Evaluation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Equine Sarcoid: An Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Histological Features
2.2. Immunohistochemical Results
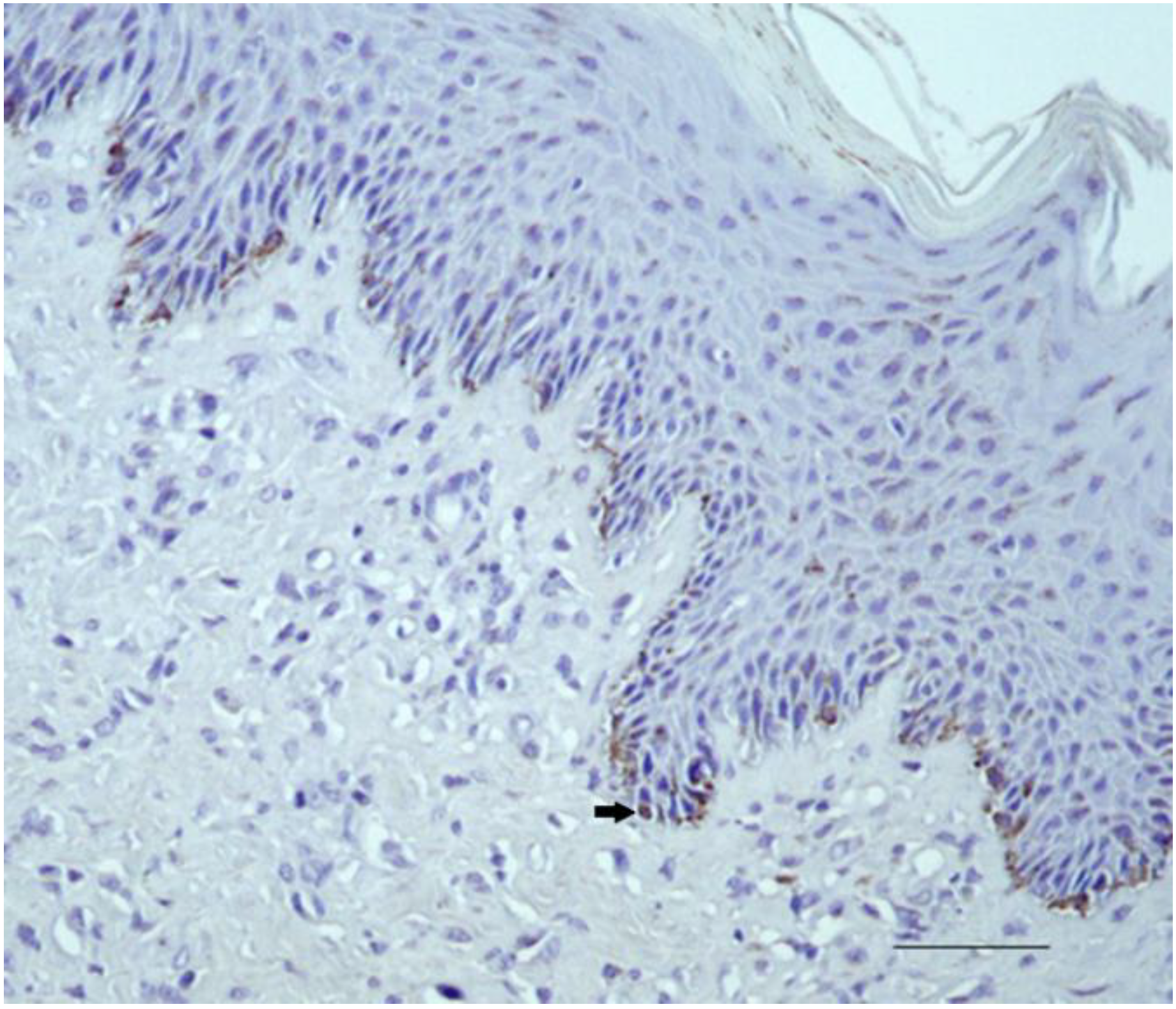
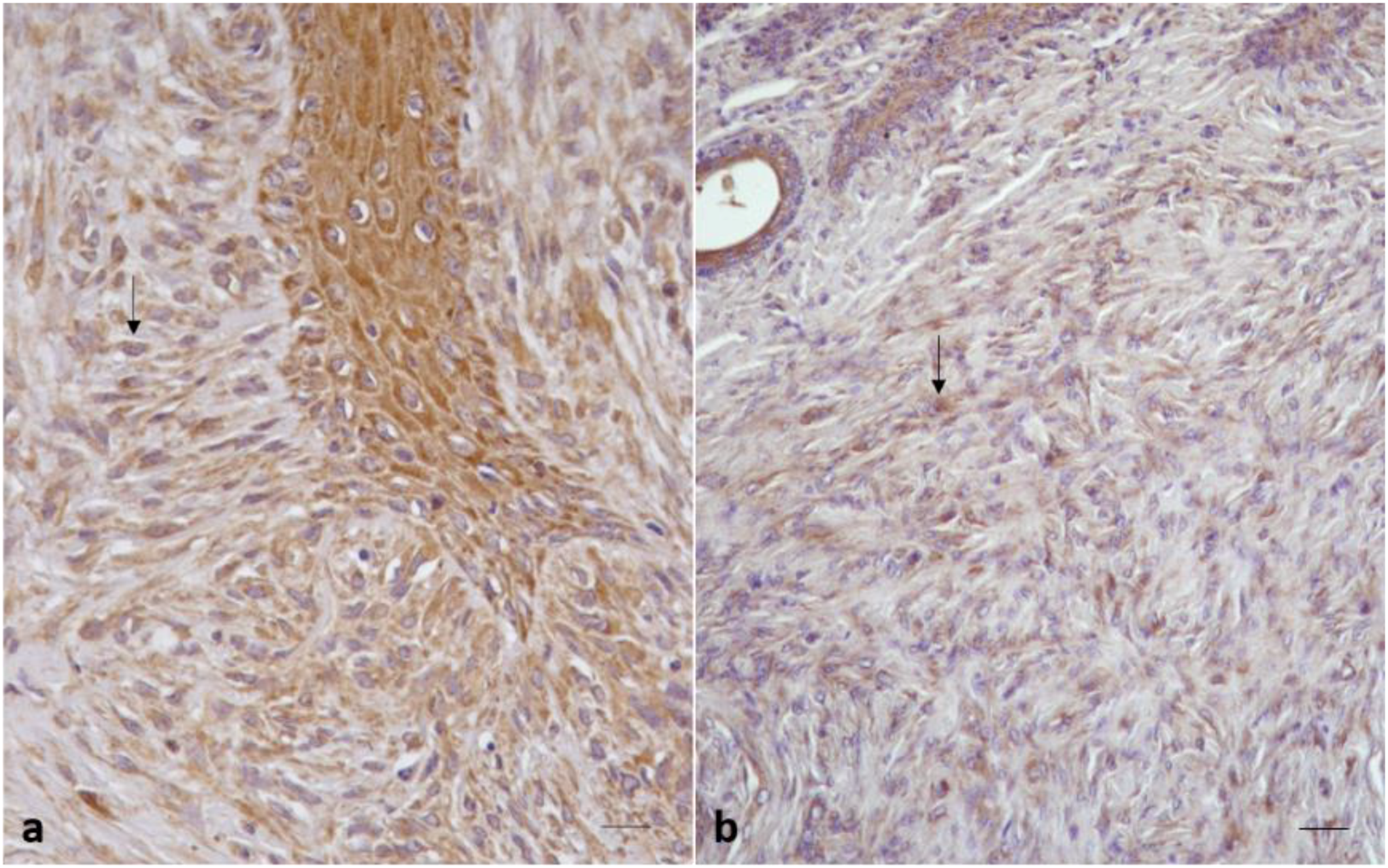
2.2.1. Control Samples
2.2.2. Sarcoid Samples
2.3. Statistical Results
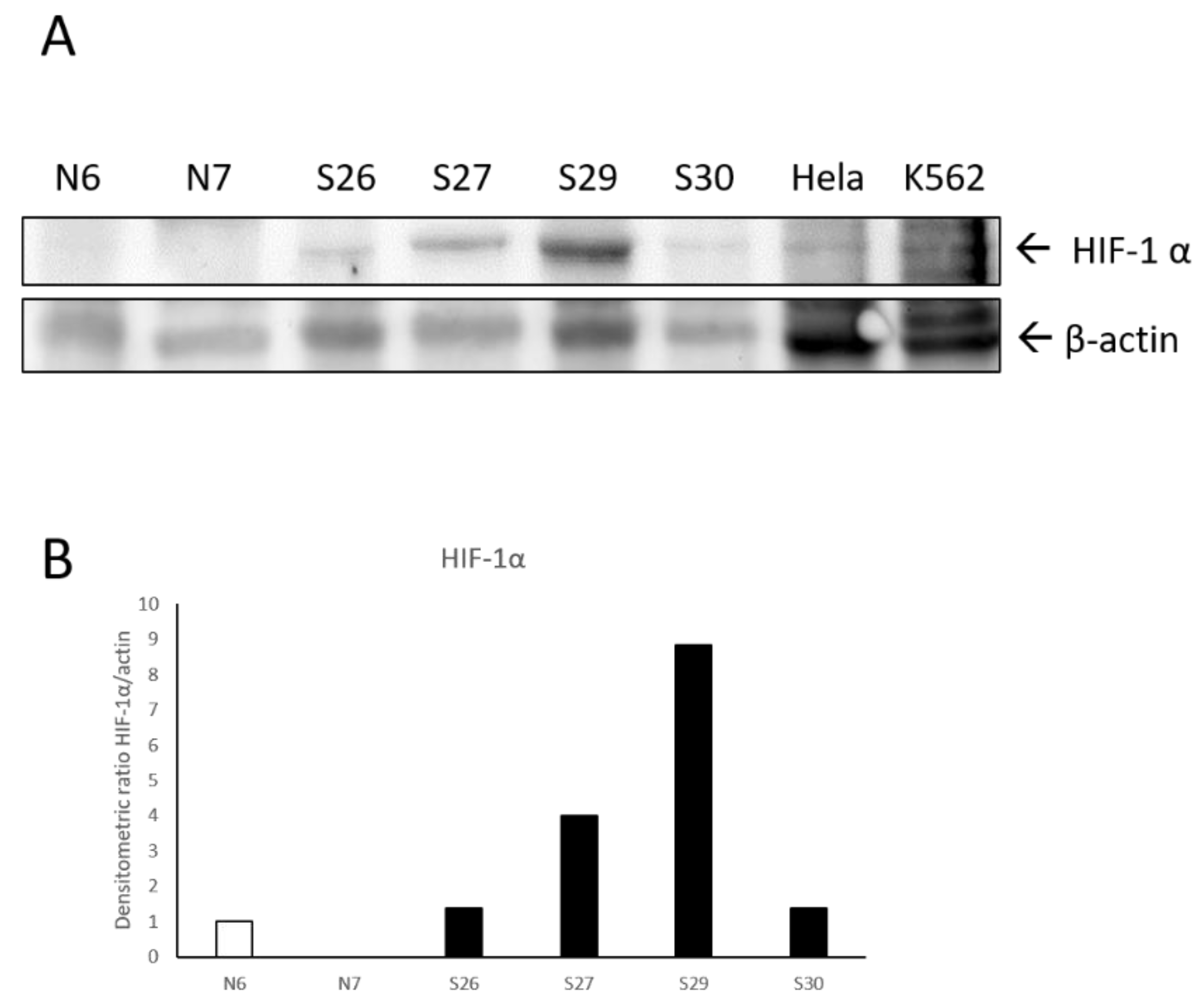
2.4. Biochemical Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tumor Samples
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Scoring of Immunoreactivity
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Protein Extraction and SDS PAGE/Western Blotting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPV-1 | Bovine papillomavirus type-1 |
| BPV-2 | Bovine papillomavirus type-2 |
| BPV-13 | Bovine papillomavirus type-13 |
| HPVs | Human Papillomaviruses |
| HIF1 | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| WB | Western Blotting |
| N | normal skin |
| PDGFβ-r | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor βeta-receptor |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| PHD | Prolyl Hydroxylases |
References
- Pascoe, R.R.; Summers, P.M. Clinical Survey of Tumours and Tumor Like Lesions in Horses in Southeast. Equ. Vet. J. 1981, 13, 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ragland, W.L.; Keown, G.H.; Spencer, G.R. Equine Sarcoid. Equ. Vet. J. 1970, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, L.; Campo, M.S. Bovine Papillomaviruses: Their Role in the Aetiology of Cutaneous Tumours of Bovids and Equids. Vet. Dermatol. 2008, 19, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzacchiello, G.; Corteggio, A. Equine Sarcoid: State of the art. Ippologia 2009, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Berruex, F.; Gerber, V.; Wohlfender, F.D.; Burger, D.; Koch, C. Clinical Course of Sarcoids in 61 Franches-Montagnes Horses over a 5–7-year Period. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, L.; Brandt, S. Papillomavirus Associated Diseases of the Horse. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelos, J.; Marti, E.; Lazary, S.; Carmichael, L. Characterization of BPV-like DNA in in Equine Sarcoids. Arch. Virol. 1991, 119, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, N.; von Tscharner, C.; Lazary, S.; Antczak, D.; Gerber, H. DNA of Bovine Papillomavirus Type 1 and 2 in Equine Sarcoids: PCR Detection and Direct Sequencing. Arch. Virol. 1993, 132, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergvall, K.E. Sarcoids. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Equine Pract. 2013, 29, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzacchiello, G.; Roperto, F. Bovine Papillomaviruses, Papillomas and Cancer in Cattle. Vet. Res. 2008, 39, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, M. Animal Models of Papilloma Virus Pathogenesis. Virus Res. 2002, 89, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.A.; Théon, A.P.; Madewell, B.R.; Hitchcock, M.E.; Schlegel, R.; Schiller, J.T. Expression of a Transforming Gene (E5) of Bovine Papillomavirus in Sarcoids Obtained from Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, A.; De Moor, A.; Ducatelle, R. PCR Detection of Bovine Papilloma Virus DNA in Superficial Swabs and Scrapings from Equine Sarcoids. Vet. J. 2001, 161, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, A.; De Moor, A.; Vlaminck, L.; Pille, F.; Steenhaut, M. Evaluation of Excision, Cryosurgery and Local BCG Vaccination for the Treatment of Equine Sarcoids. Vet. Rec. 2001, 49, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, S.; Haralambus, R.; Schoster, A.; Kirnbauer, R.; Stanek, C. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Represent a Reservoir of Bovine Papillomavirus DNA in Sarcoid-Affected Equines. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, S.; Tober, R.; Corteggio, A.; Burger, S.; Sabitzer, S.; Walter, I.; Kainzbauer, C.; Steinborn, R.; Nasir, L.; Borzacchiello, G. BPV-1 Infection is not Confined to the Dermis but Also Involves the Epidermis of Equine Sarcoids. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Armstrong, E.L.; Gofton, R.G.; Mason, J.; De Toit, N.; Day, M.J. Characterization of Early and Late Bovine Papillomavirus Protein Expression in Equine Sarcoids. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 23, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, G.; Ellsmore, V.A.; O’Brien, P.M.; Reid, S.W.; Love, S.; Campo, M.S.; Nasir, L. Association of Bovine Papillomavirus with the Equine Sarcoid. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, L.; Reid, S.W. Bovine Papillomaviral Gene Expression in Equine Sarcoid Tumours. Virus Res. 1999, 61, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araldi, R.; Melo, T.; Diniz, N.; Carvalho, R.; Beçak, W.; Stocco, R. Bovine Papillomavirus Clastogenic Effect Analyzed in Comet Assay. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, S.; Melo, T.; Assaf, S.; Araldi, R.; Mazzuchelli-de-Souza, J.; Sircili, M.; Carvalho, R.; Roperto, F.; Beçak, W.; Stocco, R. Chromosome Aberrations in Cells Infected with Bovine Papillomavirus: Comparing Cutaneous Papilloma, Esophagus Papilloma, and Urinary Bladder Lesion Cells. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 910849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, T.; Araldi, R.; Pessoa, N.; De-Sá-Júnior, P.; Carvalho, R.; Beçak, W.; Stocco, R.C. Bos Taurus Papillomavirus Activity in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Demonstrating a Productive Infection. Gen. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 16712–16727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocco dos Santos, R.C.; Lindsey, C.J.; Ferraz, O.P.; Pinto, J.R.; Mirandola, R.S.; Benesi, F.J.; Birgel, E.H.; Pereira, C.A.; Beçak, W. Bovine Papillomavirus Transmission and Chromosomal Aberrations: An Experimental Model. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzacchiello, G.; Russo, V.; Della Salda, L.; Roperto, S.; Roperto, F. Expression of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-β Receptor and Bovine Papillomavirus E5 and E7 Oncoproteins in Equine Sarcoid. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 139, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotugno, R.; Gallotta, D.; d’Avenia, M.; Corteggio, A.; Altamura, G.; Roperto, F.; Belisario, M.A.; Borzacchiello, G. BAG3 Protects Bovine Papillomavirus Type 1-Transformed Equine Fibroblasts Against Pro-Death Signals. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martano, M.; Corteggio, A.; Restucci, B.; De Biase, M.E.; Borzacchiello, G.; Maiolino, P. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Equine Sarcoid: An Immunohistochemical and Molecular Study. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martano, M.; Power, K.; Restucci, B.; Pagano, I.; Altamura, G.; Borzacchiello, G.; Maiolino, P. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in Equine Sarcoid. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Role of Angiogenesis in Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 6 (Suppl. 16), 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolino, P.; De Vico, G.; Restucci, B. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Basal Cell Tumours and in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of Canine Skin. J. Comp. Pathol. 2000, 123, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolino, P.; Papparella, S.; Restucci, B.; De Vico, G. Angiogenesis in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of Canine Skin: An Immunohistochemical and Quantitative Analysis. J. Comp. Pathol. 2001, 125, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martano, M.; Maiolino, P.; Cataldi, M.; Restucci, B. Evaluation of Angiogenesis by Morphometric Analysis of Blood Vessels in Dysplastic and Neoplastic Lesions of Canine Gingiva. Vet. Res. Commun. 2004, 28, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martano, M.; Restucci, B.; Ceccarelli, D.M.; Lo Muzio, L.; Maiolino, P. Immunohistochemical Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Canine Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 1, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restucci, B.; De Vico, G.; Maiolino, P. Evaluation of Angiogenesis in Canine Mammary Tumors by Quantitative Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Immunohistochemistry. Vet. Pathol. 2000, 37, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restucci, B.; Papparella, S.; Maiolino, P.; De Vico, G. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Canine Mammary Tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2002, 39, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restucci, B.; Maiolino, P.; Paciello, O.; Martano, M.; De Vico, G.; Papparella, S. Evaluation of Angiogenesis in Canine Seminomas by Quantitative Immunohistochemistry. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 128, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restucci, B.; Borzacchiello, G.; Maiolino, P.; Martano, M.; Paciello, O.; Papparella, S. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Flk-1 in Canine Mammary Tumours. J. Comp. Pathol. 2004, 130, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restucci, B.; Martano, M.; Maiolino, P. Expression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelin-1 Receptor A in Canine Mammary Tumours. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 100, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdos, J.I.; Ashcroft, M. Negative and Positive Regulation of HIF-1: A Complex Network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1755, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, D.J.; Kaur, B.; Van Meir, E.G. Genetic Modulation of Hypoxia Induced Gene Expression and Angiogenesis: Relevance to Brain Tumors. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majmundar, A.J.; Wong, W.J.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia Inducible Factors and the Response to Hypoxic Stress. Mol. Cells 2010, 40, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.E.S.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors: Crosstalk between Inflammation and Metabolism. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 23, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, A.; Johnson, R.S. Biology of HIF-1alpha. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebersold, D.M.; Burri, P.; Beer, K.T.; Laissue, J.; Djonov, V.; Greiner, R.H.; Semenza, G.L. Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 a Novel Predictive and Prognostic Parameter in the Radiotherapy of Oropharyngeal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beasley, N.J.P.; Leek, R.; Alam, M.; Turley, H.; Cox, G.J.; Gatter, K.; Millard, P.; Fuggle, S.; Harris, A.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 in Head and Neck Cancer: Relationship to Tumor Biology and Treatment Outcome in Surgically Resected Patients. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bos, R.; Zhong, H.; Hanrahan, C.F.; Mommers, E.C.; Semenza, G.L.; Pinedo, H.M.; Abeloff MDSimons, J.W.; van Diest, P.J.; van der Wall, E. Levels of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 during Breast Carcinogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Sivrids, E.; Turley, H.; Talks, K.; Pezzella, F.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L. Relation of Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 and 2 in Operable Non-Small Lung Cancer to Angiogenic/ Molecular Profile of Tumors and Survival. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukourakis, M.I.; Giatromanolak, I.A.; Sivrids, E.; Simopoulos, C.; Turley, H.; Talks, K.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF1 and HIF2), Angiogenesis, and Chemoradiotherapy Outcome of Squamous Cell Head-and-Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwai, T.; Kitadai, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Onogawa, S.; Matsutani, N.; Kaio, E.; Ito, M.; Chayama, K. Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha is Associated with Tumor Vascularization in Human Colorectal Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2003, 105, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivrid, S.E.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L.; Koukourakis, M.I. Association of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors 1 and 2 with Activated Angiogenic Pathways and Prognosis in Patients with Endometrial Carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuder, R.M.; Chacon, M.; Alger, L.; Wang, J.; Taraseviciene-Stewart, L.; Kasahara, Y.; Cool, C.D.; Bishop, A.E.; Geraci, M.; Semenza, G.L.; et al. Expression of Angiogenesis-Related Molecules in Plexiform Lesion in Severe Pulmonary Hypertension: Evidence for a Process of Disordered Angiogenesis. J. Pathol. 2001, 195, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagzag, D.; Zhang, H.; Scalzitti, J.M.; Laughner, E.; Simons, J.W.; Semenza, G.L. Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 in Brain Tumors: Association with Angiogenesis, Invasion, and Prognosis. Cancer 2000, 88, 2606–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, H.; Bouhamdan, M.; Bauerfeld, C.; Talreja, J.; Aoidi, R.; Houde, N.; Charron, J.; Samavati, L. MEK2 Negatively Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated IL-1β Production through HIF-1α Expression. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, M.; Stanley, S. HIF-1α as a Central Mediator of Cellular Resistance to Intracellular Pathogens. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2019, 60, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Meng, X.; Pu, Y.; Sun, F.; Man, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Overexpression of HIF-1a Could Partially Protect K562 Cells from 1,4-Benzoquinone Induced Toxicity by Inhibiting ROS, Apoptosis and Enhancing Glycolysis. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 55, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The Role of Hypoxia in Cancer Progression, Angiogenesis, Metastasis, and Resistance to Therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, T. Oxygen and Cancer. N. C. Med. J. 1997, 58, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Defining the Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 in Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Oncogene 2010, 29, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, P.J.; Wilson, W.J.; O’Brien, S.; Makino, Y.; Poellinger, L. Regulation of the Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factor 1alpha by the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6519–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Hou, M.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Y.; Gou, H. Expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in Colorectal Cancer: Association with Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Implications. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Davis-Smyth, T. The Biology of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, H.L.; Mercurio, A.M. VEGF Targets the Tumour Cell. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Yang, D.; Hu, J.; Hao, X.; Gao, J.; Mao, Z. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-alpha Expression Correlates with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Expression and Lymphangiogenesis/Angiogenesis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Metastasis of Hypoxic Breast Cancer Cells. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depping, R.; Jelkmann, W.; Kosyna, F.K. Nuclear-Cytoplasmatic Shuttling of Proteins in Control of Cellular Oxygen Sensing. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.; Nosho, K.; Shima, K.; Irahara, N.; Chan, A.T.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S. HIF1A Overexpression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in a Cohort of 731 Colorectal Cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.I.; Lim, H.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Seung, B.J.; Sur, J.H. Analysis of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression Relative to Other Key Factors in Malignant Canine Mammary Tumours. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 153, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeltzing, O.; McCarty, M.F.; Wey, J.S.; Fan, F.; Liu, W.; Belcheva, A.; Bucana, C.D.; Semenza, G.L.; Ellis, L.M. Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha in Gastric Cancer Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, and Vessel Maturation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuninghame, S.; Jackson, R.; Zehbe, I. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Its Role in Viral Carcinogenesis. Virology 2014, 456–457, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, L.; Zhang, E.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Le, A.D.; Zhou, K.; Tang, X. Overexpression of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Type 16 Oncoproteins Promotes Angiogenesis via Enhancing HIF-1a and VEGF Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 311, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Bodily, J.M.; Beglin, M.; Kyo, S.; Inoue, M.; Laimins, L.A. Hypoxia-Specific Stabilization of HIF-1alpha by Human Papillomaviruses. Virology 2009, 387, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, O.; Nacerddine, K.; Dejean, A. Human Papillomavirus Oncoprotein E7 Targets the Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein and Circumvents Cellular Senescence via the Rb and p53 Tumor Suppressor Pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuth, J.; Sharma, S.J.; Würdemann, N.; Holler, C.; Garvalov, B.K.; Acker, T.; Wittekindt, C.; Wagner, S.; Klussmann, J.P. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Activation in HPV-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89681–89691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araldi, R.P.; Assaf, S.M.R.; Carvalho, R.F.; Carvalho, M.A.C.R.; Souza, J.M.; Magnelli, R.F.; Módolo, D.G.; Roperto, F.P.; Stocco, R.C.; Beçak, W. Papillomaviruses: A Systematic Review. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayako, N.; Minoru, K.; Sho, K.; Christalle, C.T.C.; Hiroshi, H. HIF-1-Dependent Reprogramming of Glucose Metabolic Pathway of Cancer Cells and Its Therapeutic Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadari, N.; Deng, S.; Li, W. The Transcriptional Factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 and Their Novel Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Location | Number of Cases | Staining Intensity Score * | Percentage Positive Score ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neck | 2 | ++ | 3 |
| Limb | 9 | ++ | 3 |
| 1 | + | 2 | |
| Abdomen | 4 | ++ | 3 |
| 2 | + | 2 | |
| Pectoral region | 5 | ++ | 3 |
| 3 | + | 2 | |
| Head | 5 | ++ | 3 |
| 1 | + | 2 | |
| Paragenital | 3 | ++ | 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martano, M.; Altamura, G.; Power, K.; Restucci, B.; Carella, F.; Borzacchiello, G.; Maiolino, P. Evaluation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Equine Sarcoid: An Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Study. Pathogens 2020, 9, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010058
Martano M, Altamura G, Power K, Restucci B, Carella F, Borzacchiello G, Maiolino P. Evaluation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Equine Sarcoid: An Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Study. Pathogens. 2020; 9(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartano, Manuela, Gennaro Altamura, Karen Power, Brunella Restucci, Francesca Carella, Giuseppe Borzacchiello, and Paola Maiolino. 2020. "Evaluation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Equine Sarcoid: An Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Study" Pathogens 9, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010058
APA StyleMartano, M., Altamura, G., Power, K., Restucci, B., Carella, F., Borzacchiello, G., & Maiolino, P. (2020). Evaluation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Equine Sarcoid: An Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Study. Pathogens, 9(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010058






