SFTSV Prevalence in Ticks and Livestock in an SFTSV-Endemic Area in Central China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
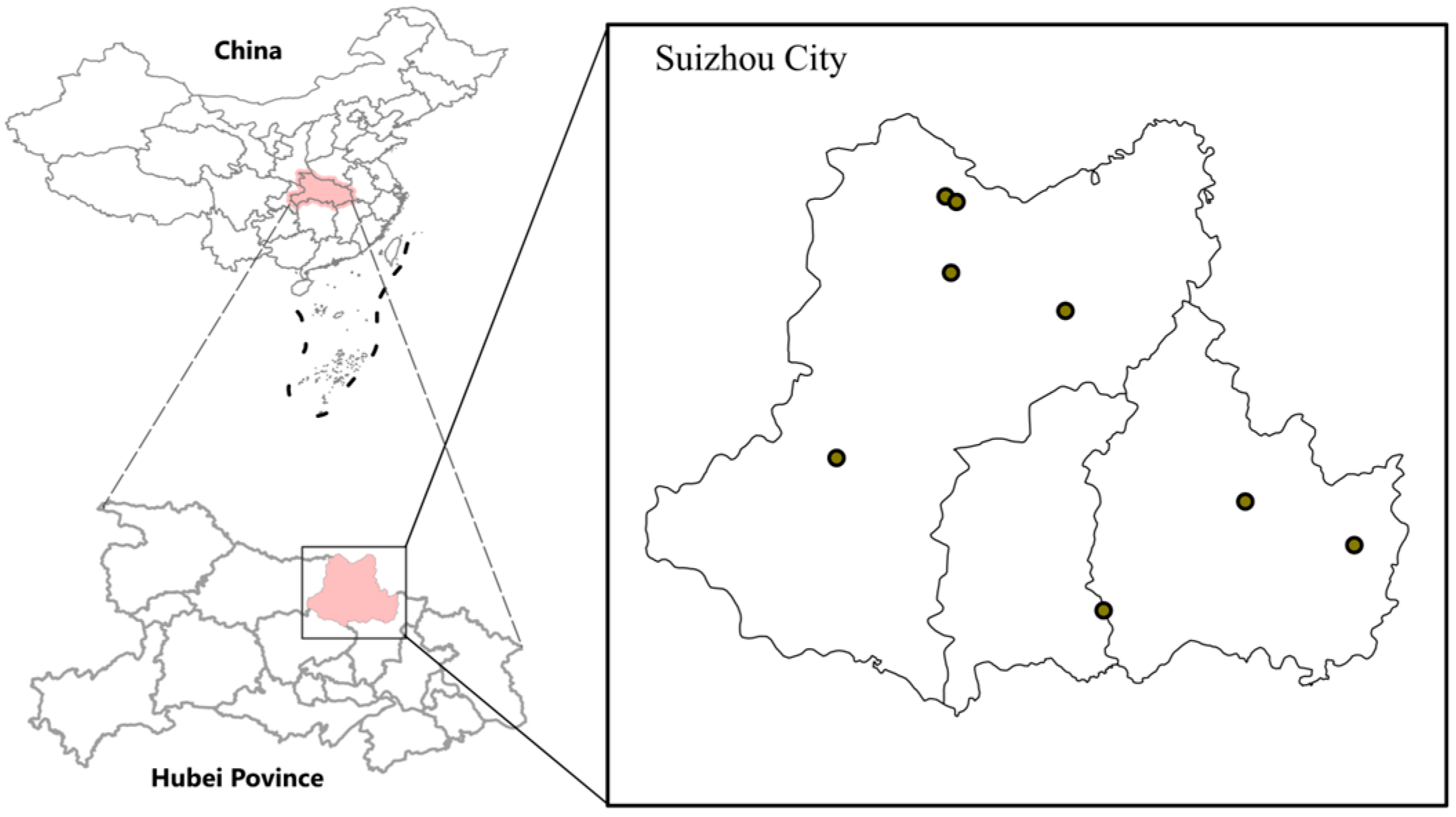
2.1. Sample Collection Sites
2.2. Animal Blood and Tick Collection
2.3. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.4. Tick Identification and Grouping
2.5. PCR and RT-PCR
3. Results
3.1. Tick Species in Suizhou City
3.2. Prevalence of SFTSV in Ticks and Animals from Suizhou City
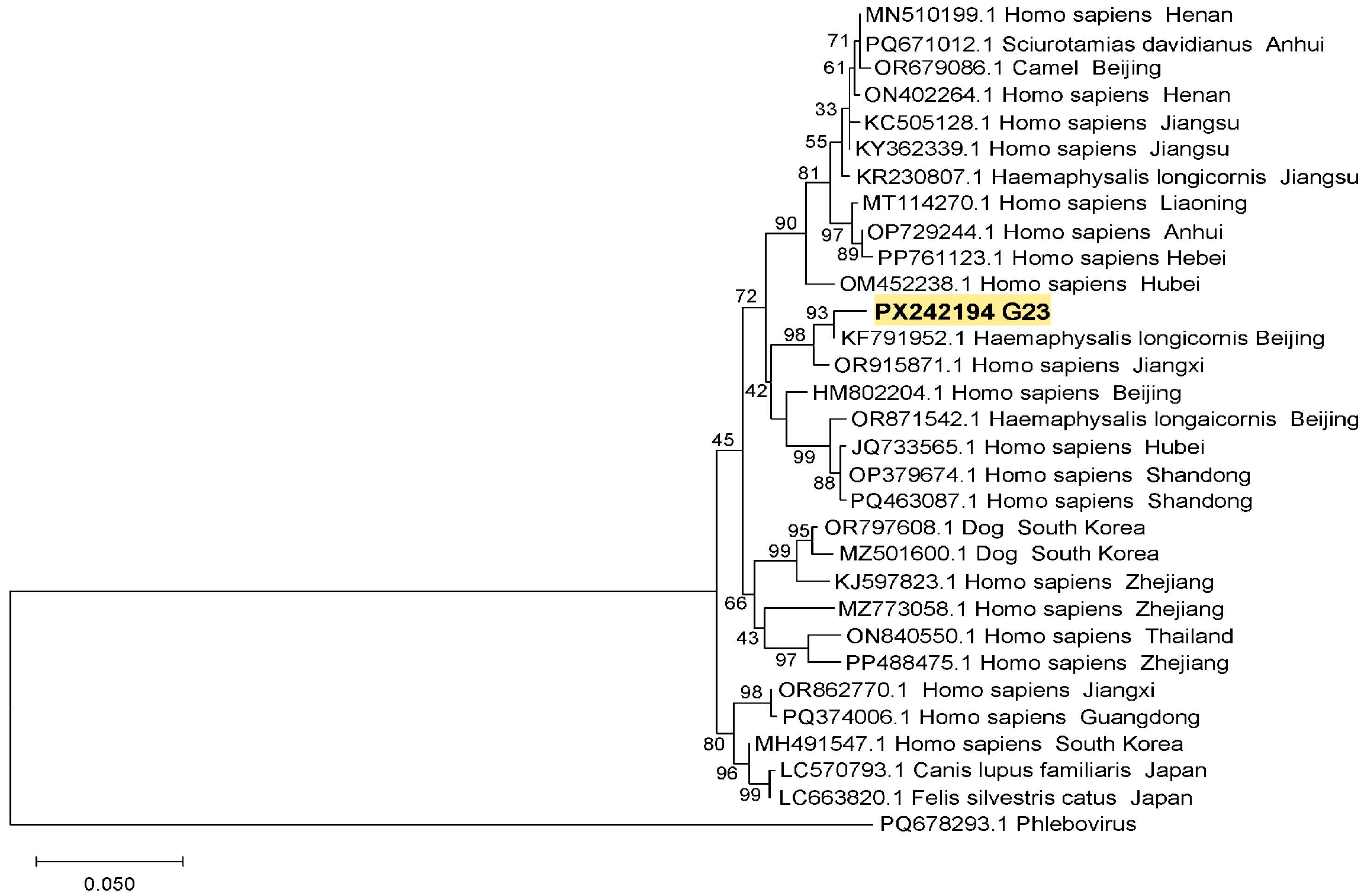
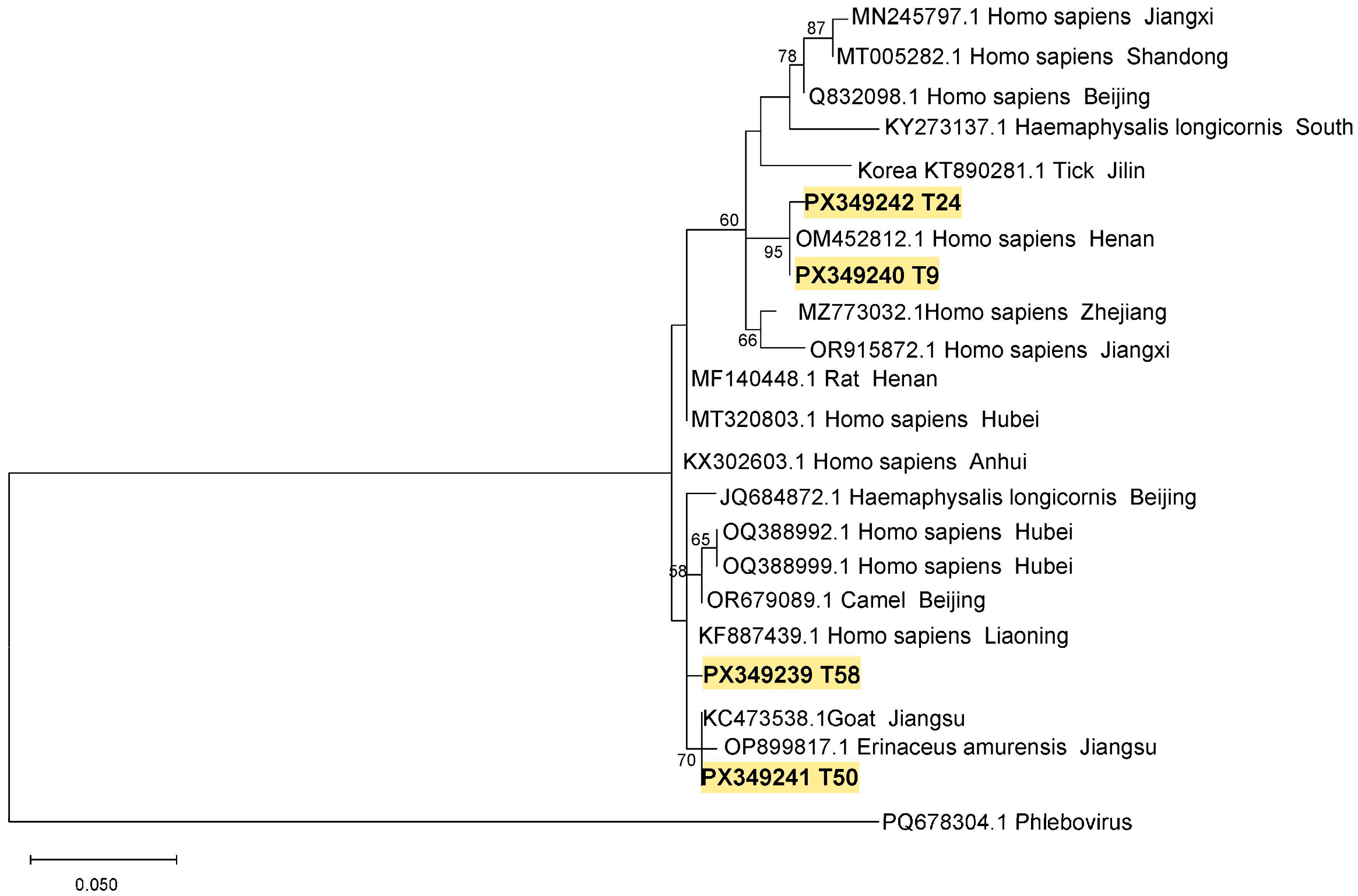
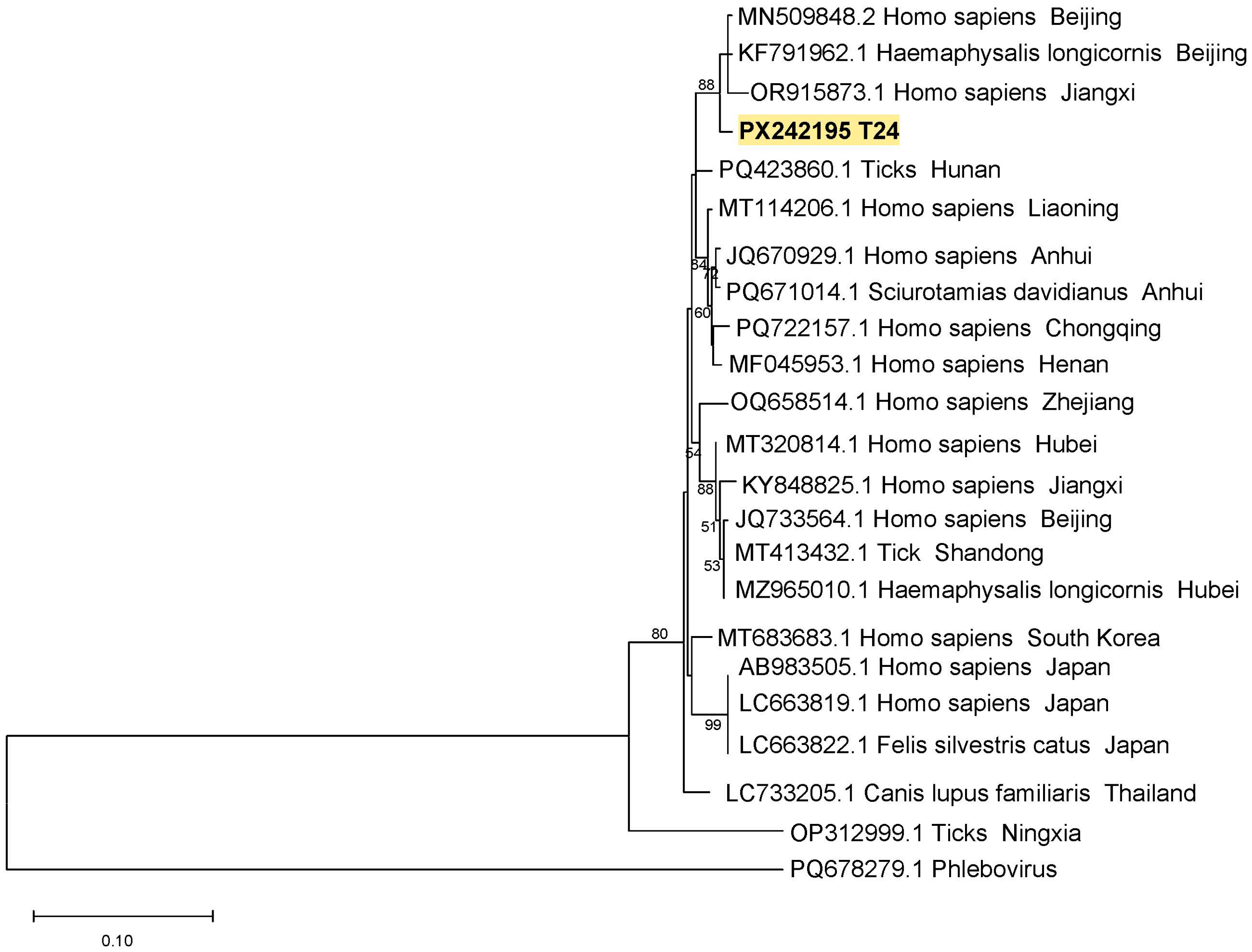
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of SFTSV from Ticks and Goats in Suizhou City
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Q.B.; Xing, B.; Zhang, S.F.; Liu, K.; Du, J.; Li, X.K.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.D.; Wang, L.Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of laboratory-diagnosed severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-17: A prospective observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-j. Risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1056–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.Z.; Dong, Y.H.; Yan, Z.J.; Zhou, C.M.; Yu, X.J.; Qin, X.R. Reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus in SFTSV infected patients. Infect. Med. 2023, 2, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Adkins, S.; Alioto, D.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ayllón, M.A.; Bahl, J.; Balkema-Buschmann, A. 2020 taxonomic update for phylum Negarnaviricota (Riboviria: Orthornavirae), including the large orders Bunyavirales and Mononegavirales. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 3023–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Qi, X.; Wang, H. A novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 862–863. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mei, L.; Walker, D.H.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.-J. Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Shimoda, T.; Matsuoka, H.; Yamada, H.; Saito, T.; Imataki, O.; Kadowaki, N.; Noguchi, K.; Maeda, K. A case of cat-to-human transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 72, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xiu, L.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, H.; et al. Direct transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from farm-raised fur animals to workers in Weihai, China. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.-M.; Qi, R.; Qin, X.-R.; Fang, L.-Z.; Han, H.-J.; Lei, X.-Y.; Yu, X.-J. Oral and ocular transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Infect. Med. 2022, 1, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Ling, F.; Shi, W.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Mao, H. Probable aerosol transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in southeastern China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Xu, N.; Guo, X.; Chen, M.; Liang, H.; Cheng, D.; Zhao, L.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus aerosol infection in C57/BL6 mice. Virology 2023, 581, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Ren, D.; Lu, L. Epidemiological characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2010–2021. Dis. Surveill. 2024, 39, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Li, A.; Wang, S.; Li, D. Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome from 2010 to 2019 in Mainland China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-C.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Fang, L.-Q.; Liu, W. Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and treatment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Infect. Med. 2022, 1, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Mekata, H.; Sudaryatma, P.E.; Kirino, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Ando, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Okabayashi, T. Isolation of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from various tick species in area with human severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome cases. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Yi, J.; Kim, G.; Choi, S.J.; Jun, K.I.; Kim, N.-H.; Choe, P.G.; Kim, N.-J.; Lee, J.-K.; Oh, M.-d. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongkittikul, S.; Watanawong, R.; Rompho, P. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: The first case report in Thailand. Bangk. Med. J. 2020, 16, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, X.C.; Yun, Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Thao, N.T.P.; Man, P.K.C.; Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Cho, N.-H.; Lee, K.H. Endemic severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, A.M.; Nguyen, Y.T.H.; Kim, Y.; Ha, N.Y.; Kang, J.G.; Kim, H.; San, B.; Kyaw, O.; Htike, W.W.; Choi, D.O.; et al. Genotypic Heterogeneity of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Scrub Typhus Patients and Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Co-infection, Myanmar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1878–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.-M.; Zhao, L.; Wen, H.-L.; Zhang, Z.-T.; Liu, J.-W.; Fang, L.-Z.; Xue, Z.-F.; Ma, D.-Q.; Zhang, X.-S.; Ding, S.-J. Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks as reservoir and vector of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Niu, G.; Wang, X.; Ding, S.; Jiang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, M.; Bi, Z.; et al. SFTS virus in ticks in an endemic area of China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Casel, M.A.B.; Jang, S.g.; Choi, J.H.; Gil, J.; Rollon, R.; Cheun, S.; Kim, Y.I.; Song, M.S.; Choi, Y.K. Seasonal dynamics of Haemaphysalis tick species as SFTSV vectors in South Korea. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0048924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Z.; Feng, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, A.; et al. Ecology of the Tick-Borne Phlebovirus Causing Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in an Endemic Area of China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.E.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Tan, Z.; Tu, C.; He, B. Genomes and seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus and Nairobi sheep disease virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks and goats in Hubei, China. Virology 2019, 529, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intirach, J.; Lv, X.; Han, Q.; Lv, Z.-Y.; Chen, T. Morphological and molecular identification of hard ticks in Hainan Island, China. Genes 2023, 14, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Zhou, X.; Guo, F.; Xu, J.; Song, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, H.; Tang, J.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Babesia infection in cattle and dogs in Suizhou City, Hubei Province, China. Infect. Med. 2025, 4, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.C.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Krücken, J.; Rehman, A.; Nijhof, A.M. Morphological and phylogenetic analyses of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Bangladesh, Pakistan and Myanmar. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.L.; Su, W.Q.; Zhou, C.M.; Fang, L.Z.; Zhu, K.; Ma, D.Q.; Jiang, F.C.; Li, Z.M.; Li, D.; Duan, S.H.; et al. SFTSV infection in rodents and their ectoparasitic chiggers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Li, F.; Guan, X.; Tong, Y.; Wu, Y. Epidemiological investigation of an epidemic of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in a county in Hubei, 2023. Dis. Surveill. 2024, 39, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Chai, T. First detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in the tick species Haemaphysalis concinna in Shandong Province, China. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4703–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-Z.; Xiao, X.; Lei, S.-C.; Liu, J.-W.; Yu, X.-J. Haemaphysalis flava ticks as a competent vector of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kelly, P.; Guo, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, C. Molecular detection of Rickettsia, Hepatozoon, Ehrlichia and SFTSV in goat ticks. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 20, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, K.; Sun, Y.; Dai, K.; Zhang, X.-A.; Zhang, P.-H.; Feng, Z.-C.; Li, H.; Liu, W. Role of three tick species in the maintenance and transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takhampunya, R.; Kim, H.C.; Chong, S.T.; Korkusol, A.; Tippayachai, B.; Davidson, S.A.; Petersen, J.M.; Klein, T.A. Francisella-Like Endosymbiont Detected in Haemaphysalis Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) From the Republic of Korea. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, G. Transport of ixodid ticks and tick-borne pathogens by migratory birds. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.J.; Noh, J.; Kim, H.C.; Chong, S.T.; Klein, T.A.; Park, C.U.; Choi, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, M.; Min, S.; et al. Molecular Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Anaplasma and Borrelia Species in Ticks Collected from Migratory Birds at Heuksan, Hong, and Nan Islands, Republic of Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cai, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Zheng, A. Comparative Analysis of Bisexual and Parthenogenetic Populations in Haemaphysalis Longicornis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A. Biology, ecology and distribution of the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2016, 64, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K.J.; Witmier, B.J.; Eckert, R.A.; Boyer, C.N.; Helwig, M.W.; Kyle, A.D. Distribution and Density of Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) on Public Lands in Pennsylvania, United States. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Thompson, A.T. Haemaphysalis longicornis (Asian longhorned tick). Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Du, L.; Ye, R.-Z.; Zhao, F.; Cao, W.-C. Haemaphysalis longicornis. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.B.; Cui, X.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Ye, R.Z.; Wu, Y.Q.; Jiang, J.F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shum, M.H.; Chang, Q.C.; et al. Metavirome of 31 tick species provides a compendium of 1,801 RNA virus genomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, D.L.; Wang, B.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, M.Z.; Wang, N.; Gao, W.Y.; Li, C.; Han, X.Y.; et al. Virome diversity shaped by genetic evolution and ecological landscape of Haemaphysalis longicornis. Microbiome 2024, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, N.; Fernandez, M.P.; Diuk-Wasser, M. Risk of tick-borne pathogen spillover into urban yards in New York City. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Source of Ticks | Adult Female Ticks | Adult Male Ticks | Nymphs | Larvae | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free-living tick | 203 | 56 | 305 | 31 | 595 | |
| Parasitic ticks | Goats | 1248 | 328 | 183 | 13 | 1772 |
| Dogs | 42 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 48 | |
| Cattle | 7 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 22 | |
| Total | 1500 | 398 | 495 | 44 | 2437 | |
| Tick and SFTSV | Primer | Primer Sequences | TEM (°C) | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tick mitochondrial | F | AGTATTTTGACTATACAAAGGTATTG | 55 | 402 | |
| 16S RNA | R | GTAGGATTTTAAAAGTTGAACAAACTT | |||
| SFTSV | Out-F | CAGCCAGTTTACCCGAACAT | 57 | 679 | [20] |
| S segment | Out-R | GAAAGACGCAAAGGAGT | |||
| In-F | TGGCTCCGCGCATCTTCACA | 57 | 560 | ||
| In-R | TGGCTCCGCGCATCTTCACA | ||||
| SFTSV | Out-F | GRCATCTGARGCCAARTGYA | 50 | 335 | This study |
| M segment | Out-R | RACRTGKATWGCTRYTTTYCC | |||
| In-F | AARCCYGGRGAAGTYGTWGT | 50 | 278 | ||
| In-R | CRACYARYGAYCCWGARTGGA | ||||
| SFTSV | Out-F | AATGATGCCAAGAAGTGGAAT | 52 | 855 | [29] |
| L segment | Out-R | ATGTAAGCATAGTCCTAGAAGC | |||
| In-F | CCACAGATTCATTTGGGCT | 55 | 367 | ||
| In-R | ATCATGATCGCTGAGTCGTC |
| Host | Infection Rate |
|---|---|
| Haemaphysalis longicornis | 0.17% (4/2424) |
| Goats’ blood samples | 0.66% (1/152) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.-Y.; Wu, G.-D.; Peng, M.; Wu, L.-B.; Luo, Y.-M.; Xia, B.; Xiong, D.; Qin, X.-R.; Guo, F.; Yu, X.-J. SFTSV Prevalence in Ticks and Livestock in an SFTSV-Endemic Area in Central China. Pathogens 2025, 14, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090944
Lu H-Y, Wu G-D, Peng M, Wu L-B, Luo Y-M, Xia B, Xiong D, Qin X-R, Guo F, Yu X-J. SFTSV Prevalence in Ticks and Livestock in an SFTSV-Endemic Area in Central China. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090944
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Hui-Ya, Guan-Du Wu, Meng Peng, Li-Bang Wu, Yi-Ming Luo, Bin Xia, Dan Xiong, Xiang-Rong Qin, Fang Guo, and Xue-Jie Yu. 2025. "SFTSV Prevalence in Ticks and Livestock in an SFTSV-Endemic Area in Central China" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090944
APA StyleLu, H.-Y., Wu, G.-D., Peng, M., Wu, L.-B., Luo, Y.-M., Xia, B., Xiong, D., Qin, X.-R., Guo, F., & Yu, X.-J. (2025). SFTSV Prevalence in Ticks and Livestock in an SFTSV-Endemic Area in Central China. Pathogens, 14(9), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090944






