Maternal Psychosocial Stress Is Associated with Reduced Diversity in the Early Infant Gut Microbiome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment and Consenting
2.2. Medical Histories and Maternal Stress Measures
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
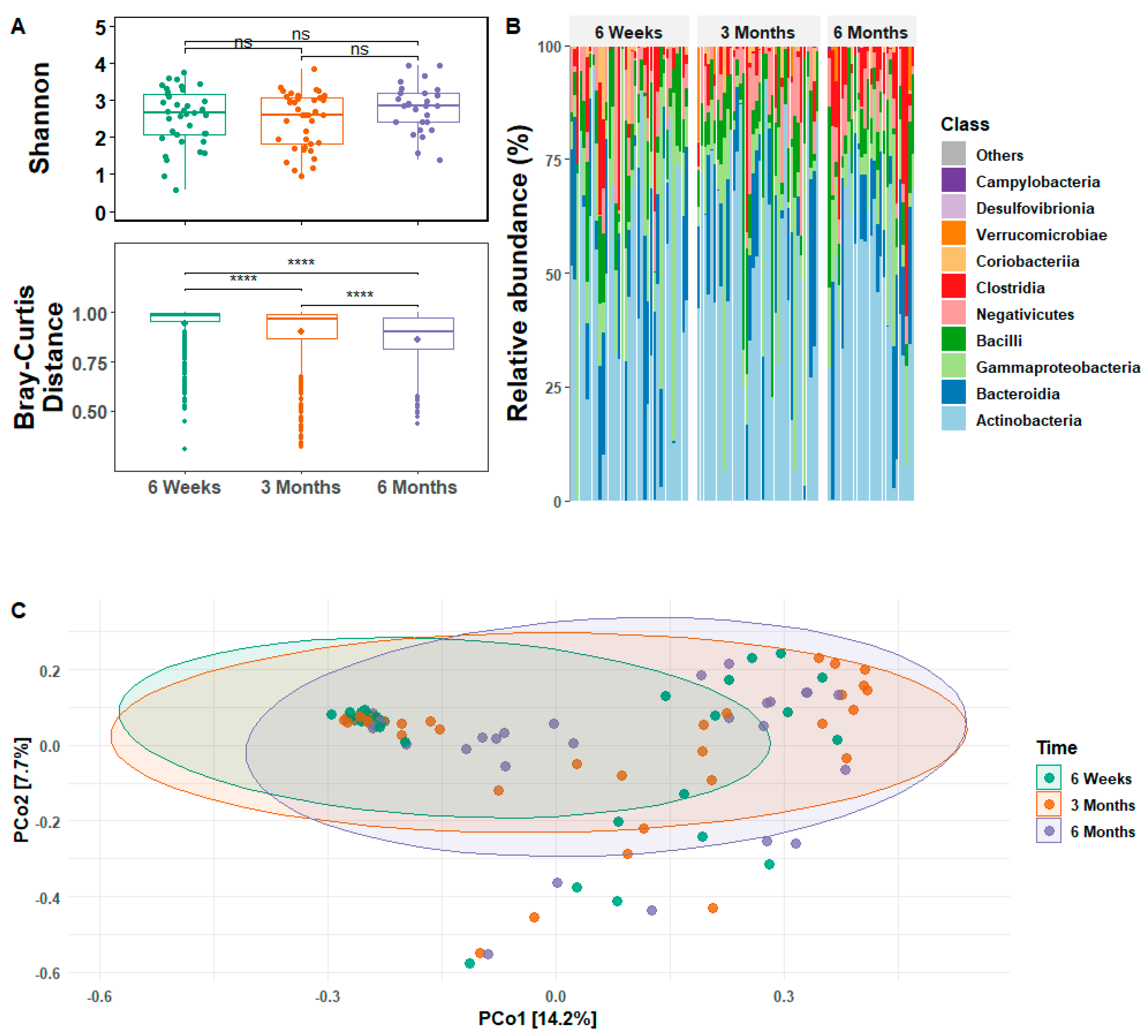
3.2. Infant Gut Microbial Relative Abundance and Diversity
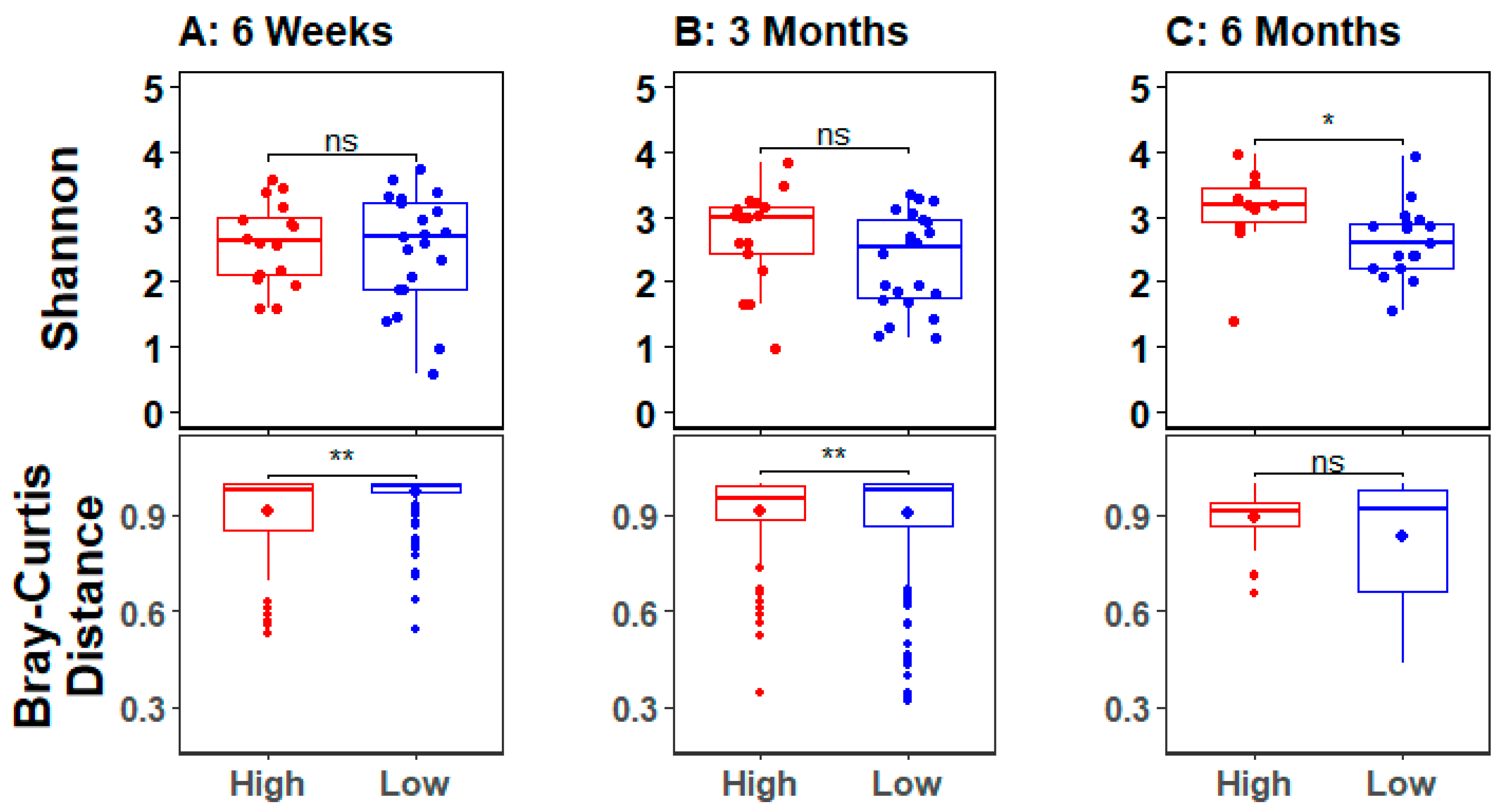
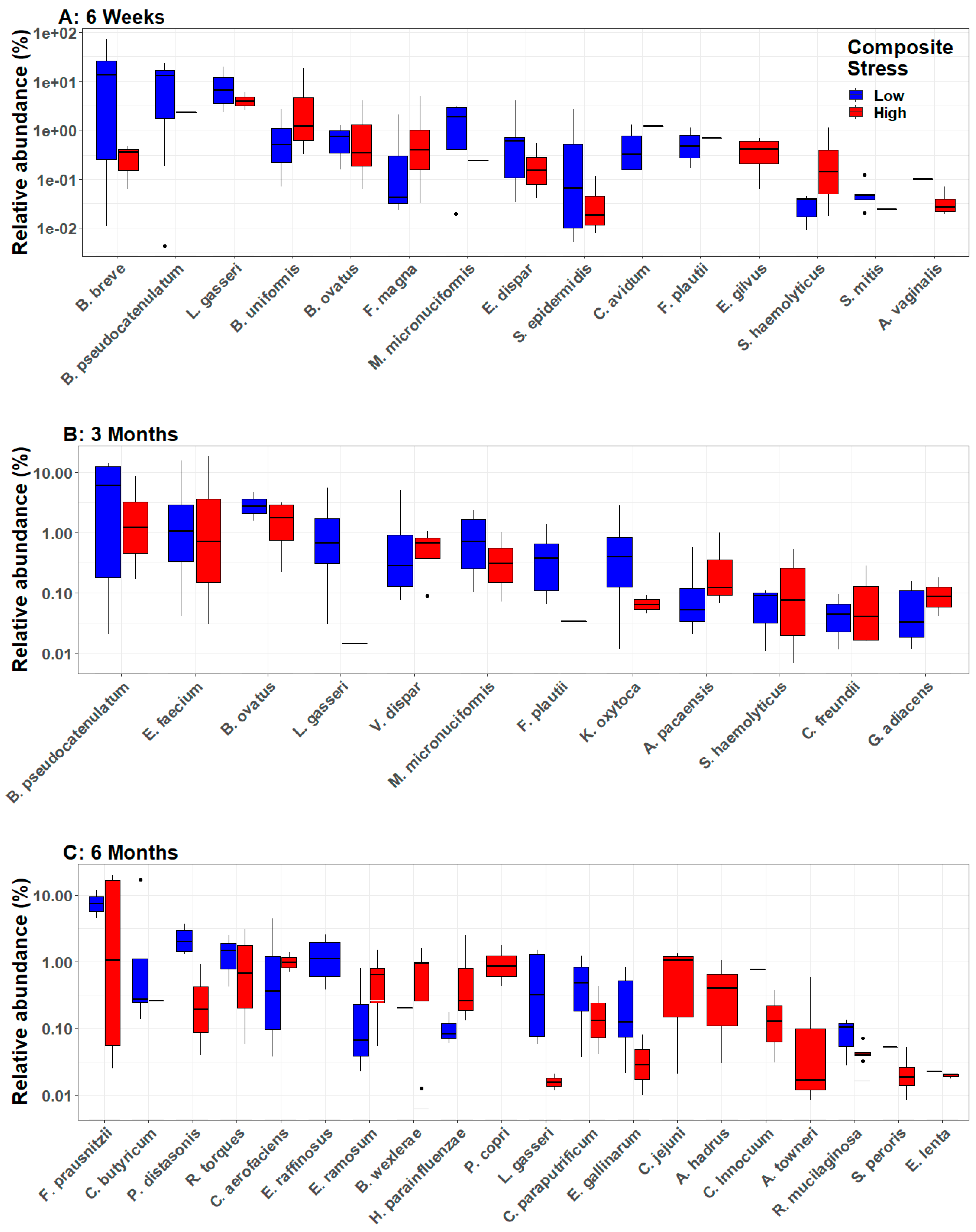
3.3. Infant Gut Microbial Diversity and Maternal Stress
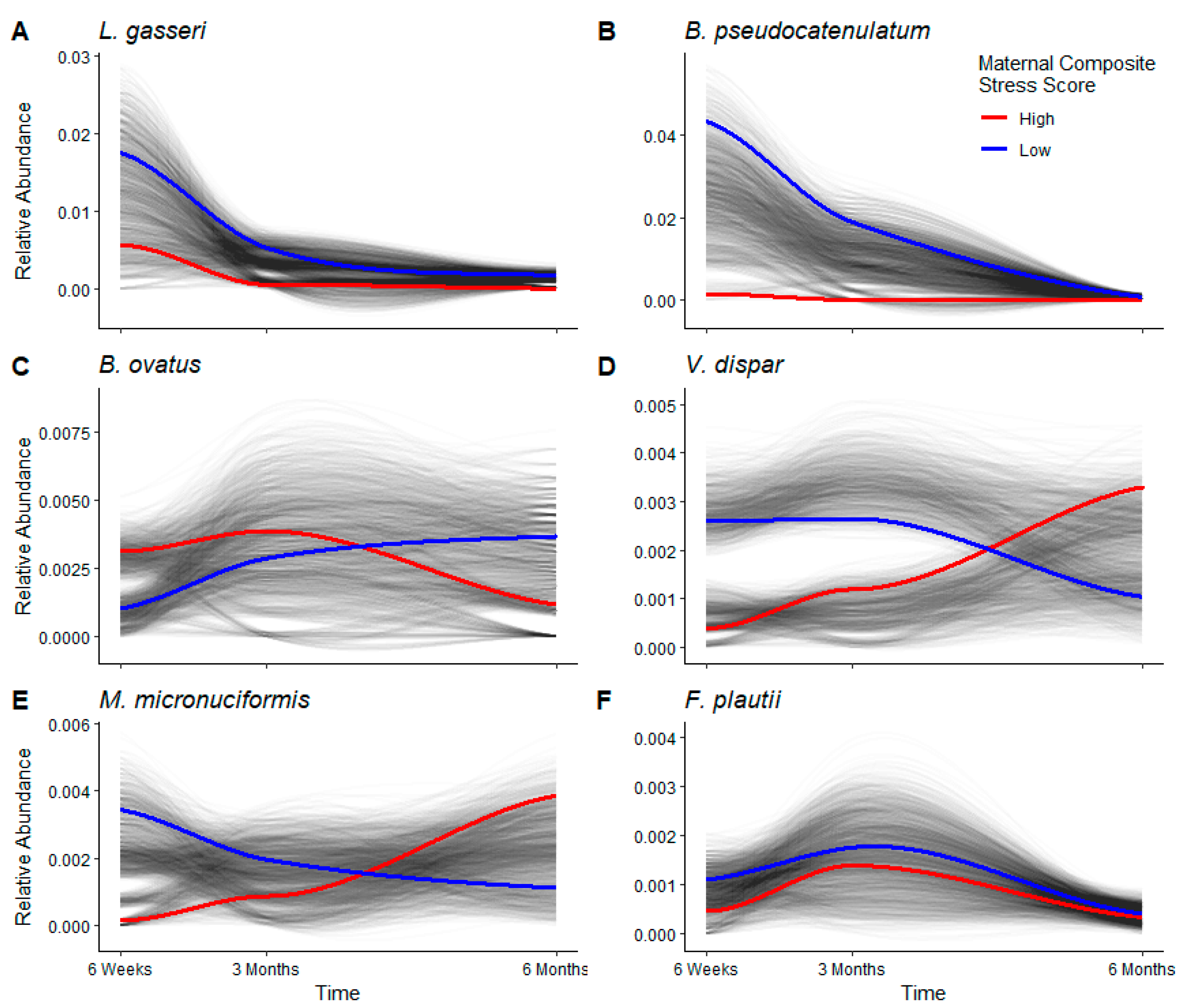
3.4. Longitudinal Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goulet, O. Potential Role of the Intestinal Microbiota in Programming Health and Disease. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Garud, N.R. Rapid Evolution and Strain Turnover in the Infant Gut Microbiome. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grech, A.; Collins, C.E.; Holmes, A.; Lal, R.; Duncanson, K.; Taylor, R.; Gordon, A. Maternal Exposures and the Infant Gut Microbiome: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1897210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avershina, E.; Storrø, O.; Øien, T.; Johnsen, R.; Pope, P.; Rudi, K. Major Faecal Microbiota Shifts in Composition and Diversity with Age in a Geographically Restricted Cohort of Mothers and Their Children. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.E.; Townsend, S.D. Temporal Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Konya, T.; Maughan, H.; Guttman, D.S.; Field, C.J.; Chari, R.S.; Sears, M.R.; Becker, A.B.; Scott, J.A.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Gut Microbiota of Healthy Canadian Infants: Profiles by Mode of Delivery and Infant Diet at 4 Months. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2013, 185, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.; Xu, W.; Janton, S.; Henderson, W.A.; Matson, A.; Mcgrath, J.M.; Maas, K.; Graf, J. Gut Microbiome Developmental Patterns in Early Life of Preterm Infants: Impacts of Feeding and Gender. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckeen, S.; Roy, N.C.; Mullaney, J.A.; Eriksen, H.; Lovell, A.; Kussman, M.; Young, W.; Fraser, K.; Wall, C.R.; Mcnabb, W.C. Adaptation of the Infant Gut Microbiome During the Complementary Feeding Transition. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, S.S.B.; Hung, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Parathan, P.; Yalcinkaya, N.; Haag, A.; Luna, R.A.; Bornstein, J.C.; Savidge, T.C.; Foong, J.P.P. Neonatal Antibiotics Have Long Term Sex-Dependent Effects on the Enteric Nervous System. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 4303–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiota-Brain Axis: Context and Causality. Science 2022, 376, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, W.F.; Ravel, J. More Data Needed on Neonatal Microbiome Seeding. Microbiome 2022, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantsoo, L.; Zemel, B.S. Stress Gets into the Belly: Early Life Stress and the Gut Microbiome. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 414, 113474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The Neuroactive Potential of the Human Gut Microbiota in Quality of Life and Depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussons-Read, M.E. Effects of Prenatal Stress on Pregnancy and Human Development: Mechanisms and Pathways. Obs. Med. 2013, 6, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; Wüst, S.; Kumsta, R.; Layes, I.M.; Nelson, E.L.; Hellhammer, D.H.; Wadhwa, P.D. Prenatal Psychosocial Stress Exposure Is Associated with Insulin Resistance in Young Adults. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol 2008, 199, e491–e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, D.P.; Brunet, A.; Schmitz, N.; Ciampi, A.; King, S. Project Ice Storm: Prenatal Maternal Stress Affects Cognitive and Linguistic Functioning in 5 1/2-Year-Old Children. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 47, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechler, C.; Borewicz, K.; Beijers, R.; Saccenti, E.; Riksen-Walraven, M.; Smidt, H.; De Weerth, C. Association between Psychosocial Stress and Fecal Microbiota in Pregnant Women. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatsinki, A.K.; Keskitalo, A.; Laitinen, V.; Munukka, E.; Uusitupa, H.M.; Lahti, L.; Kortesluoma, S.; Mustonen, P.; Rodrigues, A.J.; Coimbra, B.; et al. Maternal Prenatal Psychological Distress and Hair Cortisol Levels Associate with Infant Fecal Microbiota Composition at 2.5 Months of Age. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 119, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, J.R.; Roach, J.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Thompson, A.L. Maternal Precarity and Hpa Axis Functioning Shape Infant Gut Microbiota and Hpa Axis Development in Humans. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlmans, M.A.; Korpela, K.; Riksen-Walraven, J.M.; De Vos, W.M.; De Weerth, C. Maternal Prenatal Stress Is Associated with the Infant Intestinal Microbiota. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 53, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Wong, J.; Heiner, C.; Oh, S.; Theriot, C.M.; Gulati, A.S.; Mcgill, S.K.; Dougherty, M.K. High-Throughput Amplicon Sequencing of the Full-Length 16s Rrna Gene with Single-Nucleotide Resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, L.; Elguero, E.; Koumavor, C.K.; Renaud, N.; Prugnolle, F.; Thomas, F.; Ategbo, S.; Engoba, M.; Obengui; Leroy, E.M.; et al. Evolution in Fecal Bacterial/Viral Composition in Infants of Two Central African Countries (Gabon and Republic of the Congo) During Their First Month of Life. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.A.; Fitzstevens, J.L.; Schmidt, V.T.; Enav, H.; Huus, K.E.; Mbong Ngwese, M.; Grießhammer, A.; Pfleiderer, A.; Adegbite, B.R.; Zinsou, J.F.; et al. Codiversification of Gut Microbiota with Humans. Science 2022, 377, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, K. Q&A: Gathering Diverse Microbiome Samples. The Scientist, 3 November 2022. Available online: https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/q-a-gathering-diverse-microbiome-samples-70721 (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Rodney, N.C.; Mulligan, C.J. A Biocultural Study of the Effects of Maternal Stress on Mother and Newborn Health in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2014, 155, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertes, D.A.; Kamin, H.S.; Hughes, D.A.; Rodney, N.C.; Bhatt, S.; Mulligan, C.J. Prenatal Maternal Stress Predicts Methylation of Genes Regulating the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical System in Mothers and Newborns in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Child Dev. 2016, 87, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D.; Bolus, R.; Mayer, E.A. Psychometric Properties of the Early Trauma Inventory-Self Report. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2007, 195, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörberg, N.; Kouros, I.; Ekselius, L.; Cunningham, J.; Willebrand, M.; Ramklint, M. Early Trauma Inventory Self-Report Short Form (Etisr-Sf): Validation of the Swedish Translation in Clinical and Non-Clinical Samples. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2019, 73, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A Global Measure of Perceived Stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.J.; Wilner, N.; Alvarez, W. Impact of Event Scale: A Measure of Subjective Stress. Psychosom. Med. 1979, 41, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.L.; Holden, J.M.; Sagovsky, R. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of the 10-Item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Br. J. Psychiatry 1987, 150, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Mckenzie-Mcharg, K.; Shakespeare, J.; Price, J.; Gray, R. A Systematic Review of Studies Validating the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale in Antepartum and Postpartum Women. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2009, 119, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.E. Stai Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Islam, S.J.; Topel, M.L.; Ko, Y.A.; Mujahid, M.S.; Vaccarino, V.; Liu, C.; Sims, M.; Mubasher, M.; Searles, C.D.; et al. Individual Psychosocial Resilience, Neighborhood Context, and Cardiovascular Health in Black Adults: A Multilevel Investigation from the Morehouse-Emory Cardiovascular Center for Health Equity Study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 13, e006638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattaway, M.A.; Schaefer, U.; Tewolde, R.; Dallman, T.J.; Jenkins, C. Identification of Escherichia Coli and Shigella Species from Whole-Genome Sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 3.5.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The Silva Ribosomal Rna Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of Rrna Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcmurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. Microeco: An R Package for Data Mining in Microbial Community Ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of Compositions of Microbiomes with Bias Correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of Microbial Compositions: A Review of Normalization and Differential Abundance Analysis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S. A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex Heatmaps Reveal Patterns and Correlations in Multidimensional Genomic Data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Yassour, M.; Knights, D. Splinectomer Enables Group Comparisons in Longitudinal Microbiome Studies. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, B.G.V.; Fernandez-García, L.; Gato, E.; López, M.; Blasco, L.; Leão, R.S.; Albano, R.M.; Fernández, B.; Cuenca, F.-F.; Pascual, Á.; et al. Genome Sequence of Airborne Acinetobacter Sp. Strain 5-2ac02 in the Hospital Environment, Close to the Species of Acinetobacter Towneri. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01343-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, K.E.; Muscat, E.B.; Reyna, M.E.; Kociolek, L.K. Clostridium Innocuum: Microbiological and Clinical Characteristics of a Potential Emerging Pathogen. Anaerobe 2021, 71, 102418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, B.J.; Tai, A.Y.; Kotsanas, D.; Francis, M.J.; Roberts, S.A.; Ballard, S.A.; Junckerstorff, R.K.; Korman, T.M. Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics of Eggerthella Lenta Bacteremia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, O.; Wren, B.W. Microbe Profile: Campylobacter Jejuni–Survival Instincts. Microbiology 2020, 166, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Hou, X.G.; Todome, Y.; Sultana, F.; Hirose, K.; Shu, S.E.; Ezaki, T.; Ohkuni, H. Streptococcus Peroris Sp. Nov. And Streptococcus Infantis Sp. Nov., New Members of the Streptococcus Mitis Group, Isolated from Human Clinical Specimens. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48 Pt 3, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; You, H.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Joo, S.K.; Yu, J.; Park, S.; Kang, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Distinct Signatures of Gut Microbiome and Metabolites Associated with Significant Fibrosis in Non-Obese Nafld. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Sczesnak, A.; Longman, R.S.; Segata, N.; Ubeda, C.; Bielski, C.; Rostron, T.; Cerundolo, V.; Pamer, E.G.; Abramson, S.B.; et al. Expansion of Intestinal Prevotella Copri Correlates with Enhanced Susceptibility to Arthritis. Elife 2013, 2, e01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, J.P.; Adappa, N.D.; Krol, J.; Bhat, A.S.; Balashov, S.; Ehrlich, R.L.; Palmer, J.N.; Workman, A.D.; Blasetti, M.; Sen, B.; et al. Species-Level Bacterial Community Profiling of the Healthy Sinonasal Microbiome Using Pacific Biosciences Sequencing of Full-Length 16s Rrna Genes. Microbiome 2018, 6, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Yun, K.; Mun, S.; Chung, W.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Nam, Y.D.; Lim, M.Y.; Hong, C.P.; Park, C.; Ahn, Y.J.; et al. The Effect of Taxonomic Classification by Full-Length 16s Rrna Sequencing with a Synthetic Long-Read Technology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Pereira, J.S.; Rea, K.; Nolan, Y.M.; O’leary, O.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Depression’s Unholy Trinity: Dysregulated Stress, Immunity, and the Microbiome. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, D.; Kuwano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Hara, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Sugawara, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Rokutan, K.; Nishida, K. Daily Intake of Lactobacillus Gasseri Cp2305 Relieves Fatigue and Stress-Related Symptoms in Male University Ekiden Runners: A Double-Blind, Randomized, and Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Sawada, D.; Kuwano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Sugawara, T.; Aoki, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Rokutan, K. Daily Administration of Paraprobiotic Lactobacillus Gasseri Cp2305 Ameliorates Chronic Stress-Associated Symptoms in Japanese Medical Students. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusti, A.; Moya-Pérez, A.; Campillo, I.; Montserrat-De La Paz, S.; Cerrudo, V.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium Pseudocatenulatum Cect 7765 Ameliorates Neuroendocrine Alterations Associated with an Exaggerated Stress Response and Anhedonia in Obese Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 5337–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya-Pérez, A.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Benítez-Páez, A.; Campillo, I.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium Cect 7765 Modulates Early Stress-Induced Immune, Neuroendocrine and Behavioral Alterations in Mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morffy Smith, C.D.; Gong, M.; Andrew, A.K.; Russ, B.N.; Ge, Y.; Zadeh, M.; Cooper, C.A.; Mohamadzadeh, M.; Moore, J.M. Composition of the Gut Microbiota Transcends Genetic Determinants of Malaria Infection Severity and Influences Pregnancy Outcome. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, N.F.; Lecleir, G.R.; Denny, J.E.; Dearth, S.P.; Harding, C.L.; Sloan, S.S.; Gribble, J.L.; Campagna, S.R.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Schmidt, N.W. Composition of the Gut Microbiota Modulates the Severity of Malaria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fultz, R.; Ticer, T.; Ihekweazu, F.D.; Horvath, T.D.; Haidacher, S.J.; Hoch, K.M.; Bajaj, M.; Spinler, J.K.; Haag, A.M.; Buffington, S.A.; et al. Unraveling the Metabolic Requirements of the Gut Commensal Bacteroides Ovatus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 745469. [Google Scholar]
- Ihekweazu, F.D.; Engevik, M.A.; Ruan, W.; Shi, Z.; Fultz, R.; Engevik, K.A.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Freeborn, J.; Park, E.S.; Venable, S.; et al. Bacteroides Ovatus Promotes Il-22 Production and Reduces Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-Driven Colonic Inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 704–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libertin, C.R.; Peterson, J.H.; Brodersen, M.P.; Huff, T. A Case of Penicillin-Resistant Veillonella Prosthetic Joint Infection of the Knee. Case Rep. Orthop. 2016, 2016, 7171947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchandin, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Gay, B.; Teyssier, C.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Siméon De Buochberg, M.; Carrière, C.; Carlier, J.P. Phylogenetic Analysis of Some Sporomusa Sub-Branch Members Isolated from Human Clinical Specimens: Description of Megasphaera Micronuciformis Sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megasphaera Micronuciformis Dsm 17226 Is an Anaerobe, Mesophilic Human Pathogen That Was Isolated from Human, Liver Abscess. Available online: https://bacdive.dsmz.de/strain/17133 (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Berger, F.K.; Schwab, N.; Glanemann, M.; Bohle, R.M.; Gärtner, B.; Groesdonk, H.V. Flavonifractor (Eubacterium) Plautii Bloodstream Infection Following Acute Cholecystitis. IDCases 2018, 14, e00461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpat, I.; Karolyi, M.; Pawelka, E.; Seitz, T.; Thaller, F.; Wenisch, C. Flavonifractor Plautii Bloodstream Infection in an Asplenic Patient with Infectious Colitis. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the Human Gut Microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penders, J.; Thijs, C.; Vink, C.; Stelma, F.F.; Snijders, B.; Kummeling, I.; Van Den Brandt, P.A.; Stobberingh, E.E. Factors Influencing the Composition of the Intestinal Microbiota in Early Infancy. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdill, R.J.; Adamowicz, E.M.; Blekhman, R. Public Human Microbiome Data Are Dominated by Highly Developed Countries. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.P. Studies of Human Microbiome Have Ignored the Developing World, Potentially Compromising Treatments. Science 2022. Available online: https://www.science.org/content/article/studies-human-microbiome-ignored-developing-world-potentially-compromising-treatments (accessed on 14 November 2022).
| Variable | High Composite Stress | Low Composite Stress | Total | p-Value * | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 21) | (N = 26) | (N = 47) | (N = 47) | ||
| Mother | |||||
| Age (years) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 26.71 (8.07) | 27.85 (5.99) | 27.34 (7.02) | 0.55 | 27.34 (7.02) |
| BMI | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 27.15 (3.33) | 28.58 (4.27) | 27.93 (3.93) | 0.35 | 27.93 (3.93) |
| Height (cm) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 159 (7.5) | 159 (5.1) | 159 (7.5) | 0.34 | 159 (7.5) |
| Weight (kg) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 68.7 (9.5) | 72.3 (13.0) | 70.7 (11.7) | 0.43 | 70.7 (11.7) |
| Alcohol in pregnancy | |||||
| No | 15 | 18 | 33 | 33 | |
| Yes | 6 | 8 | 14 | 14 | |
| Smoking in pregnancy | |||||
| No | 20 | 25 | 45 | 45 | |
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Infant | |||||
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 9 | 12 | 21 | 0.82 | 21 |
| Male | 12 | 14 | 26 | 26 | |
| Length (cm) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 46.9 (1.3) | 47.3 (1.5) | 47.1 (1.4) | 0.45 | 70.7 (11.7) |
| Weight (g) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 3142 (389) | 3263 (343) | 3209 (369) | 0.22 | 3209 (369) |
| Breastfed | |||||
| No | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Yes | 21 | 26 | 47 | 47 | |
| Solid foods by 6 months | |||||
| No | 20 | 25 | 45 | 45 | |
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Antibiotic usage by 6 months | |||||
| No | 16 | 22 | 38 | 38 | |
| Yes | 5 | 4 | 9 | 9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dutton, C.L.; Maisha, F.M.; Quinn, E.B.; Morales, K.L.; Moore, J.M.; Mulligan, C.J. Maternal Psychosocial Stress Is Associated with Reduced Diversity in the Early Infant Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040975
Dutton CL, Maisha FM, Quinn EB, Morales KL, Moore JM, Mulligan CJ. Maternal Psychosocial Stress Is Associated with Reduced Diversity in the Early Infant Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(4):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040975
Chicago/Turabian StyleDutton, Christopher L., Felicien Masanga Maisha, Edward B. Quinn, Katherine Liceth Morales, Julie M. Moore, and Connie J. Mulligan. 2023. "Maternal Psychosocial Stress Is Associated with Reduced Diversity in the Early Infant Gut Microbiome" Microorganisms 11, no. 4: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040975
APA StyleDutton, C. L., Maisha, F. M., Quinn, E. B., Morales, K. L., Moore, J. M., & Mulligan, C. J. (2023). Maternal Psychosocial Stress Is Associated with Reduced Diversity in the Early Infant Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms, 11(4), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040975





