Immune Response and Apoptosis-Related Pathways Induced by Aeromonas schubertii Infection of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata♀ × Channa argus♂)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
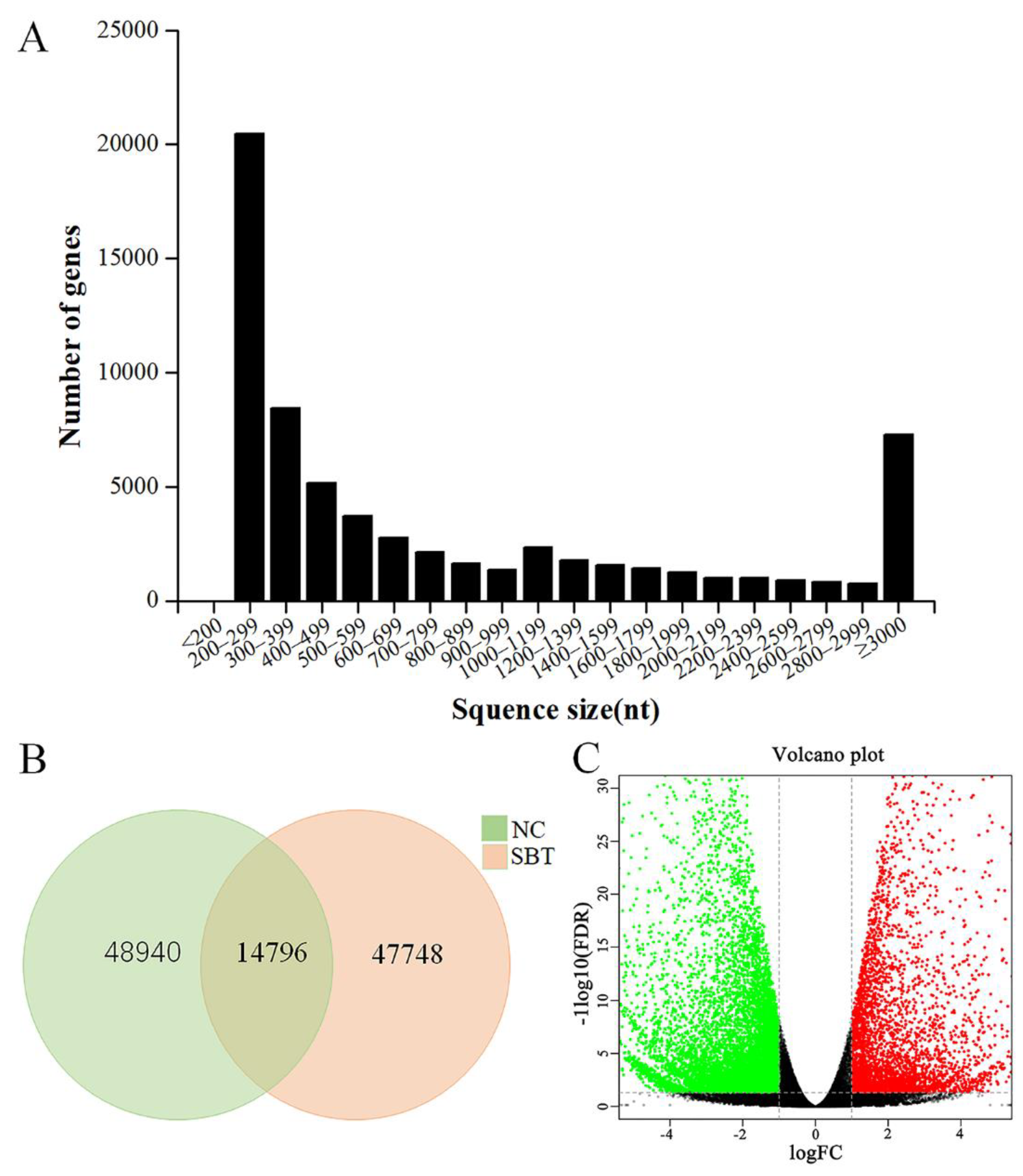
2.1. Transcriptome Sequencing and De Novo Assembly
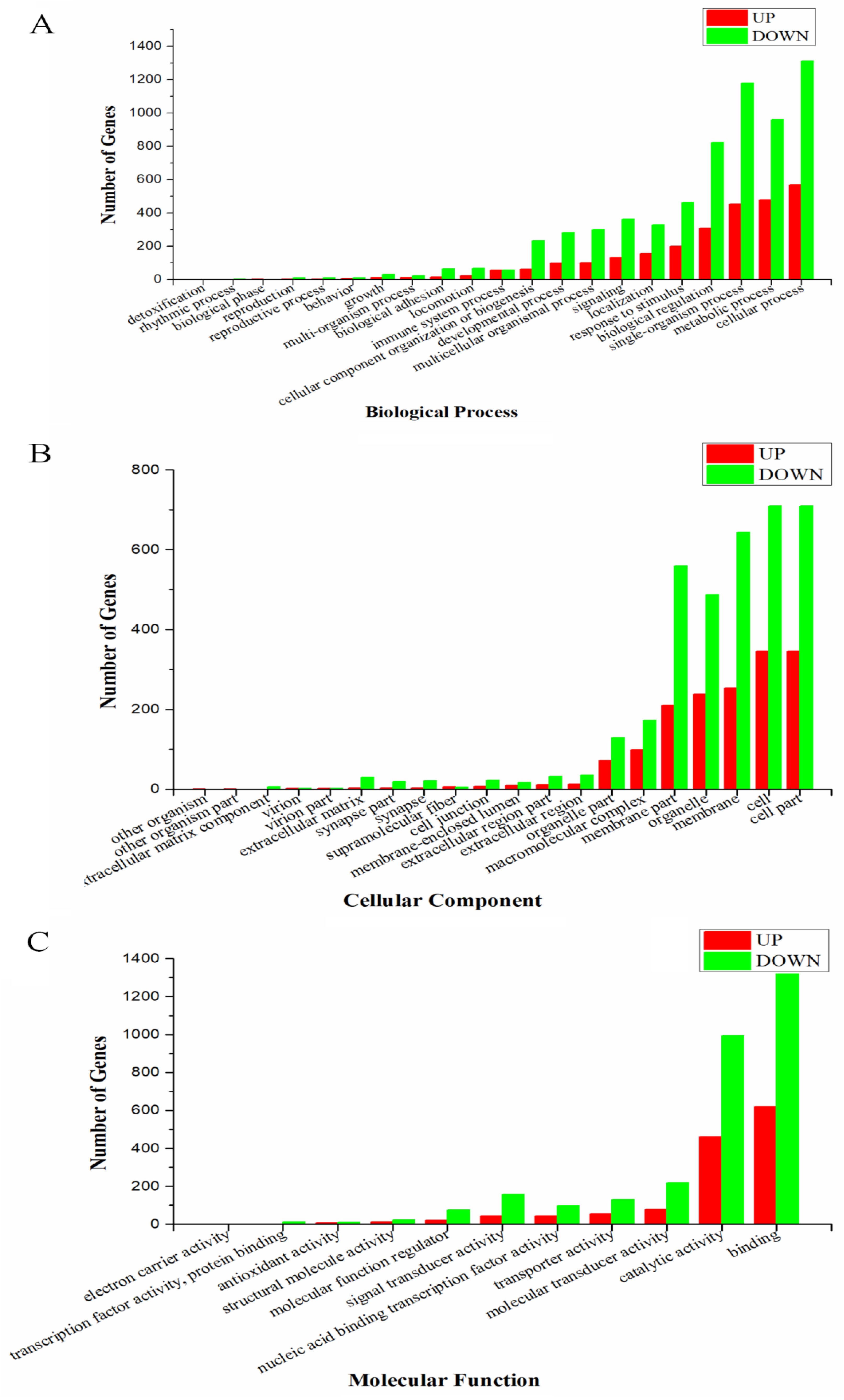
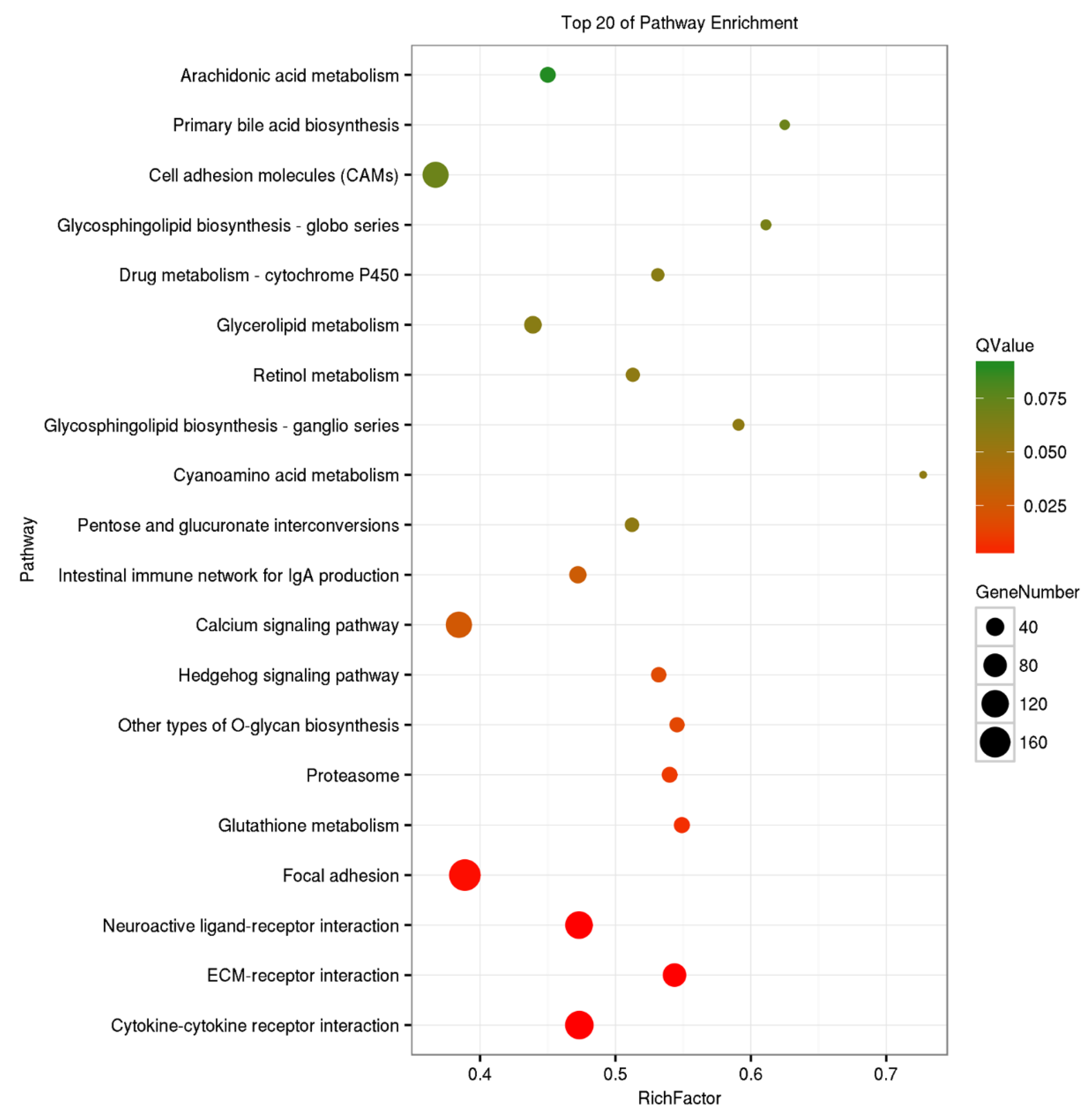
2.2. Functional Explanation of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.3. RT-qPCR Validation of DEGs
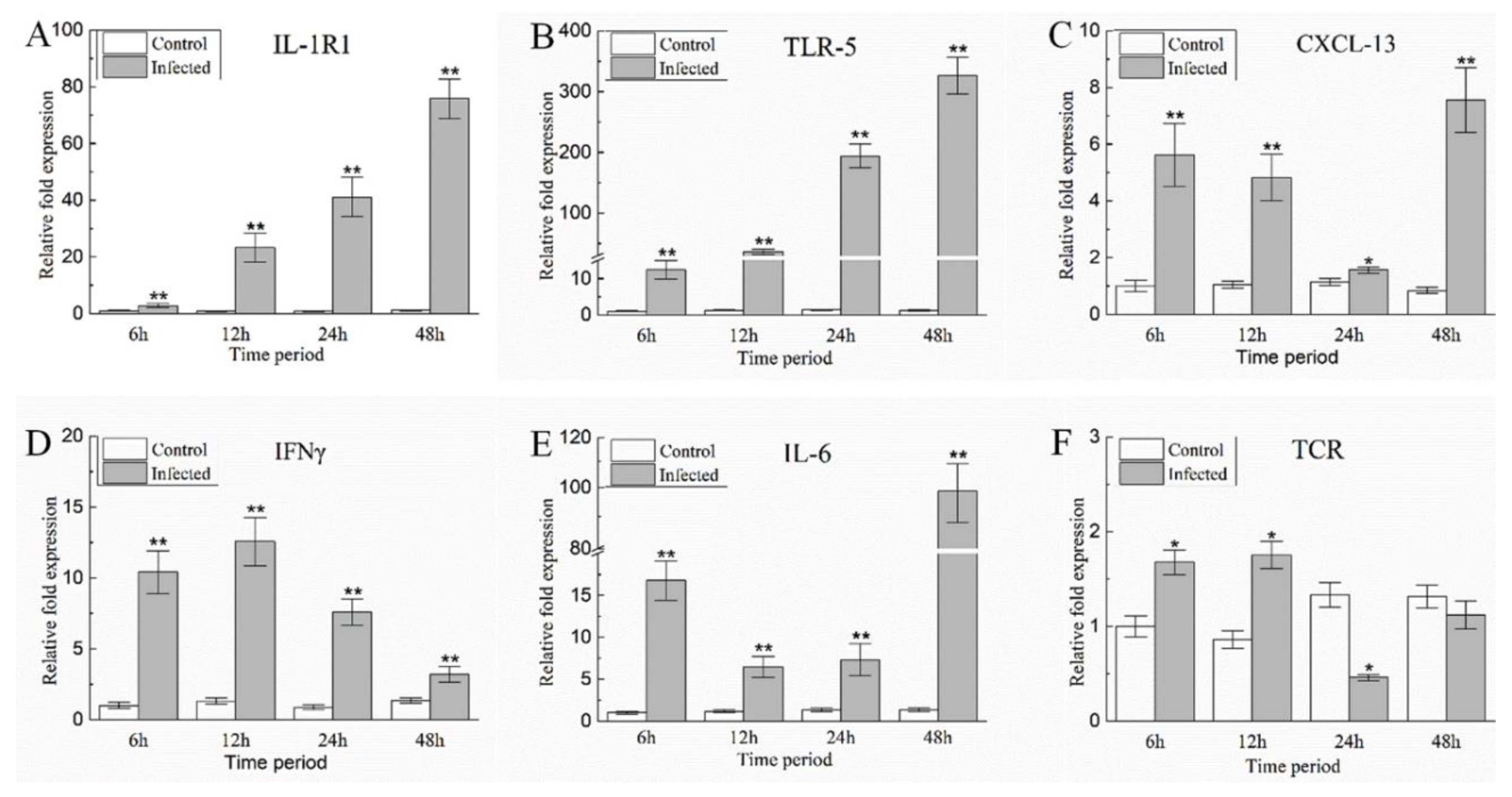
2.4. Detection of Immune-Related DEGs after Challenge with A. schubertii
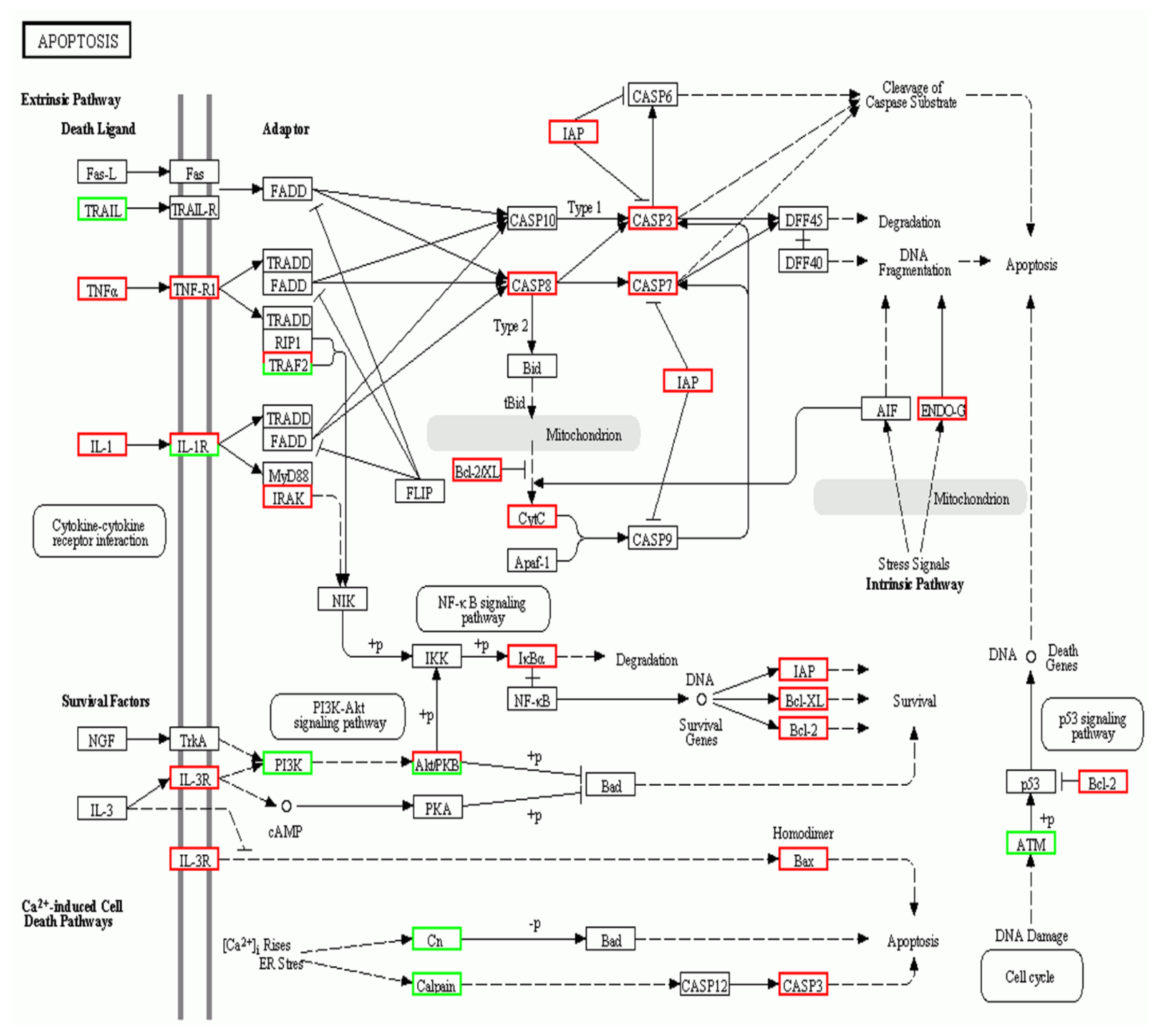
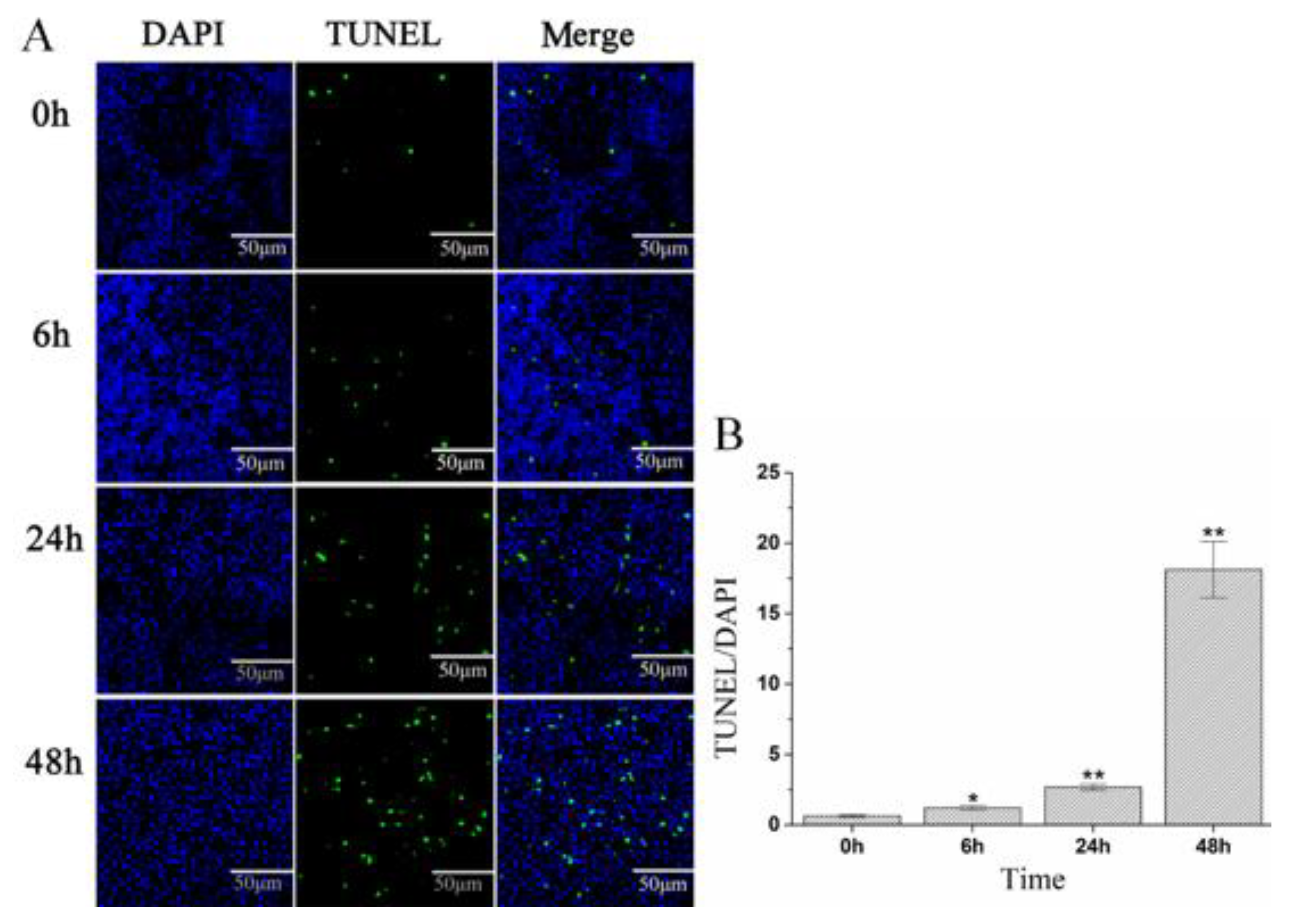
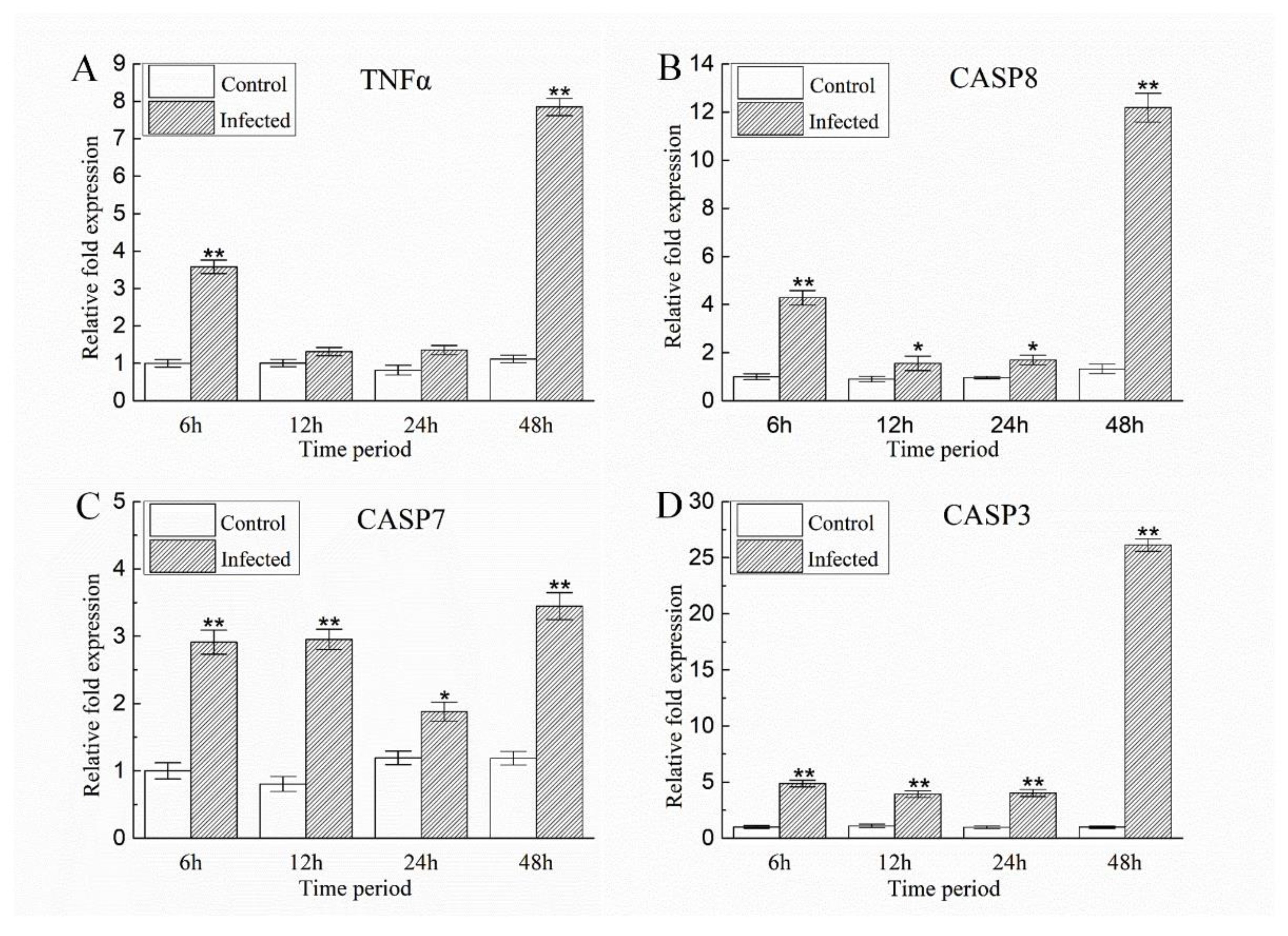
2.5. A. schubertii Infection Induced Apoptosis in Hybrid snakehead
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fish Sample, Bacteria Preparation, and Ethics
4.2. Bacterial Challenge, Sample Collection, and Total RNA Extraction
4.3. Library Preparation and RNA-seq
4.4. Transcriptome Assembly and Unigene Annotation
4.5. Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
4.6. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
4.7. Apoptosis Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, J.D.; Courtenay, W.R. Snakeheads (Pisces, Channidae)—A Biological Synopsis and Risk Assessment; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004.
- Xu, J.; Bian, C.; Chen, K.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, Q.; You, X.; Peng, W.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Draft genome of the Northern snakehead, Channa argus. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokka, R.P.; Lindquist, D.; Abbott, S.L.; Janda, J.M. Structural and pathogenic properties of Aeromonas schubertii. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hickmanbrenner, F.W.; Fanning, G.R.; Arduino, M.J.; Brenner, D.J.; Rd, F.J. Aeromonas schubertii, a new mannitol-negative species found in human clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnahan, A.M.; Marii, M.A.; Fanning, G.R.; Pass, M.A.; Joseph, S.W. Characterization of Aeromonas schubertii strains recently isolated from traumatic wound infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Y.; Li, A.H. First case of Aeromonas schubertii infection in the freshwater cultured snakehead fish, Ophiocephalus argus (Cantor), in China. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Liang, R.S.; Zhuo, X.L.; Wu, X.T.; Zou, J.X. Isolation and characterization of Aeromonas schubertii from diseased snakehead, Channa maculata (Lacepède). J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, K.B.; Wang, Q.; Chang, O.Q.; Liang, H.L.; Wang, F.; Pan, D.B.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Isolation, identification and characterization of Aeromonas schubertii from hybrid snakehead (Channa maculata♀ × C. Argus♂). J. Fish. China 2012, 36, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chang, O.Q.; Zhang, D.F.; Li, K.B.; Wang, F.; Lin, M.H.; Shi, C.B.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Bergmann, S.M. Aeromonas shuberti as a cause of multi-organ necrosis in internal organs of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, S.K. The innate immune response of finfish—A review of current knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.H.; Kang, S.; Park, H. Transcriptome analysis of immune response genes induced by pathogen agonists in the Antarctic bullhead notothen Notothenia coriiceps. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hu, X.; Sun, B.; Bo, Y.; Wu, K.; Xiao, L.; Gong, C. A transcriptome analysis focusing on inflammation-related genes of grass carp intestines following infection with Aeromonas hydrophila. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, J.; Nandi, S.; Mohanty, S.; Terhune, J.; Liu, Z.; Peatman, E. RNA-seq analysis of mucosal immune responses reveals signatures of intestinal barrier disruption and pathogen entry following Edwardsiella ictaluri infection in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.Q.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Wu, C.W.; Ke, Q.Z.; Han, K.H.; Zheng, W.Q.; Xu, N.D. Transcriptome analysis of the Larimichthys crocea liver in response to Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, Y.; Cai, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, P.; Qin, Q. Transcriptome analysis of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) spleen in response to Singapore grouper iridovirus. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, C.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Gong, G.; Ding, S.; et al. Transcriptome analysis revealed changes of multiple genes involved in immunity in Cynoglossus semilaevis during Vibrio anguillarum infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 43, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Huang, R.; Du, F.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Transcriptome analysis of head kidney in grass carp and discovery of immune-related genes. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Guo, Y.M.; Cao, J.Z.; Zhang, D.F.; Chang, O.Q.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Shi, C.B.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Detection and quantification of Aeromonas schubertii in Channa maculata by TaqMan MGB probe fluorescence real-time quantitative PCR. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, H.; Mcfadden, G. Apoptosis: An innate immune response to virus infection. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.N.; Lim, Y.J.; Choi, J.A.; Lee, J.; Go, D.; Song, C.H. Phagocytosis influences the intracellular survival of Mycobacterium smegmatis via the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, F.M.; Foster, B.; Grewal, S.; Sokolova, I.M. Apoptosis as a host defense mechanism in Crassostrea virginica and its modulation by Perkinsus marinus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birge, R.B.; Ucker, D.S. Innate apoptotic immunity: The calming touch of death. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeretssian, G.; Labbe, K.; Saleh, M. Molecular regulation of inflammation and cell death. Cytokine 2008, 43, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behar, S.M.; Martin, C.J.; Booty, M.G.; Nishimura, T.; Zhao, X.; Gan, H.X.; Divangahi, M.; Remold, H.G. Apoptosis is an innate defense function of macrophages against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lancellotti, M.; Pereira, R.F.; Cury, G.G.; Hollanda, L.M. Pathogenic and opportunistic respiratory bacteria-induced apoptosis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Sun, L. Edwardsiella tarda-Induced inhibition of apoptosis: A strategy for intracellular survival. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zychlinsky, A.; Sansonetti, P.J. Apoptosis as a proinflammatory event: What can we learn from bacteria-induced cell death? Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Apoptosis induced by bacterial pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 1994, 17, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behar, S.M.; Briken, V. Apoptosis inhibition by intracellular bacteria and its consequence on host immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2019, 60, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaik, E.J.; Chen, C.; Mertens, K.; Weber, M.M.; Samuel, J.E. Molecular pathogenesis of the obligate intracellular bacterium Coxiella burnetii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rikihisa, Y. Molecular Pathogenesis of Ehrlichia chaffeensis Infection. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matty, M.A.; Roca, F.J.; Cronan, M.R.; Tobin, D.M. Adventures within the speckled band: Heterogeneity, angiogenesis, and balanced inflammation in the tuberculous granuloma. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cronan, M.R.; Beerman, R.W.; Rosenberg, A.F.; Saelens, J.W.; Johnson, M.G.; Oehlers, S.H.; Sisk, D.M.; Jurcic, S.K.; Medvitz, N.A.; Miller, S.E.; et al. Macrophage epithelial reprogramming underlies mycobacterial granuloma formation and promotes infection. Immunity 2016, 45, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, B.M.; Frank, A.A.; Orme, I.M. Granuloma formation is required to contain bacillus growth and delay mortality in mice chronically infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunology 1999, 98, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.T.; Cambier, C.J.; Davis, J.M.; Hall, C.J.; Crosier, P.S.; Ramakrishnan, L. Neutrophils exert protection in the early tuberculous granuloma by oxidative killing of mycobacteria phagocytosed from infected macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, C.J.; Carey, A.F.; Fortune, S.M. A bug’s life in the granuloma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, A.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhou, Y. First case of Aeromonas schubertii infection in brackish water wild Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, in China. Aquaculture 2018, 501, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xia, L.; Wang, Z.; Hou, S.; Huang, J.; Lu, Y. Transcriptome analysis of immune-related gene expression in hybrid snakehead (Channa maculata female symbol × Channa argus male symbol) after challenge with Nocardia seriolae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 81, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, V.; Pasupuleti, M.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arshad, A.; Amin, S.; Yusoff, F.M.; Arockiaraj, J. A comparative transcriptome approach for identification of molecular changes in Aphanomyces invadans infected Channa striatus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2511–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Zeng, L. Transcriptome analysis of Aeromonas hydrophila infected hybrid sturgeon (Huso dauricus × Acipenser schrenckii). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eggestol, H.O.; Lunde, H.S.; Ronneseth, A.; Fredman, D.; Petersen, K.; Mishra, C.K.; Furmanek, T.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Wergeland, H.I.; Haugland, G.T. Transcriptome-wide mapping of signaling pathways and early immune responses in lumpfish leukocytes upon in vitro bacterial exposure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X. Self-regulation and cross-regulation of pattern-recognition receptor signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, T. Comparative genomic and evolution of vertebrate NOD1 and NOD2 genes and their immune response in miiuy croaker. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Yanfeng, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, S.; et al. Transcriptomic response to Yersinia pestis: RIG-I like receptor signaling response is detrimental to the host against plague. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallant, T.; Deb, A.; Kar, N.; Lupica, J.; de Veer, M.J.; Didonato, J.A. Flagellin acting via TLR5 is the major activator of key signaling pathways leading to NF-kappa B and proinflammatory gene program activation in intestinal epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood 2011, 117, 3720–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. Molecular characterization and bioactivity of a CXCL13 chemokine in large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, S.N.; Laghari, Z.A.; Huang, B.; Huo, H.J.; Li, N.; Nie, P. Receptor complex and signalling pathway of the two type II IFNs, IFN-gamma and IFN-gammarel in mandarin fish or the so-called Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 97, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Cai, J.; Yu, D.; Tang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. An IL-6 gene in humphead snapper (Lutjanus sanguineus): Identification, expression analysis and its adjuvant effects on Vibrio harveyi OmpW DNA vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Xia, L.Q.; Wang, Z.W.; Hou, S.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Lu, Y.S. Transcriptome analysis of immune-related gene expression in hybrid snakehead (Channa maculata ♀ × Channa argus ♂) after challenge with Nocardia seriolae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 91, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerschenson, L.E.; Rotello, R.J. Apoptosis: A different type of cell death. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 2450–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joselin, A.P.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schwerk, C. Loss of Acinus inhibits oligonucleosomal DNA fragmentation but not chromatin condensation during apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12475–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavrieli, Y.; Sherman, Y.; Ben-Sasson, S.A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, T.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Saha, D.R.; Sau, S.; Mazumder, S. Virulence plasmid of Aeromonas hydrophila induces macrophage apoptosis and helps in developing systemic infection in mice. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 46, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, W.; Shah, S.; Ishfaq, M.; Li, J. Mycoplasma gallisepticum infection triggered histopathological changes, oxidative stress and apoptosis in chicken thymus and spleen. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 114, 103832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbairn, I.P. Macrophage apoptosis in host immunity to mycobacterial infections. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keane, J.; Balcewicz-Sablinska, M.K.; Remold, H.G.; Chupp, G.L.; Meek, B.B.; Fenton, M.J.; Kornfeld, H. Infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis promotes human alveolar macrophage apoptosis. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.M.; Zhang, K.B.; Wang, T.P.; Sribastav, S.S.; Liu, W.S.; Liu, T. Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, I.; Rayamajhi, M.; Miao, E.A. Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitskaya, M.A.; Onishchenko, G.E. Mechanisms of apoptosis. Biochemistry 2015, 80, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.J.; Han, L.H.; Cong, R.S.; Liang, J. Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2005, 37, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunther, C.; Martini, E.; Wittkopf, N.; Amann, K.; Weigmann, B.; Neumann, H.; Waldner, M.J.; Hedrick, S.M.; Tenzer, S.; Neurath, M.F.; et al. Caspase-8 regulates TNF-alpha-induced epithelial necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature 2011, 477, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slee, E.A.; Adrain, C.; Martin, S.J. Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7320–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Chang, O.; Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, L. Investigating of type IV pili to the pathogenicity of Aeromonas schubertii. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrylkova, K.; Kyryachenko, S.; Leid, M.; Kioussi, C. Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 887, 41–47. [Google Scholar]


| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Base | GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC-1 | 33,306,402 | 32,889,174 | 4.92G | 47.02% |
| NC-2 | 33,820,162 | 33,376,306 | 4.99G | 46.84% |
| NC-3 | 36,227,606 | 35,749,772 | 5.34G | 47.11% |
| NC-total | 103,354,170 | 102,015,252 | 15.25G | 46.99% |
| SBT-1 | 30,868,936 | 30,479,570 | 4.57G | 46.76% |
| SBT-2 | 29,255,268 | 28,832,816 | 4.32G | 46.49% |
| SBT-3 | 31,578,840 | 31,111,042 | 4.67G | 47.12% |
| SBT-total | 91,703,044 | 90,423,428 | 14.55G | 46.79% |
| Database | Annotated Unigenes | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Nr | 26,981 | 40.95% |
| Swiss-Prot | 21,484 | 32.61% |
| GO | 12,786 | 19.40% |
| KEGG | 15,001 | 22.77% |
| KOG | 16,385 | 24.87% |
| All databases | 11,809 | 17.92% |
| At least one database | 27,533 | 41.79% |
| Total unigenes | 65,884 | 100% |
| Pathway ID | KEGG Pathways | DEGs | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | Down | |||
| ko04060 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 67 | 66 | 133 (6.38%) |
| ko04145 | Phagosome | 33 | 49 | 82 (3.93%) |
| ko04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 33 | 10 | 43 (2.06%) |
| ko04672 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production | 12 | 22 | 34 (1.63%) |
| ko04622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 19 | 8 | 27 (1.30%) |
| ko04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 13 | 8 | 21 (1.01%) |
| ko04623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 16 | 1 | 17 (0.82%) |
| ko04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 2 | 1 | 3 (0.14%) |
| ko04666 | Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | 0 | 2 | 2 (0.10%) |
| ko04662 | B cell receptor signaling pathway | 0 | 2 | 2 (0.10%) |
| ko04650 | Natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity | 0 | 2 | 2 (0.10%) |
| ko04664 | Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | 0 | 2 | 2 (0.10%) |
| ko04640 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | 0 | 2 | 2 (0.10%) |
| ko04610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | 1 | 0 | 1 (0.05%) |
| ko04210 | Apoptosis | 22 | 15 | 37 (1.78%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, B.; Qin, Z.; Su, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, Q. Immune Response and Apoptosis-Related Pathways Induced by Aeromonas schubertii Infection of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata♀ × Channa argus♂). Pathogens 2021, 10, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080997
Liu C, Ma J, Zhang D, Li W, Jiang B, Qin Z, Su Y, Lin L, Wang Q. Immune Response and Apoptosis-Related Pathways Induced by Aeromonas schubertii Infection of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata♀ × Channa argus♂). Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080997
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chun, Jie Ma, Defeng Zhang, Wei Li, Biao Jiang, Zhendong Qin, Youlu Su, Li Lin, and Qing Wang. 2021. "Immune Response and Apoptosis-Related Pathways Induced by Aeromonas schubertii Infection of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata♀ × Channa argus♂)" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080997
APA StyleLiu, C., Ma, J., Zhang, D., Li, W., Jiang, B., Qin, Z., Su, Y., Lin, L., & Wang, Q. (2021). Immune Response and Apoptosis-Related Pathways Induced by Aeromonas schubertii Infection of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata♀ × Channa argus♂). Pathogens, 10(8), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080997








