Reliability Analysis on Structural System of Reinforced Concrete Underground Silo Based on LHS-RSM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. LHS-RSM for Structural Reliability Analysis
2.1. Failure Probability of Structure
2.2. LHS-RSM
3. Reliability Analysis Method for Structural System
3.1. Failure Probability of Structural System
3.2. Equivalent Extreme Value Event Theory for Structural System Reliability
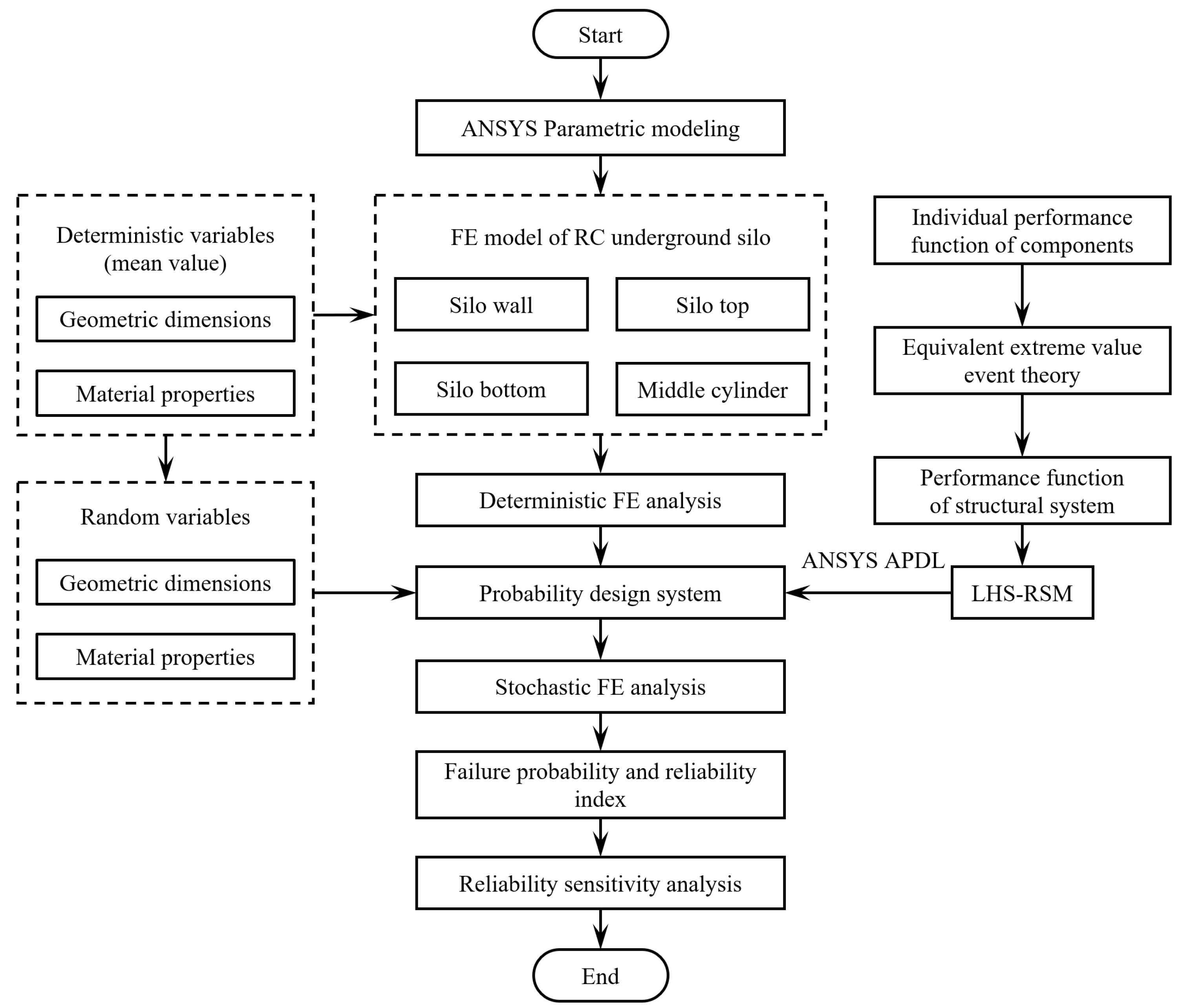
4. Structural System Reliability of Underground Silo
4.1. Engineering Background
4.2. Finite Element Modeling
4.3. Performance Function and Random Variables
4.4. Reliability Analysis Flowchart
5. Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
- (1)
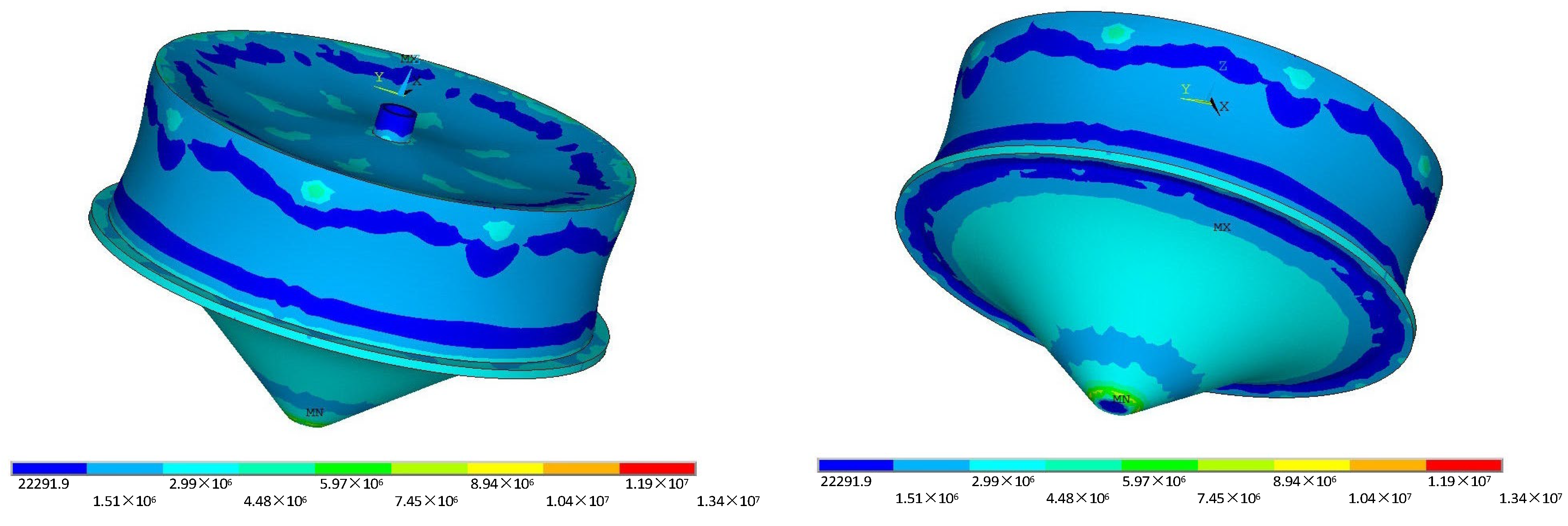
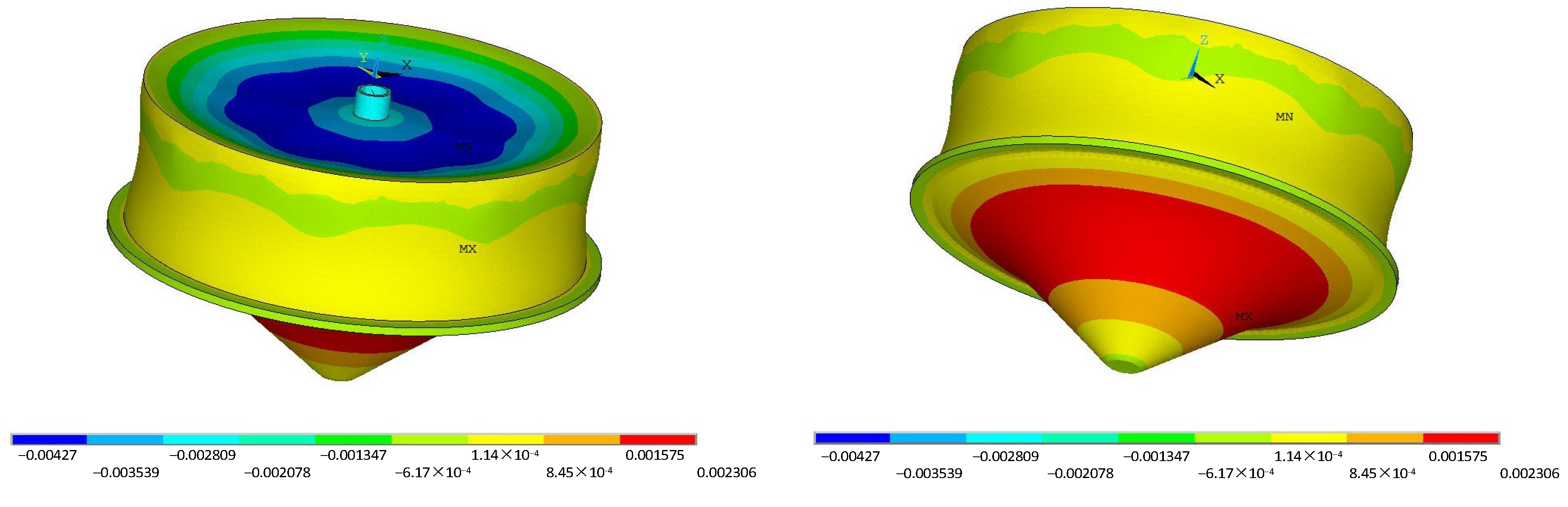
- In the FE analysis of RC underground silo structures, the locations of maximum stress and deformation in the structural system are both at the bottom of the mid-span section of the radial primary beam. The maximum von Mises stress and beam deflection are 13.4 MPa and 4.27 mm, respectively.
- (2)
- The reliability results of individual components of the RC underground silo under a single failure mode, as well as the reliability results of the structural system, can meet the requirements of the current design code. Therefore, this novel type of underground grain silo structure has high safety and applicability.
- (3)
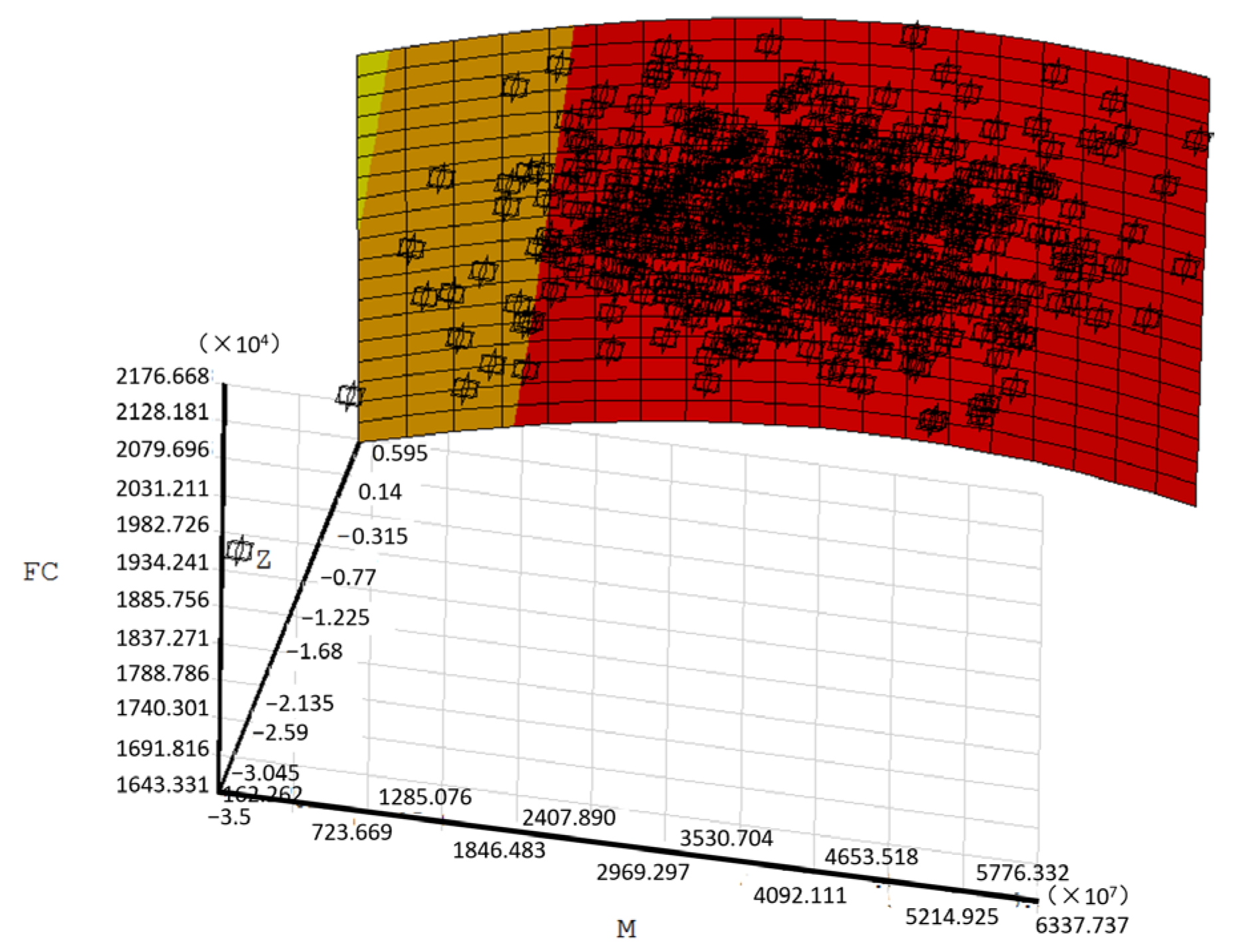
- System failure probability exceeds any individual component’s value and is not merely their sum; component-level assessment therefore underestimates the overall risk. The reliability analysis of the structure should be based on the structural system level, rather than the component level.
- (4)
- Random variable with the greatest impact on the failure probability of the underground silo structural system is the elastic modulus of concrete. In addition, the sensitivity of 11 random parameters is greater than 2.5%, indicating a significant impact on the failure probability of the underground silo structural system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RC | Reinforced Concrete |
| LHS | Latin Hypercube Sampling |
| EEVET | Equivalent Extreme Value Event Theory |
| EEVE | Equivalent Extreme Value Event |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| RSF | Response Surface Function |
| PDS | Probability Design System |
| FE | Finite Element |
References
- Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Q. Experimental study on horizontal pressure of column-supported concrete group silos under earthquake force. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2023, 22, 2827–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hou, J.; Liu, C. A Scientometric Review of Grain Storage Technology in the Past 15 Years (2007–2022) Based on Knowledge Graph and Visualization. Foods 2022, 11, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Z. Element tests and simulation of effects of vertical pressure on compression and mildew of wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Ma, H. Modeling and Application of Temporal Correlation of Grain Temperature during Grain Storage. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls, A.; García, F.; Ramírez, M.; Benlloch, J. Understanding subterranean grain storage heritage in the Mediterranean region: The Valencian silos (Spain). Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 50, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, P. Present condition and outlook for underground silos. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 29, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chuai, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Current situation and new progresses of structure design of underground silos. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 40, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Fang, H.; Li, B.; Wang, F. Stability analysis and full-scale test of a new recyclable supporting structure for underground ecological granaries. Eng. Struct. 2019, 192, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Chen, G.; Cui, C.; Liu, C.; Zhao, B. Numerical Simulation of Backfilling Construction for Underground Reinforced Concrete Grain Silos. Buildings 2024, 14, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cui, C.; Fu, Z.; Jin, L. Monitoring analysis on the stress of reinforced concrete underground grain silo. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 37, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Cui, C.; Fu, Z.; Jiang, M. Reliability sensitivity analysis of underground silo based on Monte-Carlo stochastic finite element method. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 38, 86–90, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Blight, G.E. Long-term sharing of load between steel and concrete in the walls of cylindrical reinforced concrete silos. Mag. Concr. Res. 2002, 54, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.T.; Moore, I.D.; Abdel-Fattah, T.T. A numerical investigation into the behavior of ground-supported concrete silos filled with saturated solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.T.; Moore, I.D.; Abdel-Fattah, T.T. Behaviour of elevated concrete silos filled with saturated solids. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 33, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkaya, C.; Kalkan, E.; Yuksel, S.B. Finite element analysis and practical modeling of reinforced concrete multi-bin circular silos. ACI Struct. J. 2006, 103, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapko, A. Pressure of agricultural bulk solids under eccentric discharging of cylindrical concrete silo bin. Int. Agrophysics 2010, 24, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kermiche, S.; Boussaid, O.; Redjel, B.; Amirat, A. FEM investigation of concrete silos damaged and reinforced externally with CFRP. Mech. Ind. 2017, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, L.E.; Nitin, B.; Rao, P.S. Simulation of the stress regime during grain filling in bamboo reinforced concrete silo. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 83, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiaskova, L.; Bilcik, J.; Soltesz, J. Failure analysis of reinforced concrete walls of cylindrical silos under elevated temperatures. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 109, 104281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurfinkel, G. Simple design of partially post-tensioned silos and other concrete structures under combined tension and moment. ACI Struct. J. 2000, 97, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bywalski, C.; Kamiński, M. A case study of the collapse of the over-chamber reinforced concrete ceiling of a meal silo. Eng. Struct. 2019, 192, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C. Concrete Silos: Failures, Design Issues and Repair/Strengthening Methods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawecki, B.; Halicka, A.; Podgórski, J. Buckling of cylindrical concrete tanks and silos due to prestressing—Nonlinear approach. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 176, 109339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yue, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Quasistatic temperature field simulation of reinforced concrete underground warehouse grain. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2014, 29, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Jin, L.; Shi, X.; Guo, H. Study on wall bearing capacity calculation method of reinforced concrete underground granary. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 36, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Jin, L.; Wang, Z. Earth pressure and bearing capacity analysis on the wall of reinforced concrete underground granary. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2016, 24, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Meng, W.; Wang, Z.; Tian, D.; Xu, X.; Liu, X. Buoyancy early warning of underground granary with “2:8 lime soil” backfilling. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Tianhe, M. Friction analysis of underground silos during backfilling. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Cui, C.; Fu, Z.; Jiang, M. Research on deformation and internal force of reinforced concrete underground grain silo wall. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2019, 15, 458–464. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Liang, X.; Huo, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Engineering test and numerical analysis of underground concrete silo. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2020, 42, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chuai, J.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Mechanical Properties of the Vertical Joints of Prefabricated Underground Silo Steel Plate Concrete Wall. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6643811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, K.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Plastic–Concrete Waterproof Walls of an Underground Granary Subject to Combined Bending Moment and Water Pressure. Buildings 2022, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, C.; Yang, J.; Xi, H. A hydrostatic test study on the waterproofing of an underground ecological granary using a plastic-concrete system. Structures 2022, 44, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, Z. Waterproofing performance of polypropylene—Concrete wall of underground silo under combined compressive stress and water pressure. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, C.G.; Bourgund, U. A fast and efficient response surface approach for structural reliability problems. Struct. Saf. 1990, 7, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Zheng, Y. Cumulative formation of response surface and its use in reliability analysis. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2000, 15, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Das, P.K. Improved response surface method and its application to stiffened plate reliability analysis. Eng. Struct. 2000, 22, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, A. An efficient sampling scheme: Updated Latin Hypercube Sampling. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 1992, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Fan, W. The equivalent extreme-value event and evaluation of the structural system reliability. Struct. Saf. 2007, 29, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, D. Anti-floating test in construction and closed-water test process of underground reinforced concrete silo. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 38, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, S.; Xie, W. Study of reliability criteria based on Hsich-Ting-Chen concrete strength criterion. J. North China Inst. Water Conserv. Hydroelectr. Power 2011, 32, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Xu, L.; Cheng, G. Reliability analysis for complex large-scale structures based on ANSYS software. Build. Struct. 2002, 32, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- GB 50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures (2015 Edition). China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB 50077-2017; Standard for Design of Reinforced Concrete Silos. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Li, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, C. Reliability analysis of underground rock caverns using non-intrusive stochastic finite element method. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 34, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- GB 50068-2018; Unified Standard for Reliability Design of Building Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Straub, D.; Schneider, R.; Bismut, E.; Kim, H. Reliability analysis of deteriorating structural systems. Struct. Saf. 2020, 82, 101877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naess, A.; Leira, B.J.; Batsevych, O. Reliability analysis of large structural systems. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2012, 28, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, Z. Global sensitivity analysis of reliability of structural bridge system. Eng. Struct. 2019, 194, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C. Reliability analysis of CRTS II track slab considering multiple failure modes. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
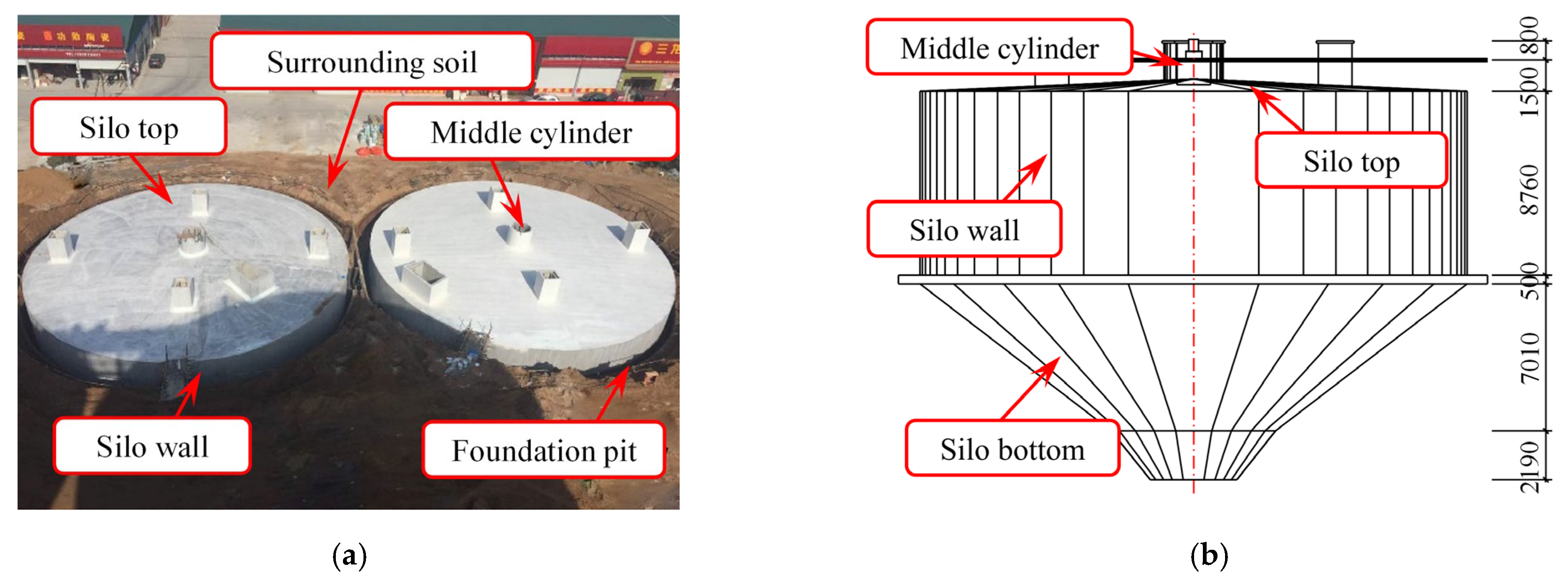
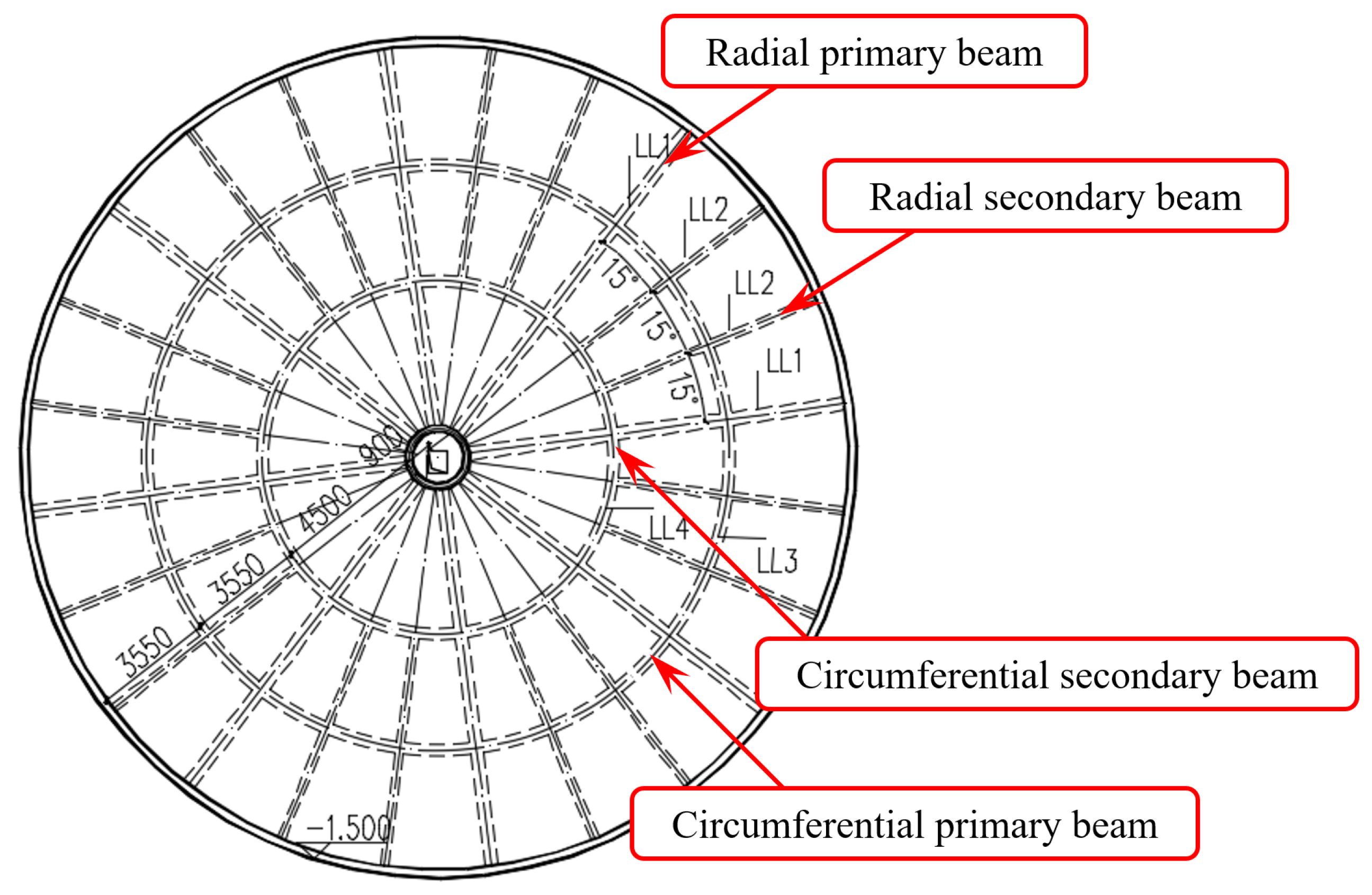
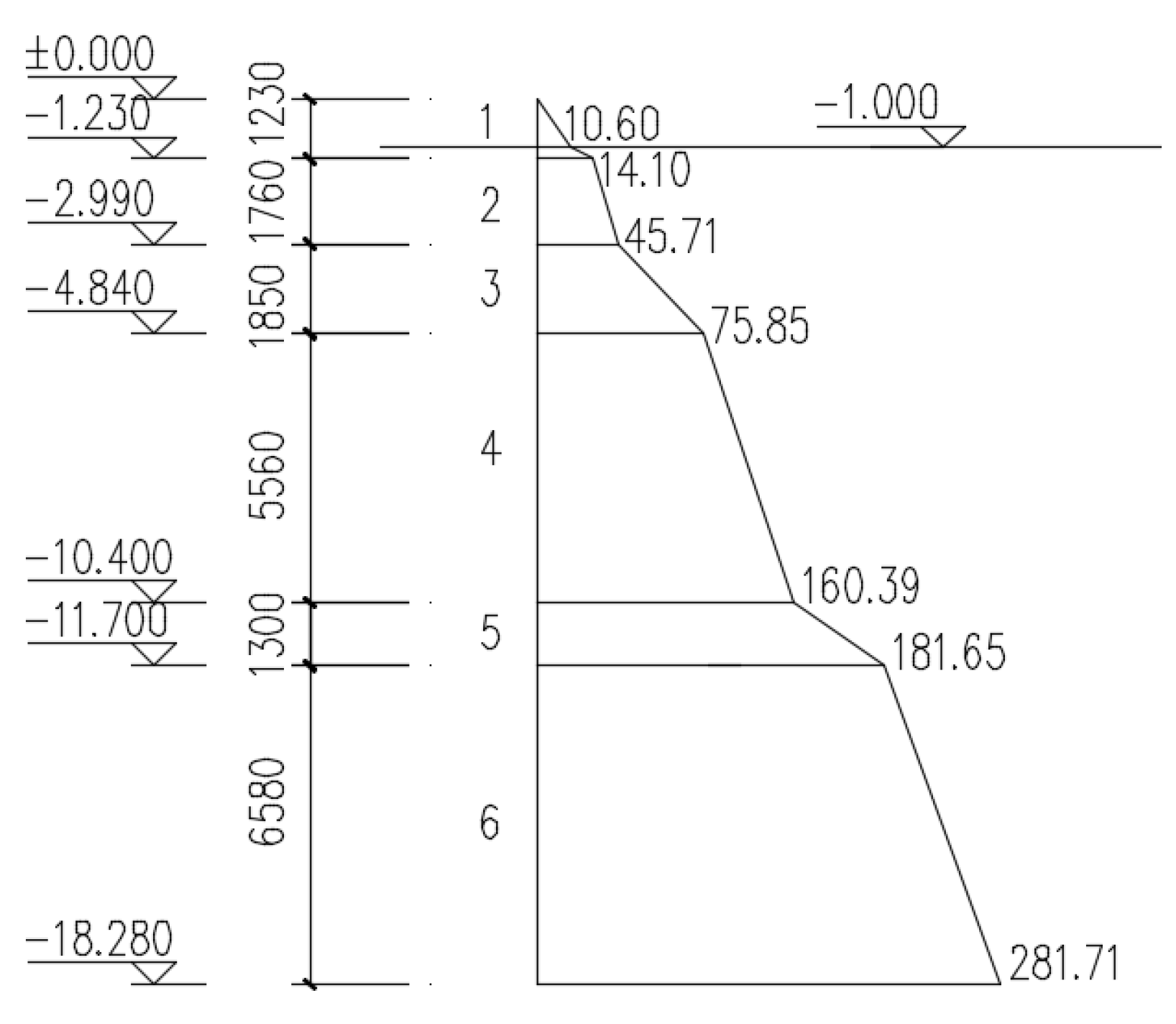
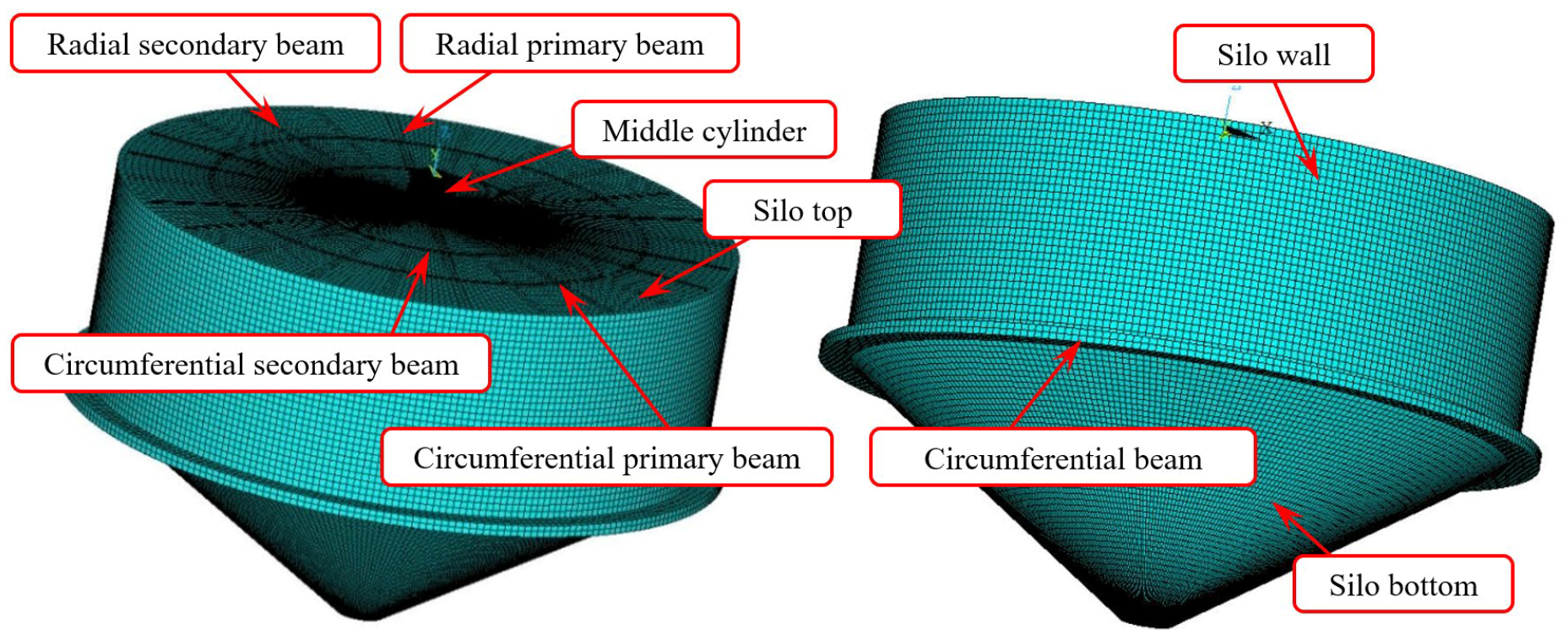
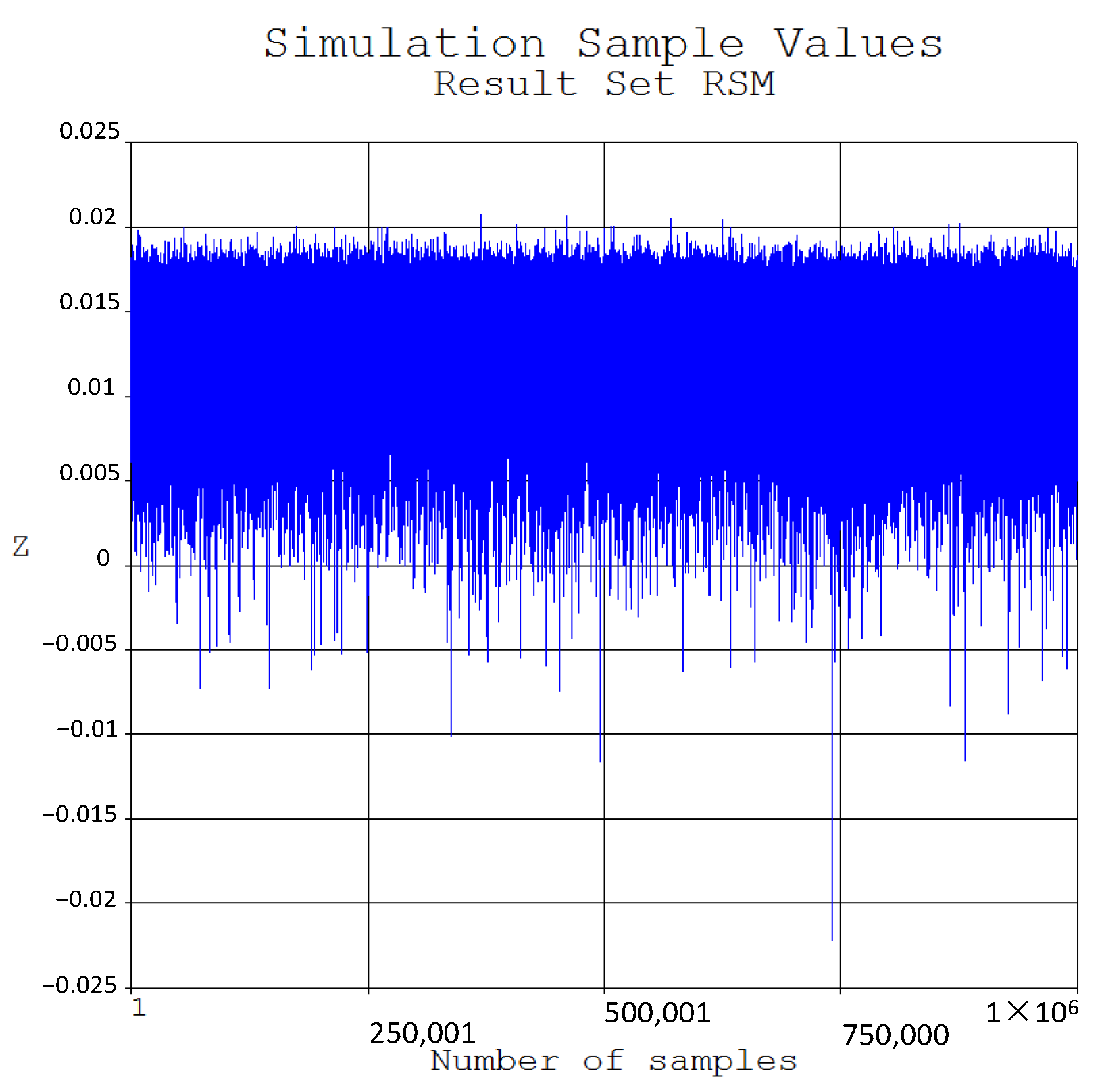
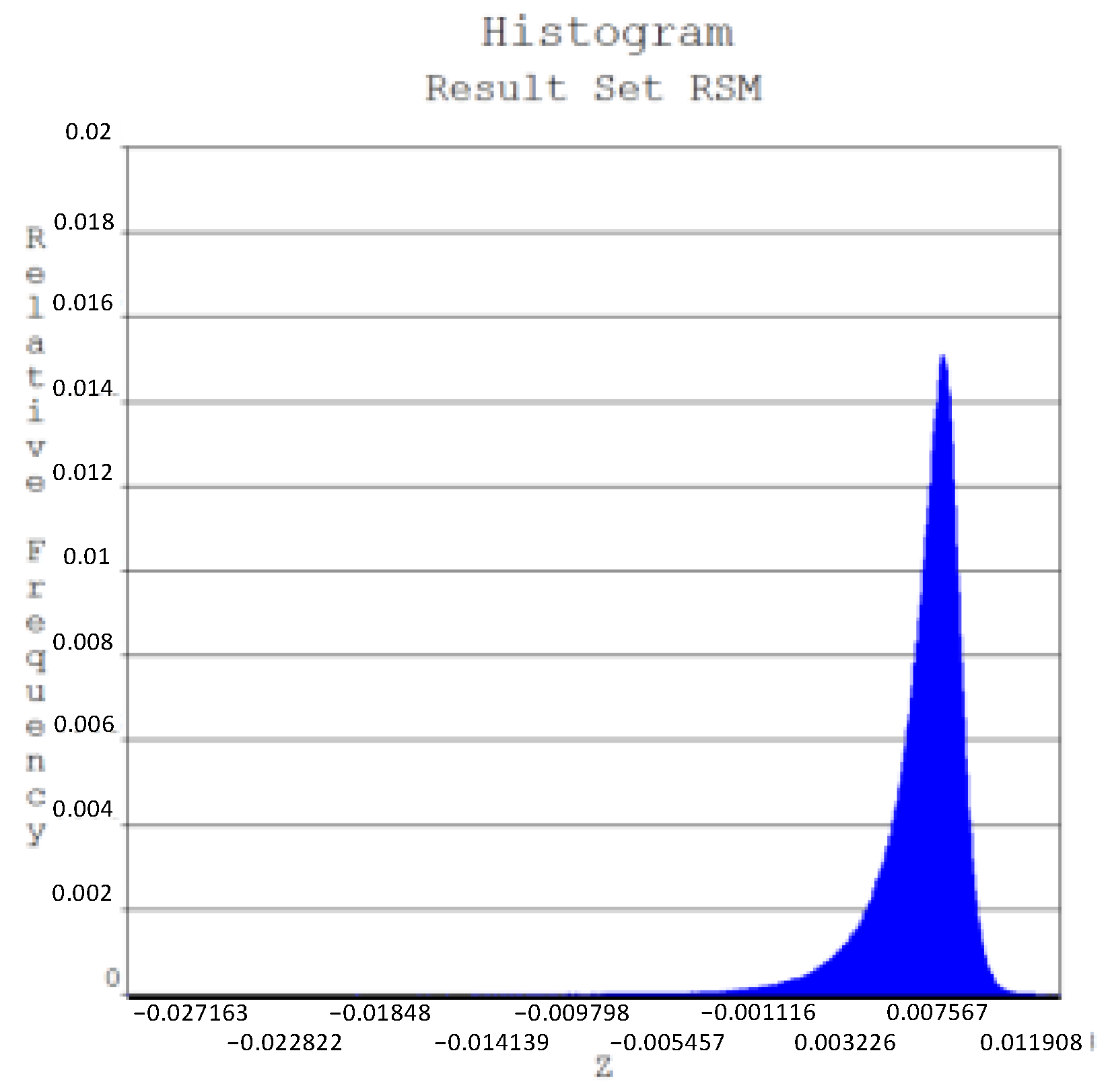
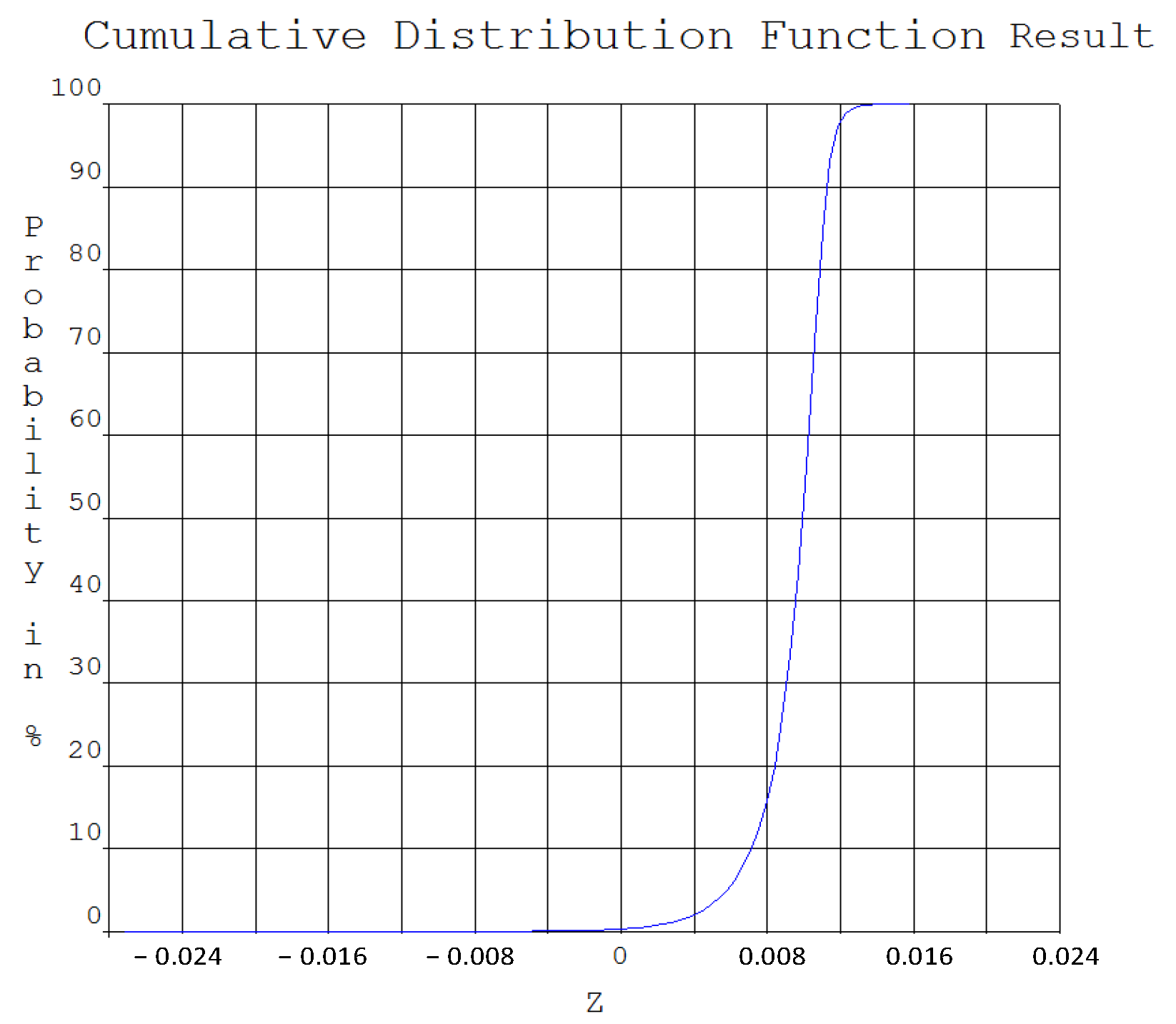
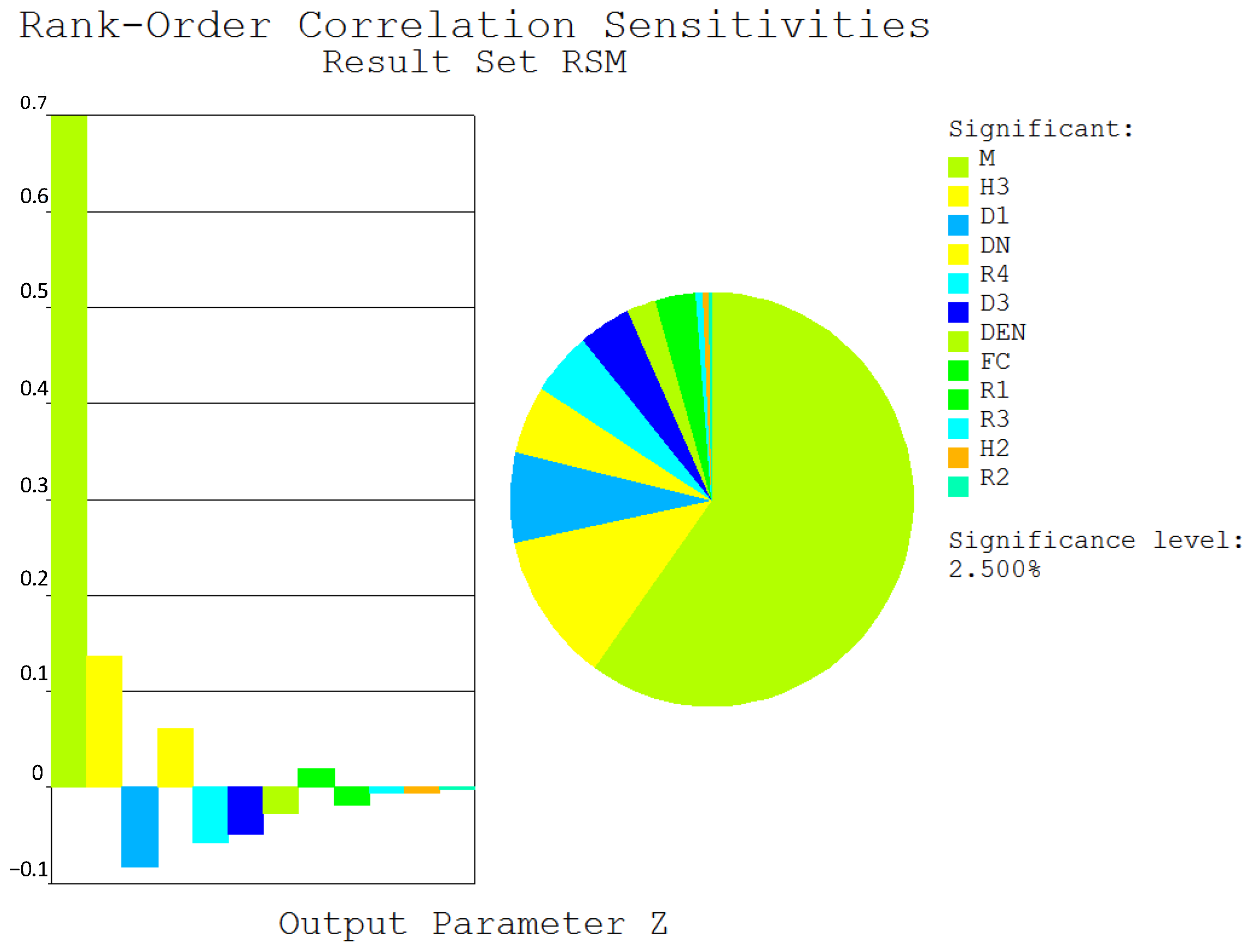
| Soil Layer | Soil Type | Average Thickness (m) | Accumulated Depth (m) | Moisture Content (%) | Specific Gravity (kN/m3) | Void Ratio | Internal Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Silty sand | 1.23 | 1.23 | 21.4 | 20 | 0.540 | 28 |
| 2 | Silty clay | 1.76 | 2.99 | 22.6 | 20.4 | 0.835 | 13.3 |
| 3 | Silt | 1.85 | 4.84 | 22.1 | 20.8 | 0.682 | 24.1 |
| 4 | Silty sand | 5.56 | 10.40 | 21.4 | 20 | 0.540 | 28 |
| 5 | Silt | 1.30 | 11.70 | 24.4 | 21.3 | 0.688 | 25.5 |
| 6 | Silty sand | 6.58 | 18.28 | 21.4 | 20 | 0.540 | 28 |
| 7 | Silt | 1.29 | 19.57 | 23.7 | 20.6 | 0.678 | 26 |
| 8 | Silty sand | 6.88 | 26.45 | 21.4 | 20 | 0.540 | 28 |
| Random Variable | Distribution | Mean Value | Variable Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness of silo top H1 | Normal | 0.150 m | 0.06 |
| Thickness of silo wall H2 | Normal | 0.300 m | 0.06 |
| Thickness of silo bottom H3 | Normal | 0.400 m | 0.06 |
| Radius of silo DN | Normal | 12.5 m | 0.05 |
| Elastic modulus of concrete M | Normal | 3.25 × 1010 Pa | 0.05 |
| Compressive strength of concrete FC | Normal | 19.1 × 106 Pa | 0.15 |
| Density of concrete DEN | Normal | 2500 kg/m3 | 0.03 |
| Random Variable | Distribution | Mean Value | Variable Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit weight of first-layer soil R1 | Gumbel | 20.00 kN/m3 | 0.03 |
| Unit weight of second-layer soil R2 | Gumbel | 20.40 kN/m3 | 0.04 |
| Unit weight of third-layer soil R3 | Gumbel | 20.80 kN/m3 | 0.03 |
| Unit weight of fourth layer soil R4 | Gumbel | 20.00 kN/m3 | 0.03 |
| Unit weight of fifth-layer soil R5 | Gumbel | 21.30 kN/m3 | 0.02 |
| Internal friction angle of first-layer soil D1 | Normal | 28.00° | 0.1 |
| Internal friction angle of second-layer soil D2 | Normal | 13.30° | 0.12 |
| Internal friction angle of third-layer soil D3 | Normal | 24.10° | 0.11 |
| Internal friction angle of fourth-layer soil D4 | Normal | 28.00° | 0.1 |
| Internal friction angle of fifth-layer soil D5 | Normal | 25.50° | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Cui, C.; Liu, C.; Zhao, B. Reliability Analysis on Structural System of Reinforced Concrete Underground Silo Based on LHS-RSM. Buildings 2025, 15, 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244498
Chen G, Zhang H, Cui C, Liu C, Zhao B. Reliability Analysis on Structural System of Reinforced Concrete Underground Silo Based on LHS-RSM. Buildings. 2025; 15(24):4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244498
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guixiang, Hao Zhang, Chenxing Cui, Chaosai Liu, and Boyi Zhao. 2025. "Reliability Analysis on Structural System of Reinforced Concrete Underground Silo Based on LHS-RSM" Buildings 15, no. 24: 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244498
APA StyleChen, G., Zhang, H., Cui, C., Liu, C., & Zhao, B. (2025). Reliability Analysis on Structural System of Reinforced Concrete Underground Silo Based on LHS-RSM. Buildings, 15(24), 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244498








