Design and Research on the Preparation of Pervious Concrete Using Carbonized Steel Slag as a Full Component
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Mix Proportion Design
2.3. Specimen Preparation
2.4. Performance Testing
3. Results
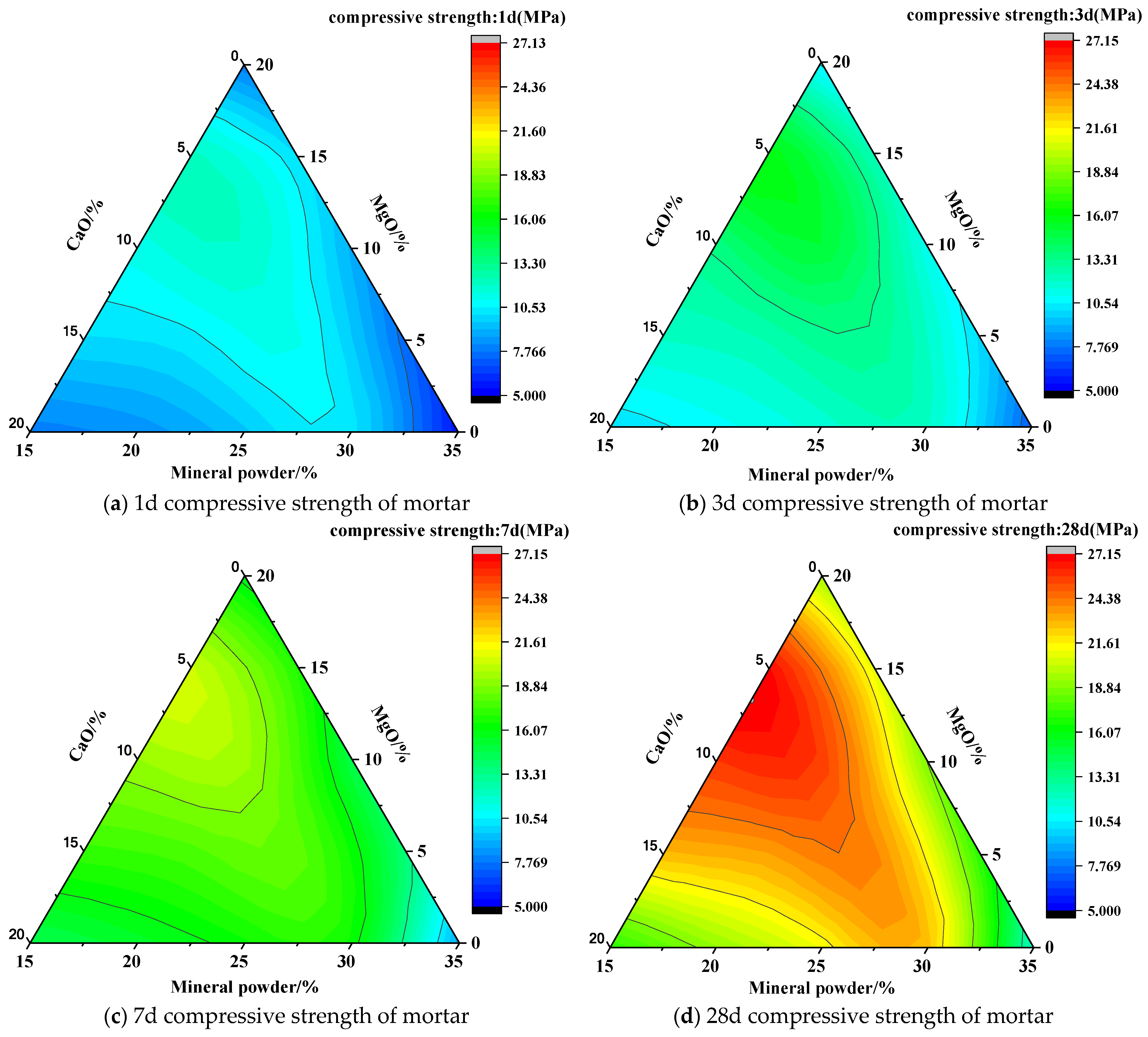
3.1. Design of the Carbonated Steel Slag Cementitious System
3.1.1. Effect of Carbonated Steel Slag Cementitious System Composition on Strength
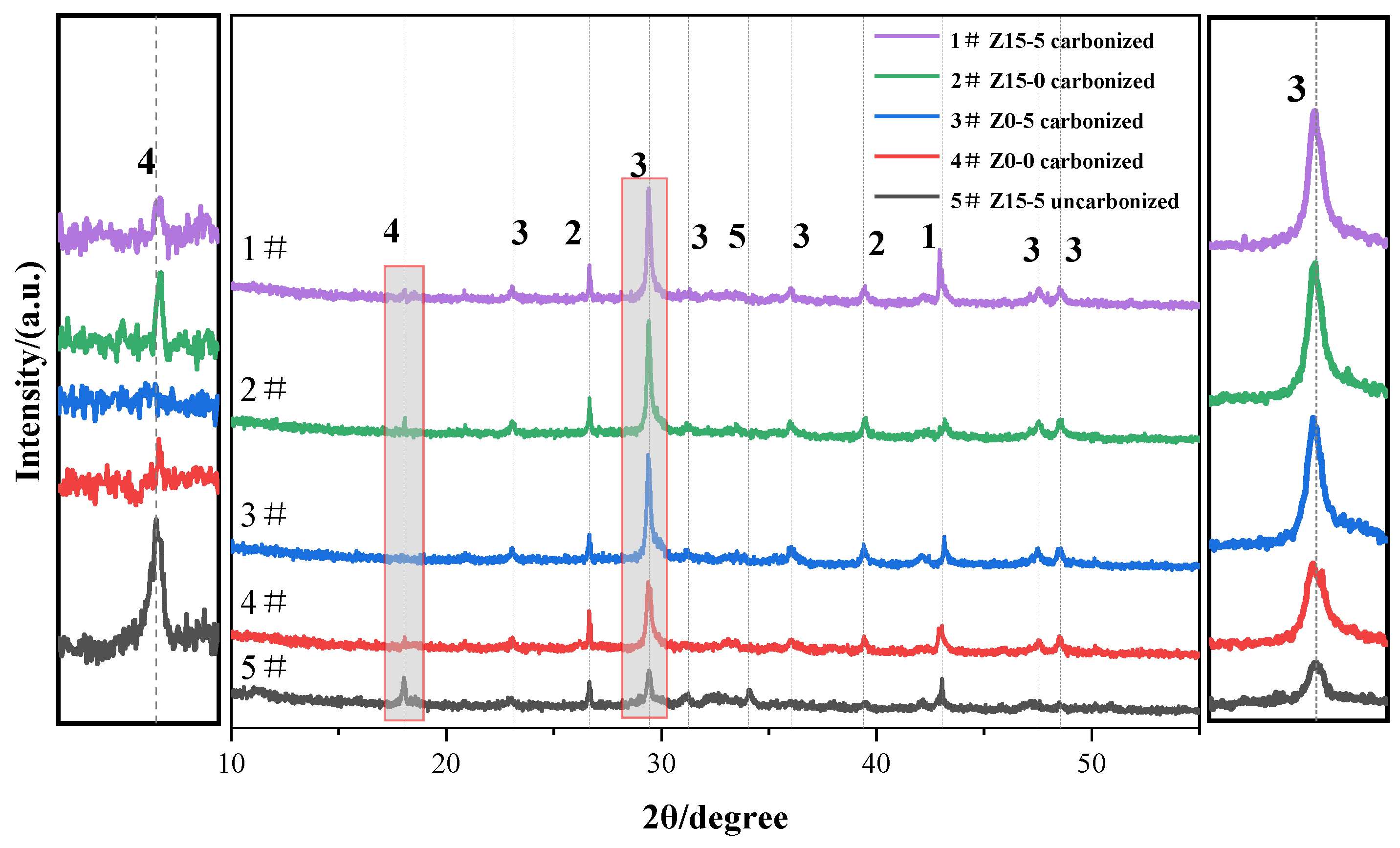
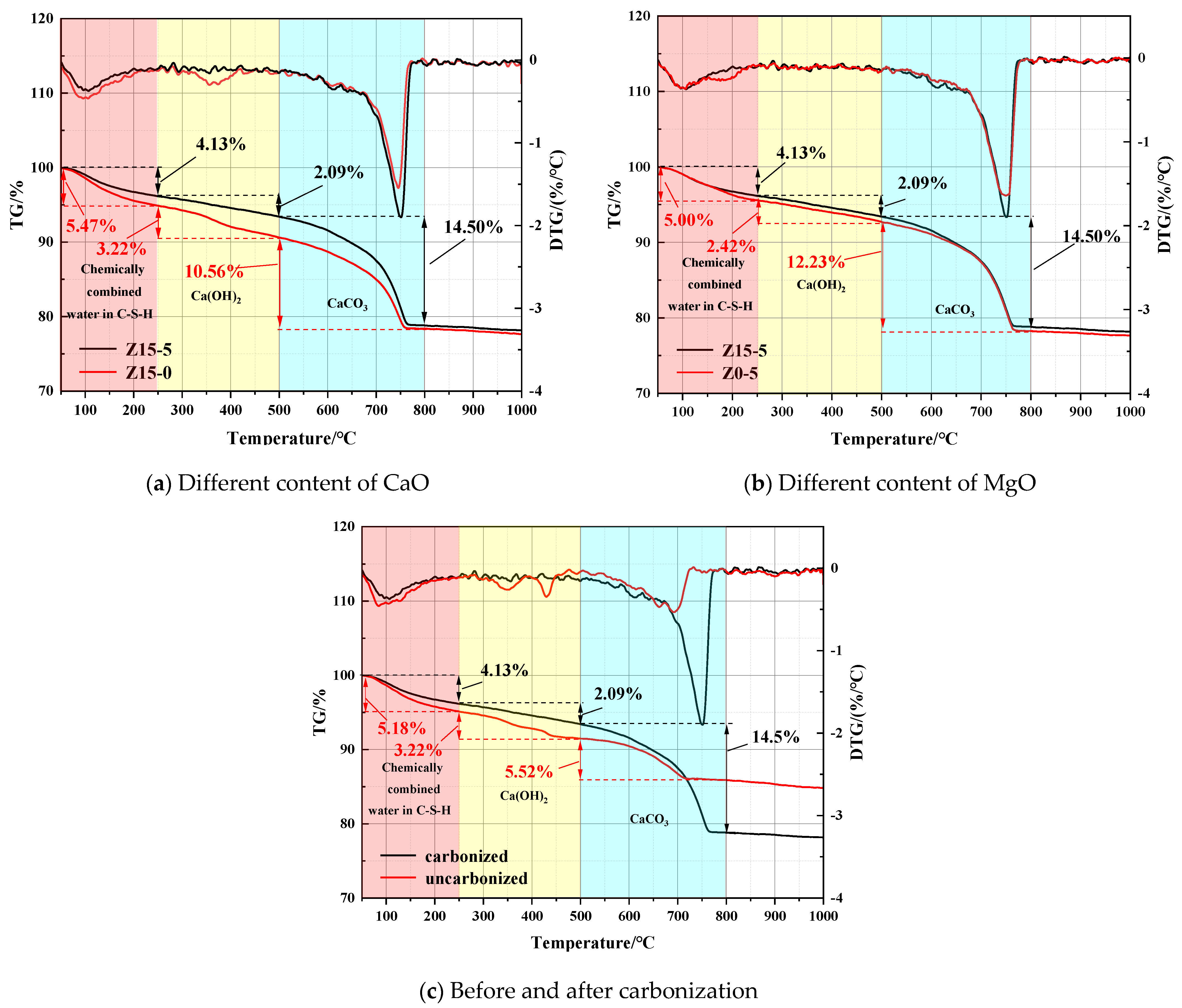
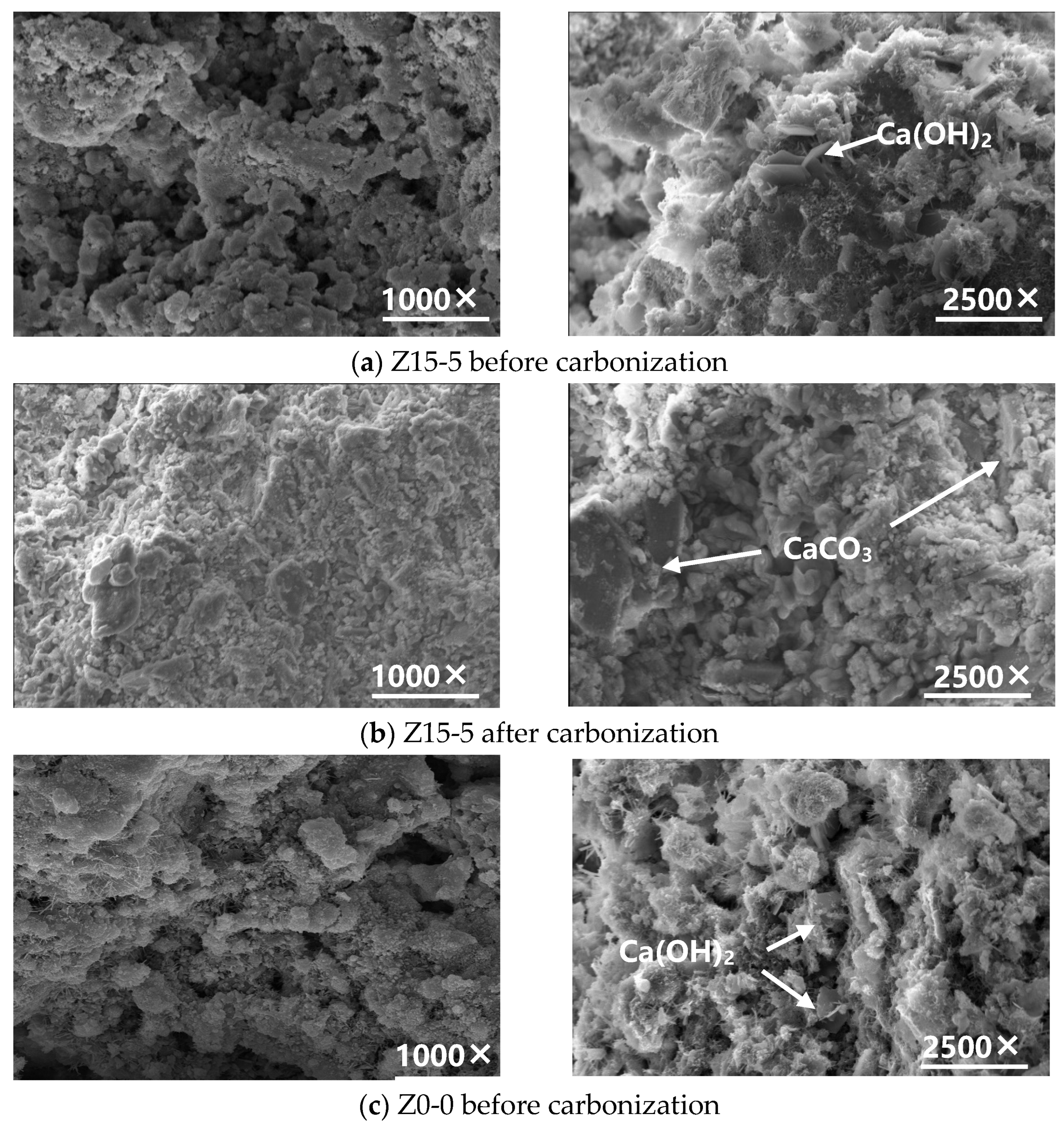
3.1.2. Microstructural Analysis of the Carbonated Steel Slag Cementitious System
3.2. Research on Carbonated Steel Slag Pervious Concrete
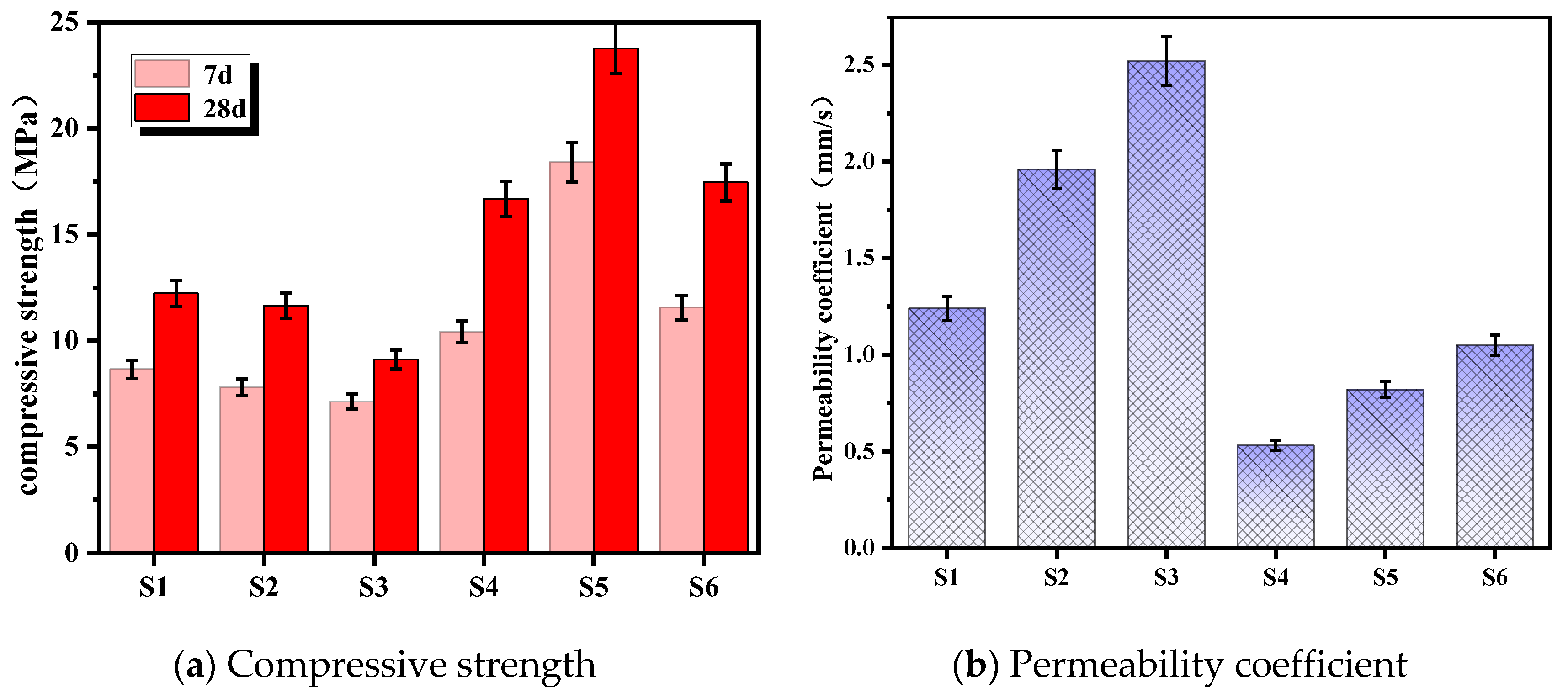
3.2.1. Effect of Gradation on Permeability and Mechanical Properties
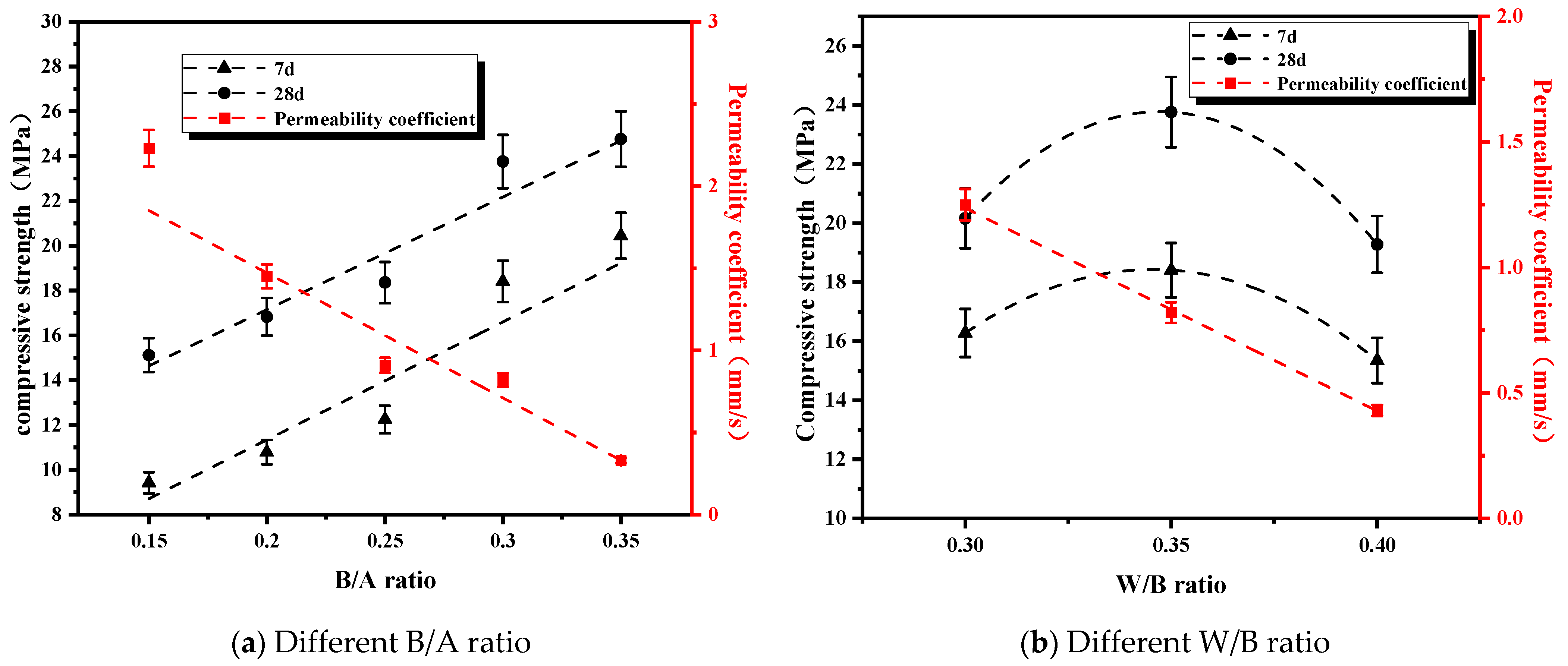
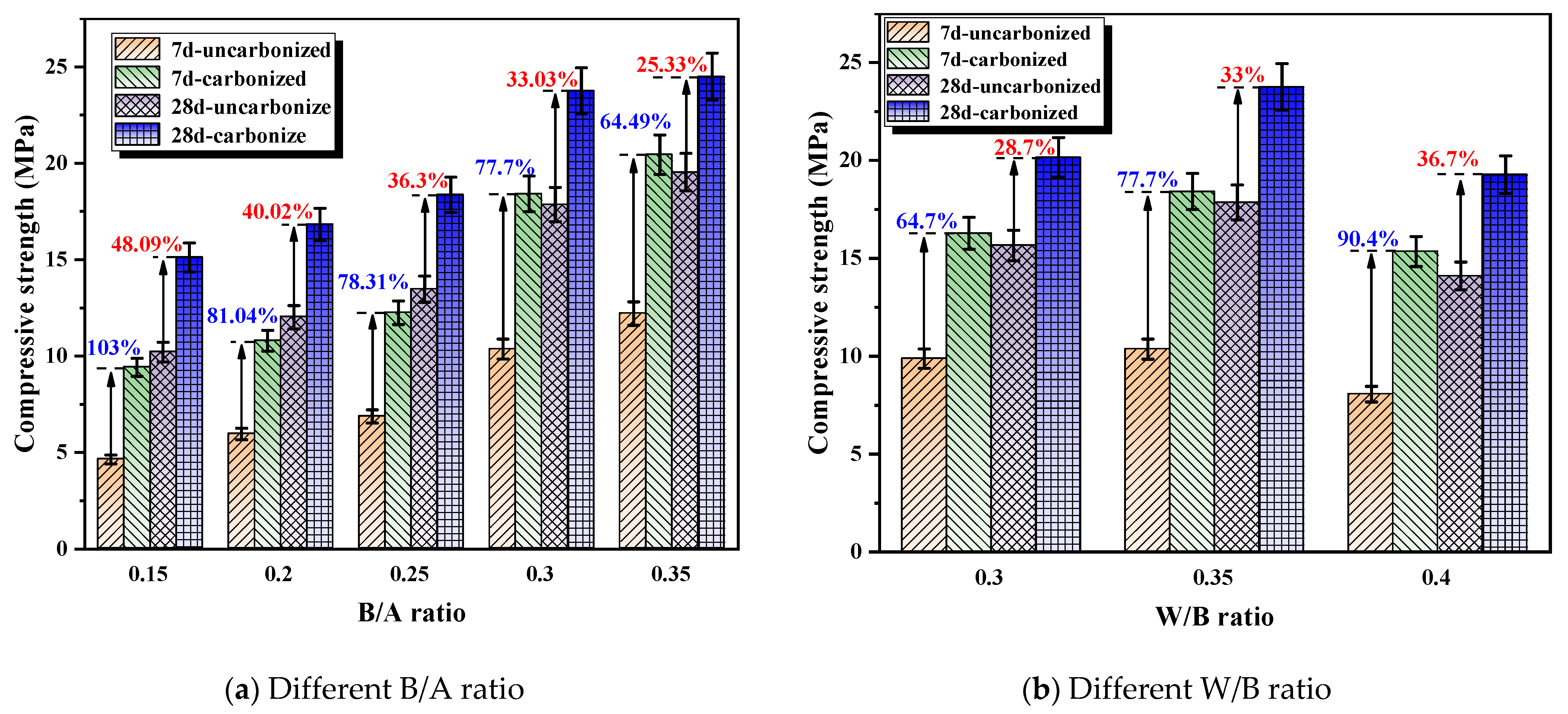
3.2.2. Effects of B/A Ratio and W/B Ratio on Permeability and Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.C.; Li, B. Low carbon transition path of China′s iron and steel industry under global temperature-control target. Iron Steel 2019, 54, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.Y.; Huang, K.; Jiang, H.Q. Research on Physical Properties and Durability of Pervious Cement Concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2007, 10, 583–587. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, J.D.; Arenas, C.; Cifuentes, H.; Peceño, B.; Leiva, C. Porous Structure by X-Ray Computed Tomography and Sound Absorption in Pervious Concretes with Air Cooled Blast Furnace Slag as Coarse Aggregate. Acoust. Aust. 2019, 47, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, L.; Duan, H.J.; Chen, B. Properties of pervious concrete made from steel slag and magnesium phosphate cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.T.; Chen, X.Q.; Dong, Q.; Yuan, J.; Hong, Q. Mechanical performance study of pervious concrete using steel slag aggregate through laboratory tests and numerical simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y. Influence of Steel Slag Powder on Compressive Strength and Durability of Concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2005, 8, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.G.; Zhao, S.Y.; Wu, G.L.; He, Y.G.; Wen, Z.Y. Compensation effect of converter steel slag powder on the shrinkage of hardened mortar prepared by ground granulated blast furnace slag and Portland cement. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2006, 2, 290–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Mo, L.W.; Deng, M.; Cai, Y. Effect of Carbonation Curing on Mechanical Strength and Microstructure of Mortars Prepared with Steel Slag-Cement-MgO-CaO Blends. J. Build. Mater. 2017, 20, 854–861. [Google Scholar]
- Panesar, D.K.; Mo, L. Properties of binary and ternary reactive MgO mortar blends subjected to CO2 curing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 38, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.F.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Kong, J.; Chang, J. A Review on Carbonation of Steel Slag and Its Application in Building Materials. Mater. Rep. 2020, 34, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Ling, T.C.; Shi, C.J.; Pan, S.-Y. Characteristics of steel slags and their use in cement and concrete—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wu, H.Z. Study on carbonation mechanism of steel slag. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 38, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.D.; Yang, Q.B. Effect of Carbonation Curing on Durability of Carbon Fixing Steel Slag Slaked Lime Brick. J. Build. Mater. 2023, 26, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, M.L.; Fang, Y. Influence of magnesium hydroxide content and fineness on the carbonation of calcium hydroxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 55, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.W.; Zhang, F.; Deng, M. Effects of carbonation treatment on the properties of hydrated fly ash-MgO-Portland cement blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- CJJ/T 135-2009; Technical Specification for Pervious Cement Concrete Pavements. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.X.; Qi, L.Q. Effects of temperature and carbonation curing on the mechanical properties of steel slag-cement binding materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, I.; Andrade, C.; Castellote, M. Natural and accelerated CO2 binding kinetics in cement paste at different relative humidities. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 49, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desilva, P.; Bucea, L.; Sirivivatnanon, V. Chemical, microstructural and strength development of calcium and magnesium carbonate binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B.Q. A Study on Mix Proportions Design and Performance of Porous Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.; Hu, J.; Ramos, A. The effect of the cementitious paste thickness on the performance of pervious concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
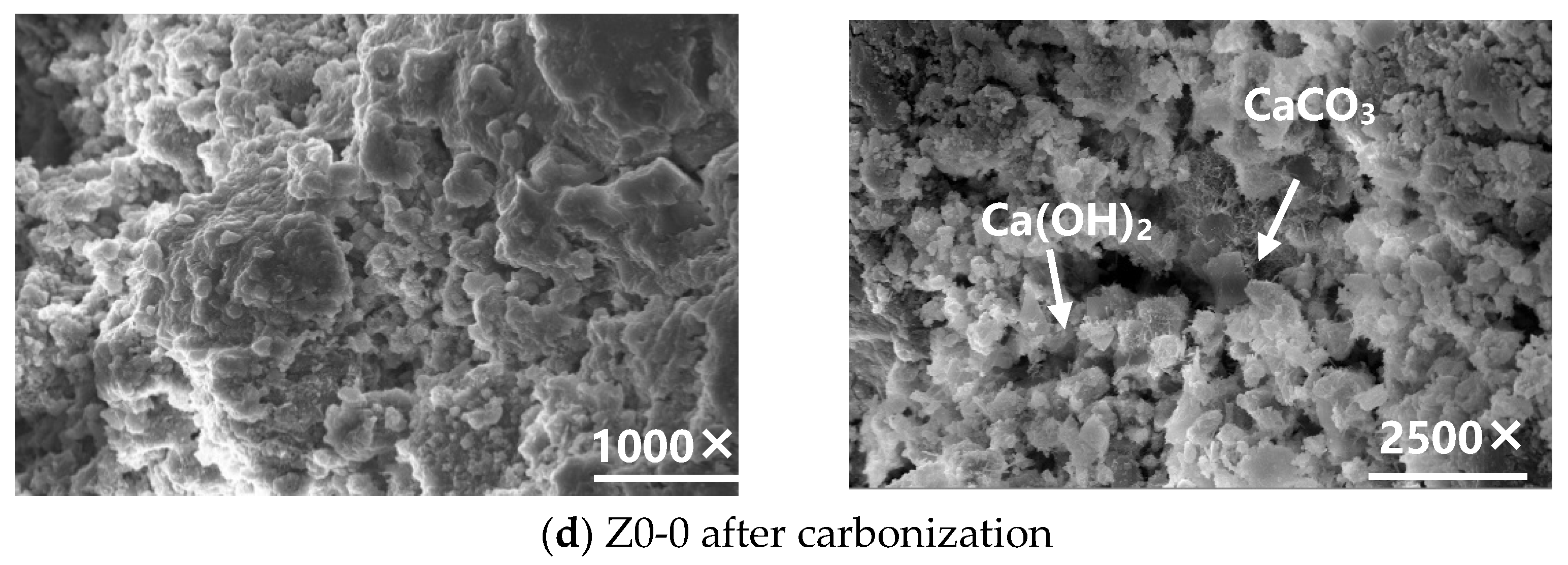

| Chemical Composition | MnO | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | Fe2O3 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel slag | 4.19 | 9.24 | 4.22 | 18.57 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 36.77 | 19.85 | 0.06 |
| Cement | 1.33 | 2.57 | 6.65 | 21.96 | 2.46 | 0.40 | 57.92 | 3.34 | 3.42 |
| Lime | 0.05 | 13.39 | 0.13 | 1.63 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 82.19 | 0.11 | 2.15 |
| Reactive MgO | 0.06 | 88.52 | 0.42 | 2.76 | 0.61 | 0.03 | 3.18 | 0.26 | 3.62 |
| Mineral powder | 0.25 | 7.81 | 13.60 | 29.73 | 1.94 | 0.47 | 41.23 | 0.33 | 1.07 |
| Loose Packing Voidage (%) | Apparent Density (g·cm−3) | Crush Value (%) | f-CaO Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 38.8 | 3.10 | 16.5 | 3.4 |
| Sample | Cement/% | Steel Slag/% | Mineral Powder/% | MgO/% | CaO/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z0-20 | 25 | 40 | 15 | 0 | 20 |
| Z5-15 | 15 | 5 | 15 | ||
| Z10-10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | ||
| Z15-5 | 15 | 15 | 5 | ||
| Z20-0 | 15 | 20 | 0 | ||
| Z0-15 | 20 | 0 | 15 | ||
| Z5-10 | 20 | 5 | 10 | ||
| Z10-5 | 20 | 10 | 5 | ||
| Z15-0 | 20 | 15 | 0 | ||
| Z0-10 | 25 | 0 | 10 | ||
| Z5-5 | 25 | 5 | 5 | ||
| Z10-0 | 25 | 10 | 0 | ||
| Z0-5 | 30 | 0 | 5 | ||
| Z5-0 | 30 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Z0-0 | 35 | 0 | 0 |
| Sample | Particle Size |
|---|---|
| S1 | 2.36–4.75 mm |
| S2 | 4.75–9.5 mm |
| S3 | 9.5–16 mm |
| S4 | 2.36–4.75 mm:9.5–16 mm = 4:6 |
| S5 | 2.36–4.75 mm:4.75–9.5 mm = 4:6 |
| S6 | 4.75–9.5 mm:9.5–16 mm = 5:5 |
| Sample | B/A Ratio | W/B Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | 0.15 | 0.35 |
| G2 | 0.20 | 0.35 |
| G3 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| G4 | 0.30 | 0.35 |
| G5 | 0.35 | 0.35 |
| G6 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| G7 | 0.30 | 0.40 |
| Sample | C-S-H Gel Dehydration/% | Decomposition of Ca(OH)2/% | Decomposition of CaCO3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncarbonized Z15-5 | 5.18 | 3.22 | 5.52 |
| Carbonized Z15-5 | 4.13 | 2.09 | 14.50 |
| Z15-0 | 5.47 | 3.22 | 10.56 |
| Z0-5 | 5.00 | 2.42 | 12.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, M. Design and Research on the Preparation of Pervious Concrete Using Carbonized Steel Slag as a Full Component. Buildings 2025, 15, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091526
Chen X, Zhang K, Wang B, Wu Z, Zhou M. Design and Research on the Preparation of Pervious Concrete Using Carbonized Steel Slag as a Full Component. Buildings. 2025; 15(9):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091526
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiao, Kai Zhang, Benren Wang, Zhiqiang Wu, and Mingkai Zhou. 2025. "Design and Research on the Preparation of Pervious Concrete Using Carbonized Steel Slag as a Full Component" Buildings 15, no. 9: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091526
APA StyleChen, X., Zhang, K., Wang, B., Wu, Z., & Zhou, M. (2025). Design and Research on the Preparation of Pervious Concrete Using Carbonized Steel Slag as a Full Component. Buildings, 15(9), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091526





