Abstract
Epitheliocystis is a disease caused by a wide variety of host-specific intracellular bacteria infecting fish gills. In the Mediterranean Sea, epitheliocystis has been recently associated with a novel genus of beta-proteobacteria, the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus. In the present study, we report a case of epitheliocystis in a wild-caught specimen of pompano Trachinotus ovatus in Crete, Greece. Molecular analysis of partial 16s rRNA sequence led to the discovery of a putative novel species of the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus. Investigation of the phylogenetic relationship between closely related sequences deposited in NCBI suggests that bacterial ancestors in gilthead seabream might have a pivotal role in the differentiation of genus.
1. Introduction
Epitheliocystis is a disease caused by intracellular bacteria that infect cells of the skin and respiratory epithelium of fish [1]. It is typically diagnosed by the observation of characteristic rounded inclusions—cysts—that are formed in a progressively hypertrophied host cell during the process of bacterial intracellular replication.
Since the intracellular nature of the infecting agents complicates the ability of in vitro cultivation, epitheliocystis is only studied during natural outbreaks, and it is closely observed mostly in aquaculture farmed species. In fact, following the first description of the disease in 1920 [2], a number of farmed fish has been reported to be affected by this condition to date, while only a small number of infections have been reported from wild host species (for an extended list of hosts and associated pathogens one might consult Blandford et al., 2018 [1]).
Aetiological agents causing epitheliocystis are host specific and include numerous members of the Chlamydial phylum (reviewed in Stride, Polkinghorne, and Nowak 2014 [3] updated in Blandford et al., 2018 [1]), and fewer but rising in number, proteobacteria including gamma-proteobacteria from the Endozoicomonas genus [4,5] and beta-proteobacteria [6,7,8,9].
Beta-proteobacteria are emerging as principal causative agents of mortalities in epitheliocystis mixed infections [6]. This phylum is receiving increasing attention since one of its members, the uncultured bacterium Ca. Branchiomonas cysticola [9], has been recently recognized as a major contributor to the complex gill disease [10], a multifactorial disease responsible for important economic losses in the Atlantic salmon aquaculture industry [11]. Epitheliocystis-related beta-proteobacteria include Ca. Branchiomonas cysticola, infecting salmonids in Norway, Ireland, Canada, and Chile [7,9,12,13,14,15], the clone BK-BJC, identified in epitheliocystis in the lake trout, Salvelinus namaycush in Canada [8], and Ca. Ichthyocystis affecting reared gilthead seabream Sparus aurata [6], and the greater amberjack Seriola dumerili [16] in the Mediterranean Sea. The Ca. Ichthyocystis genus currently includes only two species, Ca. Ichthyocystis hellenicum and Ca. Ichthyocystis sparus, coinfecting gilthead seabream in different farming areas of Greece [6] and a third putative agent in farmed greater amberjack [16]. The genus shares a common ancestor with the aforementioned clone BK-BJC and Ca. Branchiomonas cysticola and is of critical importance because currently, it comprises the only epitheliocystis-related beta-proteobacteria fully sequenced [6,17]. Their genomic analysis has, in fact, revealed a wide range of virulence factors and host-associated features [17], shedding light on the mechanisms that drive infection in epitheliocystis.
While most epitheliocystis cases are described in aquaculture fish species, as discussed earlier, uncultured wild-caught fish represent a rare excellent opportunity to explore the real extent of the environmental diversity of the agents causing this disease. In the present case report, we identified a putative novel species of the genus Ca. Ichthyocystis in a wild-caught pompano Trachinotus ovatus, (Linnaeus, 1758) (fam. Carangidae), individual from Crete, Greece, hosted in Cretaquarium, the public aquarium of the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (HCMR). The accidental findings of epitheliocystis combined with molecular data indicate that beta-proteobacteria from the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus have a wider host range and can potentially infect not only sparid but also carangid fish. The phylogenetic relationship between agents on different hosts is discussed to shape hypotheses on factors driving the evolution of the genus.
2. Materials and Methods
In January 2020, a case of mortality of wild-caught pompano, Trachinotus ovatus, was reported in the Cretaquarium, a public aquarium of the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (HCMR) in Gournes, Crete, Greece, in a tank dedicated to this fish species (single-species tank). To determine potential infectious causes of mortality in the tank, a freshly dead juvenile (9 cm in length) was brought to the microbiology laboratory of the Institute of Marine Biology, Biotechnology, and Aquaculture of the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research. The specimen was subjected to routine screening, including visual examination of mucous swabs and gills, dissection, and inspection of internal organs. Additionally, to exclude the possibility of a systemic infection, microbiological sampling of bacteria from the kidney was performed on 2% Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA 2%), and plates were inspected for growth for seven days. Following the observation of sporadic cyst-like structure in the gills (light microscopy), whole gill arches were preserved in 96% ethanol, RNA later, and 10% phosphate buffer formalin (PBF).
PBF preserved gill samples were used for histopathological examination. Fixed tissue was dehydrated in progressively increasing concentrations of ethanol (from 70 to 95%) and subsequently fixed in glycol methacrylate resin (Technovit 7100, Heraeus Kulzer, Germany) [18]. Thin sections of 4 μm were obtained with the use of a microtome (RM 2245 Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany), stained with a polychrome stain (methylene blue/azure II/basic fuchsin) [18], and visualized with a light microscope.
DNA extraction was performed on the 96% ethanol preserved gill arch, using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue kit (Qiagen inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) following the protocol Purification of Total DNA from Animal Tissues. Extracted DNA was PCR-amplified with primers for known epitheliocystis agents, including Endozoicomonas spp. [4] Ca. Ichthyocystis genus [6] and Chlamydial genus (16SIG F and 16SB1 primers) [19,20,21]. PCR products were run on 1% agarose gel and visualized with ethidium bromide transillumination. Positive 16S rRNA amplicons were purified using QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen), resuspended in ultrapure water, and sequenced using Sanger dideoxy sequencing technology (ABI3730xl). Sequenced chromatograms of both forward and reverse primers were quality inspected and aligned using Geneious 9.1. Consensus sequence was extracted and submitted to the NCBI database under the accession number OM658542.
To explore potential phylogenetic relations of the pathogen with other bacteria, its partial 16S rRNA sequence was blasted against the NCBI nucleotide database, and a selection of representative sequences with more than 90% identity was downloaded and aligned using Muscle v3.8.31 [22]. An alignment file was then used to build a maximum likelihood tree (1000 bootstrap) using MegaX (version 10.1.8) [23].
3. Results and Discussion
The sampled specimen did not display any external sign of disease (Figure 1a). Screening of mucous swabs and internal organs, and microbiological sampling of bacteria from the kidney, did not show the presence of pathogens. It was, therefore, suggested that unidentified factors other than infection or parasitism were causing the observed mortalities more likely connected to adaptation stress to captivity.
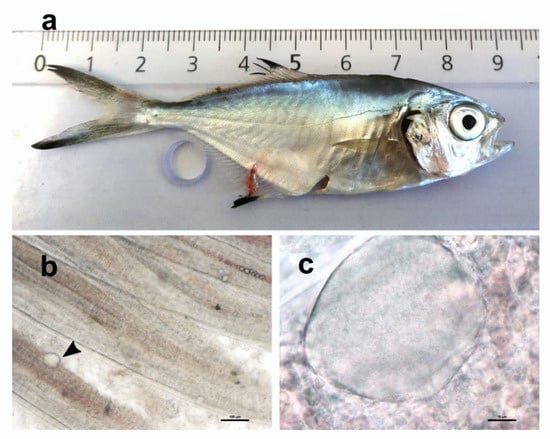

Figure 1.
(a) Sampled juvenile of pompano Trachinotus ovatus. (b) Wet mount of gill filaments visualized in the stereoscope showing a cyst-like structure (arrowhead). (c) Higher magnification of a cyst displaying granular content.
Wet mount of gill filaments indicated the infrequent presence of cyst-like structures with granular content (Figure 1b,c).
Epitheliocystis was confirmed through histology, with low intensity of infection of approximately 3 cysts in 30 filaments. Cysts were located on the secondary lamellae (Figure 2a,b) and were not associated with proliferative response, inflammation, and lesions. Inclusions had an approximate diameter of 50 μm and displayed a basophilic granular content (Figure 2b).
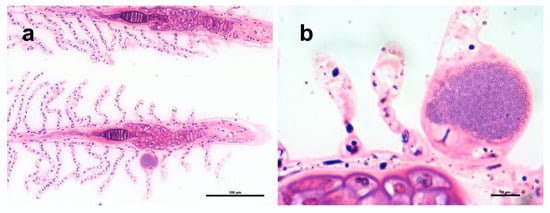
Figure 2.
Histopathology of Trachinotus ovatus gills, polychrome stain. (a) Gill filaments with a cyst on the lamella. (b) Higher magnification of a cyst with a characteristic granular texture.
Mortalities due to epitheliocystis, according to our knowledge, have never been reported in wild fish [24]. Under culture conditions, mortalities are usually associated with severe disruption of the respiratory tissue that likely causes the impairment of its functions. This includes cases in which high intensity of infection (estimated by the number of cysts per filament as in Stride and Nowak 2014 [25]) and extensive signs of host response (such as epithelial proliferation or fusion of lamellae) are observed (reviewed in [24]).
Contrarily to what is shown in other studies, where the high intensity of infection has been clearly related to mortalities [26], the low infection intensity observed here, together with the absence of epithelial proliferation or disruption of the gill epithelium, indicates that it is highly unlikely that epitheliocystis was the cause of mortality of pompano.
Since a growing number of bacteria and hosts have been associated with epitheliocystis [1] and only a generic report of the disease has been made on the pompano [27], we investigated the case further and attempted to attribute the lesions to a specific agent. Molecular analysis indicated that the gills were negative for chlamydial or Endozoicomonas spp. agents and positive for Ca. Ichthyocystis. Sequencing of the PCR product obtained with Ca. Ichthyocystis primers produced an 870 bp amplicon of high quality.
When the partial 16S rRNA sequence was blasted against the NCBI database, we found similarities with uncultured beta-proteobacteria sequences isolated from different fish hosts, including greater amberjack, Seriola dumerilii (fam: Carangidae), Pacific mackerel, Scomber japonicus (fam. Scombridae), Pacific herring, Clupea pallasii (Fam Clupeidae) and gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata (fam Sparidae) (Figure 3).
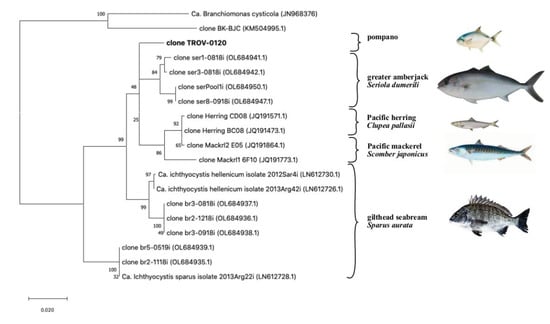
Figure 3.
Updated phylogeny of the Ca. Ichthyocystis following the sequencing of the partial 16s rRNA gene in pompano (clone TROV-0120, in bolt). Fish hosts from which sequences were obtained are shown on the right; other beta-proteobacteria known to cause epitheliocystis in fish, as clone BK-BJC [8] and Ca. Branchiomonas cysticola [9], are included as an outgroup. Highest log-likelihood tree (−4287.45) obtained in MegaX using the Maximum Likelihood method and the Tamura-Nei Model. The tree is drawn in scale using substitutions per site as a measure of branch length; percentage of trees in which sequences cluster together is shown on the branches.
The highest percentage of similarity was found with a cluster of sequences (97.5 to 97.9% identity) retrieved from epitheliocystis in greater amberjack in Crete, Greece [16]. Another group of sequences from Pacific herring and Pacific mackerel had a lower similarity (96.2 to 97.2% identity, 77% query cover). Finally, a similarity was found with sequences from the known Ca. Ichthyocystis genus previously identified from epitheliocystis lesions in gilthead seabream [6]. Specifically, the amplicon of the putative novel pathogen had an identity ranging between 95.9–96.1%, with sequences clustering with Ca. Ichthyocystis hellenicum and 93.3 to 92.7% with sequences clustering with Ca. Ichthyocystis sparus.
Although the full 16S rRNA sequence is required to define a new species, according to what was defined in Yarza et al., 2014 [28], a similarity of 97.9% with the closest relative (AN:OL684941.1) indicate that the bacterium causing epitheliocystis in Trachinotus ovatus probably belongs to a novel species of the genus Ca. Ichthyocystis. If this is the case, once again, a different bacterial species is observed in a different host, supporting the hypothesis that epitheliocystis agents are indeed host specific [1].
We observed that the novel sequence from pompano has the closest similarity to a bacterium found on another host belonging to the family Carangidae [16]; therefore, it seems that closely related agents are found on closely related hosts. Unfortunately, the low intensity of infection could not allow extraction of an adequate quantity of DNA to attempt whole genome sequencing of the putative novel agent. Such material would have been useful for comparative genomics and would offer better insights into the phylogenetic relationships between these pathogens.
Sequences from pompano, greater amberjack, Pacific mackerel, and Pacific herring share a single closer common ancestor with Ca. Ichthyocystis hellenicum and a more distant relative with Ca. Ichthyocystis sparus (Figure 3 and Figure 4). It might appear that the speciation event occurring between Ca. Ichthyocystis sparus and Ca. Ichthyocystis hellenicum emerged prior to the one parting Ca. Ichthyocystis hellenicum from agents in other hosts. The analysis of the partial 16S rRNA genes shows, therefore, that two different consecutive events lead to the speciation of bacteria in gilthead seabream (Figure 4, red dots) before epitheliocystis agents differentiated in other hosts (Figure 4, blue dot). This finding highlights the possibility that a beta-proteobacterium of the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus in Sparus aurata is an ancestor of the agents found in pompano, greater amberjack, Pacific mackerel, and Pacific herring.
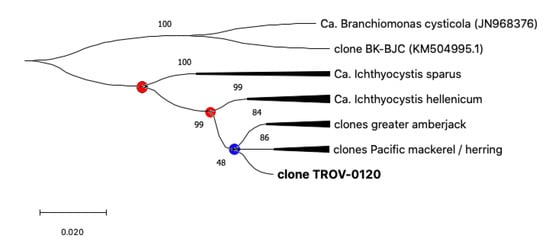
Figure 4.
Phylogeny tree of the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus. All bacterial sequences from the same host are condensed into single branches to highlight evolutionary events leading to speciation (dots). Events that lead to the speciation of bacteria in gilthead seabream are highlighted with red dots, while the blue dot is used to indicate differentiation in other hosts.
Intensive aquaculture conditions, including the high density of hosts and stress, are believed to promote epitheliocystis intensity and disease development [1,24,29]. Gilthead seabream is one of the first fish species traditionally cultivated in the Mediterranean, initially extensively in coastal lagoons and saltwater ponds, and afterward (from the 1980s) intensively in seawater cages in the Mediterranean and coastal regions of the European Atlantic Ocean [30,31]. Of the other hosts related to Ca. Ichthyocystis agents in this study, only the greater amberjack has been recently cultivated, mostly in Spain, Greece, Malta, and Italy [32].
Potential roles of gilthead seabream in the evolution of the genus Ca. Ichthyocystis might be explored in the future by screening other wild and farmed sparids, while the impact of aquaculture on speciation dynamics might be discussed if other epitheliocystis agents from intensively reared species, such as the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax), are identified in early branches of the clade. Interestingly, epitheliocystis hyper infections have been reported in European seabass [33]. Crespo and colleagues in 2001 [33] suggest morphological similarity of the infectious agent in European seabass with the ones observed in gilthead seabream [34] and greater amberjack [35], currently associated with the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus.
The current study, as well as the one on seabream [6] and a second one on greater amberjack [16], were all conducted in Greece; consequently, it might appear that the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus is especially present in the Eastern Mediterranean. On the other hand, to our understanding, most studies investigating the nature of epitheliocystis (or generally assessing gill health) in fish do not screen for this genus, potentially leading to an underestimation of the number of host species and geographic areas affected.
The presence of Ca. Ichthyocystis and epitheliocystis in natural populations of herring and mackerel must be verified. The NCBI-deposited sequences obtained from these fishes were produced during a study investigating bacterial diversity in dietary fish used to feed marine mammals in San Diego Bay of California and were not focused on epitheliocystis [36]. Bik and colleagues did not use gills but whole homogenized fish in their study; therefore, these sequences might not be associated with lesions. Moreover, since the aforementioned study was focused on mammals, the origin of the dietary fish from which the sequences were produced was not specified. Considering that the Pacific mackerel is not a Mediterranean species [37], confirming the presence of these agents in this host might lead to the expansion of the Ca. Ichthyocystis genus in other geographic regions.
4. Conclusions
This study extends the list of the beta-proteobacteria associated with epitheliocystis with the addition of a putative novel species of the genus Ca. Ichthyocystis. The genus currently comprises pathogens found in Sparidae, Carangidae, and potentially also Scombridae and Clupeidae.
Further screening of fish gills with Ca. Ichthyocystis-specific primers might be required to better appreciate the full extent of the diversity of these agents, their phylogenetic relationship, and attempt to understand the factors driving their evolution.
Funding
The research work was supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) under the HFRI Ph.D. Fellowship grant (Fellowship Number: 253).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, because no experiment was performed. The observations made were part of the routine health assessment of fish mortalities occuring in Cretaquarium and HCMR.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data have been provided in the paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the staff of Cretaquarium and especially Chrysa Doxa.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Blandford, M.I.; Taylor-Brown, A.; Schlacher, T.A.; Nowak, B.; Polkinghorne, A. Epitheliocystis in fish: An emerging aquaculture disease with a global impact. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plehn, M. Neue Parasiten in Haut and Kiemen von Fischen. Ichthyochytrium Mucophilus Zent. Bakteriol. Parasitenkd. Abt. 1920, 1, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Stride, M.C.; Polkinghorne, A.; Nowak, B.F. Chlamydial infections of fish: Diverse pathogens and emerging causes of disease in aquaculture species. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katharios, P.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Fehr, A.; Mateos, J.M.; Qi, W.; Richter, D.; Nufer, L.; Ruetten, M.; Guevara Soto, M.; Ziegler, U.; et al. Environmental marine pathogen isolation using mesocosm culture of sharpsnout seabream: Striking genomic and morphological features of novel Endozoicomonas sp. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, M.; Güiza, L.; Martinez, X.; Caraballo, X.; Rojas, J.; Aranguren, L.F.; Salazar, M. A novel agent (Endozoicomonas elysicola) responsible for epitheliocystis in cobia Rachycentrum canadum larvae. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2013, 106, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Dourala, N.; Fehr, A.; Qi, W.; Katharios, P.; Ruetten, M.; Mateos, J.M.; Nufer, L.; Weilenmann, R.; Ziegler, U.; et al. Emerging pathogens of gilthead seabream: Characterisation and genomic analysis of novel intracellular β-proteobacteria. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1791–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.O.; Steinum, T.M.; Toenshoff, E.R.; Kvellestad, A.; Falk, K.; Horn, M.; Colquhoun, D.J. Candidatus Branchiomonas cysticola is a common agent of epitheliocysts in seawater-farmed atlantic salmon Salmo salar in Norway and Ireland. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2013, 103, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contador, E.; Methner, P.; Ryerse, I.; Huber, P.; Lillie, B.N.; Frasca, S.; Lumsden, J.S. Epitheliocystis in lake trout Salvelinus namaycush (Walbaum) is associated with a β-proteobacteria. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toenshoff, E.R.; Kvellestad, A.; Mitchell, S.O.; Steinum, T.; Falk, K.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Horn, M. A novel betaproteobacterial agent of gill epitheliocystis in seawater farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gjessing, M.C.; Spilsberg, B.; Steinum, T.M.; Amundsen, M.; Austbø, L.; Hansen, H.; Colquhoun, D.; Olsen, A.B. Multi-agent in situ hybridization confirms Ca. Branchiomonas cysticola as a major contributor in complex gill disease in Atlantic salmon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. Rep. 2021, 2, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Thompson, K.D.; Ashby, A.; Rodger, H.D.; Dagleish, M.P. Complex gill disease: An emerging syndrome in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J. Comp. Pathol. 2018, 163, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.M.; Lennox, R.J.; Twardek, W.M.; Teffer, A.K.; Robertson, M.J.; Miller, K.M.; Cooke, S.J. Serial sampling reveals temperature associated response in transcription profiles and shifts in condition and infectious agent communities in wild Atlantic salmon. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 2086–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, S.; Tsairidou, S.; Jayasuriya, N.; Sobolewska, H.; Hamilton, A.; Lobos, C.; Houston, R.D.; Rodger, H.; Bron, J.; Herath, T. Assessment of marine gill disease in farmed atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in chile using a novel total gross gill scoring system: A case study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.K.; Vanderstichel, R.; Kaukinen, K.; Nekouei, O.; Laurin, E.; Miller, K.M. Infectious agent detections in archived Sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) samples from British Columbia, Canada (1985–94). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.K.; Vanderstichel, R.; Li, S.; Laurin, E.; Tucker, S.; Neville, C.; Tabata, A.; Miller, K.M. A comparison of infectious agents between hatchery-enhanced and wild out-migrating juvenile chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) from Cowichan River, British Columbia. Facets 2018, 3, 695–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cascarano, M.C.; Ruetten, M.; Vaughan, L.; Tsertou, M.I.; Georgopoulou, D.; Keklikoglou, K.; Papandroulakis, N.; Katharios, P. Epitheliocystis in Greater Amberjack: Evidence of a Novel Causative Agent, Pathology, Immune Response and Epidemiological Findings. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Vaughan, L.; Katharios, P.; Schlapbach, R.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B. Host-Associated Genomic Features of the Novel Uncultured Intracellular Pathogen Ca. Ichthyocystis Revealed by Direct Sequencing of Epitheliocysts. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 1672–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, H.S.; Wyrick, A.D.; Lee, S.W.; McNeil, J.H. Science and art in preparing tissues embedded in plastic for light microscopy, with special reference to glycol methacrylate, glass knives and simple stains. Stain Technol. 1976, 51, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukatsu, T.; Nikoh, N. Two intracellular symbiotic bacteria from the mulberry psyllid Anomoneura mori (Insecta, Homoptera). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everett, K.D.E.; Bush, R.M.; Andersen, A.A. Emended description of the order Chlamydiales, proposal of Parachlamydiaceae fam. nov. and Simkaniaceae fam. nov., each containing one monotypic genus, revised taxonomy of the family Chlamydiaceae, including a new genus and five new species, and standards. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draghi, A.; Popov, V.L.; Kahl, M.M.; Stanton, J.B.; Brown, C.C.; Tsongalis, G.J.; West, A.B.; Frasca, S. Characterization of “Candidatus Piscichlamydia salmonis”(order Chlamydiales), a Chlamydia-like bacterium associated with epitheliocystis in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5286–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) for macOS. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, B.F.; LaPatra, S.E. Epitheliocystis in fish. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stride, M.C.; Nowak, B.F. Epitheliocystis in three wild fish species in Tasmanian waters. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katharios, P.; Papadaki, M.; Papandroulakis, N.; Divanach, P. Severe mortality in mesocosm-reared sharpsnout sea bream Diplodus puntazzo larvae due to epitheliocystis infection. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2008, 82, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landsberg, J.H.; Newton, J.; Cullen, J. Ecotoxicology and Histopathology Conducted in Response to Sea Turtle and Fish Mortalities along the Texas Coast: May–June 1994. Rep. NMFS 1998, 143, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, F.P. Aquaculture disease and health management. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4201–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, L.; Moretti, A.; Crosetti, D.; Karaiskou, N.; Magoulas, A.; Rossi, A.R.; Rye, M.; Triantafyllidis, A.; Tsigenopoulos, C.S. Gilthead seabream—Sparus aurata. Genet. Impact Aquac. Act. Nativ. Popul. 2007, 47. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Philip-Mcginnity/publication/268359165_Research_Priorities_for_Modelling/links/547459fb0cf2778985abd9ef/Research-Priorities-for-Modelling.pdf#page=47 (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Pavlidis, M.A.; Mylonas, C.C. Sparidae: Biology and Aquaculture of Gilthead Sea Bream and Other Species; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 1444392204. [Google Scholar]
- Jerez Herrera, S.; Vassallo Agius, R. FAO 2022. Seriola Dumerili. Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme. Fisheries and Aquaculture Division. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/culturedspecies/seriola_dumerili/en (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Crespo, S.; Zarza, C.; Padrós, F. Short communication Epitheliocystis hyperinfection in sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.): Light and electron microscope observations. J. Fish Dis. 2001, 24, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, S.; Zarza, C.; Padros, F.; de Mateo, M.M. Epitheliocystis agents in sea bream Sparus aurata: Morphological evidence for two distinct chlamydia-like developmental cycles. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1999, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, A.; Crespo, S. Epitheliocystis in the wild and cultured amberjack, Seriola dumerili Risso: Ultrastructural observations. Aquaculture 1991, 95, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, E.M.; Costello, E.K.; Switzer, A.D.; Callahan, B.J.; Holmes, S.P.; Wells, R.S.; Carlin, K.P.; Jensen, E.D.; Venn-Watson, S.; Relman, D.A. Marine mammals harbor unique microbiotas shaped by and yet distinct from the sea. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, D. Synopsis of the Biological Data on the Pacific Mackerel, Scomber Japonicus, Houttuyn (Northeast Pacific); FAO Fisheries Synopsys 40; Bureau of Commercial Fisheries: Washinghton, DC, USA, 1969; Circular 302. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).