Economic Aspects of Demolition: Challenges and Prospects—A Case Study in the Municipality of Caivano (Campania, Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- the demolishing action, understood as the final stage in the life cycle of the built environment and thus capable of generating residual value when considering the recoverable worth of certain building components;
- (ii)
- the higher market value associated with the reconstruction of a building, compared to conservative interventions, proportional to both the formal and technological enhancement of the structure and the improvement of its energy performance;
- (iii)
- the reactivation of urban land rents previously “inhibited” by low-quality building fabrics, particularly in light of the increasing use by policymakers of measures related to the so-called “density bonus,” more commonly referred to as “building incentives” [17];
- (iv)
- the environmental impact of demolition itself, due to material disposal, which can be assessed in terms of the building product’s overall “footprint” through Life Cycle Assessment methodologies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology
2.2. Demolitions and Appraisal Aspects
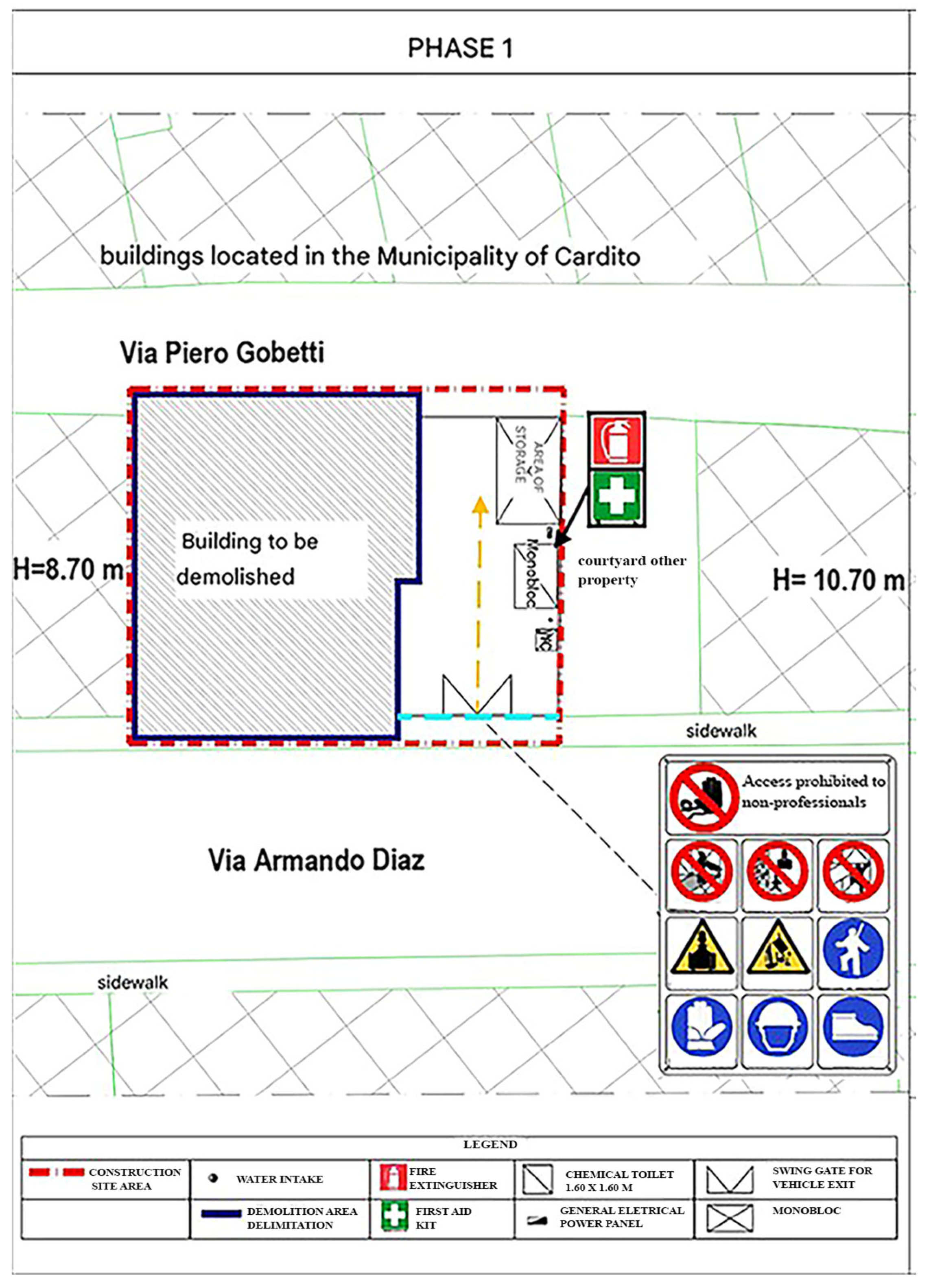
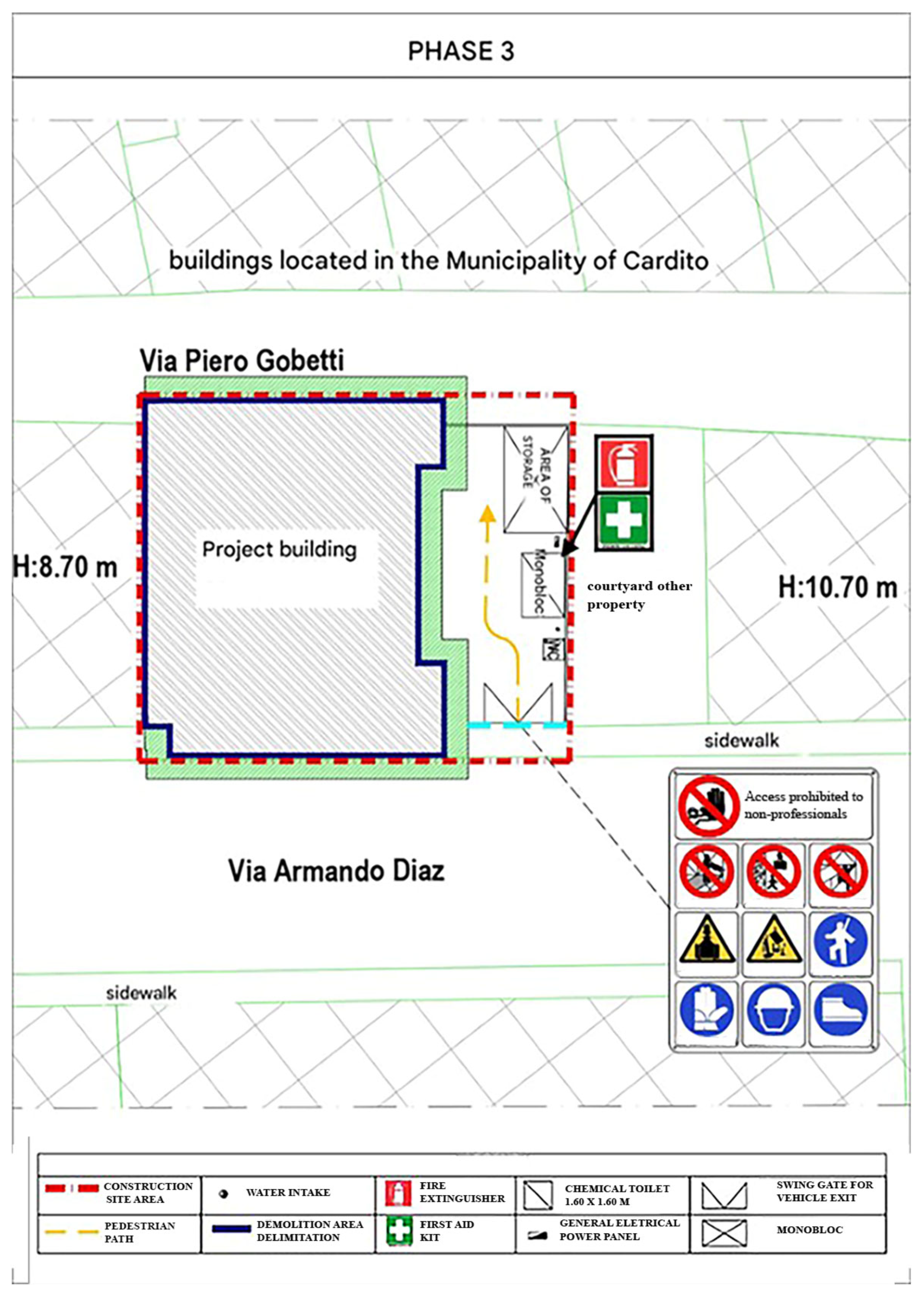
2.3. The Case Study
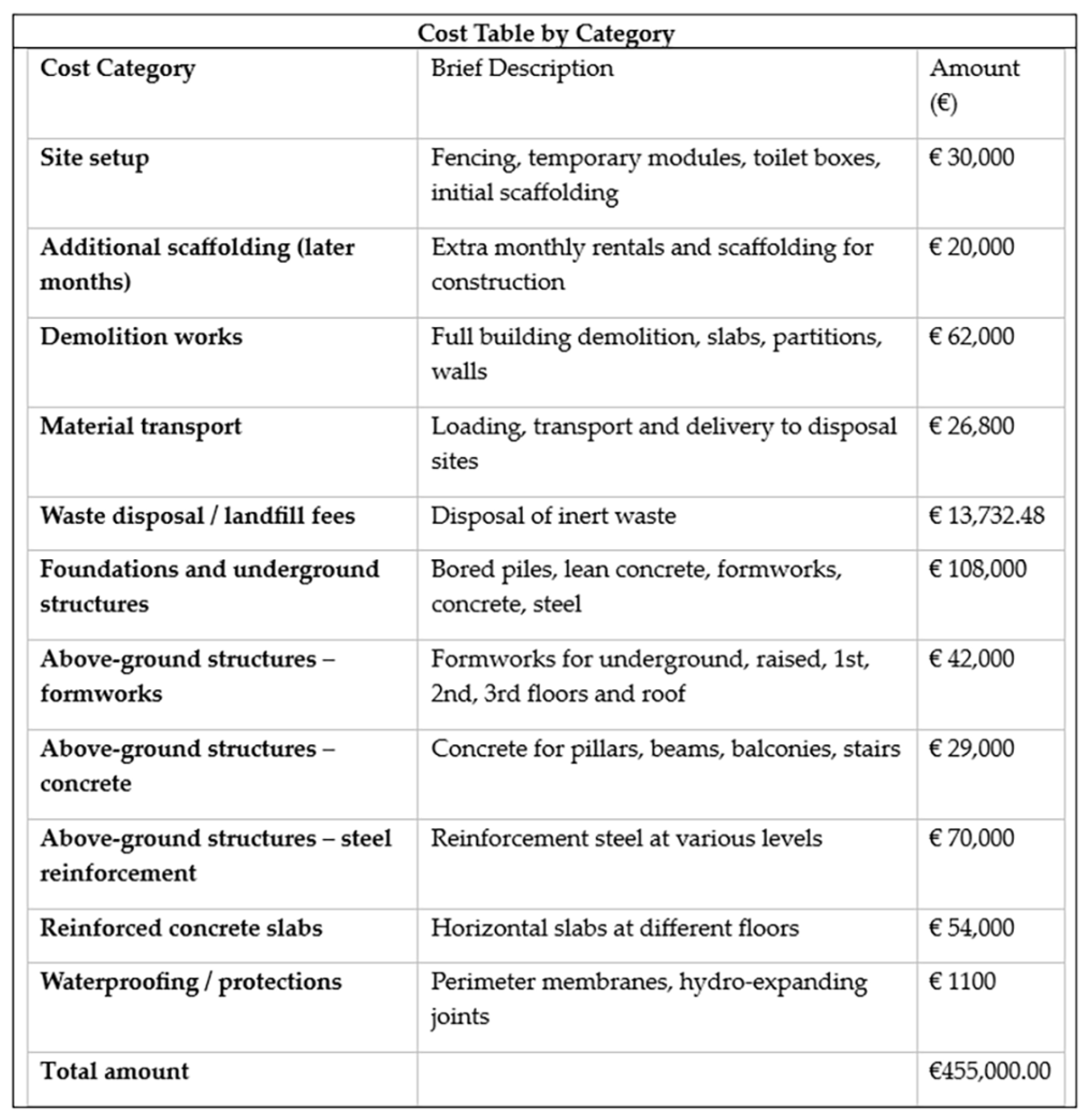
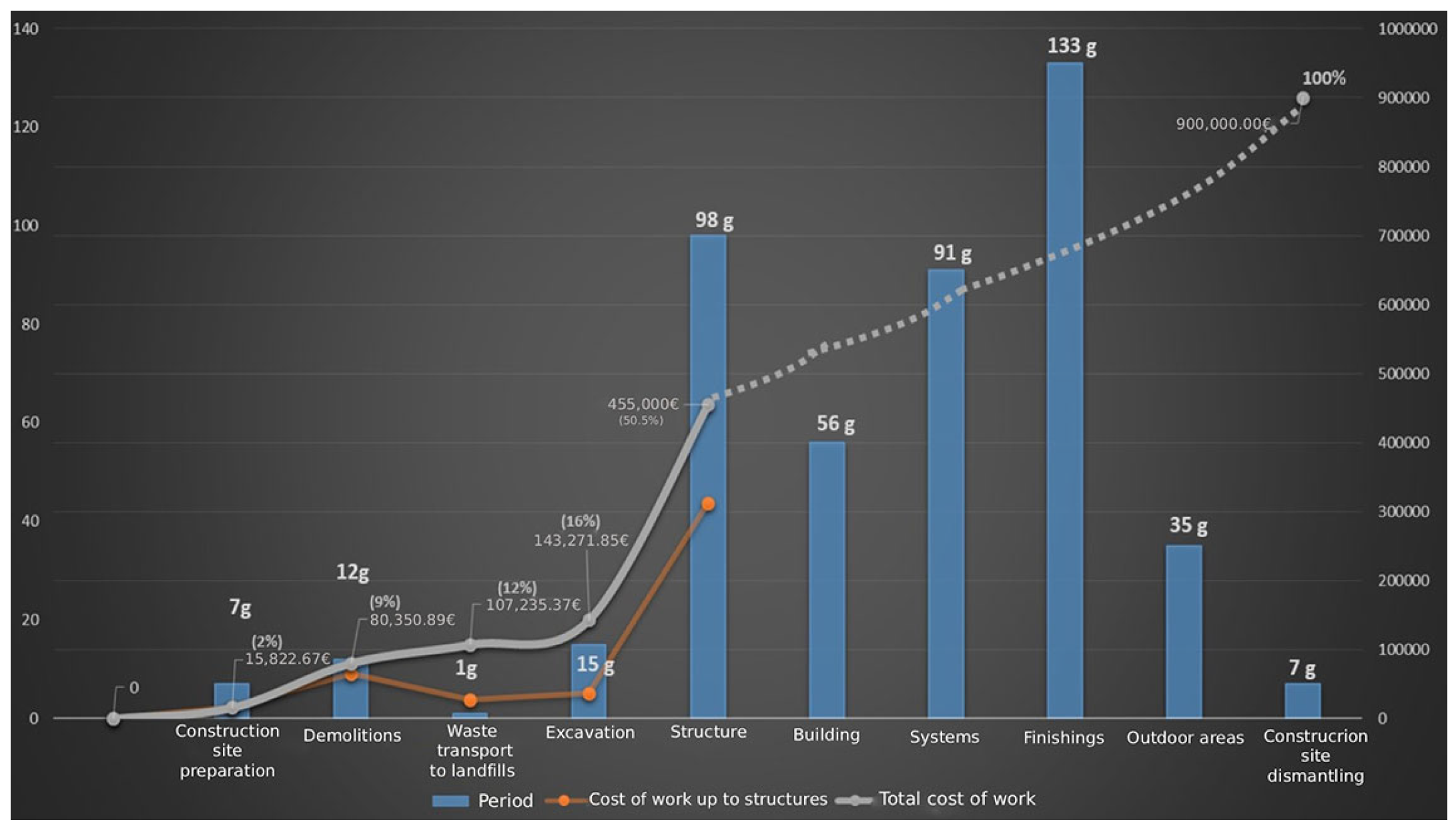
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rusci, S.; Perrone, M.A. The City to Be Demolished: A Case Study for the Analysis of Demolition and Urban Contraction Costs in Italy. Valori Valutazioni 2020, 26, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, S.Z.; Syal, M.G.M.; Lamore, R.; Berghorn, G. Approaches and Associated Costs for the Removal of Abandoned Buildings. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 31 May–2 June 2016; pp. 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lyle, B.; Langston, C. Estimating Demolition Costs for Single Residential Buildings. Aust. J. Constr. Econ. Build. 2012, 3, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15686; Buildings and Constructed Assets: Service Life Planning. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- ISO 20887; Sustainability in Buildings and Civil Engineering Works: Design for Disassembly and Adaptability—Principles, Requirements and Guidance. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Directive 2008/98/EC; Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. European Parliament and Council of the European Union: Strasbourg, France, 2008.
- European Commission. EU Construction and Demolition Waste Management Protocol; Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EU) 2020/852; On the Establishment of a Framework to Facilitate Sustainable Investment, and Amending Regulation (EU) 2019/2088 (EU Taxonomy). European Parliament and Council: Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- Damgaard, A.; Lodato, C.; Butera, S.; Fruergaard, T.A.; Kamps, M.; Corbin, L.; Tonini, D.; Astrup, T.F. Background Data Collection and Life Cycle Assessment for Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW) Management; European Environment Agency (EEA): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. EU Construction & Demolition Waste Management Protocol: Including Guidelines for Pre-Demolition and Pre-Renovation Audits of Construction Works, Updated Edition; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Norme in Materia Ambientale (Codice dell’Ambiente); Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Roma, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Adozione dei Criteri Ambientali Minimi per l’Affidamento del Servizio di Progettazione e Lavori per gli Interventi Edilizi (CAM Edilizia 2022); Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Roma, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Regolamento Recante la Disciplina Della Cessazione Della Qualifica di Rifiuto (End of Waste) dei Rifiuti Inerti da Costruzione e Demolizione e di Altri Rifiuti Inerti di Origine Minerale; Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Roma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Circular Economy Action Plan: For a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Building Performance Institute Europe (BPIE). Europe’s Buildings Under the Microscope; BPIE: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. Available online: http://bpie.eu/publication/europes-buildings-under-the-microscope/ (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (ISTAT). 15° Censimento Generale Della Popolazione e Delle Abitazioni; ISTAT: Rome, Italy, 2011. Available online: https://www.istat.it/statistiche-per-temi/censimenti/censimenti-storici/popolazione-e-abitazioni/popolazione-2011/ (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Battisti, F.; Campo, O. The Assessment of Density Bonus in Building Renovation Interventions. The Case of the City of Florence in Italy. Land 2021, 10, 1391, Correction in Land 2022, 11, 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, C. Elementi di Estimo Urbano; Etas Kompass: Milano, Italy, 1968; p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- Rosasco, P.; Sdino, L.; Magoni, S. Reclamation Costs and Their Weight in the Economic Sustainability of a Project. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 223, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordà, N. Demolizioni Civili e Industriali: Tecniche, Statica, Rischi Specifici e Interferenti, Misure, Piano di Manutenzione, Gestione Rifiuti; EPC Libri: Milano, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, C.; De Rossi, B. Principi di Economia ed Estimo; Etas Kompass: Milano, Italy, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Fiore, P.; Donnarumma, G.; Sicignano, C. Refurbishment vs. Demolition and Reconstruction: Analysis and Evaluation in Order to Choose the Intervention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Building Renovation and Regeneration, Fisciano, Italy, 3–8 September 2017; University of Salerno: Fisciano, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Decreto-Legge 15 Settembre 2023, n. 123, Convertito, con Modificazioni, Dalla Legge 13 Novembre 2023, n. 159; Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Misure Urgenti in Materia di Salute, Sostegno al Lavoro e all’Economia, Nonché di Politiche Sociali Connesse all’Emergenza Epidemiologica da COVID-19 (Decreto Rilancio); Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gotta, A. Riqualificazione di un Complesso Anni ’60 a Sampeyre come Nuovo Modello di Residenza—Study of Superbonus 110%. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bollettino Ufficiale della Regione Campania. Misure Urgenti per il Rilancio Economico, per la Riqualificazione del Patrimonio Edilizio Esistente, per la Prevenzione del Rischio Sismico e per la Semplificazione Amministrativa (Piano Casa Campania); Bollettino Ufficiale della Regione Campania: Napoli, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Resource Efficiency and Climate Change; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoli, C.; Dragonetti, L.; Ferrante, A. Renovation or Demolition and Reconstruction? Analysis of Design Scenarios Developed According to a Circular Approach; University of Bologna: Bologna, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mesa, J.A.; Fúquene-Retamoso, C.; Maury-Ramírez, A. Life Cycle Assessment on Construction and Demolition Waste: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, F.; De Paola, P. The “Future” of Urban Rent from the Perspective of the Metropolitan Territorial Plan of Naples. Valori Valutazioni 2020, 27, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialardo, A.; Micelli, E. Reconstruction or Reuse? How Real Estate Values and Planning Choices Impact Urban Redevelopment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, S.; Garbarino, E.; Cerreta, M.; Tonini, D. Sustainability assessment of Construction and Demolition Waste management applied to an Italian case. Waste Manag. 2021, 128, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menna, D.; Battisti, F.; Chioccarelli, C.; Forte, F.; Frunzio, G. Economic Aspects of Demolition: Challenges and Prospects—A Case Study in the Municipality of Caivano (Campania, Italy). Buildings 2025, 15, 4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244550
Menna D, Battisti F, Chioccarelli C, Forte F, Frunzio G. Economic Aspects of Demolition: Challenges and Prospects—A Case Study in the Municipality of Caivano (Campania, Italy). Buildings. 2025; 15(24):4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244550
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenna, Daniela, Fabrizio Battisti, Chiara Chioccarelli, Fabiana Forte, and Giorgio Frunzio. 2025. "Economic Aspects of Demolition: Challenges and Prospects—A Case Study in the Municipality of Caivano (Campania, Italy)" Buildings 15, no. 24: 4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244550
APA StyleMenna, D., Battisti, F., Chioccarelli, C., Forte, F., & Frunzio, G. (2025). Economic Aspects of Demolition: Challenges and Prospects—A Case Study in the Municipality of Caivano (Campania, Italy). Buildings, 15(24), 4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244550







