Abstract
Streptococcus suis is an emerging zoonotic bacterium causing septicemia and meningitis in humans. Due to rapid disease progression, high mortality rate, and many underdiagnosed cases by time-consuming routine identification methods, alternative diagnostic testing is essential. Among 29 broadly accepted S. suis serotypes, serotypes 2 and 14 are high prevalent; however, many PCR assays showed an inability to differentiate serotype 2 from 1/2, and 1 from 14. In this study, we developed and validated a new multiplex PCR assay that facilitates the identification of only the 29 true serotypes of S. suis and simultaneously differentiates serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 within a single reaction. Importantly, the multiplex PCR could detect S. suis directly from positive hemocultures and CSF. The results revealed high sensitivity, specificity, and 100% accuracy with almost perfect agreement (κ = 1.0) compared to culture and serotyping methods. Direct detection enables a decrease in overall diagnosis time, rapid and efficient treatment, reduced fatality rates, and proficient disease control. This multiplex PCR offers a rapid, easy, and cost-effective method that can be applied in a routine laboratory. Furthermore, it is promising for developing point-of-care testing (POCT) for S. suis detection in the future.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus suis, a Gram-positive cocci bacterium, is one of the leading causative agents of massive economic losses in the pig industry. It is also an emerging zoonotic infectious organism that has been receiving growing concern around the world [1,2]. S. suis naturally colonizes in the upper respiratory tract of pigs, particularly in tonsils and nasal cavities. On the other hand, it is responsible for meningitis, arthritis, pericarditis, polyserositis, septicemia, and sudden death of weaning piglets, as well as growing pigs [3]. Humans can be infected when in close contact with diseased pigs or consuming S. suis contaminated raw pork or pork-derived products [1]. Various symptoms, including fever, headache, septicemia, deafness to severe septic shock syndrome, and fatality, are found. The number of reported human cases has been dramatically increased in the last decade, and the vast majority are from Asia (90%) [4]. To date, S. suis has been re-classified into 29 serotypes based on genetic analysis [5,6]. Previously, S. suis has been recognized as 35 serotypes (serotype 1/2, and 1–34); however, serotypes 20, 22, 26, 32, 33, and 34 were re-identified into other species and are referred to as S. suis-like bacterium [7,8,9,10,11]. As not all serotypes are related to zoonotic potential and disease severity, it is important to know information about serotypes. Only some serotypes, such as serotypes 2 and 14, are associated with zoonotic infection; whereas, serotype 2 is the most prevalent serotype in both humans and pigs worldwide [12]. However, S. suis serotypes 1, 4, 5, 9, 16, 21, 24, and 31 have also been isolated from patients [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Serotype 1/2 is the most predominant serotype found in diseased pigs in North America [22]. In Thailand, the annual incidence rate of 0.51/100,000 persons has been reported by the Bureau of Epidemiology, Ministry of Public Health in 2020 (http://www.boe.moph.go.th/boedb/surdata/disease.php?dcontent=situation&ds=82, accessed on 15 July 2021). Serotype 2 is the most common serotype found in human S. suis infection cases (93.4%). The second most common serotype is serotype 14 (5.2%) followed by some others such as 24 (0.6%), 5 (0.4%), 4 (0.1%), 9 (0.1%), and 31 (0.1%) [15,16,17,23,24,25,26]. Serotyping is a vital diagnostic method for understanding the epidemiology of an outbreak, monitoring the prevalence of specific S. suis serotypes, and guiding vaccine development.
Serological typing was traditionally performed by a coagglutination test, precipitation test, and Neufeld’s capsular reaction test using reference antisera which is available for all serotypes in only a few laboratories around the world [27,28]. So far, many PCR-based serotypes have been developed based on capsular polysaccharide encoding gene (cps) [5,29,30,31]. Unfortunately, several PCR-based detection methods are unable to differentiate serotype 2 from 1/2, and serotype 1 from 14 as the cps gene of these serotypes are highly homologous [5]. However, it has been reported that a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the cpsK gene of these serotypes, at position 483, could differentiate between serotypes 2 and 1/2, as well as 1 and 14 [32]. The serotype 2 and 14 strains possess G nucleotide in contrast to serotype 1 and 1/2, which possess C or T at position 483 of the cpsK gene. PCR derivatives such as real-time PCR with a high resolution melting curve analysis, PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), and mismatch amplification mutation assay (MAMA-PCR) have been applied to differentiate among serotypes 2, 1/2, 1, and 14 [33,34,35]. However, these PCR assays are sophisticated and require multiple steps or special instruments.
In this study, we reported a simple, cheap, high accuracy multiplex PCR assay for differentiating among serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 based on the targeted cpsJ gene, the SNP in cpsK gene, and also the identification of S. suis using DNA repair protein gene (recN gene) that can differentiate S. suis from S. suis-like strains. This new multiplex PCR assay was validated using human and pig isolates. Moreover, we present the ability of the multiplex PCR to direct the detection of S. suis and serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 from clinical specimens by omitting the culture step. The developed assay will provide an alternative simple, rapid, high accuracy diagnostic test that allows access to well-organized treatment to reduce the severity and mortality rate of the infected patient.
2. Results
2.1. New Designed Primers and Optimization of Multiplex PCR
Two new pairs of primers were designed in this study; one pair (species-specific) primer was based on the recN gene to identify S. suis with the expected product size at 946 bp. Another primer pair was specially designed for the last nucleotide (G) at the 3′ end of the forward primer (cps2,14K) to match with the SNP at position 483 of cpsK for identifying S. suis serotypes 2 and 14 with 209 bp amplicons (Figure 1). In combination with two primer pairs from a previous study [30], the new multiplex PCR was able to differentiate serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, 14 from each other.
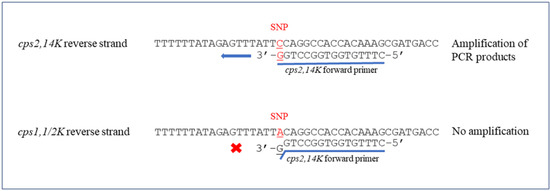
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of cps2,14K forward primer binding site. The SNP at position 483 of cpsK gene were indicated in red. × represented no amplification and ← showed the ability to amplify PCR products.
The optimal conditions of the multiplex PCR assay were initially determined using genomic DNA of reference S. suis serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 as a template. The results showed that the optimal primer ratio was 5:0.5:0.5:2, with a final concentration of 1.25 µM for all S. suis specific primers, 0.125 µM for cps1,14J primers, 0.125 µM for cps2,1/2J primers, and 0.5 µM for cps2,14K primers, respectively. The annealing temperature was determined using PCR gradients ranging from 58–64 °C and showed the best optimal annealing temperature at 61 °C.
The result interpretation for differentiation of serotype 1 from 14 and serotype 2 from 1/2 is shown in Figure 2. All serotypes could be identified as expected by gel electrophoresis: S. suis serotype 1 showed two positive bands at 946 bp of recN gene and 550 bp of cps1,14J gene; serotype 14 showed three positive bands at 946 bp of recN gene, 550 bp of cps1,14J gene, and 209 bp of cps14K gene; serotype 1/2, showed two positive bands at 946 bp of recN gene, and 450 bp of cps2,1/2J gene; and serotype 2 showed similar bands as serotype 1/2 with an additional positive band at 209 bp of cps2K gene. Using the developed method, serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 were easily discriminated within a single reaction of multiplex PCR.
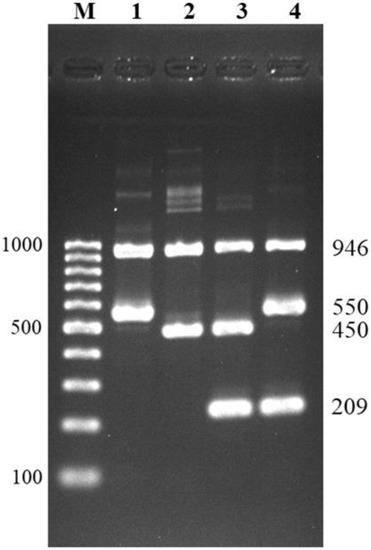
Figure 2.
Multiplex PCR for differentiation of serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14. Lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 1 = serotype 1; lane 2 = serotype 1/2; lane 3 = serotype 2; lane 4 = serotype 14.
2.2. Specificity and LOD of Multiplex PCR
To determine the cross-reactivity to other S. suis serotypes of developed multiplex PCR, 29 serotypes of S. suis reference strains and S. suis-like strains; -serotypes 20, 22, 26, 32, and 34 were used. All 29 serotypes showed a positive band and amplified only the 946 bp of recN gene, whereas S. suis-like strains could not be amplified, as expected (Figure 3). The aforementioned serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 were also shown in the correct differentiation. In addition, no cross-reaction was observed with the other 48 bacterial genera and 6 Candida species tested. From these results, 100% specificity for S. suis identification and S. suis serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 differentiation of a new multiplex PCR were derived.
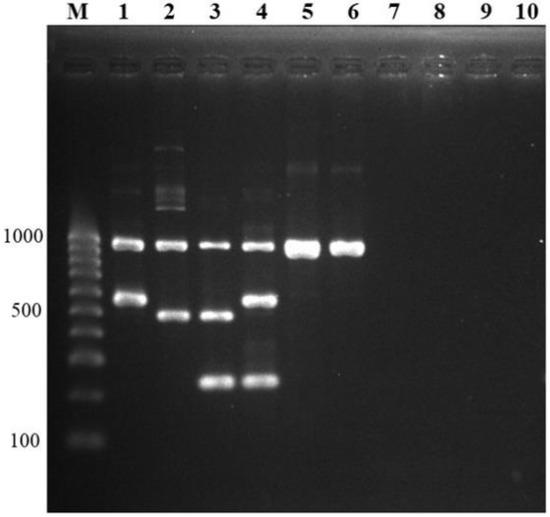
Figure 3.
Specificity testing. Multiplex PCR was tested for cross-reactivity between other S. suis serotypes, S. suis-like strains (former S. suis serotypes), and other bacterial genera and species. Lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 1, 2, 3, 4 = positive controls (serotype 1, serotype 1/2, serotype 2, serotype 14); lane 5, 6 = other S. suis serotypes (serotype 15, serotype 19); lane 7, 8 = S. suis-like strains (former serotype 22, former serotype 32); lane 9, 10 = other bacterial genera (Acinetobacter baumannii, Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, respectively).
The limit of detection for the multiplex PCR assay was performed using a 10-fold serial dilution of each serotype (1, 1/2, 2, and 14) starting at 108 CFU/mL. The detection limit of this assay was 102 CFU for serotypes 1/2, 2, 14, and 103 CFU for serotype 1 (Figure 4).
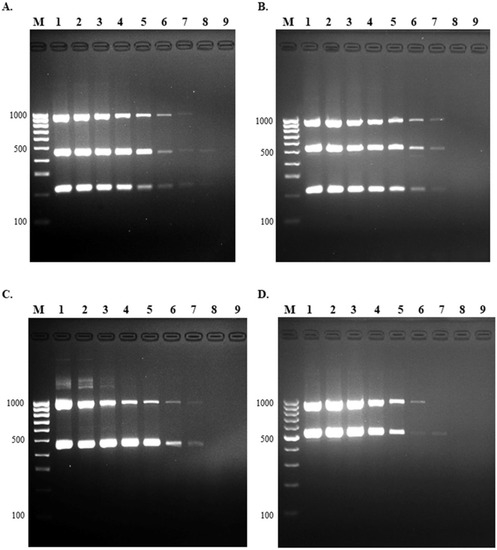
Figure 4.
Limit of detection of multiplex PCR. The LOD was evaluated using 10-fold serial dilution of standard strains of S. suis (A) serotype 2, (B) serotype 14, (C) serotype 1/2, and (D) serotype 1. Lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 1 = 108 CFU; lane 2 = 107 CFU; lane 3 = 106 CFU; lane 4 = 105 CFU; lane 5 = 104 CFU; lane 6 = 103 CFU; lane 7 = 102 CFU; lane 8 = 101 CFU, and lane 9 = no template control.
2.3. Evaluation of Multiplex PCR
A total of 190 S. suis isolates from humans and pigs were analyzed by the multiplex PCR assay. All of these isolates were also serotyped using PCR serotyping [31] combined with PCR-RFLP [34] and coagglutination serological testing [28]. Of the 190 isolates, our multiplex PCR identified serotype 2 in 126 isolates, 45 isolates as serotype 14, 2 isolates as serotype 1, and a total of 17 isolates of serotypes 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 16, 18, 19, 24, 28, and 31 were identified as S. suis (Figure 5A). The results of the assays revealed 100% accordance with serological and PCR serotyping methods. Hence, diagnostic sensitivity was 100% (98.08–100%, 95% CI) and PPV was 100%, whereas specificity and NPV could not be calculated due to all tested isolates being S. suis. The ROC curve showed that the AUC = 1.0 (Figure 5B). The kappa value for agreement between our multiplex PCR and PCR serotyping, combined with PCR-RFLP and serological testing, was in almost perfect agreement, κ = 1.00, (0.81–1.00, 95% CI, p < 0.05). The developed assay showed high sensitivity and accuracy.
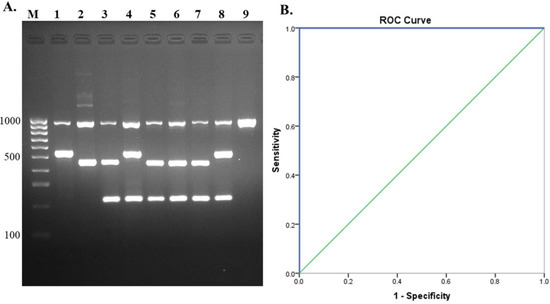
Figure 5.
Evaluation of multiplex PCR using human and pig isolates. (A) Gel electrophoresis of isolates tested, lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 1, 2, 3, 4 = positive controls (serotype 1, serotype 1/2, serotype 2, serotype 14); lane 5 = isolate 1; lane 6 = isolate 2; lane 7 = isolate 3; lane 8 = isolate 4, and lane 9 = isolate 5. (B) Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve for evaluation of multiplex PCR with S. suis isolates.
2.4. Direct Detection of S. suis from Clinical Samples
A total of 125 patient hemocultures and one CSF sample from three hospitals in the Northern part of Thailand were included in this experiment. The multiplex PCR assay revealed that 65 hemocultures and one CSF were S. suis positive for serotype 2 (100%), while the other 60 hemocultures were S. suis negative (Figure 6A). Both S. suis positive and negative results were in 100% accordance with culture results. Furthermore, all serotype results from the multiplex PCR assay were in concordance with serology results. Therefore, sensitivity = 100% (94.56–100%, 95% CI), specificity = 100% (94.04–100%, 95% CI), PPV = 100%, and NPV = 100%, respectively. The ROC curve demonstrated that AUC was 1.0 (Figure 6B). The Kappa values for multiplex PCR and culture, PCR serotyping and PCR-RFLP, and serological testing were revealed as in almost perfect agreement, κ = 1.00, (0.81–1.00, 95% CI, p < 0.05). All these results revealed that the developed assay could be applied to direct detection of clinical specimens, especially from positive hemoculture and CSF, although further testing of more CSF samples is still needed to be performed.
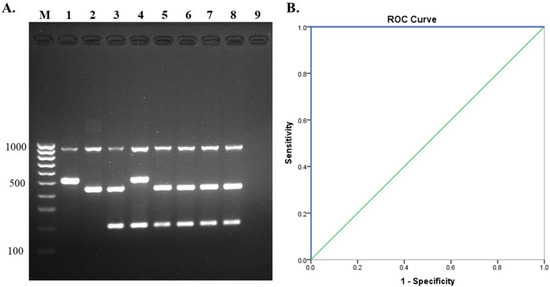
Figure 6.
Direct detection of S. suis from human clinical specimens. (A) Evaluation of multiplex PCR using hemoculture Lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder, Lane 1, 2, 3, 4 = positive controls (serotype 1, serotype 1/2, serotype 2, serotype 14), Lane 5, 6, 7, 8 = hemoculture samples, and Lane 9 = no template control, (B) receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve for direct detection of S. suis from clinical specimens.
3. Discussion
In this study, we developed a new multiplex PCR assay that detected true S. suis species along with the simultaneous differentiation of serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 from each other within a single reaction. Differentiation between serotypes 2 and 1/2, and serotypes 1 and 14, is challenging for PCR assays as these pairs of serotypes possess high similarity of the cps gene. The exact differentiation between serotypes 2 and 1/2, as well as between 1 and 14, is important for epidemiological investigation, monitoring dynamic serotype changes. Furthermore, serotypes 2 and 14 are profoundly associated with zoonotic disease [14].
S. suis serotypes are traditionally classified by coagglutination or agglutination tests using serotype-specific antisera. These techniques are simple; however, the production of specific antisera is time-consuming, expensive, laborious, and only available in reference laboratories. Cross-reaction also occurred in some serotypes; serotype 1/2 with serotypes 1 and 2, and serotypes 1 with serotype 14 [28]. Molecular PCR-based serotyping targeted the cps gene does not require expensive antisera, can be applied in many laboratories and is an alternative way for serotyping S. suis. However, these assays are not able to differentiate between serotype 2 from 1/2 and serotype 1 from 14.
Lately, it has been reported that a single nucleotide polymorphism (G to C/T) at position 483 of the cpsK gene is detectable using a short-read whole-genome sequencing and can be used to differentiate among these four serotypes [32]. The whole-genome sequencing approach is highly accurate; however, the cost per sample is high, time-consuming, and probably only available in some laboratories. Recently, the high-resolution melting curve assays, PCR-RFLP and MAMA-PCR, based on cpsK, were reported [33,34,35]. These methods could be rapid and sensitive, but a multi-reaction step is required to differentiate serotype 2 from 1/2 as well as 1 from 14. In addition, some techniques required a special instrument or another reagent, such as for the restriction of endonucleases.
Herein, we describe a simple multiplex PCR assay differentiating these four serotypes from each other based on the cps1,14J, cps2,1/2J, and cps2,14K genes within a single reaction. Furthermore, our assay included the primer targeting recN gene to specifically identify S. suis. The presence of two positive bands at the recN and cps1,14J genes for serotype 1, and the same for serotype 14 with an additional 209 bp of cps14K gene. Similarly, serotypes 1/2 and 2 are positive for the recN and cps2,1/2J genes with an additional 209 bp of the cps2K gene for serotype 2. The cpsK primer used in this study was highly specific for serotypes 2 and 14. Even with one nucleotide difference, it cannot amplify serotypes 1 and 1/2. Furthermore, a short product size enables rapid amplification and reduces turnaround time. Other S. suis serotypes, apart from these four, are positive for the recN gene, whereas S. suis-like strains are not amplified by our PCR. This is easy to perform; no additional steps, special instruments, or reagents are required. Our multiplex PCR assay also showed high sensitivity. No cross-reactions with the S. suis-like strains, other bacterial, or fungal species were observed.
Traditional serotyping using the agglutination test is still considered a reference method. Most S. suis isolates from pigs are a loss of capsular expression after culture; in these cases, the agglutination test is unable to serotype [35]. However, multiplex PCR targeting of the cps gene can resolve to predict serotypes. For example, unencapsulated S. suis serotype 31 was not serotyped by coagglutination but could identify serotype 31 by using multiplex PCR [21]. Unencapsulated strains (due to mutations in the cps locus) have been mostly associated with endocarditis in pigs [36]. Furthermore, a complete deletion of the cps locus presented in non-typeable strains was recovered from diseased pigs [37]. Furthermore, a human case of S. suis infection caused by an unencapsulated strain has been found in Thailand, and a loss of capsular expression is due to a disrupted mutation in the cpsE–cpsK region [38]. In these cases, our multiplex PCR targeted to cpsJ and cpsK could be unable to serotype; however, including a species-specific recN gene can still identify S. suis, and a low possibility of a false-negative would be detected compared to only serotype-specific PCR assays.
Multiplex PCR is a simple, rapid, low-cost method that can be applied in most laboratories. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of simultaneous single multiplex PCR differentiating S. suis serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14. Our multiplex PCR assay combined with the previously published multiplex PCR assay [31] will be achieved for serotyping of all true S. suis. Furthermore, it can overcome the limitation of traditional serotyping that could only perform in reference laboratories and required the expensive specific antisera. Note that our PCR assay was limit with few isolates of the serotypes 1 and 1/2. Notably, more field isolates of these S. suis serotypes are required to further verify the assay. Since these two serotypes have a very low prevalence in pigs in Thailand (serotype 1 (1.5%), serotype 1/2 (0.5%)) [23], not many samples were included for evaluation of multiplex PCR assay. Collectively, human infections with these two serotypes have never been reported in Thailand, or the globe, based on the fact that serotype 1 and serotype 1/2 isolates have not yet been recovered or confirmed [4,26]. Although two human cases associated with suspected S. suis serotype 1 has been documented but was established using biochemical criteria only. These strains could not be confirmed as serotype 1 by the standard technique; therefore, it is still in question [1].
As S. suis infection mostly occurs asymptomatically in the early stages, rapid disease progression can lead to death within a short period, especially in splenectomized patients (patients died within 12 h [39], or 23 days [40], after hospital admission). Therefore, early and accurate diagnosis is critically important. The routine identification methods, including culture and biochemical tests, are time-consuming and sometimes showed controversy, resulting in underdiagnoses. Other alternative methods such as the Vitek II system, Phoenix System, and MALDI-TOF have been widely used for the identification of S. suis. However, these methods are performed from pure colonies and need a culture step. In addition, some systems probably misidentify S. suis as other Streptococcal species [41,42,43]. Due to these limitations, rapid and accurate diagnostic methods are needed.
The developed multiplex PCR assay enables us to identify and serotype S. suis directly from positive hemoculture and CSF with no culture step. Notably, hemoculture contain PCR inhibitors such as sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS), a common additive to automated hemoculture media that affects PCR reactions even when used with specific commercial extraction kits for blood [44]. Hence, extracted genomic DNA by a 1:10 dilution with sterile water could be useful to avoid PCR failure. Further testing of more CSF samples and other clinical specimen types such as synovial fluid, tissues, and pleural fluid are needed to verify the effectiveness of the multiplex PCR. Our multiplex PCR assay will be more convenient than the culture method owing to the 2–3 hour turnaround time. Unlike the culture method, which takes at least 2–3 days to get a result. However, gel electrophoresis is still needed, and other approaches will be needed to develop point-of-care testing (POCT) for S. suis detection in the future.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
In order to determine the optimal conditions of multiplex PCR, reference strains of S. suis serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 were included. Reference strains of 29 S. suis serotypes and the former S. suis serotypes 20, 22, 26, 32, and 34 were used for specificity testing. Moreover, a total of 190 human (n = 165) and pig (n = 25) isolates, which have been previously serotyped using either antisera or PCR, were included in this study. We also included 48 species of other bacterial strains and 6 Candida species to observe possible cross-reactions (Table 1). S. suis was cultured onto 5% defibrinated sheep blood agar plates and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 18–24 hours. Other bacterial species were grown overnight at 37 °C, 5% CO2, on 5% defibrinated sheep blood agar or chocolate agar, depending on their optimal medium.

Table 1.
Other bacterial and fungal species used in specificity testing.
4.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
Genomic DNA of S. suis and other bacterial strains were extracted using a heat-lysis method with some modification [45]. Briefly, a loopful of the bacterial colonies were suspended into 30 µL lysis buffer (a mixture of 0.25% (vol/vol) sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), 0.05 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and distilled water), mixed by vortex and heated at 95 °C for 15 min, followed by centrifugation at 12,000× g for 5 min. Finally, the supernatant was transferred into a new tube, and we added 200 µL of sterile distilled water. The extracted genomic DNA was kept at −20 °C until used.
Genomic DNA from hemoculture was extracted using a NucleoSpin® Blood Mini kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. To remove PCR inhibitors, genomic DNA extracted from hemoculture were diluted to 1:10 with sterile distilled water prior to use as a template for PCR. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was centrifuged, and the pellet was further processed to obtain genomic DNA using the heat-lysis method.
4.3. Multiplex PCR
In this study, two new primer pairs were designed to identify only S. suis species and discriminate between serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14. To identify S. suis specifically, recN sequences of available S. suis serotypes and S. suis-liked strains were obtained from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 11 June 2020) and aligned with the Clustal Omega program (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/, accessed on 11 June 2020). The primer binding sites were analyzed and designed. Discrimination between four serotypes and a new pair of primers were designed to target the cps2K and cps14K genes that possess point mutations at position 483 (G nucleotide). This primer pair was designed using the Primer 3 PCR primer designing tool (https://primer3.ut.ee/, accessed on 11 June 2020). Two pairs of primers (cps1,14J, and cps2,1/2J) from previous studies were also included in the reaction [30]. The primer sequences used in this study are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primers and target genes used in the multiplex PCR assay.
Optimal conditions of the multiplex PCR, such as annealing temperature, primer concentration, and primer ratio, were determined using genomic DNA of reference S. suis serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 as a template. The PCR mixture contained 1× Quick Taq® HS Dye Mix (Toyobo Life Sciences, Osaka, Japan), 1.25 µM for all S. suis specific primers, 0.125 µM for cps1,14J primers, 0.125 µM for cps2,1/2J primers, 0.5 µM for cps2,14K primers and 1 µL (100 ng) of template DNA in a total of 20 µL per reaction. The thermal profile of PCR was used based on the optimal condition of multiplex PCR: initial activation of DNA polymerase at 95 °C for 3 min, 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 20 s, primer annealing and extension at 61 °C for 90 s, and final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. The PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis (2% agarose in 0.5× Tris-Acetate-EDTA (TAE) buffer) for 40 min. The gels were pre-stained with RedSafe™ Nucleic Acid Staining Solution (iNtRON Biotechnology, Inc, Seongnam-Si, Korea) and visualized under UV light (G: BOX F3, SYNGENE, Cambridge, England). The sizes of PCR products were determined by comparison with a molecular size standard (GeneRuler 100 bp DNA ladder, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
4.4. Limit of Detection (LOD)
The limit of detection of multiplex PCR was determined using a 10-fold serial dilution of each S. suis serotype (serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14). Briefly, the overnight cultures of four S. suis serotypes were harvested and washed thrice with 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Then, the pellets were suspended with 1× PBS and adjusted to the original concentration of 108 CFU/mL by measuring turbidity at an optical density of 600 nm (OD600). Measuring OD600 at 0.3 for serotype 2, 0.1 for serotype 14, 0.5 for serotype 1/2, and 0.7 for serotype 1 were performed. Starting from 108 CFU/mL, 10-fold serial dilutions were made until reaching 10 CFU/mL. Genomic DNA was extracted from 1 mL of each dilution using the heat-lysis method. At the same time, each dilution was also plated on blood agar and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2 overnight for the colony count, in order to determine the minimum colony-forming unit required for multiplex PCR.
4.5. Evaluation of Multiplex PCR Using S. suis Colonies from Human and Pig Isolates and Direct Detection of S. suis from Clinical Specimens
The multiplex PCR was validated using a pure culture of a total of 190 S. suis samples isolated from human clinical specimens and healthy pig tonsils (which have been previously serotyped by PCR serotyping [31]) combined with the PCR-RFLP method [34] and coagglutination serological testing [28]. Among 190 culture isolates, 126 isolates of serotype 2, 45 isolates of serotype 14, 2 isolates of serotype 1, and a total of 17 isolates of serotypes 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 16, 18, 19, 24, 28, and 31 were included.
Furthermore, a total of 125 hemoculture samples and one CSF sample were also included for direct detection of the assay. From culture and biochemical testing, 65 samples were identified as S. suis, and 60 samples were S. suis-negative (identified as other bacterial genera and species (n = 50), or no growth (n = 10)). One CSF sample was also identified as S. suis. Diagnosis accuracy was measured in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value, compared to either culture and biochemical testing or serological testing and PCR serotyping. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was performed. In order to describe the agreement between new multiplex PCR and culture or serotyping methods, Cohen’s kappa coefficient with a 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was calculated. Kappa values were interpreted as follow: 0.00–0.20 as poor agreement; 0.21–0.40, fair agreement; 0.41–0.60, moderate agreement; 0.61–0.80, good agreement; 0.81–1.00 almost perfect agreement [46]. All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS statistical package, release 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
5. Conclusions
The multiplex PCR assay in the current study provides an easy, rapid, cost-effective, and high accuracy method to identify and differentiate S. suis serotypes 1, 1/2, 2, and 14 from each other within a single reaction. Direct detection from hemoculture and CSF also revealed high sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy, with almost perfect agreement (κ = 1.0), compared to culture and serotyping results. This facilitates a rapid diagnosis and can be applied for an effective treatment, investigation, and control of S. suis infection in both humans and pigs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.T.; methodology, I.S.L.T., K.T., S.I. and A.K.; formal analysis, U.A.; investigation, I.S.L.T.; resources, K.T., S.I., P.K. and A.K.; data curation, I.S.L.T. and C.S.T.; writing—original draft preparation, I.S.L.T.; writing—review and editing, C.S.T. and A.K.; visualization, I.S.L.T.; supervision, C.S.T.; funding acquisition, C.S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research study was funded by a research grant from the Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, Thailand and partially supported by Chiang Mai University, Thailand.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University (approval no. AMSEC 291/2564, approved on 22 June 2021). Approval for the implementation of biosafety research was also certified by the Institutional Committee on Biosafety, Chiang Mai University (certificate no. CMUIBC A-0563003).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to using of leftover specimens.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The first author is grateful for the support of the Master’s Degree Program in Medical Technology, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, from the CMU Presidential Scholarship. We also thank Lecturer Kwanjit Duangsonk from the Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Kanya Preechasuth, and Ratchadaporn Udpaun from the Division of Clinical Microbiology, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, Kanokwan Saengsawang, Pisitphon Chiamongkhol for providing the specimens used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gottschalk, M.; Xu, J.; Calzas, C.; Segura, M. Streptococcus suis: A new emerging or an old neglected zoonotic pathogen? Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Zając, V.; Sroka, J.; Wasiński, B.; Cisak, E.; Sawczyn-Domańska, A.; Kloc, A.; Wójcik-Fatla, A. Streptococcus suis: A re-emerging pathogen associated with occupational exposure to pigs or pork products. Part II—Pathogenesis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vötsch, D.; Willenborg, M.; Weldearegay, Y.B.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Streptococcus suis—The “Two Faces” of a Pathobiont in the Porcine Respiratory Tract. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent—An update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, M.; Lachance, C.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T.; Maruyama, F.; Nozawa, T.; Nakagawa, I.; Hamada, S.; Rossignol, C.; Gottschalk, M.; et al. Development of a Two-Step Multiplex PCR Assay for Typing of Capsular Polysaccharide Synthesis Gene Clusters of Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okura, M.; Osaki, M.; Nomoto, R.; Arai, S.; Osawa, R.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D. Current Taxonomical Situation of Streptococcus suis. Pathogens 2016, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Jacques, M.; Mittal, K.R.; Henrichsen, J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 2633–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Jacques, M.; Beaudoin, M.; Henrichsen, J. Characterization of six new capsular types (23 through 28) of Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2590–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Jacques, M.; Beaudoin, M.; Henrichsen, J. Isolation and Characterization of Streptococcus suis Capsular Types 9–22. J. Veter Diagn. Investig. 1991, 3, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, R.; Gottschalk, M.; Boudreau, M.; Lebrun, A.; Henrichsen, J. Description of Six New Capsular Types (29–34) of Streptococcus suis. J. Veter Diagn. Investig. 1995, 7, 405–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tien, L.H.T.; Nishibori, T.; Nishitani, Y.; Nomoto, R.; Osawa, R. Reappraisal of the taxonomy of Streptococcus suis serotypes 20, 22, 26, and 33 based on DNA–DNA homology and sodA and recN phylogenies. Veter Microbiol. 2013, 162, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Sroka, J.; Zając, V.; Wasiński, B.; Cisak, E.; Sawczyn-Domańska, A.; Kloc, A.; Wójcik-Fatla, A. Streptococcus suis: A re-emerging pathogen associated with occupational exposure to pigs or pork products. Part I—Epidemiology. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghia, H.D.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Linh, L.D.; Campbell, J.; Diep, T.S.; Chau, N.V.V.; Mai, N.T.H.; Hien, T.T.; Spratt, B.; Farrar, J.; et al. Human Case of Streptococcus suis Serotype 16 Infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M.; Xu, J. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: The Chinese experience and the situation in North America. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Dejsirilert, S.; Sawanpanyalert, P.; Boonnark, A.; Noithachang, W.; Sriyakum, D.; Simkum, S.; Chokngam, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Akeda, Y.; et al. Sepsis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in Thailand. Lancet 2011, 378, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdsin, A.; Hatrongjit, R.; Gottschalk, M.; Takeuchi, D.; Hamada, S.; Akeda, Y.; Oishi, K. Emergence of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 infection in humans. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Gottschalk, M.; Hatrongjit, R.; Hamada, S.; Akeda, Y.; Oishi, K. Fatal Septic Meningitis in Child Caused by Streptococcus suis Serotype 24. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1519–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniyama, D.; Sakurai, M.; Sakai, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Takahashi, T. Human case of bacteremia due to Streptococcus suis serotype 5 in Japan: The first report and literature review. IDCases 2016, 6, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arends, J.P.; Zanen, H.C. Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus suis in Humans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, R.C.E.; Prieto, M.; Salamone, F.; Auger, J.-P.; Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Gottschalk, M. Atypical Streptococcus suis in Man, Argentina, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatrongjit, R.; Kerdsin, A.; Gottschalk, M.; Takeuchi, D.; Hamada, S.; Oishi, K.; Akeda, Y. First human case report of sepsis due to infection with Streptococcus suis serotype 31 in Thailand. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, A.A.; Gottschalk, M.; Rossow, S.; Rendahl, A.; Gebhart, C.; Marthaler, D.G. Serotype and Genotype (Multilocus Sequence Type) of Streptococcus suis Isolates from the United States Serve as Predictors of Pathotype. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00377-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Takeuchi, D.; Nuangmek, A.; Akeda, Y.; Gottschalk, M.; Oishi, K. Genotypic Comparison between Streptococcus suis Isolated from Pigs and Humans in Thailand. Pathogens 2020, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Oishi, K.; Sripakdee, S.; Boonkerd, N.; Polwichai, P.; Nakamura, S.; Uchida, R.; Sawanpanyalert, P.; Dejsirilert, S. Clonal dissemination of human isolates of Streptococcus suis serotype 14 in Thailand. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerdsin, A.; Dejsirilert, S.; Puangpatra, P.; Sripakdee, S.; Chumla, K.; Boonkerd, N.; Polwichai, P.; Tanimura, S.; Takeuchi, D.; Nakayama, T.; et al. Genotypic Profile of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 and Clinical Features of Infection in Humans, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerdsin, A.; Akeda, Y.; Takeuchi, D.; Dejsirilert, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Oishi, K. Genotypic diversity of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from humans in Thailand. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, R.; Gottschalk, M. An Update on Streptococcus suis Identification. J. Veter. Diagn. Investig. 1990, 2, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Boudreau, M. Use of polyvalent coagglutination reagents for serotyping of Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2192–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LZhijie, L.; Han, Z.; Marcelo, G. Development of Multiplex PCR Assays for the Identification of the 33 Serotypes of Streptococcus suis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Dejsirilert, S.; Akeda, Y.; Sekizaki, T.; Hamada, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Oishi, K. Fifteen Streptococcus suis serotypes identified by multiplex PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Akeda, Y.; Hatrongjit, R.; Detchawna, U.; Sekizaki, T.; Hamada, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Oishi, K. Streptococcus suis serotyping by a new multiplex PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Athey, T.B.T.; Teatero, S.; Lacouture, S.; Takamatsu, D.; Gottschalk, M.; Fittipaldi, N. Determining Streptococcus suis serotype from short-read whole-genome sequencing data. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherrer, S.; Rademacher, F.; Serrano, N.S.; Schrenzel, J.; Gottschalk, M.; Stephan, R.; Landolt, P. Rapid high resolution melting assay to differentiate Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 1/2, 1, and 14. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matiasovic, J.; Zouharova, M.; Nedbalcova, K.; Kralova, N.; Matiaskova, K.; Simek, B.; Kucharovicova, I.; Gottschalk, M. Resolution of Streptococcus suis Serotypes 1/2 versus 2 and 1 versus 14 by PCR-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00480-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacouture, S.; Okura, M.; Takamatsu, D.; Corsaut, L.; Gottschalk, M. Development of a mismatch amplification mutation assay to correctly serotype isolates of Streptococcus suis serotypes 1, 2, 1/2, and 14. J. Veter Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkitjaroen, N.; Takamatsu, D.; Okura, M.; Sato, M.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T. Loss of capsule among Streptococcus suis isolates from porcine endocarditis and its biological significance. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Qiu, X.; Roy, D.; Segura, M.; Du, P.; Xu, J.; Gottschalk, M. Genotyping and investigating capsular polysaccharide synthesis gene loci of non-serotypeable Streptococcus suis isolated from diseased pigs in Canada. Veter Res. 2017, 48, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerdsin, A.; Takeuchi, D.; Gottschalk, M.; Hamada, S.; Akeda, Y.; Oishi, K. A human case of Streptococcus suis infection caused by an unencapsulated strain. JMM Case Rep. 2014, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ágoston, Z.; Terhes, G.; Hannauer, P.; Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E. Fatal case of bacteremia caused by Streptococcus suis in a splenectomized man and a review of the European literature. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2020, 67, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, L.; Chang, W.; Lu, H.; Cui, P.; Ma, X. Culture-Negative Streptococcus suis Infection Diagnosed by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mai, N.T.H.; Hoa, N.T.; Nga, T.V.T.; Linh, L.D.; Chau, T.T.H.; Sinh, D.X.; Phu, N.H.; Van Chuong, L.; Diep, T.S.; Campbell, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis Meningitis in Adults in Vietnam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.T.; Teng, L.J.; Ho, S.W.; Hsueh, P.R. Streptococcus suis infection. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2005, 38, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarini, N.M.A.; Setiabudy, M.; Susilawathi, N.M.; Fatmawati, N.N.D.; Mayura, I.; Darwinata, A.E.; Sudiariani, N. Misidentification of S. suis as a Zoonotic Agent. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 2309–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fredricks, D.; Relman, D.A. Improved Amplification of Microbial DNA from Blood Cultures by Removal of the PCR Inhibitor Sodium Polyanetholesulfonate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Coenye, T.; Burns, J.L.; Whitby, P.W.; Stull, T.L.; LiPuma, J.J. Ribosomal DNA-Directed PCR for Identification of Achromobacter (Alcaligenes) xylosoxidans Recovered from Sputum Samples from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).