Molecular Survey of Selected Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens in Polish Wild Boars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
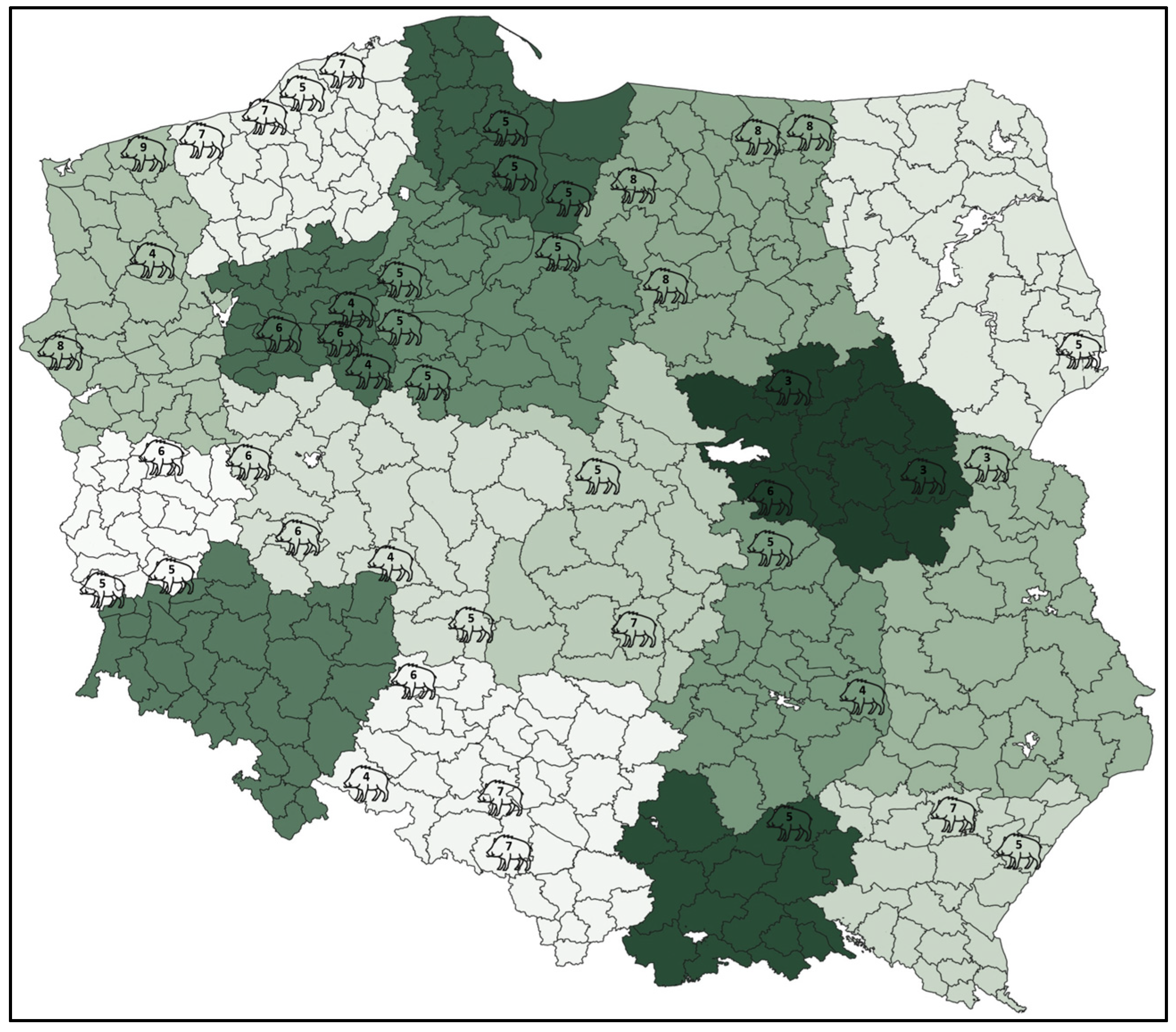
2.1. Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR for Pathogen Detection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
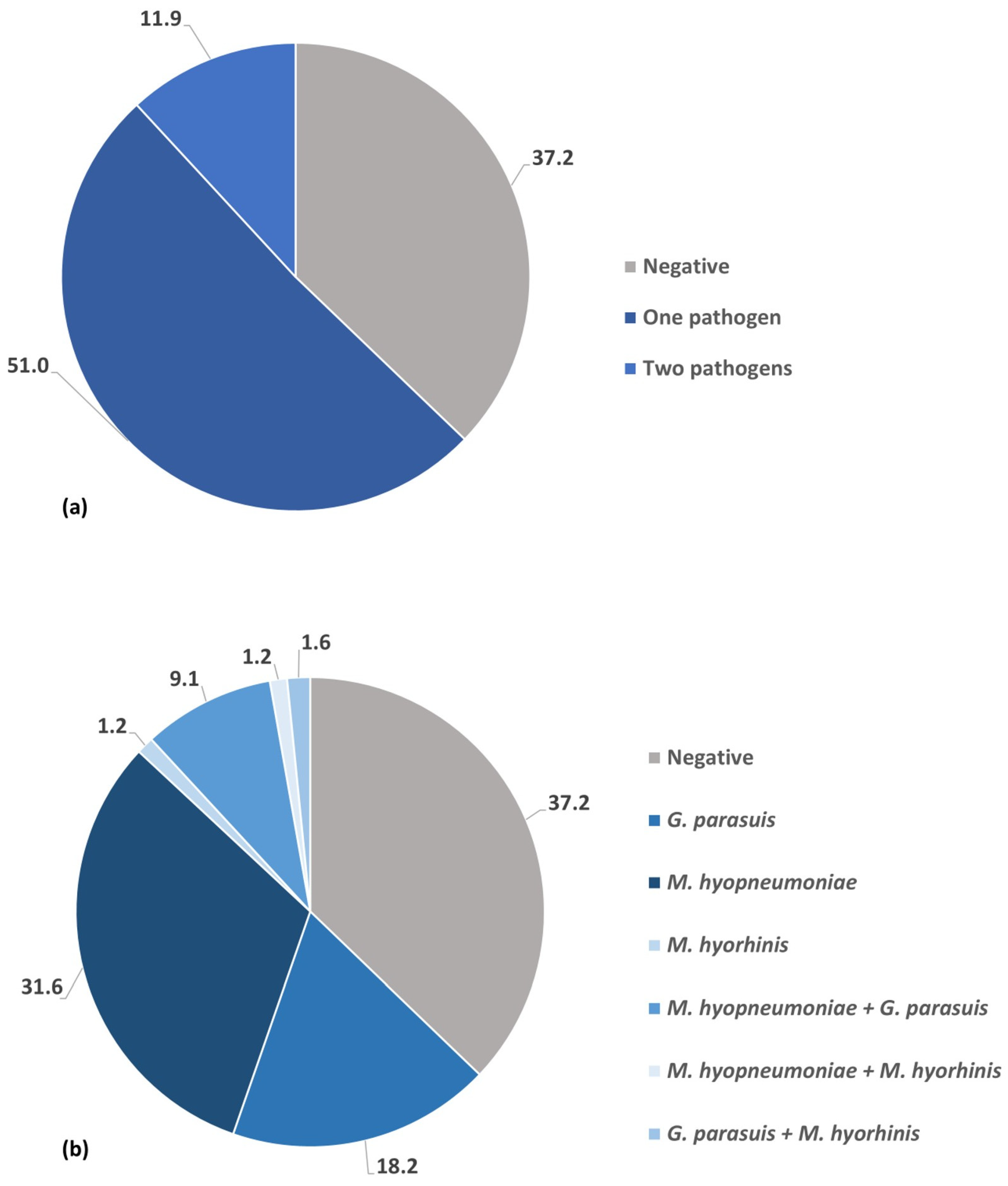
3.1. Prevalence of Respiratory Bacterial Pathogens Infection and Co-Infection
3.2. Prevalence of Respiratory Bacterial Pathogens Infection and Co-Infection Depending on Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADV | Aujeszky’s disease virus |
| EP | enzootic pneumonia |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| PCV2 | porcine circovirus type 2 |
| PRDC | porcine respiratory disease complex |
| PRRSV | porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus |
| swIAV | swine influenza A virus |
| TTSuV1a | Torque teno sus virus 1a |
| TTSuV1b | Torque teno sus virus 1b |
References
- Johann, F.; Handschuh, M.; Linderoth, P.; Dormann, C.F.; Arnold, J. Adaptation of wild boar (Sus scrofa) activity in a human-dominated landscape. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekarczyk, P.; Tajchman, K.; Belova, O.; Wójcik, M. Crop damage by wild boar (Sus scrofa L.) depending on the crop composition in Central-Eastern Poland. Balt. For. 2021, 27, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENETWILD-Consortium; Guerrasio, T.; Pelayo Acevedo, P.; Apollonio, M.; Arnon, A.; Barroqueiro, C.; Belova, O.; Berdión, O.; Blanco-Aguiar, J.A.; Bijl, H.; et al. Wild boar density data generated by camera trapping in nineteen european areas. EFSA Support. Publ. 2022, 19, 7214E. [Google Scholar]
- Abrantes, A.C.; Vieira-Pinto, M. 15 years overview of European zoonotic surveys in wild boar and red deer: A systematic review. One Health 2023, 16, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh, B.; Bochicchio, D.; Edwards, S.; Hegelund, L.; Leeb, C.; Sundrum, A.; Werne, S.; Wiberg, S.; Prunier, A. Description of organic pig production in Europe. Org. Agric. 2014, 4, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, K.D. The dynamics of Trichinella spiralis epidemiology: Out to pasture? Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 231, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, G.I.; Arsenakis, I.; Pourlis, A.; Papatsiros, V.G. Animal health and productivity of organic greek pig farms: The current situation and prospects for sustainability. Animals 2023, 13, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, G.G.; Corrales, N.L.; Talegón, G.; Aguirre, L. -Invited Review—Pig meat production in the European Union-27: Current status, challenges, and future trends. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 755–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Andrade, J.; Loiko, M.R.; Schmidt, C.; Vidaletti, M.R.; Lopes, B.C.; Cerva, C.; Varela, A.P.M.; Tochetto, C.; Maciel, A.L.G.; Bertagnolli, A.C.; et al. Molecular survey of porcine respiratory disease complex pathogens in Brazilian wild boars. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 206, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovska, I.; Dhaka, P.; Chantziaras, I.; Pessoa, J.; Dewulf, J. The role of wildlife and pests in the transmission of pathogenic agents to domestic pigs: A systematic review. Animals 2023, 13, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, C. Porcine respiratory disease complex: Interaction of vaccination and porcine circovirus type 2, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Vet. J. 2016, 212, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opriessnig, T.; Giménez-Lirola, L.G.; Halbur, P.G. Polymicrobial respiratory disease in pigs. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2011, 12, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeters, M.; Garcia-Morante, B.; van Schaik, G.; Segalés, J.; Rushton, J.; Steeneveld, W. The economic impact of endemic respiratory disease in pigs and related interventions—A systematic review. Porc. Health Manag. 2023, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, M.E.S.; Almeida, H.M.S.; Storino, G.Y.; Sonálio, K.; Souza, M.R.; Moura, C.A.A.; Costa, W.M.T.; Lunardi, L.; Linhares, D.C.L.; de Oliveira, L.G. Lung consolidation caused by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae has a negative effect on productive performance and economic revenue in finishing pigs. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 105091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, K.; Markowska-Daniel, I. Optimisation of the PCR for detection of APXIVA gene of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2011, 55, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Turni, C.; Pyke, M.; Blackall, P.J. Validation of a real-time PCR for Haemophilus parasuis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marois, C.; Dory, D.; Fablet, C.; Madec, F.; Kobisch, M. Development of a quantitative real-time taqman PCR assay for determination of the minimal dose of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae strain 116 required to induce pneumonia in SPF pigs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocqueville, V.; Ferré, S.; Nguyen, N.H.; Kempf, I.; Marois-Créhan, C. Multilocus sequence typing of Mycoplasma hyorhinis strains identified by a real-time TaqMan PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig-Pauka, I.; Hartmann, M.; Merkel, J.; Kreienbrock, L. Coinfections and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Strains Isolated from Diseased Swine in North Western Germany-Temporal Patterns in Samples From Routine Laboratory Practice From 2006 to 2020. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 802570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, H.E.; Toribio, J.-A.L.M.L.; Hernandez-Jover, M.; Marshall, D.; Lapidge, S.J. Pathogen presence in feral pigs and their movement around two commercial piggeries in Queensland, Australia. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, G.; Fresen, C.; Bronnert, S.; Haack, I.; Willems, H. Prevalence of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection in hunted wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Germany. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sárközi, R.; Makrai, L.; Fodor, L. Isolation of Biotype 1 Serotype 12 and Detection of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae from Wild Boars. Pathogens 2022, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccato, M.; Divari, S.; Ciaramita, S.; Sereno, A.; Campelli, D.; Biolatti, P.G.; Biolatti, B.; Meliota, F.; Bollo, E.; Cannizzo, F.T. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotypes by multiplex PCR identification and evaluation of lung lesions in pigs from Piedmont (Italy) Farms. Animals 2024, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risco, D.; Serrano, E.; Fernández-Llario, P.; Cuesta, J.M.; Gonçalves, P.; García-Jiménez, W.L. Severity of bovine tuberculosis is associated with co-infection with common pathogens in wild boar. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonni, M.; Formenti, N.; Boniotti, M.B.; Guarneri, F.; Scali, F.; Romeo, C.; Pasquali, P.; Pieters, M.; Maes, D.; Alborali, G.L. The role of co-infections in M. hyopneumoniae outbreaks among heavy fattening pigs: A field study. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibila, M.; Mentaberre, G.; Boadella, M.; Huerta, E.; Casas-Díaz, E.; Vicente, J.; Gortázar, C.; Marco, I.; Lavín, S.; Segalés, J. Serological, pathological and polymerase chain reaction studies on Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection in the wild boar. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiari, M.; Ferrari, N.; Zanoni, M.; Alborali, L. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae temporal trends of infection and pathological effects in wild boar populations. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.C.G.D.; Silva, V.S.; Mores, M.A.Z.; Kramer, B.; Leme, R.A.; da Silva, A.; Porto, G.; Alfieri, A.A. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in free-living wild boars in Paraná, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.; Pijoan, C. Haemophilus parasuis: New trends on diagnosis, epidemiology and control. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, G.; Fresen, C.; Bronnert, S.; Haack, I.; Willems, H. Prevalence of Haemophilus parasuis infection in hunted wildboars (Sus scrofa) in Germany. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2010, 56, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, A.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Mentaberre, G.; Casas-Diaz, E.; Lavin, S.; Marco, I.; Aragon, V. First isolation of Haemophilus parasuis and other NAD-dependent Pasteurellaceae of swine from European wild boars. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 125, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta Gerveno, J.M.; Risco Pérez, D.; Gonçalves Blanco, P.; García Jiménez, W.L.; Gil Molino, M.; Fernandez-Llario, P.; Hermoso de Mendoza Salcedo, J.; Gómez Gordo, L.J. Fatal infection due to Haemophilus parasuis in a young wild boar (Sus scrofa). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Neto, J.C.; Bower, L.; Erickson, B.Z.; Wang, C.; Raymond, M.; Strait, E.L. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction for detecting Mycoplasma hyosynoviae and Mycoplasma hyorhinis in pen-based oral, tonsillar, and nasal fluids. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 16, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Oh, Y.R.; Hwang, M.A.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Song, C.S.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, S.W. Mycoplasma hyorhinis is a potential pathogen of porcine respiratory disease complex that aggravates pneumonia caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 177, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.C.; Merodio, M.M.; Spronk, E.; Lehman, J.R.; Shen, H.; Li, G.; Derscheid, R.J.; Piñeyro, P.E. Diagnostic investigation of Mycoplasma hyorhinis as a potential pathogen associated with neurological clinical signs and central nervous system lesions in pigs. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 180, 106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gois, M.; Pospisil, Z.; Cerny, M.; Mrva, V. Production of pneumonia after intransal inoculation of gnotobiotic piglets with three strains of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. J. Comp. Pathol. 1971, 81, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Chen, S.P.; Yeh, K.S.; Weng, C.N. Mycoplasma hyorhinis in Taiwan: Diagnosis and isolation of swine pneumonia pathogen. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 115, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luehrs, A.; Siegenthaler, S.; Grützner, N.; Grosse Beilage, E.; Kuhnert, P.; Nathues, H. Occurrence of Mycoplasma hyorhinis infections in fattening pigs and association with clinical signs and pathological lesions of Enzootic Pneumonia. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourour, S.; Tocqueville, V.; Paboeuf, F.; Lediguerher, G.; Morin, N.; Kempf, I.; Marois-Créhan, C. Pathogenicity study of Mycoplasma hyorhinis and M. flocculare in specific-pathogen-free pigs pre-infected with M. hyopneumoniae. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 232, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ren, L.; Lu, B.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z. First Report of Severe Mycoplasma hyorhinis Pneumonia in Adult: A Case Report. Chest 2016, 149, A71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrough, E.; Schwartz, A.; Gauger, P.; Harmon, K.; Krull, A.; Kent, S. Comparison of postmortem airway swabs and lung tissue for detection of common porcine respiratory pathogens by bacterial culture and polymerase chain reaction assay. J. Swine Health Prod. 2018, 26, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saade, G.; Deblanc, C.; Bougon, J.; Marois-Créhan, C.; Fablet, C.; Auray, G.; Belloc, C.; Leblanc-Maridor, M.; Gagnon, C.A.; Zhu, J.; et al. Coinfections and their molecular consequences in the porcine respiratory tract. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pathogens | Target (Gene) | Oligonucleotide Sequences (5′-3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. pleuropneumoniae | apxIVA | apxIVA1-F: TGGCACTGACGGTGATGA apxIVA1-R: GGCCATCGACTCAACCAT | [15] |
| G. parasuis | infB | CTinfF1: CGACTTACTTGAAGCCATTCTTCTT CTinfR1: CCGCTTGCCATACCCTCTT CTinfP: FAM-ATCGGAAGTATTAGAATTAAGTGC-TAMRA | [16] |
| M. hyopneumoniae | p102 | P102f: GTCAAAGTCAAAGTCAGCAAAC P102r: AGCTGTTCAAATGCTTGTCC P102 probe: Cy5-ACCAGTTTCCACTTCATCGCCTCA-BHQ2 | [17] |
| M. hyorhinis | p37 | Mhr-p37-RT-F: TATCTCATTGACCTTGACTAAC Mhr-p37-RT-R: ATTTTCGCCAATAGCATTTG Mhr-p37-Probe: FAM-CATCCTCTTGCTTGACTACTCCTG-BHQ1 | [18] |
| Pathogens | Juveniles | Adolescents | Adults | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) of Positive | 95% CI | Number (%) of Positive | 95% CI | Number (%) of Positive | 95% CI | |
| G. parasuis | 7 (35.0%) | 18.1–56.7 | 20 (14.8%) | 9.8–21.8 | 18 (20.7%) | 13.5–30.4 |
| M. hyopneumoniae | 5 (25.0%) | 11.2–46.9 | 55 (40.7% a) | 32.8–49.2 | 17 (18.5% b) | 12.6–29.0 |
| M. hyorhinis | 0 (0%) | 0–16.1 | 2 (1.5%) | 0.4–5.2 | 1 (1.1%) | 0.2–6.6 |
| M. hyopneumoniae + G. parasuis | 5 (25.0% a) | 11.2–46.9 | 8 (5.9% b) | 3.0–11.3 | 7 (8.1%) | 4.0–15.7 |
| M. hyopneumoniae + M. hyorhinis | 0 (0%) | 0–16.1 | 2 (1.5%) | 0.4–5.2 | 1 (1.1%) | 0.2–6.6 |
| G. parasuis + M. hyorhinis | 0 (0%) | 0–16.1 | 2 (1.5%) | 0.4–5.2 | 2 (2.3%) | 0.6–8.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czyżewska-Dors, E.; Nowak, A.; Zębek, S.; Dors, A. Molecular Survey of Selected Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens in Polish Wild Boars. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121196
Czyżewska-Dors E, Nowak A, Zębek S, Dors A. Molecular Survey of Selected Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens in Polish Wild Boars. Pathogens. 2025; 14(12):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121196
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzyżewska-Dors, Ewelina, Agnieszka Nowak, Sylwia Zębek, and Arkadiusz Dors. 2025. "Molecular Survey of Selected Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens in Polish Wild Boars" Pathogens 14, no. 12: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121196
APA StyleCzyżewska-Dors, E., Nowak, A., Zębek, S., & Dors, A. (2025). Molecular Survey of Selected Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens in Polish Wild Boars. Pathogens, 14(12), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14121196







