Compositional Dynamics of Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiomes Associated with Dietary Transition and Feeding Cessation in Lake Sturgeon Larvae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Study Fish, Fish Husbandry, and Feeding Experiment
2.3. Morphometric Data and Survival Analyses
2.4. GI Tract Collection
2.5. Fish Dissection
2.6. DNA Extraction of GI Tract Bacteria and 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.7. Sequence Processing
2.8. Isolation of Bacterial Culture and Extracellular Protease Screening
2.9. Extracellular Protease Microbes in CR and TR Group
2.10. Analyses of Bacterial Community Profiles and Ecological Statistical Analyses
2.10.1. Alpha Diversity
2.10.2. Beta Diversity
2.11. Inferring Function of Members of GI Tract-associated Bacterial Communities
3. Results
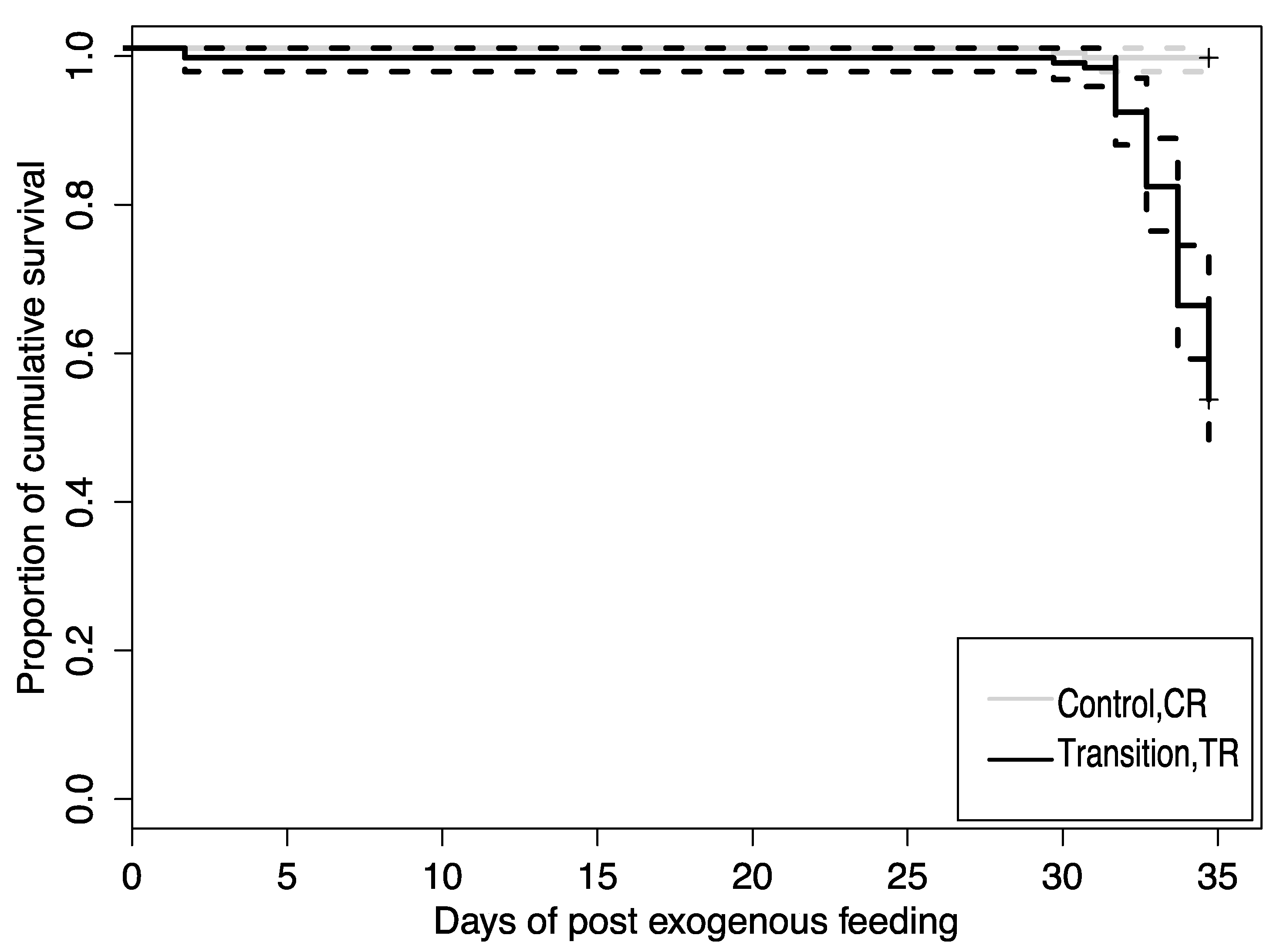
3.1. Growth and Survival
3.2. Characterization of Diversity and Taxonomic Composition of Microbial GI Tract Communities
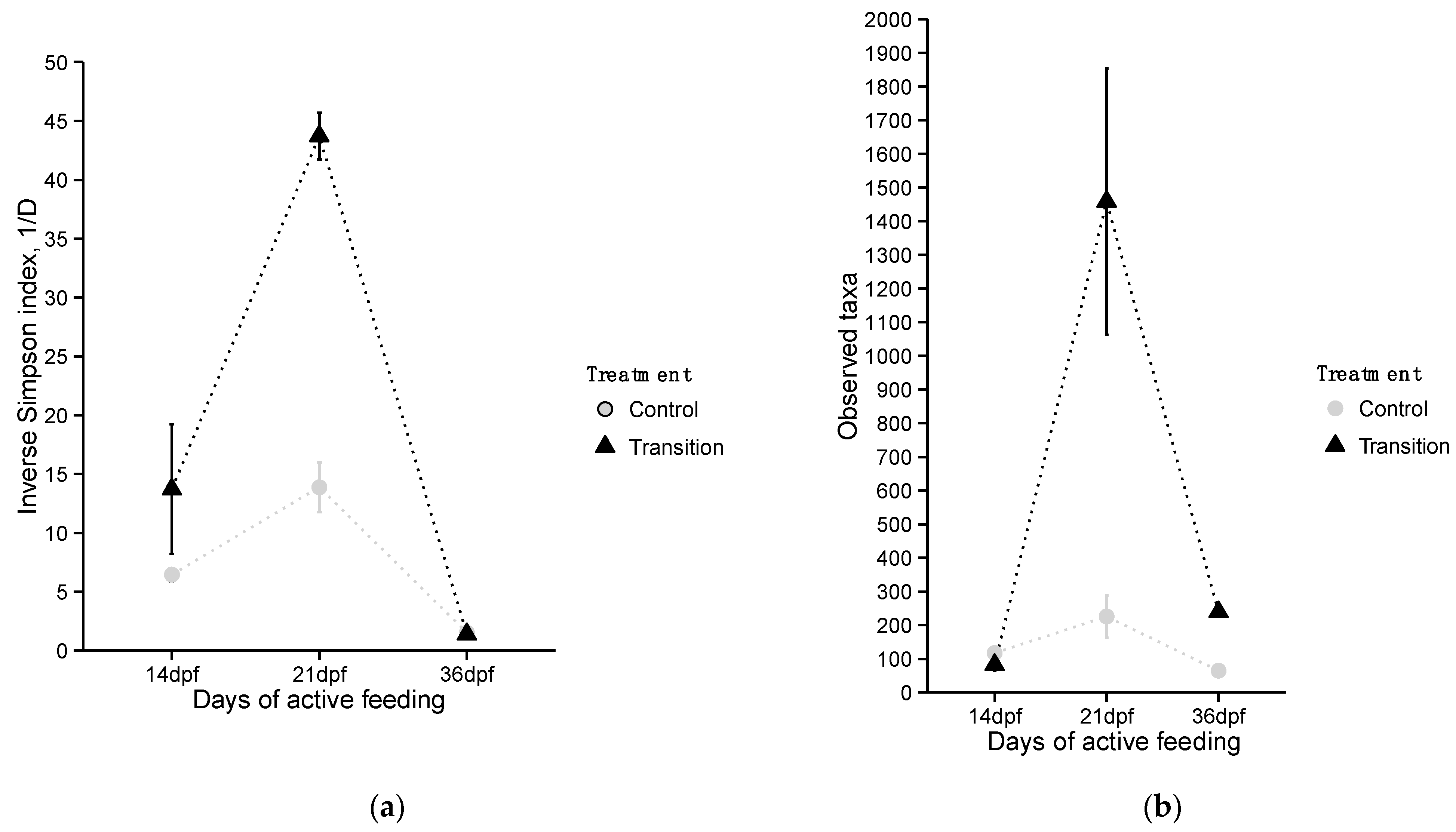
3.2.1. Estimates of Community Alpha Diversity
3.2.2. Estimates of Community Composition at the Phyla Level
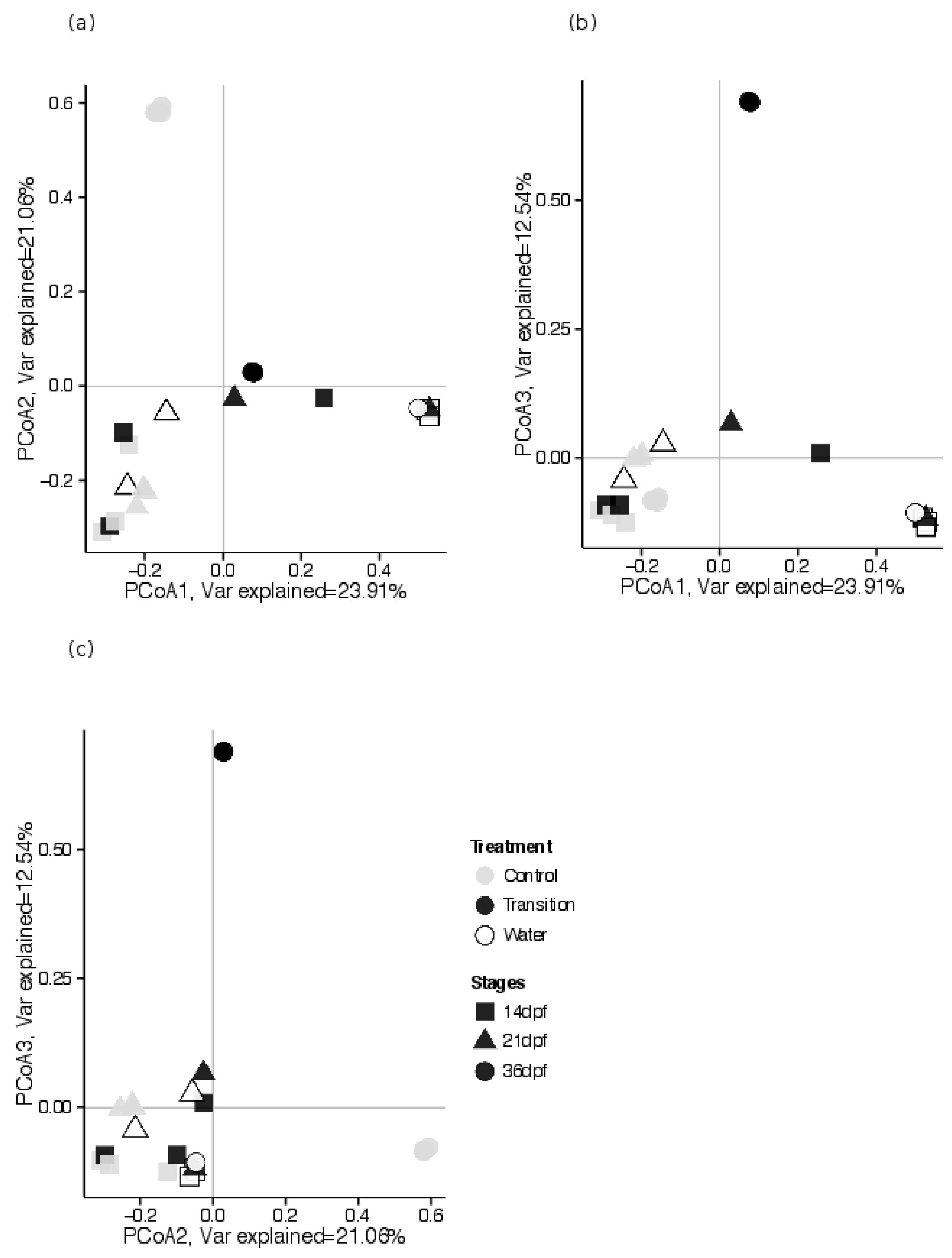
3.2.3. Estimates of Beta Diversity: Associations between GI Tract Microbial Community Composition and Feeding Treatments, across Sampling Periods
3.3. Predicted Functional Roles of Lake Sturgeon Larval GI Tract Microbiota
3.4. Activity-Based Screening for Protease-Positive Isolates
4. Discussion
4.1. Larval Growth and Survival
4.2. Characterization of Diversity and Taxonomic Composition of Microbial GI Tract Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Declarations
References
- Monaghan, P. Early growth conditions, phenotypic development and environmental change. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, E.E.; Gilliam, J.F. The Ontogenetic Niche and Species Interactions in Size-Structured Populations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1984, 15, 393–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, E.R.; Grant, J.W.A. Prey size of salmonid fishes in streams, lakes, and oceans. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.H. Ontogenetic Niche Shifts in Largemouth Bass: Variability and Consequences for First-Year Growth. Ecology 1996, 77, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliam, J. Habitat Use and Competitive Bottlenecks in Size-Structured Fish Populations; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin, H.J.; Michaels, J.T.; Beaulaton, C.M.; Main, K.L. Refining Feeding Practices for Hatchery Production of Siberian Sturgeon, Acipenser baeri. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2006, 37, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mathias, J.A. The Critical Period of High Mortality of larvae fish—A discussion based on current research. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 1987, 5, 80–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hixson, S.M. Fish Nutrition and Current Issues in Aquaculture: The Balance in Providing Safe and Nutritious Seafood, in an Environmentally Sustainable Manner. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2014, 3, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, M. Fish nutrition research: Past, present and future. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Yúfera, M.; Ueberschär, B.; Ribeiro, L.; Sæle, Ø.; Boglione, C. Feeding behaviour and digestive physiology in larval fish: Current knowledge, and gaps and bottlenecks in research. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, S59–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B.; Cech, J.J., Jr. Fishes: An Introduction to Ichthyology, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lazo, J.P.; Darias, M.J.; Gisbert, E. Ontogeny of the Digestive Tract. In Larval Fish Nutrition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 3–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hamre, K.; Yúfera, M.; Rønnestad, I.; Boglione, C.; Conceição, L.E.; Izquierdo, M. Fish larval nutrition and feed formulation: Knowledge gaps and bottlenecks for advances in larval rearing. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, S26–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedrasco, A.; Lobchenko, V.; Pirtu, I.; Billard, R. The culture of live food for sturgeon juveniles, a mini review of the Russian literature. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2002, 87, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsdottir, R.; Johannsdottir, J.; Coe, J.; Smaradottir, H.; Agustsson, T.; Sigurgisladottir, S.; Gudmundsdottir, B.K. Survival and quality of halibut larvae (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.) in intensive farming: Possible impact of the intestinal bacterial community. Aquaculture 2009, 286, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, P.; Bengston, D.A.; Sorgeloos, P.; Simpson, K.L.; Beck, A.D. The nutritional value of Artemia: A review, In Artemia Research and Its Applications; Sorgeloos, P., Bengston, D.A., Decleir, W., Jaspers, E., Eds.; Universa Press: Wetteren, Belgium, 2002; pp. 357–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ohs, C.L.; Cassiano, E.J.; Rhodes, A. Choosing an Appropriate Live Feed for Larviculture of Marine Fish; IFAS Extension University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.; Hubert, F.N.; Rodrigues, V.; Rojas-Garcia, C.; Dinis, M. Understanding Fish Larvae’s Feeding Biology to Improve Aquaculture Feeding Protocols. Oceans 2022, 3, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agh, N.; Noori, F.; Irani, A.; Makhdom, N.M. First feeding strategy for hatchery produced Beluga sturgeon, Huso huso larvae. Iran J. Fish Sci. 2012, 11, 713–723. [Google Scholar]
- Agh, N.; Noori, F.; Irani, A.; Van Stappen, G.; Sorgeloos, P. Fine tuning of feeding practices for hatchery produced Persian sturgeon, Acipenser persicus and Beluga sturgeon, Huso huso. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Bureau, D.P.; Chiu, A.; Elliott, M.; Farrell, A.P.; Forster, I.; Gatlin, D.M.; Goldburg, R.J.; Hua, K.; et al. Feeding aquaculture in an era of finite resources. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15103–15110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, J.; Brown, J.A. A pulse feeding strategy for rearing larval fish: An experiment with yellowtail flounder. Aquaculture 2000, 191, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, J.L.Z.; Cahu, C.L. Effect of nutrition on marine fish development and quality. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture Research; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2010; pp. 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bakke, A.M.; Glover, C.; Krogdahl, Å. Feeding, digestion and absorption of nutrients. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Blaxter, J.H.S. 4 Development: Eggs and Larvae. In Reproduction and Growth Bioluminescence, Pigments, and Poisons; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969; pp. 177–252. [Google Scholar]
- Houde, E.D. Patterns and trends in larval-stage growth and mortality of teleost fish. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 51, 52–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainuzzo, J.R.; Reitan, K.I.; Olsen, Y. The significance of lipids at early stages of marine fish: A review. Aquaculture 1997, 155, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, E.T.; Lu, H.; Yao, T.; Nakatsu, C.H. Microbial Ecology along the Gastrointestinal Tract. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.W.F.; Kersten, S. The role of the gut microbiota in metabolic health. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3111–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the Human Microbiome. NIH Manuscr. 2013, 70, S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl Olsen, R.E.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.; Owen, M.; et al. Effect of dietary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. A never-ending story? Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost microbiomes: The state of the art in their characterization, manipulation and importance in aquaculture and fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Amaya, J.; Passement, C.A.; Dearing, M.D.; Mccue, M.D. Unique and shared responses of the gut microbiota to prolonged fasting: A comparative study across five classes of vertebrate hosts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCue, M.D. Comparative Physiology of Fasting, Starvation, and Food Limitation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shreiner, A.B.; Kao, J.Y.; Young, V.B. The gut microbiome in health and in disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.L.; Vecsei, P.; Jennings, C.A. Ecology and biology of the lake sturgeon: A synthesis of current knowledge of a threatened North American Acipenseridae. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 2007, 17, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, J.A.; Scribner, K.T.; Yen, D.T.; Davis, C.A.; Forsythe, P.S.; Baker, E.A. Gamete and larval collection methods and hatchery rearing environments affect levels of genetic diversity in early life stages of lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens). Aquaculture 2011, 310, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeskleba, D.G.; Avelallemant, S.; Thuemler, T.F. Artifical spawning and rearing of lake sturgeon, Acipenser fulvescens, in Wild Rose State Fish Hatchery, Wisconsin, 1982–1983. In North American Sturgeons; Binkowski, F.P., Doroshov, S.I., Eds.; Dr. W. Junk Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, S.S.O.; Deng, D. Sturgeon, Acipenser spp. In Nutrient Requirements and Feeding of Finfish for Aquaculture; Webster, C.D., Lim, C., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Willingford, UK, 2002; pp. 344–357. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, C.N.; Peake, S.J. Effect of diet switch timing and food source on survival and growth of lake sturgeon. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2008, 24, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, S.A.; Bauman, J.M.; Scribner, K.T. Effects of Alternative Food Types on Body Size and Survival of Hatchery-Reared Lake Sturgeon Larvae. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2017, 79, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, J.M.; Woodward, B.M.; Baker, E.A.; Marsh, T.L.; Scribner, K.T. Effects of Family, Feeding Frequency, and Alternate Food Type on Body Size and Survival of Hatchery-Produced and Wild-Caught Lake Sturgeon Larvae. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2016, 78, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diether, N.E.; Willing, B.P. Microbial Fermentation of Dietary Protein: An Important Factor in Diet−Microbe−Host Interaction. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammerman, K.J.; Steibel, J.P.; Scribner, K.T. Relative influences of microhabitat incubation conditions and genetic parentage effects on lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) offspring traits during early ontogeny. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2020, 103, 1565–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Ley, R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.-F.; Koshio, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Bai, S.C.; Shao, Q.; Cui, Y.; Hung, S.S. Effects of feeding rate on growth performance of white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) larvae. Aquaculture 2003, 217, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modelling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Razak, S.A.; Scribner, K.T. Ecological and Ontogenetic Components of Larval Lake Sturgeon Gut Microbiota Assembly, Successional Dynamics, and Ecological Evaluation of Neutral Community Processes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02662-19. [Google Scholar]
- Callman, J.L.; Macy, J.M. The predominant anaerobe from the spiral intestine of hatchery-raised sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus), a new Bacteroides species. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 140, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddington, R.K.; Christofferson, J.P. Digestive and feeding characteristics of the chondrosteans. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1985, 14, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan-Myhre, K.; Charette, J.R.; Phennicie, R.T.; Stephens, W.Z.; Rawls, J.F.; Guillemin, K.; Kim, C.H. Study of host-microbe interactions in zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 2011, 105, 87–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the miseq illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetlock, A.; Yost, C.K.; Stavrinides, J.; Manzon, R.G. Changes in the gut microbiome of the sea lamprey during metamorphosis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7638–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J. Vegan: Ecological diversity; R Project; CRAN: Evanston, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, R.B.; Kotze, D.J. Do not log-transform count data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, A.P.; Shikon, V.; Schneider, D.C. Count data in biology—Data transformation or model reformation? Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2, Applied Spatial Data Analysis with R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-0-387-98141-3 (accessed on 16 January 2017).
- Anderson, M. A new method for non parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yufera, M. Feeding behavior in larval fish. In Larval Fish Nutrition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 284–305. [Google Scholar]
- Oie, G.; Reitan, K.I.; Evjemo, J.O.; Stottrup, J.; Olsen, Y. Live Feeds. In Larval Fish Nutrition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 307–334. [Google Scholar]
- Jawahar, J.; McCumber, A.W.; Lickwar, C.R.; Amoroso, C.R.; de la Torre Canny, S.G.; Wong, S.; Morash, M.; Thierer, J.H.; Farber, S.A.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; et al. Starvation causes changes in the intestinal transcriptome and microbiome that are reversed upon refeeding. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjørsvik, E.; Galloway, T.F.; Estevez, A.; Sæle, Ø.; Moren, M. Effects of Larval Nutrition on Development. In Larval Fish Nutrition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 219–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hasain, Z.; Ali, R.A.R.; Razak, S.A.; Azizan, K.A.; El-Omar, E.; Razalli, N.H.; Mokhtar, N.M. Gut Microbiota Signature Among Asian Post-gestational Diabetes Women Linked to Macronutrient Intakes and Metabolic Phenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 680622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCue, M.D. Starvation physiology: Reviewing the different strategies animals use to survive a common challenge. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.—A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 156, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, M.; Senderovich, Y. Chironomid Microbiome. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviad, S.; Halpern, M. Chironomids’ Relationship with Aeromonas Species. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W. Characterising the bacterial microbiota across the gastrointestinal tracts of dairy cattle: Membership and potential function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, P.A.; Crowley, J.R.; Sambandam, N.; Muegge, B.D.; Costello, E.K.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Regulation of myocardial ketone body metabolism by the gut microbiota during nutrient deprivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11276–11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.H.; Lin, G.; Fu, G.H.; Wan, Z.Y.; Lee, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.J.; Yue, G.H. The intestinal microbiome of fish under starvation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Dong, B. Seasonal dynamics and starvation impact on the gut microbiome of urochordate ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Anim. Microbiome 2020, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullam, K.E.; Rubin, B.E.; Dalton, C.M.; Kilham, S.S.; Flecker, A.S.; Russell, J.A. Divergence across diet, time and populations rules out parallel evolution in the gut microbiomes of Trinidadian guppies. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsei, P.; Peterson, D. Chapter 5 Sturgeon Ecomorphology: A Descriptive Approach. In Sturgeon & Paddlefish of North America; Lebreton, G.T.O., Beamish, F.W.H., Mckinley, R.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 103–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, T.; Ishizaki, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Kumeta, H.; Yumoto, I.; Matsuyama, H.; Ohgiya, S. Isolation of a Pseudomonas species from fish intestine that produces a protease active at low temperature. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 25, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Navarrete, P. 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Allen, D.A. Microbiology of laboratory-hatched brine shrimp (Artemia). Aquaculture 1982, 26, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargione, J.E.; Tilman, D. Diversity decreases invasion via both sampling and complementarity effects. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, M.; Mulet, M.; Altun, S.; Saticioglu, I.B.; Ozdemir, B.; Ajmi, N.; Lalucat, J.; García-Valdés, E. The diversity of Pseudomonas species isolated from fish farms in Turkey. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękala-Safińska, A. Contemporary Threats of Bacterial Infections in Freshwater Fish. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Barbary, M.; Hal, A. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Some Pseudomonas sp. Associated with Burkholderia cepacia Isolated 1FromVarious Infected Fishesle. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2017, 8, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni, N.J. Pseudomonas Classification A new case history in the taxonomy of Gram-negative bacteria. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1993, 64, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras Durand, F.; Dunière, L.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Forano, E. Microbiota Composition and Functional Profiling Throughout the Gastrointestinal Tract of Commercial Weaning Piglets. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| (a) | |||||
| Source | df | SS | MS | F | p-Value |
| Between subject (tank) effect | |||||
| Trt treatment | 1 | 191.94 | 191.94 | 64.41 | 0.001 |
| Error | 4 | 11.92 | 2.98 | ||
| Within subject (tank) effect | |||||
| Time | 2 | 416.90 | 208.44 | 119.63 | <0.0001 |
| Time*Trt | 2 | 347.10 | 173.57 | 99.62 | <0.0001 |
| Residuals | 8 | 13.90 | 1.74 | ||
| (b) | |||||
| Source | df | SS | MS | F | p-Value |
| Between-subject (tank) effect | |||||
| Trt treatment | 1 | 0.1208 | 0.1208 | 121.8 | <0.001 |
| Error | 4 | 0.0040 | 0.0010 | ||
| Within-subject (tank) effect | |||||
| Week | 3 | 0.1057 | 0.0352 | 101.5 | <0.0001 |
| Week*Trt | 3 | 0.1161 | 0.0387 | 111.5 | <0.0001 |
| Residuals | 12 | 0.0042 | 0.0004 | ||
| (a) | ||||||
| Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F-Value | R2 | Pr (>F) | |
| Stages | 3 | 2.710 | 0.903 | 3.518 | 0.273 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 1 | 1.106 | 1.106 | 4.308 | 0.111 | <0.001 |
| Stages:Treatment | 2 | 1.504 | 0.752 | 2.928 | 0.151 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 18 | 4.623 | 0.257 | 0.465 | ||
| (b) | ||||||
| Linear regression model: Pco Axes~Treatment | Least square means | |||||
| Important axes | Estimates | p-value | Control | Transitioned | ||
| PCo1 14 dpf (Before transition) | 0.321 | 0.338 | −0.160 ± 0.209 | 0.160 ± 0.209 | ||
| PCo1 21 dpf (Transition week) | −0.754 | <0.01 | 0.302 ± 0.040 | −0.453 ± 0.049 | ||
| PCo1 36 dpf (After transition) | −0.990 | <0.001 | 0.330 ± 0.002 | −0.660 ± 0.002 | ||
| PCo. Axes | Taxa | Taxonomic Identification/ Genera | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Otu1 | Clostidium_sensu stricto | 0.94 |
| 3 | Otu2 | Aeromonas | 0.97 |
| 2 | Otu10 | Unclassified Clostridiceae | 0.87 |
| 1 | Otu11 | Unclassified Betaproteobacteria | 0.92 |
| 1 | Otu12 | Unclassfied Microbacteriaceae | 0.84 |
| 1 | Otu15 | Unclassified Comamonadeceae | 0.88 |
| 1 | Otu16 | Unclassified Actinomycetales | 0.86 |
| 1 | Otu17 | Unclassified Comamonadeceae | 0.83 |
| 1 | Otu18 | Unclassified Comamonadeceae | 0.88 |
| 1 | Otu19 | Polynucleobacter | 0.89 |
| 1 | Otu24 | Unclassified Actinomycetales | 0.88 |
| 1 | Otu29 | Unclassified Sphingobacteriales | 0.88 |
| 1 | Otu31 | Unclassified Cryomorphaceae | 0.898 |
| 1 | Otu41 | Unclassified Microbacteriaceae | 0.83 |
| 1 | Otu42 | Methylophilus | 0.78 |
| 1 | Otu45 | Unclassified Cytophagaceae | 0.88 |
| 1 | Otu48 | Unclassified Sphingomonadaceae | 0.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Razak, S.; Valentine, S.; Marsh, T.; Bauman, J.; Mohd-Assaad, N.; Scribner, K.T. Compositional Dynamics of Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiomes Associated with Dietary Transition and Feeding Cessation in Lake Sturgeon Larvae. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091872
Abdul Razak S, Valentine S, Marsh T, Bauman J, Mohd-Assaad N, Scribner KT. Compositional Dynamics of Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiomes Associated with Dietary Transition and Feeding Cessation in Lake Sturgeon Larvae. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091872
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Razak, Shairah, Shaley Valentine, Terence Marsh, John Bauman, Norfarhan Mohd-Assaad, and Kim T. Scribner. 2022. "Compositional Dynamics of Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiomes Associated with Dietary Transition and Feeding Cessation in Lake Sturgeon Larvae" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091872
APA StyleAbdul Razak, S., Valentine, S., Marsh, T., Bauman, J., Mohd-Assaad, N., & Scribner, K. T. (2022). Compositional Dynamics of Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiomes Associated with Dietary Transition and Feeding Cessation in Lake Sturgeon Larvae. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091872








