Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Based on Event-Driven and Control Input Quantization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Unlike conventional USV trajectory tracking methods relying on continuous control signals [56,57,58], this study proposes a novel event-triggering mechanism. By dynamically adjusting the triggering threshold, the communication network bandwidth usage is significantly reduced while maintaining system stability. This design is especially suited for maritime applications with limited bandwidth, thereby enhancing the practicality of the strategy.
- (2)
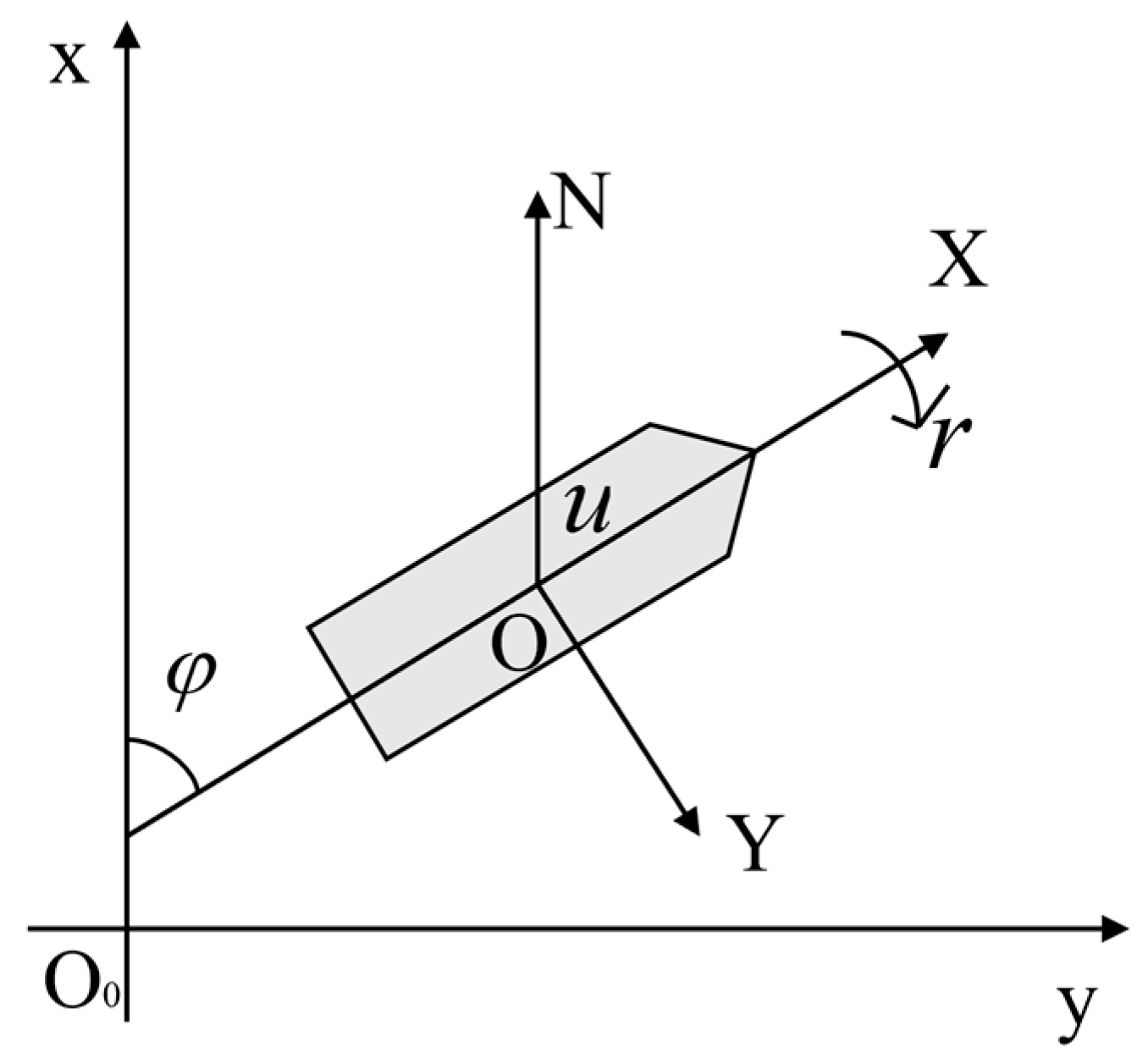
2. Problem Formulation
3. Design of Quantitative Feedback Controller
4. Stability Analysis
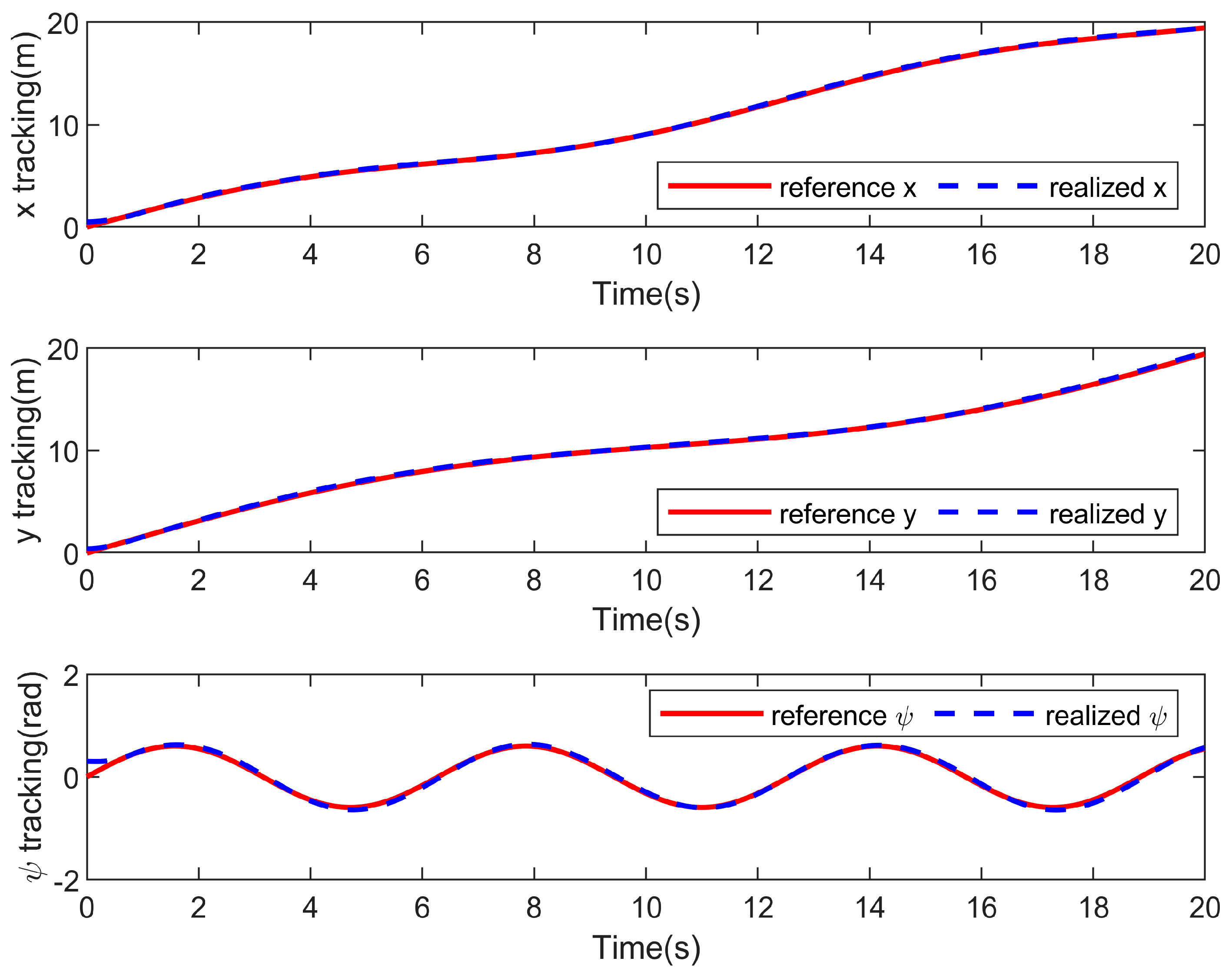
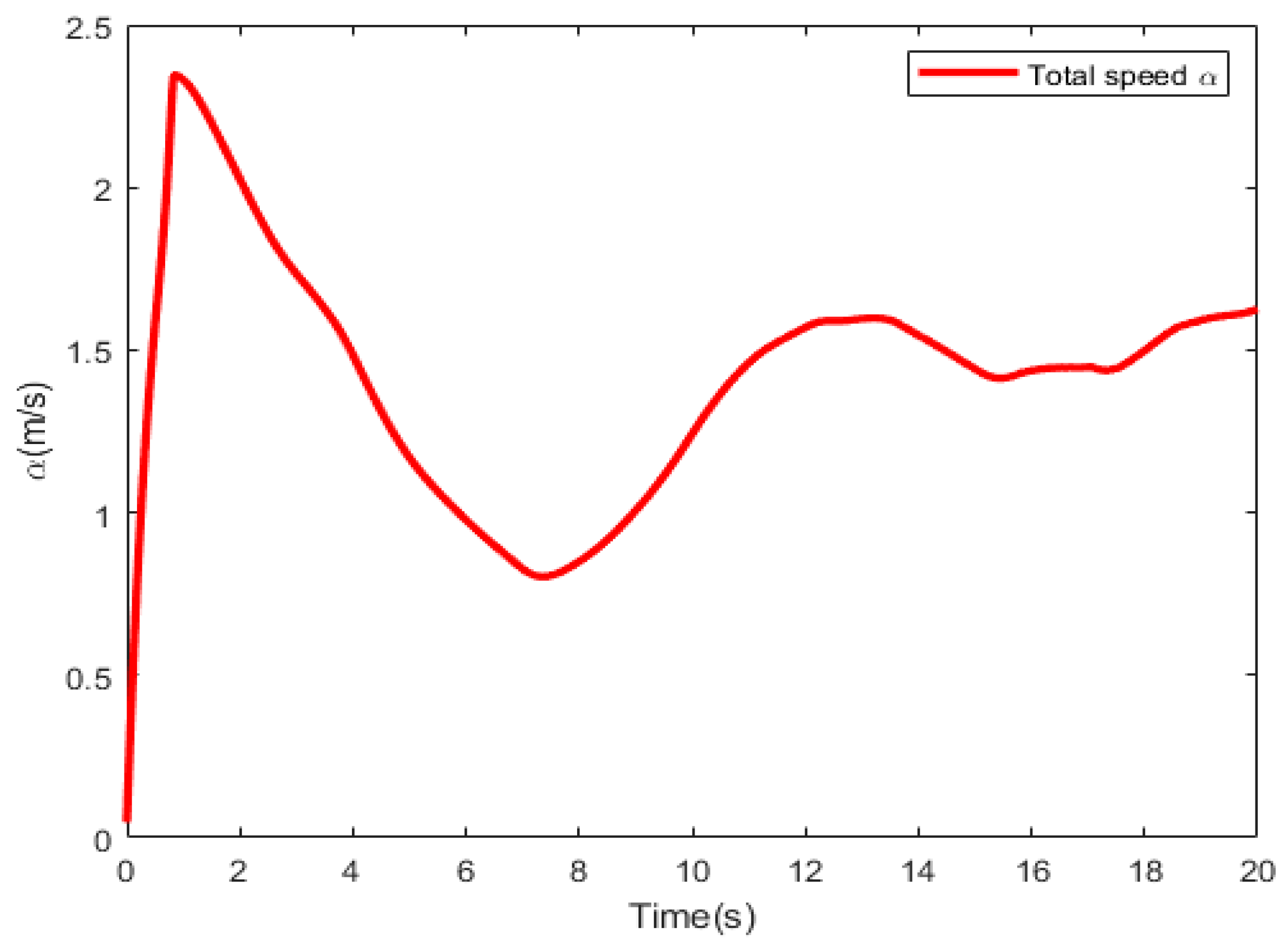
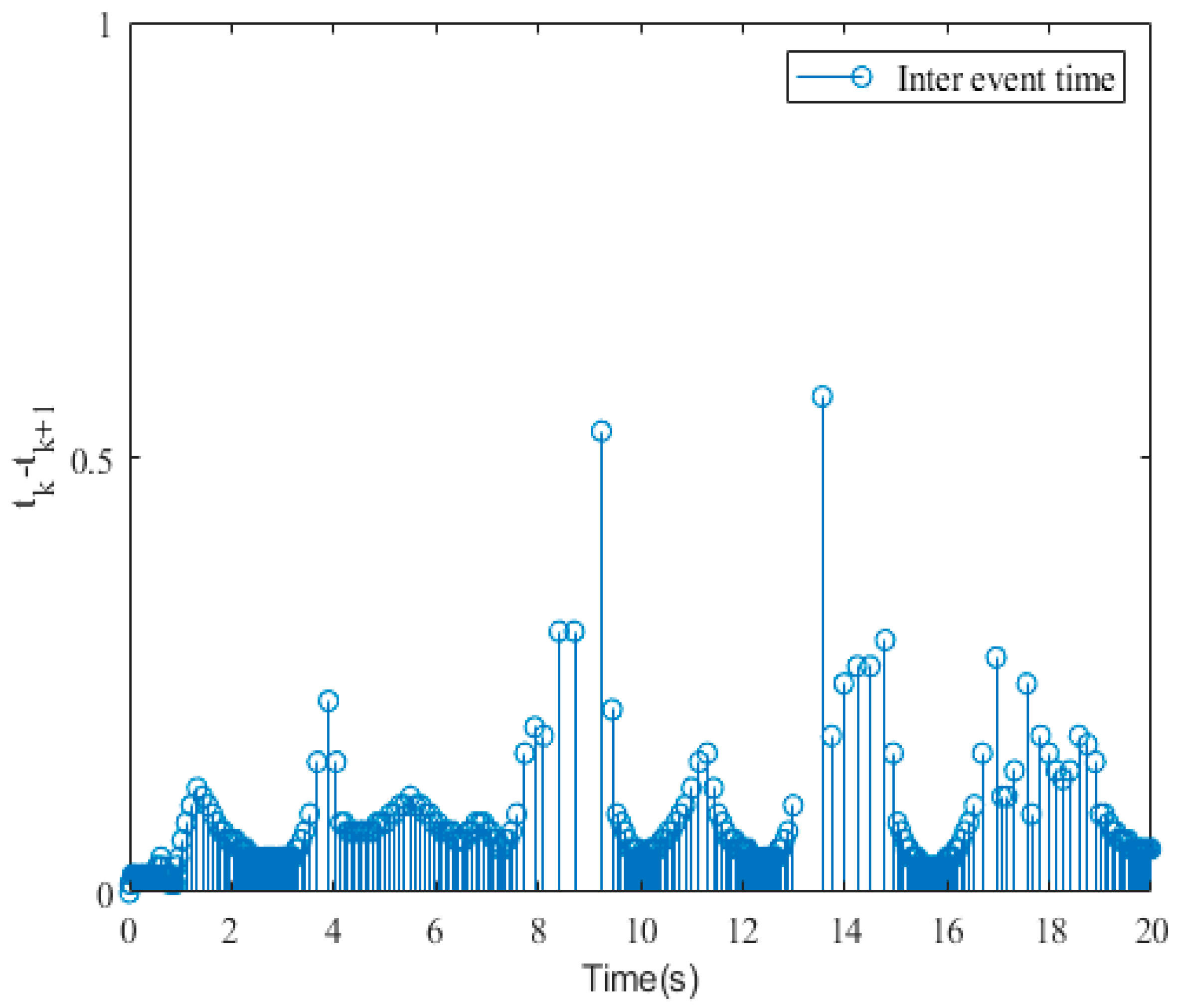
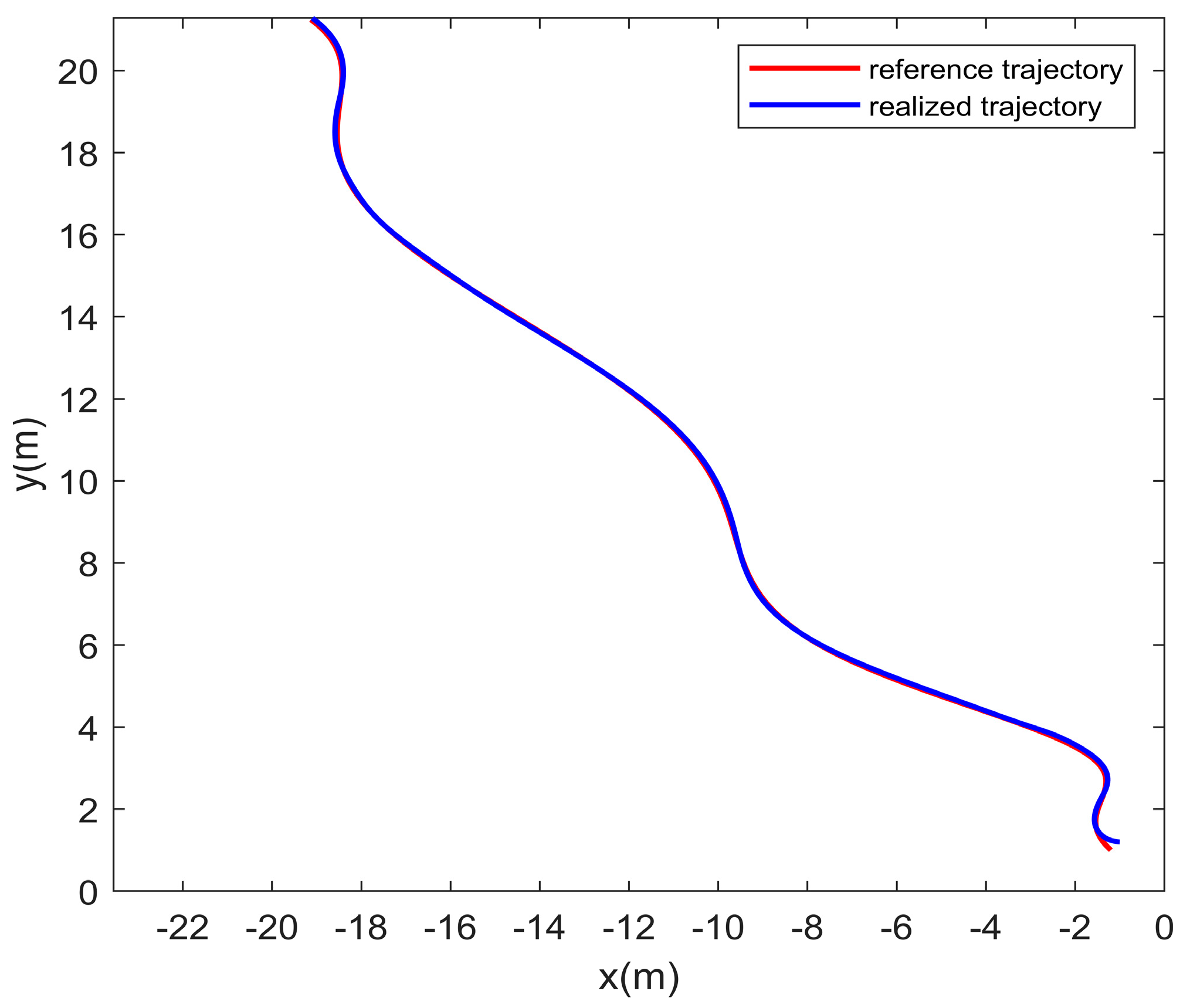
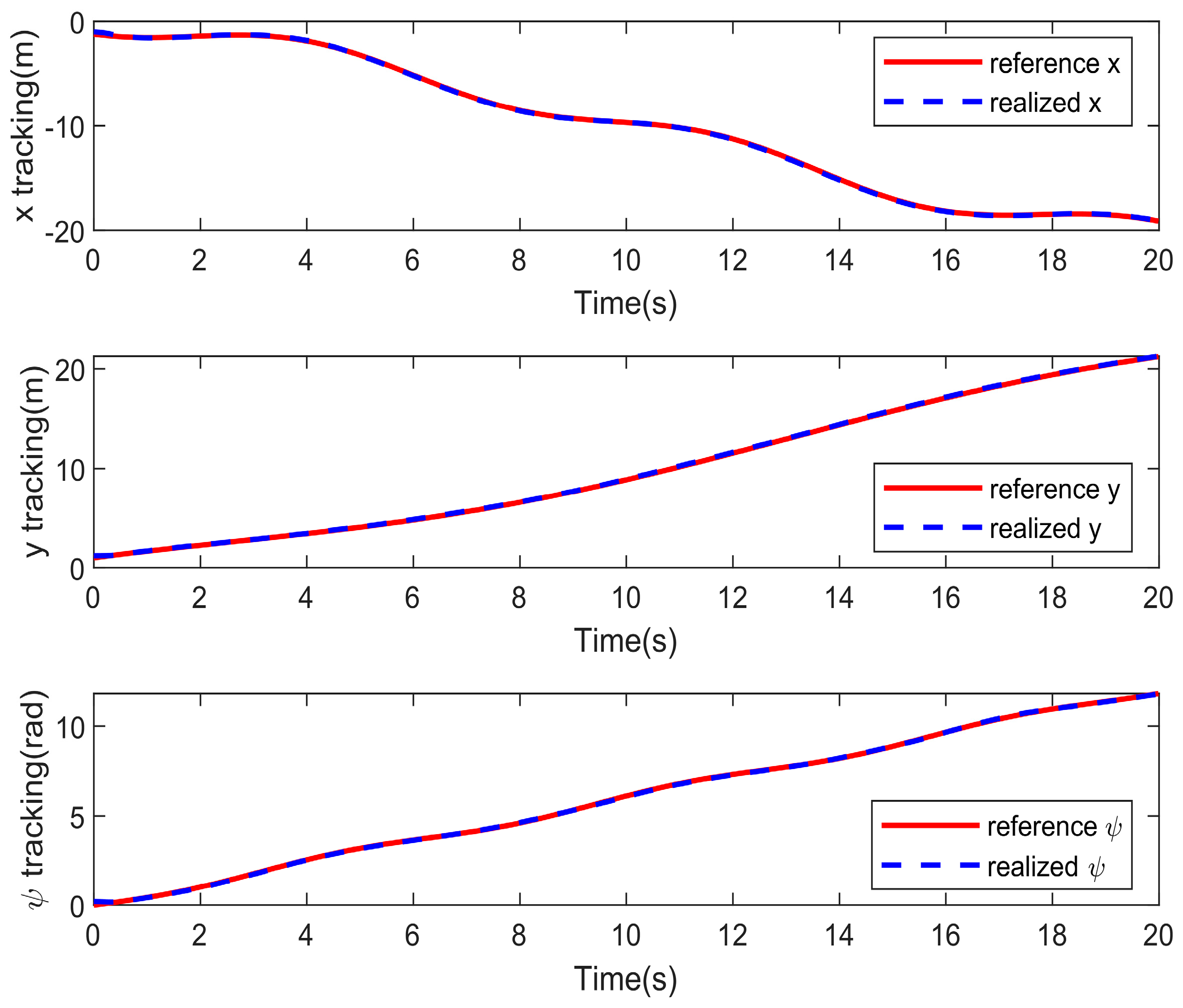
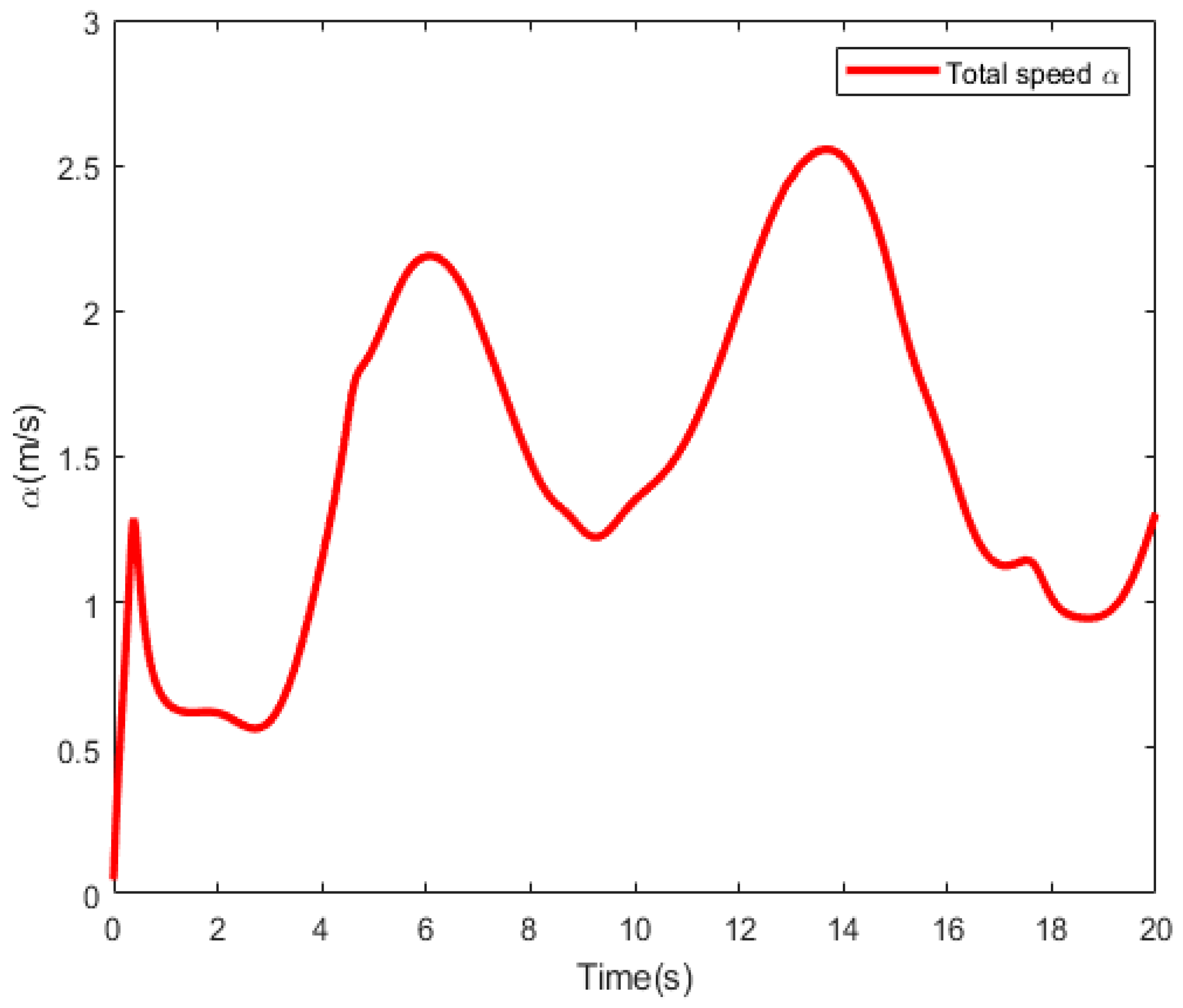
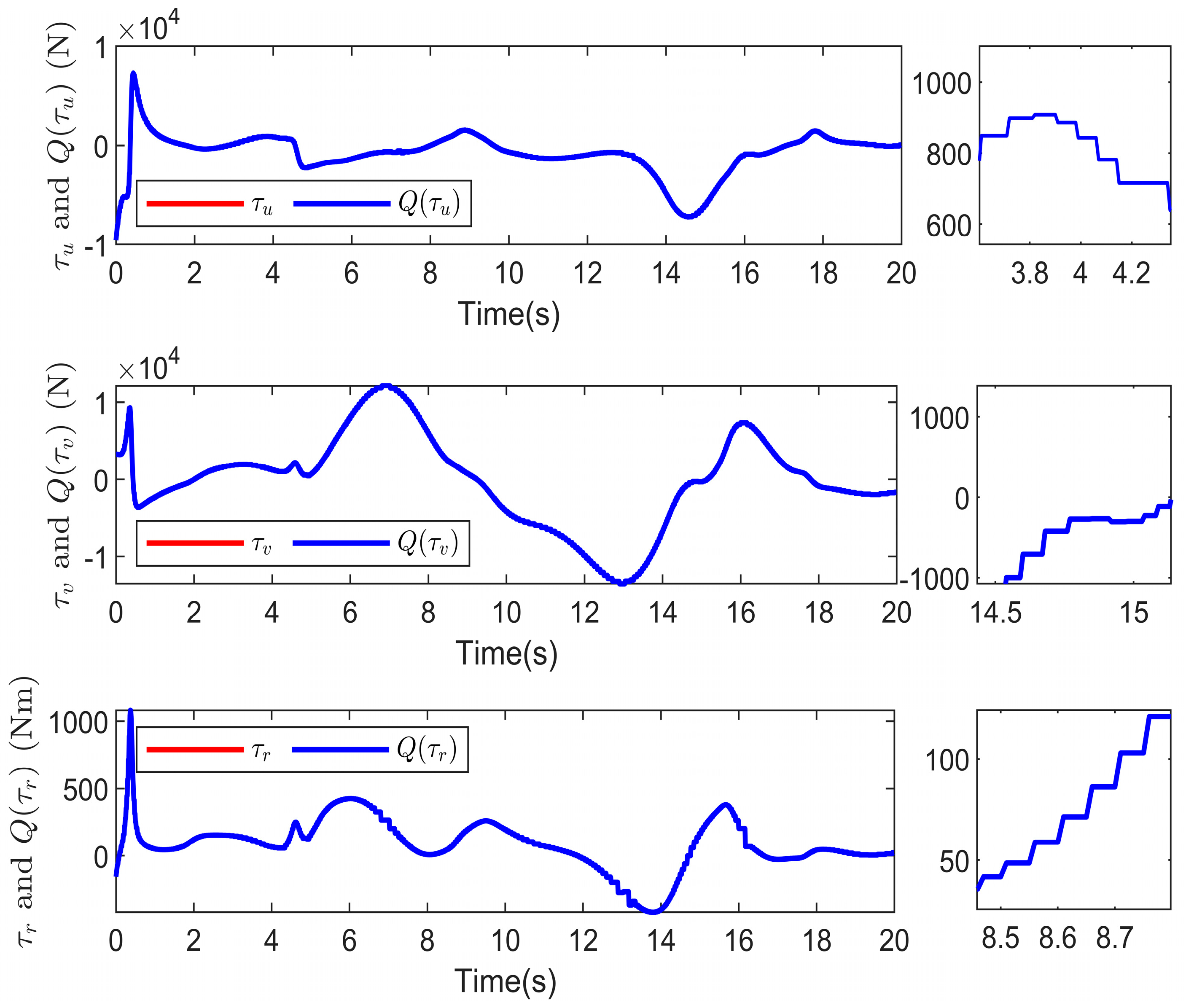
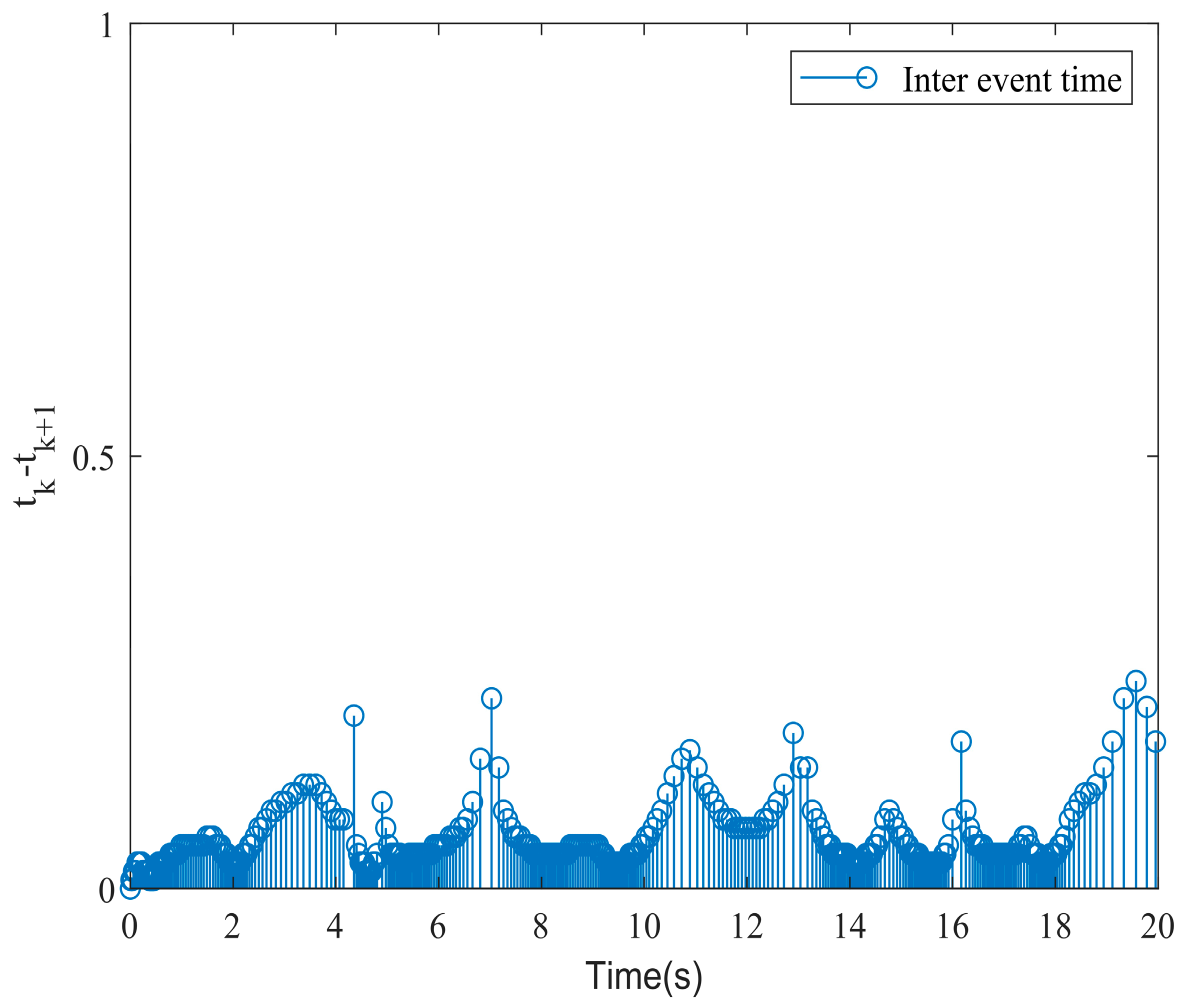
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bao, Y.; Gao, J.; Peng, P. Fuzzy adaptive fault-tolerant control for an unmanned surface vehicle with prescribed tracking performance. Front. Robot. AI 2025, 12, 1576171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Ma, T. Disturbance observer-based adaptive fuzzy finite-time cooperative control for high-order multi-agent systems with input saturation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 276, 127179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, X. Spatial–temporal intention representation with multi-agent reinforcement learning for unmanned surface vehicles strategies learning in asset guarding task. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 145, 110120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, B. Safety-aware isoline tracking control for unmanned surface vehicle. Ocean Eng. 2025, 327, 120910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Er, M.J. Direct adaptive fuzzy tracking control of marine vehicles with fully unknown parametric dynamics and uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Ma, D. Path following of underactuated surface vessels based active disturbance rejection control considering lateral drift. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2025, 239, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Xu, B.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Du, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Lian, X. Controllable preparation of low-cost coal gangue-based SAPO-5 molecular sieve and its adsorption performance for heavy metal ions. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ye, H.; Yang, X. Super-twisting sliding mode control for the trajectory tracking of underactuated USVs with disturbances. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, J.; Liu, Z.; Yan, L.; Wang, S. Control algorithm for trajectory tracking of an underactuated USV under multiple constraints. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5274452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, B.; Su, Y. Finite-time trajectory tracking control for under-actuated unmanned surface vessels with saturation constraint. Ocean Eng. 2022, 249, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pan, Y. Trajectory tracking control of unmanned surface vehicle based on exponential global fast terminal sliding mode control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2024, 238, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrougui, H.; Nejim, S.; Hachicha, S.; Zaoui, C.; Dallagi, H. Modeling, parameter identification, guidance and control of an unmanned surface vehicle with experimental results. Ocean Eng. 2021, 241, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Castaneda, H.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Gordillo, J.L. Finite-time control for an Unmanned Surface Vehicle based on adaptive sliding mode strategy. Ocean Eng. 2022, 254, 111255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, E.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.L.P.; Tong, S. Fuzzy trajectory tracking control of under-actuated unmanned surface vehicles with ocean current and input quantization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2025, 55, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tan, F.; Wang, B.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous modeling and adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control scheme for underactuated USV formation based on real-time sailing state data. Ocean Eng. 2024, 314, 119743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooban, M.H.; Vafamand, N.; Dragicevic, T.; Blaabjerg, F. Polynomial fuzzy model-based approach for underactuated surface vessels. IET Control Theory Appl. 2018, 12, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Mu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Global fixed-time adaptive fuzzy path following control for unmanned surface vehicles subject to lumped uncertainties and actuator saturation. Ocean Eng. 2023, 286, 115533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, T.; Luo, X.; Yang, Z. Adaptive fuzzy output regulation for unmanned surface vehicles with prescribed performance. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2020, 18, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, T. Fuzzy course tracking control of an unmanned surface vehicle with event-triggered mechanism and input quantization. Ocean Eng. 2023, 288, 115704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, J.; Gao, K.; Song, N.; Jia, G.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Development of an adaptive fuzzy integral-derivative line-of-sight method for bathymetric LiDAR onboard unmanned surface vessel. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, C. Adaptive neural network-based obstacle avoidance control for USVs with uncertain dynamics. Ocean Eng. 2025, 332, 121390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, S.; Franco, E.; Frye, M. DisBeaNet: A deep neural network to augment unmanned surface vessels for maritime situational awareness. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06149. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.L.P.; Li, T. Neural network observer based adaptive trajectory tracking control strategy of unmanned surface vehicle with event-triggered mechanisms and signal quantization. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Topics Comput. Intell. 2025, 9, 3136–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.; Chi, J.; Yang, Z. Adaptive NN state error PCH trajectory tracking control for unmanned surface vessel with uncertainties and input saturation. Asian J. Control 2023, 25, 3903–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Li, T.; Chen, C.L.P. Neuro-adaptive distributed formation tracking control of under-actuated unmanned surface vehicles with input quantization. Ocean Eng. 2022, 265, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ning, J.; Tong, S. Inverse Q-learning optimal control for takagi-sugeno fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2025, 33, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, F. A novel robust control and optimal design for fuzzy unmanned surface vehicles (USVs). Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 27, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lei, K. Robust fixed-time fault-tolerant control for USV with prescribed tracking performance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yin, S.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W. Intervehicle security-based robust neural formation control for multiple USVs via APS guidance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlvanna, S.; Van, M.; Sun, Y.; Naeem, W.; Liu, Z. Adaptive fixed-time control for uncertain surface vessels with output constraints using barrier Lyapunov function. Ocean Eng. 2024, 293, 116740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, X.; Tian, K. Networked predictive trajectory tracking control for underactuated USV with time-varying delays. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmokadem, T.; Zribi, M.; Youcef-Toumi, K. Terminal sliding mode control for the trajectory tracking of underactuated Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2017, 129, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavifar, H.; Qin, Y.; Hu, C. Adaptive immersion and invariance induced optimal robust control of unmanned surface vessels with structured/unstructured uncertainties. Ocean Eng. 2021, 239, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Du, Z.; Li, H.; Gan, L.; Li, X. Adaptive trajectory tracking of the unmanned surface vessel based on improved AC-MPC method. Ocean Eng. 2025, 322, 120455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Ning, J.; Hu, X.; Li, W. Event-triggered anti-disturbance trajectory tracking for under-actuated surface vehicle under multiple constraints and input quantization. Ocean Eng. 2025, 329, 121111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Yan, Y.; Yu, S.H. Adaptive sliding mode control for unmanned surface vehicles with predefined-time tracking performances. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ning, J.; Li, T.; Liu, L. Distributed extended state observer based formation tracking control of under-actuated unmanned surface vehicles with input and state quantization. Ocean Eng. 2024, 311, 118872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Guo, J.; Sung, H.-K.; Chernogor, L.; Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Hierarchical microstructure-enhanced flexible capacitive pressure sensor for high-accuracy fruit identification. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 520, 166137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Mao, L.; Su, Y.; Zheng, Y. Trajectory tracking control for underactuated USV with prescribed performance and input quantization. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, P.B.; Jin, Y.S. Robust trajectory tracking with adjustable performance of underactuated surface vessels via quantized state feedback. Ocean Eng. 2022, 246, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, P.B.; Jin, Y.S. Quantized-communication-based neural network control for formation tracking of networked multiple unmanned surface vehicles without velocity information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105160. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, H.L.; He, Z.; Ge, G.; Hui, L. Quantized sliding mode control of unmanned marine vehicles: Various thruster faults tolerated with a unified model. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 2012–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xu, D.; Yu, H. Event-triggered model-free adaptive sliding-mode heading control for unmanned surface vehicles under DoS attacks. Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 153, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Yu, H. Reinforcement learning event-triggered energy-based control for unmanned surface vessel with disturbances. Ocean Eng. 2025, 329, 121132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yin, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W. Game-based event-triggered control for unmanned surface vehicle: Algorithm design and harbor experiment. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 55, 2729–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, C.L.P. Event-triggered-based distributed formation cooperative tracking control of under-actuated unmanned surface vehicles with input and state quantization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 7081–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, C.L.P.; Tong, S. Event-triggered based trajectory tracking control of under-actuated unmanned surface vehicle with state and input quantization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Vehicles 2024, 9, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Lewis, F.L. Cooperative control of multiagent systems: A quantization feedback-based event-triggered approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 54, 1960–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Shan, Q.; Tong, S.; Chen, C.L.P. Anti-attack event-triggered control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with input quantization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 10105–10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Liu, J. Event-triggered neural network control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with input quantization. Neurocomputing 2021, 440, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hu, K.; Liu, L.; Li, J. Distributed dynamic event-triggered flocking control for multiple unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2024, 309, 118307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Ding, L. Periodic event-triggered adaptive neural control of USVs under replay attacks. Ocean Eng. 2024, 306, 118022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Nguyen, A.T.; Lauber, J.; Boada, M.J.L.; Boada, B.L. Event-triggered robust path tracking control considering roll stability under network-induced delays for autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 14743–14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Meléndez-Useros, M.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Boada, B.L.; Boada, M.J.L. Motion planning and robust output-feedback trajectory tracking control for multiple intelligent and connected vehicles in unsignalized intersections. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Meléndez-Useros, M.; Jiménez-Salas, M.; Boada, B.L. Robust adaptive control of heterogeneous vehicle platoons in the presence of network disconnections with a novel string stability guarantee. IEEE Trans. Intell. Vehicles 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Su, Z.; Wang, X. Distributed observer position-based event-triggered formation control for unmanned surface vessels with confined inter-event times. Ocean Eng. 2024, 296, 116884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Event triggered prescribed time trajectory tracking control for unmanned surface vessels with lumped disturbances and prescribed performance constraints. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zuo, Y.; Tong, S. Adaptive fuzzy finite-time event-triggered formation control for unmanned surface vehicle systems. Ocean Eng. 2024, 292, 116567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y. Event-triggered adaptive neural network trajectory tracking control for underactuated ships under uncertain disturbance. Pol. Marit. Res. 2023, 30, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. Robust neural event-triggered control for dynamic positioning ships with actuator faults. Ocean Eng. 2020, 207, 107292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Lin, B.; Zhang, C.; Dong, B.; Zhang, W. Safe deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive control for USV interception mission. Ocean Eng. 2022, 246, 110477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I.; Pettersen, K.Y.; Galeazzi, R. Line-of-sight path following for dubins paths with adaptive sideslip compensation of drift forces. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Boada, B.L.; Zhang, H.; Boada, M.J.L. Integral-Based Event Triggering Actuator Fault-Tolerant Control for an Active Suspension System Under a Networked Communication Scheme. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 13848–13860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Boada, B.L.; Boada, M.J.L.; Díaz, V. H∞ dynamic output feedback control for a networked control active suspension system under actuator faults. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 162, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, K. Application of sample-data control for a class of time-delay nonlinear systems in circuit systems. AIMS Math. 2025, 10, 11316–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; San, P.P.; Ge, S.S.; Lee, T. Adaptive dynamic surface control for a class of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with unknown backlash-like hysteresis. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009; pp. 4482–4487. [Google Scholar]





| Symbol | Physical Meaning |
|---|---|
| Total mass | |
| Center of gravity of the ship’s fixed coordinate system | |
| Yaw moment of inertia | |
| Added-mass coefficients | |
| Linear hydraulic damping Coefficient | |
| Second-order nonlinear damping coefficient | |
| High-order nonlinear damping coefficient | |
| Elements of inertia matrix | |
| Coriolis and centripetal terms | |
| Linear damping coefficients |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, M.; Jing, X.; Yuan, C.; Wang, K. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Based on Event-Driven and Control Input Quantization. Actuators 2025, 14, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090457
Li Z, Li M, Jing X, Yuan C, Wang K. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Based on Event-Driven and Control Input Quantization. Actuators. 2025; 14(9):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090457
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhihui, Mengyuan Li, Xinrui Jing, Changfu Yuan, and Kai Wang. 2025. "Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Based on Event-Driven and Control Input Quantization" Actuators 14, no. 9: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090457
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, M., Jing, X., Yuan, C., & Wang, K. (2025). Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Based on Event-Driven and Control Input Quantization. Actuators, 14(9), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090457







