Motion Control of Gallium-Based Liquid Metal Droplets in Abrasive Suspensions Within a Flow Channel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
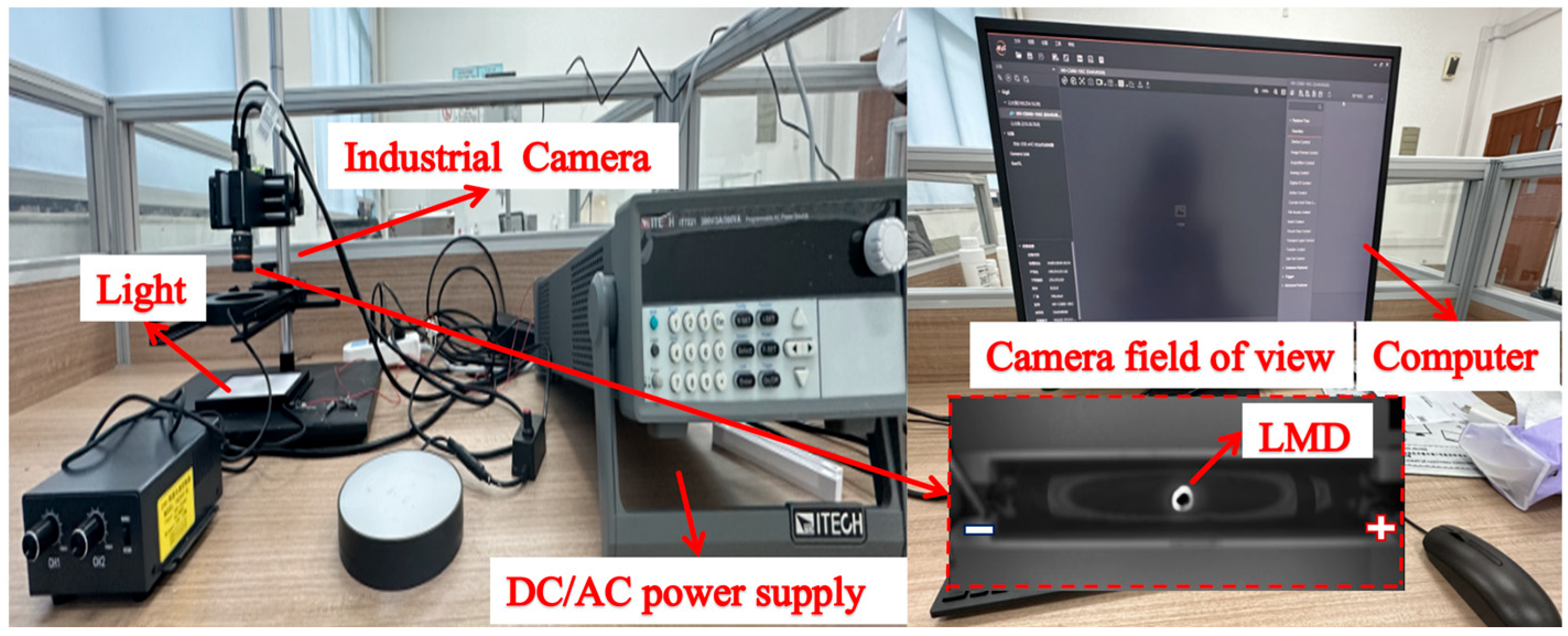
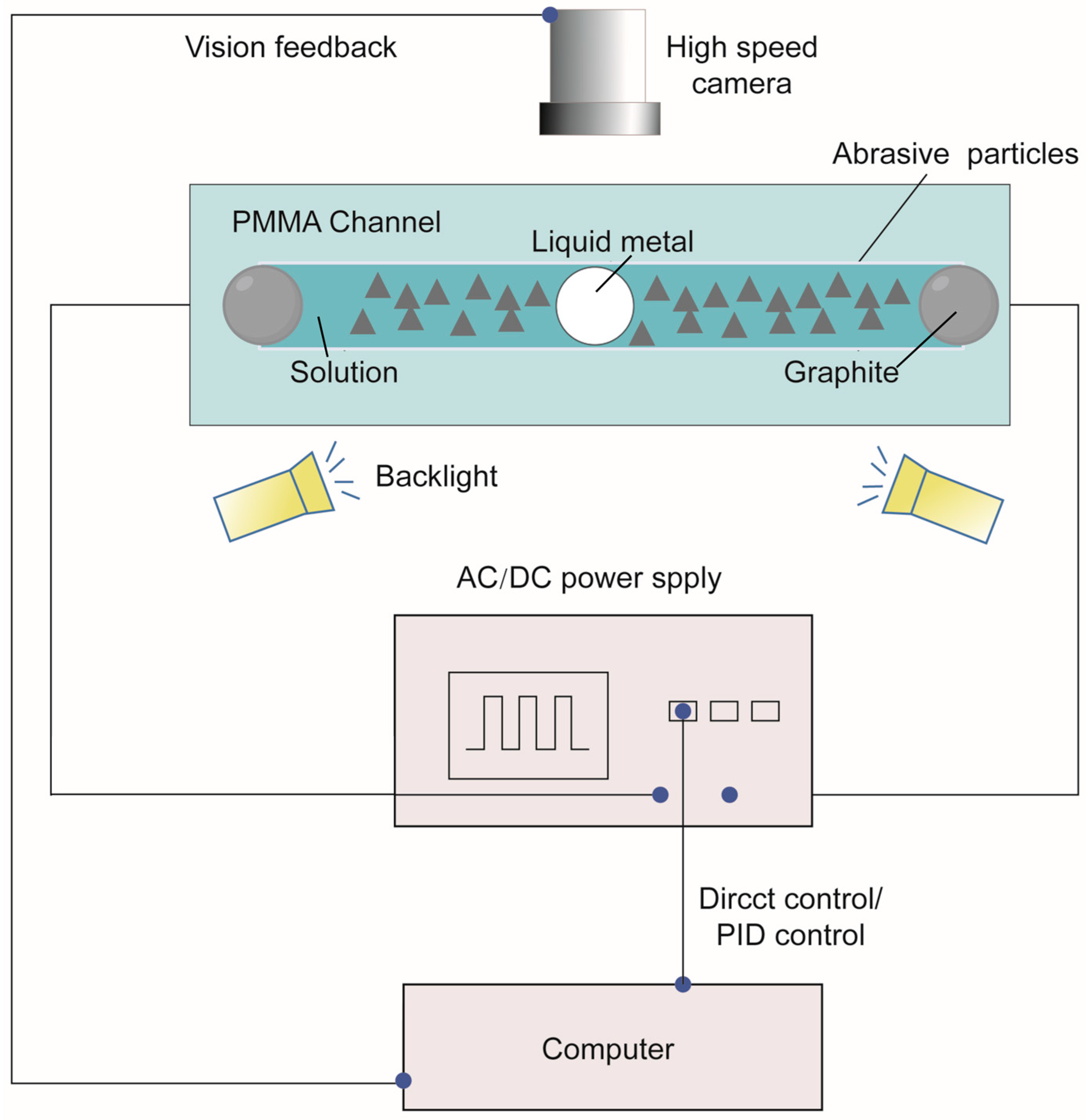
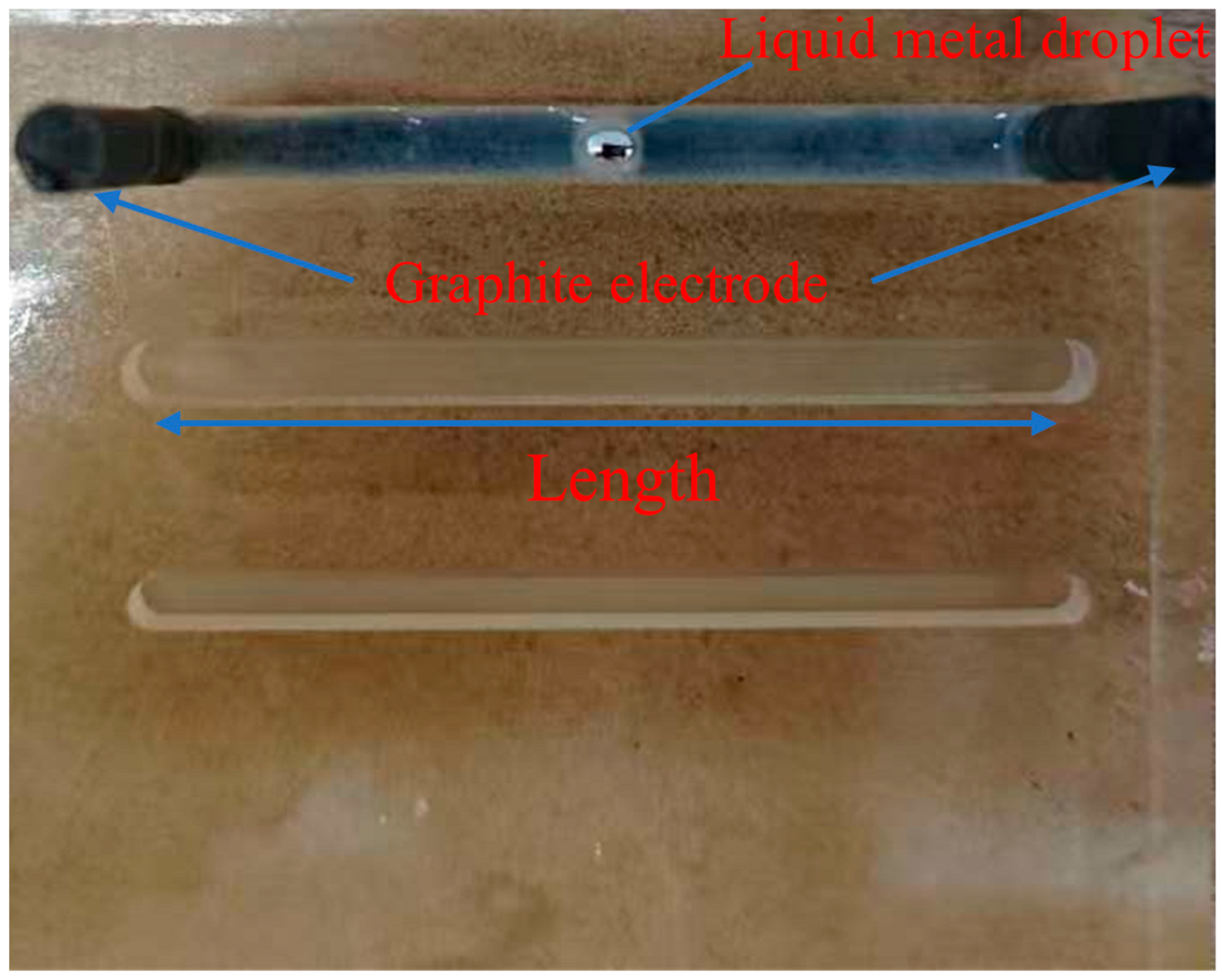
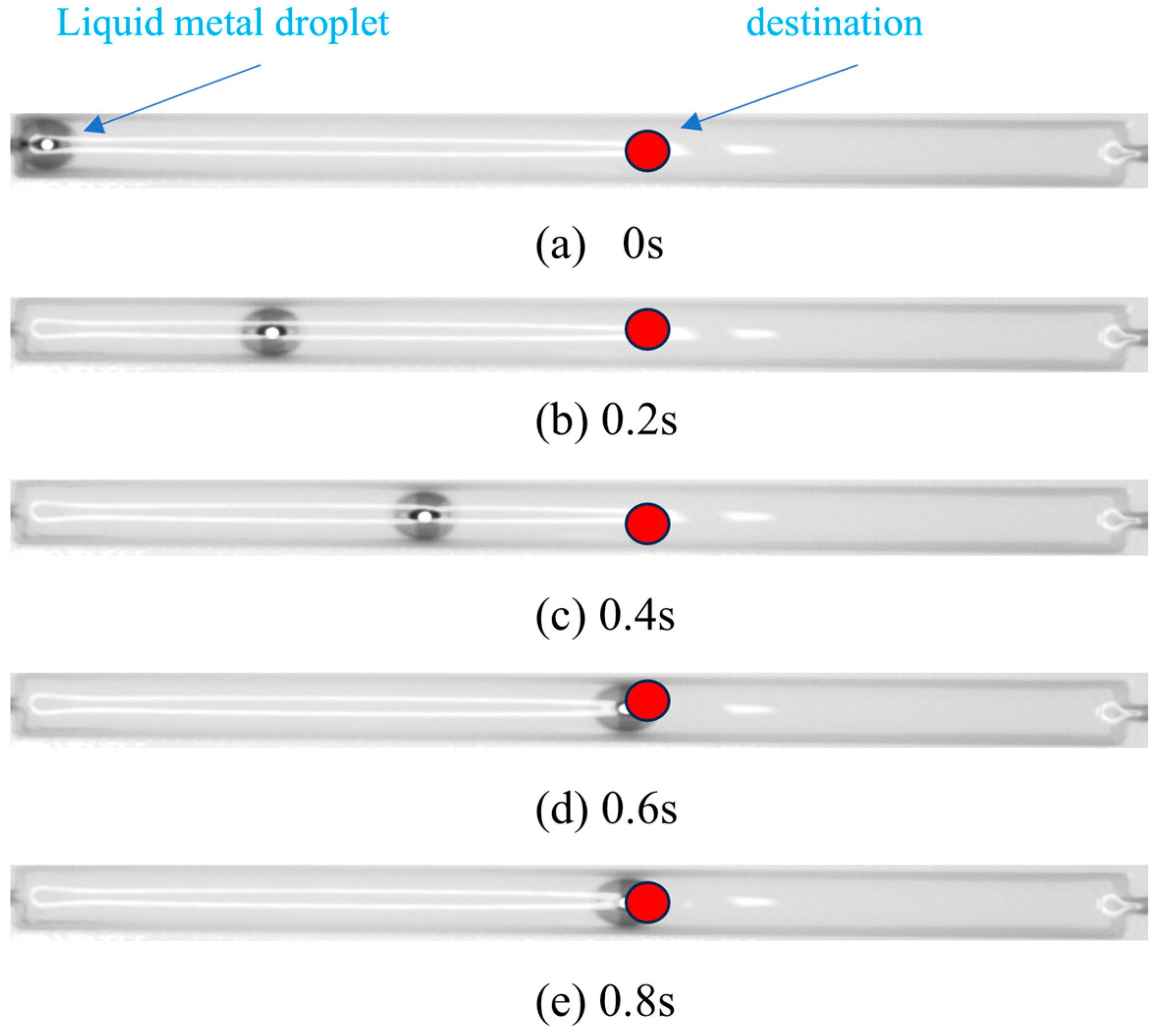
2.1. Experimental Setup and Materials
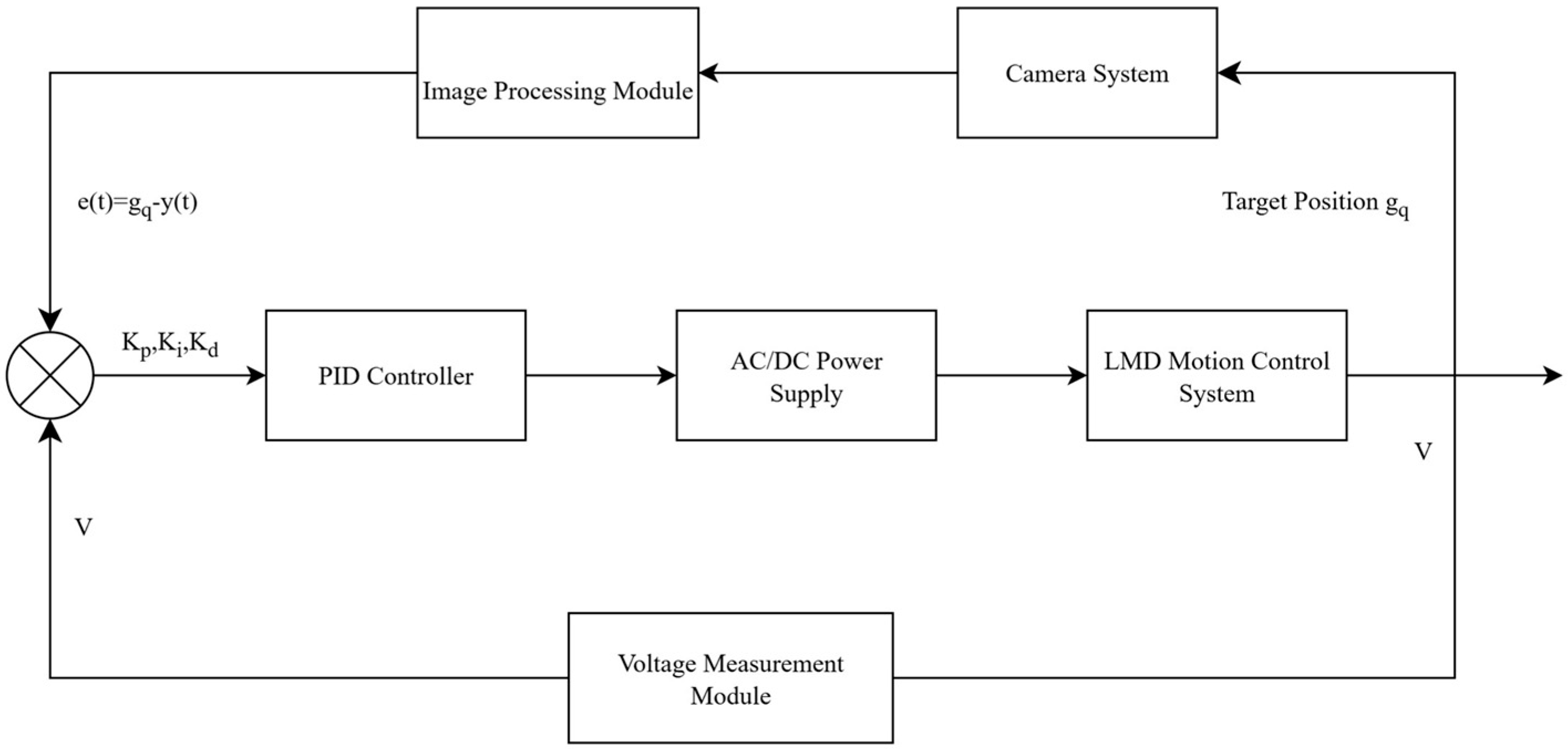
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Closed-Loop Control
3. Results and Discussion
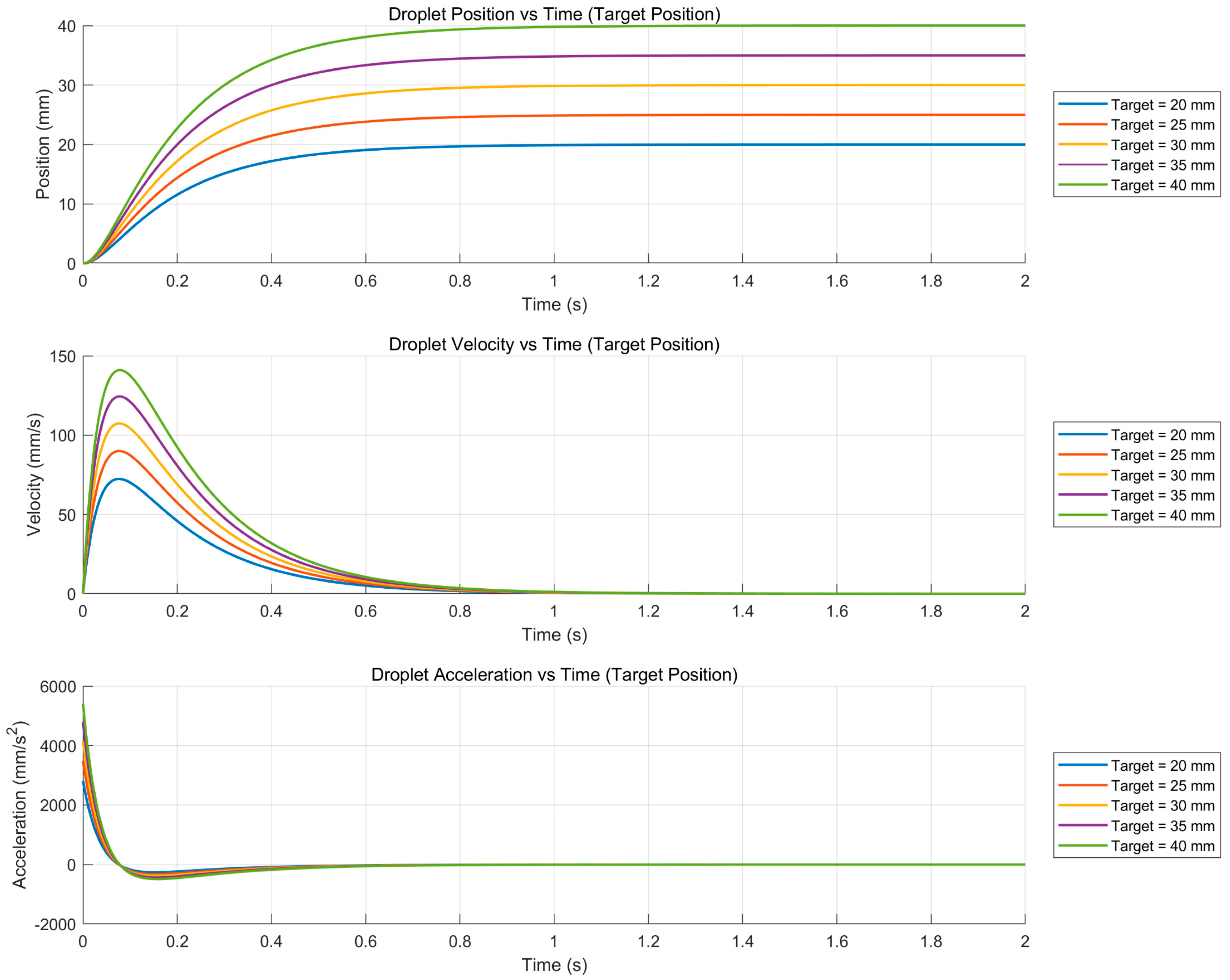
3.1. Motion Response of Liquid Metal Droplets at Different Target Positions
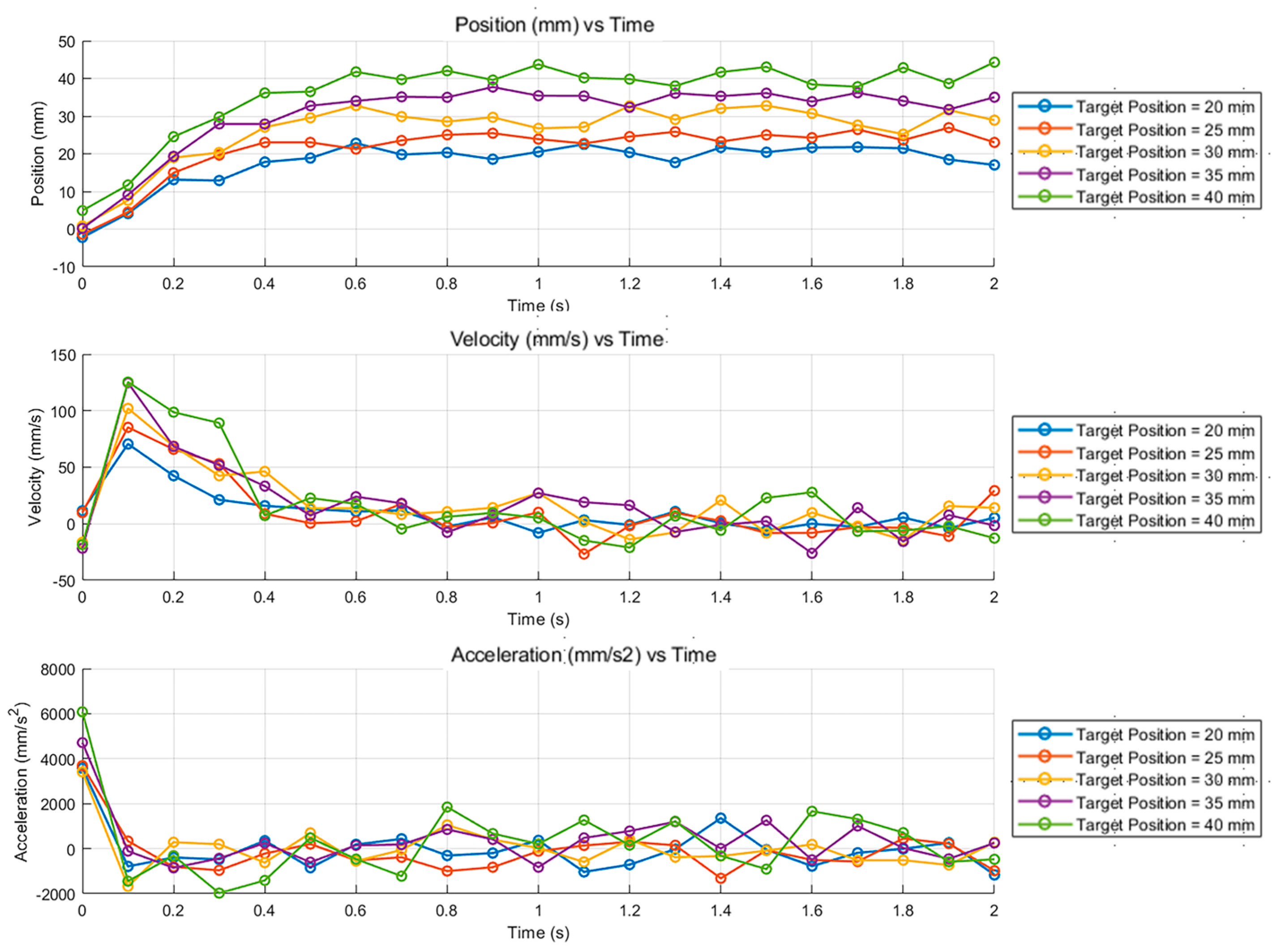
3.2. Motion Response of Liquid Metal Droplets at Different Particle Sizes and Concentrations
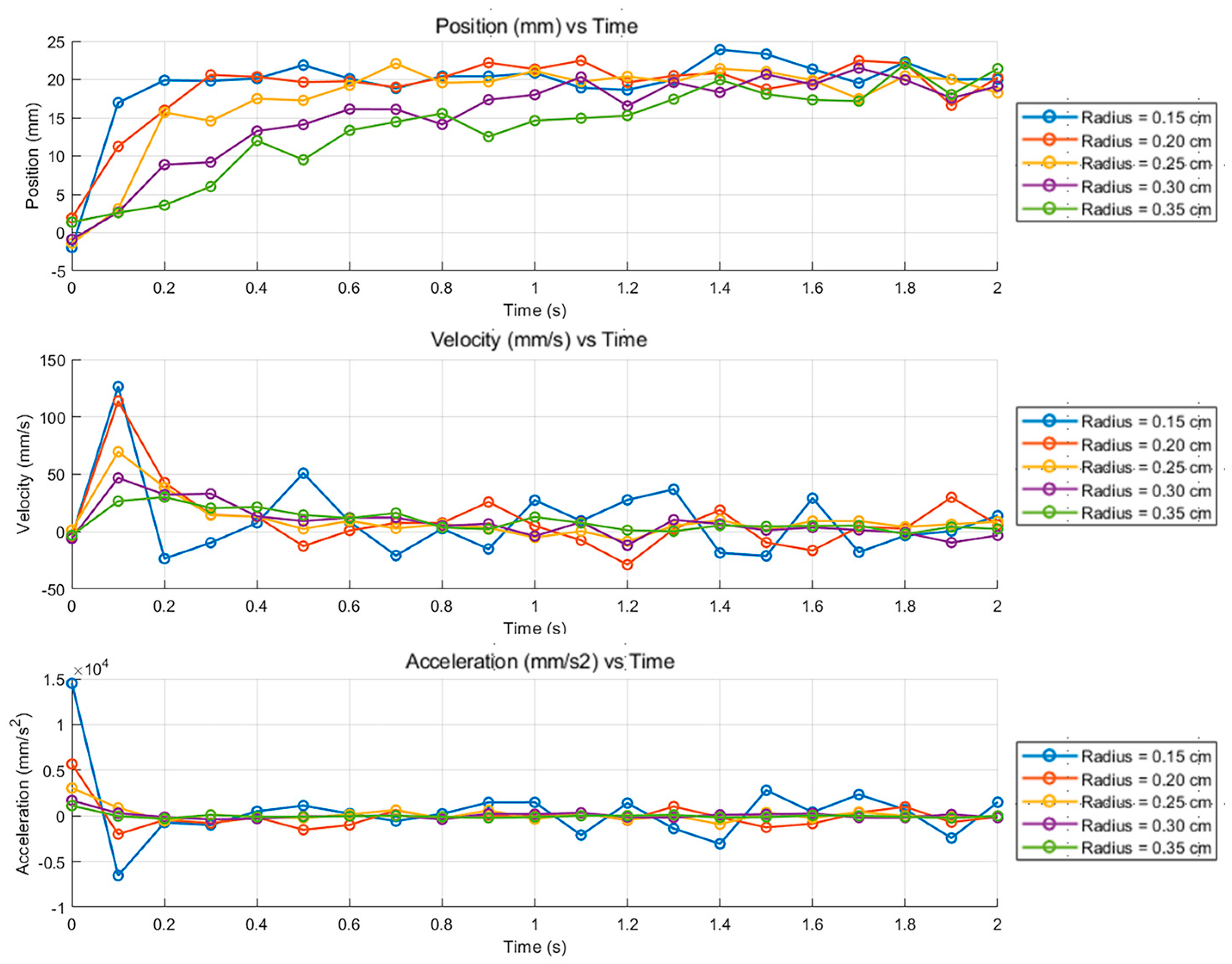
3.3. Motion Response of Liquid Metal Droplets at Different Droplet Radii
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Modeling for Controlling the Motion of a Liquid Metal Droplet
Appendix A.1. The Electrocapillarity of Galinstan

Appendix A.2. Dynamic Model

Appendix A.3. The Effect of Abrasive Particles on the Rheological Properties of Fluids
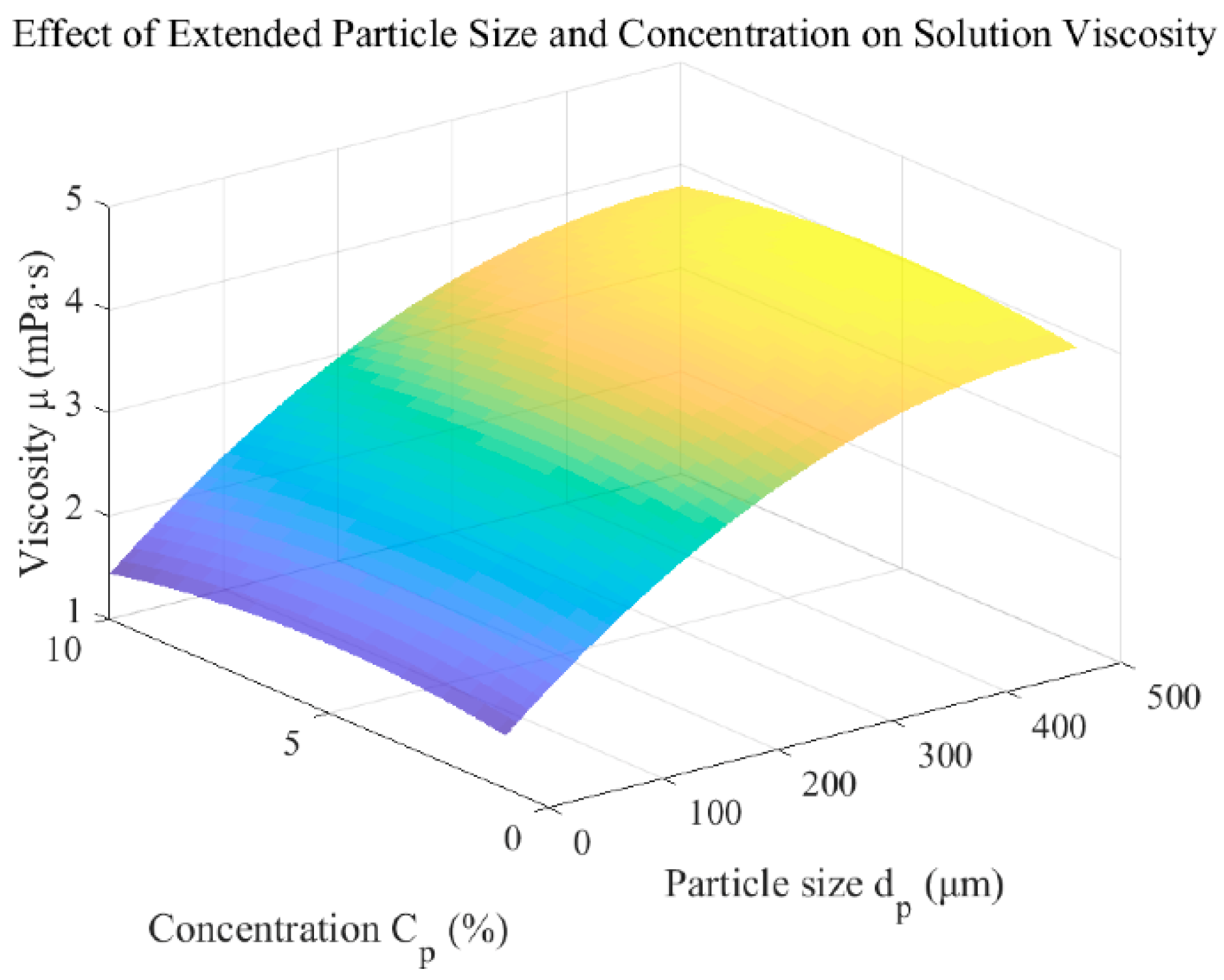
Appendix A.4. Control Design
References
- Daeneke, T.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Mahmood, N.; De Castro, I.A.; Esrafilzadeh, D.; Barrow, S.J.; Dickey, M.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Liquid Metals: Fundamentals and Applications in Chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4073–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Y.; Sen, P.; Kim, C.J. Characterization of Nontoxic Liquid-Metal Alloy Galinstan for Applications in Microdevices. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2012, 21, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, M.D.; Chiechi, R.C.; Larsen, R.J.; Weiss, E.A.; Weitz, D.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Eutectic Gallium-Indium (EGaIn): A Liquid Metal Alloy for the Formation of Stable Structures in Microchannels at Room Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monat, C.; Domachuk, P.; Eggleton, B.J. Integrated Optofluidics: A New River of Light. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ozbay, E. Plasmonics: Merging Photonics and Electronics at Nanoscale Dimensions. Science 2006, 311, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.A.; Someya, T.; Huang, Y. Materials and Mechanics for Stretchable Electronics. Science 2010, 327, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurig, D.; Mock, J.J.; Justice, B.; Cummer, S.A.; Pendry, J.B.; Starr, A.F.; Smith, D.R. Metamaterial Electromagnetic Cloak at Microwave Frequencies. Science 2006, 314, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Tang, S.-Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Schaefer, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Dickey, M.D. Liquid Metal Enabled Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 974–993. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.G.; Dickey, M.D. Strain-Controlled Diffraction of Light from Stretchable Liquid Metal Micro-Components. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2013, 193, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.C.; Tang, S.K.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Hashimoto, M.; Phillips, S.T.; Dickey, M.D.; Whitesides, G.M. Cofabrication: A Strategy for Building Multicomponent Microsystems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, J.; Tang, S.-Y.; Xu, R.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. A Controllable Untethered Vehicle Driven by Electrically Actuated Liquid Metal Droplets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, S.-Y.; Fang, T.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, S. A Wheeled Robot Driven by a Liquid-Metal Droplet. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1805039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Chen, K.; Lin, Y.; Kiriya, D.; Shiraki, H.; Yu, Z.; Ha, T.-J.; Javey, A. Highly Deformable Liquid-State Heterojunction Sensors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, V.; Tang, S.-Y.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Petersen, P.; Eshtiaghi, N.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mitchell, A. Liquid Metals: Liquid Metal Marbles (Adv. Funct. Mater. 2/2013). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed Khan, M.; Hayes, G.J.; So, J.-H.; Lazzi, G.; Dickey, M.D. A Frequency Shifting Liquid Metal Antenna with Pressure Responsiveness. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 013501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.-H.; Thelen, J.; Qusba, A.; Hayes, G.J.; Lazzi, G.; Dickey, M.D. Reversibly Deformable and Mechanically Tunable Fluidic Antennas. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3632–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Drzaic, P.; Yeo, J.-S.; Koch, T. A Critical Review of the Present and Future Prospects for Electronic Paper. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2011, 19, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupenkin, T.; Yang, S.; Mach, P. Tunable Liquid Microlens. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.-Z.; Liu, T.-Y.; Liu, J. Liquid Metal Smart Materials toward Soft Robotics. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zeng, M.; Fu, L. Surface Chemistry of Gallium-Based Liquid Metals. Matter 2020, 3, 1477–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, B.; Li, K.; Zhang, L. Application of Liquid Metal Driven-Abrasive Flow to Material Removal for the Inner Surface of Channel. Powder Technol. 2025, 452, 120487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kuang, S.; Li, X.; Shu, J.; Li, W.; Tang, S.-Y.; Zhang, S. Magnetically-and Electrically-controllable Functional Liquid Metal Droplets. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Sivan, V.; Khoshmanesh, K.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Tang, X.; Gol, B.; Eshtiaghi, N.; Lieder, F.; Petersen, P.; Mitchell, A. Electrochemically Induced Actuation of Liquid Metal Marbles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, J.-B.; Chung, S.K.; Kim, D. On-Demand Magnetic Manipulation of Liquid Metal in Microfluidic Channels for Electrical Switching Applications. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Tang, S.-Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, S. Unconventional Locomotion of Liquid Metal Droplets Driven by Magnetic Fields. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, R.C.; Morishita, A.M.; Dang, J.H.; Moorefield, M.R.; Shiroma, W.A.; Ohta, A.T. Rapid Electrocapillary Deformation of Liquid Metal with Reversible Shape Retention. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Sheng, L.; Liu, J. Self-fueled Biomimetic Liquid Metal Mollusk. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2648–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Tang, S.-Y.; Sivan, V.; Zhang, W.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Khoshmanesh, K. Photochemically Induced Motion of Liquid Metal Marbles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 174104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavabeti, A.; Daeneke, T.; Chrimes, A.F.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Zhen Ou, J.; Mitchell, A.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Ionic Imbalance Induced Self-Propulsion of Liquid Metals. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tan, S.; Yuan, B.; Liu, J. Alternating Electric Field Actuated Oscillating Behavior of Liquid Metal and Its Application. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2016, 59, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.-J. Surface-Tension-Driven Microactuation Based on Continuous Electrowetting. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, S.; O’Brien, C.; Hamza, A.; Sharma, S.; Rein, C.; Sanjaya, M.; Helmer, D.; Kotz-Helmer, F.; Pezeshkpour, P.; Rapp, B.E. An On-Chip Liquid Metal Plug Generator. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Sivan, V.; Petersen, P.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Abbott, D.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Liquid Metal Enabled Pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3304–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, F.; Kuang, S.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Modeling and Motion Control of a Liquid Metal Droplet in a Fluidic Channel. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 25, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, K.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Behaviour of Electrically Driven Liquid Metal Droplets in Abrasive Particle Suspensions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2025, 27, 14999–15008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharmann, F.; Cherkashinin, G.; Breternitz, V.; Knedlik, C.; Hartung, G.; Weber, T.; Schaefer, J.A. Viscosity Effect on GaInSn Studied by XPS. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, J. Gallium-Based Thermal Interface Material with High Compliance and Wettability. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 107, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.O. Modern Electrochemistry: An Introduction to an Interdisciplinary Area; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Beni, G.; Hackwood, S.; Jackel, J.L. Continuous Electrowetting Effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1982, 40, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Liu, W.; Jiang, T.; Song, C.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y. Pumping of Ionic Liquids by Liquid Metal-Enabled Electrocapillary Flow under DC-Biased AC Forcing. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschuh-Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gan, T.; Zhou, X. Electric Actuation of Liquid Metal Droplets in Acidified Aqueous Electrolyte. Langmuir 2019, 35, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, H. Versatile Movements of Liquid Metal Droplet under Electrostatic Actuation in Alkaline Solutions. Materials 2020, 13, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.F.; Jin, M.J.; Jin, X.J.; Zuo, S.G. Modeling of Movement of Liquid Metal Droplets Driven by an Electric Field. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 18505–18513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacuycuy, S.; Shiroma, W.; Ohta, A. Electrocapillary Actuation of Liquid Metal in Microchannels. Micromachines 2022, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, H.C. A Calculation of the Viscous Force Exerted by a Flowing Fluid on a Dense Swarm of Particles. Flow Turbul. Combust. 1949, 1, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.C.; Wang, D.Q.; Sun, Y.C. Region-Reaching Control of Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, D. Moving Groups of Microparticles into Array with a Robot–Tweezers Manipulation System. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Y.; Liu, J. A Polarized Liquid Metal Worm Squeezing across a Localized Irregular Gap. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11049–11056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Feng, B.; Li, K.; Zhang, L. Motion Control of Gallium-Based Liquid Metal Droplets in Abrasive Suspensions Within a Flow Channel. Actuators 2025, 14, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090456
Ma Y, Feng B, Li K, Zhang L. Motion Control of Gallium-Based Liquid Metal Droplets in Abrasive Suspensions Within a Flow Channel. Actuators. 2025; 14(9):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090456
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yapeng, Baoqi Feng, Kaixiang Li, and Lei Zhang. 2025. "Motion Control of Gallium-Based Liquid Metal Droplets in Abrasive Suspensions Within a Flow Channel" Actuators 14, no. 9: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090456
APA StyleMa, Y., Feng, B., Li, K., & Zhang, L. (2025). Motion Control of Gallium-Based Liquid Metal Droplets in Abrasive Suspensions Within a Flow Channel. Actuators, 14(9), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090456





