In Vitro Activity of Statins against Naegleria fowleri
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
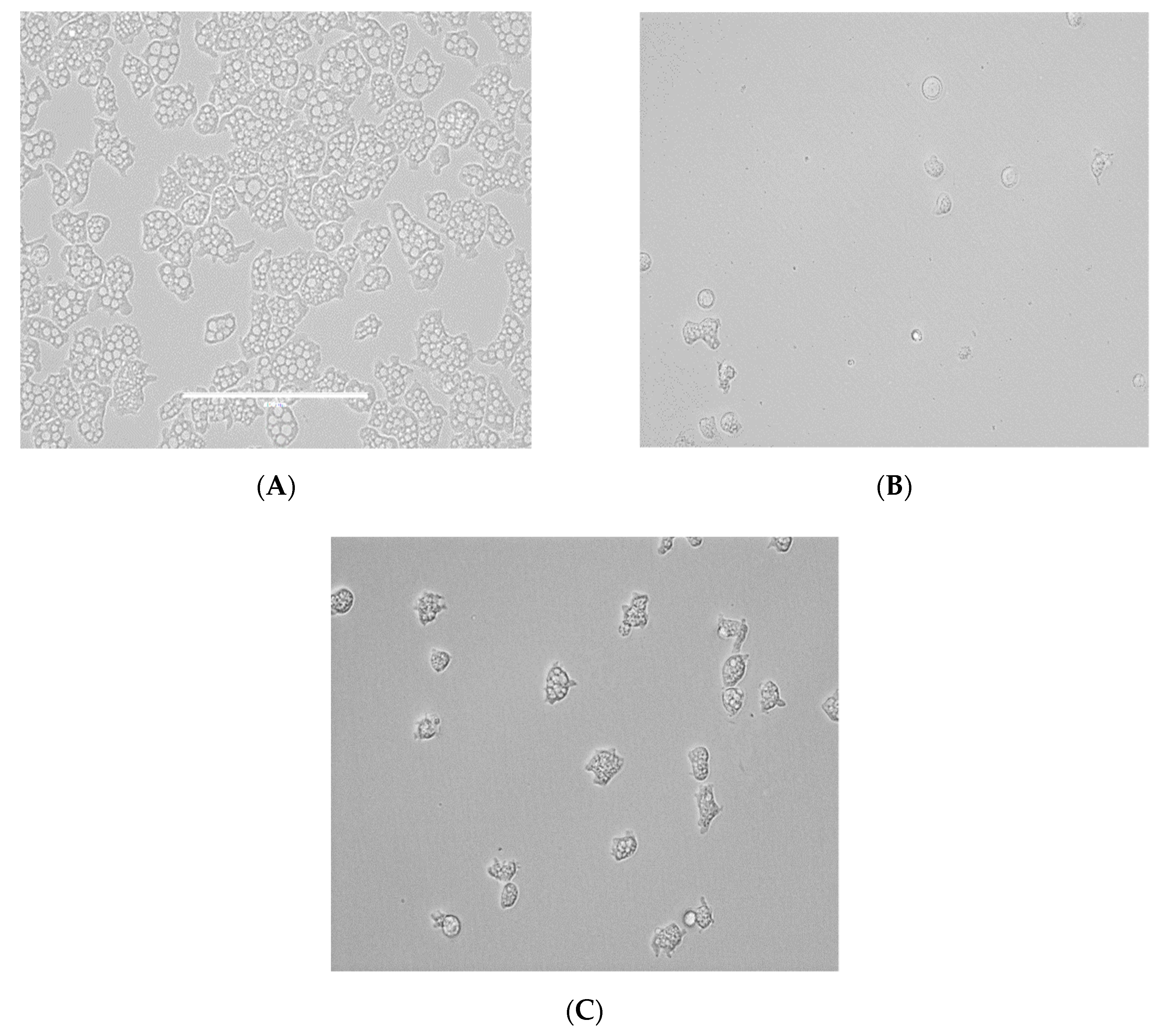
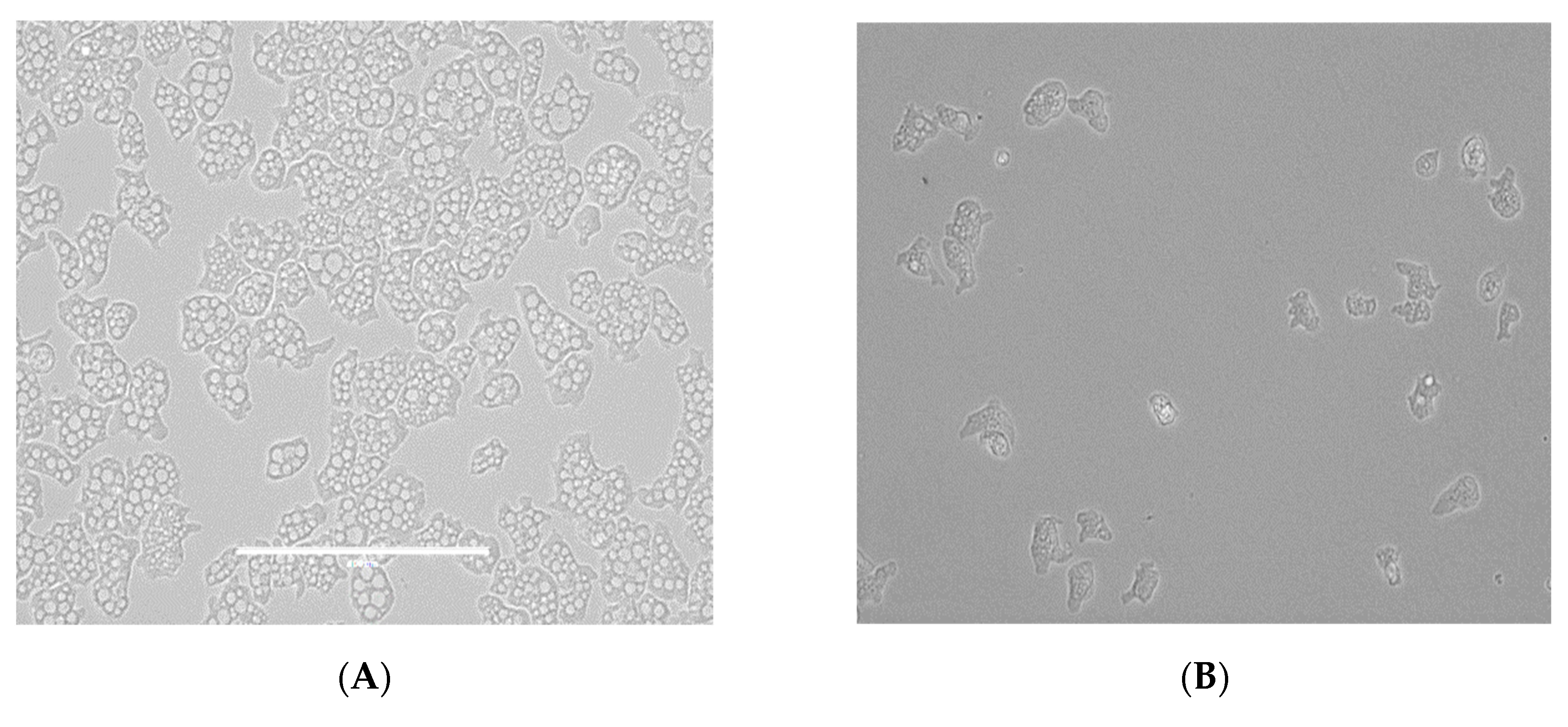
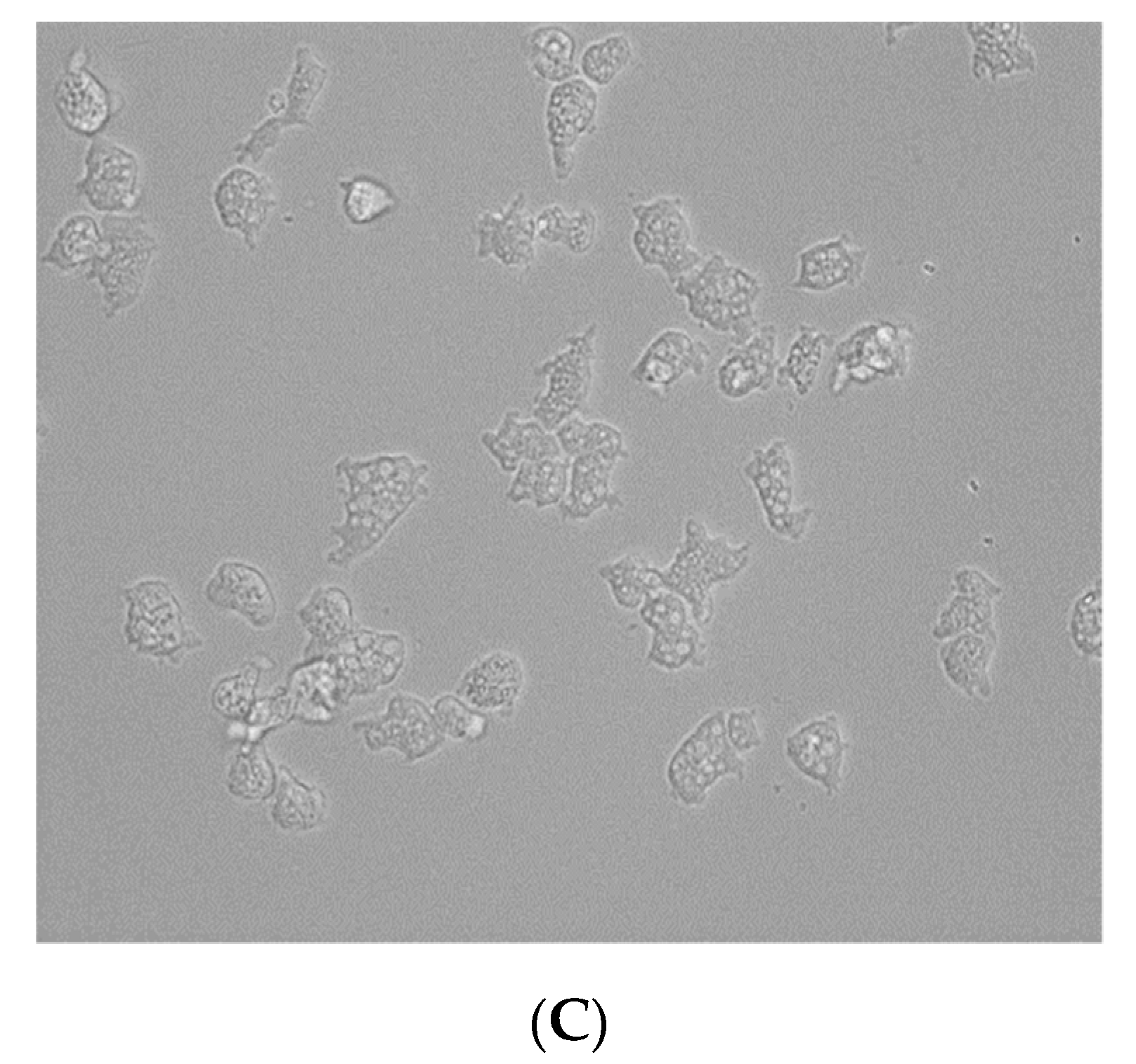
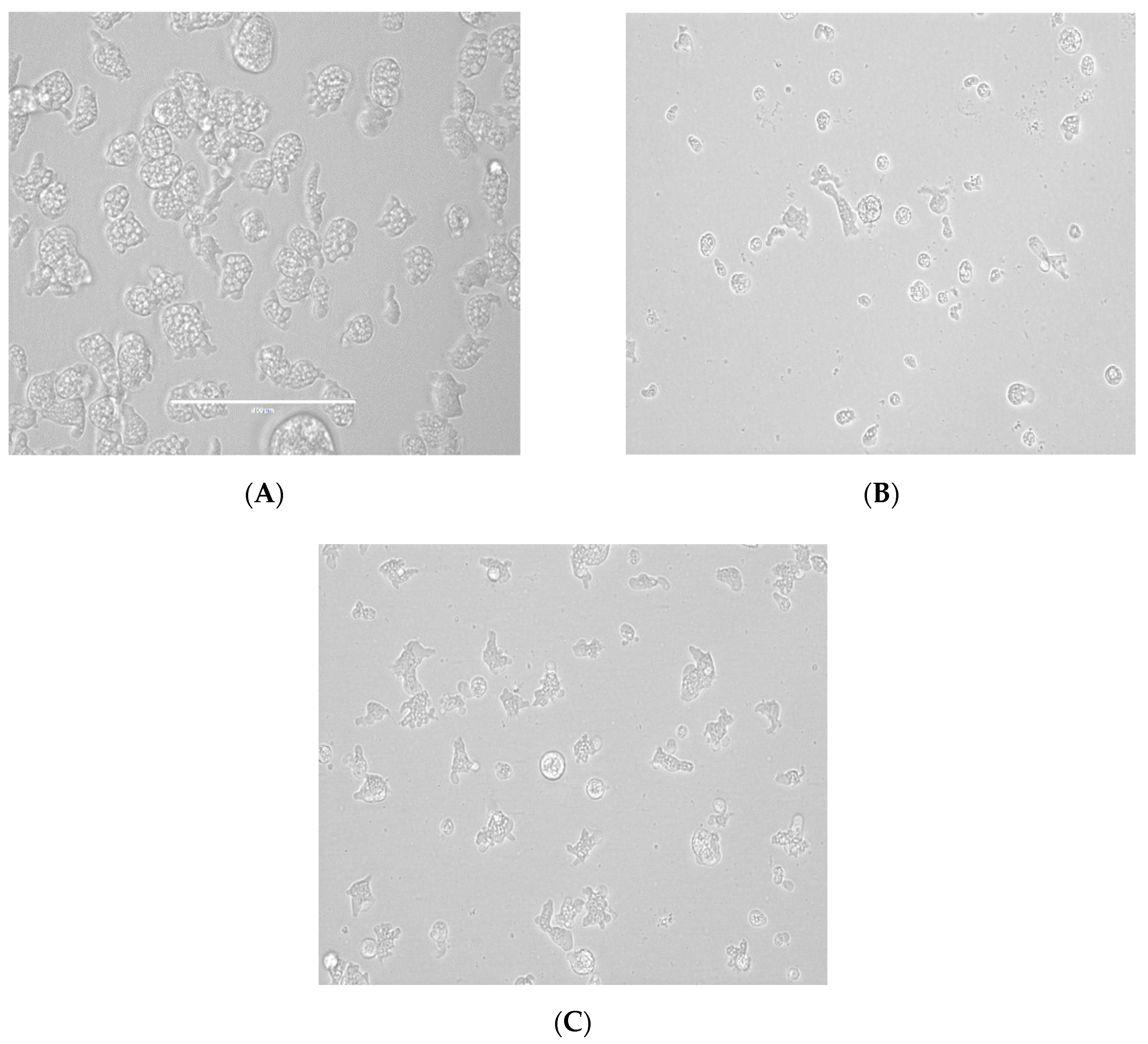
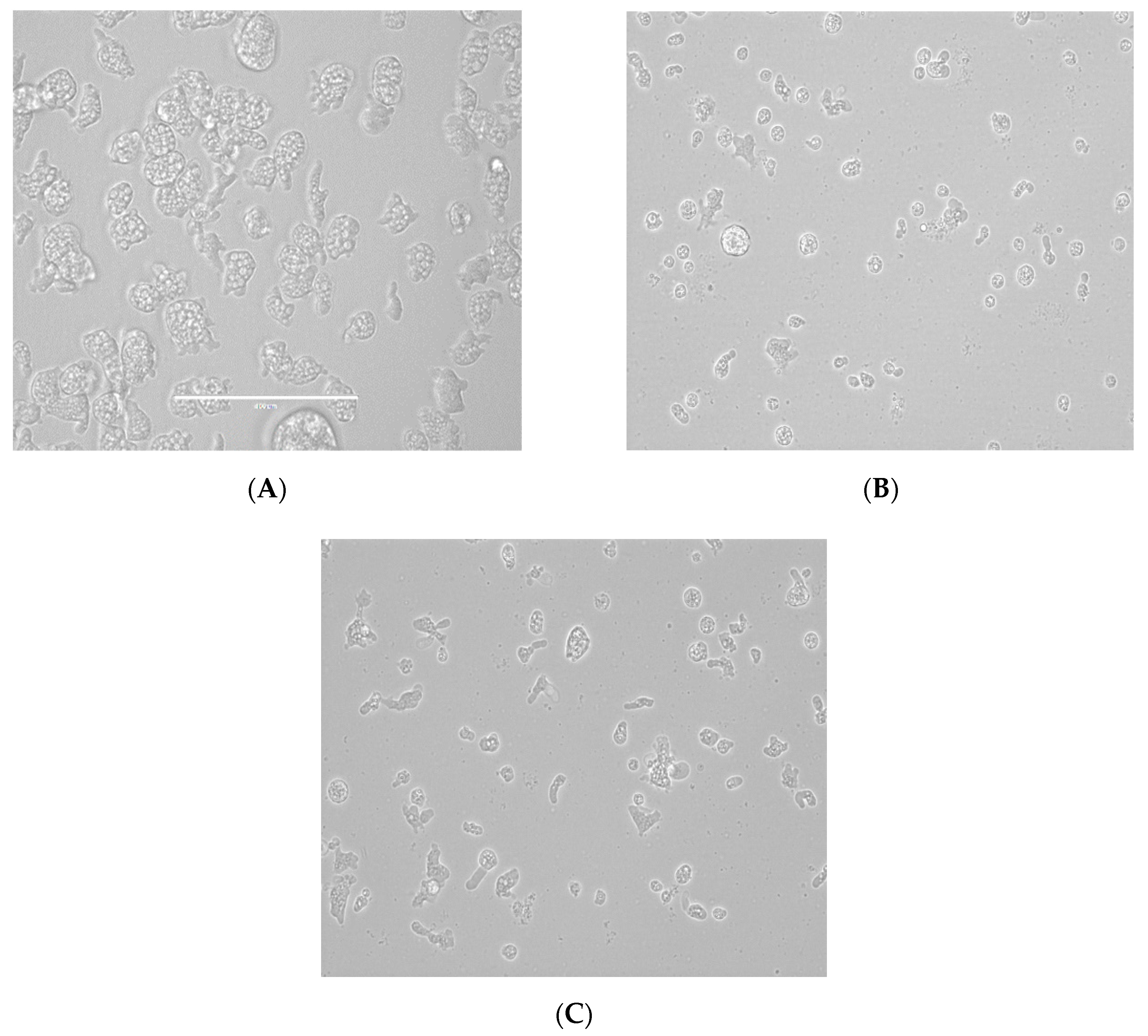
2.1. In Vitro Activity of the Tested Statins against the Trophozoite Stage of Naegleria fowleri
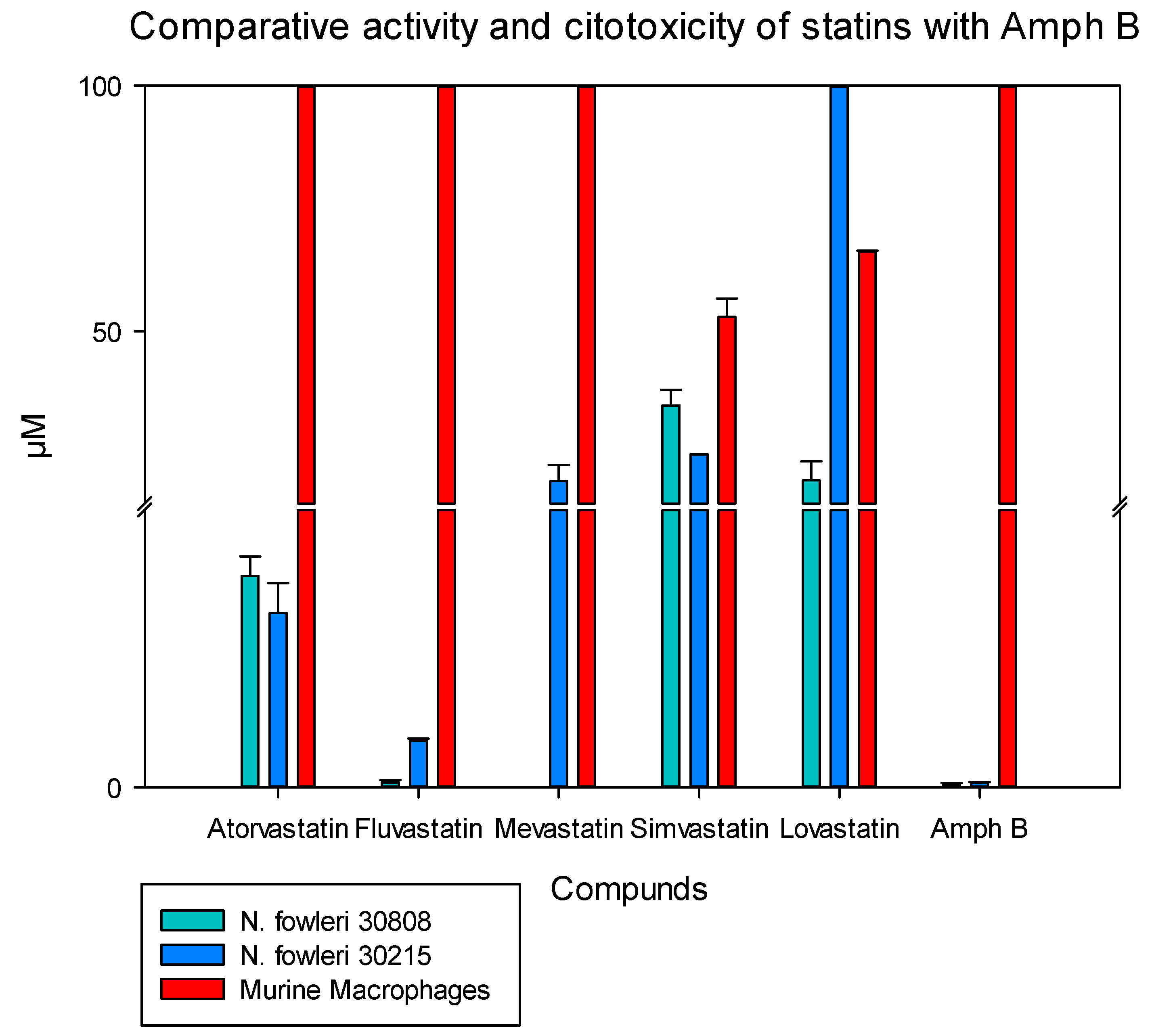
2.2. In Vitro Toxicity against Murine Macrophages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Amoebic Cultures
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. In Vitro Activity Assays against the Trophozoite Stage of Naegleria fowleri
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assays
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Červa, L.; Novák, K. Amoebic meningoencephalitis: Sixteen fatalities. Science 1968, 160, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Batlle, M.; Rizo-Liendo, A.; Viera-Santana, R.A.; Afonso-Morales, S.; López-Arencibia, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Chiboub, O.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Nicolás-Hernández, D.S.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; et al. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Naegleria australiensis in Irrigation Water of Fuerteventura Island, Spain. Acta Parasitol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.; Ali, I.K.M.; Cope, J.R.; Khan, N.A. Biology and pathogenesis of Naegleria fowleri. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvesvara, G.S.; Moura, H.; Schuster, F.L. Pathogenic and opportunistic free–living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp. Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. Fems Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 50, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jonckheere, J.F. Origin and evolution of the worldwide distributed pathogenic amoeboflagellate Naegleria fowleri. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.E.; Chavez-Munguia, B.; Omana-Molina, M.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Naegleria fowleri. Trends Parasitol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.; Budge, P.; Chen, J.; Bilyeu, S.; Mirza, A.; Custodio, H.; Irazuzta, J.; Visvesvara, G.; Sullivan, K.J. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis: A case report and literature review. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2012, 28, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvesvara, G.S. Infections with free-living amebae. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grace, E.; Asbill, S.; Virga, K. Naegleria fowleri: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6677–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castillo, M.; Cárdenas-Zúñiga, R.; Coronado-Velázquez, D.; Debnath, A.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. Naegleria fowleri after 50 years: Is it a neglected pathogen? J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvesvara, G.S. Free-Living Amebae as Opportunistic Agents of Human Disease. J. Neuroparasitol. 2010, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graciaa, D.S.; Cope, J.R.; Roberts, V.A.; Cikesh, B.L.; Kahler, A.M.; Vigar, M.; Hilborn, E.D.; Wade, T.J.; Backer, L.C.; Montgomery, S.P.; et al. Outbreaks Associated with Untreated Recreational Water United States, 2000-2014. Am. J. Transpl. 2018, 18, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis caused by Naegleria fowleri: An old enemy presenting new challenges. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phu, N.H.; Mai, H.N.T.; Nghia, H.D.; Chau, T.T.; Loc, P.P.; Thai le, H.; Phuong, T.M.; Thai, C.Q.; Man, D.N.; Van Chau, N.; et al. Fatal consequences of freshwater pearl diving. Lancet 2013, 381, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.; Carter, R.F. Acute pyogenic meningitis probably due to Acanthamoeba sp.: A preliminary report. Br. Med. J. 1965, 2, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, N.K.; Santos, T.M.; da Silva, M.T.A.; Thiemann, O.H. The therapeutic strategies against Naegleria fowleri. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 187, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, A.; Nelson, A.T.; Silva-Olivares, A.; Shibayama, M.; Siegel, D.; McKerrow, J.H. In Vitro efficacy of Ebselen and BAY 11-7082 against Naegleria fowleri. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.O.; Cope, J.R.; Moskowitz, M.; Kahler, A.; Hill, V.; Behrendt, K.; Molina, L.; Fullerton, K.E.; Beach, M.J. Notes from the Field: Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis Associated with Exposure to Swimming Pool Water Supplied by an Overland Pipe Inyo County, California, 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, J.S.; Straif-Bourgeois, S.; Roy, S.L.; Moore, T.A.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Ratard, R.C.; Hill, V.R.; Wilson, J.D.; Linscott, A.J.; Crager, R.; et al. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis deaths associated with sinus irrigation using contaminated tap water. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capewell, L.G.; Harris, A.M.; Yoder, J.S.; Cope, J.R.; Eddy, B.A.; Roy, S.L.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Fox, L.M.; Beach, M.J. Diagnosis, Clinical Course, and Treatment of Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in the United States, 1937-2013. J. Pediatric. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, N.; Blackall, D. Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis. Blood 2012, 119, 353136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linam, W.M.; Ahmed, M.; Cope, J.R.; Chu, C.; Visvesvara, G.S.; da Silva, A.J.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Green, J. Successful treatment of an adolescent with Naegleria fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifaoui, I.; Martín-Navarro, C.; López-Arencibia, A.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Valladares, B.; Piñero, J.; Maciver, S.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Optimized combinations of statins and azoles against Acanthamoeba trophozoites and cysts in vitro. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2019, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C.A.; Colon, B.L.; Alp, M.; Goker, H.; Boykin, D.W.; Kyle, D.E. Bis-benzimidazole hits against Naegleria fowleri discovered with new high-throughput screens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, J.R.; Conrad, D.A.; Cohen, N.; Cotilla, M.; DaSilva, A.; Jackson, J.; Visvesvara, G.S. Use of the Novel Therapeutic Agent Miltefosine for the Treatment of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis: Report of 1 Fatal and 1 Surviving Case. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.J. Contact-independent cell death of human microglial cells due to pathogenic Naegleria fowleri trophozoites. Korean J. Parasitol. 2008, 46, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, F.L.; Guglielmo, B.J.; Visvesvara, G.S. In vitro activity of miltefosine and voriconazole on clinical isolates of free-living amebas: Balamuthia mandrillaris, Acanthamoeba spp. and Naegleria fowleri. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.L.; Sharma, S.; Puri, S.; Kumar, R.; Midha, V.; Bansal, R. A rare case of survival from primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 16, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Prabhakar, S.; Modi, M.; Bhatia, R.; Sehgal, R. Naegleria meningitis: A rare survival. Neurol. India 2002, 50, 470–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Debnath, A.; Jennings, G.; Hahn, H.J.; Vanderloop, B.H.; Chaudhuri, M.; Nes, W.D.; Podust, L.M. Enzymatic chokepoints and synergistic drug targets in the sterol biosynthesis pathway of Naegleria fowleri. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Navarro, C.M.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Machin, R.P.; López-Arencibia, A.; García-Castellano, J.M.; de Fuentes, I.; Loftus, B.; Maciver, S.K.; Valladares, B.; Piñero, J.E. Inhibition of 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl–Coenzyme A Reductase and Application of Statins as a Novel Effective Therapeutic Approach against Acanthamoeba Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Navarro, C.M.; López-Arencibia, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Valladares, B.; Martínez-Carretero, E.; Piñero, J.E.; Maciver, S.K.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Statins and Voriconazole Induce Programmed Cell Death in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, J.; Ingram, P.R.; Henriquez, F.L.; Roberts, C.W. Development of Colorimetric Microtiter Plate Assay for Assessment of Antimicrobials against Acanthamoeba. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Navarro, C.M.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Cabrera-Serra, M.G.; Rancel, F.; Coronado-Alvarez, N.M.; Piñero, J.E.; Valladares, B. The potential pathogenicity of chlorhexidine-sensitive Acanthamoeba strains isolated from contact lens cases from asymptomatic individuals in Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachter, M. Chemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of statins: An update. Fundam. Clin. Pharm. 2005, 19, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riekse, R.G.; Li, G.; Petrie, E.C.; Leverenz, J.B.; Vavrek, D.; Vuletic, S.; Albers, J.J.; Montine, T.J.; Lee, M.; Seubert, P.; et al. Effect of statins on Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2006, 10, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, B.A.; Evans, J.E.; Baker, S.P.; Kane, K.; Swearer, J.; Hinerfeld, D.; Caselli, R.; Rogaeva, E.; St George-Hyslop, P.; Moonis, M.; et al. Long-term statin therapy and CSF cholesterol levels: Implications for Alzheimer’s diseases. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2009, 27, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiboub, O.; Sifaoui, I.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Abderrabba, M.; Mejri, M.; Fernandez, J.J.; Piñero, J.E.; Diaz-Marrero, A.R. Spiralyde A, an Antikinetoplastid Dolabellane from the Brown Alga Dictyota spiralis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cen-Pacheco, F.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Souto, M.L.; Hernandez-Daranas, A.; Piñero, J.E.; Fernandez, J.J. Evaluation of Oxasqualenoids from the Red Alga Laurencia viridis against Acanthamoeba. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound (µM) | Structure | N. fowleri ATCC 30808 IC50 (µM) | N. fowleri ATCC 30215 IC50 (µM) | Murine Macrophages CC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atorvastatin | 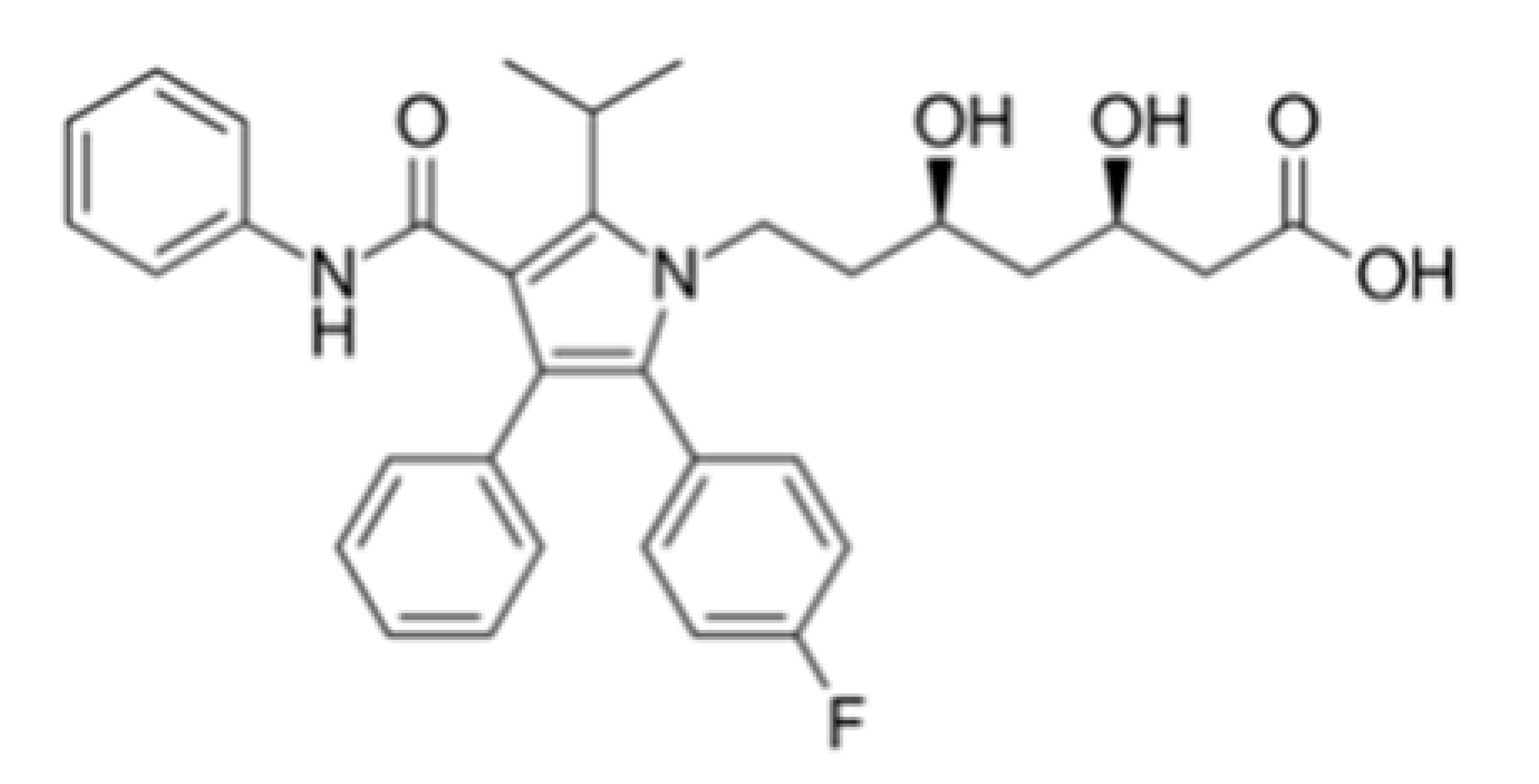 | 7.629 ± 0.696 | 6.278 ± 1.085 | ≥200 |
| Fluvastatin | 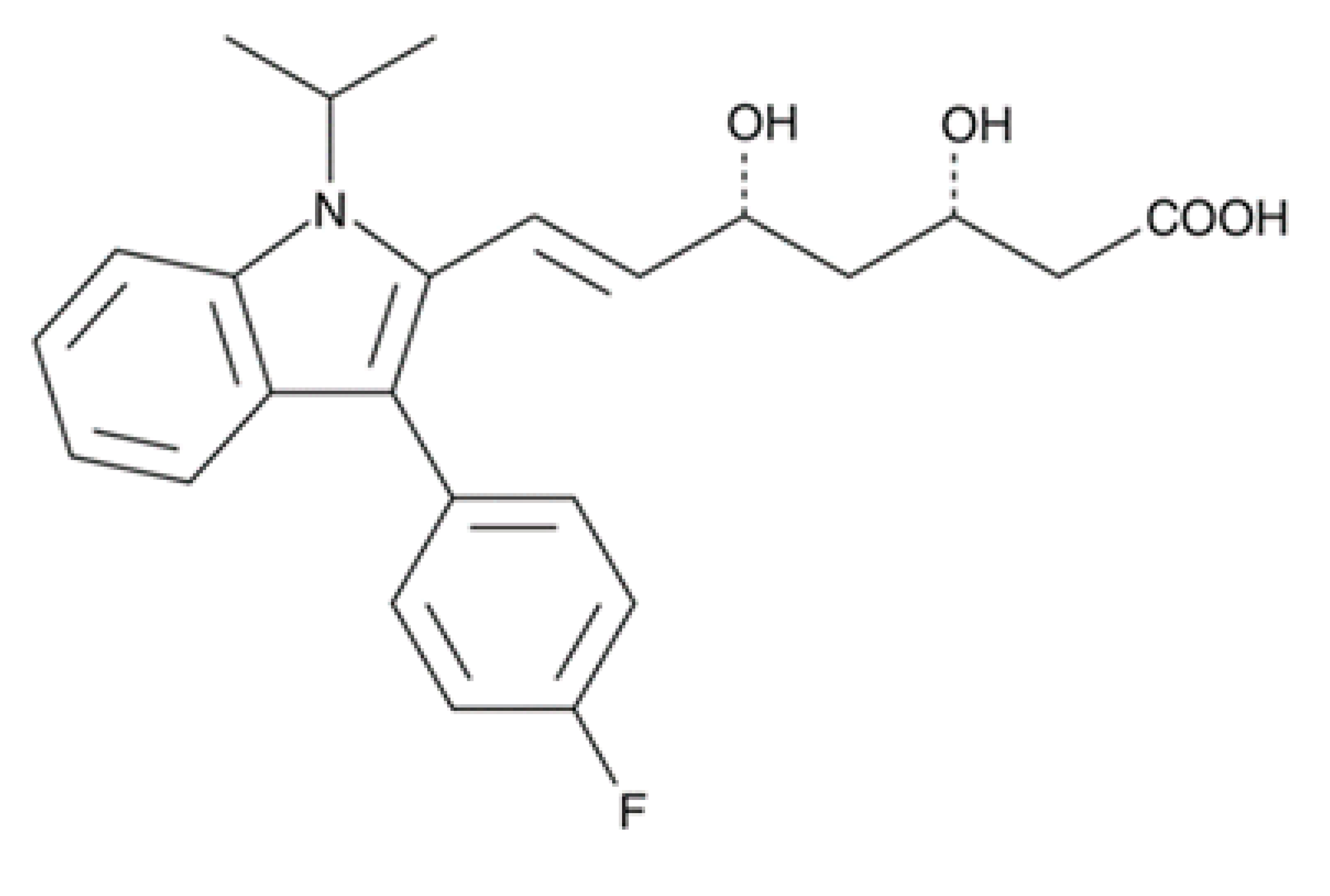 | 0.179 ± 0.078 | 1.682 ± 0.775 | ≥200 |
| Pravastatin | 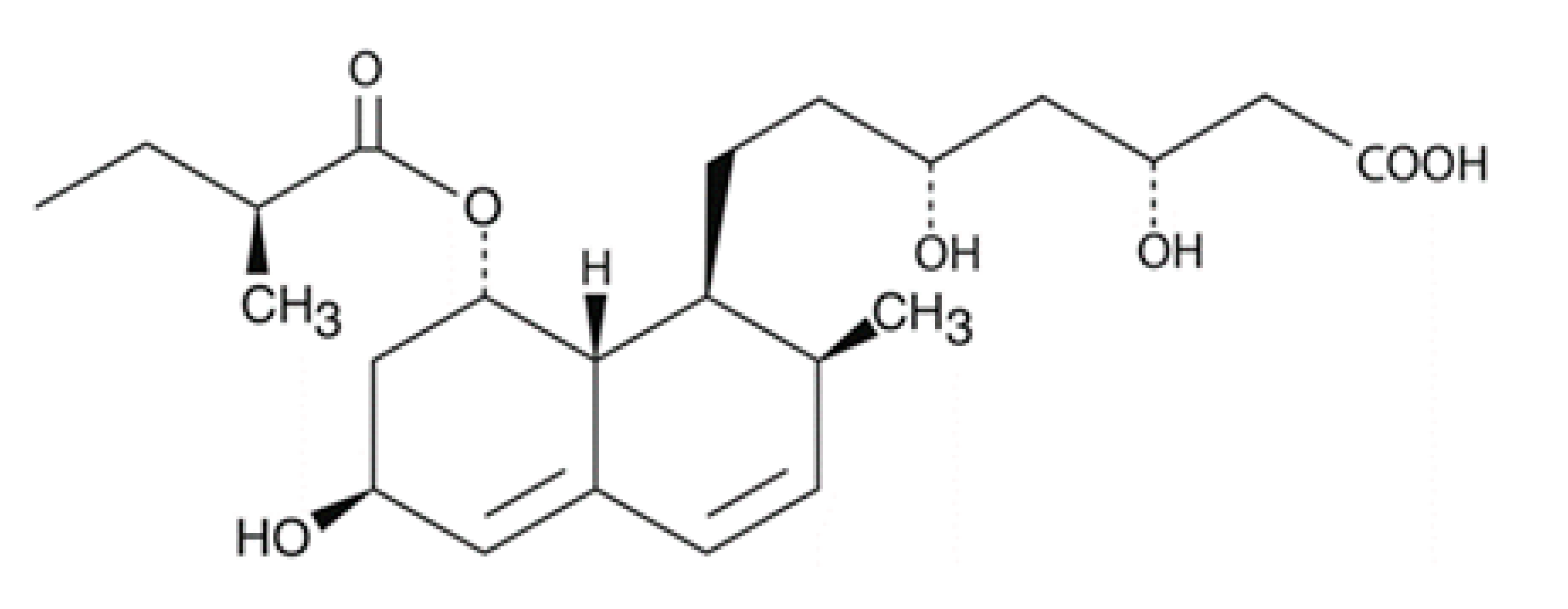 | Amoebostatic | Amoebostatic | ≥100 |
| Mevastatin | 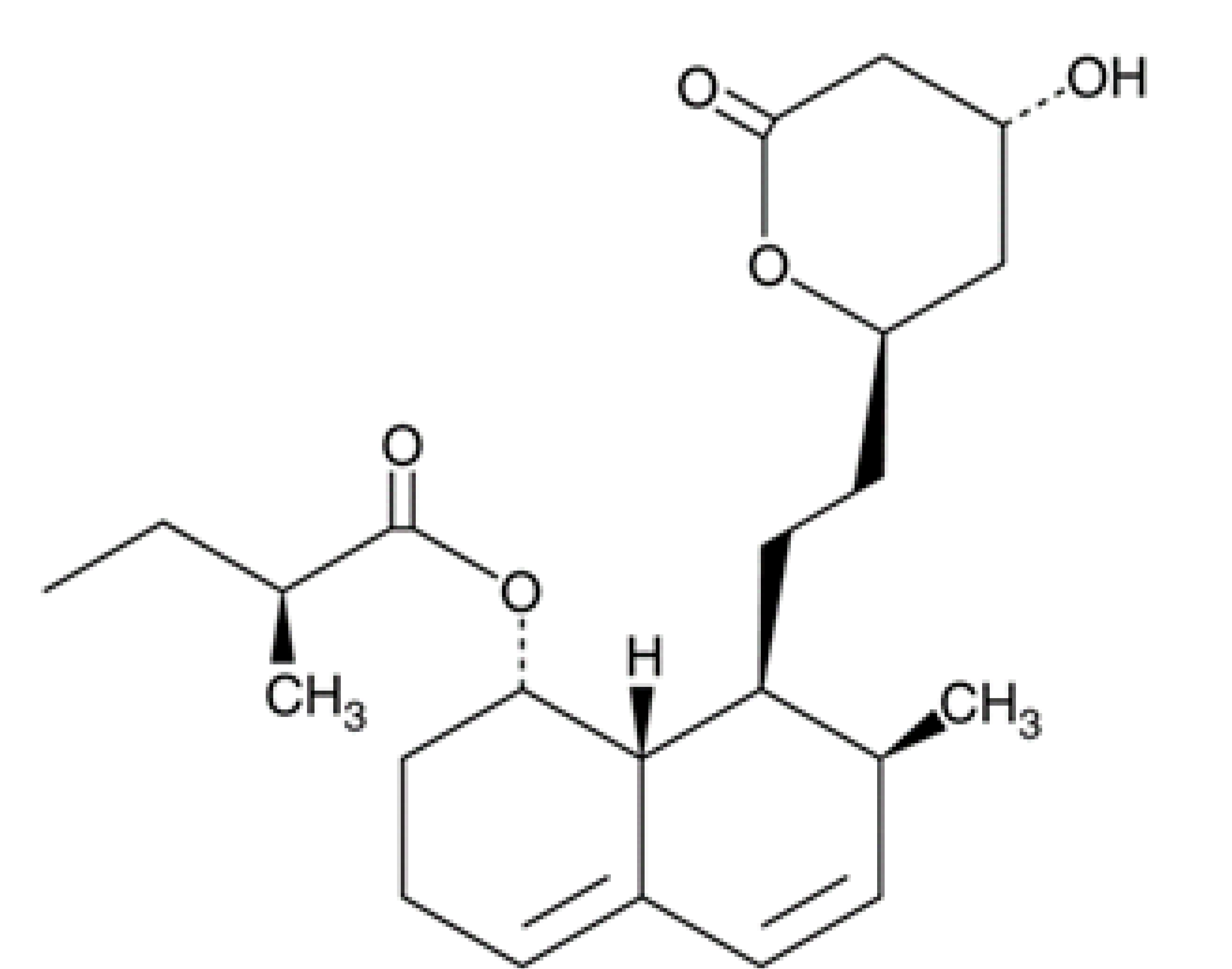 | Amoebostatic | 19.542 ± 3.295 | ≥200 |
| Simvastatin | 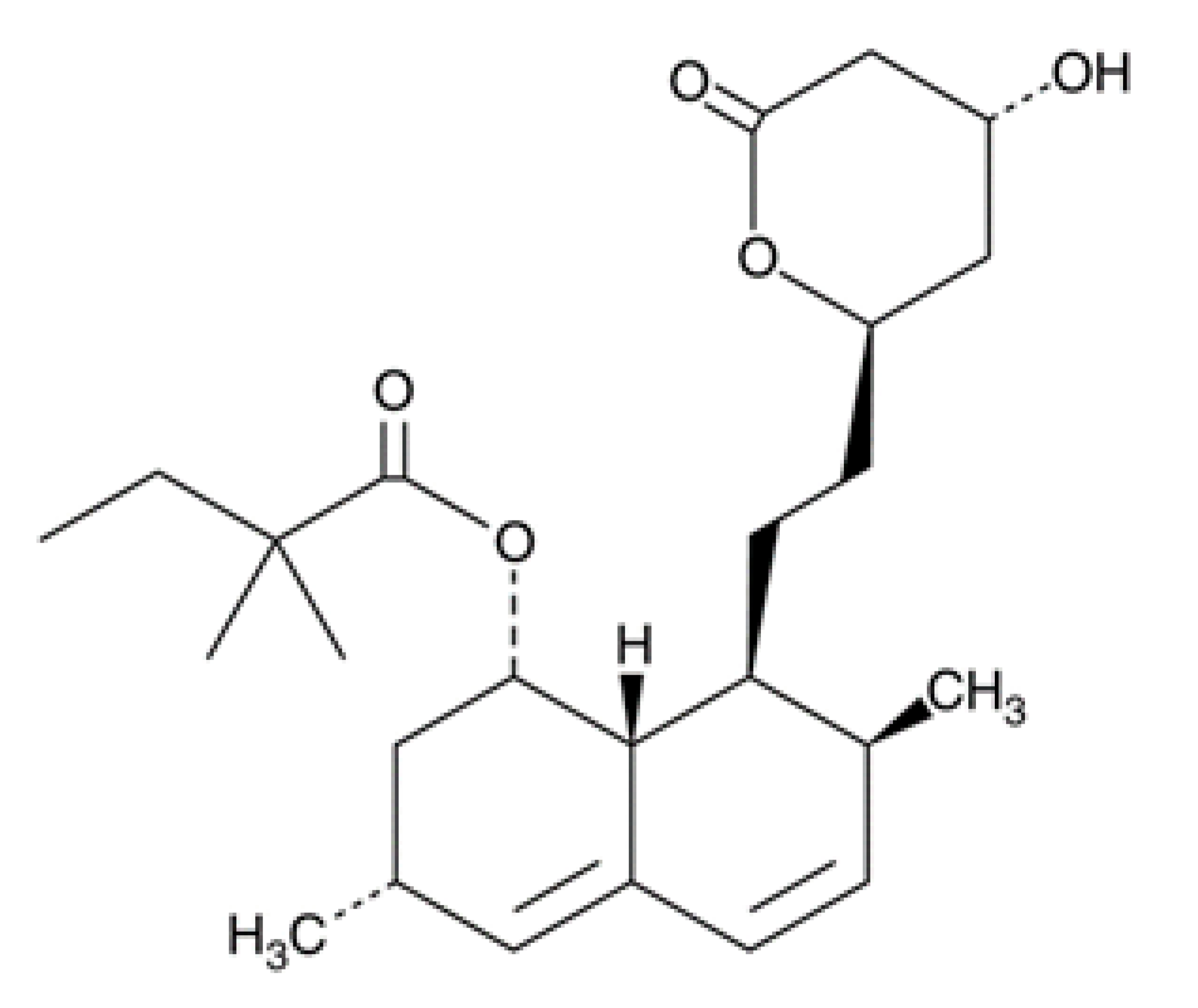 | 34.943 ± 3.149 | ≈25 | 52.971 ± 3.691 |
| Lovastatin |  | 19.742 ± 3.824 | ≥100 | 66.170 ± 0.268 |
| Amphotericin B | 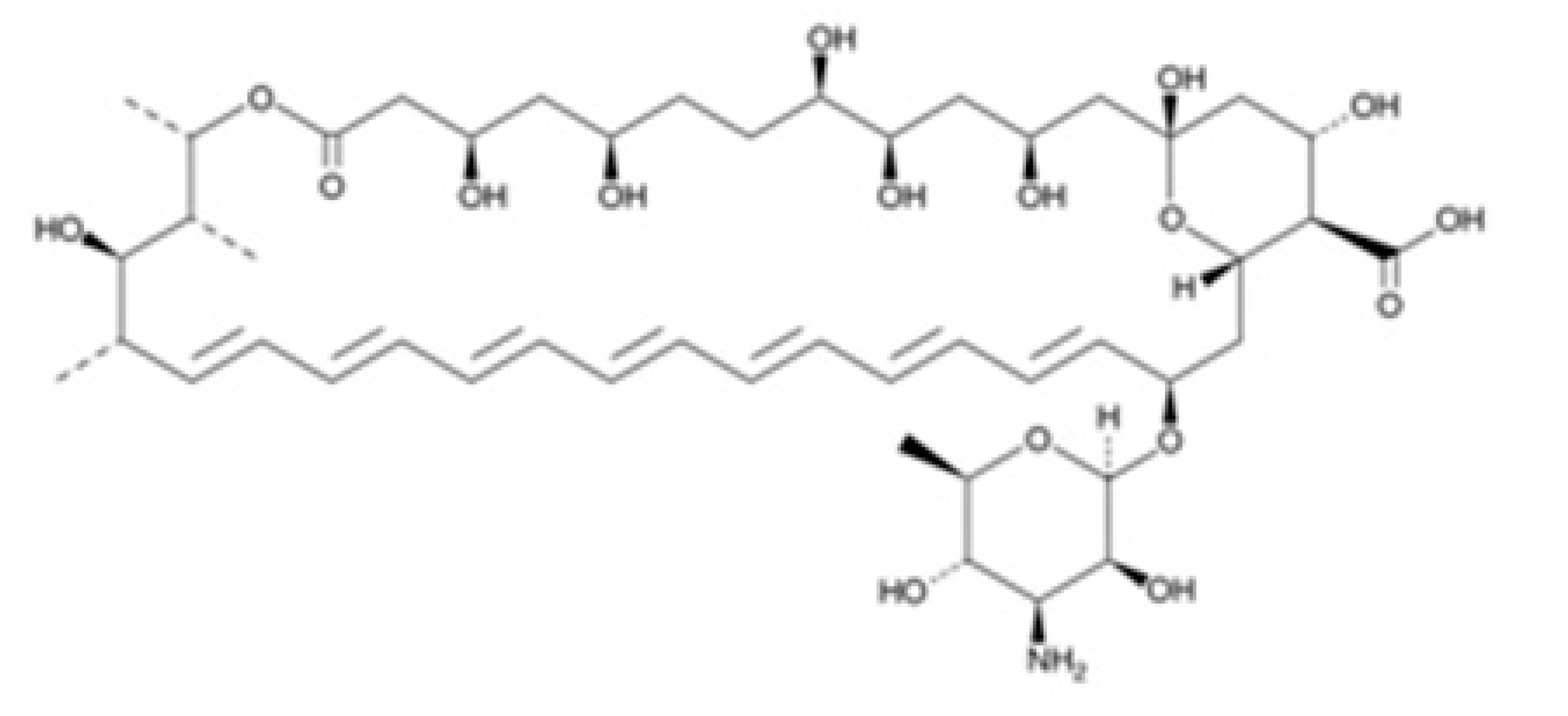 | 0.121 ± 0.032 | 0.166 ± 0.026 | ≥200 |
| Selectivity Index (CC50/IC50) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compounds (µM) | ATCC 30808 | ATCC 30215 |
| Atorvastatin | ≥26.215 | ≥31.857 |
| Fluvastatin | ≥1117.318 | ≥118.906 |
| Pravastatin | ND | ND |
| Mevastatin | ND | ≥10.234 |
| Simvastatin | ≥1.6197 | ≈2.264 |
| Lovastatin | ≥3.3517 | ND |
| Amphotericin B | ≥1652.893 | ≥1204.819 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizo-Liendo, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Chiboub, O.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; San Nicolás-Hernández, D.; Hendiger, E.B.; López-Arencibia, A.; Rocha-Cabrera, P.; et al. In Vitro Activity of Statins against Naegleria fowleri. Pathogens 2019, 8, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030122
Rizo-Liendo A, Sifaoui I, Reyes-Batlle M, Chiboub O, Rodríguez-Expósito RL, Bethencourt-Estrella CJ, San Nicolás-Hernández D, Hendiger EB, López-Arencibia A, Rocha-Cabrera P, et al. In Vitro Activity of Statins against Naegleria fowleri. Pathogens. 2019; 8(3):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030122
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizo-Liendo, Aitor, Ines Sifaoui, María Reyes-Batlle, Olfa Chiboub, Rubén L. Rodríguez-Expósito, Carlos J. Bethencourt-Estrella, Desirée San Nicolás-Hernández, Edyta B. Hendiger, Atteneri López-Arencibia, Pedro Rocha-Cabrera, and et al. 2019. "In Vitro Activity of Statins against Naegleria fowleri" Pathogens 8, no. 3: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030122
APA StyleRizo-Liendo, A., Sifaoui, I., Reyes-Batlle, M., Chiboub, O., Rodríguez-Expósito, R. L., Bethencourt-Estrella, C. J., San Nicolás-Hernández, D., Hendiger, E. B., López-Arencibia, A., Rocha-Cabrera, P., Piñero, J. E., & Lorenzo-Morales, J. (2019). In Vitro Activity of Statins against Naegleria fowleri. Pathogens, 8(3), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030122








