Advancing Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Performance, Crack Resistance Mechanism, and Future Innovations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Crack Development and Growth
3. Effectiveness of Fibers Before and After Crack Formation
4. Influence of Different Fibers on Concrete Behavior and Characteristics
4.1. Workability
4.2. Compressive Strength
4.3. Splitting Tensile Strength
4.4. Flexural Strength
4.5. Ductility and Toughness
4.6. SEM Characterization of Fiber–Matrix Interaction in FRC
5. Addressing Knowledge Gaps and Shaping Future Research in FRC
- Investigating Hybrid Fiber Interactions:
- Advanced imaging techniques such as micro-CT scanning and SEM analysis play a crucial role in understanding the multi-scale interactions between ST and SYN fibers in hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete (HFRC). These techniques provide detailed, high-resolution images of the concrete’s internal structure at different scales, allowing researchers to observe the fibers’ distribution, alignment, and interaction with the surrounding matrix.
- Micro-CT scanning offers three-dimensional imaging, enabling the visualization of the fiber–matrix interface and the porosity within the concrete at a microstructural level. This technique helps in identifying how fibers are distributed within the matrix, whether they are well dispersed or aggregated, and how this affects the overall performance of the material. It can also reveal the interactions between different types of fibers, such as ST and SYN, and their respective roles in improving concrete’s mechanical properties [293,294,295].
- Fiber Design Innovations:
- Research should explore novel fiber designs, such as three-dimensional geometries or chemically modified surfaces, to improve bonding properties.
- Integration of Functional and Smart Fibers:
- ST fibers with electrical conductivity or SYN fibers impregnated with nanomaterials could improve the dual functionality of concrete.
- Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials:
- These developments could reduce the environmental impact while maintaining or enhancing the mechanical and durability characteristics of HPFRC.
- Enhanced Testing Methodologies:
- This approach will enhance the understanding of the long-term durability of HPFRC and the contributions of ST and SYN fibers in real-world conditions.
- Synergistic Benefits of Hybrid ST and SYN Fibers in Concrete:
- Final Observations:
- While ST and SYN fibers have proven effective in improving concrete performance, further research is essential to optimize their potential.
- Future studies should address the existing knowledge gaps and explore innovative solutions for developing the next generation of HPFRC materials.
6. Conclusions
- Overview of Findings:
- The review analyzed the effects of ST and SYN fibers on concrete’s workability, mechanical properties, and microstructure.
- Fiber reinforcement plays a vital role in HPFRC, enhancing durability, strength, and resistance under various loading and environmental conditions.
- Key Points:
- ST fibers reduce workability due to their stiffness and increased density, making placement and compaction challenging.
- SYN fibers have less impact on workability, but issues may arise at higher dosages.
- Fiber type, content, shape, and surface treatment influence workability and performance.
- Future Research Directions:
- Focus on admixtures, mix designs, and enhanced placement methods to reduce fiber-related workability issues.
- Explore hybrid ST and SYN fiber systems for improved crack resistance, ductility, and energy absorption.
- Investigate surface treatments for SYN fibers to improve adhesion and bonding with the matrix.
- Microstructural Insights:
- SEM analysis shows that ST fibers promote strong mechanical interlocking and crack-bridging.
- SYN fibers are effective in bridging micro-cracks but require surface modification for better adhesion.
- Long-Term Performance and Sustainability:
- More research is needed to understand FRC’s performance under prolonged mechanical, thermal, and chemical stress.
- The environmental impact of fiber production and the recyclability of FRC should be explored.
- Incorporating sustainable fibers and smart fibers for health monitoring and damage detection holds great potential.
- Collaboration and Standardization:
- Collaboration between academia and industry is crucial to convert research into practical applications.
- Standardizing testing procedures and performance criteria will encourage wider adoption of FRC.
- Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of different fiber types and doses will help identify economical solutions.
- Optimal Ratio and Distribution: Determining the optimal ratio and distribution of ST and SYN fibers within the concrete matrix is a key challenge. The differences in characteristics, such as fiber length, stiffness, and surface properties, complicate the blending process, making it difficult to fully optimize their synergistic effects. Achieving uniform dispersion of both fiber types is critical, as uneven distribution can diminish their effectiveness in enhancing concrete strength and durability.
- Economic and Environmental Considerations: The increased cost of fiber reinforcement presents a challenge in terms of the economic feasibility of using hybrid systems on a larger scale. Additionally, understanding the long-term behavior of hybrid fiber systems under various environmental conditions, including freeze–thaw cycles, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures, is essential. Addressing these challenges will require extensive research and development to improve the effectiveness, practicality, and sustainability of hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete in construction applications.
- The use of HPFRC on infrastructure projects: High-performance fiber-reinforced concrete (HPFRC) is increasingly being utilized in infrastructure projects due to its enhanced strength and durability. It is particularly suitable for applications such as seismic retrofitting of bridge columns, strengthening of parking garage slabs, and the replacement of bridge decks. The superior resistance of HPFRC to cracking, corrosion, and environmental degradation makes it ideal for structures exposed to harsh conditions, where traditional materials may deteriorate over time. Its ability to incorporate various types of fibers, such as steel and synthetic fibers, provides added benefits like improved crack resistance and better post-cracking behavior. Additionally, HPFRC’s lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of structures, enhancing their seismic performance and reducing the load on foundations. The material’s high toughness and energy absorption capabilities also contribute to its ability to withstand dynamic and extreme loads. HPFRC can be tailored to meet specific project requirements, offering greater flexibility in design and cost-effectiveness. As the demand for more sustainable and high-performing infrastructure grows, HPFRC presents an ideal solution for constructing durable, resilient, and efficient structures.
- Final Remarks:
- This review consolidates the existing knowledge on ST and SYN fibers, highlighting their benefits, challenges, and opportunities.
- It provides valuable insights for developing advanced FRC materials tailored to meet the needs of modern construction while ensuring durability and sustainability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aïtcin, P.C. Cements of yesterday and today: Concrete of tomorrow. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K. Advancements in concrete technology. Concr. Int. 1999, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, C. Concrete and sustainable development. ACI Spec. Publ. 2002, 206, 501–512. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.Y.; Peng, G.F.; Chan, J.K. Comparison between high strength concrete and normal strength concrete subjected to high temperature. Mater. Struct. 1996, 29, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.M.; Brooks, J.J. Concrete Technology; Longman Scientific & Technical: London, UK, 1987; Volume 438. [Google Scholar]
- Paktiawal, A.; Alam, M. Experimental evaluation of sorptivity for high strength concrete reinforced with zirconia rich glass fiber and basalt fiber. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Abbas, S.; de Azevedo AR, G.; Marvila, M.T.; Khan, M.I.; Rafiq, W. Experimental and analytical investigation on the confinement behavior of low strength concrete under axial compression. Structures 2022, 36, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golewski, G.L. The phenomenon of cracking in cement concretes and reinforced concrete structures: The mechanism of cracks formation, causes of their initiation, types and places of occurrence, and methods of detection—A review. Buildings 2023, 13, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Belie, N.; Lenehan, J.J.; Braam, C.R.; Svennerstedt, B.; Richardson, M.; Sonck, Y. Durability of building materials and components in the agricultural environment, Part III: Concrete structures. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 76, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalis, S.A.; Lampropoulos, A.P. Developments in the use of ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete as strengthening material. Eng. Struct. 2021, 233, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumar, A.; Rana, S.; Sahoo, N.G.; Jamil, M.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Li, C.; Kumar, A.; Eldin, S.M.; et al. Critical review on advancements on the fiber-reinforced composites: Role of fiber/matrix modification on the performance of the fibrous composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 2975–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushimimana, A.; Niyonsenga, A.A.; Nzamurambaho, F. A review on strength development of high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 124865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeed, M.H.; Qaidi, S.; Ahmed, H.U.; Faraj, R.H.; Mohammed, A.S.; Emad, W.; Tayeh, B.A.; Azevedo, A.R. Ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Part IV: Durability properties, cost assessment, applications, and challenges. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B.H.; Sherwani AF, H.; Faraj, R.H.; Qadir, H.H.; Younis, K.H. Mechanical properties and ductility behavior of ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concretes: Effect of low water-to-binder ratios and micro glass fibers. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M. Significance of fiber characteristics on the mechanical properties of steel fiber-reinforced high-strength concrete at different water-cement ratios. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Grünewald, S.; Schlangen, E.; Luković, M. Strengthening of concrete structures with ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete (UHPFRC): A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 336, 127398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, R. Research on different types of fiber reinforced concrete in recent years: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Elchalakani, M.; Karrech, A.; Dong, M.; Mohamed Ali, M.S.; Yang, H. ECO-UHPC with high-volume class-F fly ash: New insight into mechanical and durability properties. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, P.; Nagamani, K. Tensile strength and durability characteristics of high-performance fiber reinforced concrete. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2008, 33, 307–319. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Jang, J.G.; Bansal, P.P. A comprehensive review on effects of mineral admixtures and fibers on engineering properties of ultra-high-performance concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L. Property assessment of high-performance concrete containing three types of fibers. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2021, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Montesinos, G.J. High-performance fiber-reinforced cement composites: An alternative for seismic design of structures. ACI Struct. J. 2005, 102, 668. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, R.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Development of sustainable steel fibre-reinforced dry ultra-high performance concrete (DUHPC). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, G.; Wong, L.S.; Abid, S.R. A Comprehensive Review of Drop Weight Impact Testing: Evaluating the Pros and Cons in Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Performance Assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Saidi, T.; Jamil, M.; Amalia, Z.; Mubarak, A. Mechanical properties and absorption of high-strength fiber-reinforced concrete (HSFRC) with sustainable natural fibers. Buildings 2022, 12, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Chen, B.; Afgan, S.; Haque, M.A.; Wu, M.; Han, J. Experimental research on ductility enhancement of ultra-high performance concrete incorporation with basalt fibre, polypropylene fibre and glass fibre. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, J.D.; Leiva, C.; Ariza, M.P.; Seitl, S.; Cifuentes, H. Analysis of the tensile fracture properties of ultra-high-strength fiber-reinforced concrete with different types of steel fibers by X-ray tomography. Mater. Des. 2019, 165, 107582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z.; Wang, F. A review on fracture properties of steel fiber reinforced concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 67, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Huang, H.; Wei, J.; Jiao, C.; Miao, Q. Investigation of fatigue crack propagation behavior in steel fiber-reinforced ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) under cyclic flexural loading. Compos. Struct. 2022, 282, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Lai, J.; Xie, Y. Steel fiber reinforced concrete: A review of its material properties and usage in tunnel lining. Structures 2021, 34, 1080–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.M.; Seo, D.J.; Lim, D.Y.; Park, J.G.; Heo, G.H. Effect of carbon and steel fibers on the strength properties and electrical conductivity of fiber-reinforced cement mortar. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z. Tensile strength and fracture toughness of steel fiber reinforced concrete measured from small notched beams. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01401. [Google Scholar]
- Nana WS, A.; Tran, H.V.; Goubin, T.; Kubisztal, G.; Bennani, A.; Bui, T.T.; Cardia, G.; Limam, A. Behaviour of macro-SYN fibers reinforced concrete: Experimental, numerical and design code investigations. Structures 2021, 32, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, A.; Soroushian, P.; Jahangirnejad, S. Structural design methodologies for concrete pipes with steel and synthetic fiber reinforcement. ACI Struct. J. 2014, 111, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Medeghini, F.; Tiberti, G.; Guhathakurta, J.; Simon, S.; Plizzari, G.A.; Mark, P. Fiber orientation and orientation factors in steel fiber-reinforced concrete beams with hybrid fibers: A critical review. Struct. Concr. 2024, 26, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, J.M.; Blanco, A.; Pujadas, P.; Aguado, A.; Juan-García, P.; Sánchez-Moragues, M.Á. Inductive method for assessing the amount and orientation of steel fibers in concrete. Mater. Struct. 2012, 45, 1577–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolander, J.E.; Choi, S.; Duddukuri, S.R. Fracture of fiber-reinforced cement composites: Effects of fiber dispersion. Int. J. Fract. 2008, 154, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, A.; Gambarelli, S.; Martinelli, E.; Nisticò, N.; Pepe, M. Experimental characterization of the post-cracking response in hybrid steel/polypropylene fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Pan, X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, T.; Li, W. Drop-weight impact responses and energy absorption of lightweight glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite hierarchical cylindrical structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 184, 110468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, T.; Kiani, B.; Sami, F.; Fard, B.N.; Farnam, Y.; Shekarchizadeh, M. Durability of glass, polypropylene and steel fiber reinforced concrete. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Durability of Building Materials and Components, Porto, Portugal, 12–15 April 2011; pp. 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Walraven, J.C. High performance fiber reinforced concrete: Progress in knowledge and design codes. Mater. Struct. 2009, 42, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroughsabet, V.; Biolzi, L.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. High-performance fiber-reinforced concrete: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 6517–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthia, N.; Gupta, R. Hybrid fiber reinforced concrete (HyFRC): Fiber synergy in high strength matrices. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, A.; Rosati, G. Design and construction of a bridge in very high performance fiber-reinforced concrete. J. Bridg. Eng. 2003, 8, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehbaghi, K.; Chenery, R. Fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) for high rise construction: Case studies. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 272, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, Ž.; Kroviakov, S.; Mishutin, A.; Poltorapavlov, A. An experimental study on the properties of concrete and fiber-reinforced concrete in rigid pavements. Materials 2023, 16, 5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.V.K.V.; Krishnamoorthy, C.S. Computational model for discrete crack growth in plain and reinforced concrete. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2002, 191, 2699–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, F.O.; Hover, K.C. Microcracking in concrete. In Fracture Mechanics of Concrete: Material Characterization and Testing; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 137–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, L.; Arulrajah, A. A novel three-dimensional DEM model for recycled aggregate concrete considering material heterogeneity and microcrack evolution. Compos. Struct. 2025, 352, 118677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bai, Z.; Wu, J.; Long, H.; Deng, H.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, X. Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 2078–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Shi, H.; Xu, L.; Ye, G.; De Schutter, G. Microstructural characterization of ITZ in blended cement concretes and its relation to transport properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiuddin, M.; Kaish, A.A.; Woon, C.O.; Raman, S.N. Early-age cracking in concrete: Causes, consequences, remedial measures, and recommendations. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.H.; Quek, S.T. Tensile strength versus toughness of cement-based materials against high-velocity projectile impact. Int. J. Prot. Struct. 2011, 2, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuaguluchi, O.; Banthia, N. Plant-based natural fibre reinforced cement composites: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 68, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Kawashima, S.; Marchon, D.; Vasilic, K.; Wolfs, R. Recent advances on yield stress and elasticity of fresh cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Yang, K.H.; Mun, J.H. Flexural tests on externally post-tensioned lightweight concrete beams. Eng. Struct. 2018, 164, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafey, A.A.; Dawood, N.; Marzouk, H.; Haddara, M. Predicting of crack spacing for concrete by using neural networks. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 31, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, M.; Fowler, D.W.; Nawy, E.G.; Allen, J.H.; Halvorsen, G.T.; Poston, R.W.; Frosch, R.J. Control of cracking in concrete structures. Rep. ACI Comm. 2001, 224, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Skaf, M.; Santamaría, A.; Espinosa, A.B.; Ortega-Lopez, V. Self-compacting concrete with recycled concrete aggregate subjected to alternating-sign temperature variations: Thermal strain and damage. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Kang, S.T.; Lee, B.Y.; Koh, K.T.; Ryu, G.S. Improvement in predicting the post-cracking tensile behavior of ultra-high performance cementitious composites based on fiber orientation distribution. Materials 2016, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.K.; Li, V.C. Effect of fiber inclination on crack bridging stress in brittle fiber reinforced brittle matrix composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1992, 40, 1333–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerlein, I.J.; Phoenix, S.L.; Raj, R. Time evolution of stress redistribution around multiple fiber breaks in a composite with viscous and viscoelastic matrices. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1998, 35, 3177–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Oh, S.K.; Kim, B. Effect of load transfer section to toughness for steel fiber-reinforced concrete. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudadu, A.; Tiberti, G.; Germano, F.; Plizzari, G.A.; Morbi, A. The effect of fiber orientation on the post-cracking behavior of steel fiber reinforced concrete under bending and uniaxial tensile tests. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.J.; Afroz, M.; Mahmud HM, I. An experimental investigation on mechanical behavior of macro synthetic fiber reinforced concrete. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2011, 11, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Van der Meer, F.P.; Sluys, L.J.; Ke, L. Modeling of dynamic mode I crack growth in glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites: Fracture energy and failure mechanism. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 243, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, J.; Xie, X.; Suo, T. Experimental and numerical study on the loading rate dependent tensile behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy interface. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 284, 111732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; Qin, Y. Research on compressive damage mechanism of concrete based on material heterogeneity. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trawiński, W.; Bobiński, J.; Tejchman, J. Two-dimensional simulations of concrete fracture at aggregate level with cohesive elements based on X-ray μCT images. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 168, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Wei, B.; Li, Y. 3D mesoscale discrete element modeling of hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 447, 138006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, W.; He, J. Experimental and multi-scale numerical investigation of ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete (UHPFRC) with different coarse aggregate content and fiber volume fraction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, J.K.; Rao, M.S.; Mousavi, S.S.; Reddy, V.S.; Bhojaraju, C. Hybrid steel/glass fiber-reinforced self-consolidating concrete considering packing factor: Mechanical and durability characteristics. Structures 2020, 28, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.; Ali, M. Behavior of fiber reinforced concrete for controlling the rate of cracking in canal-lining. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.Y.F.; El-Emam, H.M.; Seleem, M.H.; Sallam HE, M.; Moawad, M. Effect of crack and fiber length on mode I fracture toughness of matrix-cracked FRC beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saradar, A.; Tahmouresi, B.; Mohseni, E.; Shadmani, A. Restrained shrinkage cracking of fiber-reinforced high-strength concrete. Fibers 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri Far, B.; Zanotti, C. Concrete–Concrete bond in mode-I: A study on the synergistic effect of surface roughness and fiber reinforcement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.A.; Nguyen, G.D.; Bui, H.H.; Sheikh, A.H.; Kotousov, A. Incorporation of micro-cracking and fibre bridging mechanisms in constitutive modelling of fibre reinforced concrete. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 133, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, K.P. The effect of the synthetic fibre reinforcement on the fracture energy of the concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 613, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accornero, F.; Rubino, A.; Carpinteri, A. Post-cracking regimes in the flexural behaviour of fibre-reinforced concrete beams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2022, 248, 111637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Iqbal Khan, M. Fiber–matrix interactions in fiber-reinforced concrete: A review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, K.; Lim, Y.M.; Bolander, J.E. Modeling of fiber-reinforced cement composites: Discrete representation of fiber pullout. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroughsabet, V.; Biolzi, L.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Influence of double hooked-end steel fibers and slag on mechanical and durability properties of high performance recycled aggregate concrete. Compos. Struct. 2017, 181, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Suwatnodom, P.; Ju, J.W. Micromechanics of crack bridging stress-displacement and fracture energy in steel hooked-end fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2013, 22, 829–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetens, T.; Matthys, S. Different methods to model the post-cracking behaviour of hooked-end steel fibre reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shen, A.; Ren, G.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y. Dynamic mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, F.; Cui, G.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z. Combined effect of coarse aggregate and fiber on tensile behavior of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wu, F.; Chi, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, Q. Effects of coarse aggregate and steel fibre contents on mechanical properties of high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdosian, I.; Camões, A. Mechanical performance and post-cracking behavior of self-compacting steel-fiber reinforced eco-efficient ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 121, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberti, G.; Germano, F.; Mudadu, A.; Plizzari, G.A. An overview of the flexural post-cracking behavior of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Struct. Concr. 2018, 19, 695–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, H. Investigation on the flexural behaviour and crack propagation of hybrid steel fibre reinforced concrete with a low fibre content for tunnel structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Su, Y.; Qian, C. Coupled effect of PP fiber, PVA fiber and bacteria on self-healing efficiency of early-age cracks in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, K.; El-Tawil, S.; Naaman, A.E. Properties of strain hardening ultra high performance fiber reinforced concrete (UHP-FRC) under direct tensile loading. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 48, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinteri, A. Mechanical Damage and Crack Growth in Concrete: Plastic Collapse to Brittle Fracture; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Ding, Y. An experimental study on the workability of self-compacting lightweight concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengaram, U.J.; Salam, A.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Jaafar, F.F.; Saad, H.B. Properties of high-workability concrete with recycled concrete aggregate. Mater. Res. 2011, 14, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews-Phaedonos, F. Factors with significant negative influence on the quality and durability of concrete construction for major infrastructure. In Proceedings of the ARRB Conference, 27th, 2016, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 16–18 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, R.M.; Butt, F.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, T.; Tufail, R.F. A comprehensive study on the factors affecting the workability and mechanical properties of ambient cured fly ash and slag based geopolymer concrete. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, I.; Libre, N.A.; Shekarchi, M.; Khanjani, M. Effect of workability characteristics on the hardened performance of FRSCCMs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmaran, M.; Yurtseven, A.; Yaman, I.O. Workability of hybrid fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Lopez, V.; Garcia-Llona, A.; Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Santamaría, A.; San-Jose, J.T. Fiber-reinforcement and its effects on the mechanical properties of high-workability concretes manufactured with slag as aggregate and binder. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.D. Measures of the workability of steel fiber reinforced concrete and their precision. Cem. Concr. Aggregates 1984, 6, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulthan, F. Influence of steel fiber shapes on fresh and hardened properties of steel fiber reinforcement self-compacting concrete (SFRSCC). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 849, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.P.; Sahoo, K.; Panda, H.S.; Pradhan, A.; Jena, B. Experimental study on the effect of superplasticizer on workability and strength characteristics of recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, S.; Akbulut, Z.F. Effect of high-temperature on the behavior of single and hybrid glass and basalt fiber added geopolymer cement mortars. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, P.; Abolmaali, A. Macro synthetic fibers as reinforcement for deep beams with discontinuity regions: Experimental investigation. Eng. Struct. 2019, 200, 109672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khitab, A.; Arshad, M.T.; Hussain, N.; Tariq, K.; Ali, S.A.; Kazmi SM, S.; Munir, M.J. Concrete reinforced with 0.1 vol% of different SYN fibers. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 934–939. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdipour, I.; Vahdani, M.; Libre, N.A.; Shekarchi, M. Relationship between workability and mechanical properties of fibre-reinforced self-consolidating mortar. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Yen, C.H. Workability, fiber distribution, and mechanical properties of UHPC with hooked end steel macro-fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarifard, A.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Dalvand, A.; Sattarifard, A.R. Fresh and hardened-state properties of hybrid fiber–reinforced high-strength self-compacting cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, L.; Park, Y.D.; Shah, S.P. A method for mix-design of fiber-reinforced self-compacting concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Spiesz, P.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Mix design and properties assessment of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete (UHPFRC). Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 56, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeed, M.H.; Qaidi, S.; Faraj, R.H.; Majeed, S.S.; Mohammed, A.S.; Emad, W.; Tayeh, B.A.; Azevedo, A.R. Ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Part V: Mixture design, preparation, mixing, casting, and curing. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luccioni, B.; Isla, F.; Codina, R.; Ambrosini, D.; Zerbino, R.; Giaccio, G.; Torrijos, M.C. Effect of steel fibers on static and blast response of high strength concrete. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 107, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Mousavi, S.S.; Dehestani, M. Influence of nano-coated micro steel fibers on mechanical and self-healing properties of 3D printable concrete using graphene oxide and polyvinyl alcohol. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 1312–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Cui, X.; Yuan, J.; Sun, W.; Cui, C.; Wu, Y.; Feng, J. The influence of fiber, aggregate and cementitious materials on the mechanical properties of ultra-high content steel fiber reinforced reactive powder concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, R.F. Fiber-reinforced concrete: An overview after 30 years of development. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1997, 19, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerini, V.; Conforti, A.; Plizzari, G.; Kawashima, S. Influence of steel and macro-SYN fibers on concrete properties. Fibers 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrinejad, I.; Madandoust, R.; Ranjbar, M.M. The mechanical and durability properties of concrete containing hybrid SYN fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkadi, A.A.; Aggoun, S.; Amouri, C.; Geuttala, A.; Houari, H. Effect of vegetable and synthetic fibers on mechanical performance and durability of Metakaolin-based mortars. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 1670–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, H.R.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. SYN fibers for cementitious composites: A critical and in-depth review of recent advances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 491–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Valukolaee, S.; Hashemi, S.K.; Nematzadeh, M. Effect of steel fiber on flexural performance of bilayer concrete beams with steel and GFRP rebars: Experiments and predictions. Structures 2022, 39, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.; Leshchinsky, D.; Ling, H.I.; Perry, E.B. Effect of short polymeric fibers on crack development in clays. Soils Found. 1998, 38, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, S.M.; Sheikhzadeh, M.; Abtahi, S.M.; Zadhoush, A. A simple review of soil reinforcement by using natural and SYN fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, G.; Vardhan, C.V.; Sruthee, P.; Charmily, P. Influence of steel fibre on concrete. Prism 2012, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Rahman, M.B.; Alya’a, A.A.; Younus, A.M. Effecting of steel fibers and fly ash on the properties of concrete. Tikrit J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 25, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najem, K.B.; Rejeb, S.K.; Salih, S.A. The effect of steel fibers on the mechanical properties of high performance concrete. Al-Rafidain Eng. J. 2005, 13, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalel, R.I.; Sarsam, K.F.; Al-Shamma, B.A. Influence of steel fibers on the behavior of spirally RC short columns. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 737, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsanov, A.I.; Stolyarov, O.N. Mechanical properties of synthetic fibers applied to concrete reinforcement. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2018, 4, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Grzeszczyk, S.; Matuszek-Chmurowska, A.; Vejmelková, E.; Černý, R. Reactive powder concrete containing basalt fibers: Strength, abrasion and porosity. Materials 2020, 13, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Ge, Y.; Ruan, W.; Meng, J. Effects of PVA fiber on shrinkage deformation and mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Yang, L. Comparative study on the effect of steel and plastic SYN fibers on the dynamic compression properties and microstructure of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Compos. Struct. 2023, 324, 117570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwesabi, E.A.; Bakar, B.A.; Alshaikh, I.M.; Abadel, A.A.; Alghamdi, H.; Wasim, M. An experimental study of compressive toughness of Steel–Polypropylene hybrid Fibre-Reinforced concrete. Structures 2022, 37, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Shafei, B. Investigation of five SYN fibers as potential replacements of steel fibers in ultrahigh-performance concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahake, H.B.; Shinde, B.H. A Review on Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Self-compacting Concrete: Properties & Challenges. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2024, 49, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. Enhancing concrete performance: A comprehensive review of hybrid fiber reinforced concrete. Structures 2024, 64, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Hu, S. Influence of fibers on the mechanical properties and durability of ultra-high-performance concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, N.; Hosseinpoor, M.; Yahia, A.; Khayat, K.H. Coupled effect of fiber and granular skeleton characteristics on packing density of fiber-aggregate mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, A.; Lyu, Z.; He, Z.; Nguyen, K.T. Fresh and rheological characteristics of fiber reinforced concrete. A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, E.; Park, C. Effects of double-arched geometry and tensile strength on the pullout resistance of fibers. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J.; He, J.; Yu, T.; Cai, C.; Huang, D. Compressive behaviours, splitting properties, and workability of lightweight cement concrete: The role of fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, M. Synergistic effect of microfibers and oriented steel fibers on mechanical properties of UHPC. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Rui, Y.; Liu, K.; Tan, J.; Shui, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Guan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Su, Q. Optimized design of steel fibres reinforced ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) composites: Towards to dense structure and efficient fibre application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121698. [Google Scholar]
- Turjo, S.K.S.; Hossain, M.F.; Rana, M.S.; Al-Mamun, M.; Ferdous, M.S. Durability and mechanical characteristics of unidirectional jute/banana and synthetic fiber reinforcement epoxy composite. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Luo, S.; Lin, K.; Wang, D. Effects of SYN fibres on the fracture behaviours of recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 418, 135370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, J.R.; Altoubat, S.A.; Lange, D.A.; Rieder, K.A.; Ulreich, G.R. Effect of synthetic fibers on structural behavior of concrete slabs-on-ground. ACI Mater. J. 2006, 103, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Asghar, M.F.; Khattak, M.J. Evaluation of mixture design and tensile characteristics of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–fiber reinforced HMA mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2024, 17, 258–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Banthia, N. High-performance strain-hardening cementitious composites with tensile strain capacity exceeding 4%: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, W.L.; Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Sahmaran, M. A review on the durability of concrete-to-concrete bond in recent rehabilitated structures. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporace-Guimil, B.; Mudadu, A.; Conforti, A.; Plizzari, G.A. Influence of fiber orientation and structural-integrity reinforcement on the flexural behavior of elevated slabs. Eng. Struct. 2022, 252, 113583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarżyński, Ł.; Suchorzewski, J. Mechanical and fracture properties of concrete reinforced with recycled and industrial steel fibers using Digital Image Correlation technique and X-ray micro computed tomography. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R. Influence of steel fiber distribution on splitting damage and transport properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 126, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wu, B.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z. Study on dynamic splitting tensile mechanical properties and microscopic mechanism analysis of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Structures 2023, 58, 105502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujalli, M.A.; Dirar, S.; Mushtaha, E.; Hussien, A.; Maksoud, A. Evaluation of the tensile characteristics and bond behaviour of steel fibre-reinforced concrete: An overview. Fibers 2022, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Kang, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Lei, M. Tensile performance test research of hybrid steel fiber—Reinforced self-compacting concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, H. Experimental investigation on axial compressive and splitting tensile behaviour of reinforced concrete with a low content of hybrid steel fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Galal, S.; Hassan, A.; Salman, A. Utilization of carbon nanotubes and steel fibers to improve the mechanical properties of concrete pavement. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Shi, Z.; Kanstad, T.; Baghban, M.H.M.; Ji, G. Application of steel fiber reinforced-concrete in post-tensioned flat slabs: A numerical study. Eng. Struct. 2025, 324, 119347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo, R.; Altamirano, M.G.; Giaccio, G.M.; Zerbino, R.L. Design and Execution of Floors on Ground and Industrial Pavements with Fibre Reinforced Concrete. In Fibre Reinforced Concrete: Improvements and Innovations II: X RILEM-fib International Symposium on Fibre Reinforced Concrete (BEFIB); Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 10, pp. 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Xia, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Guo, W.; Wang, H. Study and data-driven modeling of flexural behaviors of ultra-high-performance concrete reinforced by milling steel fiber. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 31, 9873–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, O.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Shi, J.; Benli, A.; Bodur, B.; Turkoglu, M. The effect of steel fiber aspect-ratio and content on the fresh, flexural, and mechanical performance of concrete made with recycled fine aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wen, T.; Tian, L. Size effects in compressive and splitting tensile strengths of polypropylene fiber recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Mohammed, I.I. Effect of fiber parameters on the strength properties of concrete reinforced with PET waste fibers. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2021, 45, 1493–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B.; Hang, W.; Zheng, Z. Experimental study on residual mechanical properties of steel-PVA hybrid fiber high performance concrete after high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Farzadnia, N.; Khayat, K.H. Synergistic effect of macro SYN fiber and shrinkage-reducing admixture on engineering properties of fiber-reinforced super-workable concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, D.F.; Selvan, S.S. Experimental study on addition of Steel Fibres in Conventional Concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1130, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, J.P.; Desmettre, C.; Androuët, C. Flexural and shear behaviors of steel and synthetic fiber reinforced concretes under quasi-static and pseudo-dynamic loadings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoyebi, O.D.; Odeyemi, S.O.; Bello, S.A.; Ogbeifun, C.O. Splitting tensile strength assessment of lightweight foamed concrete reinforced with waste tyre steel fibres. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. (IJCIET) 2018, 9, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, E.; Ribellato, C.; Mohamedelhassan, E. Improving concrete properties with fibers addition. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2014, 8, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.D.; Zhang, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.K.; Xie, X.C. Experimental and mesoscale numerical investigation on tensile properties of steel fibre-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ali, M. A Review on Improving the Design and Performance of Rigid Pavements with Fiber Concrete. Constr. Technol. Archit. 2025, 15, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Gu, Q.; Gao, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tian, S.; Ruan, Z.; Huang, J. Effect of basalt fibers and silica fume on the mechanical properties, stress-strain behavior, and durability of alkali-activated slag-fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 418, 135440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayudhya, N.; Israngkura, B. Compressive and splitting tensile strength of autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) containing perlite aggregate and polypropylene fiber subjected to high temperatures. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 33, 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Khieu, H.H.; Black, J.R.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Tran, P. Two-scale 3D printed steel fiber reinforcements strategy for concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Sheng, D.; Huo, X.; Chai, Z. A Combined Damage and Mesomechanics Model for Recycled Aggregate Concrete Reinforced with Steel–Polypropylene Fibers. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 04024534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Tang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Bai, W.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of the performance and effect of steel fiber reinforced cellular concrete for underwater blast protection under contact explosion loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 313, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaif, A.; Alharbi, Y.R. Strength, durability and shrinkage behaviours of steel fiber reinforced rubberized concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazli, M.; Heitzmann, M.; Hernandez, B.V. Hybrid fibre reinforced polymer and seawater sea sand concrete structures: A systematic review on short-term and long-term structural performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, K.R.; Ipek, M. Effect of different fiber combinations and optimisation of an ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) mix applicable in structural elements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Meng, Q.; Huo, F.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J. A State-of-the-Art Assessment in Developing Advanced Concrete Materials for Airport Pavements with Improved Performance and Durability. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Yin, J.; Shi, C. Evaluation of tensile failure behavior of ultra high performance concrete under double-edge wedge splitting and direct tension loadings. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 90, 109480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koura, M.M.; Tahwia, A.M.; Matthana, M.H. Influence of macro-SYN fibers on the flexural behavior of high strength concrete beams reinforced with GFRP bars. Mansoura Eng. J. 2024, 49, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Gu, Q.; Tian, S.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, X. Flexural fatigue behavior of hooked-end steel fibres reinforced concrete using centrally loaded round panel test. Mater. Struct. 2023, 56, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, W.F.; Elbialy, S.; El-Zohairy, A.; Soliman, A.M.; Shawky, S.M.M.; Selouma, T.I.; Al Sayed, A.A.-K.A. Examining Mechanical Property Differences in Concrete with Natural and SYN Fiber Additives. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Zhao, J. Effects of steel fibers on the flexural behavior of recycled concrete beam: Testing and analysis. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 85, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro-Barceló, J.; Lenz, E.; Torres, B.; Estevan, L. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete reinforced with conventional and recycled steel fibers and exposed to high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 452, 138976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, Z.; Wu, P. Mechanical properties of steel fiber RPC, basalt fiber RPC, and hybrid fiber RPC: A review of research progress. Struct. Concr. 2024, 25, 3953–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankir, S.; Bikce, M. Experimental investigation and statistical evaluation of the effects of steel fiber aspect ratio and fiber rate on static and dynamic mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 135064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Tang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhou, A.; Wu, K.; Zou, D.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; De Schutter, G. Predicting the tensile strength of ultra-high performance concrete: New insights into the synergistic effects of steel fiber geometry and distribution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rifai, M.M.; Sikora, K.S.; Hadi, M.N. Effect of micro steel fibers volume fraction on behavior of high-strength self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodeiri, A.H.; Quitalig, R.J. Effect of wirand FS7-II steel wire fibre on flexural capacity of reinforced concrete beam. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2012, 2, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danha, L.S.; Abdul-Hussien, Z.A.; Abduljabbar, M.S.; Yassin, L.A.G. Flexural behavior of hybrid ultra-high-performance concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 737, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiş, C.D.; Karahan, O. Properties of steel fiber reinforced fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazy, J.; Drobiec, Ł.; Wolka, P. Flexural tensile strength of concrete with SYN fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Savio, A.A.; Esquivel, D.L.T.; de Andrade Silva, F.; Agreda Pastor, J. Influence of SYN fibers on the flexural properties of concrete: Prediction of toughness as a function of volume, slenderness ratio and elastic modulus of fibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopko, M.; Najimi, M.; Shafei, B.; Wang, X.; Taylor, P.; Phares, B.M. Flexural performance evaluation of fiber-reinforced concrete incorporating multiple macro-SYN fibers. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutsos, M.N.; Le, T.T.; Lampropoulos, A.P. Flexural performance of fibre reinforced concrete made with steel and SYN fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maida, P.; Sciancalepore, C.; Radi, E.; Bondioli, F. Effects of nano-silica treatment on the flexural post cracking behaviour of polypropylene macro-SYN fibre reinforced concrete. Mech. Res. Commun. 2018, 88, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, D.; Locke, D.C.; Cannone, L.J. SYN fibers as indicators of municipal sewage sludge, sludge products, and sewage treatment plant effluents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998, 103, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.; Scott, H.N., III. Ultra-thin, fiber-reinforced concrete overlays for urban intersections. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1532, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cen, G.; Cui, Y. Comparative study on the effect of SYN fiber on the preparation and durability of airport pavement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy Özbay, A.E.; Erkek, O.; Çeribaşı, S. The effect of polypropylene, steel, and macro synthetic fibers on mechanical behavior of cementitious composites. Rev. Constr. 2021, 20, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.H.; Abd, S.K.R.H.T. Effect of hybrid fibers on the mechanical properties of high strength concrete. Tikrit J. Eng. Sci. 2014, 21, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, E.K.M. Behavior and Strength of Steel-Carbon-Plastic Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 518, 022061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, W.; Lian, Y.; Li, L. An experimental investigation on nonlinear behaviors of SYN fiber ropes for deepwater moorings under cyclic loading. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2014, 45, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, A.; Tiberti, G.; Plizzari, G.A.; Caratelli, A.; Meda, A. Precast tunnel segments reinforced by macro-SYN fibers. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnam, S.; Selvaranjan, K.; Jayasooriya, D.; Rajeev, P.; Sanjayan, J. Applications of natural and SYN fiber reinforced polymer in infrastructure: A suitability assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, A.; Motavalli, M.; Shahverdi, M. Recent advancements in the applications of fiber-reinforced polymer structures in railway industry. A review. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.N.; Poh, L.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.H. Critical parameters for the compressive strength of high-strength concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 82, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orouji, M.; Zahrai, S.M.; Najaf, E. Effect of glass powder & polypropylene fibers on compressive and flexural strengths, toughness and ductility of concrete: An environmental approach. Structures 2021, 33, 4616–4628. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.M.; Min, K.H.; Shin, H.O.; Yoon, Y.S. Effect of steel and SYN fibers on flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beams reinforced with FRP bars. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.X.; Luo, R.H.; Su, J.Y.; Guo, Y.C.; Chen, W.S. Coarse SYN fibers (PP and POM) as a replacement to steel fibers in UHPC: Tensile behavior, environmental and economic assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, J.R.; Lange, D.A.; Altoubat, S.A.; Rieder, K.A.; Ulreich, G.R. Fracture of plain and fiber-reinforced concrete slabs under monotonic loading. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2004, 16, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremannejad, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Saleh, A.E.; Abhaee, S.; Abolmaali, A. Experimental investigation and identification of single and multiple cracks in SYN fiber concrete beams. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 9, e00182. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, S.S.; Muthusamy, N.; Anbarasu, N.A. The structural performance of fiber-reinforced concrete beams with nanosilica. Mater. Jan. 2024, 29, e20240194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkarim, A.; El-Sayed, A.K.; Alsaif, A.S.; Fares, G.; Alhozaimy, A.M. Behavior of lightweight self-compacting concrete with recycled tire steel fibers. Buildings 2024, 14, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Advanced monitoring of damage behavior and 3D visualization of fiber distribution in assessing crack resistance mechanisms in steel fiber-reinforced concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, N.; Patrisia, Y.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.W.; Houshyar, S.; Setunge, S. Shrinkage induced crack control of concrete integrating SYN textile and natural cellulosic fibres: Comparative review analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 427, 136275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permanoon, A.; Pouraminian, M.; Khorami, N.; GanjiMorad, S.; Azarkhosh, H.; Sadrinejad, I.; Pourbakhshian, S. Improving Mixed-Mode Fracture Properties of Concrete Reinforced with MacroSYN Plastic Fibers: An Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Buildings 2024, 14, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Sarfarazi, V.; Haeri, H.; Wang, Z.; Fatehi Marji, M. Improving the tensile strength of reinforced concrete: Evaluating the impact of different fiber additives through numerical and experimental analysis. Comput. Part. Mech. 2024, 12, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewage, D.K.; Camille, C.; Mirza, O.; Mashiri, F.; Kirkland, B.; Clarke, T. Effect of post-peak flexural toughness on the residual performance of macro SYN fibre reinforced concrete sleepers subjected to impact loading. Eng. Struct. 2024, 307, 117913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.; Ghiji, M.; Fragomeni, S.; Guerrieri, M. Mechanical properties of macro synthetic fiber reinforced concrete at elevated temperatures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 1244–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddafi, A.K.F.; Alengaram, U.J.; Bunnori, N.M.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Ibrahim, S.; Govindasami, S. Enhancement of ductility characteristics of fiber-reinforced ternary geopolymer mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Khan, M.I.; Shafiq, N.; Abbas, Y.M.; Khatib, J.M. Achieving superior mechanical performance in one-part geopolymer composites through innovative hybrid fiber systems of recycled steel and PVA fibers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1772–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shu, W.; Xu, H.; Rui, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, S.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Z. Experimental study on flexural toughness of fiber reinforced concrete beams: Effects of cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol and polyolefin fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 81, 108144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y. Experimental Research on Crack Resistance of Steel–Polyvinyl Alcohol Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Materials 2024, 17, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayeb, H.H.; Mo, K.H.; Sulong, N.R. The impact of using hybrid polyvinyl alcohol–steel fibre ECC on the seismic behaviour of precast beam-to-column joints. Structures 2024, 70, 107849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, A.; Hassanli, R.; Zhuge, Y.; Ma, X.; Chow, C.W.; Bazli, M.; Manalo, A. Synergistic effects of fiber hybridization on the fracture toughness of seawater sea-sand concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Cao, M.; Si, W. Influence of CaCO3 Whiskers and PVA Fibers on the Flexural Properties of Steel Fiber–Reinforced Cementitious Composites. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04024381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Alonso, Á.; González, D.C.; Mínguez, J.; Vicente, M.A. Size effect on the flexural fatigue behavior of high-strength plain and fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, L. A review on the damage behavior and constitutive model of fiber reinforced concrete at ambient temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, A.M.; Bakir, B.B. Parametric study on the flexural behavior of steel fiber reinforced concrete beams utilizing nonlinear finite element analysis. Structures 2024, 65, 106688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guan, C.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Liang, L. Size-dependent fracture behavior of steel fiber reinforced cement mortar modified by polymer. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamata, A.; Mihashi, H.; Fukuyama, H. Properties of hybrid fiber reinforced cement-based composites. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2003, 1, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhu, Z.; Su, C.; Zhang, T.; Ji, Y.; Huang, L. Experimental study and prediction on tensile behavior of steel fiber-reinforced-carbon/glass hybrid composite bars in concrete environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.O.; Forti, N.C.d.S.; Pimentel, L.L.; Jacintho, A.E.P.G.d.A. A Study of the Shear Behavior of Concrete Beams with Synthetic Fibers Reinforced with Glass and Basalt Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Bars. Buildings 2024, 14, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saingam, P.; Gadagamma, C.K.; Hussain, Q.; Ejaz, A.; Hlaing, H.H.; Suwannatrai, R.; Khan, K.; Suparp, S. Large rupture strain cotton ropes hybridized with affordable fiberglass chopped strand mat sheets for enhanced compressive behavior of reinforced concrete columns. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Qian, Y.; Dai, J.G. Enhancing the flexural performance of concrete beams with 3D-printed UHP-SHCC permanent formwork via graded fiber volume fraction. Compos. Struct. 2024, 341, 118211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pise, M.; Brands, D.; Schröder, J. Development and Calibration of a Phenomenological Material Model for Steel-Fiber-Reinforced High-Performance Concrete Based on Unit Cell Calculations. Materials 2024, 17, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibe, A.A.; Vemuganti, S. Flexural Response Comparison of Nylon-Based 3D-Printed Glass Fiber Composites and Epoxy-Based Conventional Glass Fiber Composites in Cementitious and Polymer Concretes. Polymers 2025, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, R.; Fathi, A.; Schlangen, E.; Fotouhi, M. Bending performance of concrete beams retrofitted with mechanochromic glass/carbon hybrid composites: Combining structural reinforcement and visual health monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, S.M.; Salman, W.D.; Ahmed, Q.W. Behavior of Hybrid Composite System for Fibrous Ferro-Foam Cement. J. Compos. Adv. Mater. Rev. Compos. Matér. Av. 2024, 34, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Thermou, G.E. Shear Performance of RC Beams Strengthened with High-Performance Fibre-Reinforced Concrete (HPFRC) Under Static and Fatigue Loading. Materials 2024, 17, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorsaheli, H.B.; Behravan, A.; Aghda ST, T.; Gholami, A. A study on the durability parameters of concrete structures reinforced with synthetic fibers in high chloride concentrated shorelines. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, B.D.; Flessati, L.; Marveggio, P.; Martinelli, P.; Fraraccio, G.; di Prisco, C.; di Prisco, M. Experimental tests on shallow foundations of onshore wind turbine towers. Struct. Concr. 2022, 23, 2986–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Tang, S. Influences of MgO and PVA fiber on the abrasion and cracking resistance, pore structure and fractal features of hydraulic concrete. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Bordelon, A.C.; Kim, M.O. Effects of Macro Fibers on Crack Opening Reduction in Fiber Reinforced Concrete Overlays. Polymers 2024, 16, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, I.Y.; Amin, M.; Abdelsalam, B.A.; Tayeh, B.A.; Althoey, F.; Agwa, I.S. Effects of nano-silica and micro-steel fiber on the engineering properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2022, 82, 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Xu, K.; Ding, W.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, L. Microstructural characteristics and their impact on mechanical properties of steel-PVA fiber reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Jang, Y.S.; Oh, T.; Banthia, N. Use of engineered steel fibers as reinforcements in ultra-high-performance concrete considering corrosion effect. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 133, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemian, M.; Shafei, B. Mechanical properties of hybrid fiber-reinforced concretes made with low dosages of SYN fibers. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Feng, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T. Synergetic effects of hybrid steel and recycled tyre polymer fibres on workability, mechanical strengths and toughness of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.; Kim, S.; Yoo, D.Y. Benefits of chemically treated steel fibers on enhancing the interfacial bond strength from ultra-high-performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Xiong, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Experimental Investigation on the Dynamic Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Deterioration of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Subjected to Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Buildings 2022, 12, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, S.; He, S.; Schlangen, E.; Ferrara, L. Effect of matrix self-healing on the bond-slip behavior of micro steel fibers in ultra-high-performance concrete. Mater. Struct. 2023, 56, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Effect of chloride-induced corrosion on bond performance of various steel fibers in cracked SFRC. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 140, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.M.; Leuteritz, A.; Stommel, M.; Kühnert, I.; Mechtcherine, V.; Scheffler, C. Micromechanical study on polypropylene-bicomponent fibers to improve mechanical interlocking for application in strain-hardening cement-based composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, T.; Cao, X.; Yu, L.; Qi, H. Comparison of the Mechanical Properties and Crack Expansion Mechanism of Different Content and Shapes of Brass-Coated Steel Fiber-Reinforced Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syduzzaman, M.; Rumi, S.S.; Fahmi, F.F.; Akter, M.; Dina, R.B. Mapping the recent advancements in bast fiber reinforced biocomposites: A review on fiber modifications, mechanical properties, and their applications. Results Mater. 2023, 20, 100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, H.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Fu, T.; Yu, D. Influence of Modified PVA Fiber on Ultra-High Performance Concrete and Its Enhancing Mechanism. Polymers 2024, 16, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, J.R.; Bochen, J.; Gołaszewska, M. Experimental studies on the effect of natural and SYN fibers on properties of fresh and hardened mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconello, V.; Poletto, M. Effect of Graphene Oxide Surface Deposition Process on SYN Macrofibers and Its Results on the Microstructure of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Polymers 2024, 16, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, T.D.S.; Cardoso, D.C.; Bitencourt, L.A., Jr. Macro SYN fiber pullout behavior in short-and long-term tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, D.; Ma, X.; Hassanli, R.; Duan, J.; Zhuge, Y. Microstructural behaviour and shrinkage properties of high-strength fiber-reinforced seawater sea-sand concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, H.Ö.; Güneş, M.; Yücel, H.E.; Ersoy, O.; Sever, Y.; Demirel, S. Life cycle assessment and shrinkage properties of high performance mortars incorporating SYN wollastonite microfibers. Adv. Cem. Res. 2022, 35, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölfel, E.; Brünig, H.; Curosu, I.; Mechtcherine, V.; Scheffler, C. Dynamic single-fiber pull-out of polypropylene fibers produced with different mechanical and surface properties for concrete reinforcement. Materials 2021, 14, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feo, L.; Ascione, F.; Penna, R.; Lau, D.; Lamberti, M. An experimental investigation on freezing and thawing durability of high performance fiber reinforced concrete (HPFRC). Compos. Struct. 2020, 234, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlůžek, R.; Trejbal, J.; Nežerka, V.; Demo, P.; Prošek, Z.; Tesárek, P. Improvement of bonding between SYN fibers and a cementitious matrix using recycled concrete powder and plasma treatment: From a single fiber to FRC. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 3880–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Chai, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, M.; Liang, D. Exploring the brittleness and fractal characteristics of basalt fiber reinforced concrete under impact load based on the principle of energy dissipation. Mater. Struct. 2022, 55, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Ge, Y.; Zheng, Z. Mussel adhesive protein inspired functionalization of steel fibers for better performance of steel fibers reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 436, 136887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanpour, H.; Subasi, S.; Guntepe, S.; Emiroglu, M.; Marasli, M. Investigation of fracture mechanics, physical and dynamic properties of UHPCs containing PVA, glass and steel fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshfar, M.; Hassani, A.; Aliha MR, M.; Sadowski, T.; Karimi, A. Experimental Model for Study of Thickness Effect on Flexural Fatigue Life of Macro-SYN-Fiber-Reinforced Concretes. Buildings 2023, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Jia, Y. Experimental study on the mechanical properties, water absorption, and fiber degradation of naturally aged glass fiber and polypropylene fiber-reinforced concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Xia, X. A Study on the Mechanical and Wear-Resistance Properties of Hybrid Fiber Mortar Composites with Low Water–Cement Ratios. Materials 2024, 17, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, B.; Anitha, D.; Arunkumar, K.; Rameshkumar, D.; Swaminathan, P.; Saxena, K.K.; Jisha, P.K.; Abdo, H.S.; Alnaser, I. A study on the mechanical performance, shrinkage and morphology of high-performance fiber reinforced concrete with varying SCMs and geometry of steel fibers. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, P.V.; Dhineshbabu, N.R.; Varsala, P.; Devi, S.A.; Sitaramamurty, A.S.; Saleel, C.A.; Hasan, N. Effects of asna fibre reinforced with epoxy resin with and without steel wire mesh and simulation of car bumper. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 055301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Bundela, A.S.; Choudhary, P.; Pai, Y.; Pai, D.G. Effect of carbon-Kevlar intraply surface layers on the mechanical and vibrational properties of basalt reinforced polymer composites. Cogent Eng. 2024, 11, 2403704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adili, E.; Kheyroddin, A. Fiber interfacial transition zone concept for steel fiber-reinforced concrete by SEM observation. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2021, 19, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharda, V.; Němeček, J.; Stemberk, P. Micromechanical performance of interfacial transition zone in fiber-reinforced cement matrix. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 246, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig-Flores, M.; Šimičević, F.; Maričić, A.; Serna, P.; Horvat, M. Interfacial Transition Zone in Mature Fiber-Reinforced Concretes. ACI Mater. J. 2018, 115, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazami, M.; Gupta, R. Influence of polypropylene, carbon and hybrid coated fiber on the interfacial microstructure development of cementitious composites. Fibers 2021, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.A.; Ahmadi, M.; Dalvand, A.; Aslani, F. Effect of single and hybrid fibers on mechanical properties of high-strength self-compacting concrete incorporating 100% waste aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04022365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asil, M.B.; Ranjbar, M.M. Hybrid effect of carbon nanotubes and basalt fibers on mechanical, durability, and microstructure properties of lightweight geopolymer concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 357, 129352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Somasekharaiah, H.M.; Rao, H.S.; Ghorpade, V.G. Durability and micro-structure studies on fly ash and silica fume based composite fiber reinforced high-performance concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, G.; Abid, S.R.; Al-Lami, K.; Vatin, N.I.; Dixit, S.; Fediuk, R. Pure and mixed-mode (I/III) fracture toughness of preplaced aggregate fibrous concrete and slurry infiltrated fibre concrete and hybrid combination comprising nano carbon tubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 362, 129696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanuy, C. Recent Developments on High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Hybrid Mixes and Combinations with Other Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalel, H.; Khan, M.; Starr, A.; Khan, K.A.; Muhammad, A. Performance of engineered fibre reinforced concrete (EFRC) under different load regimes: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, P.; Li, L.; Fatima, S.; Sofi, M. Mechanical performance and numerical simulation of high-performance steel fiber reinforced concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hagri, M.G.; Döndüren, M.S. Effect of single and hybrid incorporation of steel, polypropylene, and PET fibers on the properties of concrete under static and impact loading. Mag. Concr. Res. 2025, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shu, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Wu, B. Effects of Fiber Shape and Nanopalygorskite on the Long-Term Performance of Steel Fiber–Reinforced Ultrahigh-Performance Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 04025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.R.; Suthar, M. Utilizing machine learning approaches within concrete technology offers an intelligent perspective towards sustainability in the construction industry: A comprehensive review. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshinawy, A.; Elshikh MM, Y.; Kaloop, M.R.; El-Demerdash, W.E.; Elemam, W.E. An experimental investigation on mechanical characteristics of steel-fiber-reinforced volcanic concrete. Next Mater. 2025, 6, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, H. Experimental study on hybrid fiber reinforced high performance concrete properties: Investigatingcomprehensive energy consumption capacity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srividhya, S.; Prakash, R.; Kumar, M.V.; Mukilan, K.; Premkumar, R. Impact of Various Fibers on the Mechanical and Durability Performance of Fibre-reinforced Concrete with SBR Latex. J. Polym. Compos. 2024, 12, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nikbin, I.M.; Dezhampanah, S.; Charkhtab, S.; Mehdipour, S.; Shahvareh, I.; Ebrahimi, M.; Pournasir, A.; Pourghorban, H. Life cycle assessment and mechanical properties of high strength steel fiber reinforced concrete containing waste PET bottle. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso-Morato, J.; Hurtado-Alonso, N.; Revilla-Cuesta, V.C.; Skaf, M.; Ortega-López, V. Fiber-Reinforced concrete and its life cycle assessment: A systematic review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 110062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M.; Abellan-Garcia, J.; Castro-Cabeza, A. Eco-efficient ultra-high-performance concrete formulation utilizing electric arc furnace slag and recycled glass powder–advanced analytics and lifecycle perspectives. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashiri Rezaie, A.; Liebscher, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Ahmad, M.S.; Mechtcherine, V. Smart PE Fibers to Monitor Water Ingress in Normal and High-Strength Cementitious Matrices. In RILEM-Fib International Symposium on Fibre Reinforced Concrete; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Rama, M.; Sudarsan, J.S.; Sunmathi, N.; Nithiyanantham, S. Behavioral assessment of intrinsically formed smart concrete using steel fibre and carbon black composite. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hindawi, L.A.A.; Al-Dahawi, A.M.; Al-Zuheriy, A.S.J. A Novel Way of Using Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag and Steel Shaving Fibers for Production of Sustainable and Smart Rigid Pavement. Int. J. Eng. 2024, 37, 1622–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balea, A.; Fuente, E.; Monte, M.C.; Blanco, A.; Negro, C. Recycled fibers for sustainable hybrid fiber cement based material: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, R.; Cui, Z.; Jeong, J.W.; Yoo, D.Y. Optimal multi-walled carbon nanotube dosage for improving the mechanical and thermoelectric characteristics of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 462, 139927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hála, P.; Hurtig, K.; Řídký, R.; Sovják, R.; Konvalinka, P. Resistance of High-Performance Concrete Panels with Dispersed Fiber Reinforcement to Oblique-Angle Projectile Impact. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 04024455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shareef, N.A.; Kadhum, M.M. Numerical simulation of post fire-behaviour of high strength lightweight reinforced concrete beams strengthened with basalt fiber-reinforced polymer grid and engineered cementitious composites jacket. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2025, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Billington, S.L. Impact of cyclic loading on longitudinally-reinforced UHPC flexural members with different fiber volumes and reinforcing ratios. Eng. Struct. 2021, 241, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Ding, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y. Effect of lightweight aggregate pre-wetting degree on the chloride ion permeability of ultra-high performance concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 100, 111777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, Q.U.Z. Optimizing Hybrid Fiber Concrete: An Experimental Analysis of Steel and Polypropylene Fiber Composites Using RSM. Mater. Res. Express 2025, 12, 025304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumaran, S.; Krishna, A.; Karuppanan, K. Opening and out-of-plane shear fracture performance of steel and natural sisal hybrid fiber reinforced concrete. Struct. Concr. 2025, 26, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Shi, X.Z.; Zhang, N.; Hu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.Q. Prediction of bond strength between fibers and the matrix in UHPC utilizing machine learning and experimental data. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qi, Z.; Li, L.; Feng, X.; Fan, C. Experimental research on dynamic impact mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete after high temperature. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 102, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.J.; Hao, Z.H.; Sun, H.Q.; Zeng, W.B.; Fan, T.H.; Zhuge, Y. Durability assessment of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) and FRP grid-reinforced UHPC plates under marine environments. Eng. Struct. 2025, 323, 119313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Charca, S.; Valverde, B.; Loya, J.A.; Santiuste, C. Experimental Analysis of Hybrid Panels Combining Flax/PLA Composite with UHMWPE and Steel Under Ballistic Impact. J. Nat. Fibers 2025, 22, 2445574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtegar, B.; Bagheri, M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Shear strength of steel fiber-unconfined reinforced concrete beam simulation: Application of novel intelligent model. Compos. Struct. 2019, 212, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Shafighfard, T.; Yoo, D.Y. Data-driven modeling of mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced concrete: A critical review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 2049–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qi, C.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Dong, X. Prediction of dynamic increase factor for steel fibre reinforced concrete using a hybrid artificial intelligence model. Eng. Struct. 2019, 189, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Sufian, M.; Hakamy, A.; Farouk Deifalla, A.; El-Said, A. Application of machine learning algorithms to evaluate the influence of various parameters on the flexural strength of ultra-high-performance concrete. Front. Mater. 2023, 9, 1114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrossadat, E.; Basarir, H.; Karrech, A.; Elchalakani, M. Multi-objective mixture design and optimisation of steel fiber reinforced UHPC using machine learning algorithms and metaheuristics. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38 (Suppl. S3), 2569–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatief, M.; Wong, L.S.; Din, N.M.; Mo, K.H.; Ahmed, A.N.; El-Shafie, A. Evaluating enhanced predictive modeling of foam concrete compressive strength using artificial intelligence algorithms. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 110022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdasi, P.; Heid, A.E.; Chao, S.H. Developing Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Rein forced Concrete for Large-Scale Structural Applications. ACI Mater. J. 2016, 113, 559–570. [Google Scholar]
- Charalambidi, B.G.; Rousakis, T.C.; Karabinis, A.I. Fatigue behavior of large-scale reinforced concrete beams strengthened in flexure with fiber-reinforced polymer laminates. J. Compos. Constr. 2016, 20, 04016035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ji, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, G.; Mechtcherine, V.; Pan, J.; Wang, L.; Ding, T.; Duan, Z.; Du, S. Large-scale 3D printing concrete technology: Current status and future opportunities. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 122, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Khatun, M.S.; Islam MR, U.; Dola, J.F.; Hussan, M.; Siddique, A. Finite element analysis of steel fiber reinforced concrete (SFRC): Validation of experimental shear capacities of beams. Procedia Eng. 2014, 90, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y. Evaluation of elastic properties of fiber reinforced concrete with homogenization theory and finite element simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmarajaiah, S.K.; Ramaswamy, A. A finite element assessment of flexural strength of prestressed concrete beams with fiber reinforcement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, M.M.; Nadjai, A.; Ali, F. Finite element modeling of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer reinforced concrete beams under elevated temperatures. ACI Struct. J. 2008, 105, 701. [Google Scholar]
- Posani, M.; Voney, V.; Odaglia, F.; Du, Y.; Komkova, A.; Brumaud, C.; Dillenburger, B.; Habert, G. Low-carbon indoor humidity regulation via 3D-printed superhygroscopic building components. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
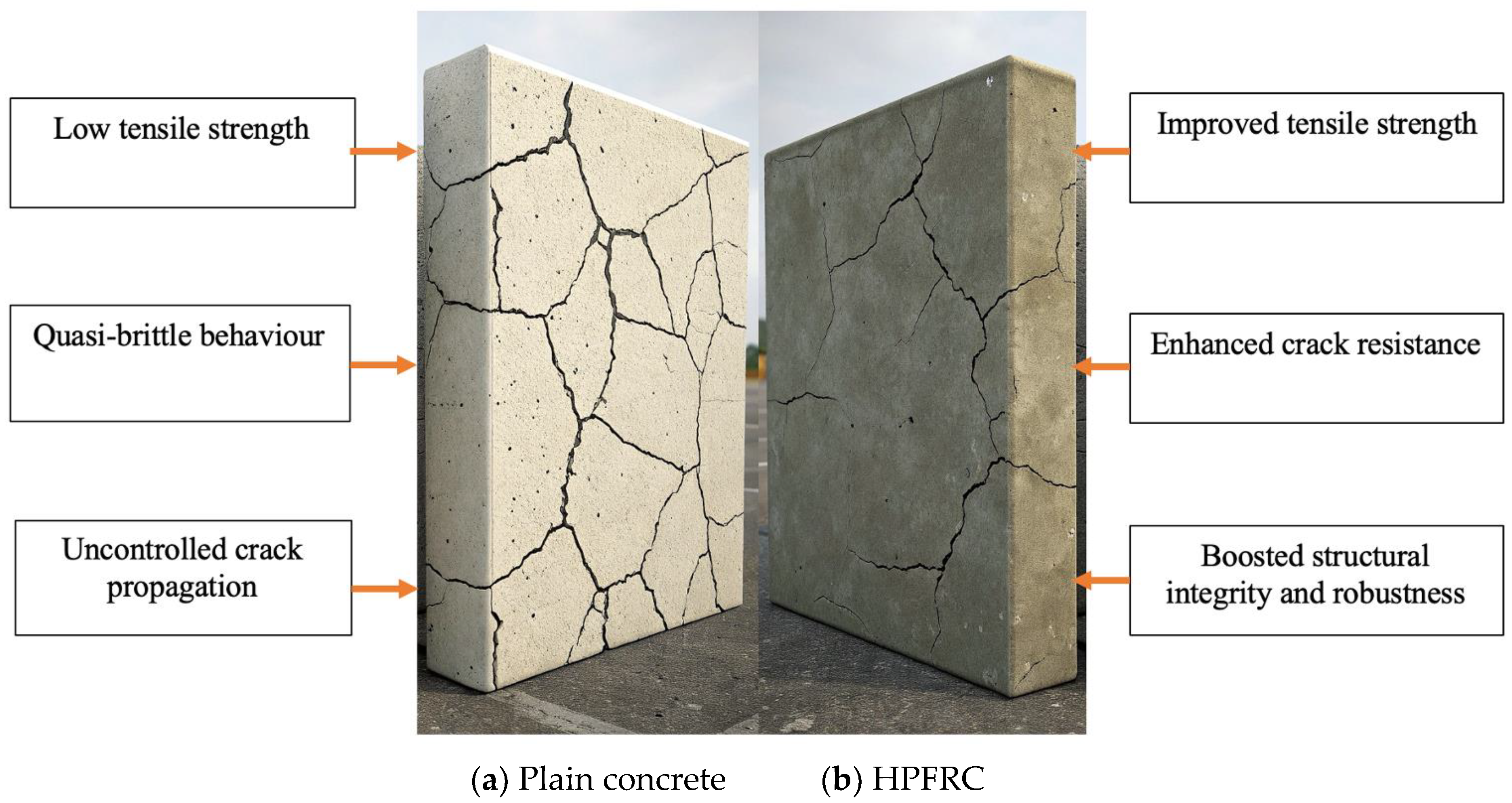

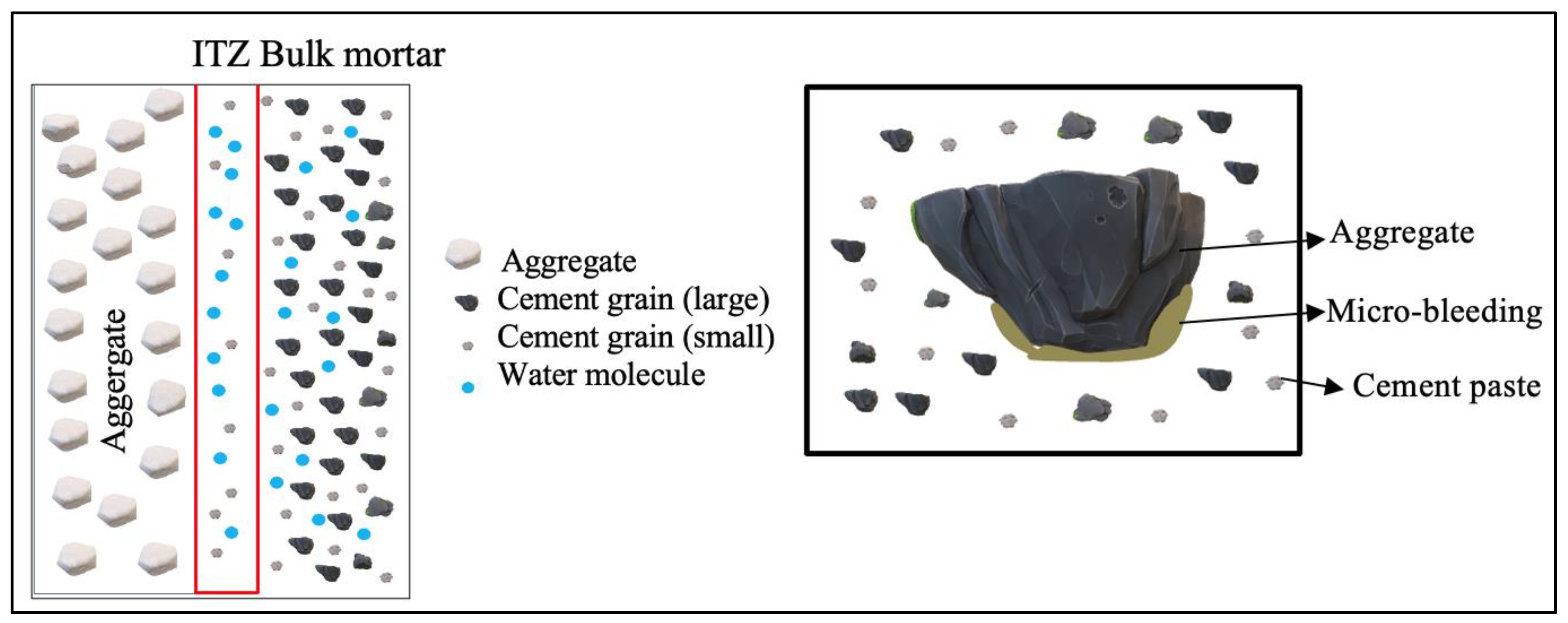
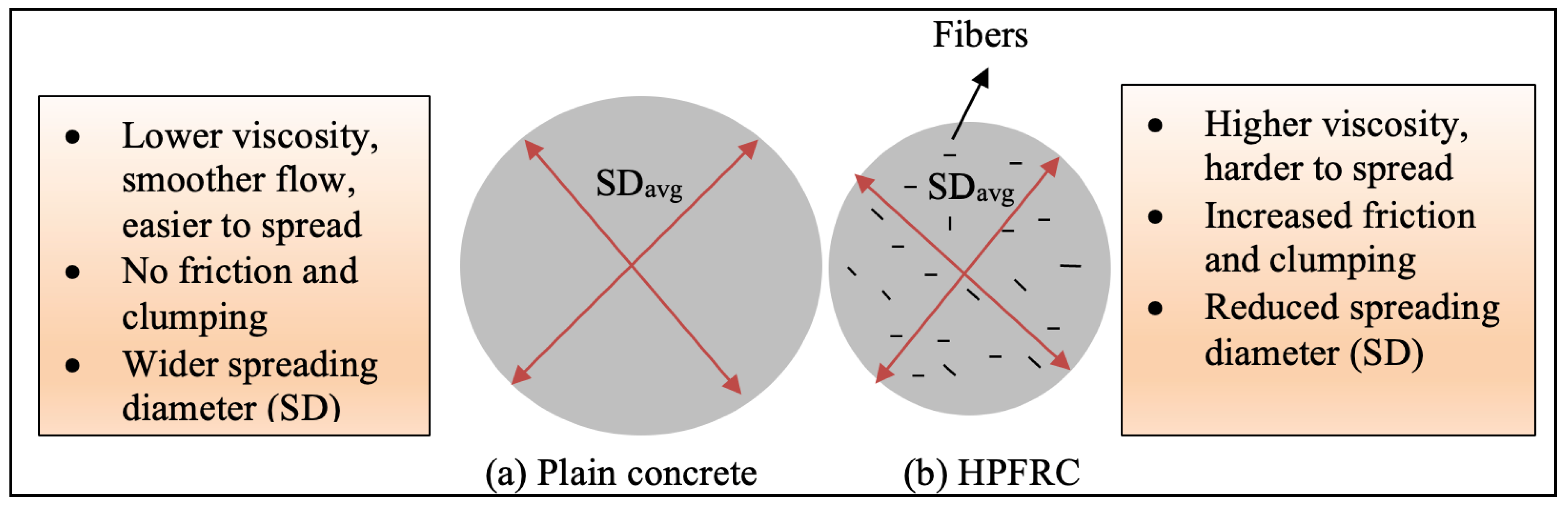
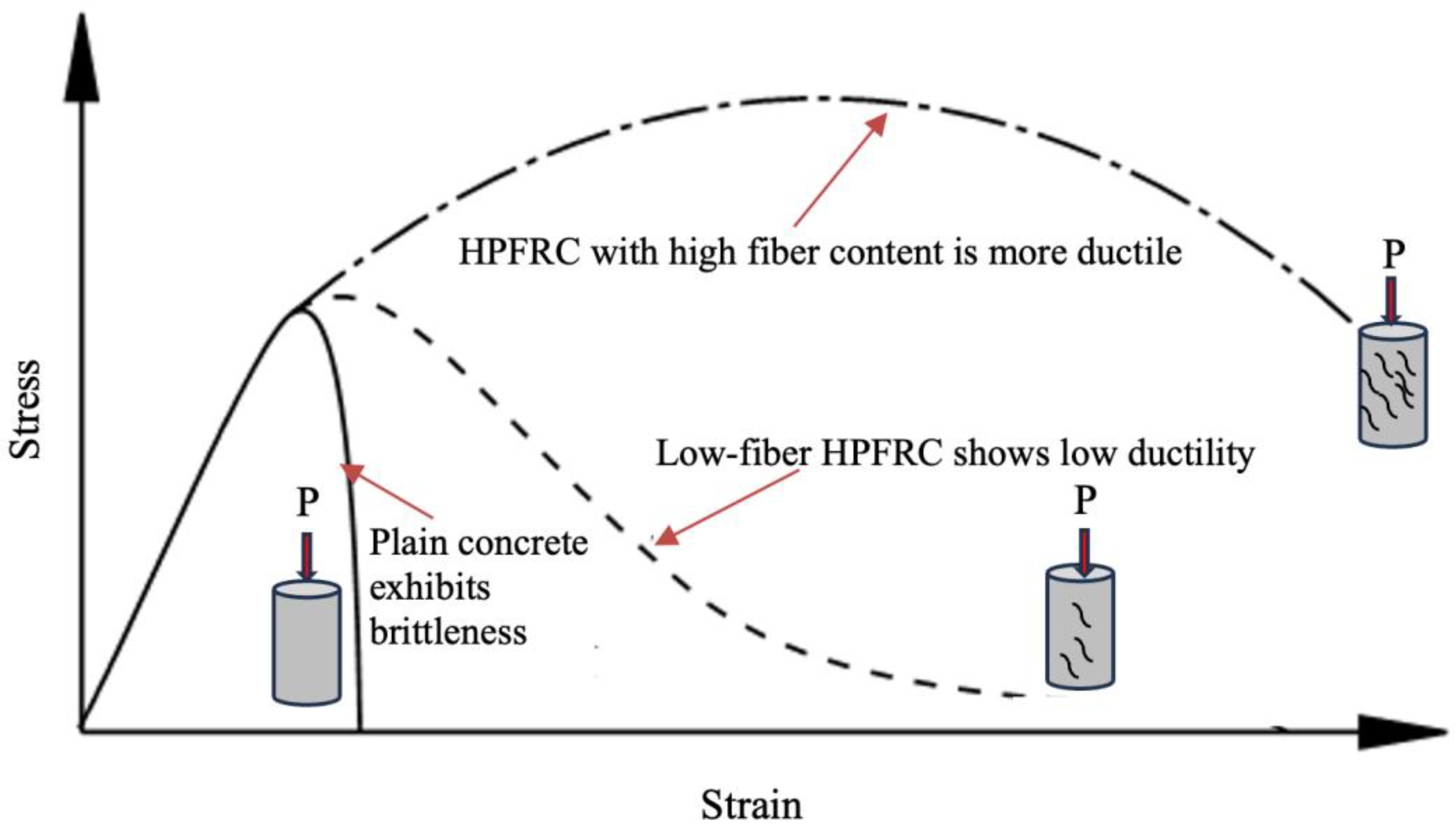
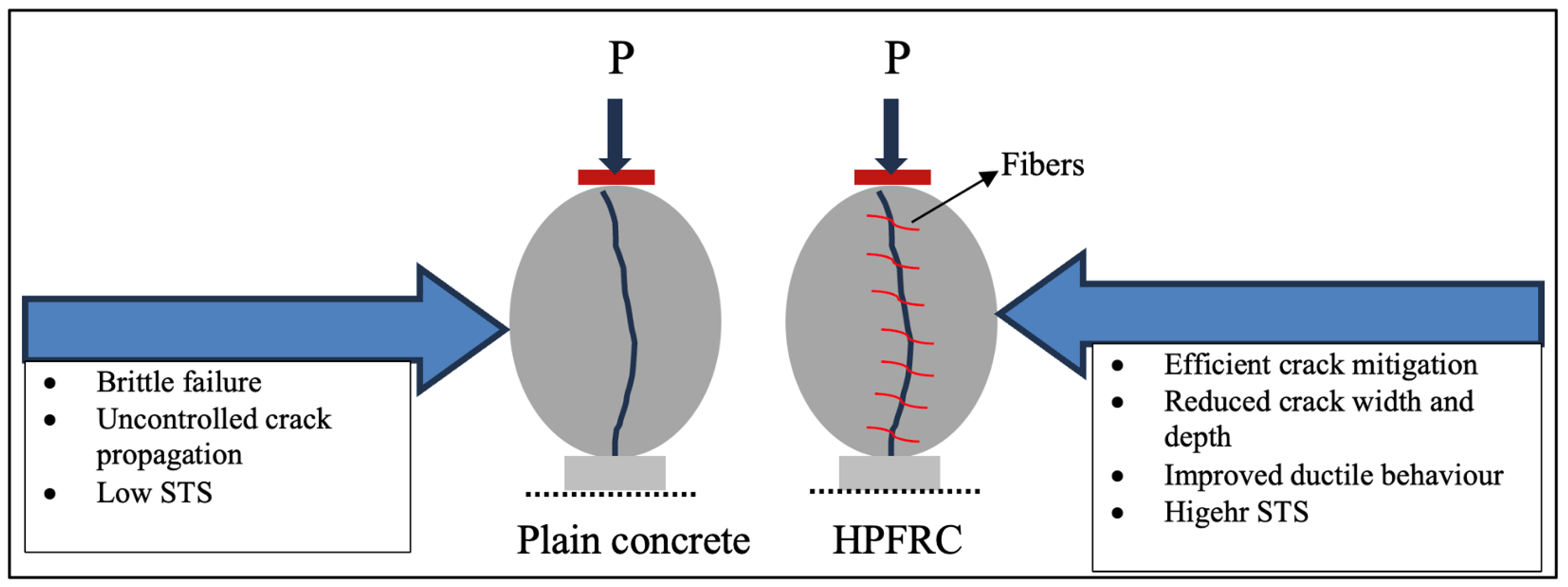
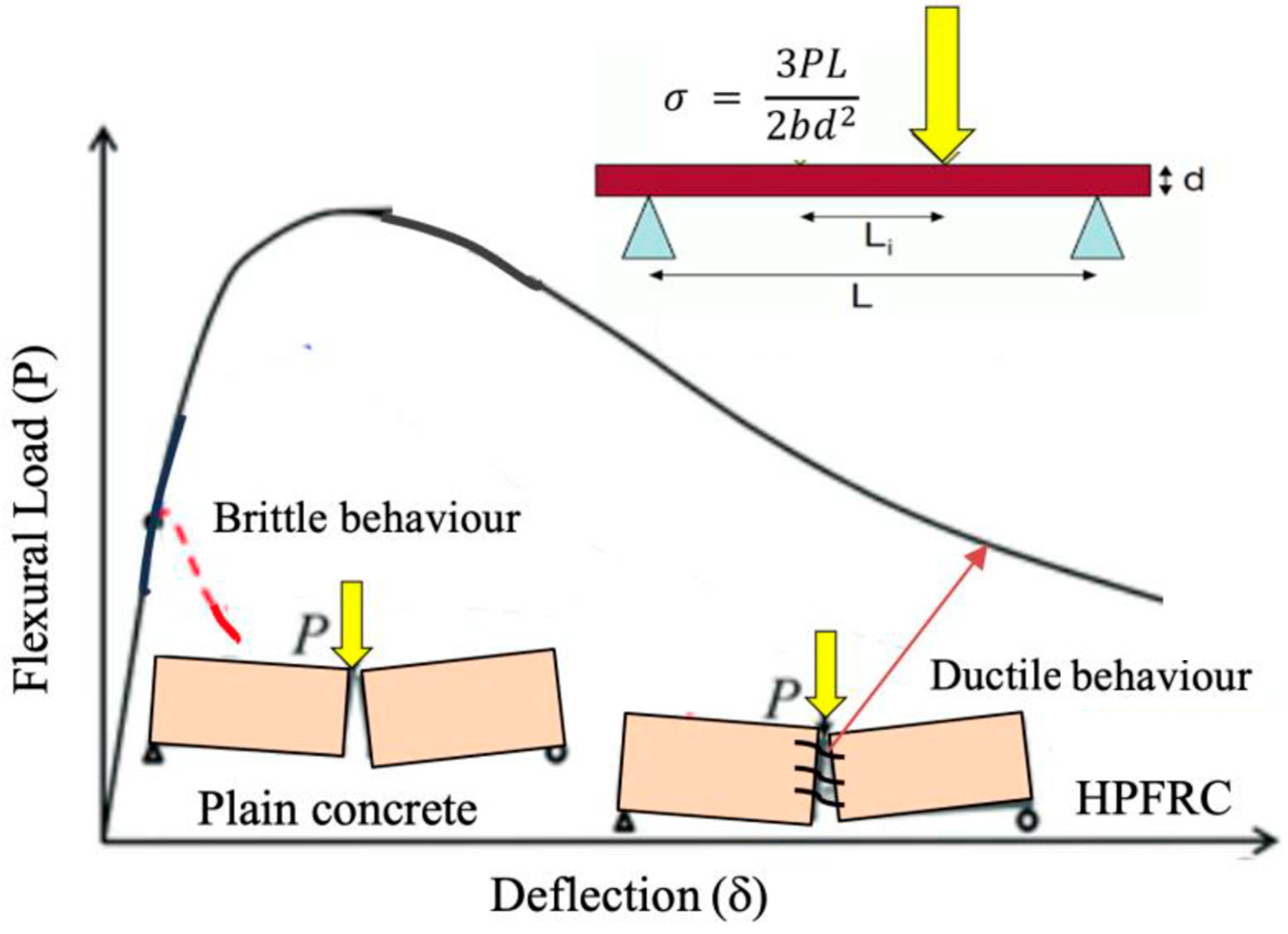

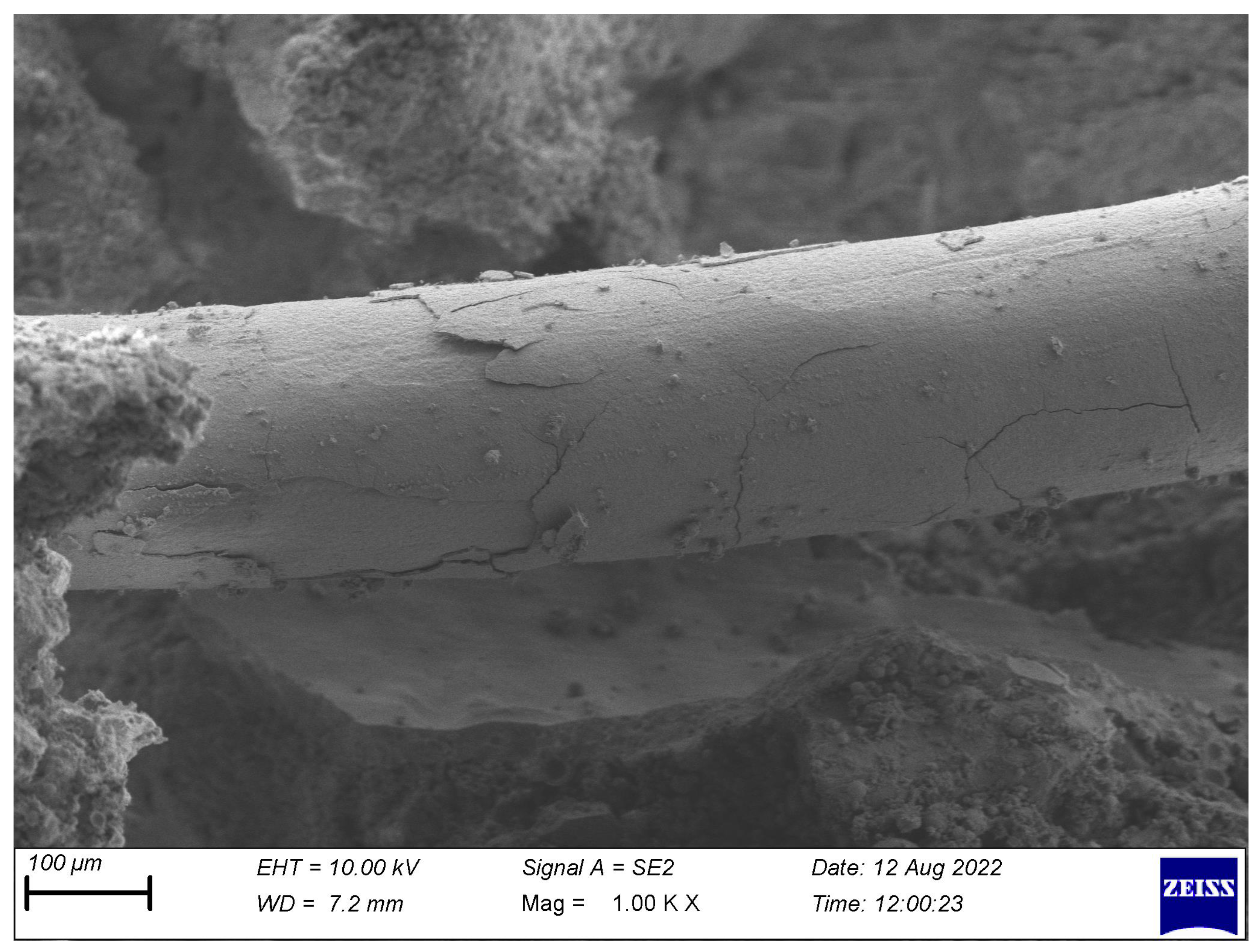
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbulut, Z.F.; Tawfik, T.A.; Smarzewski, P.; Guler, S. Advancing Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Performance, Crack Resistance Mechanism, and Future Innovations. Buildings 2025, 15, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081247
Akbulut ZF, Tawfik TA, Smarzewski P, Guler S. Advancing Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Performance, Crack Resistance Mechanism, and Future Innovations. Buildings. 2025; 15(8):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081247
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbulut, Zehra Funda, Taher A. Tawfik, Piotr Smarzewski, and Soner Guler. 2025. "Advancing Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Performance, Crack Resistance Mechanism, and Future Innovations" Buildings 15, no. 8: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081247
APA StyleAkbulut, Z. F., Tawfik, T. A., Smarzewski, P., & Guler, S. (2025). Advancing Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Performance, Crack Resistance Mechanism, and Future Innovations. Buildings, 15(8), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081247








