mechanisms in reclaimed Pinus tabuliformis forests of Xishan mining area. Environ. Sci. 2025, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Manoharan, L.; Rosenstock, N.P.; Olsson, P.A.; Hedlund, K. Long-term agricultural fertilization alters arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community composition and barley (Hordeum vulgare) mycorrhizal carbon and phosphorus exchange. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, D.A.; Lindahl, B.D. Disentangling global soil fungal diversity: A worldwide sampling effort reveals the global drivers of soil fungal biodiversity. Science 2014, 346, 1052–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.R.; Liu, Y.F.; Huang, Z.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.L. Restoration of a hillslope grassland with an ecological grass species (Elymus tangutorum) favors rainfall interception and water infiltration and reduces soil loss on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2022, 219, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ding, M.J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Huang, P.; Wu, Y.P.; Zou, T.E.; Wang, N.Y.; Zeng, H. Steppe under degradation interaction effects of vegetation and soil factors on microbial communities in alpine. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4251–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.X.; Pei, X.J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, R.J.; Wang, B.H.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.Y.; Lei, N.F.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, Q. Synergistic restoration effect of vegetation and soil microorganisms in the wound ecological restoration area of Jiuzhaigou Project. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 17, 8570–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.Q.; Song, Y.Y.; Duan, Z.Y.; He, H.X.; Chen, Y.B.; Qiao, C. Effects of reseeding on soil physicochemical properties and microbial community structure in Yili natural mowing land. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 33, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Yu, W.Y.; Ma, L.N.; Ye, X.H.; Enkhmaa, E.; Wang, R.Z.; Huang, Z.Y.; Tuvshintogtokh, I.; Liu, G.F. Biotic and abiotic drivers of ecosystem multifunctionality: Evidence from the semi-arid grasslands of northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
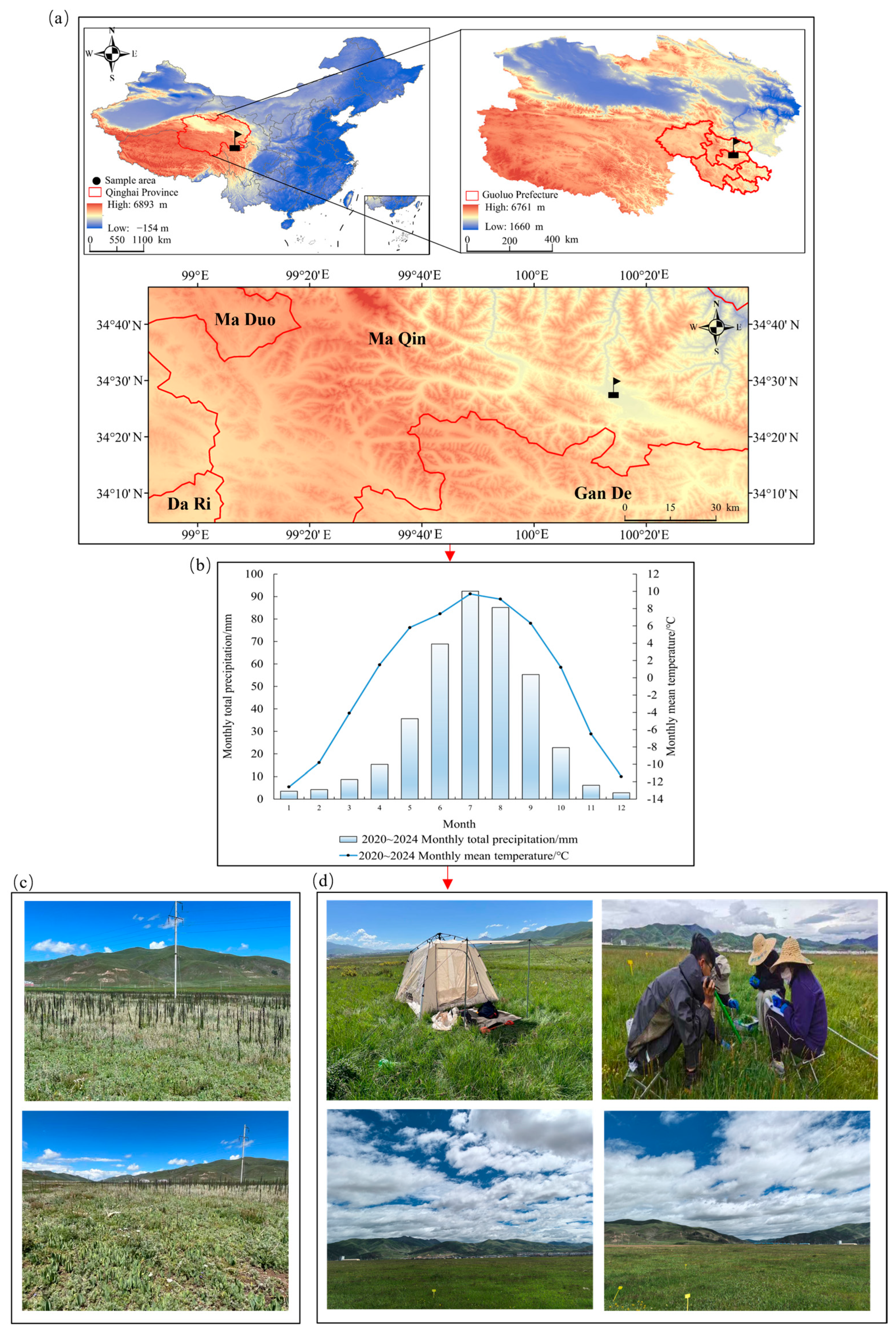
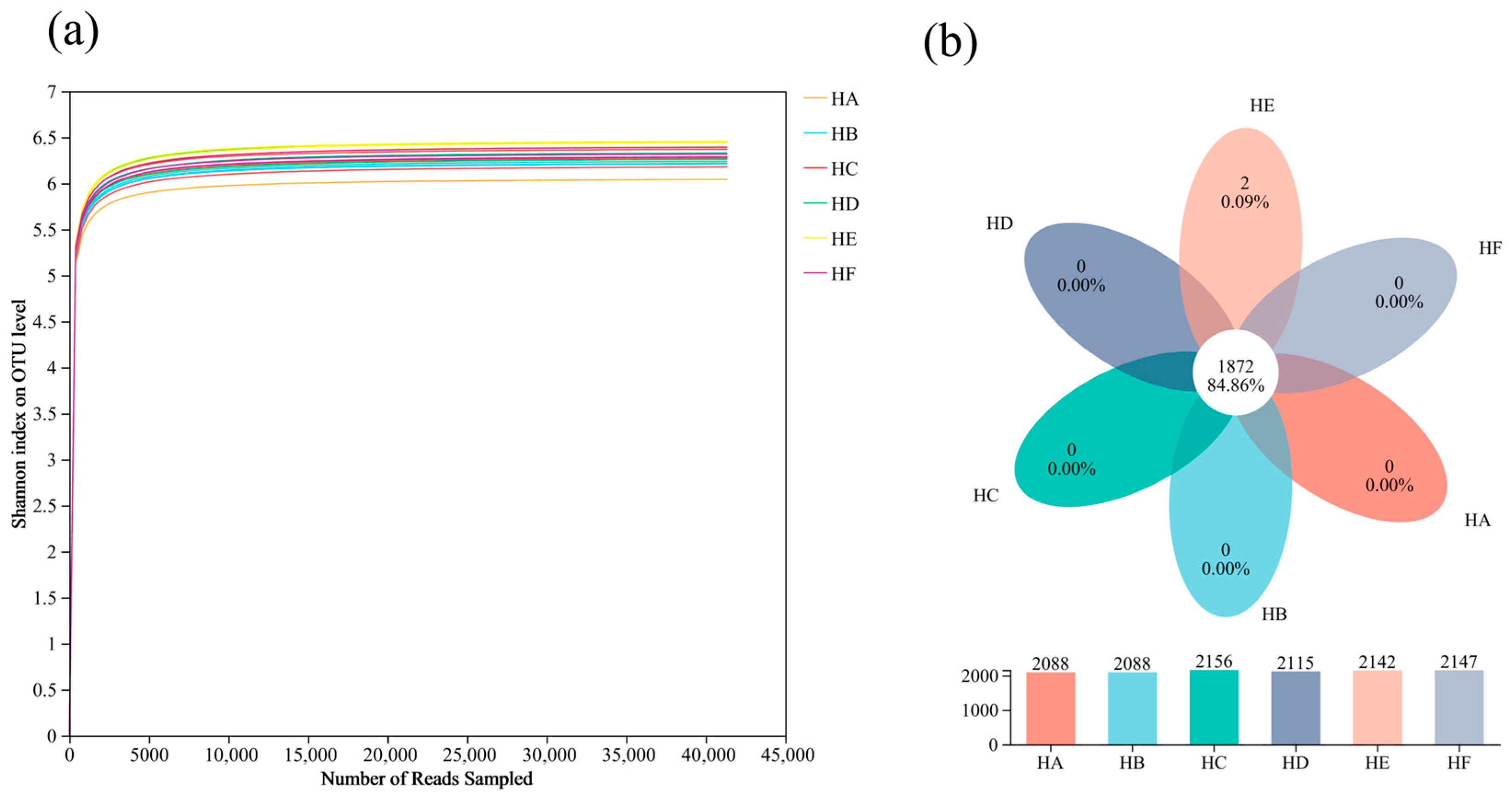

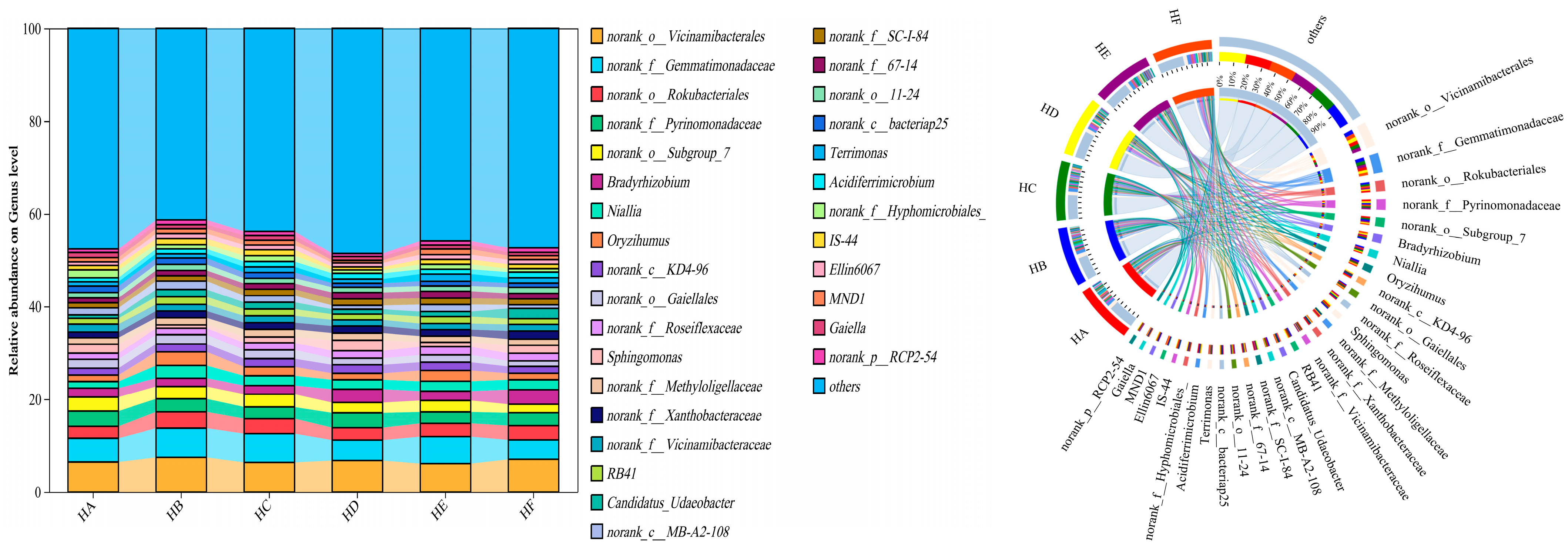
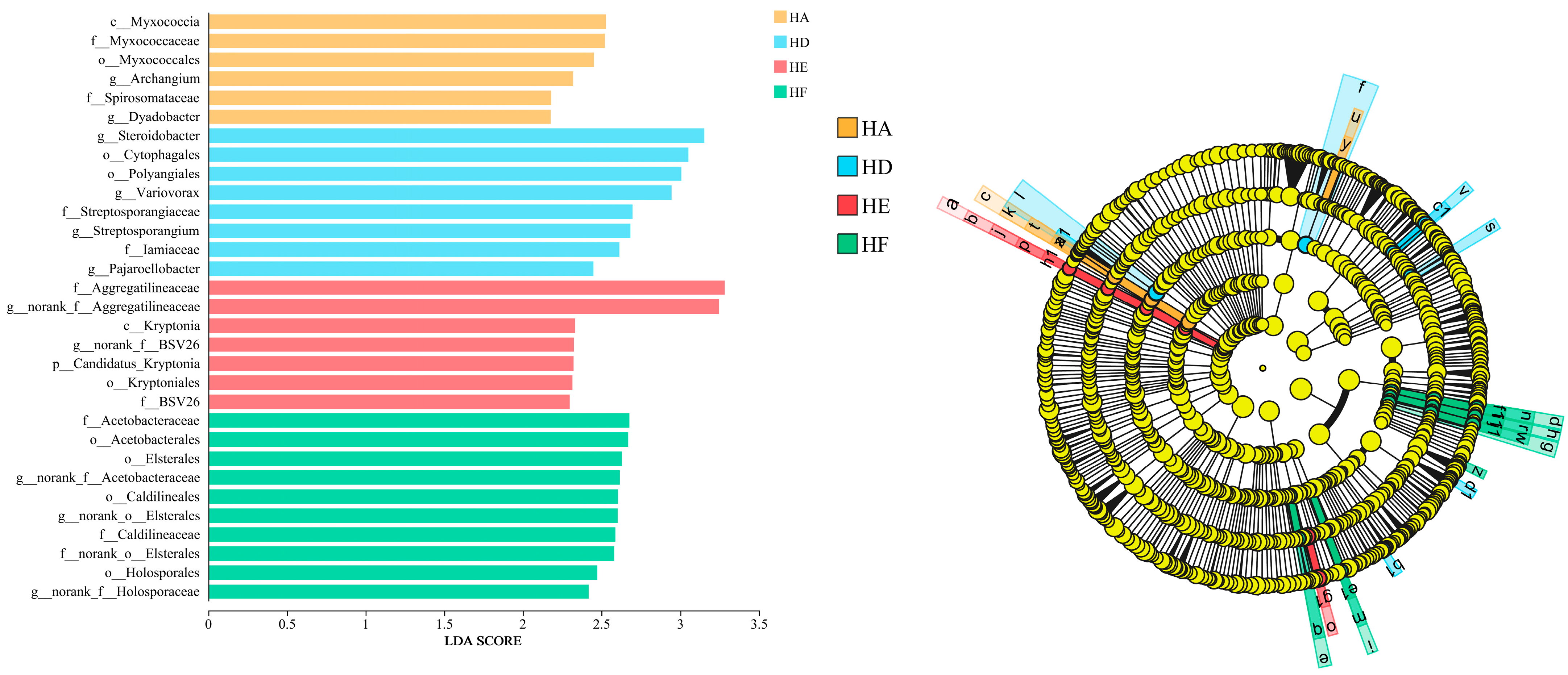



| No. | Treatment Code | Grass Species Combination | Mixed-Seeding Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HA | Elymus nutans Griseb. | 1 |
| 2 | HB | Elymus nutans Griseb. + Poa crymophila Keng ex L. Liu cv. ‘Qinghai’ | 1:1 |
| 3 | HC | Elymus nutans Griseb. + Poa crymophila Keng ex L. Liu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Festuca sinensis Keng ex S. L. Lu cv. ‘Qinghai’ | 1:1:1 |
| 4 | HD | Elymus nutans Griseb. + Poa crymophila Keng ex L. Liu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Festuca sinensis Keng ex S. L. Lu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Poa poophagorum Bor. | 1:1:1:1 |
| 5 | HE | Elymus nutans Griseb. + Poa crymophila Keng ex L. Liu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Festuca sinensis Keng ex S. L. Lu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Poa poophagorum Bor. + Festuca kryloviana Reverd. cv. ‘Huanhu’ | 1:1:1:1:1 |
| 6 | HF | Elymus nutans Griseb. + Poa crymophila Keng ex L. Liu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Festuca sinensis Keng ex S. L. Lu cv. ‘Qinghai’ + Poa poophagorum Bor. + Festuca kryloviana Reverd. cv. ‘Huanhu’ + Elymus breviaristatus Linn. | 1:1:1:1:1:1 |
| Year | Treatment | Vegetation Height/cm | Plant Coverage/% | Density/Plant·m−2 | Aboveground Biomass/(g·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | HA | 35.8 ± 1.17 c | 72.0 ± 2.65 d | 708 ± 18.7 d | 951 ± 19.5 c |
| HB | 40.5 ± 1.40 b | 80.0 ± 4.36 bc | 791 ± 11.8 c | 1241 ± 77.1 b | |
| HC | 42.1 ± 0.97 b | 90.3 ± 3.51 a | 913 ± 25.5 a | 1580 ± 141.3 a | |
| HD | 45.9 ± 2.15 a | 92.3 ± 3.21 a | 855 ± 16.4 b | 1574 ± 94.8 a | |
| HE | 39.2 ± 0.83 b | 84.0 ± 3.61 b | 734 ± 21.7 d | 1154 ± 97.4 bc | |
| HF | 32.5 ± 2.21 d | 76.3 ± 3.21 cd | 651 ± 18.8 e | 978 ± 98.0 c | |
| 2024 | HA | 32.0 ± 2.65 c | 75.3 ± 3.79 d | 665 ± 20.6 d | 1079 ± 131.2 c |
| HB | 39.3 ± 2.08 b | 86.3 ± 3.21 bc | 800 ± 15.4 c | 1388 ± 95.4 b | |
| HC | 50.0 ± 2.65 a | 95.3 ± 2.08 a | 942 ± 17.9 a | 1645 ± 76.9 a | |
| HD | 45.0 ± 4.58 a | 90.7 ± 3.21 ab | 902 ± 18.5 b | 1431 ± 64.4 b | |
| HE | 34.0 ± 3.61 bc | 83.0 ± 4.36 c | 811 ± 20.5 c | 1206 ± 91.9 c | |
| HF | 28.3 ± 2.08 c | 77.0 ± 2.00 d | 692 ± 15.5 d | 1022 ± 124.2 c |
| Year | Treatment | SWC/% | SEC/(μs·cm−1) | pH | SOM/(g·kg−1) | TN/(g·kg−1) | TP/(g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | HA | 20.6 ± 0.77 d | 838 ± 37.5 a | 8.35 ± 0.11 a | 129 ± 9.87 b | 4.49 ± 0.14 e | 1.15 ± 0.16 c |
| HB | 24.2 ± 0.64 c | 492 ± 38.6 cd | 7.70 ± 0.12 c | 139 ± 12.29 b | 4.45 ± 0.10 e | 1.23 ± 0.15 c | |
| HC | 27.5 ± 1.20 b | 428 ± 48.3 d | 7.34 ± 0.07 d | 197 ± 13.08 a | 7.16 ± 0.15 a | 1.84 ± 0.12 a | |
| HD | 30.5 ± 1.49 a | 564 ± 68.3 bc | 7.55 ± 0.19 cd | 187 ± 14.00 a | 6.42 ± 0.12 b | 2.01 ± 0.12 a | |
| HE | 25.0 ± 1.47 c | 618 ± 65.6 b | 8.02 ± 0.17 b | 152 ± 9.07 b | 6.16 ± 0.18 c | 1.51 ± 0.11 b | |
| HF | 22.5 ± 1.37 cd | 828 ± 38.4 a | 8.25 ± 0.13 ab | 129 ± 14.00 b | 5.01 ± 0.12 d | 1.22 ± 0.10 c | |
| 2024 | HA | 20.8 ± 2.37 c | 832 ± 65.6 a | 8.22 ± 0.13 a | 132 ± 12.66 b | 4.38 ± 0.09 e | 1.28 ± 0.13 c |
| HB | 24.6 ± 1.11 bc | 768 ± 43.5 ab | 7.81 ± 0.12 b | 147 ± 10.02 b | 6.13 ± 0.14 b | 1.53 ± 0.08 bc | |
| HC | 30.0 ± 2.23 a | 402 ± 63.3 c | 7.38 ± 0.12 d | 195 ± 17.79 a | 7.41 ± 0.15 a | 2.36 ± 0.17 a | |
| HD | 26.9 ± 1.35 ab | 649 ± 37.8 b | 7.53 ± 0.10 cd | 164 ± 13.01 b | 5.81 ± 0.12 c | 2.31 ± 0.20 a | |
| HE | 23.8 ± 1.64 bc | 709 ± 58.4 ab | 7.70 ± 0.11 bc | 153 ± 9.17 b | 5.10 ± 0.14 d | 1.65 ± 0.09 b | |
| HF | 20.3 ± 2.58 c | 802 ± 63.6 a | 8.13 ± 0.10 a | 141 ± 15.0 b | 4.54 ± 0.13 e | 1.42 ± 0.13 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Z.; Shi, J.; Fu, S.; Lv, L.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bao, S. Ecological Effects and Microbial Regulatory Mechanisms of Functional Grass Species Assembly in the Restoration of “Heitutan” Degraded Alpine Grasslands. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102341
Cai Z, Shi J, Fu S, Lv L, Li F, Liu Q, Zhang H, Bao S. Ecological Effects and Microbial Regulatory Mechanisms of Functional Grass Species Assembly in the Restoration of “Heitutan” Degraded Alpine Grasslands. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102341
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Zongcheng, Jianjun Shi, Shouquan Fu, Liangyu Lv, Fayi Li, Qingqing Liu, Hairong Zhang, and Shancun Bao. 2025. "Ecological Effects and Microbial Regulatory Mechanisms of Functional Grass Species Assembly in the Restoration of “Heitutan” Degraded Alpine Grasslands" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102341
APA StyleCai, Z., Shi, J., Fu, S., Lv, L., Li, F., Liu, Q., Zhang, H., & Bao, S. (2025). Ecological Effects and Microbial Regulatory Mechanisms of Functional Grass Species Assembly in the Restoration of “Heitutan” Degraded Alpine Grasslands. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102341






