Gut Microbiome Transplants and Their Health Impacts across Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
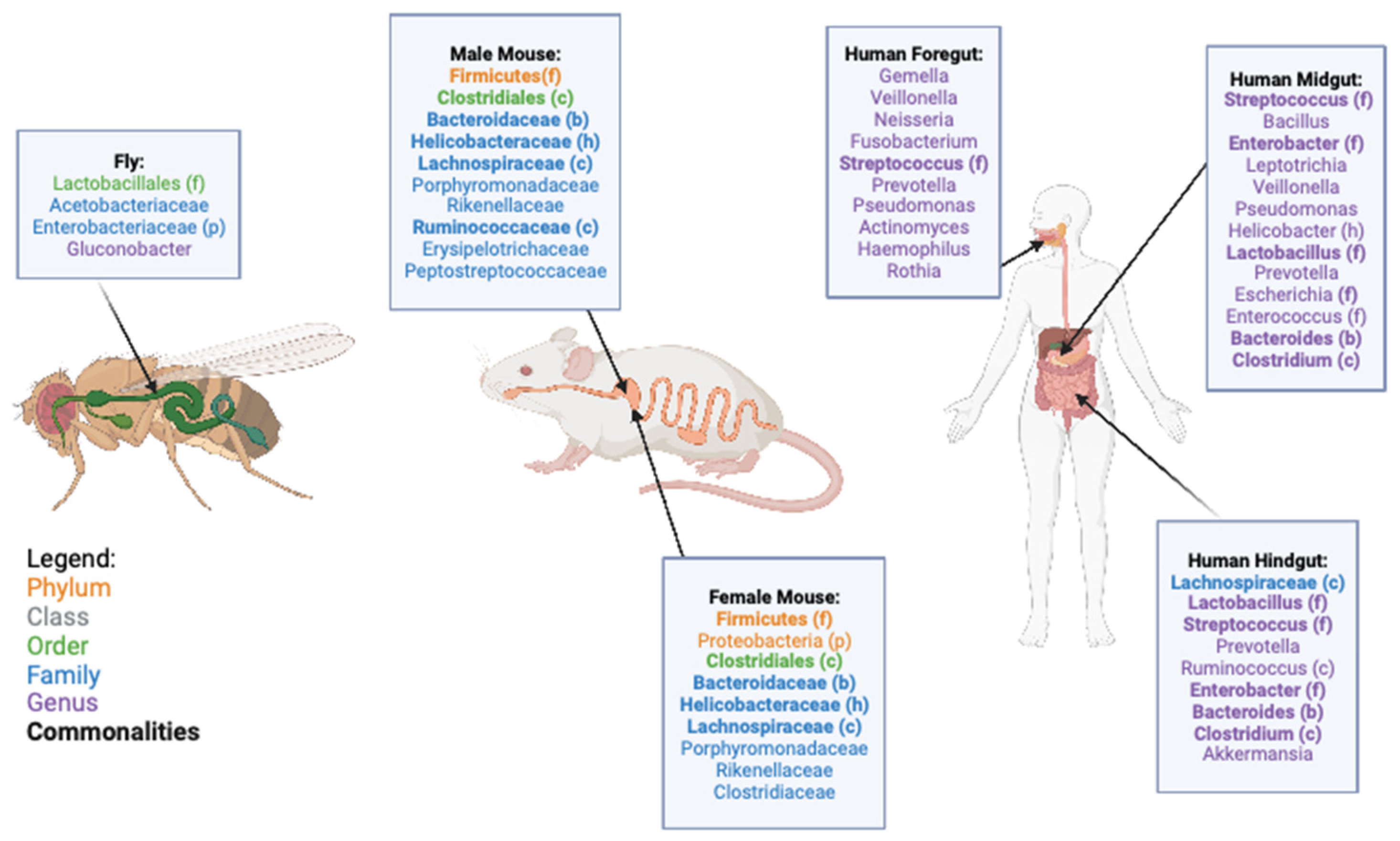
2. Microbiome and Gut Structure of D. melanogaster, M. musculus, and H. sapiens
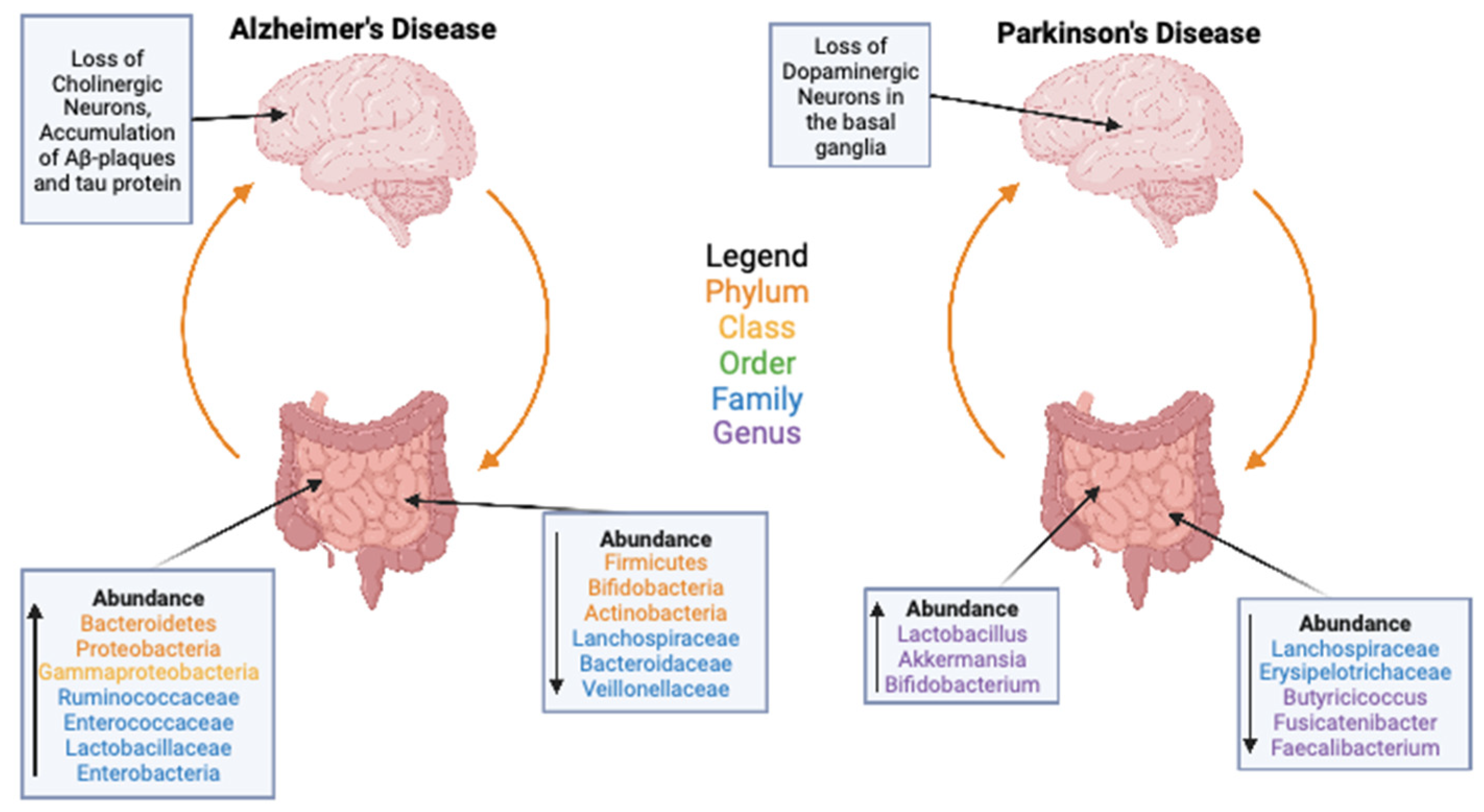
3. Gut Microbiome and Health
4. Microbiome Transplants
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallo, R.L. Human Skin Is the Largest Epithelial Surface for Interaction with Microbes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinane, C.M.; Cotter, P.D. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: Understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kasper, L.H. The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, P.F.; Frissen, M.N.; de Clercq, N.C.; Nieuwdorp, M. Fecal microbiota transplantation in metabolic syndrome: History, present and future. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.R.; de Leon, L.; Jasutkar, N. Fecal microbiota transplantation for relapsing Clostridium difficile infection in 26 patients: Methodology and results. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ser, H.L.; Letchumanan, V.; Goh, B.H.; Wong, S.H.; Lee, L.H. The Use of Fecal Microbiome Transplant in Treating Human Diseases: Too Early for Poop? Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 519836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, S.; de Menezes, A.B.; Birtles, R.J.; Fenn, J.; Lowe, A.E.; MacColl, A.D.C.; Poulin, B.; Young, S.; Bradley, J.E.; Taylor, C.H. Geographical location influences the composition of the gut microbiota in wild house mice (Mus musculus domesticus) at a fine spatial scale. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, N.; Carlsen, B.; Christensen, M.H.; Pertoldi, C.; Nielsen, J.L. The Gut Microbiome of 54 Mammalian Species. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 886252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, N.A.; Lemaitre, B. Gut-associated microbes of Drosophila melanogaster. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.A.; Lang, J.M.; Bhatnagar, S.; Eisen, J.A.; Kopp, A. Bacterial communities of diverse Drosophila species: Ecological context of a host-microbe model system. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.E.; Jeon, C.O.; Hyun, S. Comparative Analysis of Drosophila melanogaster Gut Microbiota with Respect to Host Strain, Sex, and Age. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubach, F.; Baines, J.F.; Kunzel, S.; Bik, E.M.; Petrov, D.A. Host species and environmental effects on bacterial communities associated with Drosophila in the laboratory and in the natural environment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.C.; Dobson, A.J.; Douglas, A.E. Gut microbiota dictates the metabolic response of Drosophila to diet. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1894–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Manara, S.; Zolfo, M.; Truong, D.T.; Scholz, M.; Armanini, F.; Ferretti, P.; Gorfer, V.; Pedrotti, A.; Tett, A.; et al. Studying Vertical Microbiome Transmission from Mothers to Infants by Strain-Level Metagenomic Profiling. mSystems 2017, 2, e00164-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, J.; Simpson, S.J.; Ponton, F. Direct and trans-generational effects of male and female gut microbiota in Drosophila melanogaster. Biol. Lett. 2017, 13, 20160966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakula, M. The persistence of a microbial flora during postembryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1969, 14, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obadia, B.; Keebaugh, E.S.; Yamada, R.; Ludington, W.B.; Ja, W.W. Diet influences host-microbiota associations in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4547–E4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, C.; Staubach, F.; Kuenzel, S.; Baines, J.F.; Roeder, T. Noninvasive analysis of microbiome dynamics in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6984–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesperance, D.N.A.; Broderick, N.A. Meta-analysis of Diets Used in Drosophila Microbiome Research and Introduction of the Drosophila Dietary Composition Calculator (DDCC). G3 2020, 10, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Hougen, H.; Vollmer, A.C.; Hiebert, S.M. Gut bacteria profiles of Mus musculus at the phylum and family levels are influenced by saturation of dietary fatty acids. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, F.; de Vos, W.M. Mouse models for human intestinal microbiota research: A critical evaluation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.A.; King, K.Y.; Baldridge, M.T. Mouse Microbiota Models: Comparing Germ-Free Mice and Antibiotics Treatment as Tools for Modifying Gut Bacteria. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, H.; Gholami, A.M.; Berry, D.; Desmarchelier, C.; Hahne, H.; Loh, G.; Mondot, S.; Lepage, P.; Rothballer, M.; Walker, A.; et al. High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in mice. ISME J. 2014, 8, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Engevik, M.A.; Spinler, J.K.; Versalovic, J. Healthy Human Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Composition and Function After a Decade of Exploration. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society for Microbiology. FAQ: E. Coli: Good, Bad, & Deadly; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, E.L.; Ogle, J.M.; Finck, A.M. The Human Microbiome as a Focus of Antibiotic Discovery: Neisseria mucosa Displays Activity Against Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 577762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, V.; Scaldaferri, F.; Putignani, L.; Del Chierico, F. The Role of Enterobacteriaceae in Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, D.; Hoare, A.; Soto, C.; Valenzuela, M.A.; Quest, A.F. Helicobacter pylori in human health and disease: Mechanisms for local gastric and systemic effects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3071–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.A.; Garrett, W.S. Fusobacterium nucleatum-symbiont, opportunist and oncobacterium. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eribe, E.R.K.; Olsen, I. Leptotrichia species in human infections II. J. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 9, 1368848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; He, P. Clostridium species as probiotics: Potentials and challenges. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanchi, H.; Mottawea, W.; Sebei, K.; Hammami, R. The Genus Enterococcus: Between Probiotic Potential and Safety Concerns-An Update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglewski, B.H. Pseudomonas. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jayananda, S.; Gollol-Raju, N.S.; Fadul, N. Gemella Species Bacteremia and Stroke in an Elderly Patient with Respiratory Tract Infection. Case Rep. Med. 2017, 2017, 1098527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononen, E.; Wade, W.G. Actinomyces and related organisms in human infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 419–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Reau, A.J.; Suen, G. The Ruminococci: Key symbionts of the gut ecosystem. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Remes Troche, J.; Coss Adame, E.; Angel Valdovinos Diaz, M.; Gomez Escudero, O.; Eugenia Icaza Chavez, M.; Antonio Chavez-Barrera, J.; Zarate Mondragon, F.; Antonio Ruiz Velarde Velasco, J.; Rafael Aceves Tavares, G.; Antonio Lira Pedrin, M.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus LB: A useful pharmabiotic for the treatment of digestive disorders. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820971201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinovic, A.; Cocuzzi, R.; Arioli, S.; Mora, D. Streptococcus thermophilus: To Survive, or Not to Survive the Gastrointestinal Tract, That Is the Question! Nutrients 2020, 12, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazkour, S.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Basiri, S. The effects of supplementation of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus coagulans spores on the intestinal microflora and growth performance in rat. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musher, D.M. Haemophilus Species. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Takagi, T. A next-generation beneficial microbe: Akkermansia muciniphila. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2018, 63, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberger, R.; Gupta, V. Streptococcus Group A. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanan, P.; Barreto, J.N.; Osmon, D.R.; Tosh, P.K. Rothia bacteremia: A 10-year experience at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3184–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, D.P.; Washio, J.; Abiko, Y.; Domon, H.; Takahashi, N. Nitrite Production from Nitrate and Its Link with Lactate Metabolism in Oral Veillonella spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01255-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Sun, Y.; Ip, L.Y.T.; Wang, L.; Chan, F.K.L.; Miao, Y.; Ng, S.C. Prevotella species in the human gut is primarily comprised of Prevotella copri, Prevotella stercorea and related lineages. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Unno, T.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, M.S. Sex Differences in Gut Microbiota. World J. Men’s Health 2020, 38, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renson, A.; Herd, P.; Dowd, J.B. Sick Individuals and Sick (Microbial) Populations: Challenges in Epidemiology and the Microbiome. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2020, 41, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.W.; Priya, S.; Blekhman, R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Gut microbiota diversity across ethnicities in the United States. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelius, J.W.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; McDonald, D.; Xu, Z.; Wolfe, E.; Knight, R. Turning Participatory Microbiome Research into Usable Data: Lessons from the American Gut Project. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2016, 17, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.E.; Engen, P.A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Shaikh, M.; Sikaroodi, M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Mutlu, E.; Keshavarzian, A. Lower Neighborhood Socioeconomic Status Associated with Reduced Diversity of the Colonic Microbiota in Healthy Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prehn-Kristensen, A.; Zimmermann, A.; Tittmann, L.; Lieb, W.; Schreiber, S.; Baving, L.; Fischer, A. Reduced microbiome alpha diversity in young patients with ADHD. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel-Aliaga, I.; Jasper, H.; Lemaitre, B. Anatomy and Physiology of the Digestive Tract of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2018, 210, 357–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. The Drosophila model for microbiome research. Lab Anim. 2018, 47, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, B.; Miguel-Aliaga, I. The digestive tract of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 377–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sayadian, A.C.; Lowe, N.; Lovegrove, H.E.; St Johnston, D. An alternative mode of epithelial polarity in the Drosophila midgut. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e3000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Roman, A.K.; Shivdasani, R.A. Boundaries, junctions and transitions in the gastrointestinal tract. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, K.; Pfaff, J. The forestomach in rats and mice, a food store without bacterial protein digestion. Zentralbl. Veterinarmed. A 1979, 26, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The human microbiome: At the interface of health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Stilling, R.M.; Kennedy, P.J.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Minireview: Gut microbiota: The neglected endocrine organ. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M. Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. N. Y. 2013, 9, 560–569. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.A.; Jeffery, I.B.; Beaumont, M.; Bell, J.T.; Clark, A.G.; Ley, R.E.; O’Toole, P.W.; Spector, T.D.; Steves, C.J. Signatures of early frailty in the gut microbiota. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.H.; Kim, W.U. Dysregulation of gut microbiota and chronic inflammatory disease: From epithelial defense to host immunity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farre, R.; Fiorani, M.; Abdu Rahiman, S.; Matteoli, G. Intestinal Permeability, Inflammation and the Role of Nutrients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.J.; Ghosh, S. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, LPS Translocation, and Disease Development. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakaroun, R.M.; Massier, L.; Kovacs, P. Gut Microbiome, Intestinal Permeability, and Tissue Bacteria in Metabolic Disease: Perpetrators or Bystanders? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambring, C.B.; Siraj, S.; Patel, K.; Sankpal, U.T.; Mathew, S.; Basha, R. Impact of the Microbiome on the Immune System. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 39, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGruttola, A.K.; Low, D.; Mizoguchi, A.; Mizoguchi, E. Current Understanding of Dysbiosis in Disease in Human and Animal Models. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2016, 22, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, A.M.; Shanmugarajah, N.; Buchon, N.; Clark, A.G. Drosophila Genotype Influences Commensal Bacterial Levels. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaston, J.M.; Dobson, A.J.; Newell, P.D.; Douglas, A.E. Host Genetic Control of the Microbiota Mediates the Drosophila Nutritional Phenotype. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumbo-Lucioni, P.; Ayroles, J.F.; Chambers, M.M.; Jordan, K.W.; Leips, J.; Mackay, T.F.; De Luca, M. Systems genetics analysis of body weight and energy metabolism traits in Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, F.; Nguyen, T.L.; Brinkman, B.; Yunta, R.G.; Cauwe, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Liston, A.; Raes, J. Inflammation-associated enterotypes, host genotype, cage and inter-individual effects drive gut microbiota variation in common laboratory mice. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knights, D.; Silverberg, M.S.; Weersma, R.K.; Gevers, D.; Dijkstra, G.; Huang, H.; Tyler, A.D.; van Sommeren, S.; Imhann, F.; Stempak, J.M.; et al. Complex host genetics influence the microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmitt, B.A.; Corley, R.P.; Huibregtse, B.M.; Keller, M.C.; Hewitt, J.K.; McQueen, M.B.; Knight, R.; McDermott, I.; Krauter, K.S. Genetic influences on the human oral microbiome. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Silva, T.; Salatino-Oliveira, A.; Genro, J.P.; Meyer, F.D.T.; Li, Y.; Rohde, L.A.; Hutz, M.H.; Tovo-Rodrigues, L. Host genetics influences the relationship between the gut microbiome and psychiatric disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Vich Vila, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Fu, J.; Gevers, D.; Visschedijk, M.C.; Spekhorst, L.M.; Alberts, R.; Franke, L.; van Dullemen, H.M.; et al. Interplay of host genetics and gut microbiota underlying the onset and clinical presentation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018, 67, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dai, R.; Yang, L.; He, C.; Xu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Inheritance and Establishment of Gut Microbiota in Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; D’Souza, R.; Hong, S.T. The role of gut microbiota in the gut-brain axis: Current challenges and perspectives. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, K.; Nawaz, H.; Abid, S. Functional gastrointestinal disorders and gut-brain axis: What does the future hold? World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Knight, R.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Tillisch, K. Gut microbes and the brain: Paradigm shift in neuroscience. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15490–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, P.; Lee, H.U.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Tay, E.X.Y.; Kim, H.; Faylon, L.E.; Martin, K.A.; Purbojati, R.; Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Neurogenesis and prolongevity signaling in young germ-free mice transplanted with the gut microbiota of old mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Luo, W.; Shi, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ji, G. Should we standardize the 1,700-year-old fecal microbiota transplantation? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1755, author reply pp. 1755–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiseman, B.; Silen, W.; Bascom, G.S.; Kauvar, A.J. Fecal enema as an adjunct in the treatment of pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Surgery 1958, 44, 854–859. [Google Scholar]
- Torrijo Gomez, I.; Uribe Quintana, N.; Catala Llosa, J.; Raga Vazquez, J.; Selles Dechent, R.; Martin Dieguez, M.C.; Baguena Requena, G.; Asencio Arana, F. [Fulminant Clostridium difficile colitis]. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 39, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borody, T.J.; Campbell, J. Fecal microbiota transplantation: Current status and future directions. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borody, T.J.; George, L.; Andrews, P.; Brandl, S.; Noonan, S.; Cole, P.; Hyland, L.; Morgan, A.; Maysey, J.; Moore-Jones, D. Bowel-flora alteration: A potential cure for inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome? Med. J. Aust. 1989, 150, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nood, E.; Vrieze, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Fuentes, S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Visser, C.E.; Kuijper, E.J.; Bartelsman, J.F.; Tijssen, J.G.; et al. Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Seo, G.S. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: Is It Safe? Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvede, M.; Tinggaard, M.; Helms, M. Rectal bacteriotherapy for recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea: Results from a case series of 55 patients in Denmark 2000–2012. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePeters, E.J.; George, L.W. Rumen transfaunation. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162 Pt A, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebino, K.Y.; Shutoh, Y.; Takahashi, K.W. Coprophagy in rabbits: Autoingestion of hard feces. Jikken. Dobutsu. 1993, 42, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Sun, H.; Yang, W.; Gao, M.; Xu, H. Transfer of Human Microbiome to Drosophila Gut Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker-Character, J.; Hager, D.R.; Call, T.B.; Pickup, Z.S.; Turnbull, S.A.; Marshman, E.M.; Korch, S.B.; Chaston, J.M.; Call, G.B. An altered microbiome in a Parkinson’s disease model Drosophila melanogaster has a negative effect on development. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikha, S.R.J.; Lee, D.M.; Ecton, K.E.; Wrigley, S.D.; Vazquez, A.R.; Litwin, N.S.; Thomas, K.N.; Wei, Y.; Battson, M.L.; Johnson, S.A.; et al. Transplantation of an obesity-associated human gut microbiota to mice induces vascular dysfunction and glucose intolerance. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1940791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.P.; Wang, B.; Jain, S.; Ding, J.; Rejeski, J.; Furdui, C.M.; Kitzman, D.W.; Taraphder, S.; Brechot, C.; Kumar, A.; et al. A mechanism by which gut microbiota elevates permeability and inflammation in obese/diabetic mice and human gut. Gut 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.; Romano, S.; Ansorge, R.; Aboelnour, A.; Le Gall, G.; Savva, G.M.; Pontifex, M.G.; Telatin, A.; Baker, D.; Jones, E.; et al. Fecal microbiota transfer between young and aged mice reverses hallmarks of the aging gut, eye, and brain. Microbiome 2022, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Lucarini, E.; Man, A.L.; Le Gall, G.; Branca, J.J.V.; Ghelardini, C.; Amedei, A.; Bertelli, E.; Regoli, M.; et al. Faecal microbiota transplant from aged donor mice affects spatial learning and memory via modulating hippocampal synaptic plasticity- and neurotransmission-related proteins in young recipients. Microbiome 2020, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borody, T.; Leis, S.; Campbell, J.; Torres, M.; Nowak, A. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) in Multiple Sclerosis (MS): 942. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol.|ACG 2011, 106, S352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, L.; Peng, G.; Han, Y.; Tang, R.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, L.; Yue, S.; Zhou, K.; et al. Altered microbiomes distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from amnestic mild cognitive impairment and health in a Chinese cohort. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.Q.; Shen, L.L.; Li, W.W.; Fu, X.; Zeng, F.; Gui, L.; Lu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhu, C.; Tan, Y.L.; et al. Gut Microbiota is Altered in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varesi, A.; Pierella, E.; Romeo, M.; Piccini, G.B.; Alfano, C.; Bjorklund, G.; Oppong, A.; Ricevuti, G.; Esposito, C.; Chirumbolo, S.; et al. The Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, R.; Wu, S. Structural and Functional Dysbiosis of Fecal Microbiota in Chinese Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 634069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Provasi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Festari, C.; Ferrari, C.; Guerra, U.P.; Paghera, B.; Muscio, C.; et al. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblhuber, F.; Steiner, K.; Geisler, S.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. On the Possible Relevance of Bottom-up Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Peng, J.; Huang, X.; Xiao, L.; Huang, F.; Zuo, Z. Gut Microbiome Features of Chinese Patients Newly Diagnosed with Alzheimer’s Disease or Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 80, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.O.; O’Donnell, D.; Jain, N.; Ulrich, J.D.; Herz, J.; Li, Y.; Lemieux, M.; Cheng, J.; Hu, H.; Serrano, J.R.; et al. ApoE isoform- and microbiota-dependent progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Science 2023, 379, eadd1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubomski, M.; Xu, X.; Holmes, A.J.; Muller, S.; Yang, J.Y.H.; Davis, R.L.; Sue, C.M. The Gut Microbiome in Parkinson’s Disease: A Longitudinal Study of the Impacts on Disease Progression and the Use of Device-Assisted Therapies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 875261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.; Savva, G.M.; Bedarf, J.R.; Charles, I.G.; Hildebrand, F.; Narbad, A. Meta-analysis of the Parkinson’s disease gut microbiome suggests alterations linked to intestinal inflammation. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, D.; Ali Shah, S.Z.; Wu, W.; Lai, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Guan, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; et al. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clairembault, T.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Coron, E.; Bourreille, A.; Le Dily, S.; Vavasseur, F.; Heymann, M.F.; Neunlist, M.; Derkinderen, P. Structural alterations of the intestinal epithelial barrier in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bao, X.Q.; Shang, M.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, D. Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, J.; Kim, J.S.; Cha, B.; Lee, S.; Kwon, K.S.; Shin, Y.W.; Choi, S.H. Cognitive function improvement after fecal microbiota transplantation in Alzheimer’s dementia patient: A case report. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2021, 37, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, S. Rapid improvement in Alzheimer’s disease symptoms following fecal microbiota transplantation: A case report. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520925930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xu, H.; Luo, Q.; He, J.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, Y. Fecal microbiota transplantation to treat Parkinson’s disease with constipation: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.G.; Goldman, S.M. Modulation of the Microbiome in Parkinson’s Disease: Diet, Drug, Stool Transplant, and Beyond. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Lv, Q.; Tan, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, N.; He, Z.; Kou, Y.; Tan, Y.; et al. Establishment and resilience of transplanted gut microbiota in aged mice. iScience 2022, 25, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levine, B.H.; Hoffman, J.M. Gut Microbiome Transplants and Their Health Impacts across Species. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061488
Levine BH, Hoffman JM. Gut Microbiome Transplants and Their Health Impacts across Species. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061488
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevine, Benjamin H., and Jessica M. Hoffman. 2023. "Gut Microbiome Transplants and Their Health Impacts across Species" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061488
APA StyleLevine, B. H., & Hoffman, J. M. (2023). Gut Microbiome Transplants and Their Health Impacts across Species. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061488





