Abstract
Oral candidiasis is particularly evident, not only in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy, but also in elderly people with xerostomy. In general, Candida is an opportunistic pathogen, causing infections in immunocompromised people and, in some cases, when the natural microbiota is altered. Chitosan, a natural derivative of chitin, is a polysaccharide that has been proven to possess a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity that encompasses action against fungi, yeast and bacteria. While recent studies have revealed a significant antibiofilm activity upon several microorganisms, including C. albicans, little is known regarding the impact of chitosan upon the adhesive process or mature biofilms. With that in mind, the purpose of this work was to evaluate, in vitro, the capability of chitosan to inhibit C. albicans growth and biofilm formation. The results obtained showed that chitosan is capable of inhibiting C. albicans planktonic growth (HMW, 1 mg/mL; LMW, 3 mg/mL). Regarding biofilm growth, chitosan inhibited C. albicans adhesion (ca. 95%), biofilm formation (percentages above 90%) and reduced mature biofilms by ca. 65% and dual species biofilms (C. albicans and S. mutans) by ca. 70%. These results display the potential of this molecule to be used as an effective anti-Candida agent capable of acting upon C. albicans infections.
1. Introduction
Since the 1970s, there has been an increase in candidiasis incidence, mostly due to the use of plastic permanent catheters, antibiotics and immunosuppressive drugs [1]. These Candida-derived infections may occur in the skin, mucous membranes (such as the mouth and vagina) and in the viscera, with the main etiological agent being Candida albicans [1,2]. Among the various human fungal pathogens, C. albicans accounts for the majority of systemic infections in immunocompromised patients, with overall mortality rates ranging from 29% to 76% [2,3,4,5,6]. This opportunistic fungi causes great problems, as it is resistant to most antimicrobial compounds, namely amphotericin-B, which is considered the standard for the treatment of systemic mycoses. Despite still being considered the drug of choice against C. albicans, these antifungal agents are being increasingly reported as inefficient with numerous cases of resistances, particularly to fluconazole, being observed [1,2,3,4]. This problem has led to the search for alternative drugs and compounds to be used in the treatment and management of C. albicans infections.
Chitin is the primary structural component of the shells of crustaceans, arthropods and the fungal cell wall and is obtained mainly as a byproduct of the fishing industry. Partial deacetylation of chitin leads to chitosan, a polysaccharide composed of units of glucosamine (2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucose) and N-acetyl glucosamine (2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d–glucose) linked by β(1→4) bonds. Chitosan is the only natural polysaccharide that presents a cationic character due to its amino groups, which, at low pH, are protonated and can interact with negatively-charged compounds, such as proteins, anionic polysaccharides (e.g., alginates, carraghenates, pectins), fatty acids, bile acids and phospholipids [7]. This behavior, along with its biocompatibility, biodegradability and lack of toxicity, has led to the usage of chitosan in diverse fields, such as technology, food, cosmetics, medicine, biotechnology, agriculture and the paper industry [8,9]. However, chitosan possesses some limitations, namely its insolubility in water, high viscosity and tendency to coagulate proteins at high pH [10,11,12].
Chitosan’s antimicrobial activity is well established against a variety of microorganisms, including fungi [10,13,14,15]. When considering chitosan antifungal activity, several authors have already shown that it is active upon yeasts, molds and dermatophytes [16,17,18,19]. While the antifungal activity of chitosan upon C. albicans is well established, the same cannot be said regarding the effect of chitosan upon C. albicans biofilm formation. Early reports [20,21,22] suggest that chitosan may be active upon C. albicans biofilms; however, the real effect of chitosan upon the different steps of C. albicans biofilms has not yet been fully explored. As such, the aim of this work was to fully assess chitosan’s potential as a means to prevent C. albicans-derived infections through the control of its growth, adhesion and biofilm formation.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. MIC Determination
The MIC values, obtained by broth microdilution, for chitosan activity upon C. albicans were relatively low. In fact, HMW chitosan presented a MIC value of 1 mg/mL and LMW chitosan a MIC value of 3 mg/mL. The antifungal activity of chitosan upon C. albicans is well established, with several authors [16,17,18,19] presenting various MIC values for different chitosans against this yeast. Tayel, Moussa, El-Tras, Knittel, Opwis and Schollmeyer [2] previously reported a MIC of 1.25 mg/mL (32 kDa, deacetylation degree (DD) 86%). Qin et al. [23] reported an even lower MIC of 0.8 mg/mL (2.91 kDa, DD 86.4%), and Şenel et al. [24] reported a MIC of 10 mg/mL (1,000 kDa, DD 80%). Comparing these results with the ones obtained, it is possible to see that for LMW chitosan, the MIC value obtained was slightly superior to those previously reported [2,23], with this differences being probably due to the higher DD used in those assays. On the other hand, for HMW chitosan, the values here obtained were significantly lower than those reported by Şenel, İkinci, Kaş, Yousefi-Rad, Sargon and Hıncal [24]. From here, the ½ and the ¼ of the MIC were calculated to be used in the biofilm assays, as previously described by Cerca et al. [25].
2.2. Adherence to Coated Surfaces
The effect of chitosan upon C. albicans adhesion to surfaces can be seen in Figure 1. The results obtained showed that both MW and the times tested were capable of producing adhesion inhibition percentages above 90%. In fact, the lowest inhibition percentage was obtained for LMW chitosan after only 30 s of exposure. When considering the differences between 30 s and 90 s of exposure, there were no significant statistical differences (p > 0.05) found, either for HMW or LMW chitosan. On the other hand, when considering the impact of the MW and the exposure time, some differences are ascertainable; 90 s of exposure for HMW presented statistically significant (p < 0.05) higher inhibition values than both LMW assays; LMW, at 30 s of exposure, presented a significantly lower (p < 0.05) inhibition value than the one registered in both HMW assays. These results are in line with those previously reported by Carlson, Taffs, Davison and Stewart [20], who showed that chitosan reduced C. albicans adhesion up to 99%.
2.3. Microtiter-Plate Test
When considering the impact of chitosan upon C. albicans biofilm formation (Figure 2), here analyzed indirectly through biomass production, one can see that, as with the previous assay, the highest inhibition percentage (66.94%) was obtained for HMW chitosan (0.5 mg/mL) and the lowest inhibition percentage (37.97%) was obtained for LMW chitosan (0.75 mg/mL). When comparing the results obtained for the ½ and ¼ of the MIC of both MWs, no statistically significant (p > 0.05) differences were found when considering the effect of the MW upon chitosan’s activity. On the other hand, when considering the effect of the MW in conjunction with the concentration, one can see clear differences in behavior (Figure 2). In fact, 0.5 mg/mL of HMW chitosan presented significantly higher (p < 0.05) inhibition values than the remaining assays, while no significant (p > 0.05) differences were found between the ¼ of the MIC for HMW (0.25 mg/mL) and ½ of the MIC for LMW (1.5 mg/mL). On the other hand, 0.75 mg/mL of LMW chitosan presented statistically significant (p < 0.05) lower inhibition percentages than the remaining assays. These results are in line with those registered by Martinez, Mihu, Tar, Cordero, Han, Friedman, Friedman and Nosanchuk [22], who reported that chitosan was capable of reducing C. albicans biofilm formation by a 2.5 factor, and by those of Cobrado et al. [26] and of Cobrado et al. [27], who showed that chitosan was capable of reducing C. albicans biomass production up to 90%.
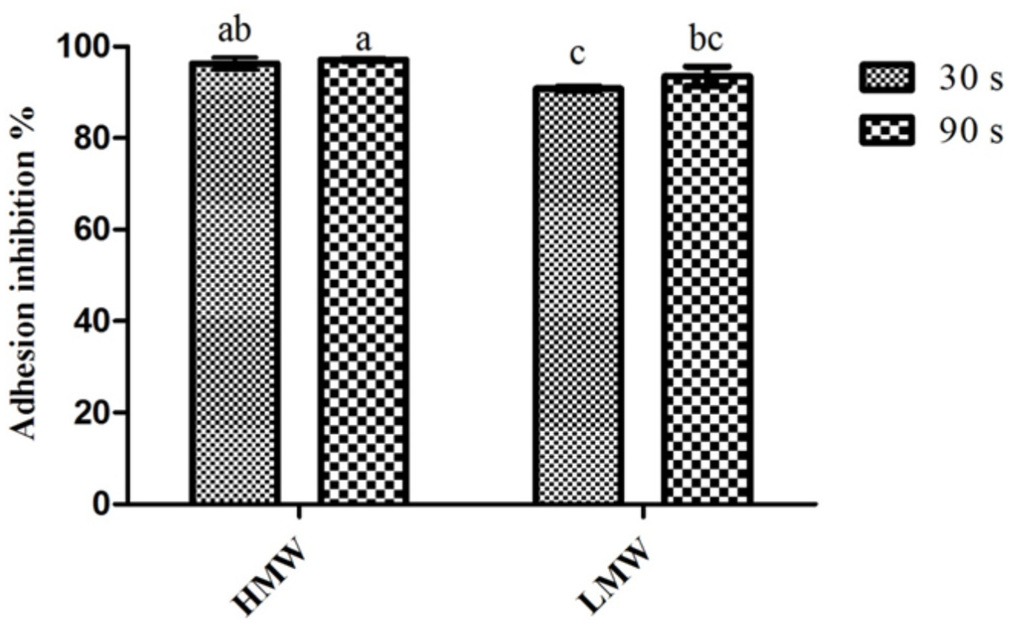
Figure 1.
Inhibitory effect of chitosan upon C. albicans adhesion. Values obtained given as the percentage of adhesion inhibition. Different letters represent the statistically significant differences found (p < 0.05). All assays performed in triplicate. HMW, high molecular weight; LMW, low molecular weight.
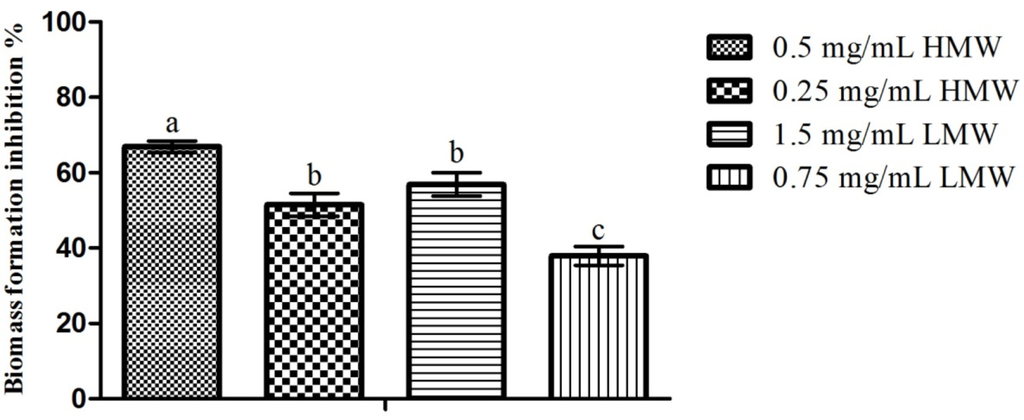
Figure 2.
Effect of sub-MIC concentrations of chitosan (½ and ¼ of the MICs; values in mg/mL) upon C. albicans biofilm formation. Values obtained are given as the percentage of biofilm formation inhibition. Different letters represent the statistically significant differences found (p < 0.05). All assays were performed in triplicate.
2.4. Mature Biofilms Assays
Regarding the effect of chitosan upon C. albicans mature biofilms, the results obtained can be seen in Figure 3. Once again, the highest inhibition percentage was obtained for HMW chitosan (51.77% for 0.25 mg/mL), and the lowest inhibition was registered for LMW chitosan (45.37% for 1.5 mg/mL). Statistical analysis of the results showed that when considering the effect of the MW, there were statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between HMW chitosan at 0.25 mg/mL and both LMW concentrations tested. Simultaneously, when considering the effect of the MW in conjunction with concentration (Figure 3), differences were also observed with 0.25 mg/mL HMW chitosan, presenting significantly (p < 0.05) higher inhibition values than the assays that utilized LMW chitosan. Between the remaining assays, no statistically significant (p > 0.05) differences were found.
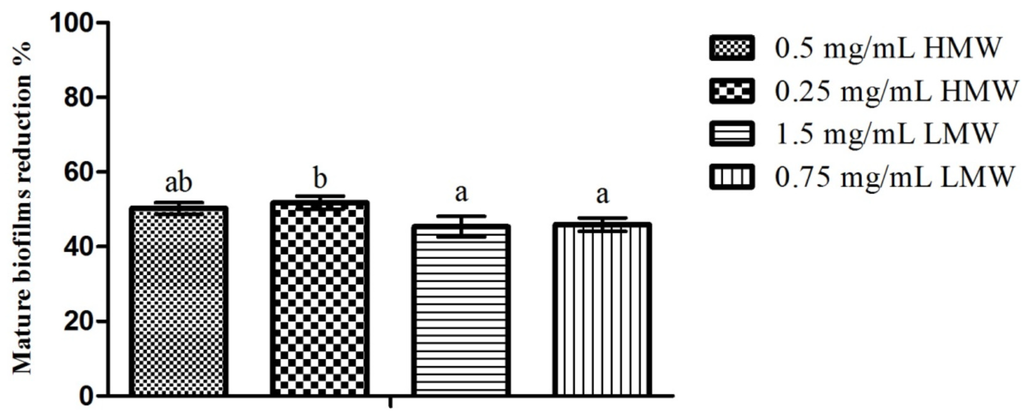
Figure 3.
Effect of sub-MIC concentrations of chitosan (½ and ¼ of the MICs; values in mg/mL) upon C. albicans mature biofilms. Results are presented as biofilm reduction percentages. Different letters represent the statistically significant differences found (p < 0.05). All assays performed in triplicate.
2.5. Dual-Species Biofilms
Results obtained regarding the activity of chitosan upon C. albicans mature biofilms can be observed in Figure 4. Contrary to the pattern observed in previous assays, LMW chitosan presented the highest biofilm inhibition percentage (66.77% for 0.75 mg/mL) and HMW chitosan the lowest (55.10% for 0.25 mg/mL). Statistical analysis of the results showed that the only statistically significant difference observed was for 0.25 mg/mL of HMW chitosan, which presented an inhibition value significantly lower than the inhibition values obtained in the remaining test conditions. When considering the differences in chitosan’s activity between single species C. albicans biofilm and dual species C. albicans and S. mutans biofilms (Figure 5), the statistical analysis shows that there are statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) in LMW chitosan’s activity between a single and a dual species population. On a closer look, LMW chitosan presents a statistically significant (p < 0.05) increase in activity between single species and dual species biofilms. This translates as an increase of biomass production inhibition of ca. 10%, for 1.5 mg/mL, and of ca. 31%, for 0.75 mg/mL of chitosan, for LMW chitosan between populations.
Despite the lack of previous results regarding the effect of chitosan upon C. albicans mature and dual species biofilms, the inhibitions here registered are quite interesting, especially when considering that C. albicans biofilms produce an exopolymeric matrix that serves as a diffusion barrier to antimicrobials and that, under these conditions, Candida cells overexpress efflux pumps to enhance antifungal resistance [28]. This mechanism may be the reason why HMW chitosan possessed higher activity than LMW upon mature biofilms, as it is known that the latter must enter the cells in order to be active [15]. In the dual species biofilms, one cannot underestimate the importance of S. mutans, as it is known to be crucial to C. albicans colonization of the oral cavity, mainly due to providing adhesion sites and producing lactate that can be used as a carbon source by yeasts. This symbiosis has been well established in several studies, which have shown that there is a strong coadherence between these microorganisms [29]. Considering that, both S. mutans and C. albicans, have been described as being more sensitive to HMW chitosan [16,17,18,19,30], it is somewhat surprising that LMW chitosan presented higher inhibition percentages than HMW chitosan for the dual species biofilms. It is possible that an unknown mechanism, possibly located at the adhesins level, as hypothesized by Azcurra et al. [31], or at the cell to cell communication level, where the larger HMW molecules are incapable of acting, is responsible for the higher activity registered for LMW chitosan.
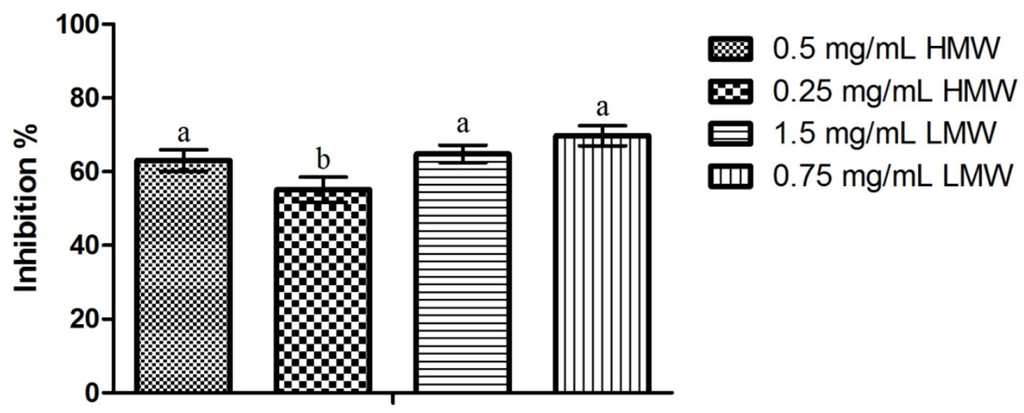
Figure 4.
Effect of sub-MIC concentrations of chitosan (½ and ¼ of the MICs; values in mg/mL) upon biofilms formed by C. albicans and S. mutans. Results presented as the percentage of biofilm formation inhibition. Different letters represent the statistically significant differences found (p < 0.05). All assays performed in triplicate.
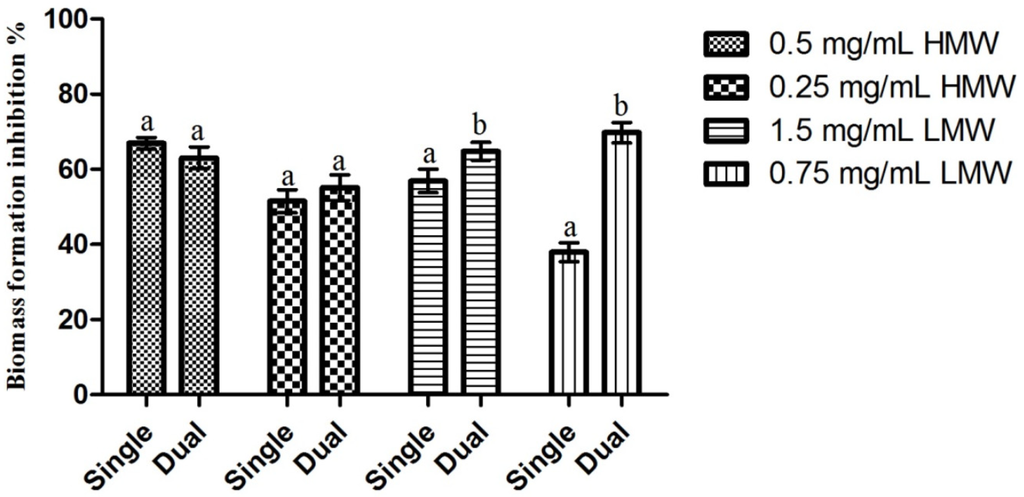
Figure 5.
Comparison of the effect of sub-MIC concentrations of chitosan upon C. albicans single species and dual species biofilms. Results presented as the percentage of biofilm formation inhibition. Different letters represent the statistically significant differences found (p < 0.05). All assays performed in triplicate.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sources of Chitosan and Microorganisms
High and low molecular weight chitosan were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). High molecular weight chitosan was characterized by a DD > 75% and a MW of 624 kDa. Low molecular weight chitosan was characterized by a DD between 75% and 85% and a MW of 107 kDa. Chitosan solutions were prepared in 1% (v/v) solution of glacial acetic acid 99% (Panreac, Barcelona, Spain). Chitosan was added to 1% acetic acid to the desired concentration. Afterwards, the solution was stirred overnight at 50 °C to promote complete dissolution of chitosan. The pH was adjusted with NaOH (Merck, Darmstad, Germany) to a final value of 5.6–5.8, and solutions were stored at refrigerated temperature.
Candida albicans used in this study was obtained from the culture collection of the Göteburg University (CCUG) (Sweden) (CCUG 49242). Inocula were prepared in yeast malt broth (YMB) (Difco, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Viable counts were performed in yeast malt agar (YMA) (Difco, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
3.2. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
Determination of the MIC was performed as described by Costa, Silva, Pina, Tavaria and Pintado [10]. Briefly, an inoculum of 0.5 in the MacFarland scale (1.5 × 108 CFU/mL) of C. albicans was prepared from overnight cultures and inoculated in YMB with chitosan concentrations ranging from 0.1 mg/mL to 7 mg/mL. Two controls were simultaneously assessed: one with 0.1 mg/mL chitosan, but without inoculum, and another where chitosan was replaced by sterile water and with added inoculum. The MIC was determined by observing the lowest concentration of chitosan that inhibited microbial growth. All assays were performed in triplicate.
3.3. Adherence
The effect of chitosan on C. albicans adhesion to surfaces was performed as described by Costa, Silva, Tavaria and Pintado [30], tested using 24-well microplates. Briefly, 1 cm aluminum disks were dipped for 30 or 90 s in a well containing either 1% (v/v) HMW or LMW chitosan. Following that, the disks were rinsed with sterile water and submerged in a well containing inoculum for 60 s, after which disks were placed into wells containing the appropriate medium and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Two controls were simultaneously assessed. In the first one, disks were dipped in sterile water and then inoculated and incubated. In the second one, disks were dipped in the test solutions and, after rinsing in sterile water, were then incubated without inoculum. After 24 h, the disks were recovered, and after serial dilutions, viable counts were assessed by the drop method, as described by Miles et al. [32], in YMA. Plates were then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h under aerobic conditions. Results were given as inhibition percentages using the following formula:
% I = 100 − (log CFU sample/log CFU control) × 100
All assays were performed in duplicate.
3.4. Microtiter-Plate Test
Biofilm quantification was carried out by adapting the protocol of Stepanovic et al. [33]. Briefly, in a flat bottom, 96-well microplate, wells were filled with 200 µL of test solutions with chitosan added at sub-MIC concentrations (½ and ¼ of the MIC) and inoculated at 1% (v/v). The plate was then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h in aerobiosis. All assays were performed in triplicate in the appropriate media supplemented with 5% sucrose.
To visualize adhesion, the contents of each well were discarded and then washed 3 times with sterile deionized water in order to remove non-adherent cells. The remaining attached microorganisms were fixed with 200 µL of ethanol (Panreac, Barcelona, Spain) for 15 min. Ethanol was discarded, and the wells were air dried. After that, 200 µL of crystal violet solution were added to the wells for 5 min, the excess stain removed by rinsing the plate under tap water followed by air drying. Adherence was quantified by measuring the OD at 630 nm using a microplate reader (FLUOstar, OPTIMA, BGM Labtech).
Optical density values from wells with liquid media, chitosan and no inoculum were used as negative controls, while OD from wells with liquid media, deionized water and inoculum were used as positive controls. Additionally, a control with 1% (v/v) acetic acid for each microorganism was used.
Results for this test were given as the percentage of biofilm formation inhibition applying the following formula:
% biofilm formation inhibition = 100 − (ODassay/ODcontrol) × 100
3.5. Mature Biofilms Assay
The assessment of chitosan’s effect on mature biofilms was performed through adaptation of the microplate protocol described by Stepanovic, Vukovic, Dakic, Savic and Svabic-Vlahovic [33]. Briefly, in a flat bottom 96-well microplate, wells were filled with 200 µL of medium, inoculated at 1% (v/v) and incubated 48 h at 37 °C. After 48 h, the medium was carefully aspirated, and the wells were rinsed with phosphate buffer. Following that, 200 µL of medium, with chitosan at sub-MIC concentrations, was added and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h.
To visualize biofilms, the contents of each well were discarded and the wells washed 3 times with sterile deionized water in order to remove non-adherent cells. The remaining attached microorganisms were fixed with 200 µL of ethanol (Panreac, Barcelona, Spain) for 15 min. Ethanol was then discarded and the wells air dried. After that, 200 µL of crystal violet solution (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) were added to the wells for 5 min. Excess stain was removed by rinsing the plate under tap water followed by air drying of the plate.
Adherence was quantified by measuring the OD at 660 nm using a microplate reader.
All experiments were done in triplicate for each microorganism. OD values from wells only with YMB were used as negative controls. A positive control with media and sterile deionized water was used. Additionally a control with 1% (v/v) acetic acid for each microorganism was used.
Results for this test were given as the reduction of the present biofilm, applying the following formula:
Mature biofilm inhibition percentage = 100 − (ODassay/ODcontrol) × 100
3.6. Dual-Species Biofilms
Quantification of the effect of chitosan upon biofilms formed by two different microorganisms was performed as previously described by Costa, Silva, Tavaria and Pintado [30]. Briefly, a test solution, with chitosan at sub-MIC concentrations, was inoculated with C. albicans and Streptococcus mutans (CCUG 45091) (1:1) to achieve a 2% (v/v) inoculum concentration. Impact upon biofilm formation was evaluated using the biofilm microtiter plate assay as described above. Results were obtained as referred above, and all assays were done in triplicate.
3.7. Statistical Treatment
The statistical differences in the methods were evaluated using PASW Statistics v. 21.0.0.0 (New York, NY, USA). The normality of the results’ distribution was evaluated through Shapiro–Wilk’s test. The differences were assessed using the one-way ANOVA test associated with Scheffe’s test (for normal distributions). The differences were considered significant at a 0.05 significance level.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, chitosan showed remarkable potential as a possible anti-candidiasis agent, as it was active upon C. albicans in the planktonic state and, more importantly, upon its sessile growth, with significant activity upon the several phases—adhesion, formation, mature and co-aggregation—of biofilm establishment and growth.
Acknowledgments
The author hereby gratefully acknowledges the Agency of Innovation (Agência de Inovação, ADI, Portugal) and Quadro de Referência Estratégico Nacional (QREN, Portugal), which, through the project “QUITORAL—Desenvolvimento de novas formulações de quitosanos com aplicação em medicina oral” (QREN-ADI 3474) and the National Funds from FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia) through project PEst-OE/EQB/LA0016/2013, provided funding for the realization of this work.
Author Contributions
Eduardo Costa was responsible for the experimental planning and execution, data processing and writing of the article; Sara Silva was responsible for the experimental execution, data processing, statistical analysis and writing of the article; Freni Tavaria was responsible for the experimental planning, data validation, article proofing and validation; Manuela Pintado was responsible for the experimental planning and article proofing and validation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Seyfarth, F.; Schliemann, S.; Elsner, P.; Hipler, U.C. Antifungal effect of high- and low-molecular-weight chitosan hydrochloride, carboxymethyl chitosan, chitosan oligosaccharide and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine against candida albicans, candida krusei and candida glabrata. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 353, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Tayel, A.A.; Moussa, S.; El-Tras, W.F.; Knittel, D.; Opwis, K.; Schollmeyer, E. Anticandidal action of fungal chitosan against candida albicans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgherri, C.; Porta, A.; Castellano, S.; Pinzino, C.; Quartacci, M.F.; Calucci, L. Effects of azole treatments on the physical properties of Candida albicans plasma membrane: A spin probe epr study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Ebbers, J.; Geurtz, L.; Stefanik, D.; Major, Y.; Edmond, M.B.; Wenzel, R.P.; Seifert, H. Nosocomial bloodstream infections due to Candida spp. In the USA: Species distribution, clinical features and antifungal susceptibilities. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agent 2014, 43, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortholary, O.; Renaudat, C.; Sitbon, K.; Madec, Y.; Denoeud-Ndam, L.; Wolff, M.; Fontanet, A.; Bretagne, S.; Dromer, F. Worrisome trends in incidence and mortality of candidemia in intensive care units (Paris area, 2002–2010). Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Merelli, M.; Righi, E.; Diaz-Martin, A.; Rosello, E.M.; Luzzati, R.; Parra, A.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Sanguinetti, M.; Posteraro, B.; et al. Epidemiology, species distribution, antifungal susceptibility, and outcome of candidemia across five sites in Italy and Spain. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4167–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, V.M.; Rodrıguez, N.M.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Heras, A.; Agulló, E. Modified chitosan carrying phosphonic and alkyl groups. Carbohydrate Polymers 2003, 51, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Rajapakse, N. Enzymatic production and biological activities of chitosan oligosaccharides (COS): A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittur, F.S.; Kumar, A.B.V.; Gowda, L.R.; Tharanathan, R.N. Chitosanolysis by a pectinase isozyme of Aspergillus niger—A non-specific activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Pina, C.; Tavaria, F.K.; Pintado, M.M. Evaluation and insights into chitosan antimicrobial activity against anaerobic oral pathogens. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: Applications and mode of action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, L.; Singh, J.; Agarwal, V.; Tewari, R.P. Biomedical applications of carboxymethyl chitosans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 452–466. [Google Scholar]
- Leceta, I.; Guerrero, P.; Ibarburu, I.; Dueñas, M.T.; de la Caba, K. Characterization and antimicrobial analysis of chitosan-based films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Sahl, H.G. Chitosan and its antimicrobial potential—A critical literature survey. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.; Tarsi, R.; Filippini, O.; Giovanetti, E.; Biagini, G.; Varaldo, P.E. Antimicrobial properties of N-carboxybutyl chitosan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 2019–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, G.; del Monaco, S.; Cerrutti, P.; Galvagno, M. Selective antimicrobial activity of chitosan on beer spoilage bacteria and brewing yeasts. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Li, P. Novel derivatives of chitosan and their antifungal activities in vitro. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, A.; Boorsma, A.; Brul, S.; Hellingwerf, K.J.; Klis, F.M. Transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the plasma membrane-perturbing compound chitosan. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.P.; Taffs, R.; Davison, W.M.; Stewart, P.S. Anti-biofilm properties of chitosan-coated surfaces. J. Biomater. Sci. Poly. Ed. 2008, 19, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinabeck, M.K.; Long, L.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Chandra, J.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Mohamed, S.; Ghannoum, M.A. Rabbit model of Candida albicans biofilm infection: Liposomal amphotericin B antifungal lock therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.R.; Mihu, M.R.; Tar, M.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Han, G.; Friedman, A.J.; Friedman, J.M.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Demonstration of antibiofilm and antifungal efficacy of chitosan against candidal biofilms, using an in vivo central venous catheter model. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y. Water-solubility of chitosan and its antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenel, S.; İkinci, G.; Kaş, S.; Yousefi-Rad, A.; Sargon, M.F.; Hıncal, A.A. Chitosan films and hydrogels of chlorhexidine gluconate for oral mucosal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 193, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerca, N.; Martins, S.; Pier, G.B.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. The relationship between inhibition of bacterial adhesion to a solid surface by sub-mics of antibiotics and subsequent development of a biofilm. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 156, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrado, L.; Azevedo, M.M.; Silva-Dias, A.; Ramos, J.P.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. Cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin as novel biofilm inhibitors? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrado, L.; Silva-Dias, A.; Azevedo, M.M.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. In vivo antibiofilm effect of cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin against usual agents of catheter-related bloodstream infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuéllar-Cruz, M.; Vega-González, A.; Mendoza-Novelo, B.; López-Romero, E.; Ruiz-Baca, E.; Quintanar-Escorza, M.A.; Villagómez-Castro, J.C. The effect of biomaterials and antifungals on biofilm formation by Candida species: A review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 2513–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwalli, K.H.; Khan, S.A.; Krom, B.P.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Streptococcus mutans, Candida albicans, and the human mouth: A sticky situation. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Tavaria, F.K.; Pintado, M.M. Study of the effects of chitosan upon streptococcus mutans adherence and biofilm formation. Anaerobe 2013, 20, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcurra, A.I.; Barembaum, S.R.; Bojanich, M.A.; Calamari, S.E.; Aguilar, J.; Battellino, L.J.; Dorronsoro, S.T. Effect of the high molecular weight chitosan and sodium alginate on Candida albicans hydrophobicity and adhesion to cells. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2006, 11, E120–E125. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, A.A.; Misra, S.S.; Irwin, J.O. The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood. J. Hyg–Camb. 1938, 38, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic, S.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Savic, B.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).