Microbial Quality of Leafy Greens Grown Under Soilless Production Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
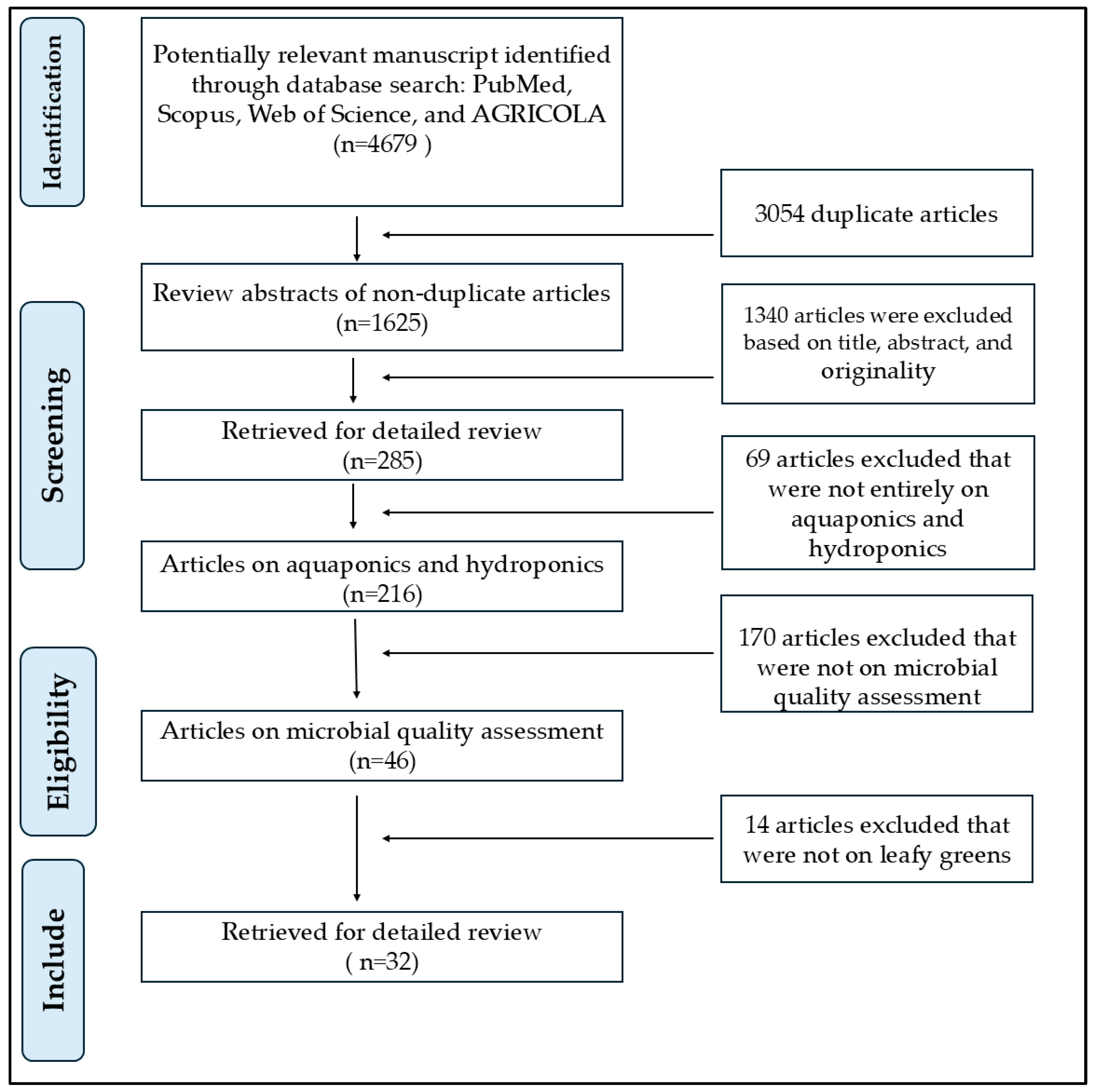
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Limitations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soilless Systems and Associated Microbes
3.1.1. Beneficial Microbes
3.1.2. Pathogenic Microbes
| Microbes | Source System/Crop | References |
|---|---|---|
| Mesophilic aerobic bacteria, enterobacteria, and psychrophilic bacteria | Aquaponic (rainbow trout: Oncorhynchus mykiss) and hydroponic: Lettuce | Edgar Wilber et al., 2019 [64] |
| Coliform, Yeast, and Filamentous fungi | Hydroponic and Aquaponic | Artimová et al., 2023 [36] |
| Coliforms, Coliforms, E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella | Hydroponic: Bell peppers | Avila-Vega et al., 2014 [65] |
| Pythium aphanidermatum and P. dissotocum | Greenhouse: Spinach [66] | Bates, 1984 [66] |
| Total coliforms and thermotolerant bacteria | Aquaponic: Lettuce | Bianchini et al., 2020 [54] |
| Aerobic bacteria, coliform bacteria, and yeast | Hydroponic: Lettuce | Dankwa et al., 2020 [67] |
| Coliforms, yeast, and mold | Aquaponic: Lettuce | Dankwa et al., 2021 [55] |
| Pseudomonas spp. and Clostridium spp. | Hydroponic: Microgreens | Dong and Feng, 2022 [58] |
| P. aeruginosa and Aeromonas hydrophila | Hydroponic- Lettuce | Dong and Feng, 2022 [58] |
| P. aeruginosa and A. hydrophilia | Aquaponic (Nile Tilapia) | Dorick et al., 2024 [52] |
| Verrucomicrobia, Proteobacteria, Planctomycetes, Nitrospire, Gemmatimonadetes, Fusobacteria, Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria, Chloroflexi, Chlorobi, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Acidobacteria. | Aquaponic | Eck et al., 2019 [37] |
| Luteolibacter, Flavobacterium, Nitrospira, gammaproteobacteria, Flavobacterium, Pseudomonadaceae, and Sphingomonadaceae | Aquaponic (Tilapia): Lettuce. | Eck et al., 2021 [41] |
| Actinobacter, Pseudomonas, Shigella, and Aeromonas genera. | Aquaponic (Mozambique tilapia: Oreochromis mossambicus)- Lettuce- | Kasozi et al., 2022 [63] |
| L. monocytogenes | Hydroponic: Lettuce | Kyere et al., 2019 [68] |
| Listeria spp. and E. coli | Hydroponic: Tomato | Lopez-Galvez et al., 2014 [69] |
| Generic E. coli, coliforms, Salmonella spp., E. coli O157:H7, L. monocytogenes, S. aureus, yeast and mold | Hydroponic: Lettuce | Mohammad et al., 2022 [56] |
| Coliforms, Enterobacteriaceae, anaerobic mesophilic bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, Pseudomonas spp., enterococci, yeasts and molds | Aquaponic (Tilapia) and hydroponic: Lettuce | Nissen et al., 2021 [62] |
| Enterobacteriaceae, coliforms, E. coli, and Salmonella | Hydroponic: Tomato | Orozco et al., 2008 [70] |
| Mesophilic bacteria, yeasts and molds, and Enterobacteriaceae | Hydroponic: Lettuce | Scuderi et al., 2011 [61] |
| Mesophilic bacteria, coliforms, yeast, and mold | Hydroponic: Lettuce | Selma et al., 2012 [60] |
| Coliform, E. coli, yeast, and mold | Aquaponic: Lettuce | Sirsat and Neal, 2013 [59] |
| Mesophilic bacteria, coliforms, and Salmonella | Hydroponic: Lettuce | Tham et al., 2021 [71] |
| Shiga toxin-producing E. coli | Aquaponic (Nile tilapia: Oreochromis niloticus L.) and hydroponic- Lettuce, basil, and tomato | Wang et al., 2020 [57] |
| Coliforms and E. coli | Hydroponic: Cucumber | Xu and Warriner, 2005 [72] |
3.2. Factors Influencing Human Pathogenic Microorganisms in Soilless Systems
3.2.1. Environmental Conditions
3.2.2. Poor Personal Hygiene and Cross-Contamination
| Source/Sample | Pathogen | System | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | |||
| Stormwater retention ponds | S. Typhimurium | Hydroponic | FDA, 2022 [75] |
| Puddles | Salmonella | Hydroponic | Orozco et al., 2008 [73] |
| Reclaimed and surface water | E. coli and Salmonella spp. | Hydroponic | Lopez-Galvez et al., 2014 [69] |
| Water and fertilizer solutions | E. coli | Hydroponic | Lopez-Galvez et al., 2016 [78] |
| Well water | E. coli and coliforms | Hydroponic | Xu et al., 2005 [72] |
| Substrate (peat moss) and seedling water reservoir | Coliforms | Hydroponic | Dankwa et al., 2020 [67] |
| Conveyor belt | Salmonella | Hydroponic | Avila-Vega et al., 2014 [65] |
| Water | Total and thermotolerant coliforms | Aquaponic | Bianchini et al., 2020 [54] |
| Water | E. coli | Aquaponic | Dorick et al., 2021 [51] |
| Plant growth medium (hydroton) and water | Yeast, mold, coliform bacteria, and E. coli | Aquaponic | Tunçelli et al., 2023 [74] |
| Recirculating water | Shiga toxin-producing E. coli | Hydroponic and Aquaponic | Wang et al., 2020 [57] |
| Water and biofilm | Candida albicans, C. parapsilosis Aspergillus flavus, A. niger, Rhizopus, Fusarium sp., Trichoderma, and Penicillium sp. | Aquaponic | Sheema et al., 2017 [79] |
| Wild and domestic animals | |||
| Opossums and mice | S. Montevideo | Hydroponic | Orozco et al., 2008 [73] |
| Goat | Salmonella serotype F | Hydroponic | Orozco et al., 2008 [73] |
| Fish: Aquaponic | |||
| Fish: catfish | Aeromonas spp., Pseudomonas spp. and Staphylococcus spp. | Aquaponic | Chitmanat et al., 2015 [80] |
| Fish feces: Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) | Shiga toxin-producing E. coli | Aquaponic | Wang et al., 2020 [57] |
| Poor Personal Hygiene | |||
| Personnel shoes | Salmonella serotype F | Hydroponic | Orozco et al., 2008 [73] |
| Farm worker’s shoes | E. coli and P. aeruginosa | Hydroponic and aquaponic | Dong and Feng, 2022 [58] |
| Personnel cloths | Salmonella | Hydroponic | Orozco et al., 2008 [73] |
| Root/seed internalization: Experimental findings | |||
| Inoculated seedlings and uptake from nutrient solution | E. coli O157:H7 | Hydroponic | Franz et al., 2007 [81] |
| Uptake from nutrient solution | E. coli O157:H7 | Hydroponic | Sharma et al., 2009 [82] |
| Uptake from nutrient solution | E. coli | Hydroponic | Warriner et al., 2003 [83] |
| Seeds soaked in bacterial cell suspension | E. coli O157:H7 and S. Typhimurium | Hydroponic | Jablasone et al., 2005 [84] |
| Plant roots soaked in nutrient solution containing bacteria | S. Montevideo | Hydroponic | Guo et al., 2002 [85] |
3.2.3. Plant Tissue Damage
3.2.4. Fish Species and Human Pathogens Contamination in Aquaponic Systems
3.3. Microbial Control in Soilless Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EI-Kazzaz, A. Soilless Agriculture a New and Advanced Method for Agriculture Development: An Introduction. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, H.M. Hydroponic Food Production: A Definitive Guidebook for the Advanced Home Gardener and the Commercial Hydroponic Grower, 7th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.A. A Review on Hydroponic Greenhouse Cultivation for Sustainable Agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Food Sci. 2018, 2, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D. Water for Food Water for Life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; Taylor and Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2013; pp. 4–25. [Google Scholar]
- Savvas, D. Hydroponic Production of Vegetables and Ornamentals; Embryo Publications: Athens, Greece, 2002; pp. 299–343. [Google Scholar]
- Love, D.C.; Fry, J.P.; Li, X.; Hill, E.S.; Genello, L.; Semmens, K.; Thompson, R.E. Commercial Aquaponics Production and Profitability: Findings from an International Survey. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despommier, D. The Vertical Farm: Controlled Environment Agriculture Carried Out in Tall Buildings Would Create Greater Food Safety and Security for Large Urban Populations. J. Verbrauch. Lebensm. Sicherheit. 2011, 6, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, F.; Lindholm-Lehto, P.; Pirhonen, J. Is Aquaponics Beneficial in Terms of Fish and Plant Growth and Water Quality in Comparison to Separate Recirculating Aquaculture and Hydroponic Systems? Water 2022, 14, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgari, R.; Baldi, A.; Ferrante, A.; Lenzi, A. Yield and Quality of Basil, Swiss Chard, and Rocket Microgreens Grown in a Hydroponic System. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2017, 45, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinev, T.; Velichkova, K.; Stoyanova, A.; Sirakov, I. Microbial Pathogens in Aquaponics Potentially Hazardous for Human Health. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.G.; Phuc, P.D.; Hiep, N.T.; Samuelsen, H.; Jensen, P.K.; Dalsgaard, A.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Konradsen, F. The Fear of Awful Smell: Risk Perceptions among Farmers in Vietnam Using Wastewater and Human Excreta in Agriculture. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raviv, M.; Lieth, J.H.; Bar-Tal, A. Significance of Soilless Culture in Agriculture. In Soilless Culture: Theory and Practice; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tuxun, A.; Xiang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Son, J.E.; Yamada, M.; Yamada, S.; Tagawa, K.; Baiyin, B.; Yang, Q. Soilless Cultivation: Precise Nutrient Provision and Growth Environment Regulation Under Different Substrates. Plants 2025, 14, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, M.T. Fitness of Human Enteric Pathogens on Plants and Implications for Food Safety. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Manure-Borne Pathogens as an Important Source of Water Contamination: An Update on the Dynamics of Pathogen Survival/Transport as Well as Practical Risk Mitigation Strategies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 227, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Singleton, I.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Sources and Contamination Routes of Microbial Pathogens to Fresh Produce during Field Cultivation: A Review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N.S. Advances in Soilless Culture and Growing Media in Today’s Horticulture—An Editorial. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Iqbal, K.; Aziem, S.; Mahato, P.; Negi, A.K. A Review On The Science of Growing Crops Without Soil (Soilless Culture)—A Novel Alternative For Growing Crops. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2014, 7, 833–842. [Google Scholar]
- Shrouf, A.; Alshrouf, A. Hydroponics, Aeroponic and Aquaponic as Compared with Conventional Farming. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2017, 27, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, P.H.V.; Trientini, M.F.; Fisher, P.R. Biofilm Management in Irrigation Lines and Hydroponic Lettuce Solutions Using Sanitizing Chemicals. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1335, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.; Helterbran, K.; Evans, M.R.; Currey, C. Growth of Escherichia Coli O157:H7, Non-O157 Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli, and Salmonella in Water and Hydroponic Fertilizer Solutions. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.M.; Holden, N.J. Quantification and Colonisation Dynamics of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Inoculation of Microgreens Species and Plant Growth Substrates. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 273, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridier, A.; Sanchez-Vizuete, P.; Guilbaud, M.; Piard, J.C.; Naïtali, M.; Briandet, R. Biofilm-Associated Persistence of Food-Borne Pathogens. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Briandet, R. Editorial: Biofilms from a Food Microbiology Perspective: Structures, Functions, and Control Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussy, A.; Papenbrock, J. An Overview of Soil and Soilless Cultivation Techniques—Chances, Challenges and the Neglected Question of Sustainability. Plants 2022, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela Saldinger, S.; Rodov, V.; Kenigsbuch, D.; Bar-Tal, A. Hydroponic Agriculture and Microbial Safety of Vegetables: Promises, Challenges, and Solutions. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.E.; Masser, M.P.; Losordo, T.M. Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems: Aquaponics-Integrating Fish and Plant Culture; SRAC Publication—Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MI, USA, 2006; 454p. [Google Scholar]
- Buhmann, A.; Papenbrock, J. Biofiltering of Aquaculture Effluents by Halophytic Plants: Basic Principles, Current Uses and Future Perspectives. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, B.; Vandorou, F.; Balafoutis, A.T.; Vaiopoulos, K.; Kyriakarakos, G.; Manolakos, D.; Papadakis, G. Energy Use in Greenhouses in the EU: A Review Recommending Energy Efficiency Measures and Renewable Energy Sources Adoption. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.N.; Topalcengiz, Z.; Gibson, K.E. Growing Safer Greens: Exploring Food Safety Practices and Challenges in Indoor, Soilless Production Through Thematic Analysis of Leafy Greens Grower Interviews. J. Food. Prot. 2023, 86, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, K.M.; Hall, A.J.; Gould, L.H. Outbreaks Attributed to Fresh Leafy Vegetables, United States, 1973–2012. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID). 2022. Available online: www.cdc.gov/norsdashboard (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- CDC. Outbreak of E. coli Infections Linked to Clover Sprouts; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://archive.cdc.gov/www_cdc_gov/ecoli/2020/o103h2-02-20/index.html (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- FDA. Revolution Farms Announces the Voluntary Recall of Lettuce Because of Possible Health Risk. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/safety/recalls-market-withdrawals-safety-alerts/revolution-farms-announces-voluntary-recall-lettuce-because-possible-health-risk (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- FDA. Outbreaks of Foodborne Illness. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/recalls-outbreaks-emergencies/outbreaks-foodborne-illness (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Artimová, R.; Játiová, M.; Baumgartnerová, J.; Lipková, N.; Petrová, J.; Maková, J.; Javoreková, S.; Hleba, L.; Medová, J.; Medo, J. Microbial Communities on Samples of Commercially Available Fresh-Consumed Leafy Vegetables and Small Berries. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.; Sare, A.R.; Massart, S.; Schmautz, Z.; Junge, R.; Smits, T.H.M.; Jijakli, M.H. Exploring Bacterial Communities in Aquaponic Systems. Water 2019, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmautz, Z.; Walser, J.C.; Espinal, C.A.; Gartmann, F.; Scott, B.; Pothier, J.F.; Frossard, E.; Junge, R.; Smits, T.H.M. Microbial Diversity Across Compartments in an Aquaponic System and Its Connection to the Nitrogen Cycle. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelme, R.P.; Smith, M.C.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Newton, R.J. Component Microenvironments and System Biogeography Structure Microorganism Distributions in Recirculating Aquaculture and Aquaponic Systems. mSphere 2019, 4, e00143-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Scicchitano, D.; Palladino, G.; Nanetti, E.; Candela, M.; Furones, D.; Sanahuja, I.; Carbó, R.; Gisbert, E.; Andree, K.B. Microbiome Study of a Coupled Aquaponic System: Unveiling the Independency of Bacterial Communities and Their Beneficial Influences Among Different Compartments. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.; Szekely, I.; Massart, S.; Jijakli, M.H. Ecological Study of Aquaponics Bacterial Microbiota over the Course of a Lettuce Growth Cycle. Water 2021, 13, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, B.R. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Mechanisms and Applications. Scientifica 2012, 2012, e963401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Alsanius, B.W. Utilisation of Carbon Sources by Pythium, Phytophthora and Fusarium Species as Determined by Biolog® Microplate Assay. Open Microbiol. J. 2009, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sutton, J.C.; Grodzinski, B.; Kloepper, J.W.; Reddy, M.S. Biological Control of Pythium Root Rot of Chrysanthemum in Small-Scale Hydroponic Units. Phytoparasitica 2007, 35, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, M. Effects of Lactate, Humate and Bacillus subtilis on the Growth of Tomato Plants in Hydroponic Systems. Acta Hortic. 1999, 481, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas García, J.A.; Probanza, A.; Ramos, B.; Ruiz Palomino, M.; Gutiérrez Mañero, F.J. Effect of Inoculation of Bacillus Licheniformis on Tomato and Pepper. Agronomie 2004, 24, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Aoyama, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Watanabe, A.; Ohmori, H.; Uehara, Y.; Takano, M. Microbial Mineralization of Organic Nitrogen into Nitrate to Allow the Use of Organic Fertilizer in Hydroponics. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldreich, E.E.; Clarke, N.A. Bacterial Pollution Indicators in the Intestinal Tract of Freshwater Fish. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelme, R.P.; Oyserman, B.O.; Blom, J.E.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Newton, R.J. Stripping Away the Soil: Plant Growth Promoting Microbiology Opportunities in Aquaponics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.X.; Moorman, G.W. Plant Pathogens in Irrigation Water: Challenges and Opportunities. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorick, J.; Hayden, M.; Smith, M.; Blanchard, C.; Monu, E.; Wells, D.; Huang, T.S. Evaluation of Escherichia Coli and Coliforms in Aquaponic Water for Produce Irrigation. Food Microbiol. 2021, 99, 10380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorick, J.; Kumar, G.D.; Macarisin, D.; Andrew Widmer, J.; Stivers, T.; Dunn, L.L. Longitudinal Survey of Aeromonas Hydrophila and Foodborne Pathogens in a Commercial Aquaponics System. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, C.; Hayes, L.; Ringle, D. Food Safety Hazards Associated with Smooth-Textured Leafy Greens Produced in Aquaponic, Hydroponic, and Soil based Systems with and Without Roots at Retail. University of Minnesota Aquaponics. 2015. Available online: https://aquaponics.umn.edu/ (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Bianchini, P.P.T.; Cardoso, S.B.; Pantaleão, J.A.F.; Okura, M.H. Analysis of Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa) Production in Different Substrates in an Aquaponic System Using an IBC Container. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2020, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankwa, A.S.; Machado, R.M.; Perry, J.J. Sanitizer Efficacy in Reducing Microbial Load on Commercially Grown Hydroponic Lettuce. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2021, 101, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, Z.H.; do Prado, I.; Sirsat, S.A. Comparative Microbial Analyses of Hydroponic Versus In-Soil Grown Romaine Lettuce Obtained at Retail. Heliyon 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Deering, A.J.; Kim, H.J. The Occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Feng, H. Microbial Community Analysis and Food Safety Practice Survey-Based Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment for Controlled Environment Hydroponic/Aquaponic Farming Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 879260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirsat, S.A.; Neal, J.A. Microbial Profile of Soil-Free versus in-Soil Grown Lettuce and Intervention Methodologies to Combat Pathogen Surrogates and Spoilage Microorganisms on Lettuce. Foods 2013, 2, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma, M.V.; Luna, M.C.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Tudela, J.A.; Beltrán, D.; Baixauli, C.; Gil, M.I. Sensory Quality, Bioactive Constituents and Microbiological Quality of Green and Red Fresh-Cut Lettuces (Lactuca Sativa L.) Are Influenced by Soil and Soilless Agricultural Production Systems. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 63, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, D.; Restuccia, C.; Chisari, M.; Barbagallo, R.N.; Caggia, C.; Giuffrida, F. Salinity of Nutrient Solution Influences the Shelf-Life of Fresh-Cut Lettuce Grown in Floating System. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 59, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, L.; Casciano, F.; Gianotti, A. Plant Volatiles of Lettuce and Chicory Cultivated in Aquaponics Are Associated to Their Microbial Community. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, N.; Kaiser, H.; Wilhelmi, B. Determination of Phylloplane Associated Bacteria of Lettuce from a Small-Scale Aquaponic System via 16S RRNA Gene Amplicon Sequence Analysis. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcarraz, Q.E.W.; Tapia, L.O.; Alcarraz, Q.Y.M. Microbiological Analysis of Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L.) Grown in an Aquaponic and Hydroponic System. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 7, 500–557. [Google Scholar]
- Avila-Vega, D.E.; Álvarez-Mayorga, B.; Arvizu-Medrano, S.M.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Martínez-Peniche, R.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M. Microbiological Profile and Incidence of Salmonella and Listeria Monocytogenes on Hydroponic Bell Peppers and Greenhouse Cultivation Environment. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.L. Root Rot of Hydroponically Grown Spinach Caused by Pythium Aphanidermatum and P. Dissotocum. Plant. Dis. 1984, 68, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankwa, A.S.; Machado, R.M.; Perry, J.J. Sources of Food Contamination in a Closed Hydroponic System. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyere, E.O.; Foong, G.; Palmer, J.; Wargent, J.J.; Fletcher, G.C.; Flint, S. Rapid Attachment of Listeria Monocytogenes to Hydroponic and Soil Grown Lettuce Leaves. Food Control 2019, 101, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Galvez, F.; Allende, A.; Pedrero-Salcedo, F.; Alarcon, J.J.; Gil, M.I. Safety Assessment of Greenhouse Hydroponic Tomatoes Irrigated with Reclaimed and Surface Water. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 191, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, L.; Rico-Romero, L.; Escartín, E.F. Microbiological Profile of Greenhouses in a Farm Producing Hydroponic Tomatoes. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, C.A.T.; Zwe, Y.H.; Li, D. Microbial Study of Lettuce and Agriculture Water Used for Lettuce Production at Singapore Urban Farms. Food Control 2021, 126, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Warriner, K. Coliphage as an Indicator of Fecal Contamination in Hydroponic Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L) Greenhouses. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 2397–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, R.L.; Iturriaga, M.H.; Tamplin, M.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Call, J.E.; Luchansky, J.B.; Escartin, E.F. Animal and Environmental Impact on the Presence and Distribution of Salmonella and Escherichia Coli in Hydroponic Tomato Greenhouses. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunçelli, G.; Can Tunçelli, İ.; Memiş, D. Evaluation of Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L.) in Aquaponic System in Terms of Food Safety. Ege J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 40, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Investigation Report: Factors Potentially Contributing to the Contamination of Packaged Leafy Greens Implicated in the Outbreak of Salmonella Typhimurium During the Summer of 2021; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022.
- Gurtler, J.B.; Gibson, K.E. Irrigation Water and Contamination of Fresh Produce with Bacterial Foodborne Pathogens. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende, A.; Monaghan, J. Irrigation Water Quality for Leafy Crops: A Perspective of Risks and Potential Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7457–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Galvez, F.; Gil, M.I.; Pedrero-Salcedo, F.; Alarcón, J.J.; Allende, A. Monitoring Generic Escherichia Coli in Reclaimed and Surface Water Used in Hydroponically Cultivated Greenhouse Peppers and the Influence of Fertilizer Solutions. Food Control 2016, 67, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheema, K.; Dorai, M.; Paul, D. Fungi in Aquaponics. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 5, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitmanat, C.; Pimpimol, T.; Chaibu, P. Investigation of Bacteria and Fish Pathogenic Bacteria Found in Freshwater Aquaponic System. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, E.; Visser, A.A.; Van Diepeningen, A.D.; Klerks, M.M.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Quantification of Contamination of Lettuce by GFP-Expressing Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Ingram, D.T.; Patel, J.R.; Millner, P.D.; Wang, X.; Hull, A.E.; Donnenberg, M.S. A Novel Approach to Investigate the Uptake and Internalization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Spinach Cultivated in Soil and Hydroponic Medium. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warriner, K.; Ibrahim, F.; Dickinson, M.; Wright, C.; Waites, W.M. Interaction of Escherichia coli with Growing Salad Spinach Plants. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablasone, J.; Warriner, K.; Griffiths, M. Interactions of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria Monocytogenes Plants Cultivated in a Gnotobiotic System. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 99, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Van Iersel, M.W.; Chen, J.; Brackett, R.E.; Beuchat, L.R. Evidence of Association of Salmonellae with Tomato Plants Grown Hydroponically in Inoculated Nutrient Solution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3639–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupitski, Y.; Golberg, D.; Belausov, E.; Pinto, R.; Swartzberg, D.; Granot, D.; Sela, S. Internalization of Salmonella Enterica in Leaves Is Induced by Light and Involves Chemotaxis and Penetration Through Open Stomata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6076–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macarisin, D.; Patel, J.; Sharma, V.K. Role of Curli and Plant Cultivation Conditions on Escherichia coli O157: H7 Internalization into Spinach Grown on Hydroponics and in Soil. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 173, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruscavage, D.; Miller, S.A.; Lewis Ivey, M.L.; Lee, K.E.N.; LeJeune, J.T. Survival and Dissemination of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on Physically and Biologically Damaged Lettuce Plants. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulaosmanovic, E.; Lindblom, T.U.T.; Windstam, S.T.; Bengtsson, M.; Rosberg, A.K.; Mogren, L.; Alsanius, B.W. Processing of Leafy Vegetables Matters: Damage and Microbial Community Structure from Field to Bag. Food Control 2021, 125, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesse, L.L.; Løvold, T.; Bergsjø, B.; Nordby, K.; Wallace, C.; Holstad, G. Persistence of Orally Administered Salmonella Enterica Serovars Agona and Montevideo in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, K.A.; Nakao, J.H.; Taylor, E.V.; Eggers, C.; Gould, L.H. Fish-Associated Foodborne Disease Outbreaks: United States, 1998–2015. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, J.; Smith, R. Transmission of Waterborne Fish and Plant Pathogens in Aquaponics and Their Control with Physical Disinfection and Filtration: A Systematized Review. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, M.J.; Semmens, K.; Bissonnette, G.K.; Jaczynski, J. Inactivation with UV-Radiation and Internalization Assessment of Coliforms and Escherichia Coli in Aquaponically Grown Lettuce. LWT 2018, 89, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-García, T.; González-Estrada, R.R.; Chiquito-Contreras, R.G.; Reyes-Pérez, J.J.; González-Salas, U.; Hernández-Montiel, L.G.; Murillo-Amador, B. Biocontrol of Phytopathogens under Aquaponics Systems. Water 2020, 12, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouvenakers, G.; Dapprich, P.; Massart, S.; Jijakli, M.H. Plant Pathogens and Control Strategies in Aquaponics. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 353–370. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheruiyot, R.K.; Mechesso, A.F. Microbial Quality of Leafy Greens Grown Under Soilless Production Systems. Pathogens 2025, 14, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090943
Cheruiyot RK, Mechesso AF. Microbial Quality of Leafy Greens Grown Under Soilless Production Systems. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090943
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheruiyot, Robert Korir, and Abraham Fikru Mechesso. 2025. "Microbial Quality of Leafy Greens Grown Under Soilless Production Systems" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090943
APA StyleCheruiyot, R. K., & Mechesso, A. F. (2025). Microbial Quality of Leafy Greens Grown Under Soilless Production Systems. Pathogens, 14(9), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090943






