Abstract
A Streptococcus suis strain isolated from the blood of a patient in Zhejiang Province, China, was analysed using whole-genome sequencing and tested for antimicrobial resistance. The isolated strain was identified as S. suis serotype 2, and classified to ST25 on multilocus sequence typing (MLST). The minimum core genome group of the strain was identified as Group 4, and multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis (MLVA) assigned it as type 2, 4.4, 0, 9, 3, 2, 0, 0. An antimicrobial resistance analysis showed that the strain was resistant to clindamycin, tetracycline, azithromycin, and erythromycin but sensitive to 11 other antibiotics. In a genomic evolution analysis, this isolate clustered on the same branch as North American pig isolate, Chinese pig isolates from Tianjin, and Hubei pig isolates.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus suis infection is a serious zoonotic disease affecting both humans and pigs. The clinical manifestations include meningitis, sepsis, and endocarditis, with high mortality rates and hearing loss as a sequela [1]. S. suis is currently classified into 29 serotypes based on the antigenicity of the capsular polysaccharide [2,3,4]. Among these, S. suis serotype 2 (SS2) is the most prevalent type and severely pathogenic in both humans and pigs. It frequently causes occupational contact infections in adults and is notably the predominant pathogenic serotype in Southeast Asian nations, including Thailand and Vietnam, as well as China [5]. SS2 was responsible for three outbreaks of human S. suis infection in China: Jiangsu Province (1998), Sichuan Province (2005), and Guangxi Province (2016) [6,7,8], which resulted in multiple infections and deaths, attracting public health attention. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST; https://pubmlst.org/ssuis/, accessed on 15 July 2025) has defined 3030 multilocus sequence types (STs) for S. suis, among which ST1 is prevalent worldwide (predominantly in Eurasia) [5,9,10], while ST7 has been reported only in China and Italy [11,12]. The ST7 strain caused the 1998 and 2005 outbreaks in China and carries the 89K pathogenicity island (89K PAI). All previously reported human infections in Zhejiang Province were attributed to SS2, including ST7 and ST1 [13]. In 2018, an ST25 SS2 strain was detected for the first time in Zhejiang Province. This sequence type is predominantly reported in North American pigs with high detection rates [11,14,15], suggesting specific, previously unnoticed changes in epidemic strains of S. suis in Zhejiang Province in recent years. Antibiotics plays an important role in treating S. suis infection in both species; monitoring the antimicrobial susceptibility of the ST25 strain may help optimize antibiotic therapy. We used the microdilution method to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for the strain. Moreover, whole-genome sequencing (second-generation combined with third-generation sequencing) was conducted to analyse virulence, antimicrobial resistance, and phylogeny.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
The experimental strain ZJSS31 was isolated from a sporadic human S. suis infection case and submitted to the Huzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Zhejiang Province (2018). Genomic sequences of the reference strains were obtained from GenBank, including: the highly virulent strain SS2 ST1 strain P1/7 (GCA_000091905.1), moderately virulent ST25 strain 85-1591 (GCA_000167375.1) and NSUI060 (GCA_001572685.1), and the low/avirulent ST28 strain NSUI002 (GCA_001272635.1).
2.2. Case Information
A 51-year-old male working in raw pork sales developed a fever of unknown origin on 2 August 2018. He denied headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhoea. On 5 August, he presented to a private clinic with a body temperature of 39 °C and was referred to a Zhejiang Province hospital for suspected infectious fever. Physical examination revealed no skin bleeding spots, petechiae, or ecchymoses. His maximum temperature was 39.5 °C without nuchal stiffness, toxic shock syndrome, respiratory distress syndrome, or meningeal irritation signs. 6 August laboratory tests showed: white blood cell (WBC) count 15.8 × 109/L, neutrophil (N) 81.6%, lymphocyte (L) 12.9%, and platelets (PLTs) 164 × 109/L. S. suis was isolated from bacterial culture (8 August). He received anti-infective and supportive therapy; follow-up tests on 9 August showed: WBC count 9.4 × 109/L, N 61.7%, L 28.4%, PLT 241 × 109/L, and normal coagulation, liver, and kidney function. The patient recovered and was discharged on 16 August.
2.3. Reagents, Instruments, and Strain Identification
Columbia blood agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK), S. suis antiserum (Statens Serum Institut, Copenhagen, Denmark), and Streptococcus susceptibility plates (Shanghai Thermo Fisher Scientific, Shanghai, China) were used. Instruments used in this study included: VITEK 2 Compact advanced system (v05.01; bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France), VITEK MS mass spectrometer (V2.3.3; bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France), carbon dioxide (CO2) incubator (Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA), and Mastercycler gradient PCR and centrifuge (Eppendorf Company, Hamburg, Germany).
Single colonies were picked from blood agar and incubated (37 °C, 5% CO2 18–24 h). Strain identification was performed by Gram staining, the VITEK 2 Compact and VITEK MS. Serotyping used S. suis type 1/2 antisera in a slide agglutination test (normal saline control). Genus, species, serotype-specific genes, virulence genes, and genotyping were determined via PCR as previously published [13,16].
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
AST was performed using the microdilution method for azithromycin, cefepime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, daptomycin, ertapenem, erythromycin, levofloxacin, linezolid, meropenem, penicillin, tetracycline, and vancomycin (the microdultion of the antimicrobial agents is shown in Supplementary Figure S1). The American Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI, M100-S23) breakpoints for S. viridanin were applied [17]. S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 was the quality control strain for AST. The protocol is listed briefly as follows: After culturing at 37 °C under 5% CO2 for 16–18 h, single colonies were picked and suspended in 5 mL of CAMHBT Broth to 0.5 McFarland standard. Then 100 μL suspension was added to 11 mL of Mueller–Hinton (MH) broth containing horse blood. Aliquots of the MH broth suspension (100 μL) were transferred to susceptibility plates according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Plates were sealed with adhesive film and incubated (37 °C, non-CO2, 24 h) before reading.
2.5. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
Both second- and third-generation sequencing were performed by Zhejiang Tianke High-tech Development Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). (1) DNA extraction: Genomic DNA was extracted using Gentra Puregene Yeast/Bact. Kit (Qiagen, Redwood, CA, USA). DNA concentration was measured (NanoDrop™ 2000, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and verified via agarose gel electrophoresis. An amount of >5 μg of DNA was used for library preparation. (2) Sequencing: Libraries were prepared with TruePrep™ DNA Library Prep Kit V2 (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) and the Ligation Sequencing Kit (SQ-LSK109, Oxford Nanopore, Oxford, UK). Sequencing was conducted on the Illumina NovaSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) and the GridION X5 platform (Oxford Nanopore, UK). (3) Assembly: Canu v1.8 (https://canu.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html, accessed on 25 July 2025) processed raw reads from both platforms to generate high-quality data. Unicycler v0.4.5 (https://github.com/rrwick/Unicycler, accessed on 25 July 2025) assembled Illumina reads and Nanopore reads into a complete genome. Circos (v0.69) was used to plot the genome.
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
We downloaded genomic sequences of 34 ST25 strains from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database (Table 1). A whole-genome SNPs-based phylogenetic tree of ZJSS31 strain and these strains was constructed using SplitsTree4.

Table 1.
Information on the 34 ST25 strains of S. suis used in this study.
The ST of S. suis isolates was determined using multilocus sequence typing software (https://www.pubmlst.org, accessed on 15 July 2025). Antimicrobial-resistant genes and plasmid profiles were analysed using ResFinder (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/ResFinder/, accessed on 13 October 2024) and PlasmidFinder (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/PlasmidFinder/, accessed on 13 October 2024). The detection of virulence genes was performed using VFDB online database10 (http://www.mgc.ac.cn/VFs/, accessed on 13 October 2024). Annotation of mobile elements was carried out using online databases, such as ISfinder (https://www-is.biotoul.fr/credits.php, accessed on 15 July 2025). Plasmid sequence alignment was performed using Easyfig v2.2.5 (https://mjsull.github.io/Easyfig/, accessed on 13 October 2024).
3. Results
3.1. Strain Identification
Alpha haemolysis was evident surrounding the colonies. Gram staining revealed Gram-positive cocci arranged in pairs or short chains under oil immersion microscope. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI–TOF-MS) identification confirmed the strain to be S. suis, with agglutination observed for SS2 diagnostic antiserum but not SS1 antiserum. No agglutination occurred in the saline control. PCR [13,16] identified the genotype as MLST/ST25, MCG/Group 4, and MLVA/(2, 4.4, 0, 9, 3, 1, 2, 0, 0). This strain is hereafter designated ‘ZJSS31/ST25’.
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
The AST of the strain showed resistance to clindamycin, tetracycline, azithromycin, and erythromycin, but sensitivity to 11 other antimicrobial agents: cefepime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, daptomycin, ertapenem, levofloxacin, linezolid, meropenem, penicillin, and vancomycin (Table 2).

Table 2.
AST of the ZJSS31 isolate using a panel of 15 antimicrobial agents.
3.3. Comparison of Genomic Sequences
The complete genome of ZJSS31/ST25 (Genbank accession number: 2813098) was 2,300,455 bp (GC content: 41.02%), encoding four 5S/16S/23S rRNAs, 57 tRNAs, 42 ncRNAs, 2351 open reading frames (ORF), 1912 coding sequences (CDSs), and 17 pseudogenes. The genome is enriched with insertion sequences (IS), transposons (e.g., Tn917), prophages, and integrative conjugative elements (ICEs). Five large mobile genetic elements (MGEs) were identified: three unclassified MGEs and two integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs), one carrying the ermB macrolide-resistance gene. Insertion sequence (IS) elements included ICESsuYS66, IMESsuYS67, IS4, ISL3, IS982, IS110, IS200, IS605, IS630, and IS30. Pilus genes (srtA, srtE, srtF, srtG, sfp1, sfp2, sipF) and virulence genes (lysozyme-releasing protein gene mrp, capsular polysaccharide gene cpsA) were detected (Figure 1A). Nine prophages and a plamid of 5581 bp were predicted.
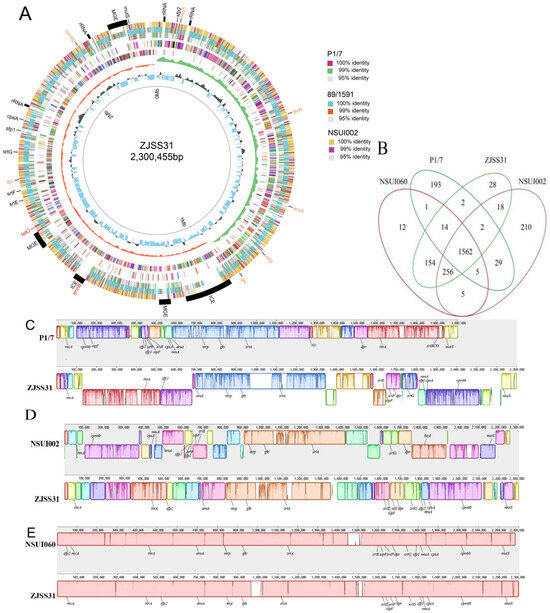
Figure 1.
Whole genome analysis of ZJSS31 and genomic comparison with P1/7, NSUI002, and NSUI060. (A) Circular genome representation (inner to outer rings): 1. Genome scale; 2. GC content; 3. GC skew (green represents the positive and orange represents negative); 4. CDSs on negative strand, and different colours represent different clusters of orthologous genes (COG) annotation categories of the CDSs; 5. CDSs on the positive strand, and different colours represent the different COG annotation categories of the CDSs; 6. TBLASTN results with strain P1/7; 7. TBLASTN results with strain 89/1591; 8. TBLASTN results with strain NSUI002; 9. Annotation of key features: capsule- and pilus-related genes, rRNA, mobile genetic elements (MGEs) (marked in orange), drug-resistance genes (marked in red), and virulence genes (marked in blue). (B) Venn diagram of shared gene clusters among ZJSS31, P1/7, NSUI002, and NSUI060s. (C) Collinearity comparison between ZJSS31 genome and P1/7 genome (ProgressiveMauve). (D) Collinearity comparison between the ZJSS31 genome and the NSUI002 genome. (E) Collinearity comparison between the ZJSS31 genome and NSUI060 genome.
Orthology analysis showed ZJSS31/ST25 shares: 1562 gene clusters with strains P1/7/ST1, NSUI002/ST28, and NSUI060/ST25; 1986 gene clusters with strain NSUI060/ST25; 1838 gene clusters with strain NSUI002/ST28; and 1580 gene clusters with P1/7/ST1 (Figure 1B).
Genome collinearity revealed ZJSS31/ST25′s genome size was similar to NSUI002/ST28 and NSUI060/ST25 but larger than P1/7/ST1 (Figure 1C–E). ZJSS31/ST25 showed the highest homology with NSUI060/ST25. Unlike P1/7/ST1 (which carries the srtBCG, mrp, the extracellular protein factor gene epf, and the hemolysin virulence gene sly), ZJSS31/ST25, NSUI002/ST28, and NSUI060/ST25 possess only mrp and srtG pilus island. Chromosomal rearrangements were observed in pilus islands and cpsA loci across strains.
3.4. Antibiotic-Resistance Genes, ICEs, and Phylogeny
ZJSS31/ST25 carries the tetracycline-resistance tet(O) gene and allelic macrolide-resistance gene ermB, like Chinese (Tianjin: GCA_022964955.1; Hubei: GCA_022427625.1) and North American pig strains (two strains from the United States and three strains from Canada). It also harbours two drug-resistance genes (patA and patB) and allelic insertion elements (ICEs9/10). The ICE distribution varied among strains as shown in Figure 2.
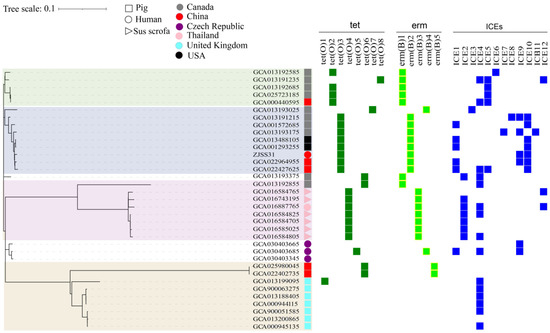
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic, antimicrobial resistance, and ICE analyses of 35 ST25 strains of S. suis. Phylogenetic tree showing genetic relationship, with branches colour-coded by geographic clade, Canada (green), North America (blue), Thailand (red), and the UK (yellow). The right side of the figure describes the host, country of origin, and presence of ICEs and/or resistance genes. Strains isolated from pigs are represented by squares; strains isolated from wild pigs are represented by triangles, and those isolated from humans are represented by circles. Strains isolated from different countries are shown in different colours: grey for Canada, purple for Czech Republic, pink for Thailand, light blue for the UK, and black for the USA. Tetracycline-resistance genes are shown in green, and erythromycin-resistance genes in light green. ICEs are shown in dark blue.
A neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree of 35 ST25 strains (based on 2155 SNPs) revealed four clades: United Kingdom, Thailand, North America, and Canada. ZJSS31/ST25 clustered within the North American clade but showed closest affinity to Chinese pig strains from Tianjin and Hubei, China.
4. Discussion
The diverse and sporadic human S. suis strains pose public health risks [18]. Without vaccines, antimicrobial treatment remains critical. Consequently, the prompt surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in S. suis is a critical global concern. In this study, we tested the MICs of 15 antibacterial agents for strain ZJSS31/ST25, and found that the strain is resistant to clindamycin, tetracycline, azithromycin, and erythromycin (the antibiotic type belongs to the lincosamide, tetracycline, and macrolide classes), and is sensitive to the other antibacterial agents tested. This contradicts findings of Athey et al. [15], which indicated that SS2/ST25 strains are mainly resistant to tetracycline and erythromycin. However, it is consistent with Nedbalcova et al. also reporting that S. suis is resistant to more than two types of antibiotics, including clindamycin and tetracycline [19,20,21]. High-level antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to tetracyclines, macrolides, and lincosamides has been reported in both human and swine isolates of S. suis [22,23,24]. As the ARGs (antibiotic resistance genes) tet(O) and ermB are the most common genes associated with AMR, monitoring antibiotic sensitivity will help to optimize antibiotic therapy in humans and swine.
Next-generation sequencing is a potent diagnostic technique for detecting bacterial infections [25]. Whole-genome sequencing has emerged as an essential and robust tool for investigating the genetic diversity of S. suis, identifying novel sequence types, and determining virulence factors [26]. At present, these technologies are the principal means of evaluating the genetic similarity of isolates sourced from various origins and have been extensively used to categorize and investigate the genetic relationship of S. suis across diverse regions and hosts. In this study, we used second- and third-generation sequencing to analyse strain ZJSS31/ST25, and found that it carries two drug-resistance genes, tet(O) and ermB, which confer resistance to tetracyclines and macrolides, respectively. Tet(O) is located on the original chromosome, whereas ermB is located on an ICE, suggesting the horizontal acquisition of the ermB. Tet(O) and ermB are the primary resistance genes identified in strains resistant to tetracycline and macrolides [26]. The sequencing results showed that antibiotic resistance genes in strain ZJSS31/ST25 were consistent with AST and literature reports. While patA and patB, which encode the ABC transporter associated with fluoroquinolone resistance, were also detected in strain ZJSS31/ST25 (60% sequence similarity between ZJSS31/ST25 sequence and the reference sequences), no phenotypic resistance was observed in AST. Interestingly, the AST showed that ZJSS31/ST25 is resistant to clindamycin, but this lacks a genetic explanation.
The acquisition of antibiotic resistance facilitated by ICEs carrying antibiotic resistant genes in zoonotic pathogens poses a significant public health concern. Various Streptococcus species share similar ICE insertion sites, potentially allowing interspecies ICE integration [24]. Research has indicated that S. suis ICEs can undergo recombination with ICEs originating from other streptococcal species, such as S. agalactiae and S. pyogenes [27]. The ZJSS31/ST25 genome harbours five MGEs, including diverse IS elements and prophages. It is clear that strains under environmental selective pressures frequently acquire or passively adapt to incorporate foreign DNA gene segments. This phenomenon can lead to genetic heterogeneity within populations of the strain during its evolution. ZJSS31/ST25 and P1/7/ST1 carry different virulence genes. The former only carries one virulence gene, mrp, whereas three major virulence genes were detected in the latter, mrp, epf, and sly, which are the major virulence genes of S. suis. However, the highly virulent 89 K pathogenic island found in the strains responsible for the Chinese outbreaks was not detected in either strain. The significance of the pilus in S. suis virulence remains contentious [28,29]. Strain ZJSS31/ST25 also differs from strain P1/7/ST1 in terms of the pilus islands or clusters carried. Specifically, the former contains the srtG pilus island but lacks the srtBCG pilus cluster, whereas the latter has the reverse configuration. The presence of the srtBCG pilus cluster differs significantly between virulent and avirulent strains [30] insofar as it is present in all highly virulent strains but not in any avirulent strain. Therefore, the virulence of the Chinese human strain ZJSS31/ST25 is weaker than that of P1/7/ST1, which is also a moderately virulent strain, belonging to the same cluster as the NSUI060/ST25 pig strain [14]. The capsular polysaccharide is a major virulence factor and has been proposed as a suitable antigen for vaccinology and molecular typing [31]. Both ZJSS31/ST25 and the reference strains carry the cpsA gene. There are gene rearrangements in the pilus islands and at the cpsA locus in the reference strains. The causality and effects of these changes require further study.
A collinearity analysis indicated that the genome size of strain ZJSS31/ST25 is close to NSUI002/ST28 and NSUI060/ST25, but is much larger than that of virulent strain P1/7/ST1. This variation may stem from the presence of ICEs, transposons, plasmids, and prophages within strain ZJSS31/ST25. Orthology analysis revealed that the genome of strain ZJSS31/ST25 shares markedly more gene clusters with NSUI002/ST28 and NSUI060/ST25, indicating relatively close relationships among them. The genomes of avirulent strains tend to be larger than those of virulent strains, and avirulent strains typically carry more prophage sequences than virulent strains [32], confirming that Chinese human strain ZJSS31/ST25 is less virulent than strain P1/7/ST1 and may be a moderately virulent strain. This requires confirmation in future studies.
Phylogenetic analysis indicated 35 ST25 strains clustered into four major clades: UK, Thailand, North America, and Canada (the North American clade was subdivided into two subclades, North America and Canada), based on the allelic resistance genes, ICE types, and ICE abundances. ZJSS31/ST25 clusters with the North American strain, indicating a close relationship. Pig-derived strains of Tianjin and Hubei (GCA_022964955.1 and GCA_022427625.1) in China showed closer affinities with strain ZJSS31/ST25. This implies that the Chinese human-derived strain ZJSS31/ST25 shares homology with native pig-derived strains in China, in a same cluster with the lineage in North America.
SS2/ST25 strains are the most common serotype in North America (accounting for 44% of all reported strains) [27,33], yet human infections and deaths are rare in this region, which demonstrates differences in pathogenicity among different S. suis populations. A significant portion of the variance in disease occurrence and severity can be attributed partly to variations among strains. Cases involving ST25 strains were documented in Hong Kong (2007) and Shenzhen (2022), China [34,35]. The human isolate examined in this present study was first identified in Zhejiang Province in 2001. Therefore, understanding the antimicrobial resistance patterns, population structures, and genetic diversity of human-infecting strains will assist clinicians in rational drug use and aid epidemiology personnel in dealing with potentially virulent strains with significant genetic variability. In summary, pathogen studies enhance our understanding of their risks while providing a molecular basis for vaccine development and strain selection.
5. Limitations of the Study
This study focused on a single isolate, limiting broader epidemiological interpretations. Field validation requires more additional strains to confirm circulation patterns. The virulence of ZJSS31/ST25 was not assessed in animal models and requires further investigation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens14080742/s1, Figure S1: The microdilution of antimicrobial agents in the Streptococcus susceptibility plate.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: S.Z., X.W. and W.Y.; data curation: Z.W. and W.Y.; formal analysis: L.W.; funding acquisition: Y.Z. and B.W.; methodology: W.Y.; writing—original draft: S.Z.; writing—review: Z.Y.; editing: Z.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China 2023YFC2605103 and 2023YFC2605100, 6 December 2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The ethics statement was approved by the Ethics Committee at Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, and informed consent was acquired for clinical and biological information.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was acquired for clinical and biological information.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in National Microbiology data center at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank, reference number 2813098 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tharavichitkul, P.; Wongsawan, K.; Takenami, N.; Pruksakorn, S.; Fongcom, A.; Gottschalk, M.; Khanthawa, B.; Supajatura, V.; Takai, S. Correlation between PFGE Groups and mrp/epf/sly Genotypes of Human Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 in Northern Thailand. J. Pathog. 2014, 2014, 350416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongkiettrakul, S.; Maneerat, K.; Arechanajan, B.; Malila, Y.; Srimanote, P.; Gottschalk, M.; Visessanguan, W. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis isolated from diseased pigs, asymptomatic pigs, and human patients in Thailand. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ji, S.; Liu, Z.; Lan, R.; Huang, Y.; Bai, X.; Gottschalk, M.; Xu, J. Eight Novel Capsular Polysaccharide Synthesis Gene Loci Identified in Nontypeable Streptococcus suis Isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4111–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Qiu, X.; Roy, D.; Segura, M.; Du, P.; Xu, J.; Gottschalk, M. Genotyping and investigating capsular polysaccharide synthesis gene loci of non-serotypeable Streptococcus suis isolated from diseased pigs in Canada. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Hu, D.; Wang, C. Streptococcus suis infection: An emerging/reemerging challenge of bacterial infectious diseases? Virulence 2014, 5, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Zhu, X.; Jing, H.; Du, H.; Segura, M.; Zheng, H.; Kan, B.; Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Streptococcus suis sequence type 7 outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, M.; Hao, H.; Yang, R.; Xie, J.; Su, J.; Lin, M.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, Y. Genomic epidemiological investigation of a Streptococcus suis outbreak in Guangxi, China, 2016. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 68, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leengoed, L.A.; Vecht, U.; Verheyen, E.R. Streptococcus suis type 2 infections in pigs in the Netherlands (Part two). Vet. Q. 1987, 9, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultsz, C.; Jansen, E.; Keijzers, W.; Rothkamp, A.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van der Ende, A. Differences in the population structure of invasive Streptococcus suis strains isolated from pigs and from humans in The Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Du, P.; Wang, J.; Lan, R.; Huang, J.; Luo, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Quan, Y.; Shi, Z.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology of Streptococcus suis Sequence Type 7 Sporadic Infections in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China. Pathogens 2019, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucco, L.; Paniccià, M.; Massacci, F.R.; Morelli, A.; Ancora, M.; Mangone, I.; Di Pasquale, A.; Luppi, A.; Vio, D.; Cammà, C.; et al. New Sequence Types and Antimicrobial Drug-Resistant Strains of Streptococcus suis in Diseased Pigs, Italy, 2017–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.R.; Chen, J.C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y.J. Molecular characteristics of Streptococcus suis type 2 from humans in Zhejiang Province. Chin. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 40, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- April, A.A.; Gottschalk, M.; Rossow, S.; Rendahl, A.; Gebhart, C.; Marthaler, D.G. Serotype and Genotype (Multilocus Sequence Type) of Streptococcus suis Isolates from the United States Serve as Predictors of Pathotype. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00377-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, T.B.; Teatero, S.; Takamatsu, D.; Wasserscheid, J.; Dewar, K.; Gottschalk, M.; Fittipaldi, N. Population Structure and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Sequence Type 25 Strains. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.R.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, P.P.; Yang, Y.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y.J. Identification and characterization of the virulence of Streptococcus suis from human patients in Zhejiang Province, China. Chin. J. Zoonoses. 2021, 37, 808–814. [Google Scholar]
- M100-S28E; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th Informational Supplement. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024.
- Hu, Y.; Fu, S.; Zou, G.; Kerdsin, A.; Chen, X.; Dong, X.; Teng, L.; Li, J. Genome analysis provides insight into hyper-virulence of Streptococcus suis LSM178, a human strain with a novel sequence type 1005. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedbalcova, K.; Kucharovicova, I.; Zouharova, M.; Matiaskova, K.; Kralova, N.; Brychta, M.; Simek, B.; Pecha, T.; Plodkova, H.; Matiasovic, J. Resistance of Streptococcus suis Isolates from the Czech Republic during 2018–2022. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarska, A.; Molska, E.; Janas, K.; Skoczyńska, A.; Stefaniuk, E.; Hryniewicz, W.; Sadowy, E. Streptococcus suis in invasive human infections in Poland: Clonality and determinants of virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamphensin, N.; Chopjitt, P.; Hatrongjit, R.; Boueroy, P.; Fittipaldi, N.; Gottschalk, M.; Kerdsin, A. Non-Penicillin-Susceptible Streptococcus suis Isolated from Humans. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, M.; Tamang, M.D.; Moon, D.C.; Kim, S.R.; Jeong, J.H.; Jang, G.C.; Jung, S.C.; Park, Y.H.; Lim, S.K. Molecular basis of resistance to selected antimicrobial agents in the emerging zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2332–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Oshima, M.; Yamagishi, J.; Muramatsu, C.; Asai, T. Changes in antimicrobial resistance phenotypes and genotypes in Streptococcus suis strains isolated from pigs in the Tokai area of Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aradanas, M.; Poljak, Z.; Fittipaldi, N.; Ricker, N.; Farzan, A. Serotypes, virulence-associated factors, and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus suis isolates recovered from sick and healthy pigs determined by whole-genome sequencing. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 742345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Sekizuka, T.; Ishikawa, D.; Imai, M.; Fujita, M.; Kuroda, M.; Saruki, N. Next-generation DNA sequencing analysis of two Streptococcus suis ST28 isolates associated with human infective endocarditis and meningitis in Gunma, Japan: A case report. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raberahona, M.; Rasoanandrasana, S.; Rahajamanana, V.L.; Ranaivo-Rabetokotany, F.; Andriananja, V.; Rakotomalala, F.A.; Randria, M.J.D.; Rakotovao, L.; Marois-Créhan, C.; Tocqueville, V.; et al. Novel Streptococcus suis Sequence Type 834 among Humans, Madagascar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, C.; Magi, G.; Mingoia, M.; Bagnarelli, P.; Ripa, S.; Varaldo, P.E.; Facinelli, B. Characterization of a Streptococcus suis tet(O/W/32/O)-carrying element transferable to major streptococcal pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4697–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, E.; Palmieri, C.; Magi, G.; Facinelli, B. Recombination between Streptococcus suis ICESsu32457 and Streptococcus agalactiae ICESa2603 yields a hybrid ICE transferable to Streptococcus pyogenes. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Takamatsu, D.; de la Cruz Domínguez-Punaro, M. Mutations in the gene encoding the ancillary pilin subunit of the Streptococcus suis srtF cluster result in pili formed by the major subunit only. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, M.; Osaki, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Gottschalk, M.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D. The minor pilin subunit Sgp2 is necessary for assembly of the pilus encoded by the srtG cluster of Streptococcus suis. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Du, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, W. Pan-genome analysis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 revealed genomic diversity among strains of different virulence. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; Fernandez, A.; Arnal, J.L.; Del Pozo, M.; Amoribieta, M.C.; de Blas, I.; Jurado, P.; Calvo, J.H.; Gottschalk, M.; González-Vázquez, L.D.; et al. Genomic and phenotypic analysis of invasive Streptococcus suis isolated in Spain reveals genetic diversification and associated virulence traits. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Xu, J.; Lacouture, S.; Tharavichitkul, P.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D.; Gottschalk, M. Lineage and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolates from North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.W.; Cheung, T.K.; Chu, M.Y.; Tsang, V.Y.; Fung, J.T.; Kam, K.M.; Lo, J.Y. Resistance to tetracycline, erythromycin and clindamycin in Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in Hong Kong. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2009, 34, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, F.; Hu, Q.; Xu, L.; Duan, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, S.; Chen, Q.; Wu, S.; et al. Epidemiological and genomic analyses of human isolates of Streptococcus suis between 2005 and 2021 in Shenzhen, China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).