The Gut–Liver Axis in Pediatric Liver Health and Disease
Abstract
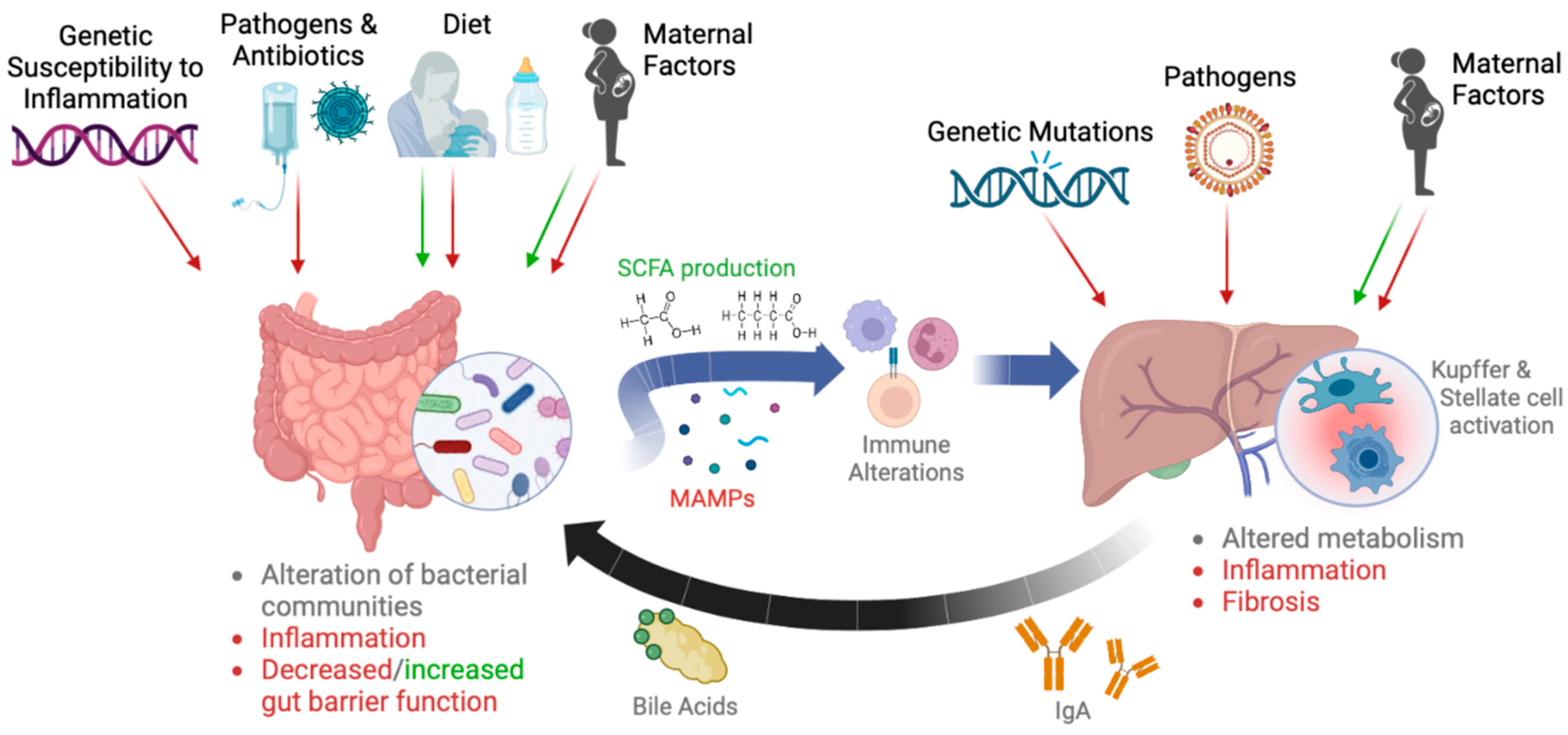
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Pediatric Gut Microbiota
1.2. The Gut–Liver Axis
1.3. The Pediatric Liver
2. Interactions between the Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Hepatobiliary Disorders (Table 1)
2.1. Biliary Atresia
2.2. Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
2.3. Wilson’s Disease
2.4. Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease (CFLD)
2.5. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
2.6. Hepatitis B Infection
3. Discussion: Therapeutic Outlooks
| Condition | Clinical Findings | Preclinical Findings | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biliary Atresia (BA)/Cholestasis |
|
| [26,28,29,30] |
| Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) |
|
| [40,44,46,47,48,49] |
| Wilson’s Disease |
|
| [53,54,55,56] |
| Cystic Fibrosis (CF) |
|
| [65,66,68,69] |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) |
| [77,78] | |
| Hepatitis B Virus |
|
| [87,88] |
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, A.M.; Sun, E.W.; Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J. The Influence of the Gut Microbiome on Host Metabolism Through the Regulation of Gut Hormone Release. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Nunez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors affecting the composition of the gut microbiota, and its modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, C.Y.L.; Bloomfield, F.H.; O’Sullivan, J.M. Factors Affecting Gastrointestinal Microbiome Development in Neonates. Nutrients 2018, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanidad, K.Z.; Zeng, M.Y. Neonatal gut microbiome and immunity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 56, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.M.; Mazzoni, C.; Hogstrom, L.; Bryant, A.; Bergerat, A.; Cher, A.; Pochan, S.; Herman, P.; Carrigan, M.; Sharp, K.; et al. Delivery Mode Affects Stability of Early Infant Gut Microbiota. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, M.F.; Bahl, M.I.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. First Foods and Gut Microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, E.C.; Wang, M.; Donovan, S.M. The role of early life nutrition in the establishment of gastrointestinal microbial composition and function. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, A.; Skov, T.H.; Bahl, M.I.; Roager, H.M.; Christensen, L.B.; Ejlerskov, K.T.; Molgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. Establishment of intestinal microbiota during early life: A longitudinal, explorative study of a large cohort of Danish infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derrien, M.; Alvarez, A.S.; de Vos, W.M. The Gut Microbiota in the First Decade of Life. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbitt, N.; Kimura, S.; Isse, K.; Specht, S.; Chedwick, L.; Rosborough, B.R.; Lunz, J.G.; Murase, N.; Yokota, S.; Demetris, A.J. Gut bacteria drive Kupffer cell expansion via MAMP-mediated ICAM-1 induction on sinusoidal endothelium and influence preservation-reperfusion injury after orthotopic liver transplantation. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paik, Y.H.; Schwabe, R.F.; Bataller, R.; Russo, M.P.; Jobin, C.; Brenner, D.A. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandl, K.; Kumar, V.; Eckmann, L. Gut-liver axis at the frontier of host-microbial interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G413–G419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Backhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giancotti, A.; Monti, M.; Nevi, L.; Safarikia, S.; D’Ambrosio, V.; Brunelli, R.; Pajno, C.; Corno, S.; Di Donato, V.; Musella, A.; et al. Functions and the Emerging Role of the Foetal Liver into Regenerative Medicine. Cells 2019, 8, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grijalva, J.; Vakili, K. Neonatal liver physiology. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 22, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpen, S.J.; Suchy, F.J. Structural and functional development of the liver. In Liver Disease in Children; Suchy, F.J., Sokol, R.J., Balistreri, W.F., Eds.; Lippincot Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Beath, S.V. Hepatic function and physiology in the newborn. Semin. Neonatol. 2003, 8, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro-Carrero, V.C.M.; Piñeiro, E.O. Liver. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, R.B.; Schneider, A.C.; da Silveira, T.R. Cirrhosis in children and adolescents: An overview. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.I.; Ahmad, T. Biliary Atresia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jee, J.J.; Yang, L.; Shivakumar, P.; Xu, P.P.; Mourya, R.; Thanekar, U.; Yu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Maternal regulation of biliary disease in neonates via gut microbial metabolites. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.T.; Cresci, G.A.M. The Immunomodulatory Functions of Butyrate. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6025–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Qiu, C.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Zhao, R.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Cholestatic Infants and Their Correlation With Hepatic Function. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Qian, T.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, S.; Dong, R. Gut microbial profile in biliary atresia: A case-control study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaine Chen, Y.F.; Lai, M.W.; Tsai, C.N.; Lai, J.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Chen, S.Y. Association of gut microbiota composition and copy number variation with Kasai procedure outcomes in infants with biliary atresia. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020, 61, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiyama, G.; Pandak, W.M.; Gillevet, P.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Heuman, D.M.; Daita, K.; Takei, H.; Muto, A.; Nittono, H.; Ridlon, J.M.; et al. Modulation of the fecal bile acid profile by gut microbiota in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiippala, K.; Kainulainen, V.; Suutarinen, M.; Heini, T.; Bowers, J.R.; Jasso-Selles, D.; Lemmer, D.; Valentine, M.; Barnes, R.; Engelthaler, D.M.; et al. Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory and Epithelium Reinforcing Bacteroides and Parabacteroides Spp. from A Healthy Fecal Donor. Nutrients 2020, 12, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, T.; Fu, J.; Verkade, H.J. The role of the gut microbiome in graft fibrosis after pediatric liver transplantation. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulthess, J.; Pandey, S.; Capitani, M.; Rue-Albrecht, K.C.; Arnold, I.; Franchini, F.; Chomka, A.; Ilott, N.E.; Johnston, D.G.W.; Pires, E.; et al. The Short Chain Fatty Acid Butyrate Imprints an Antimicrobial Program in Macrophages. Immunity 2019, 50, 432–445 e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly, Y.M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorgenson, M.R.; Descourouez, J.L.; Siodlak, M.; Tjugum, S.; Rice, J.P.; Fernandez, L.A. Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Liver Transplantation. Pharmacotherapy 2018, 38, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.L.; Schwimmer, J.B. Epidemiology of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2021, 17, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabke, K.; Hendrick, G.; Devkota, S. The gut microbiome and metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4050–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheithauer, T.P.M.; Rampanelli, E.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Vallance, B.A.; Verchere, C.B.; van Raalte, D.H.; Herrema, H. Gut Microbiota as a Trigger for Metabolic Inflammation in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 571731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliomaki, M.; Collado, M.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Early differences in fecal microbiota composition in children may predict overweight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, G.D.P.; Ayres, L.F.A.; Barreto, D.S.; Henriques, B.D.; Prado, M.; Passos, C.M.D. Acquisition of microbiota according to the type of birth: An integrative review. Rev. Lat.-Am. Enferm. 2021, 29, e3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorio, J.; Lavine, J.E. Recent advances in understanding and managing pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. F1000Research 2020, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Gaskins, A.J.; Blaine, A.I.; Zhang, C.; Gillman, M.W.; Missmer, S.A.; Field, A.E.; Chavarro, J.E. Association Between Cesarean Birth and Risk of Obesity in Offspring in Childhood, Adolescence, and Early Adulthood. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, e162385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandona, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raman, M.; Ahmed, I.; Gillevet, P.M.; Probert, C.S.; Ratcliffe, N.M.; Smith, S.; Greenwood, R.; Sikaroodi, M.; Lam, V.; Crotty, P.; et al. Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 868–875.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famouri, F.; Shariat, Z.; Hashemipour, M.; Keikha, M.; Kelishadi, R. Effects of Probiotics on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alisi, A.; Bedogni, G.; Baviera, G.; Giorgio, V.; Porro, E.; Paris, C.; Giammaria, P.; Reali, L.; Anania, F.; Nobili, V. Randomised clinical trial: The beneficial effects of VSL#3 in obese children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkiourtzis, N.; Kalopitas, G.; Vadarlis, A.; Bakaloudi, D.R.; Dionysopoulos, G.; Karanika, E.; Tsekitsidi, E.; Chourdakis, M. The Benefit of Probiotics in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 75, e31–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderborg, T.K.; Clark, S.E.; Mulligan, C.E.; Janssen, R.C.; Babcock, L.; Ir, D.; Young, B.; Krebs, N.; Lemas, D.J.; Johnson, L.K.; et al. The gut microbiota in infants of obese mothers increases inflammation and susceptibility to NAFLD. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrei, A.; Ozturk, Y.; Khalfaoui-Hassani, B.; Rauch, J.; Marckmann, D.; Trasnea, P.I.; Daldal, F.; Koch, H.G. Cu Homeostasis in Bacteria: The Ins and Outs. Membranes 2020, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalecki, A.G.; Crawford, C.L.; Wolschendorf, F. Copper and Antibiotics: Discovery, Modes of Action, and Opportunities for Medicinal Applications. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2017, 70, 193–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Lee, E.; Kang, D.K. Trace metals and animal health: Interplay of the gut microbiota with iron, manganese, zinc, and copper. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Vos, M.B.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Rouchka, E.C.; Yin, X.; et al. Dietary copper-fructose interactions alter gut microbial activity in male rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 314, G119–G130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, D.; Yang, H.; Yin, Y. Effect of Dietary Copper on Intestinal Microbiota and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Escherichia coli in Weaned Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Shu, S.; Dong, J.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Han, Y.; Hu, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, R.; Cheng, N. Association study of gut flora in Wilson’s disease through high-throughput sequencing. Medicine 2018, 97, e11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Deng, L.; Ma, X.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, M.; Guan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; et al. Altered diversity and composition of gut microbiota in Wilson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, K.W.; Munck, A.; Pollitt, R.; Travert, G.; Zanolla, L.; Dankert-Roelse, J.; Castellani, C. A survey of newborn screening for cystic fibrosis in Europe. J. Cyst. Fibros 2007, 6, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scotet, V.; Gutierrez, H.; Farrell, P.M. Newborn Screening for CF across the Globe-Where Is It Worthwhile? Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobelska-Dubiel, N.; Klincewicz, B.; Cichy, W. Liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2014, 9, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, U.; Dockter, G.; Lammert, F. Cystic fibrosis-associated liver disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavamani, A.; Salem, I.; Sferra, T.J.; Sankararaman, S. Impact of Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Cystic Fibrosis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, L.; Gilkes, A.; Ashworth, M.; Rowland, V.; Harries, T.H.; Armstrong, D.; White, P. Association between antibiotics and gut microbiome dysbiosis in children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budden, K.F.; Gellatly, S.L.; Wood, D.L.; Cooper, M.A.; Morrison, M.; Hugenholtz, P.; Hansbro, P.M. Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, A.T.; Marsland, B.J. Microbes, metabolites, and the gut-lung axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madan, J.C.; Koestler, D.C.; Stanton, B.A.; Davidson, L.; Moulton, L.A.; Housman, M.L.; Moore, J.H.; Guill, M.F.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; et al. Serial analysis of the gut and respiratory microbiome in cystic fibrosis in infancy: Interaction between intestinal and respiratory tracts and impact of nutritional exposures. mBio 2012, 3, e00251-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoen, A.G.; Li, J.; Moulton, L.A.; O’Toole, G.A.; Housman, M.L.; Koestler, D.C.; Guill, M.F.; Moore, J.H.; Hibberd, P.L.; Morrison, H.G.; et al. Associations between Gut Microbial Colonization in Early Life and Respiratory Outcomes in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 138–147.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, C.E.; O’Toole, G.A. The Gut-Lung Axis in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0031121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, D.; El Mourabit, H.; Merabtene, F.; Brot, L.; Ulveling, D.; Chretien, Y.; Rainteau, D.; Moszer, I.; Wendum, D.; Sokol, H.; et al. Diet-Induced Dysbiosis and Genetic Background Synergize With Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Deficiency to Promote Cholangiopathy in Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 1533–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flass, T.; Tong, S.; Frank, D.N.; Wagner, B.D.; Robertson, C.E.; Kotter, C.V.; Sokol, R.J.; Zemanick, E.; Accurso, F.; Hoffenberg, E.J.; et al. Intestinal lesions are associated with altered intestinal microbiome and are more frequent in children and young adults with cystic fibrosis and cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasame, A.; Stokes, D.; Bourke, B.; Connolly, L.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Rowland, M. The impact of liver disease on mortality in cystic fibrosis-A systematic review. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, M.B.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Howell, J.; Westaby, D.; Khan, S.A.; Bilton, D.; Simmonds, N.J. The emerging burden of liver disease in cystic fibrosis patients: A UK nationwide study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Manne, S.; Treem, W.R.; Bennett, D. Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Pediatric and Adult Populations: Recent Estimates From Large National Databases in the United States, 2007–2016. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.B.; de la Morena, M.T.; Suskind, D.L. The Growing Need to Understand Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 675186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Karthik, S.V.; Ng, R.T.; Ong, S.Y.; Ong, C.; Chiou, F.K.; Wong, S.Y.; Quak, S.H.; Aw, M.M. Characteristics and outcome of primary sclerosing cholangitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease in Asian children. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2019, 60, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deneau, M.R.; El-Matary, W.; Valentino, P.L.; Abdou, R.; Alqoaer, K.; Amin, M.; Amir, A.Z.; Auth, M.; Bazerbachi, F.; Broderick, A.; et al. The natural history of primary sclerosing cholangitis in 781 children: A multicenter, international collaboration. Hepatology 2017, 66, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabibian, J.H.; O’Hara, S.P.; Lindor, K.D. Primary sclerosing cholangitis and the microbiota: Current knowledge and perspectives on etiopathogenesis and emerging therapies. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cortez, R.V.; Moreira, L.N.; Padilha, M.; Bibas, M.D.; Toma, R.K.; Porta, G.; Taddei, C.R. Gut Microbiome of Children and Adolescents With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Association With Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 598152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, S.L.; Hoffman, K.L.; Tessier, M.E.; Petrosino, J.; Miloh, T.; Kellermayer, R. Microbiome Responses to Vancomycin Treatment in a Child With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Ulcerative Colitis. ACG Case Rep. J. 2021, 8, e00577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharska, M.; Daniluk, U.; Kwiatek-Sredzinska, K.A.; Wasilewska, N.; Filimoniuk, A.; Jakimiec, P.; Zdanowicz, K.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Hepatobiliary manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease in children. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniluk, U.; Kwiatek-Sredzinska, K.; Jakimiec, P.; Daniluk, J.; Czajkowska, A.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Liver Pathology in Children with Diagnosed Inflammatory Bowel Disease—A Single Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusateri, A.J.; Kim, S.C.; Dotson, J.L.; Balint, J.P.; Potter, C.J.; Boyle, B.M.; Crandall, W.V. Incidence, pattern, and etiology of elevated liver enzymes in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, R.S.; Sanderson, I.R.; Claesson, M.J. Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease and its Relationship with the Microbiome. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 82, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirusanti, N.I.; Baldridge, M.T.; Harris, V.C. Microbiota regulation of viral infections through interferon signaling. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Elena, S.F. The Interplay between the Host Microbiome and Pathogenic Viral Infections. mBio 2021, 12, e0249621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trehanpati, N.; Hissar, S.; Shrivastav, S.; Sarin, S.K. Immunological mechanisms of hepatitis B virus persistence in newborns. Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 700–710. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics; Kimberlin, D.W.; Barnett, E.D.; Lynfield, R.; Sawyer, M.H.; Hepatitis, B. Red Book: 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics: Itasca, IL, USA, 2021; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H.H.; Chien, W.H.; Wu, L.L.; Cheng, C.H.; Chung, C.H.; Horng, J.H.; Ni, Y.H.; Tseng, H.T.; Wu, D.; Lu, X.; et al. Age-related immune clearance of hepatitis B virus infection requires the establishment of gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sehgal, R.; Bedi, O.; Trehanpati, N. Role of Microbiota in Pathogenesis and Management of Viral Hepatitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lei, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, L. Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlFaleh, K.; Anabrees, J. Probiotics for prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD005496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.D.; Messina, J.A.; Cortina, C.; Owens, T.; Fowler, M.; Foster, M.; Gbadegesin, S.; Clark, R.H.; Benjamin, D.K., Jr.; Zimmerman, K.O.; et al. Probiotic Use and Safety in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Matched Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2020, 222, 59–64.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Kuo, K.C.; Chen, W.H.; Su, C.H.; Lee, C.P.; Chen, K.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Yen, J.B.; Sheen, J.M. Maternal risk factors associated with offspring biliary atresia: Population-based study. Pediatr. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querter, I.; Pauwels, N.S.; De Bruyne, R.; Dupont, E.; Verhelst, X.; Devisscher, L.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Geerts, A.; Lefere, S. Maternal and Perinatal Risk Factors for Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, S. They Are What You Eat: Can Nutritional Factors during Gestation and Early Infancy Modulate the Neonatal Immune Response? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpuri, J. Evidence for maternal diet-mediated effects on the offspring microbiome and immunity: Implications for public health initiatives. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.E.; O’Brien, E.C.; Moore, R.L.; Byrne, D.F.; Geraghty, A.A.; Saldova, R.; Murphy, E.F.; Van Sinderen, D.; Cotter, P.D.; McAuliffe, F.M. The association between the maternal diet and the maternal and infant gut microbiome: A systematic review. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, D.M.; Antony, K.M.; Ma, J.; Prince, A.L.; Showalter, L.; Moller, M.; Aagaard, K.M. The early infant gut microbiome varies in association with a maternal high-fat diet. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.M.; Hossain, M.B.; Monirujjaman, M.; Islam, S.; Huda, M.N.; Kabir, Y.; Raqib, R.; Lonnerdal, B.L. Maternal zinc supplementation improves hepatitis B antibody responses in infants but decreases plasma zinc level. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rager, S.L.; Zeng, M.Y. The Gut–Liver Axis in Pediatric Liver Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030597
Rager SL, Zeng MY. The Gut–Liver Axis in Pediatric Liver Health and Disease. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030597
Chicago/Turabian StyleRager, Stephanie L., and Melody Y. Zeng. 2023. "The Gut–Liver Axis in Pediatric Liver Health and Disease" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030597
APA StyleRager, S. L., & Zeng, M. Y. (2023). The Gut–Liver Axis in Pediatric Liver Health and Disease. Microorganisms, 11(3), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030597







