Abstract
Multiferroic magnetoelectric (ME) composites are attractive materials for various electrically and magnetically cross-coupled devices. Many studies have been conducted on fundamental understanding, fabrication processes, and applications of ME composite material systems in the last four decades which has brought the technology closer to realization in practical devices. In this article, we present a review of ME composite materials and some notable potential applications based upon their properties. A brief summary is presented on the parameters that influence the performance of ME composites, their coupling structures, fabrications processes, characterization techniques, and perspectives on direct (magnetic to electric) and converse (electric to magnetic) ME devices. Overall, the research on ME composite systems has brought us closer to their deployment.
1. Introduction
The multifunctional properties of multiferroics enable the design of novel electronic devices for various sensing, transduction and memory applications. Muliferroic materials are characterized by two or more ferroic orders, such as ferroelectric, ferromagnetic, or ferroelastic, and the interactions between these order parameters, as shown in Figure 1. In multiferroic magnetoelectric (ME) materials, coupling occurs between the magnetic and electric subsystems. This enables the control of dielectric polarization P by a magnetic field H (direct ME (DME) effect: ΔP = αH ΔH) and the manipulation of magnetization M by an electric field E (converse ME (CME) effect: µ0 ΔM = αE ΔE), with µ0 denoting the vacuum permeability. The ME response is quantified in terms of the ME coupling coefficient (αH or αE), which represents the coupling efficiency between the electric and magnetic fields. This is considered as the figure of merit for the strength of ME coupling [1]. This article discusses the present status and recent progress in the development of ME materials and their applications in devices.
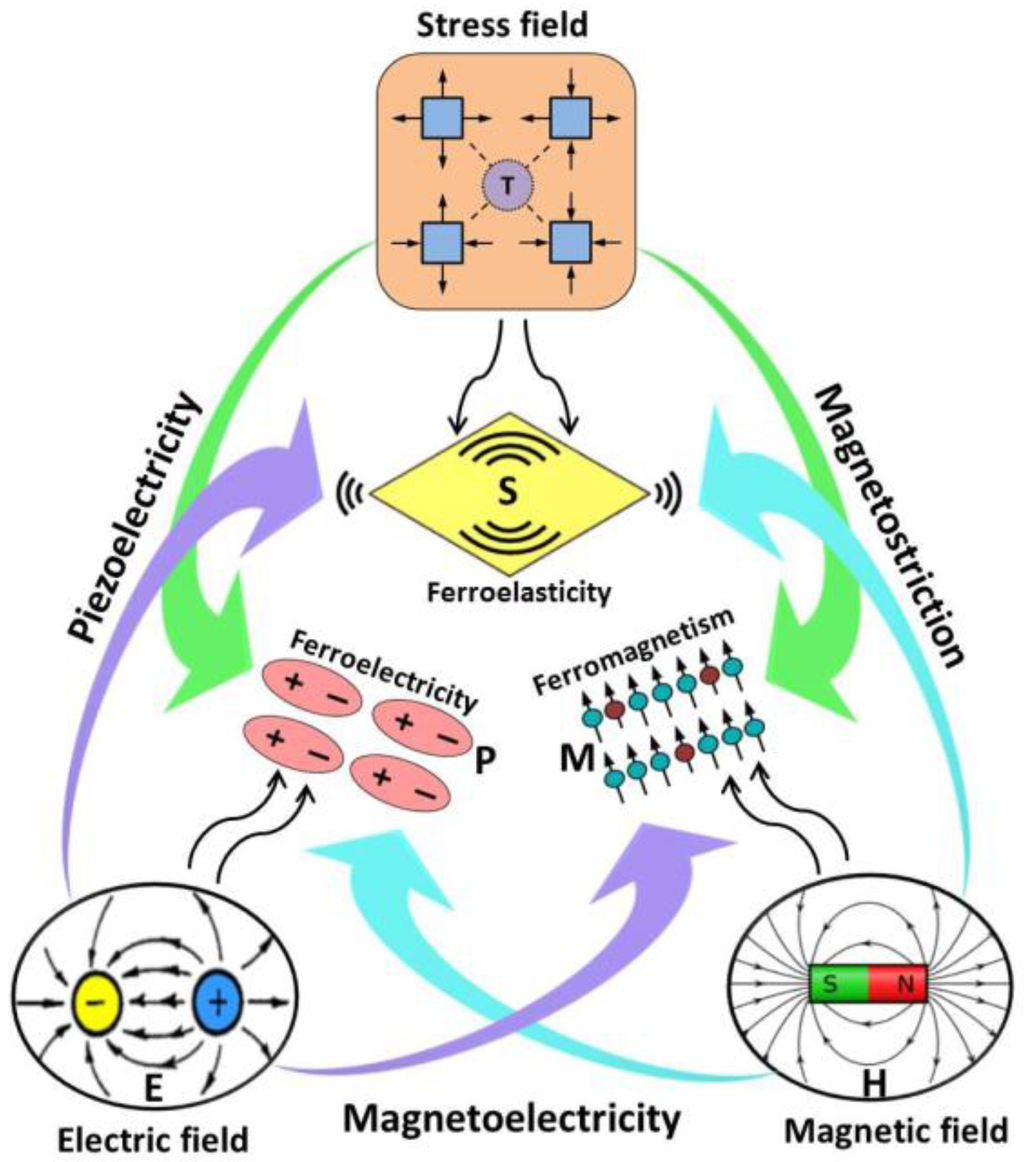
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrating magnetic-elastic-electric couplings in multiferroic materials. Here, M is magnetization, S is mechanical strain, and P is dielectric polarization.
Single phase magnetoelectrics are chemically homogenous and isotropic compounds. They exhibit intrinsic ME coupling but require the co-existence of magnetic moments and electric dipoles with long-range ordering. From a fundamental point of view, the coupling between the magnetic and polar sublattices in single phase ME compounds is fascinating. However, due to the mutual exclusion of ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity, only few monolithic ME materials exhibiting non-zero coupling at room temperature have been found so far. Most of the single phase materials possess either low permittivity or low permeability at room temperature and thus exhibit weak ME coupling which hinders their applications. For example, BiFeO3, the archetype of single phase ME compounds, displays good ferroelectricity but weak ferromagnetic properties above room temperature [2].
ME composites, the focus of this review, consist of physically separated magnetic and electric order phases. These composites show coupling with orders of magnitude larger than those found in single phase materials at room temperature [3]. Current understanding suggests that ME coupling in composites occurs extrinsically in three different ways mediated through (i) strain, (ii) charge carrier, and (iii) spin exchange. Among these mechanisms, the strain-mediated ME coupling has been widely studied, while the investigations on the other two mechanisms are still in early stages [4]. In this paper, the ME composites based on the strain-mediated coupling will be discussed in detail, and their applications in potential devices will be highlighted.
The strain-mediated ME effect in composites is a product tensor property and results from the elastic coupling between the piezoelectric and magnetostrictive components as illustrated in Figure 2 [5,6]. In DME coupling, the applied magnetic field generates strain in the magnetic layer via the magnetostriction effect, and this strain is transferred to the piezoelectric layer resulting in an electric displacement or a dielectric polarization through the piezoelectric effect. In CME coupling, an external electric field induces strain in the ferroelectric layer due to the inverse piezoelectric effect, and the strain transferred to the magnetic layer produces a magnetization change or domain reorientation by the piezomagnetic effect.
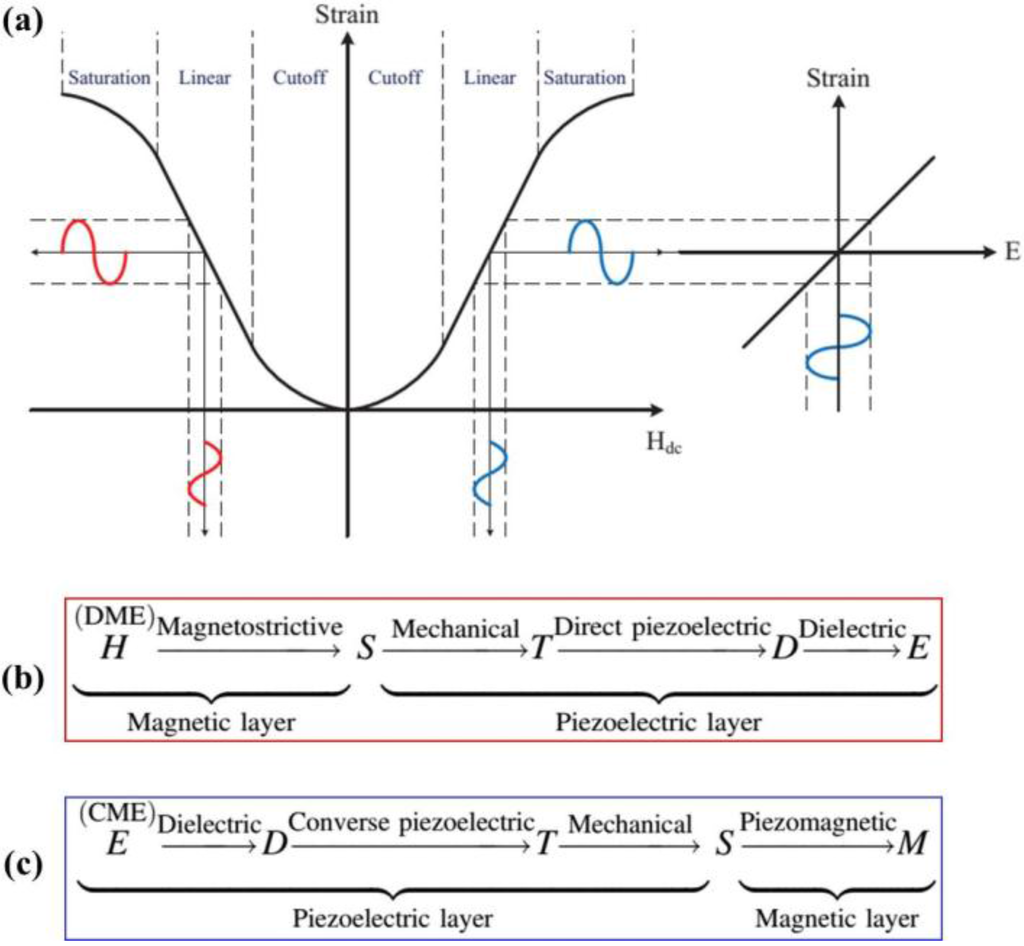
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the (a) ME effect utilizing the product property (Adapted from [6]). (b) DME effect and (c) CME effect in composites [7]. Here, H is magnetic field, S is mechanical strain, T is mechanical stress, D is electric displacement, E is electric field, and M is magnetization.
2. Factors Affecting ME Coupling in Composites
In recent years, ME composites have been extensively studied due to the ease of fabrication and design flexibility. ME composites have been developed with a diverse set of materials, properties, and microstructures using a variety of processing techniques. The parameters and variables that should be taken into account for developing high performance composites with strong ME coupling are summarized in this section.
2.1. Connectivity and Interface Bonding
The phase connectivity and interfacial bonding of the piezoelectric and magnetostrictive constituents have a strong influence on elastic coupling in the composite and its ME response. Good mechanical bonding at the interface between the composite phases, characterized by the interface coupling factor (kc), facilitates efficient strain transfer. Though several connectivity schemes have been proposed for designing two-phase composites [8], ME composites have been commonly prepared with 0-3, 1-3, and 2-2 connectivity, as shown in Figure 3a, d, and g, respectively. Here, the numbers represent the connectivity of the magnetic and piezoelectric phases, respectively. In the 0-3 particle-matrix composites, magnetic particles are embedded in the piezoelectric matrix. 1-3 cylinder-matrix composites are formed by embedding magnetic fibers/rods/tubes/wires in the piezoelectric matrix. The particles (in the 0-3 composite) and fibers (in the 1-3 composite) can be either randomly dispersed or periodically aligned [9]. A 2-2 laminate composite consists of alternating magnetic and piezoelectric layers. Such laminates can be prepared in different shapes and geometries, including discs, squares, rectangles, and rings, with different dimensions. They can be arranged as unimorphs and bimorphs as well as bilayered and multilayered structures. Further, for all of the above composites, the volume fraction and dimensions of the constituents can be altered to tailor the properties of the composite. The 2-2 composites preserve the physical characteristics of individual phases, and they are comparatively simpler to fabricate. These composites can be poled to a higher degree since the piezoelectric and the low resistivity magnetic phases are separated. Results of both theoretical and experimental studies have shown that the 2-2 layered composites exhibit higher ME responses compared to the 0-3 and 1-3 composites. There have been other composite structures reported in the literature. Park et al. [10] reported the development of a 3-2 structured composite consisting of a (Ni0.6Cu0.2Zn0.2)Fe2O4 [NCZF] phase with 2D connectivity dispersed in a 0.8Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3–0.2Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 [PZNT] matrix. Recently, Gillette et al. [11] fabricated a quasi-one-dimensional ME composite by inserting a magnetostrictive wire (FeNi/FeGa/FeCoV) into a PZT tube where the tube-wire interface bonding was made with silver paste. Comparing the results from these prior studies, it can be stated that 2-2 composite structure has inherent advantages in terms of fabrication and performance.
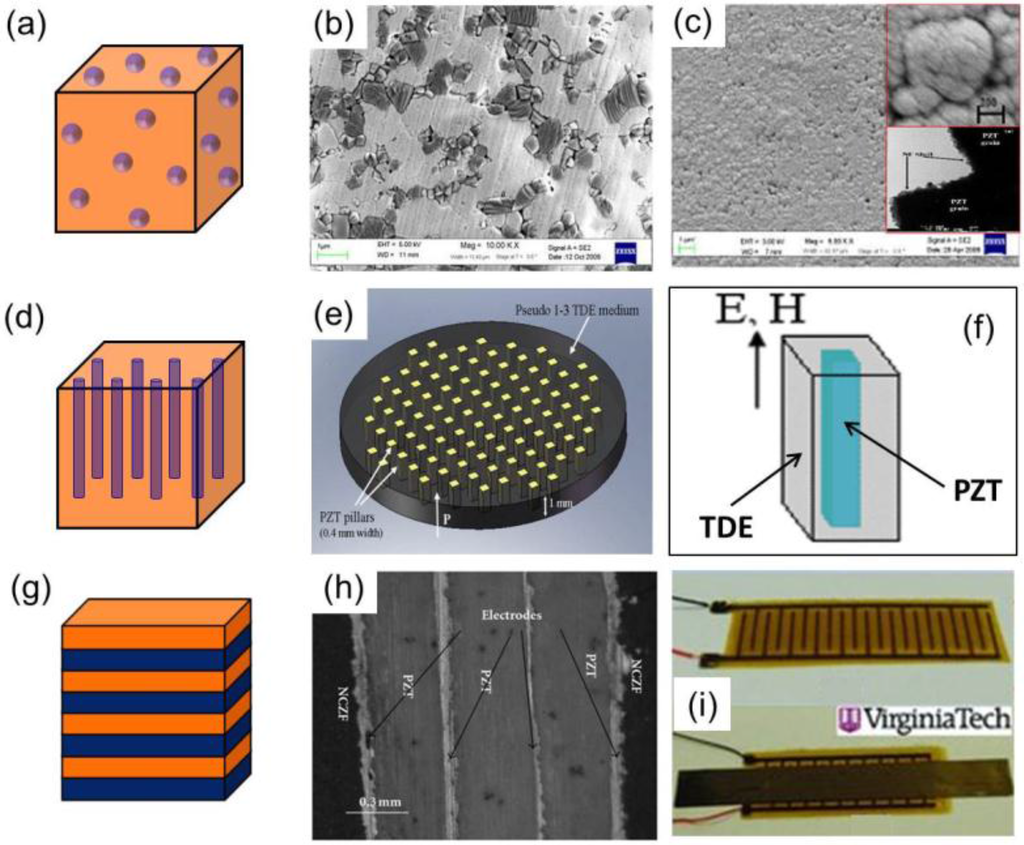
Figure 3.
Development of bulk ME composites with different phase connectivity: (a)–(c) 0-3 connectivity [13,18]; (d)–(f) 1-3 connectivity [20,21]; and (g)–(i) 2-2 connectivity [22,24].
2.2. Materials and Their Properties
The selection of suitable materials is a primary step in fabricating a composite with good ME response. Various piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials commonly used for synthesizing ME composites are listed in Table 1. Enhanced piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties can be achieved in ceramics through (a) composition selection (ideally near morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) or polymorphic phase transition (PPT)) and modification (by doping); and (b) microstructure design (via domain engineering and texturing) [12]. Among piezoelectric materials, PZT-based ceramics have been widely employed to fabricate the ME composites due to their low cost, high piezoelectric response, and flexibility in modifying the composition to achieve desired properties for targeted applications. For the magnetic component in ME composites, Terfenol-D with high magnetostriction and Metglas (amorphous Fe-alloy) with high magnetic permeability have been the most used materials. Besides magnetic properties, factors such as the processing temperatures, electrical resistance of the material, magnitude of the bias field, phase connectivity have been considered in choosing the magnetostrictive materials.

Table 1.
List of well-known piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials used as constituents of ME composites.
The material properties that are considered important when developing ME composites include electrical properties such as dielectric constant or permittivity ( εr), dielectric loss (tan δ), Curie temperature (TC), remnant polarization (Pr), coercive electric field (Ec), piezoelectric strain constant (dij), piezoelectric voltage constant (gij), electromechanical coupling factor (kij), mechanical quality factor (Qm), and acoustic impedance (Z). The magnetic properties of relevance include magnetic permeability (μ), remnant magnetization (Mr), coercive magnetic field (Hc), magnetostriction (λij), piezomagnetic coefficient (qij), and Curie and Neel temperatures (TC and TN). Generally, to obtain a better ME response from the composite, the combination of a piezoelectric material displaying a high piezoelectric voltage constant (gij = dij/ε) and low dielectric and piezoelectric losses, and a magnetostrictive material exhibiting a high magnetostriction coefficient (qij) and good interfacial coupling between these two phase components is desired.
2.3. Fabrication of ME Composites
2.3.1. Bulk ME Composites
A widely used method for synthesizing of 0-3 particulate composites consists of sintering a mixture of ceramic oxide powders at high temperature. This ceramic sintering process is simple and the properties of the composite can be conveniently tailored by selecting the constituent phases, their starting particle sizes, and processing parameters. Using this method, mainly magnetic ferrites have been co-processed with piezoelectric ceramics due to their high temperature stability. Figure 3b shows the microstructure of a Pb(Zr0.56Ti0.44)O3–Ni0.6Zn0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 sample sintered at 1000 °C [13]. At present, the measured ME coupling of 0-3 particulate composites are far lower than the theoretically predicted ones. This can be attributed to several factors: (a) the misfit strain at the interface arising from the thermal expansion mismatch between the piezoelectric and ferrite phases, which reduces the densification; (b) the interdiffusion and/or chemical reactions between the two phases during high-temperature sintering, which deteriorates the piezoelectricity and/or magnetostriction of constituent phases and the strain transfer between two phases; and (c) current leakage due to the low resistivity in the randomly distributed magnetic phase with low percolation threshold, which makes the electric poling of these ME composites quite difficult [2,3]. Some efforts have been made to solve these issues. Hot pressing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) have been utilized to achieve high density while avoiding possible reaction between the constituent phases [14,15]. A modified precipitation method involving a controlled annealing, quenching, and aging cycle [16] has been employed to obtain good dispersion of ferrite (NiFe1.9Mn0.1O4) particles in the matrix (PZT) phase. Core/shell (ferrite/piezoceramic) structured composites have been synthesized to avoid the contact of the conductive ferrite particles during sintering [17]. Unlike the other cases, Islam et al. [18] reported a PZT core/NiFe2O4 shell ME composite (Figure 3c). To circumvent the problem of high conductivity through the ferrite phase, a 100-mm layer of PZT was used to cover both faces of the sintered pellet.
Very few attempts have been made to fabricate 1-3 type bulk ME composites [19,20,21]. Shi et al. [19] prepared a pseudo-1-3 type ME composite consisting of a PZT rod array (with base) and Terfenol-D/epoxy matrix (TDE) using the dice-and-fill technique, where diced PZT sample was filled with an epoxy resin solution containing Terfenol-D particles (Figure 3e). A peak ME response of 6 V/cm·Oe was obtained between 80 and 110 kHz. Lam et al. [20] studied the frequency response of PZT-TDE composite, made using the same dice-and-fill method, under magnetic bias field. It was found that the resonance shifted to a lower frequency with increasing magnetic bias field. Ma and colleagues [21] presented a simple 1-3 composite made up of just a single PZT rod embedded in a TDE mixture (Figure 3f), which avoided the need for dicing of the PZT rod arrays. This composite exhibited a maximum ME response of 18.2 V/cm·Oe at 84 kHz. Such a large ME response was attributed to the enhancement of coupling at electromechanical resonance, which assisted the elastic interaction between the TDE medium and PZT rod.
Preparation of bulk 2-2 laminate composites has been mainly conducted by epoxy bonding and co-firing [5,22,23,24,25,26]. The most common geometries in laminate composites are either bilayer structure of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric layers or a sandwich structure, whereby the piezoelectric layer is arranged between two magnetostrictive ones. Laminate composites made by bonding magnetostrictive and piezoelectric layers with silver epoxy are usually cured at a lower temperature (80–100 °C). The epoxy acts as a conductive bond and strengthens the interface between the composite layers, although the epoxy layer must be kept as thin as possible to obtain good ME coupling. Various combinations of piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials can be used to fabricate different types of ME composites with this bonding process as it does not involve high temperatures. However, the mechanically soft and viscoelastic epoxy layer will dampen the generated strain and induce a noise floor, suppressing the interface coupling and thus the ME response. Co-firing is an established process used for sintering multilayer capacitors. Besides strengthening the interface in layered ME composites, the co-firing process also provides the possibility of cost-effective mass production. Figure 3h shows the cross-sectional optical image of a NCZF-stack [0.9 PZT-0.1 PZN]-NCZF trilayer co-fired at 900 °C for 3 h [22]. Despite its advantages, the high temperature co-firing process, similar to the ceramic sintering of 0-3 particulate composites, is challenging owing to the different shrinkage rates, thermal expansion mismatch, and interface inhomogeneities.
Piezoelectric macro-fiber composites (MFCs) offer better flexibility and higher performances than the traditional monolithic piezoelectric ceramics. Compared to a PZT plate, MFCs are easier to elongate and shrink when force is applied. Several ME composites have been developed based on these MFC structures, which employ an interdigitated electrode (IDE) [23,24]. Figure 3i displays picture of an IDE/piezofiber core composite and its implementation in a complete Metglas/piezofiber ME sensor. This composite structure yielded a giant ME response with an extremely low equivalent magnetic noise. Some polymer-based laminate ME composites prepared using polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF), a piezopolymer possessing a low ε and a high g, in combination with Metglas or Vitrovac (Fe-based amorphous alloy) and Terfenol-D, have also shown large ME coupling behavior [25,26].
2.3.2. Film-Based ME Composites
As device design trends towards miniaturization and multifunctionality, thin film conformations are highly desired for application in integrated magnetic/electric devices. In film-based ME composites, optimized interface coupling can be achieved through the direct bonding of components. Moreover, large electric fields can be comfortably applied to thin films since they require relatively smaller bias voltages than those needed for bulk samples. This extends the scope of thin films for devices which have limitations on their operating voltages [27]. The greater freedom and flexibility in the fabrication of film-based ME composites render their property tuning, through interfacial coupling and strain engineering, control of crystal structure and orientation, grain size, and layer thickness, as well as chemical modification with a wide range of substituents, etc. Composite films can also facilitate the understanding of the physical phenomena involved in ME effects at lower dimensions, and thus enable the design of new types of magnetoelectrics with novel phase structures. A number of ME composite films have been recently prepared using various film deposition methods. Some of these methods can yield excellent thin film epitaxial growth with atomic scale thickness control and coherent interfaces [12]. However, most ME composite films reported in the literature show very low ME properties due to reduced electromechanical parameters as a consequence of substrate clamping.
Since ME coupling occurs through interfacial strain transfer, the ME response of 0-3 type ME nanocomposites can be enhanced by dispersing magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) with large interfacial area in a piezoelectric matrix. Based on this idea, McDannald et al. [28] synthesized PZT-CFO nanocomposite films (Figure 4a) via spin coating, and the ME coupling was modulated by controlling the concentration of CFO NPs dispersed in the PZT matrix. A high ME coefficient of 0.549 V/cm·Oe was obtained with a low concentration of CFO NPs, and the subsequent decrease in ME response with higher CFO concentrations was ascribed to the enhanced agglomeration of NPs.
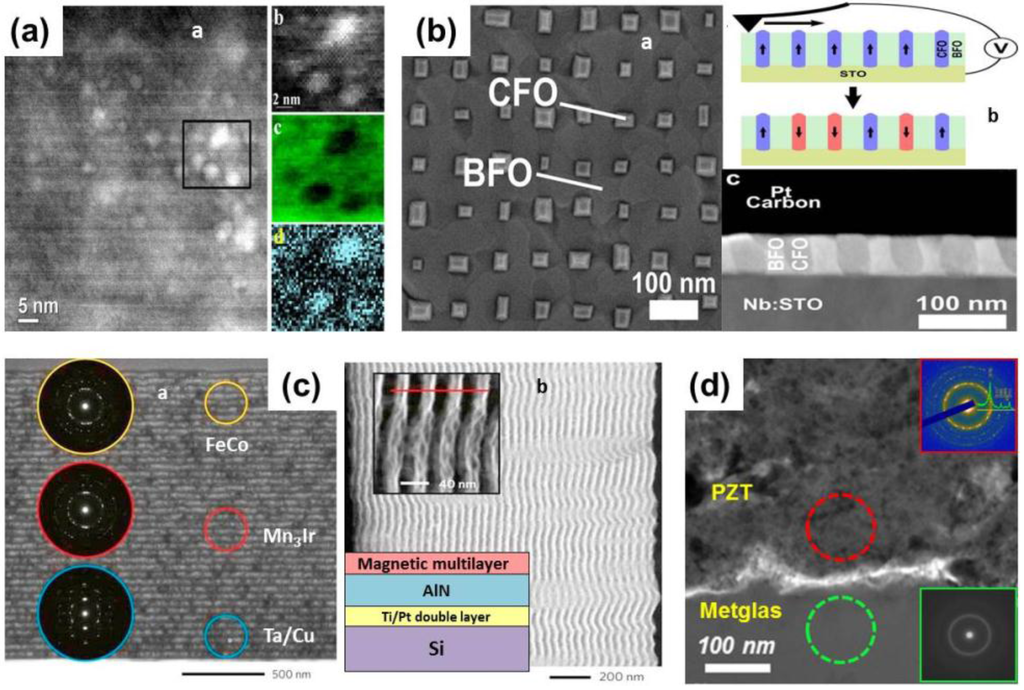
Figure 4.
Development of film-based ME composites with (a) 0-3 connectivity [28]; (b) 1-3 connectivity [30]; (c) and (d) 2-2 connectivity [33,39].
The 1-3 type ME film composites have mainly been explored at the micro- and nanoscale where they can be easily synthesized through the self-assembly process [29]. Aimon et al. [30] developed self-assembled BiFeO3−CoFe2O4 nanocomposites (Figure 4b) that were templated into ordered structures in which the ferrimagnetic CoFe2O4 pillars formed square arrays having periods of 60−100 nm in a ferroelectric BiFeO3 matrix. The 1-3 ME composites prepared via self-assembly were reported to exhibit a reduced substrate clamping effect and more efficient strain coupling, as a result of their large interfacial surface area [12]. However, the design and control of such a structure remains a challenge, and their ME coefficients could not be directly measured because of the leakage problem, which resulted from the low resistance of the magnetic pillars penetrating through the films.
Deposition methods that have been used to develop thin film-based 2-2 type ME composites include pulsed laser deposition, chemical vapor deposition, sputtering, molecular beam epitaxy, spin coating, spray pyrolysis, and spin-spray techniques [31,32]. Self-biased ME film composites that show high sensitivity to AC magnetic fields were reported by Lage et al. [33] These thin film 2-2 ME composites fabricated by magnetron sputtering on silicon-cantilever substrates consisted of piezoelectric AlN and multilayers having the sequence Ta/Cu/Mn70Ir30/Fe50Co50 or Ta/Cu/Mn70Ir30/Fe70.2Co7.8Si12B10 serving as the magnetostrictive component (Figure 4c). Giant ME couplings were reported for ME thin film composites based on BaTiO3-CoFe-BaTiO3, and AlN-(Fe90Co10)78Si12B10 systems [34,35]. Thick film-based 2-2 layered ME composites have been prepared by employing several deposition techniques such as tape casting [36], aerosol deposition [37], electrophoretic deposition (EPD) [38], granule spray in vacuum deposition (GSV) [39], electrodeposition [40], and electroless deposition [41]. Recently, a unique fabrication approach involving a combination of room temperature deposition (GSV) and localized annealing of PZT thick film by laser radiation has been demonstrated [39] to synthesize PZT/Metglas ME film composites (Figure 4d). Localized heating through selective absorption of laser irradiation in the PZT film not only induced significant improvement in its dielectric and ferroelectric properties but also contributed to a colossal ME output by avoiding thermal damage to the Metglas substrate and preserving its inherent magnetic properties. Alternatively, photonic sintering or flash light irradiation can also be used to induce localized annealing effects in films deposited on thermally sensitive substrates. This method, commonly employed in printed electronics, uses broadband (ultraviolet to infrared) intense light pulses generated from a Xenon flash lamp to control the thermal diffusion in the nanostructured films.
3. Recent Advances in the Development of ME Composites
3.1. Realization of Broadband ME Response with Piezoelectric Anisotropy
In general, depending upon the material properties, the ME coefficient of laminate composites exhibit maxima at a specific DC bias under off-resonance condition. In the resonant condition, ME laminates exhibit a sharp peak around the resonance frequency. Such behavior limits their ability to sense wide ranges of both DC and AC magnetic fields. The broadband/wideband behavior is characterized by flat ME response over a given AC frequency range and DC magnetic bias. Limited efforts have been made to achieve a wide bandwidth around resonance frequency either by combining several PZT/Terfenol-D bilayers through parallel and series electrical connections [42] or by developing composite structures of PZNT/Metglas with a dimensionally gradient architecture [43,44]. These peak broadening approaches have indeed shown some promise, but they only cover a limited range of frequencies with a non-uniform power distribution. Patil et al. [45] demonstrated a resonant ME response with a wide bandwidth by adopting tri-layer ME laminates (Ni/PMN-PZT/Ni) having inherent multiple resonance frequencies, attributable to the anisotropic piezoelectric response of the [011]-oriented PMN-PZT single crystal. The required broadening of the resonance frequencies was achieved by serially connecting three ME laminates with different thickness ratios of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric layers. Such a wide bandwidth, along with the giant ME coupling, could be used in multifunctional devices such as broadband energy harvesters or field sensors. Further, Patil et al. [46] demonstrated the presence of giant ME voltage coefficients and magnetic-field-direction dependent ME signals at both low frequencies and resonance frequency in a symmetric ME laminate (Metglas/PMN-PT/Metglas). High performance resulted from the anisotropic transverse piezoelectric coefficients of the [011]-oriented PMN-PT single crystal. In another study, Kambale et al. [47] designed the ME rectangular unimorph cantilever beam structure consisting of Ni and PMN-PZT single crystal with <001> and <011>-cut crystallographic directions and investigated their mechanical vibration-based energy harvesting behavior. Both the ME voltage coefficient (αME) and mechanically harvested power output was found to be strongly dependent on the crystallographic cut directions of the PMN-PZT single crystals.
3.2. ME Composites with Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics
To achieve high ME coefficients, it is necessary to use a piezoelectric material exhibiting a high magnitude of piezoelectric voltage constant (g = d/ε). However, piezoelectric ceramic compositions having a high d33 usually show a low g33, while high g33 compositions possess a low d33. Thus, the achievement of both high d and g from a single piezoelectric composition has been challenging. Though domain-engineered, relaxor piezoelectric single crystals such as PMN-PT and PZN-PT exhibit excellent piezoelectric properties, their application has been limited due to the high production cost and small size of useful samples. PZT-based compositions cannot be readily grown in single crystal form because of their incongruent melting behavior [48]. Alternately, textured ceramics based on PMN-PT and PMN-PZT have been prepared using the templated grain growth (TGG) method. Here, the texturing produces an engineered domain state resulting in high d values and the use of oriented and platelet shaped template crystals having low permittivity suppresses the increase in ε of the textured ceramic, thereby achieving low cost high performance piezoelectric ceramics suitable for ME composites. Yan et al. [49] reported an enhanced αME for Metglas/textured PMN-PZT/Metglas laminate compared to Metglas/random PMN-PZT/Metglas, where the maximum αME was found to be 0.348 V/cm·Oe and 1.49 V/cm·Oe, respectively. Because of the environmental concerns of using lead containing materials, recent investigations have focused on developing ME composites employing lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with compositions based on KNN, NBT, and BT. A large value of maximum αME (1.32 V/cm·Oe) has been reported from a laminate ME composite of Terfenol-D/Mn-doped NBT–BT single crystal/ Terfenol-D [50].
3.3. Self-Biased ME Composites
Most conventional ME composites need a DC bias, to obtain the maximum ME response, and that necessitates the use of permanent magnets or electromagnets resulting in bulky devices and problems of electromagnetic interference. To circumvent these issues, self-biased magnetoelectric (SME) composites that provide sizeable ME coupling under an external AC magnetic field in the absence of a DC magnetic field have been proposed [51]. This would enable device miniaturization and the development of ME composite-based circuit components for integrated electronics and medical applications. The SME composites are categorized into five groups according to their working mechanism: (a) functionally graded FM-based SME; (b) exchange bias-mediated SME; (c) magnetostriction hysteresis-based SME; (d) built-in stress-mediated SME; and (e) non-linear SME composites (Figure 5). Large and tunable SME responses have been reported for both bulk and film-based ME composite systems [33,52]. A recent review by Zhou et al. [51] provides a comprehensive coverage of the development and prospects of the SME composites.
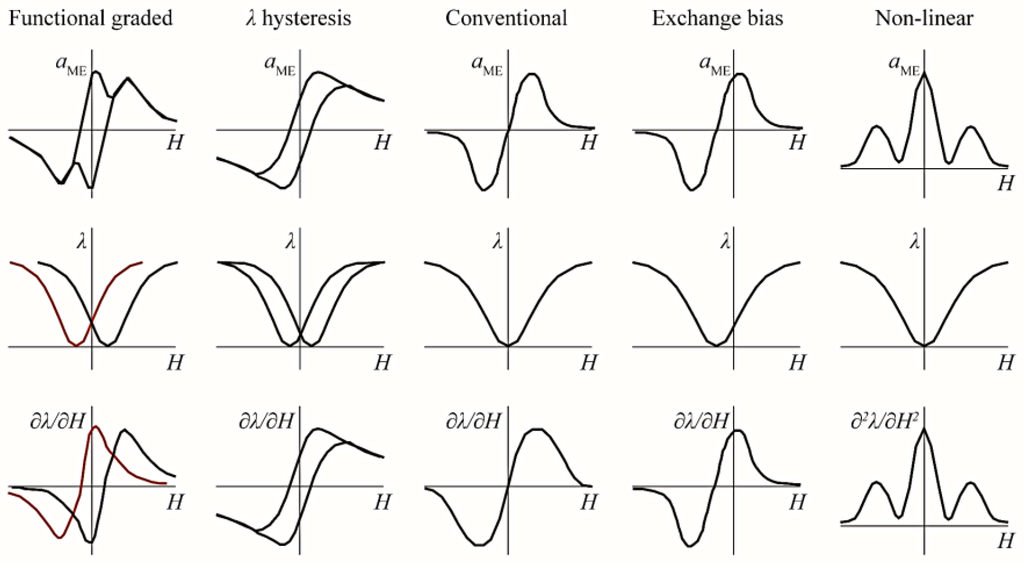
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of different types of self-biased ME composites with different αME-H (top row), λ-H (middle row), and q-H curves (bottom row) [51].
3.4. ME Composites with Novel Structures
ME composites with a range of composite connectivity, including new connectivity designs that cannot be readily synthesized by traditional routes are being developed through the fabrication of nanostructured ME materials. In recent years, there have been some studies on the synthesis of ME nanocomposites having core/shell arrangement in the form of nanoparticles, nanowire arrays, and nanotubes. Other 1D composite structures with random and Janus-type arrangements have also been prepared (Figure 6). These nanostructured composites were prepared using different wet chemical synthesis methods. Kalyan et al. [53] synthesized CoFe2O4/BaTiO3 core/shell nanoparticles (Figure 6a) using a combination of solution processing and high temperature calcination. Rongzheng et al. [17] demonstrated the formation of ferrite/perovskite oxide core/shell nanostructures in several multiferroic systems such as Fe3O4/PbTiO3, γ-Fe2O3/PbTiO3, γ-Fe2O3/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3, CoFe2O4/BaTiO3, CoFe2O4/PbTiO3 and CoFe2O4/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 using a combined hydrothermal and annealing process. For synthesizing ordered arrays of NiFe2O4/PZT core/shell nanowires (Figure 6b), Ming et al. [54] developed a method involving the combination of a modified sol-gel process, electrochemical deposition, and subsequent oxidization in anodized nanoporous alumina membranes. Recently, Andrew et al. [55,56] reviewed the efforts in the development of multiferroic nanofibers with core/shell, random, and Janus-type arrangements (Figure 6c–e), fabricated by electrospinning. Nevertheless, some of the challenges in the practical implementation of these ME nanocomposites include forming isolated multiferroic particles that are free of agglomerates, substrate free assembling of nanofibers into ordered structures, and difficulties in accessing their ME properties. Further, in some cases, these nanostructured ME composites will have to be consolidated into a dense form for device applications which may affect the stability of nanostructures.
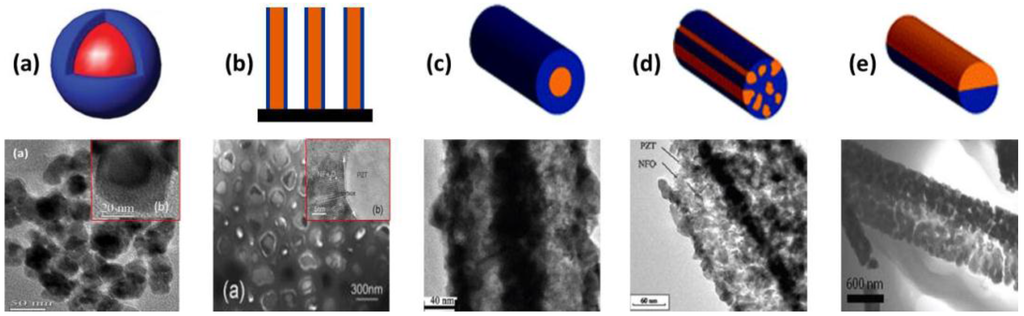
Figure 6.
Bi-phasic ME composites with different types of arrangements between the two phases (a–c) core/shell arrangement: (a) nanoparticles [53]; (b) nanowires [54]; and (c) nanotubes [57]; (d) random arrangement [58]; and (e) Janus-type arrangement [56].
4. Characterization of ME Coupling
To understand the effect of multiple parameters and variables (materials, connectivity, operational mode, synthesis method, etc.) on the ME coupling, and to predict the performance of ME composites in various applications, investigations on their working behavior are essential. Several characterization tools have been reported in literature on DME and CME coupling, based on the measurement as a function of an applied magnetic field or an electric field over a range of frequencies from DC to 110 GHz. Some of these analysis techniques have been discussed in detail by Srinivasan [59]. The primary tools for studying DME coupling are measurements of the low-frequency ME voltage coefficient, voltage output in response to applied magnetic fields at the bending and electromechanical resonance modes, nonlinear ME effects for large AC magnetic fields, static magnetic field-induced polarization, and magneto-dielectric effects. Studies on the nature of CME coupling include low-frequency ME effects under an applied AC electric field and measurement of the induced magnetic flux in a coil wound around the composite, static electric field E-induced magnetization, E-tuning of inductance, or ferromagnetic resonance. Recently, ME measurements on thin films and nanostructured composites have been made by employing scanning probe microscopy (SPM). Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) under an applied magnetic field is used for studies on DME, and magnetic force microscopy (MFM) under an applied voltage is used for analyzing the CME.
From the point of view of functional devices, it is important to control the magnitude of the ME voltage coefficient and its behavior [60]. In a ME composite, the measured DME coupling coefficient is the field conversion ratio between applied Hac and induced Eac under a bias field Hdc, αME = δEac/δHac. For such measurements, it is necessary to first pole (DC poling or Corona poling) the ferroelectric phase in the composite. In general, under a constant applied AC magnetic field, the ME coupling coefficient first increases with increasing Hdc, reaching a maximum at an optimized DC bias (Hbias), and then decreases with further increasing Hdc. When the bias field is reversed, the ME voltage shows a 180° phase shift. The H-dependence tracks the slope of λ versus H. Saturation of λ at high H leads to αME = 0 [27]. For strain-mediated ME composites, it has been shown that αME ∝ qij = (dλij)/dH. This indicates that the ME coefficient is directly related to the nature of the ferromagnetic phase and the effectiveness of elastic coupling between the two phases. Figure 7a demonstrates the typical behavior of the αME, λ, q, and their relationship as a function of Hdc. The variation of magnetostriction as a function of H and the dependence of αME on q suggests the need for additional Hdc. Usually, the αME value is higher when H and δH are parallel to each other and to the sample plane, compared to the out-of-plane magnetic fields due to demagnetization. So far, giant ME responses have been reported in a variety of composite systems and the highest αME was reported for composites with ferromagnetic alloys. Figure 8 summarizes the best values of αME obtained for different combinations of materials in bulk and film-based ME composites having 0-3, 1-3, and 2-2 connectivity.
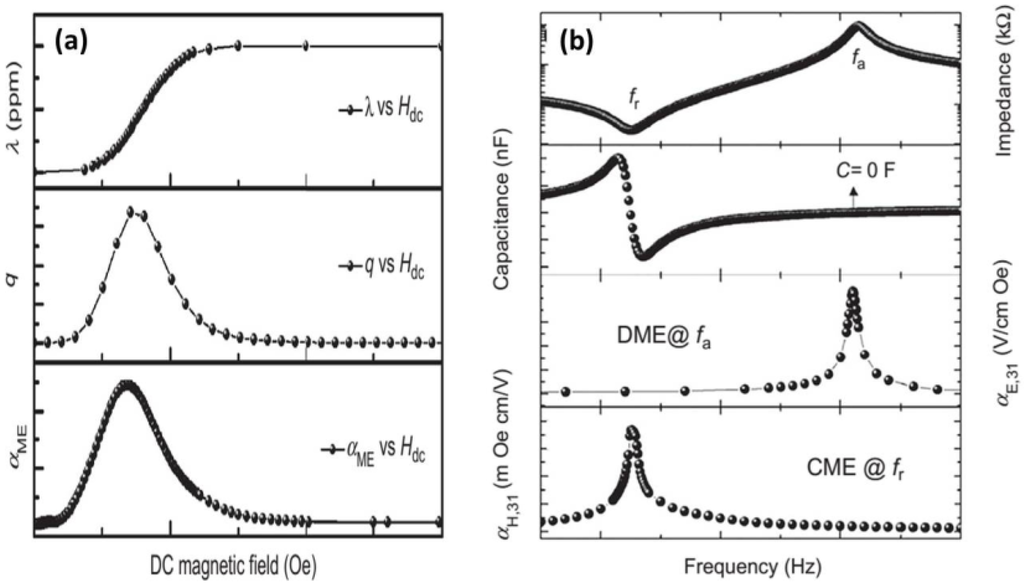
Figure 7.
(a) Typical behaviors of magnetostriction, piezomagnetic coefficient, and ME coefficient as a function of DC magnetic field [60]; (b) Typical behaviors of impedance, capacitance, and DME and CME coefficients as a function of AC frequency [7].

Figure 8.
Reported values of off-resonance ME voltage coefficients for various material systems: (a) bulk and (b) film-based ME composites. Data taken are from Ref. [5,11,21,23,24,25,26,28,34,35,36,37,39,50,52,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71].
Another parameter of importance is the change in ME coupling as a function of applied AC magnetic field frequency (ME vs. fac), which depends on the sample dimensions. When AC magnetic field is applied at a frequency corresponding to the electromechanical resonance (EMR) of the piezoelectric phase, or the ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) of the magnetic phase in the ME composite, the ME voltage coefficient shows a peak behavior, with as much as a 100-fold increase in its magnitude compared to the off-resonance condition. Cho et al. [7] found that the DME coupling was maximized at the anti-resonance frequency (fa), while the CME coupling exhibited peak at the EMR frequency (fr) of the piezoelectric layer, as shown in Figure 7b. This phenomenon was further explained by using piezoelectric constitutive equations and combining them with the frequency-dependent capacitance of the piezoelectric layer. Comparison of both DME and CME coefficients have rarely been performed because it has been challenging to achieve strong DME and CME coupling simultaneously [72].
5. Magnetoelectric Devices and Applications
Several of the bulk as well as film-based ME composites have been reported to exhibit strong ME responses under both off/on resonance conditions. Based on the type of ME coupling and the mechanisms used to control the order parameters, a variety of applications have been proposed, including magnetic sensors, high-frequency inductors, memory devices, and high-frequency signal processing devices (Table 2). Recent progress on the design and development of some of the ME devices will be discussed in this section.

Table 2.
Classification of different ME devices. Adapted from [72].
5.1. Devices Based on the DME Effect
5.1.1. Magnetic Field Sensors
ME material-based sensor devices are considered to be promising alternatives for conventional Hall sensors and giant magnetoresistive (GMR) devices. Because of their passive nature and self-powered operation at room temperature, ME sensors may be able to replace bulky and expensive superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). ME sensors have the potential to perform biomagnetic measurements analogous to all of those performed by MEG and fMRI. The key requirements for magnetic field sensors in this application are (i) sensitivity of ~pT to fT per √Hz at low frequencies (10−2 to 103 Hz); and (ii) ambient temperature and wide bandwidth (0.1 to 100 Hz) operation [73]. The direct ME coupling effect, where the ME voltage coefficient is dependent on AC and DC magnetic fields, would allow the ME composites to sense either an AC or DC magnetic field by monitoring the output electrical signals. Since a current passing through a wire generates a magnetic field in the surrounding space, the ME composite can also be used as a current probe for detecting current by monitoring the corresponding magnetic flux.
Various ME laminate-based sensors have been reported in the literature over the last decade to detect minuscule magnetic fields which could have applications ranging from medical imaging to oil prospecting. Efforts have focused on: (a) different categories of sensor construction [24,74,75,76], geometry and other features [77,78,79,80]; (b) packaging of the sensor units; (c) improvements in fabrication techniques [81]; (d) signal processing conditions [82,83]; and (e) gradiometric configurations to reduce environmental noise sources [84]. The multi-push-pull configurations, multilayer configuration, and bimorphs, all of which exhibit an improved ME voltage coefficient, have demonstrated considerable potential for sensing low-frequency magnetic field variations. A push-pull mode ME laminate consists of a symmetric longitudinally poled piezoelectric PMN-PT single crystal and two longitudinally magnetized magnetostrictive Terfenol-D layers. The symmetric nature allows for optimized elastic coupling between consecutive layers. As a result, a large ME coefficient of 30 V/cm·Oe at a resonance of 77.8 kHz was obtained with a magnetic field sensitivity of 136 pT/√Hz [74]. The very low sensitivity of 5.1 pT/√Hz, which is very close to the predicted value of 4.2 pT/√Hz, has been achieved for a Metglas/PMNT laminate structure with a multi-push-pull (M-P-P) mode that is longitudinally magnetized and longitudinally poled, coupled with a low noise charge amplifier [24]. Fang et al. [85] very recently proposed a Metglas/Mn-PMNT laminate composite consisting of longitudinal magnetized Metglas layers and different numbers (N) of transversely polarized Mn-PMNT fibers connected in series, as illustrated in Figure 9. An ultralow magnetic field sensitivity of 0.87 pT/√Hz at room temperature was reported for these Metglas/Mn-PMNT fiber laminate composites.
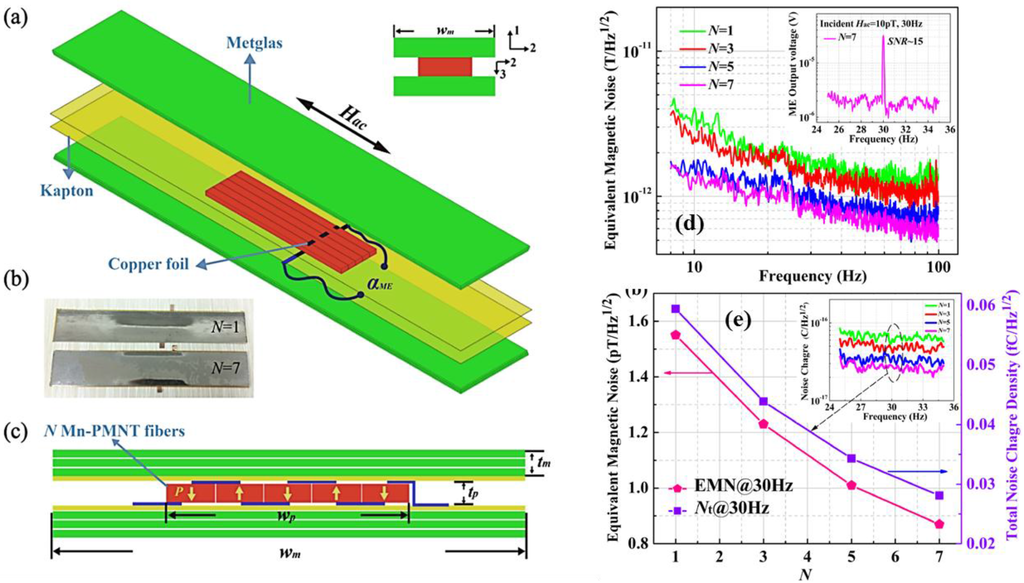
Figure 9.
(a)–(c) 3D structure, photograph, cross-sectional schematic diagram, respectively, of the Metglas/Mn-PMNT composite. (d) and (e) Equivalent magnetic noise level and total noise charge density of the ME magnetic sensors [85].
Thin film-based ME sensors enable the fabrication of miniaturized low-cost sensor devices with high sensitivity and high spectral resolution [86]. Thin film-based architecture also provides the capability for designing sensor arrays that can be integrated with other circuit components. Zhao et al. [87] reported the fabrication of a thin film ME sensor by sputter depositing a Fe0.7Ga0.3 film (1.5 μm thick) over a sol-gel derived PZT film (1.5 μm thick) on a micromachined Si (35 μm thick) cantilever. Substantial improvement in ME coupling was observed due to reduction in substrate clamping by decreasing the Si cantilever thickness (from 180 to 35 μm). The sensor device showed a maximum ME coefficient of 1.81 V/cm·Oe at the electromechanical resonance frequency of 333 Hz and could detect a 2.3 × 10−8 T (2.3 × 10−4 Oe) AC magnetic field with the 50 nV noise floor. Marauska et al. [86] developed a ME sensor system with a stack of SiO2/Ti/Pt/AlN/Cr/FeCoSiB fabricated on a 150 mm thick Si wafer cantilever. The AlN piezoelectric layer (1 μm thick) was grown by reactive pulsed-dc magnetron sputtering, and a (Fe90Co10)78Si12B10 magnetostricitve layer (2.2 μm thick) was sputter deposited in a magnetic bias field of 10 mT. The ME sensor exhibited a maximum ME coefficient of 1000 (V/m)/(A/m) (= 795.8 V/cm·Oe) under resonance at 2.4 kHz with sensitivity of 780 V/T and noise level above 100 pT/√ Hz. Recently, Lee et al. [88] demonstrated all-thin-film ME ac/dc magnetic field sensor arrays made by using PZT and Terfenol-D thin films in the form of 2.98-μm-thick and 300-μm-long microcantilevers (Figure 10a,b). The PZT films, displaying a columnar structure, were deposited by the sol-gel method. Terfenol-D films deposited using the RF magnetron sputtering method formed well crystallized large grains (Figure 10c). The ME voltages were measured at 60 Hz from the cantilevers with the PZT and PZT/Terfenol-D layers with increasing magnetic field between 2 × 10−9 T to 20 × 10−9 T. It was observed that the PZT/Terfenol-D cantilever produced a significant voltage output, while the PZT-only cantilever showed a negligible output (Figure 10d). There was also a gradual increment in the ME voltage of PZT/Terfenol-D in proportion to the DC magnetic field. The minimum detectable DC magnetic field was estimated by applying a DC current of 0.005 μA corresponding to 1 × 10−12 T, and the ME voltage from the sensor measured at 60 Hz AC field in off-resonance mode was found to be 86 μV with a 150-nV noise floor (Figure 10e).

Figure 10.
SEM images and ME properties of ME microcantilever array consisting of Terfenol-D and PZT thin film [88].
5.1.2. Electric Current Sensors
Conventional current sensors, which operate by detecting the electric current induced by magnetic fields are best represented by Hall effect and reluctance devices [89]. Hall devices need to be powered by highly stable constant current supplies, and their inherently weak Hall voltages (5 to 40 μV/Oe) impose great demands on signal conditioners. Reluctance devices require being interfaced with highly precise integrators, and real-time measurements are generally inhibited at low frequencies (100 Hz). In contrast, current sensors based on ME composites do not suffer from these problems due to the extrinsic ME effect exhibited by the composites. In principle, a straight wire carrying an AC or a DC current will excite an AC or DC vortex magnetic field around this wire according to Ampère’s Law. The strength of the magnetic field depends on the current I in the wire and r, the distance from the wire (H = I/2πr). Ring-type ME laminates, therefore, have the essential configurations of electric current sensors. For example, Leung et al. [90] demonstrated a ring-type electric current sensor (Figure 11) operating in vortex magnetic field detection mode. The sensor design was based on a ring-shaped magnetoelectric laminate consisting of an axially polarized PZT piezoelectric ceramic ring bonded between two circumferentially magnetized epoxy-bonded Terfenol-D short-fiber/NdFeB magnet magnetostrictive composite rings. The sensitivity of the electric current sensor was evaluated, both theoretically and experimentally. It was reported that the output voltage had good linear responses to the electric current. The sensor showed a high off-resonance sensitivity of 12.6 mV/A over a flat frequency range of 1 Hz–30 kHz and a large resonance sensitivity of 92.2 mV/A at the resonance of 67 kHz. Excellent linearity and large current sensitivity of 114.2 mV/A was observed in a Metglas/PZT laminate when measuring low-frequency alternating magnetic fields of 50 Hz [91]. This sensor is ideally suited for power-line current measurement. By combining an ME ring with a piezoelectric transformer structure, Zhang et al. [92] achieved a high resonance sensitivity of ∼157 mV/A at electromechanical resonance frequency of 62 kHz. Yu et al. [93] have recently reported the design and implementation of a cantilever-type device for a current sensor based on two layers of longitudinally magnetized Terfenol-D and one layer of transversely polarized piezoelectric PZT material. The layers were epoxy-bonded, and the wire conducting the current was coiled along the device and the output voltage was obtained across the two surfaces of the PZT. Compared with a ring-type current sensor, this sensor could be installed and maintained without any interruption in the power supply, which was very convenient and practical. The high-sensitivity, power-free, bias-free, and wide-bandwidth nature of the ME current sensor also provided great potential for real-time monitoring of the conditions of engineering systems which have electric current-carrying cables or conductors.
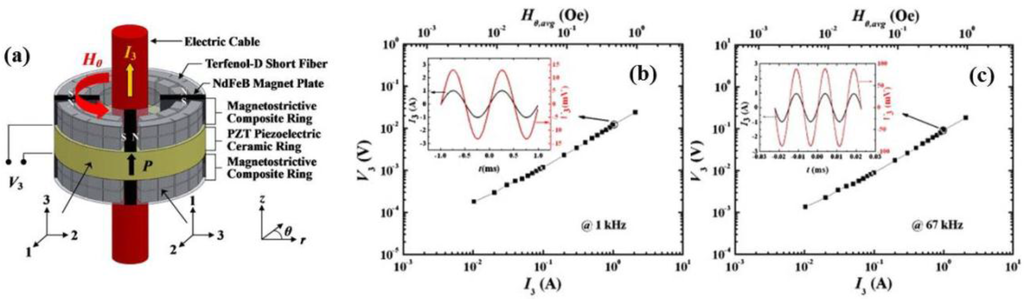
Figure 11.
(a) Schematic diagram of the proposed ring-type electric current sensor. (b) and (c) The AC electric voltage (V3) output from the sensor as a function of both the AC electric current (I3) and its associated average AC vortex magnetic field (Hθ,avg) [90].
5.1.3. Energy Harvesters
Harvesting energy from ambient energy sources such as vibrations, sound, radiofrequency waves, light, temperature gradients, wind, and others is an area of focus for current and next-generation remote monitoring electronic devices and self-powered wireless sensor networks with the goal of improving device lifetime and addressing the limitations of conventional batteries. In addition, the ambient environment is filled with magnetic noise of 50–60 Hz almost everywhere these days. Harvesting this weak and low-frequency magnetic noise (< 1 mT = 10 G) to develop a consistent electricity source remains a difficult challenge. Over the last decade, Ryu group [47,94,95] and other researchers [96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105] have investigated methods to obtain optimum electricity from the tiny magnetic fields in the surroundings, using magneto-mechano-electric (MME) mechanism. The operation mechanism can be described as follows: When the ME composite is placed in an AC magnetic field, the magnetostrictive layer in the composite responds to the mechanical vibration (magneto-mechano coupling), thereby straining the piezoelectric layer, which results in an output voltage across the electrical load through the direct piezoelectric effect (mechano-electric coupling). Due to the existence of the piezoelectric phase in the ME composite, any mechanical oscillation applied to the composite directly creates electrical voltage. Consequently, the MME generator could be used to harvest energy from both the magnetic field and external vibrations at the same time [95]. This sequential operating process is schematically depicted in Figure 12a.
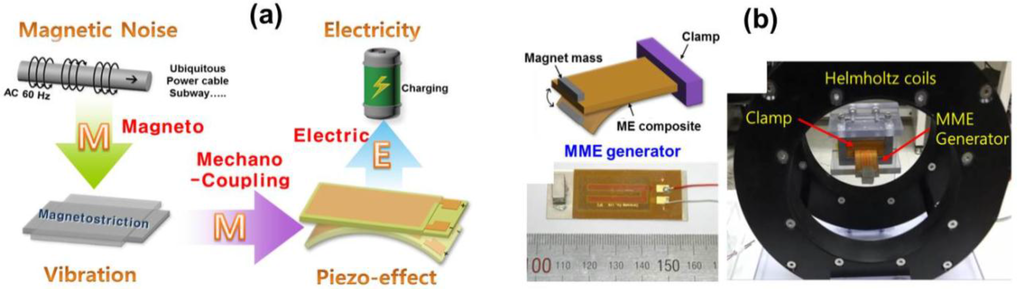
Figure 12.
(a) Schematic depicting the working principle of Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) energy harvester; (b) Schematic and photo of cantilever structured MME energy harvester [95].
By selecting high performance piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials and by optimizing the composite structure, it is expected that high electric power density can be obtained from a low-frequency magnetic field using the MME generator. Gao et al. [103] designed an asymmetrical bi-layered push-pull mode Metglas/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 laminate, and obtained a giant αME of more than 400 V/cm·Oe with a tunable resonance frequency in the range of 60 Hz to 220 Hz by tip mass loading. The maximum harvested power output was about 16 µW/Oe with a 6 MΩ resistance load, with a corresponding power density of 200 µW/cm3 at 60 Hz. Dong et al. [104] achieved a power output of 420 µW/Oe across a 50 kΩ load under an AC magnetic field of 1 Oe at about 21 kHz using an ME cantilever based on the push-pull type Metglas/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 laminate. The ME laminate configuration, with an optimized beam aspect ratio of 0.86, exhibited an output power gain of 52.5 mW, and a corresponding power density of about 28.5 mW/cm3 at 30 Hz under 6.9 m/s excitation (0.7 g acceleration) at the resonance frequency, even in the absence of a DC bias magnetic field [105].
Ryu et al. [95] demonstrated an MME generator constructed using an anisotropic and flexible piezoelectric Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 (PMN–PT) single crystal fiber composite (SFC), a cost-effective magnetostrictive Ni plate and Nd permanent magnetic proof mass (Figure 12b). The flexibility of the SFC ensures the high compliance of the sample, which is ideal for achieving low resonance frequency in a cantilever structure. The flexibility also increases device durability and enables the application of increased strain magnitudes. The Ni plate can be easily self-biased and generates a linear strain response in a low-level magnetic field environment. The performance of the MME generator containing an anisotropic <011> SFC with d32 mode under a small noise level magnetic field is shown in Figure 12b. At 60 Hz, and Hac∼500 µT, the maximum generated voltage was ∼34 Vpp (∼12.4 Vrms). The power from the MME generator was high enough to fully charge a 220-µF electrolytic capacitor after rectifying for 3 min. Using the stored power in the charged capacitor, the device was able to turn on 35 commercial high intensity LEDs with a turn on/off frequency of ∼1 Hz. Seeking to improve the output power density, many research groups have developed various MME harvesters using different combinations of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric materials; some of these are summarized in Figure 13. These results represent significant advances towards next-generation remote monitoring electronic devices and self-powered wireless sensor networks.

Figure 13.
Summary of reported power densities from the MME harvesters made with different composite systems. Data are from references [94,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105].
Efforts have also been made to develop energy harvesters based on ME composite films. Onuta and colleagues [101] developed miniaturized energy harvesters using all-thin-film ME structures consisting of piezoelectric Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 (PZT) and magnetostrictive Fe0.7Ga0.3 layers (Figure 14). The device was fabricated on a micromachined Si cantilever coated with a silicon oxide/nitride/oxide (ONO) stack (3.8 μm thick). The Fe0.7Ga0.3 layer (500 nm thick) was sputtered on the Pt-buffered PZT layer (500 nm thick) deposited over the ONO stack. The film-stress in the ONO stack was engineered, and a photo-lithographic process was employed to make an unbent, free-standing cantilever beam structure (950 μm long and 200 μm wide). The chip (6.6 mm × 6.6 mm) containing six cantilever devices was mounted in a vacuum chamber placed between a pair of Helmholtz coils, and it was aligned parallel to the magnetic fields. The results of the energy harvesting measurements from a single ME device are shown in Figure 14b,c. The voltage output from the harvesting device became saturated at higher external loading, while the power output was peaked at a load impedance of 12.5 kΩ (Figure 14b) from which the peak power density was determined to be 0.7 mW/cm3 (RMS). Further, both the voltage and power outputs have shown saturation plateaus with respect to increasing Hac (Figure 14c), and such behavior was attributed to the saturation of the internal stress of magnetic origin that involves the rotation of the magnetization vector.
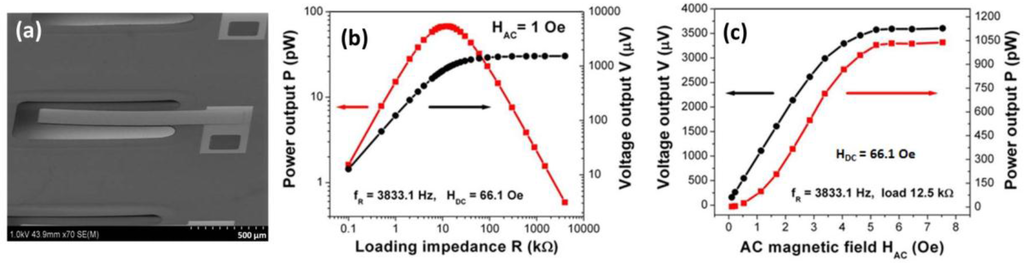
Figure 14.
(a) SEM micrograph of a thin film ME energy harvester based on PZT/FeGa and (b,c) its energy harvesting properties [101].
5.1.4. Magnetic Recording Read Head
Magnetic recording read heads in hard disk drives function based on one of the magneto-resistance (MR) effects, i.e., anisotropic magneto-resistance (AMR), giant magneto-resistance (GMR) or tunneling magneto-resistance (TMR). The MR read head contains a sensing stack along with several additional layers and structures that ensures the proper biasing and shielding of the sensor [106,107]. During operation, the internal resistance of the MR sensor changes due to interaction with the stray fields from the recorded bits of a magnetic recording medium. The change in resistance (∆R) is translated into a read signal as a voltage amplitude change ∆V = I × ∆R. However, it is necessary to pass a constant DC test current through the sensor stack to detect the change in the resistance/amplitude. Higher recording densities can be achieved by reducing the shield-to-shield spacing, which is possible by thinning down the sensor stack. But such a trimming of the sensor size inflicts complications in fabrication and in the operation of the sensor and the read head.
Vopson et al. [106] proposed a new design for a magnetic recording read head sensor based on the DME, i.e. the magnetically induced ME effect, as shown in Figure 15a,b. The proposed sensor stack incorporates a tri-layer ME composite structure and consists of 7 layers, arranged as seed/AFM/FM/FE/FM/AFM/cap, which is much simplified in comparison with the existing TMR sensor stack, which has around 15 layers. The two AFM layers added adjacent to the FM layers produce the required DC bias magnetic field. This design will facilitate reduction in sensor size without sensitivity loss and will eliminate the need for permanent magnets currently used for horizontal biasing. Since the ME-based sensors operate without using any electric power, there will be no need for the DC test current through the sensor, and the data can be read back directly as an induced voltage. This will reduce power consumption as well as minimize the Joule heating issues that occur in the high resistance TMR sensors.
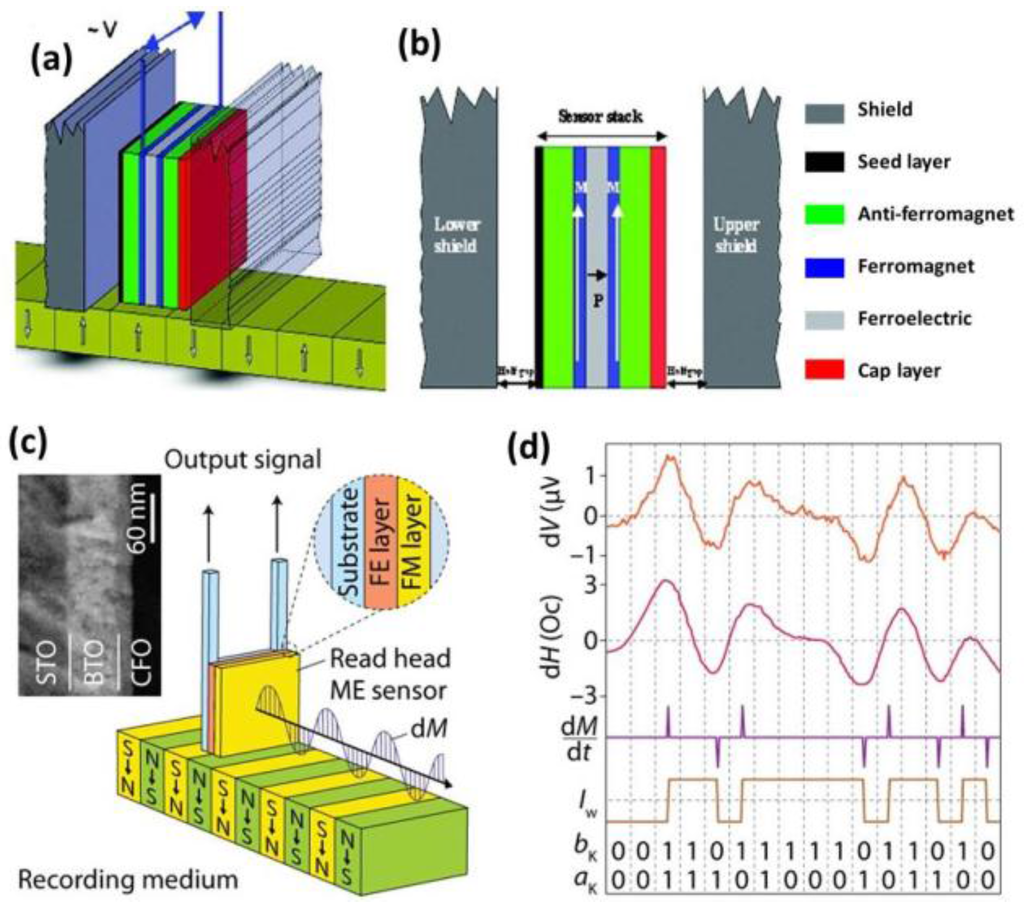
Figure 15.
(a) and (b) 3D diagram and cross-section of the magnetic read head proposed by Vopson et al. [106] (c) and (d) Schematic, TEM image (inset) and voltage output of an ME read-head sensor based on a bilayer CFO/BTO heterostructure grown on a single-crystal STO substrate [107].
Zhang et al. [107] developed a prototype ME read head (Figure 15c) fabricated with BTO-NFO and BTO-CFO bilayered heterostructures that was grown using PLD on 0.7% Nb-doped STO single crystal substrates. The ME sensitivity of this structure was measured to be about 0.5 V/Oe at 1 kHz. To illustrate the reading and writing process, a primal 16-bit input signal (ak) was written on the disk tracks by a writing current (Iw) in non-return-to-zero format after being encoded into a new signal (bk). These written bits bk were able to yield a media field δH in the recording medium. A small in-plane δH (about a few Oersted) that was considered to model the media fields (Figure 15d) from the bits in the recording medium was generated using a set of small Helmholtz coils, and a response signal of 1–2 μV was obtained. In the fully developed device case, greatly enhanced outputs (mV) were expected by applying higher amplitudes of media fields (∼100 Oe) and by operating the device at the resonance frequency.
5.1.5. Biomedical Applications
Motivated by the advances in multiferroics, ME composites have been suggested for biomedical applications such as wireless endoscopy, minimally invasive surgical tools, and stimulation of functions of living cells [73,108]. The potential use of ME nanoparticles (MENs) as carriers for on-demand drug release and to artificially stimulate the neural activity deep in the brain has also been suggested [109,110].
Wireless capsule endoscopes (WCEs) are often used to examine the gastrointestinal (GI) tract for clinical diagnosis (Figure 16a). Though the WCEs are far less invasive compared to conventional endoscopes, the passive nature of WCEs makes it difficult to control their position and orientation as the capsule moves along the GI tract. Currently, tracking of WCEs is carried out by methods such as radio frequency (RF) triangulation, magnetic tracking, radiation vision, and ultrasound sensing. However, accurate localization and high fidelity tracking of WCEs is still a challenging task. In the magnetic tracking method, a permanent magnet is placed inside the wireless capsule, which is located at an x, y, z location inside the human GI tract with respect to a reference frame. Since the permanent magnet emits a magnetic field, it can be identified using a magnetic sensor, such as a 3-axis magnetic sensor, which can approach nT sensitivity. It has been proposed that multiferroic ME transducers are promising candidates to provide WCE position feedback, by using them in the form of enhanced sensitivity (pT range) magnetic field sensors [73]. By incorporating a MEMS-based ME composite structure into the WCE capsule, power can be generated on demand as required for recharging the battery of the WCE. Further, the use of self-biased ME composites will reduce complexity in the device design. To improve its diagnostic capabilities, focused efforts are needed, particularly to achieve reliable control over the movement and orientation of the capsule within the constraints of the size and shape of the device.
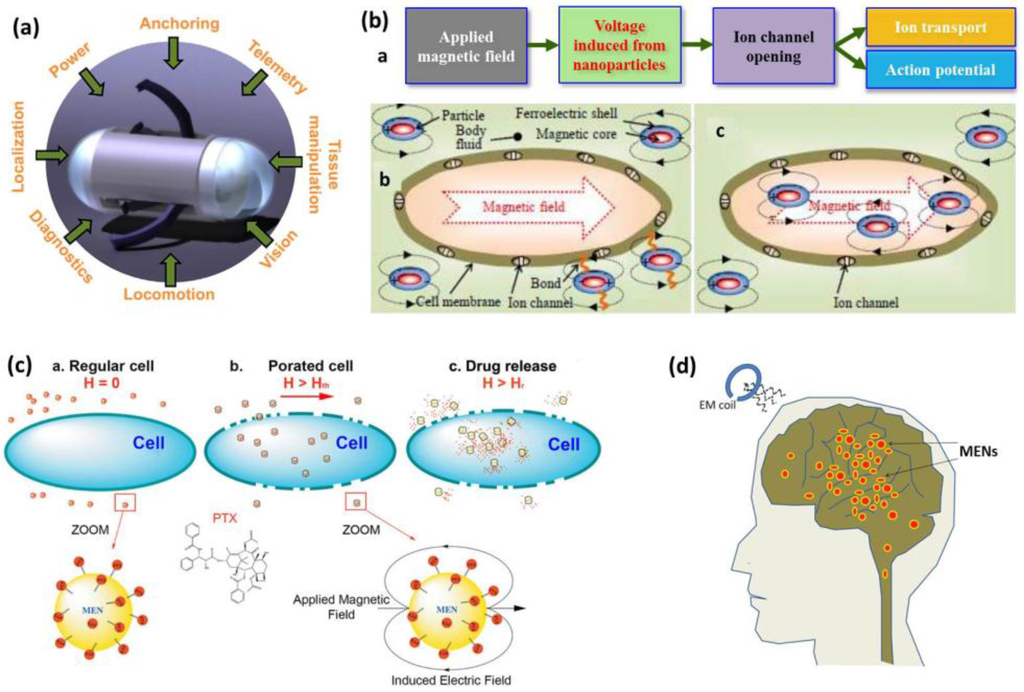
Figure 16.
(a) Key functionalities that complement the wireless capsule endoscopes [73]; (b) Illustration of possible mechanisms of stimulation of ion channels: a chain of actions triggered by the applied magnetic field pulses, external and internal stimulation by uptaken nanoparticles [108]; (c) MENs as field-controlled nano-electroporation sites to let the drug through the cancer cell membranes [109]; (d) Illustration of the deep brain stimulation approach [110].
Controlling the function of biological macromolecules is of vital importance in health science studies. Approaches used to stimulate cell functions include the use of the heat generated by hysteresis losses in magnetic nanoparticles placed in a high-frequency magnetic field, and the mechanical agitation of magnetic nanoparticles attached to cells using external low-frequency magnetic fields [111,112]. The interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological macromolecules can be understood by studying the ion channels which regulate several cellular processes, such as action potentials in neurons or muscle contraction. Ion channels are membrane proteins that form pores for the controlled exchange of ions across cellular membranes [113]. The common type, voltage-gated ion channels open or close in response to a transmembrane electric field. Ion channel-related disorders have been found to cause several health issues, which are usually treated using pharmacological agents that modify the gating kinetics, or block the channel transiently or permanently. Recently, Kargol et al. [108] proposed an innovative approach, based on the use of core/shell structured MENs with a ferromagnetic core and a ferroelectric shell, that would allow the remote control of ion channel gating via externally applied magnetic fields (Figure 16b). In this approach, electric fields in the vicinity of the cells generated by MENs introduced extra- or intracellularly can be locally modified to invoke appropriate conformational changes in the ion channels. The resulting local depolarization or hyperpolarization of the membrane will lead to opening or closing of the ion channels accordingly. Because of the remote way in which the stimulation will be performed, individual cells or selected groups of cells can be targeted, rather than whole tissues.
Targeted drug delivery with adequate high specificity (to tumor cells) remains a formidable task in the treatment of cancer in general, particularly ovarian cancer. Although the survival rates have been improved by intraperitoneal (IP) delivery through a surgically implanted catheter, toxicity and catheter complications have precluded widespread adoption of this invasive means of delivery. Guduru et al. [109] addressed this challenge by exploiting the dependence of the membrane’s porosity on the electric field, i.e. electroporation that can be utilized to trigger drug delivery into the cells. Above a threshold magnetic field (Hth), the MENs loaded with the drug and optionally with the biomarker-specific antibodies (for delivery to the tumor cells) can generate localized fields large enough to open up the membrane pores in their proximity and thus allow the delivery of the drug inside the tumor cells. The drug can be released off the MENs by further increasing the field above the second critical value, Hr, necessary for overcoming the drug-MEN binding energy. This hypothesis was testified through in vitro studies on human ovarian carcinoma cell (SKOV-3) and healthy cell (HOMEC) lines, where a 30-Oe DC bias was applied to trigger high-specificity uptake of Paclitaxel (PTX) loaded on 30-nm CoFe2O4/BaTiO3 core/shell MENs. The drug penetrated through the membrane and completely eradicated the tumor within 24 h without affecting the normal cells.
In the human neural network, chemical and electrical synapses transfer information between adjacent axons and dendrites directly or indirectly through electric field energy. The ability to efficiently control the network at micro- or even nano-scale can enable significant control over important brain functions. Existing non-invasive brain stimulation methods including repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) are limited in their depth and locality. A potential solution would be to use MENs for non-invasive control of the neural network. In this approach, very low intensity external magnetic field is required to stimulate brain activity at any depth in the brain and the field can be focused to act upon MENs in any particular region of the brain. The external magnetic field generates AC signals in ME nanoparticles that are correlated with the frequency spectrum of the neural activity, which in turn causes neurons in that region to fire at similar frequencies (Figure 16d). Yue et al. [110] modeled the effect of MENs to non-invasively stimulate the brain of a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Using the optimized values for the concentration of the 20-nm nanoparticles (with αME of 100 mV/cm·Oe in the aqueous solution) of 3 × 106 particles/cc and excitation frequency of the externally applied 300-Oe magnetic field of 80 Hz, the pulsed sequences of the electric field were brought to the levels comparable to those of healthy people.
5.2. Devices Based on the CME Effect
5.2.1. Magnetoelectric Random Access Memory
Ferroelectric random access memory (FeRAM) stores binary information using ferroeletric polarization states, while magnetic random access memory (MRAM) stores data bits using magnetization states and the property of magneto-resistance in multilayers. Applications of these memory devices are limited by the need for destructive read and reset operations in FeRAM, and by inconveniences in the write process in MRAM caused by the requirement for large currents for magnetization reversal. The mutual control of magnetic order and electric polarization in ME materials can be exploited to combine the best features of FeRAM and MRAM, and thus create a novel type of non-volatile RAM, i.e. MeRAM with multiple memory states [114]. This approach would offer greater memory density, reduced power consumption, and improved thermal stability. Bibes et al. [115] proposed a hybrid MeRAM device that combines the ME coupling in a multiferroic (consisting of FE and AFM phases) layer with the interfacial exchange bias between the multiferroic AFM phase and a FM layer to induce magnetization switching through voltage control. One challenging task in the realization of practical MeRAM devices is the achievement of reversible 180° deterministic switching of magnetization, on which existing magnetic memories, including hard disk drives and MRAMs, rely upon. Heron et al. [116] approached this issue through E-field control of exchange bias in multiferroic/magnetic (CoFe/BiFeO3) heterostructures. Xue et al. [117] demonstrated that the E-field induced near 180° magnetization switching in the AFM/FM/FE heterostructures through voltage-controlled tuning of exchange bias and through manipulation of coercive fields. The irreversibility of the E-field induced near 180° magnetization switching in AFM/FM/FE heterostructures was resolved by employing a magnetic impulse, which could switch the magnetization back and lead to a continuous magnetization switching [118]. The heterostructure was formed by epoxy gluing of the magnetron sputtering deposited exchange coupled multilayer structure of NiFe/NiCoO/glass to a (011) cut PZN-PT single crystal, with the magnetic easy axis along the [100] or [] PZN-PT crystal directions (Figure 17a). Switching magnetization was very close to the saturation magnetization (from ~Ms to −0.95 Ms along PZN-PT []; from 0.76 Ms to −0.9 Ms along PZN-PT [100]), which implies that near 180° magnetization reversal was observed in the NiFe/NiCoO/glass/PZN-PT heterostructure. The reported findings are a significant advancement in realizing the voltage writing of magnetic bits in MeRAM.

Figure 17.
Magnetization switching by E-field in NiFe/NiCoO/glass/PZN-PT heterostructure-based MeRAM [117].
5.2.2. Phase Shifters
Microwave phase shifters are important elements for radar applications, telecommunications, oscillators and phased array antenna systems. A wide variety of phase shifters based on semiconductors, ferrites, and ferroelectrics have been developed [119,120,121]. The ferrite-based phase shifters are based on the Faraday rotation of electromagnetic radiation in magnetized ferrite rods in waveguides. Large magnetic bias fields are required for phase tuning, which involves huge power dissipation; consequently they cannot be miniaturized in size or made compatible with integrated circuit technologies. A second class of microwave phase shifters is based on ferroelectric materials. Their distinguishing features are fast electric tunability and low power consumption. However, such phase shifters are very lossy at frequencies above 1–5 GHz. A ferrite-ferroelectric layered structure, such as a ME composite, opens up the possibility of dual-tunable microwave devices, which offers higher efficiency, lower noise, compact size and lightweight compared to conventional microwave deceives. Following theoretical investigations, Ustinov et al. [122] reported the development of such ME devices. Their ME dual phase shifter based on FMR is a bilayer ME composite consisting of a ferrite YIG layer with a thickness of 5.7 μm and a ferroelectric BST layer with a thickness of 500 μm. The schematic structure of the cross-section of a ME dual phase shifter is displayed in Figure 18a. The electric field control of the phase shift arises through a strong ME coupling in between the ferrite and ferroelectric layers. For an applied electric field E = 20 kV/cm, a maximum differential phase shift, Δφ = 650° was achieved. The estimated figure of merit of the phase shifter was about 25 °/dB. An electric field tunable YIG/PZT phase shifter was also designed and characterized by Tatarenko et al. [123]. For E = 5–8 kV/cm and Δφ = 90–1800, an insertion loss of 1.5–4 dB was obtained. The observed insertion loss was somewhat closer to the desirable 0.5 dB needed for practical applications. Recently, bilayers of hexaferrites and piezoelectric PZT were used for novel design of phase shifters. For a strip-line Zn2Y/PMN-PT phase shifter, data on the differential phase shift versus E indicated a differential phase shift of 500 for E = 12 kV/cm, a linear variation in the phase shift with E, and an insertion loss of 4–8 dB [124].
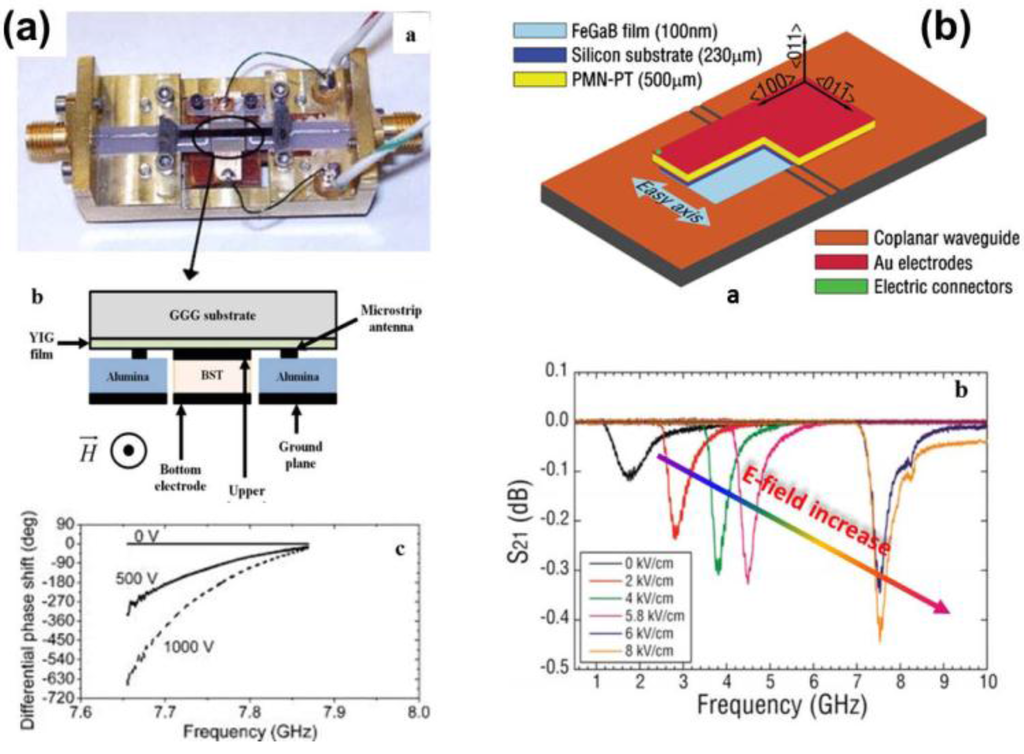
Figure 18.
(a) Experimental prototype of the YIG/BST phase shifter, schematic of cross-section of the device and the YIG/BST layered structure, and electrically induced differential phase shift [122]; (b) Schematic of sample configuration and microwave measurement setup, and electric field dependence of the transmission coefficient (S21) spectra of the FeGaB/PZN-PT resonator [132,133].
5.2.3. Resonators
Resonators are front-end elements in phased array radars, and are also used in filters and phase shifters. At the ferromagnetic resonance (FMR), a ferromagnetic material is subjected to high-frequency excitations [125]. FMR devices based on soft magnetic materials are utilized in microwave signal processing devices, resonators, band-pass/band-stop filters and phase shifters. Such devices require a magnetic field to operate and to achieve frequency tuning, which creates disadvantages like slow operation, high noise levels, large power consumption, and limited miniaturization. By replacing ferrite materials with ME composites, electrical tuning of FMR is possible. Fetisov et al. [126] experimentally demonstrated an electric field tunable 1–10 GHz microwave planar resonator using a YIG/PZT composite. The device consisted of a single micro strip (50 mm thick and 3 mm long) deposited onto an Al2O3 substrate. For a signal input of 2–10 GHz, 0.1 mW of power was applied to the microstrip transducer. Low input power was chosen to prevent heating of the sample due to power absorption at the FMR. For zero applied electric field (E = 0), the spectra contained a well-defined FMR absorption peak at about 3.5 GHz, with a maximum insertion loss of 45 dB and a 3-dB line-width of Δf = 3.4 MHz. The off-resonance loss could be partially due to ferroelectric losses in the PZT. When the electric field E = 10 kV/cm was applied, the FMR peak shifted by 40 MHz to a lower frequency. When the electric field E = −10 kV/cm was applied by reversing the voltage applied to the PZT, the peak up-shifted by 38 MHz. The converse ME coupling constant A = Δf/E ≈ 4 MHz cm/kV, and the voltage tuning for E = ±10 kV/cm was only about 2% of the central frequency. Li et al. [127] reported X-band resonator studies using epitaxial nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) films (thickness of about 2.0 μm) deposited on PZN-PT or PMN-PT substrates using direct liquid injection chemical vapor deposition. A strong ME coupling resulting in large shifts in the FMR profile was observed, and were due to electrostatic field-induced anisotropic magnetic field changes. The data indicated an ME coefficient A = δH/E = 20 Oe·cm/kV (or 60 MHz cm/kV) at 9 GHz and 11 GHz, which is an order of magnitude higher than that for YIG/PZT. The main drawback with the use of ferrite material is the large FMR line-width.
Recently, hexagonal ferrites have been used for resonators over a wide frequency range from 15 to 110 GHz [128,129,130]. The Y-(Ba2Zn2Fe12O22:ZnY) and Z-type (Ba3Co2Fe24O41) hexagonal ferrites with easy-plane magnetic anisotropy are preferred for use at 10–40 GHz [128]. M-type hexaferrites, MFe12O19 (M = Ba, Sr) with uniaxial magnetic anisotropy are ideal for the frequency range 40–75 GHz [129]. The Al doped M-type hexaferrites further increase the resonance frequency, and are suitable for 50–110 GHz devices [130]. Tatarenko et al. [131] reported the converse ME effect over the 8–25 GHz range in bilayers of single crystal ZnY and polycrystalline PZT or single crystal PMN-PT. The resonator was tuned by 120 MHz with E = 12 kV/cm, and corresponding ME coupling strength A was about 10 MHz cm/kOe. Lou et al. [132,133] reported a layered ferroic FeGaB and single crystal piezoelectric PZN-PT-based resonator. They observed that a large electric field induced an effective magnetic anisotropy field of 750 Oe with a narrow FMR line-width of 50 Oe at X-band. This resonator achieved a large electric field tunable FMR frequency range between 1.75 and 7.57 GHz even at zero magnetic bias field, as shown in Figure 18b, which corresponds to a mean tunable frequency per unit electric field of about 970 MHz cm/kOe. The giant tunable magnetic field and FMR frequency of the FeGaB/PZN-PT resonator makes it a promising candidate for wide-band electric field tunable microwave devices. Compared to conventional tunable microwave magnetic devices, which are tuned by magnetic fields, these electrostatically tunable microwave multiferroic devices are much less noisy, and more energy efficient, compact, and lightweight.
5.2.4. Inductors
One of the three fundamental components for electronic circuits, tunable inductors, find widespread use in various applications such as communication systems and power electronics. Most tunable inductors are magnetically tuned by using electromagnets. Since electromagnets are typically bulky, noisy and energy consuming, they are inconvenient for use in such applications. Efforts have been made to develop electronically tunable inductors that have large tunability, high quality factors, and low energy consumption. For example, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS)-based tunable inductors can have very high quality factors, although they have a limited tunable range of 20% and are difficult to fabricate. The use of ME composites as a core material could be advantageous for tunable inductor applications since tuning magnetic properties by electric field is possible even at low fields. A variety of ME composite-based inductors have been made using different structures. Tunability is calculated from inductance (L) using the formula [ΔL/L0 = (L − L0)/L0] × 100. Fang et al. [134] have reported a PZT/MnZn/PZT composite inductor that showed a small tunable inductance range ΔL/Lmin of up to 20%. Lou et al. [135] reported a composite consisting of a combination of PZT slab and two layers of amorphous Metglas ribbons with a large tunable inductance range ΔL/Lmin of up to 450%, together with improved quality factors (Figure 19a). This tunability of inductance and increased quality factor were due to strong ME coupling in the composite core, which led to electric field-induced permeability change. However, due to the relatively large thickness of the Metgals ribbons (∼25 µm), excessive eddy current loss limits the operational frequency range of the conventional Metglas-based inductors to be <100–200 kHz, and leads to low quality factors of these inductors at microwave frequencies. Recently, Lin et al. [136] investigated the effect of ferromagnetic layer thickness on the performance of ME inductors. The inductance tunable range of ΔL/Lmin of 370% was achieved, together with a significant 3-fold enhancement in quality factor, with an increase in the operational frequency range. To miniaturize the inductor, a ring inductor was designed by Mandal et al. [137] using insulating single phase Bi0.7Dy0.3FeO3 multiferroic material, but the tunability of the inductor was only about 18%.
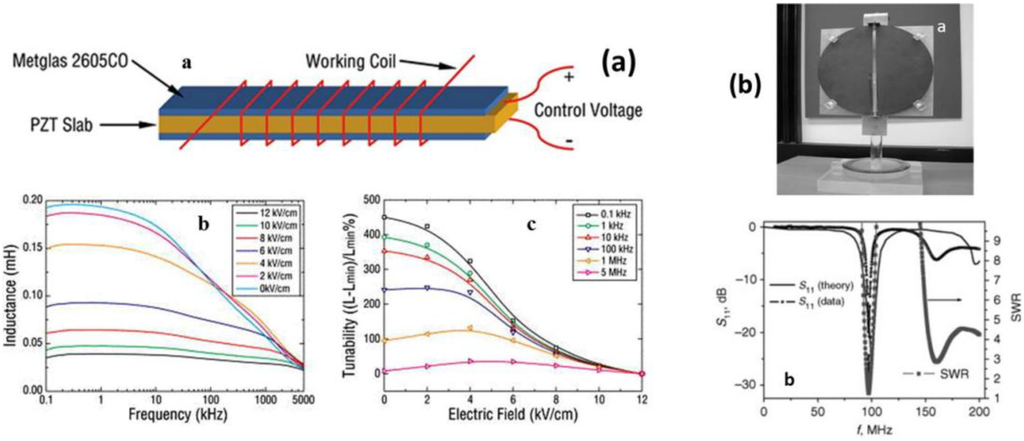
Figure 19.
(a) Schematic of the magnetoelectric inductor, inductance spectra, and inductance tunability at different frequencies and electric field [135]; (b) Miniature microstrip antenna on NZFO/BST composite substrate, measured and estimated return loss and measured SWR for the antenna [140].
5.2.5. ME Antenna
In recent years, reduction in antenna size, which is suitable for lower frequency bands where wavelength is larger, has received significant attention because of the demands of numerous mobile communication systems. Several approaches have been devised to achieve antenna size reductions [138,139]. The first is to use capacitive or inductive loadings and/or meandered lines to obtain slow-wave resonance. The main drawbacks to these approaches are increased ohmic losses and narrow bandwidths. The second is to reduce the wavelength of the structure using dielectric materials, but this is prone to surface-wave excitations and corresponding losses of efficiency. A new approach was recently found that uses a novel engineered ME composite material. A half-wavelength resonant microstrip antenna on an ME composite of nickel zinc ferrites (Ni1-xZnxFe2O4:NZFO) and ferroelectric BST was made by Petrov et al. [140]. They concentrated on the miniaturization of the 100-MHz antenna, and its effects on impedance matching, bandwidth and efficiency (Figure 19b). The ME composite disc with a diameter of 22 cm and thickness of 0.85 cm was metallized on one side, and the microstrip had a length of 22 cm and width of 0.65 cm. A vector network analyzer was used for measurements of return and transmission losses. The measured SWR at resonance was close to 1.3 and indicated good impedance matching with free space. The absence of reflection at the boundary between the substrate of the antenna and the surrounding medium reduced the energy absorbed in the substrate. The helical antennas were fabricated using Co2Z type hexaferrite and ferrite substrates [141,142]. The resonant frequency and bandwidth at 10 dB for the antennas were measured to be 195 MHz and 27 MHz, and 209 MHz and 41 MHz, respectively. A helical antenna was also fabricated on (Co/Ti) doped BaM substrate (45 × 11 × 3.8 mm3), and the antenna was then mounted on an FR4 board (10 × 5 mm2) with an 8 × 5 mm2 copper ground [143]. A 50-Ω coaxial cable was used to feed the antenna. The antenna performance was characterized with a network analyzer and a Wheeler cap. The antenna resonant frequency shifted from 231 to 201 MHz with increasing permeability from 4.51 to 8.58. This data indicates that the factor of miniaturization of the antenna is about 7% with a permeability of 8.58. It is worth noting here that the low-loss (Co/Ti) doped BaM is an excellent soft magnetic material for miniature antenna applications in a very high-frequency (30–300 MHz) range.
6. Summary
In recent years, much attention has been paid towards exploiting the promising technological potential of magnetoelectric coupling in materials. Although there has been tremendous progress in the development of both bulk and film-based ME composites, efforts are likely to continue in the pursuit of desired levels of performance. To realize strong ME coupling and high performance ME composites it is essential to select the appropriate combination of piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials with better properties; adopt a suitable fabrication approach and configuration of the composite constituents; optimize interfacial coupling; reduce the noise contributions to the output signal; tune and control other dynamic parameters; and achieve a comprehensive understanding of the contributing factors and physical phenomena by theoretical modeling. To effectively employ the coupling across interfaces in ME composites and to achieve giant ME effects, the nature of the interfaces should be unraveled. ME-based devices are compact, light-weight, fast in response, less noisy, and energy-efficient and thus are viable alternatives for some existing conventional electrical and magnetic devices. Although some prototype devices based on bulk ME composites have been demonstrated, challenges still exist in terms of obtaining control over materials properties and fabrication, and optimization of the device performance. Further, the reliability of the ME composite systems needs to be evaluated in practical device designs. While much work remains to be done to accomplish on-chip integration of the ME devices, there is significant scope, and many avenues can be explored.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Global Frontier R&D Program (Grant Nos. 2013M3A6B1078872) on Center for Hybrid Interface Materials (HIM) of the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, Korea and internal R&D program of Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS). S.P. would like to acknowledge the financial support from Office of Basic Energy Science, Department of Energy, USA through Grant No. DE-FG02-06ER46290.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Lin, Y.; Nan, C.-W. Multiferroic magnetoelectric composite nanostructures. NPG Asia Mater. 2010, 2, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Islam, R.; Dong, S.; Viehland, D. Recent advancements in magnetoelectric particulate and laminate composites. J. Electroceram. 2007, 19, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.-W.; Bichurin, M.I.; Dong, S.; Viehland, D.; Srinivasan, G. Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: Historical perspective, status, and future directions. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 031101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, C.A.F.; Hoffman, J.; Ahn, C.H.; Ramesh, R. Magnetoelectric coupling effects in multiferroic complex oxide composite structures. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2900–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Priya, S.; Uchino, K.; Kim, H.-E. Magnetoelectric Effect in Composites of Magnetostrictive and Piezoelectric Materials. J. Electroceram. 2002, 8, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Datta, S. Ultra sensitive magnetic sensors integrating the giant magnetoelectric effect with advanced microelectronics. Ph.D. Thesis, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.-H.; Priya, S. Direct and converse effect in magnetoelectric laminate composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 232904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnham, R.E.; Skinner, D.P.; Cross, L.E. Connectivity and piezoelectric-pyroelectric composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 1978, 13, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.-W.; Jia, Q. Obtaining ultimate functionalities in nanocomposites: Design, control, and fabrication. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Ryu, J.; Choi, J.J.; Park, D.S.; Ahn, C.W.; Priya, S. Giant Magnetoelectric Coefficient in 3–2 Nanocomposite Thick Films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 080204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, S.M.; Fitchorov, T.; Obi, O.; Jiang, L.; Hao, H.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Harris, V.G. Effects of intrinsic magnetostriction on tube-topology magnetoelectric sensors with high magnetic field sensitivity. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17C734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Priya, S. Multiferroic Magnetoelectric Composites/Hybrids. In Hybrid and Hierarchical Composite Materials; Kim, C.-S., Randow, C., Sano, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 95–160. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, R.; Rong, C.-B.; Liu, J.P.; Priya, S. Effect of gradient composite structure in cofired bilayer composites of Pb(Zr0.56Ti0.44)O3–Ni0.6Zn0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 system on magnetoelectric coefficient. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 6337–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G.; DeVreugd, C.P.; Flattery, C.S.; Laletsin, V.M.; Paddubnaya, N. Magnetoelectric interactions in hot-pressed nickel zinc ferrite and lead zirconante titanate composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2550–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.H.; Shen, Z.J.; Zhou, J.P.; Shi, Z.; Nan, C.-W. Magnetoelectric composites of nickel ferrite and lead zirconnate titanate prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.A.; Priya, S. Synthesis of high magnetoelectric coefficient composites using annealing and aging route. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Tech. 2006, 3, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H. Multiferroic ferrite/perovskite oxide core/shell nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10665–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.A.; Bedekar, V.; Poudyal, N.; Liu, J.P.; Priya, S. Magnetoelectric properties of core-shell particulate nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Nan, C.W.; Zhang, J.; Cai, N.; Li, J.-F. Magnetoelectric effect of Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 rod arrays in a (Tb,Dy)Fe2/epoxy medium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 012503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.; Lo, C.Y.; Chan, H.L.W. Frequency response of magnetoelectric 1–3-type composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 093901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shi, Z.; Nan, C.W. Magnetoelectric properties of composites of single Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 rods and Terfenol-D/Epoxy with a single-period of 1–3-type structure. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2571–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.A.; Ni, Y.; Khachaturyan, A.G.; Priya, S. Giant magnetoelectric effect in sintered multilayered composite structures. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhai, J.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Near-ideal magnetoelectricity in high-permeability magnetostrictive/piezofiber laminates with a (2–1) connectivity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 252904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gray, D.; Berry, D.; Gao, J.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. An extremely low equivalent magnetic noise magnetoelectric sensor. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4111–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Wuttig, M. Magnetoelectric coupling in Terfenol-D/polyvinylidenedifluoride composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Reis, S.; Lehmann, C.S.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Lasheras, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Barandiarán, J.M. Optimization of the Magnetoelectric Response of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/Epoxy/Vitrovac Laminates. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 10912–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawes, G.; Srinivasan, G. Introduction to magnetoelectric coupling and multiferroic films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phy. 2011, 44, 243001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDannald, A.; Staruch, M.; Sreenivasulu, G.; Cantoni, C.; Srinivasan, G.; Jain, M. Magnetoelectric coupling in solution derived 3–0 type PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3:xCoFe2O4 nanocomposite films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 122905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Lofland, S.E.; Ma, Z.; Mohaddes-Ardabili, L.; Zhao, T.; Salamanca-Riba, L.; Shinde, S.R.; Ogale, S.B.; Bai, F.; et al. Multiferroic BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 nanostructures. Science 2004, 303, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimon, N.M.; Kim, D.H.; Sun, X.; Ross, C.A. Multiferroic behavior of templated BiFeO3-CoFe2O4 self-assembled nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2015, 7, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, G. Layered multiferroic composites. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, N.X. Multiferroic nanostructures. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, E.; Kirchhof, C.; Hrkac, V.; Kienle, L.; Jahns, R.; Knöchel, R.; Quandt, E.; Meyners, D. Exchange biasing of magnetoelectric composites. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greve, H.; Woltermann, E.; Quenzer, H.-J.; Wagner, B.; Quandt, E. Giant magnetoelectric coefficients in (Fe90Co10)78Si12B10-AlN thin film composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 182501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.S.; Pookat, G.; Saravanan, V.; Anantharaman, M.R. Lead free heterogeneous multilayers with giant magneto electric coupling for microelectronics/microelectromechanical systems applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 064309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G.; Rasmussen, E.T.; Gallegos, J.; Srinivasan, R.; Bokhan, Y.I.; Laletin, V.M. Magnetoelectric bilayer and multilayer structures of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric oxides. Phys. Rev. B. 2001, 64, 214408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambale, R.C.; Ryu, J.; Patil, D.R.; Chai, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, W.-H.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Park, D.-S.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, J.-J.; et al. Colossal magnetoelectric response of PZT thick films on Ni substrates with a conductive LaNiO3 electrode. J. Phys. D Appl. Phy. 2013, 46, 092002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Jian, G.; Zheng, Y.; Gong, S.; Shi, F. Electrophoretic deposition of BaTiO3/CoFe2O4 multiferroic composite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7621–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palneedi, H.; Maurya, D.; Kim, G.-Y.; Priya, S.; Kang, S.-J.L.; Kim, K.-H.; Choi, S.-Y.; Ryu, J. Enhanced off-resonance magnetoelectric response in laser annealed PZT thick film grown on magnetostrictive amorphous metal substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 012904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.A.; Bai, Y.; Chu, W.Y.; Qiao, L.J. Ni–PZT–Ni trilayered magnetoelectric composites synthesized by electro-deposition. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2008, 20, 025203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, K.; Wang, Y.G.; Wu, W.; Pan, D.A. The large magnetoelectric effect in Ni–lead zirconium titanate–Ni trilayers derived by electroless deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phy. 2010, 43, 132002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.G.; Liu, J.-M. Magnetoelectric resonance-bandwidth broadening of Terfenol-D/epoxy-Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 bilayers in parallel and series connections. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 032508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-S.; Ahn, C.-W.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, W.-H.; Park, D.-S.; Kim, H.-E.; Priya, S. Design and characterization of broadband magnetoelectric sensor. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 094111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-S.; Priya, S. Broadband/wideband magnetoelectric response. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 2012, 323165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.R.; Kambale, R.C.; Chai, Y.; Yoon, W.-H.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Park, D.-S.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, J.-J.; Ahn, C.-W.; Hahn, B.-D.; et al. Multiple broadband magnetoelectric response in thickness-controlled Ni/[011] Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 single crystal/Ni laminates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 052907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.R.; Chai, Y.; Kambale, R.C.; Jeon, B.-G.; Yoo, K.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, W.-H.; Park, D.-S.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Lee, S.-G.; et al. Enhancement of resonant and non-resonant magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroic laminates with anisotropic piezoelectric properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 062909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambale, R.C.; Yoon, W.-H.; Park, D.-S.; Choi, J.-J.; Ahn, C.-W.; Kim, J.-W.; Hahn, B.-D.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Lee, B.-C.; Chung, G.-S.; et al. Magnetoelectric properties and magnetomechanical energy harvesting from stray vibration and electromagnetic wave by Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 single crystal/Ni cantilever. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 204108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Yang, S.C.; Maurya, D.; Yan, Y. Recent advances in piezoelectric and magnetoelectric materials phenomena. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 103–157. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Cho, K.-H.; Maurya, D.; Kumar, A.; Kalinin, S.; Khachaturyan, A.; Priya, S. Giant energy density in [001]-textured Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbZrO3-PbTiO3 piezoelectric ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 042903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Di, W.; Luo, H.; Leung, C.M.; Or, S.W. Lead-free magnetoelectric laminated composite of Mn-doped Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–BaTiO3 single crystal and Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.92 alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 2010, 496, L4–L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Maurya, D.; Yan, Y.; Srinivasan, G.; Quandt, E.; Priya, S. Self-biased magnetoelectric composites: An overview and future perspectives. Energy Harvest. Syst. 2016, 3, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.K.; Sreenivasulu, G.; Petrov, V.M.; Srinivasan, G. Magnetization-graded multiferroic composite and magnetoelectric effects at zero bias. Phys. Rev. B. 2011, 84, 014432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raidongia, K.; Nag, A.; Sundaresan, A.; Rao, C.N.R. Multiferroic and magnetoelectric properties of core-shell CoFe2O4@BaTiO3 nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 062904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Imrane, H.; Chen, Y.; Goodrich, T.; Cai, Z.; Ziemer, K.S.; Huang, J.Y.; Sun, N.X. Synthesis of ordered arrays of multiferroic NiFe2O4-Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 core-shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 152501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, J.D.; Andrew, J.S. Janus-type bi-phasic functional nanofibers. Chem. Comm. 2013, 49, 4151–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, J.S.; Starr, J.D.; Budi, M.A.K. Prospects for nanostructured multiferroic composite materials. Scripta Mater. 2014, 74, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ma, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Multiferroic CoFe2O4-Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 core-shell nanofibers and their magnetoelectric coupling. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3152–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.H.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lan, L.N.; Jin, G.; Zhou, Y.C. Electrospinning and multiferroic properties of NiFe2O4–Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 composite nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 024115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G. Magnetoelectric characterization techniques. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Apo, D.J.; Sanghadasa, M.; Bichurin, M.; Petrov, V.M.; Priya, S. Magnetoelectric energy harvester. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Zhai, J.; Xing, Z.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Giant magnetoelectric effect (under a dc magnetic bias of 2 Oe) in laminate composites of FeBSiC alloy ribbons and Pb(Zn1∕3Nb2∕3)O3–7%PbTiO3 fibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 022915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-S.; Cho, K.-H.; Arat, M.A.; Evey, J.; Priya, S. High magnetic field sensitivity in Pb(Zr,Ti)O3–Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 single crystal/Terfenol-D/Metglas magnetoelectric laminate composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 094109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V.; Reddy, N.R.; Sreenivasulu, G.; Kumar, K.V.S.; Murty, B.S.; Murthy, V.R.K. Enhanced mangnetoelectric voltage in multiferroic particulate Ni0.83Co0.15Cu0.02Fe1.9O4−δ/PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 composites—dielectric, piezoelectric and magnetic properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, G.; Fetisov, L.Y.; Fetisov, Y.K.; Srinivasan, G. Piezoelectric single crystal langatate and ferromagnetic composites: Studies on low-frequency and resonance magnetoelectric effects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 052901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gillette, S.M.; Fitchorov, T.; Jiang, L.; Hao, H.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Geiler, A.; Vittoria, C.; Harris, V.G. Quasi-one-dimensional miniature multiferroic magnetic field sensor with high sensitivity at zero bias field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 042505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Fan, J.; Rong, X.; Cao, H.; Wei, J. Magnetoelectric effect in laminate composites of Tb1−xDyxFe2−y and Fe-doped BaTiO3. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 063907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.A.; Kim, H.; Priya, S.; Stephanou, H. Piezoelectric transformer based ultrahigh sensitivity magnetic field sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 152908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Wang, J.-J.; Hu, J.-M.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Li, H.-B.; Shen, Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, L.-Q.; Nan, C.-W. Optimizing direct magnetoelectric coupling in Pb(Zr,Ti)O3/Ni multiferroic film heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 072901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, K.; Barzegar, A.; Ding, J.; Herng, T.S.; Huang, A.; Shannigrahi, S. Magnetoelectric effect in Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 and CoFe2O4 heteroepitaxial thin film composite. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2370–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Kumar, A.; Palai, R.; Srinivasan, G.; Katiyar, R.S. Observation of strong magnetoelectric effects in Ba0.7Sr0.3TiO3/La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 thin film heterostructures. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 104104. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.-S.; Khachaturyan, A.; Priya, S. Giant magnetoelectric coupling in laminate thin film structure grown on magnetostrictive substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 192904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.X.; Srinivasan, G. Voltage control of magnetism in multiferroic heterostructures and devices. SPIN 2012, 2, 1240004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluszek, M.; Avirovik, D.; Zhou, Y.; Kundu, S.; Chopra, A.; Montague, R.; Priya, S. Magnetoelectric composites for medical application. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 297–327. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Zhai, J.; Bai, F.; Li, J.-F.; Viehland, D. Push-pull mode magnetostrictive /piezoelectric laminate composite with an enhanced magnetoelectric voltage coefficient. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 062502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Das, J.; Xing, Z.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Comparison of noise floor and sensitivity for different magnetoelectric laminates. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 084509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Giant magnetoelectric effect in self-biased laminates under zero magnetic field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 082404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hasanyan, D.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Equivalent magnetic noise in multi-push-pull configuration magnetoelectric composites: Model and experiment. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2013, 60, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Gao, J.; Xing, Z.; Li, J.F.; Viehland, D. Enhancement in the field sensitivity of magnetoelectric laminate heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 092501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gray, D.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Enhanced dc magnetic field sensitivity by improved flux concentration in magnetoelectric laminates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 153502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Hasanyan, D.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Geometry-induced magnetoelectric effect enhancement and noise floor reduction in Metglas/piezofiber sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 092905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Berry, D.; Das, J.; Gray, D.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Enhanced sensitivity and reduced noise floor in magnetoelectric laminate sensors by an improved lamination process. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 3738–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Gao, J.Q.; Li, M.H.; Shen, Y.; Hasanyan, D.; Li, J.F.; Viehland, D. A review on equivalent magnetic noise of magnetoelectric laminate sensors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. A 2014, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Quasi-static (f<10−2 Hz) frequency response of magnetoelectric composites based magnetic sensor. Mater. Lett. 2012, 85, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Gao, J.; Shen, L.; Gray, D.; Li, J.; Finkel, P.; Viehland, D.; Zhuang, X.; Saez, S.; Dolabdjian, C. Analysis of the environmental magnetic noise rejection by using two simple magnetoelectric sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 171, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Jiao, J.; Ma, J.; Lin, D.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Luo, H. Significant reduction of equivalent magnetic noise by in-plane series connection in magnetoelectric Metglas/Mn-doped Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 laminate composites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phy. 2015, 48, 465002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, M.; Robert, J.; Henry, G.; Eckhard, Q.; Reinhard, K.; Bernhard, W. MEMS magnetic field sensor based on magnetoelectric composites. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 065024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, Z.; Hunter, D.; Suchoski, R.; Gao, C.; Mathews, S.; Wuttig, M.; Takeuchi, I. Fabrication and characterization of all-thin-film magnetoelectric sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 243507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Kim, S.M.; Yoo, Y.K.G.; Han, J.H.; Chun, D.W.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, K.S.; Kim, T.S.; Jo, W.W.; et al. Ultra-sensitive magnetoelectric microcantilever at a low frequency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 182902. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden, E. Hall-Effect Sensors: Theory and Applications; Newnes Publications: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, C.M.; Or, S.W.; Zhang, S.; Ho, S.L. Ring-type electric current sensor based on ring-shaped magnetoelectric laminate of epoxy-bonded Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.92 short-fiber/NdFeB magnet magnetostrictive composite and Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 piezoelectric ceramic. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09D918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, P.; Wen, Y.; Yang, A.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.; He, W.; Zhang, J. Magnetoelectric composite Metglas/PZT-based current sensor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Leung, C.M.; Kuang, W.; Or, S.W.; Ho, S.L. Concurrent operational modes and enhanced current sensitivity in heterostructure of magnetoelectric ring and piezoelectric transformer. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17C733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lou, G.; Chen, H.; Wen, C.; Lu, S. A slice-type magnetoelectric laminated current sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5839–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.R.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, J.-E.; Sharpes, N.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Kim, Y.-D.; Kim, K.H.; Priya, S.; Ryu, J. Anisotropic self-biased dual-phase low frequency magneto-mechano-electric energy harvesters with giant power densities. APL Mater. 2014, 2, 046102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kang, J.-E.; Zhou, Y.; Choi, S.-Y.; Yoon, W.-H.; Park, D.-S.; Choi, J.-J.; Hahn, B.-D.; Ahn, C.-W.; Kim, J.-W.; et al. Ubiquitous magneto-mechano-electric generator. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2402–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Apo, D.J.; Priya, S. Dual-phase self-biased magnetoelectric energy harvester. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 192909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ci, P.; Dong, S. Energy harvesting from ambient low-frequency magnetic field using magneto-mechano-electric composite cantilever. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 032908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheras, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Reis, S.; Sousa, D.; Silva, M.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Shishkin, D.A.; Potapov, A.P. Energy harvesting device based on a metallic glass/PVDF magnetoelectric laminated composite. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 065024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wen, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, X.; Jia, C. A magnetoelectric energy harvester and management circuit for wireless sensor network. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 2010, 157, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.X.; He, J. Magnetic energy harvesting properties of piezofiber bimorph/NdFeB composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 093901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuta, T.-D.; Wang, Y.; Long, C.J.; Takeuchi, I. Energy harvesting properties of all-thin-film multiferroic cantilevers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 203506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Wen, Y.; Li, P.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, M. Magnetoelectric transducer with high quality factor for wireless power receiving. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 150, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hasanyan, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Giant resonant magnetoelectric effect in bi-layered Metglas/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhai, J.; Li, J.F.; Viehland, D.; Priya, S. Multimodal system for harvesting magnetic and mechanical energy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Park, H.-Y.; Heo, J.S.; Priya, S. Structure-performance relationships for cantilever-type piezoelectric energy harvesters. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 204108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopsaroiu, M.; Blackburn, J.; Muniz-Piniella, A.; Cain, M.G. Multiferroic magnetic recording read head technology for 1Tbit/in.2 and beyond. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07F506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y.; Nan, C.-W. Demonstration of magnetoelectric read head of multiferroic heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 152510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargol, A.; Malkinski, L.; Caruntu, G. Biomedical applications of multiferroic nanoparticles. In Advanced Magnetic Materials; Malkinski, L., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 89–118. [Google Scholar]
- Guduru, R.; Liang, P.; Runowicz, C.; Nair, M.; Atluri, V.; Khizroev, S. Magneto-electric nanoparticles to enable field-controlled high-specificity drug delivery to eradicate ovarian cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Guduru, R.; Hong, J.; Liang, P.; Nair, M.; Khizroev, S. Magneto-electric nano-particles for non-invasive brain stimulation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J. Remote control of cellular behaviour with magnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nano 2008, 3, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Delikanli, S.; Zeng, H.; Ferkey, D.M.; Pralle, A. Remote control of ion channels and neurons through magnetic-field heating of nanoparticles. Nat. Nano. 2010, 5, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcroft, F.M. Ion Channels and Disease; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Vopson, M.M. Fundamentals of multiferroic materials and their possible applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibes, M.; Barthelemy, A. Multiferroics: Towards a magnetoelectric memory. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heron, J.T.; Trassin, M.; Ashraf, K.; Gajek, M.; He, Q.; Yang, S.Y.; Nikonov, D.E.; Chu, Y.H.; Salahuddin, S.; Ramesh, R. Electric-field-induced magnetization reversal in a ferromagnet-multiferroic heterostructure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 217202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, B.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, W.; Ren, T.; Yang, X.; Nan, T.; Sun, N.X.; et al. Electric field induced reversible 180° magnetization switching through tuning of interfacial exchange bias along magnetic easy-axis in multiferroic laminates. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lou, J.; Li, S.; Sun, N.X. E-field control of exchange bias and deterministic magnetization switching in AFM/FM/FE multiferroic heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.F. Review of semiconductor microwave phase shifters. Proc. IEEE 1968, 56, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.R. A 60 GHz dual-mode ferrite phase shifter. In Proceedings of the 1982 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–17 June 1982; pp. 257–259.
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Choi, K.; Lugo, C.; Hunt, A.T. Ferroelectric Phase Shifters at 20 and 30 GHz. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, A.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Kalinikos, B.A. Ferrite-ferroelectric hybrid wave phase shifters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 031913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarenko, A.S.; Srinivasan, G.; Bichurin, M.I. Magnetoelectric microwave phase shifter. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 183507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarenko, A.S.; Srinivasan, G. A strain engineered voltage tunable millimeter-wave ferrite phase shifter. Microwave Opt. Technol. Lett. 2011, 53, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, C. On the theory of ferromagnetic resonance absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetisov, Y.K.; Srinivasan, G. Electric field tuning characteristics of a ferrite-piezoelectric microwave resonator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 143503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, N.X.; Murthy, D.V.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Klein, T.M.; Petrov, V.M.; Gupta, A. Electrostatic tuning of ferromagnetic resonance and magnetoelectric interactions in ferrite-piezoelectric heterostructures grown by chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 192502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G. Microwave and millimeter-wave multiferroic devices. In Composite Magnetoelectrics; Srinivasan, G., Priya, S., Sun, N.X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 241–264. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.G.; Yoon, S.D.; Vittoria, C. Microwave and magnetic properties of double-sided hexaferrite films on (111) magnesium oxide substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 6728–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, A.B.; Tatarenko, A.S.; Srinivasan, G.; Balbashov, A.M. Al substituted Ba-hexaferrite single-crystal films for millimeter-wave devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 023908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarenko, A.S.; Murthy, D.V.B.; Srinivasan, G. Hexagonal ferrite-piezoelectric composites for dual magnetic and electric field tunable 8–25 GHz microstripline resonators and phase shifters. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2012, 54, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Reed, D.; Pettiford, C.; Liu, M.; Han, P.; Dong, S.; Sun, N.X. Giant microwave tunability in FeGaB/lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate multiferroic composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 262502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Liu, M.; Reed, D.; Ren, Y.; Sun, N.X. Giant electric field tuning of magnetism in novel multiferroic FeGaB/Lead Zinc Niobate–Lead Titanate (PZN-PT) Heterostructures. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4711–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Converse magnetoelectric effects on heterotype electrostrain-piezopermeability composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Reed, D.; Liu, M.; Sun, N.X. Electrostatically tunable magnetoelectric inductors with large inductance tenability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 112508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwaider, L.; Jing, L.; Yuan, G.; Hasegawa, R.; Ming, L.; Howe, B.; Jones, J.; Brown, G.; Sun, N.X. Voltage tunable magnetoelectric inductors with improved operational frequency and quality factor for power electronics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Duttagupta, S.P.; Palkar, V.R. Study of multiferroic Bi0.7Dy0.3FeO3 based tunable ring inductor. J. Phys. D Appl. Phy. 2013, 46, 325001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R. Microstrip Antenna Design Handbook; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D. Planar magneto-dielectric metasubstrate for miniaturization of a microstrip patch antenna. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2012, 54, 2871–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, R.V.; Tatarenko, A.S.; Pandey, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Mantese, J.V.; Azadegan, R. Miniature antenna based on magnetoelectric composites. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Hong, Y.K.; Lee, J.J.; Jalli, J.; Abo, G.S.; Lyle, A.; Seong, W.M.; Kum, J.S. Low loss Z-type barium ferrite (Co2Z) for terrestrial digital multimedia broadcasting antenna application. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 07A515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Hong, Y.K.; Lee, J.J.; Abo, G.S.; Jalli, J.; Park, J.H.; Seong, W.M.; Kum, J.S.; Ahn, W.K.; Park, S.H. Miniaturized broadband ferrite T-DMB antenna for mobile-phone applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2361–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, Y.-K.; Lee, W.; Abo, G.S.; Park, J.; Neveu, N.; Seong, W.-M.; Park, S.-H.; Ahn, W.-K. Soft M-type hexaferrite for very high frequency miniature antenna applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).