Quantifying the Impact of Soil–Structure Interaction on Performance-Based Seismic Design of Steel Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Seismic Design and Performance Levels Considered
2.1. Seismic Design of Frames
2.2. Performance Levels Considered
3. Modeling of Steel MRFs for the Nonlinear Time-History Analyses
3.1. Modeling of the Superstructure
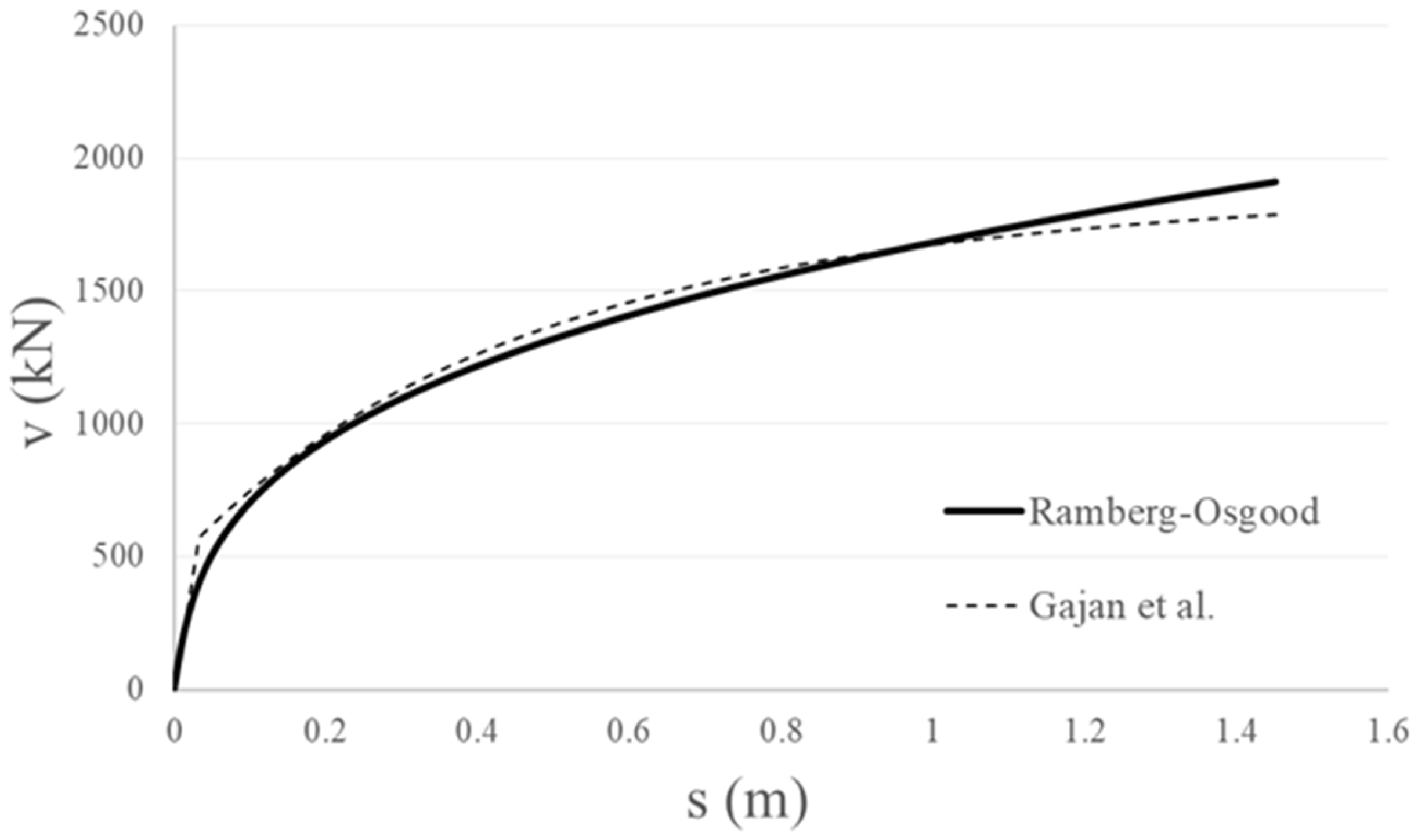
3.2. Modeling of the SSI System
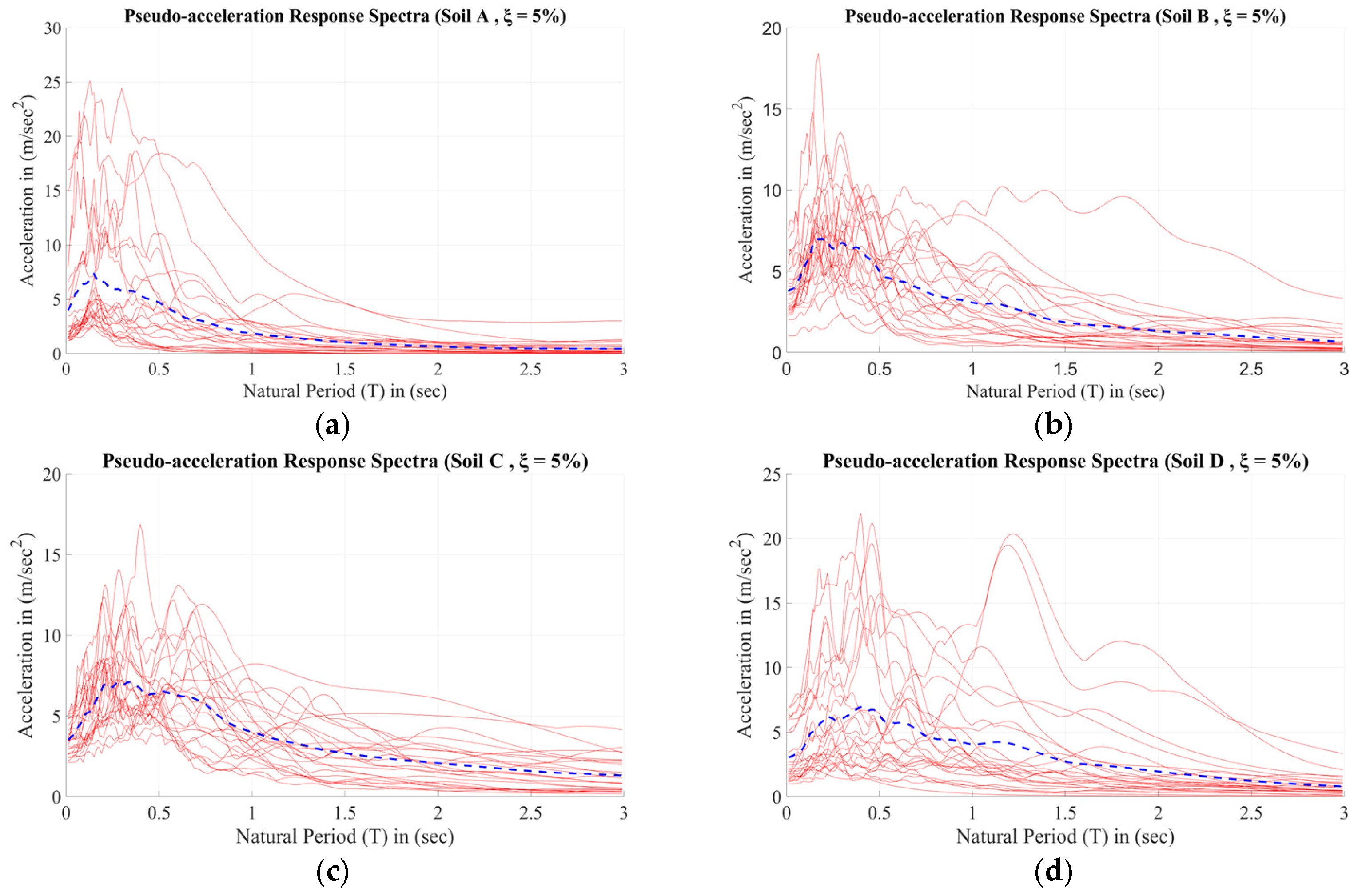
3.3. Seismic Records Considered
4. Results of the Analyses
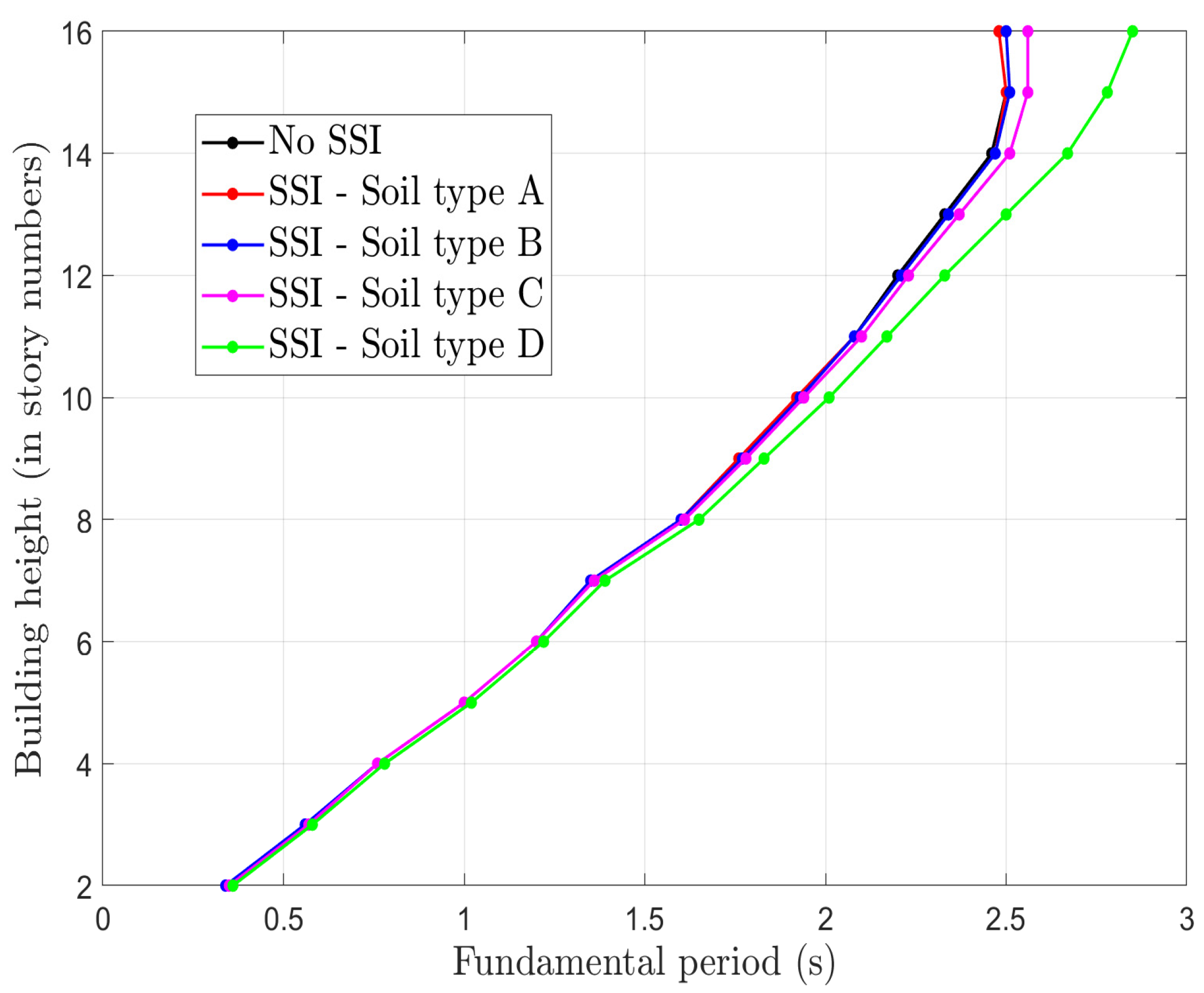
4.1. Effect of SSI on the Fundamental Period
4.2. Influence of SSI on Base Shear
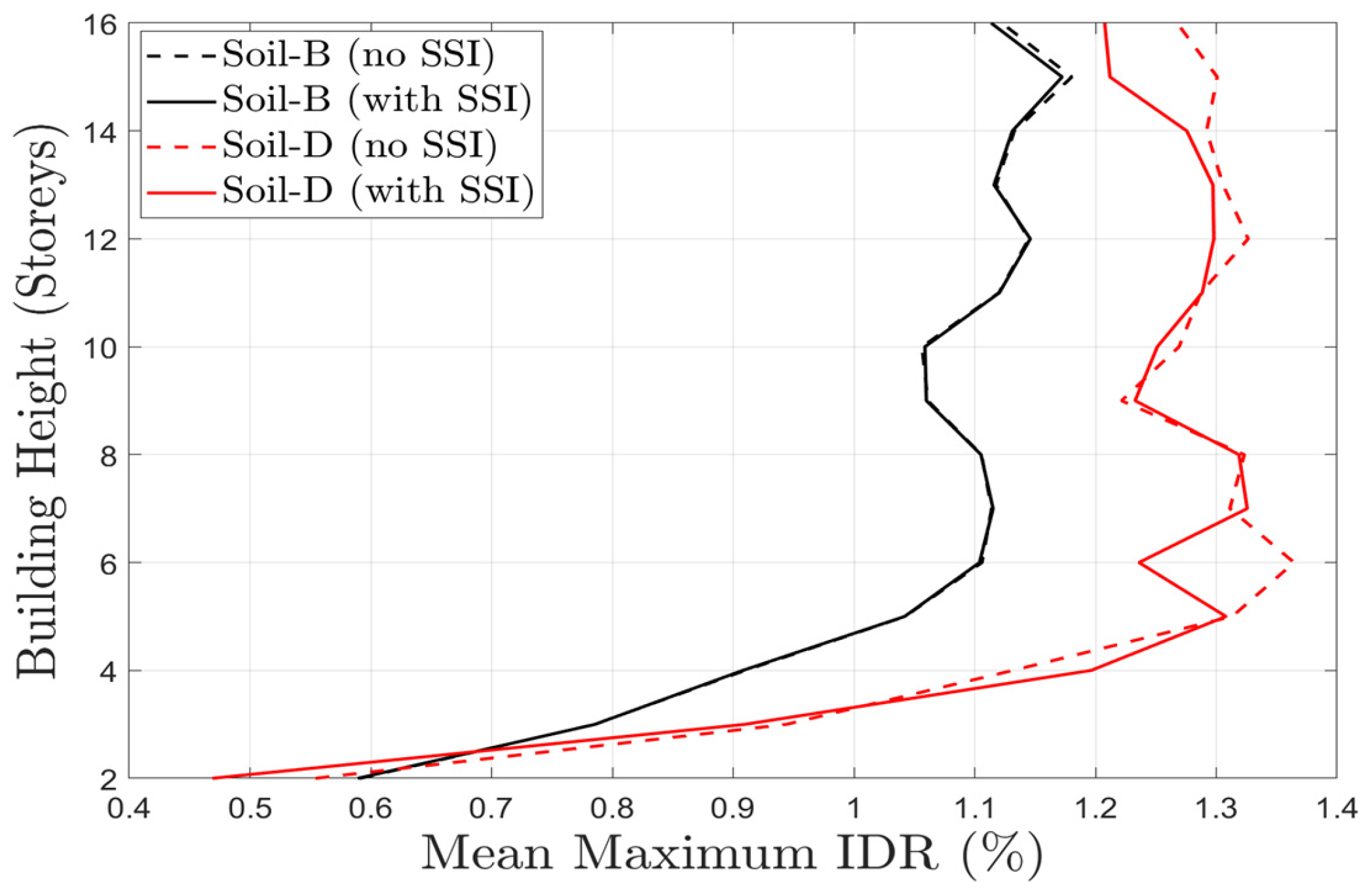
4.3. Impact of Soil Conditions on Maximum IDR Profiles
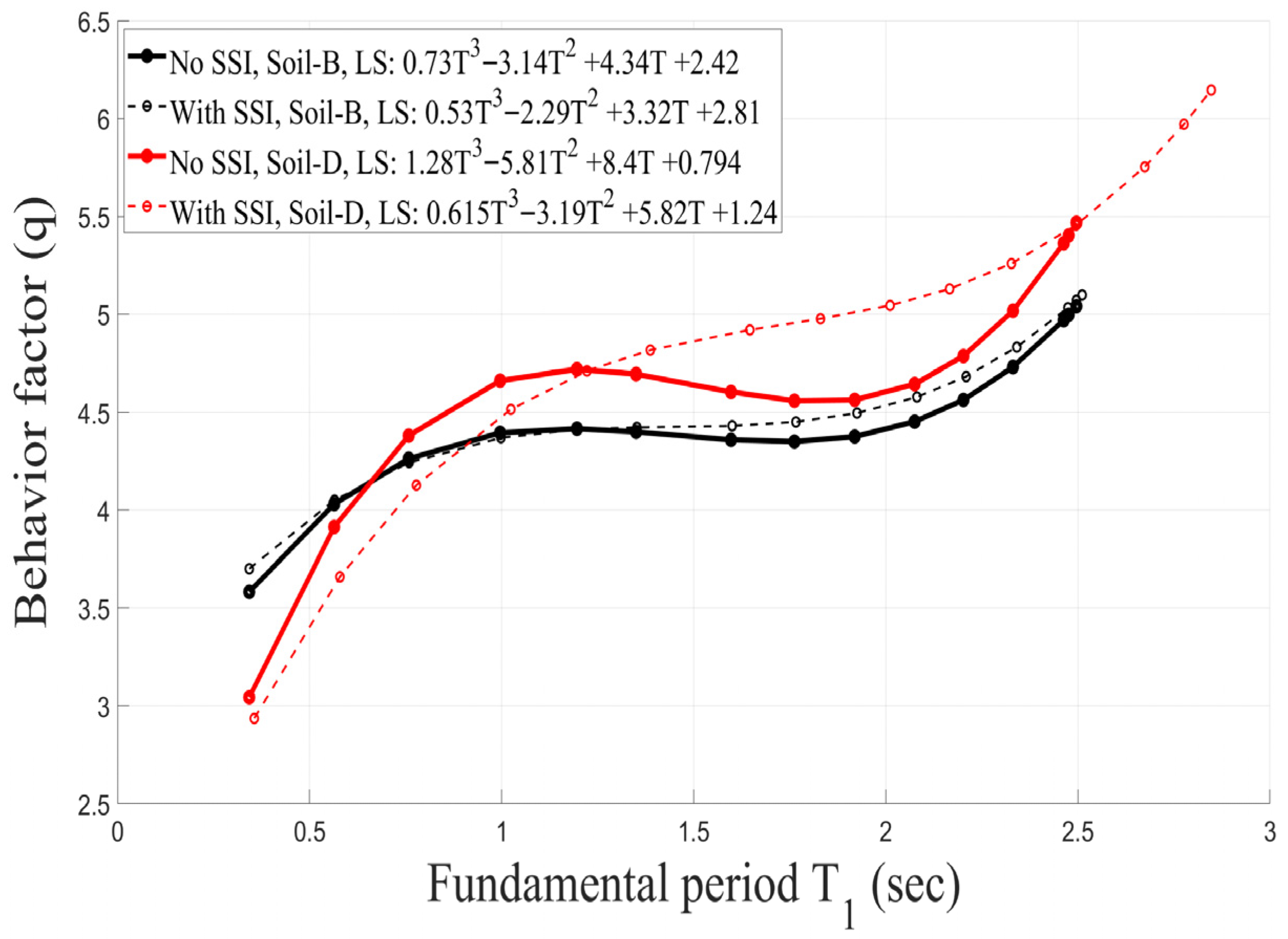
4.4. Influence of Soil Conditions on the Seismic Behavior Factor
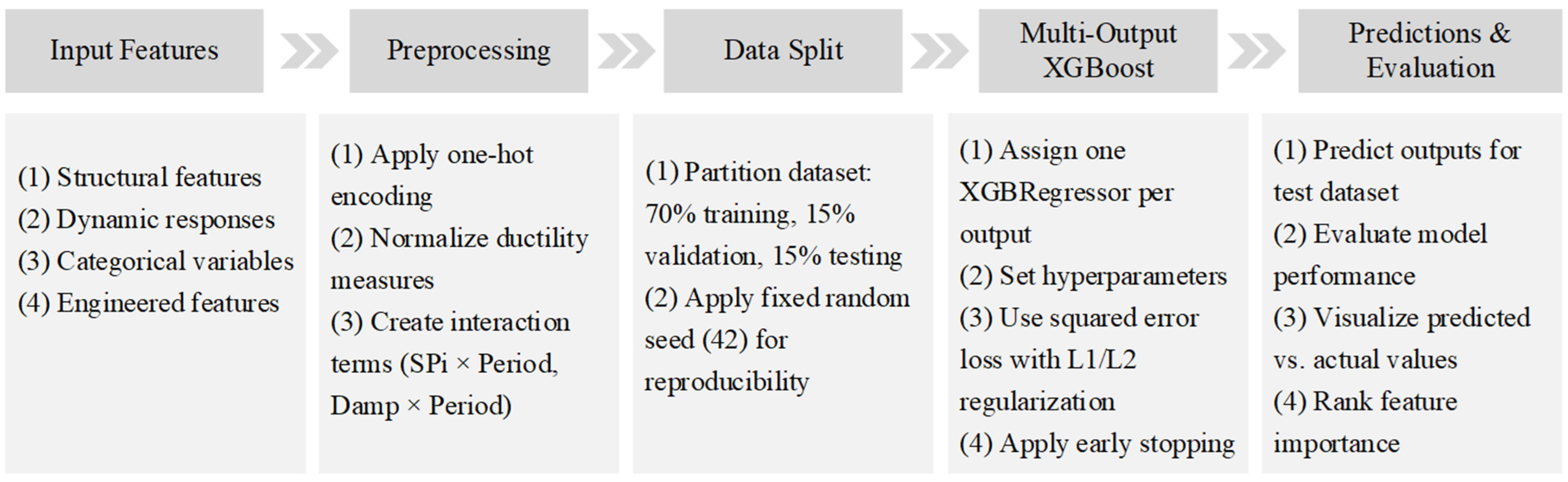
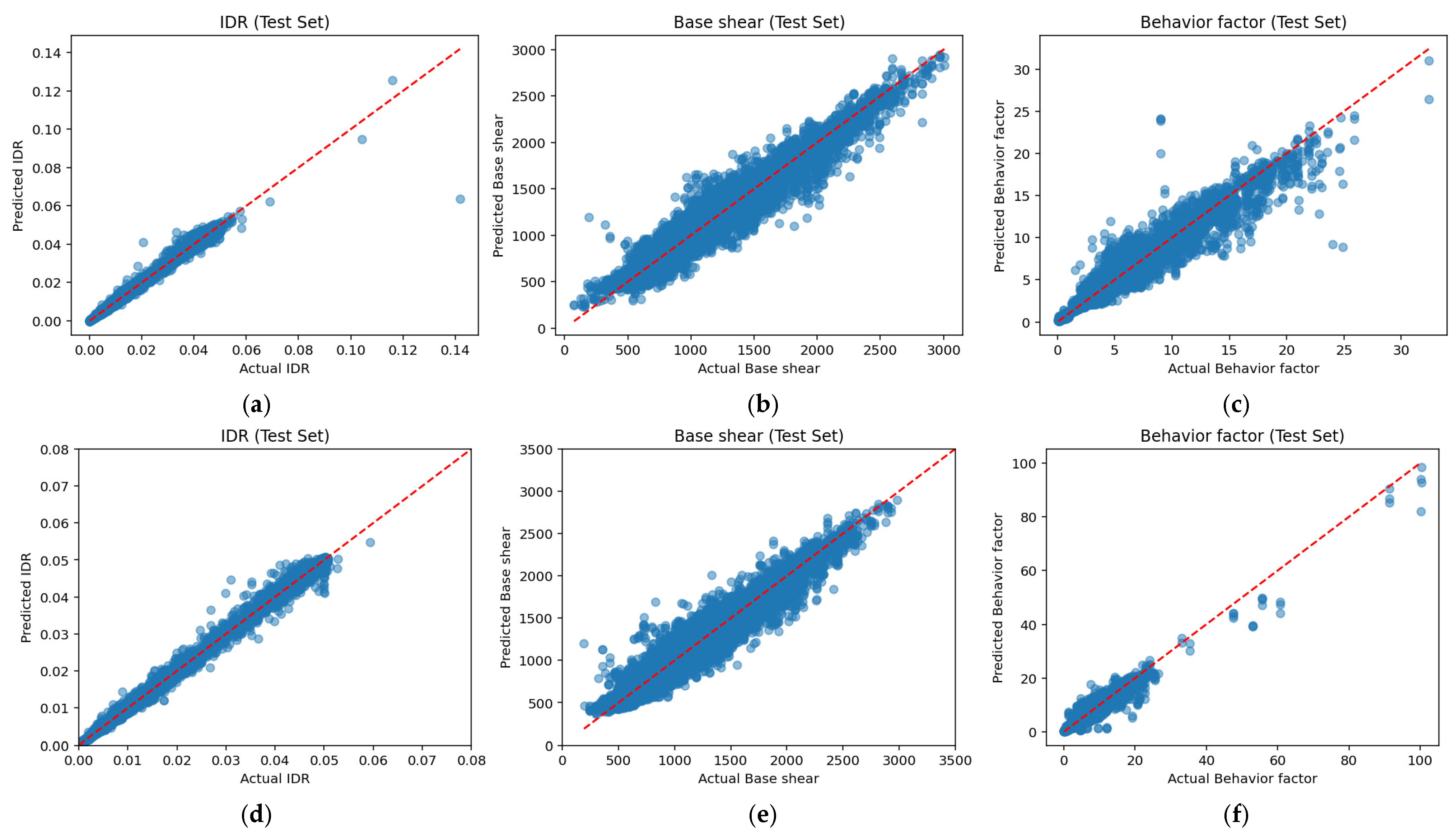
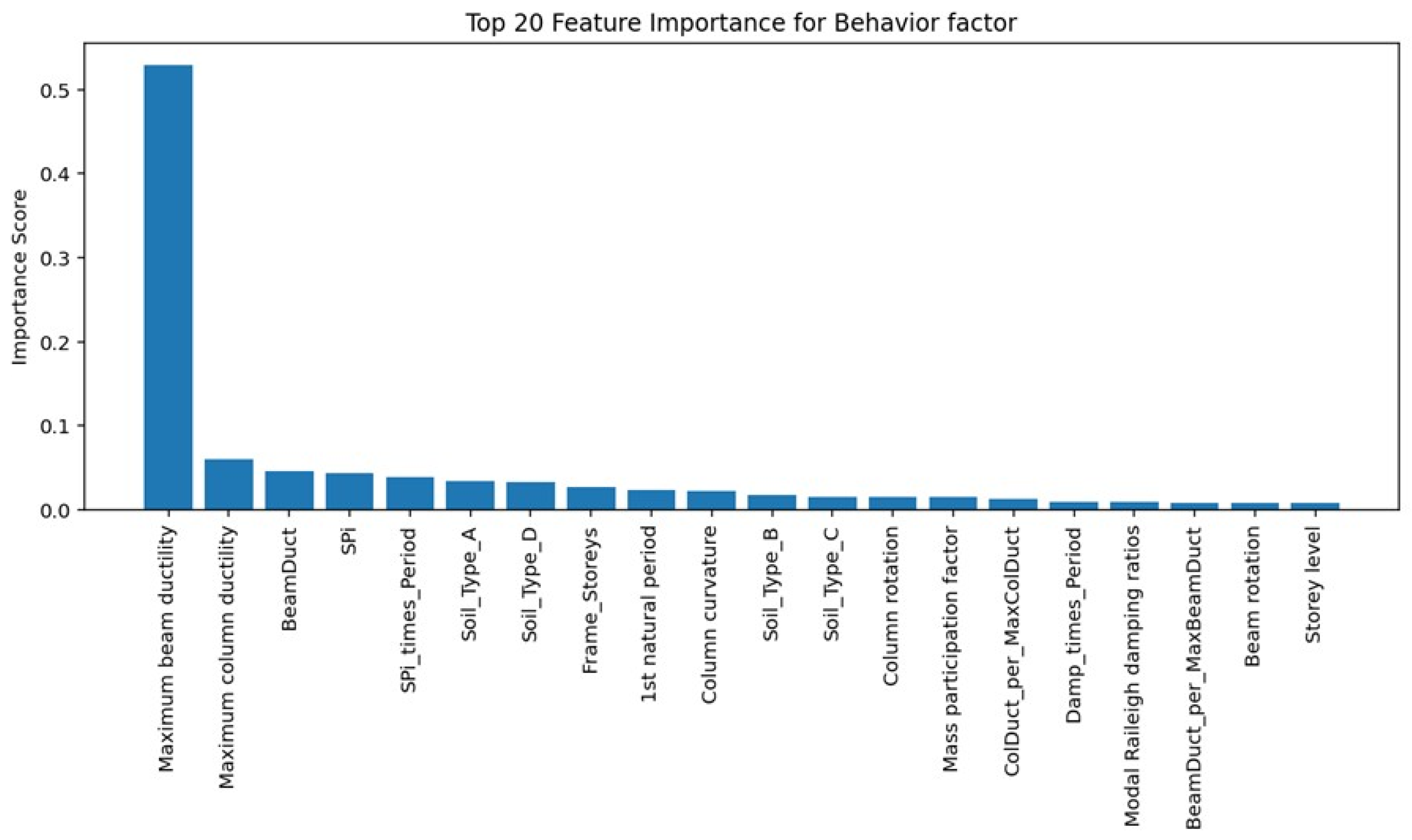
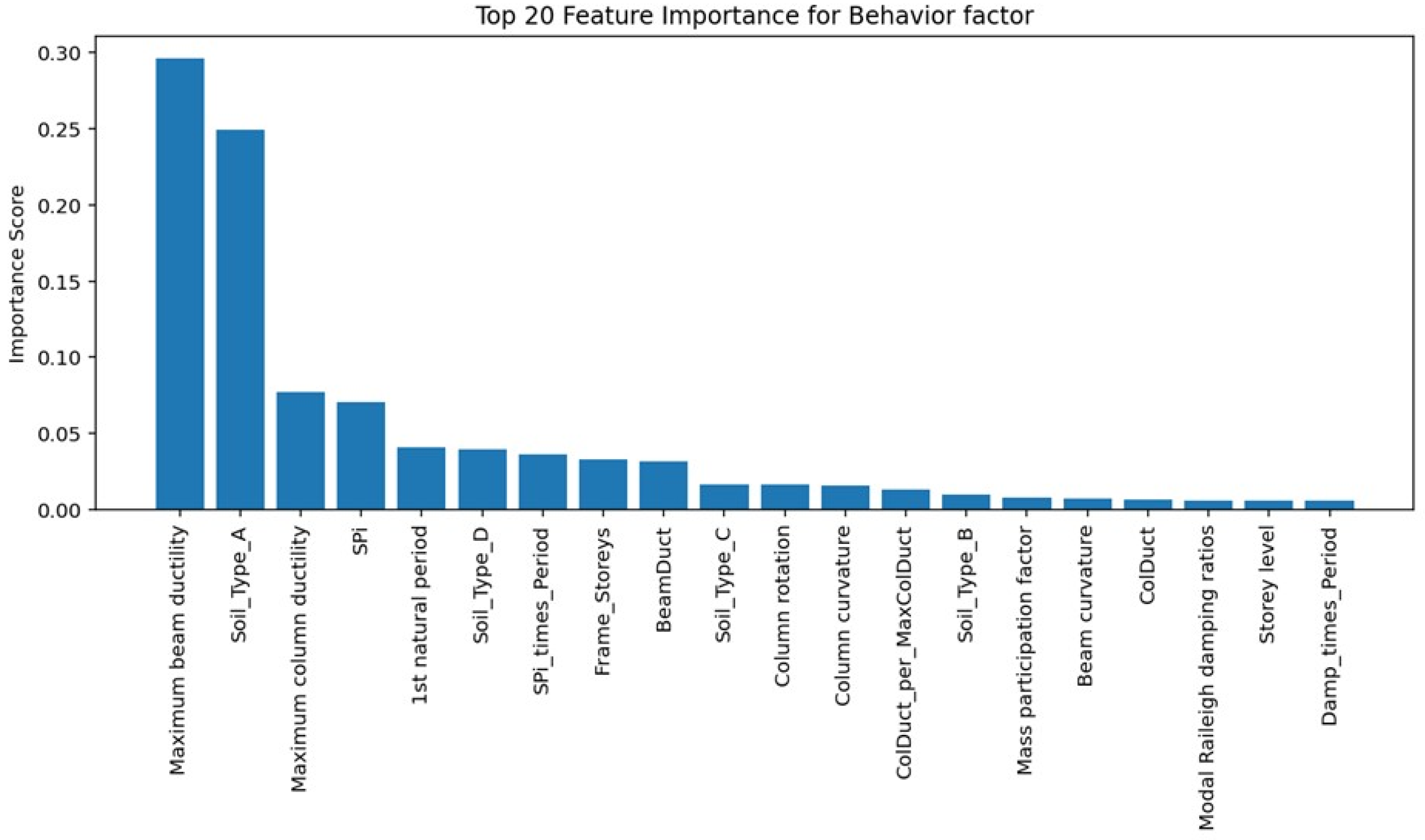
4.5. Machine Learning Methodology and Validation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BNWF | Beam on nonlinear Winkler foundation |
| CP | Collapse prevention |
| DBD | Displacement-based design |
| DCM | Ductility class medium |
| DL | Damage limitation |
| EC3 | Eurocode 3 |
| EC8 | Eurocode 8 |
| FBD | Force-based design |
| FE | Finite element |
| HFD | Hybrid force–displacement |
| IDA | Incremental dynamic analysis |
| IDR | Inter-story drift ratio |
| IO | Immediate occupancy |
| LS | Life safety |
| MRF | Moment-resisting frame |
| PBSD | Performance-based design |
| SF | Scale factor |
| SLS | Serviceability limit state |
| SSI | Soil–structure interaction |
| ULS | Ultimate limit state |
References
- EN 1998-1; Eurocode 8, Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance, Part 1: General Rules, Seismic Actions and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Bazeos, N. Comparison of three seismic design methods for plane steel frames. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2009, 29, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.A.; Krawinkler, H. Evaluation of drift demands for the seismic performance assessment of frames. J. Struct. Eng. 2005, 131, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardis, M.N.; Carvalho, E.; Elnashai, A.; Faccioli, E.; Pinto, P. Designers’ Guide to EN 1998-1 and EN 1998-5 Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance; Thomas Telford: Telford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Karavasilis, T.L.; Bazeos, N.; Beskos, D.E. Deformation demands in plane steel frames with setbacks. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2008, 37, 929–948. [Google Scholar]
- Tzimas, A.S.; Karavasilis, T.L.; Bazeos, N.; Beskos, D.E. A hybrid force/displacement seismic design method for steel building frames. Eng. Struct. 2013, 56, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEAOC. Recommended Lateral Force Requirements and Commentary; Structural Engineers Association of California: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kalapodis, N.A.; Muho, E.V.; Beskos, D.E. Structure-specific, multi-modal and multi-level scalar intensity measures for steel plane frames. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 190, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muho, E.V.; Kalapodis, N.A.; Beskos, D.E. Multi-modal and multi-level structure-specific spectral intensity measures for seismic evaluation of reinforced concrete frames. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 22, 6955–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapodis, N.A.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Beskos, D.E. Modal strength reduction factors for seismic design of plane steel braced frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 147, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Beskos, D.E. Towards a seismic design method for plane steel frames using equivalent modal damping ratios. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 30, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muho, E.V.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Beskos, D.E. Deformation dependent equivalent modal damping ratios for the performance based seismic design of plane R/C structures. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 129, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muho, E.V.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Beskos, D.E. A seismic design method for reinforced concrete moment resisting frames using modal strength reduction factors. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 337–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapodis, N.A.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A. Seismic design of plane steel braced frames using equivalent modal damping ratios. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 129, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, M.J.N.; Calvi, G.M.; Kowalsky, M.J. Displacement-Based Seismic Design of Structures; IUSS Press: Pavia, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalsky, M.J.; Priestley, M.J.N.; MacRae, G.A. Displacement-based design of RC bridge columns in seismic regions. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1995, 24, 1623–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.J.; Priestley, M.J.N.; Calvi, G.M. Direct displacement-based seismic design of frame-wall structures. J. Earthq. Eng. 2006, 10, 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, G.M. A displacement-based approach for vulnerability evaluation of classes of buildings. J. Earthq. Eng. 1999, 3, 411–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.K.; Goel, R.K. Direct displacement-based design: Use of inelastic vs. elastic design spectra. Earthq. Spectra 2001, 17, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, T.B.; Fardis, M.N. A displacement-based seismic design procedure for RC buildings and comparison with Eurocode 8. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2001, 30, 1439–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.J.; Calvi, G.M.; Priestley, M.J.N.; Kowalsky, M.J. The limitations and performances of different displacement based design methods. J. Earthq. Eng. 2003, 7, 201–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muho, E.V.; Qian, J.; Beskos, D.E. A direct displacement-based seismic design method using a MDOF equivalent system: Application to R/C framed structures. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 4157–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapodis, N.A.; Muho, E.V.; Beskos, D.E. Seismic design of plane steel MRFS, EBFS and BRBFS by improved direct displacement-based design method. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 153, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, C.; Qian, J.; Muho, E.V.; Beskos, D.E. A hybrid force/displacement seismic design method for reinforced concrete moment resisting frames. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 129, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapodis, N.A.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Beskos, D.E. A comparison of three performance-based seismic design methods for plane steel braced frames. Earthq. Struct. 2020, 18, 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Skalomenos, K.A.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.D.; Beskos, D.E. Application of the hybrid force/displacement seismic design method to composite steel/concrete plane frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 115, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajan, S.; Raychowdhury, P.; Hutchinson, T.C.; Kutter, B.L.; Stewart, J.P. Application and validation of practical tools for nonlinear soil–foundation interaction analysis. Earthq. Spectra 2010, 26, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazetas, G. Formulas and charts for impedances of surface and embedded foundations. J. Geotech. Eng. 1991, 117, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Truong, G.T.; Shin, M. Development of extreme gradient boosting model for prediction of punching shear resistance of r/c interior slabs. Eng. Struct. 2021, 235, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1993-1-1; Eurocode 3, Design of Steel Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Computers and Structures Inc. SAP2000, version 19; Analysis Reference Manual; Computers and Structures Inc.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019.
- Carr, A.J. Theory and User Guide to Associated Programs—Ruaumoko Manual; Department of Engineering, University of Canterbury: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kalapodis, N.A. Influence of Panel Zone Modeling on the Seismic Behavior of Steel Moment-Resisting Frames: A Numerical Study. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignos, D.G.; Krawinkler, H. Deterioration Modeling of Steel Components in Support of Collapse Prediction of Steel Moment Frames Under Earthquake Loading. J. Struct. Eng. 2011, 137, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.P.; Amidi, A. Seismic Behavior of Steel Frames with Deformable Panel Zones. J. Struct. Eng. 1998, 124, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applied Technology Council. ATC-40—Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of Concrete Buildings; Applied Technology Council: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1996; Volume 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Harden, C.W.; Hutchinson, T.C. Beam-on-Nonlinear-Winkler-Foundation Modeling of Shallow, Rocking-Dominated Footings. Earthq. Spectra 2009, 25, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, R.W.; Curras, C.J.; Kutter, B.L.; Wilson, D.W.; Abghari, A. Seismic soil-pile-structure interaction experiments and analyses. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1999, 125, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychowdhury, P.; Hutchinson, T.C. Nonlinear Material Models for Winkler-Based Shallow Foundation Response Evaluation. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2008, 134, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar]
- PEER. Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, Strong Ground Motion Database; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- COSMOS. Consortium of Organizations for Strong Motion Observation Systems; COSMOS: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, F.; Iervolino, I.; Cosenza, E. Unscaled, Scaled, Adjusted and Artificial Spectral Matching Accelerograms: Displacement and Energy-Based Assessment. In Proceedings of the 13th Congress of the Italian National Association of Earthquake Engineering (ANIDIS), Bologna, Italy, 28 June–2 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Uang, C.M. Establishing R (or Rw) and Cd Factors for Building Seismic Provisions. J. Struct. Eng. 1991, 117, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; Song, J. XGBoost-based prediction of on-site acceleration response spectra with multi-feature inputs from P-wave arrivals. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 178, 108503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEMA P-695; Quantification of Building Seismic Performance Factors. Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Whittaker, A.; Atkinson, G.; Baker, J.; Bray, J.; Grant, D.; Hamburger, R.; Haselton, C.; Somerville, P. NISTGCR 11-917-15—Selecting and Scaling Earthquake Ground Motions for Performing Response-History Analyses; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASCE/SEI 7-22; Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures. American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2022.
- EN 1998-5; Eurocode 8, Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance, Part 5: Foundations, Retaining Structures and Geotechnical Aspects. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- FEMA P-58-1; Applied Technology Council, Seismic Performance Assessment of Buildings, Volume 1—Methodology. Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Ganjavi, B.; Gholamrezatabar, A.; Hajirasouliha, I. Effects of Soil-Structure Interaction and Lateral Design Load Pattern on Performance-Based Plastic Design of Steel Moment Resisting Frames. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2019, 28, e1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Frame | Story | Frame Sections HEB (Columns)—IPE (Beams) | T1 (s) | T2 (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 400-300 (1), 360-270 (2) | 0.343 | 0.08 |
| 2 | 3 | 400-300 (1), 360-270 (2–3) | 0.564 | 0.14 |
| 3 | 4 | 400-300 (1–2), 360-270 (3–4) | 0.758 | 0.21 |
| 4 | 5 | 400-300 (1–2), 360-270 (3–5) | 0.996 | 0.29 |
| 5 | 6 | 400-300 (1–3), 360-270 (4–6) | 1.196 | 0.36 |
| 6 | 7 | 450-330 (1), 400-300 (2–4), 360-270 (5–7) | 1.350 | 0.42 |
| 7 | 8 | 450-330 (1), 400-300 (2–4), 360-270 (5–8) | 1.597 | 0.51 |
| 8 | 9 | 450-330 (1–2), 400-300 (3–5), 360-270 (6–9) | 1.762 | 0.57 |
| 9 | 10 | 450-330 (1–3), 400-300 (4–6), 360-270 (7–10) | 1.919 | 0.64 |
| 10 | 11 | 450-330 (1–4), 400-300 (5–7), 360-270 (8–11) | 2.075 | 0.71 |
| 11 | 12 | 500-360 (1), 450-330 (2–5), 400-300 (6–8), 360-270 (9–12) | 2.202 | 0.76 |
| 12 | 13 | 500-360 (1–2), 450-330 (3–6), 400-300 (7–9), 360-270 (10–13) | 2.331 | 0.81 |
| 13 | 14 | 500-360 (1–3), 450-330 (4–7), 400-300 (8–10), 360-270 (11–14) | 2.463 | 0.87 |
| 14 | 15 | 550-400 (1–2), 500-360 (3–5), 450-330 (6–8), 400-300 (9–11), 360-270 (12–15) | 2.496 | 0.89 |
| 15 | 16 | 550-400 (1–4), 500-360 (5–7), 450-330 (8–10), 400-300 (11–13), 360-270 (14–16) | 2.476 | 0.90 |
| Performance Level | IDR | θp |
|---|---|---|
| SP1 or IO | 0.7% | 0 |
| SP2 or DL | 1.5% | θy |
| SP3 or LS | 2.5% | 3.5 θy |
| SP4 or CP | 5.0% | 6.5 θy |
| № | Date | Record Name | Comp. | Station Name | PGA (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 October 1987 | Whittier Narrows | NS | 24399 Mt Wilson-CIT Station | 0.158 |
| 2 | 4 October 1987 | Whittier Narrows | EW | 24399 Mt Wilson-CIT Station | 0.142 |
| 3 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | 056-N | HWA056 | 0.107 |
| 4 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | 056-N | HWA056 | 0.107 |
| 5 | 1 October 1987 | Whittier Narrows | NS | 24399 Mt Wilson-CIT Station | 0.186 |
| 6 | 1 October 1987 | Whittier Narrows | EW | 24399 Mt Wilson-CIT Station | 0.123 |
| 7 | 9 February 1971 | San Fernando | N069 | 127 Lake Hughes 9 | 0.157 |
| 8 | 9 February 1971 | San Fernando | N159 | 127 Lake Hughes 9 | 0.134 |
| 9 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | NS | 90019 San Gabriel-E. Gr. Ave. | 0.256 |
| 10 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | EW | 90019 San Gabriel-E. Gr. Ave. | 0.141 |
| 11 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | NS | TAP103 | 0.177 |
| 12 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | EW | TAP103 | 0.122 |
| 13 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | N005 | 90017 LA-Wonderland Ave | 0.172 |
| 14 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | N175 | 90017 LA-Wonderland Ave | 0.112 |
| 15 | 7 June 1975 | Northern Calif | N060 | 1249 Cape Mendocino, Petrolia | 0.115 |
| 16 | 7 June 1975 | Northern Calif | N150 | 1249 Cape Mendocino, Petrolia | 0.179 |
| 17 | 8 July 1986 | N. Palm Springs | NS | 12206 Silent Valley | 0.139 |
| 18 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | N205 | 58539 San Francisco | 0.105 |
| 19 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | NS | 47379 Gilroy Array 1 | 0.473 |
| 20 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | EW | 47379 Gilroy Array 1 | 0.411 |
| 21 | 17 August 1999 | Kocaeli, Turkey | NS | Gebze | 0.137 |
| 22 | 17 August 1999 | Kocaeli, Turkey | EW | Gebze | 0.244 |
| 23 | 28 June 1992 | Landers | NS | 21081 Amboy | 0.115 |
| 24 | 28 June 1992 | Landers | EW | 21081 Amboy | 0.146 |
| 25 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | N034 | TCU046 | 0.133 |
| № | Date | Record Name | Comp. | Station Name | PGA (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 April 1992 | Cape Mendocino | NS | 89509 Eureka | 0.154 |
| 2 | 25 April 1992 | Cape Mendocino | EW | 89509 Eureka | 0.178 |
| 3 | 9 June 1980 | Victoria, Mexico | N045 | 6604 Cerro Prieto | 0.621 |
| 4 | 9 June 1980 | Victoria, Mexico | N135 | 6604 Cerro Prieto | 0.587 |
| 5 | 25 April 1992 | Cape Mendocino | EW | 89324 Rio Dell Overpass | 0.385 |
| 6 | 25 April 1992 | Cape Mendocino | NS | 89324 Rio Dell Overpass | 0.549 |
| 7 | 13 August 1978 | Santa Barbara | N048 | 283 Santa Barbara Courthouse | 0.203 |
| 8 | 13 August 1978 | Santa Barbara | N138 | 283 Santa Barbara Courthouse | 0.102 |
| 9 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | NS | TCU095 | 0.712 |
| 10 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | EW | TCU095 | 0.378 |
| 11 | 6 August 1979 | Coyote Lake | N213 | 1377 San Juan Bautista | 0.108 |
| 12 | 6 August 1979 | Coyote Lake | N303 | 1377 San Juan Bautista | 0.107 |
| 13 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | NS | 90021 LA-N Westmoreland | 0.361 |
| 14 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | EW | 90021 LA-N Westmoreland | 0.401 |
| 15 | 8 July 1986 | N. Palm Springs | NS | 12204 San Jacinto-Soboba | 0.239 |
| 16 | 8 July 1986 | N. Palm Springs | EW | 12204 San Jacinto-Soboba | 0.25 |
| 17 | 12 September 1970 | Lytle Creek | N115 | 290 Wrightwood | 0.162 |
| 18 | 12 September 1970 | Lytle Creek | N205 | 290 Wrightwood | 0.2 |
| 19 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | NS | 58065 Saratoga-Aloha Ave | 0.324 |
| 20 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | EW | 58065 Saratoga-Aloha Ave | 0.512 |
| 21 | 28 June 1992 | Landers | NS | 22170 Joshua Tree | 0.284 |
| 22 | 28 June 1992 | Landers | EW | 22170 Joshua Tree | 0.274 |
| 23 | 15 September 1976 | Friuli, Italy | NS | 8014 Forgaria Cornino | 0.212 |
| 24 | 15 September 1976 | Friuli, Italy | EW | 8014 Forgaria Cornino | 0.26 |
| 25 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | N045 | TCU045 | 0.512 |
| № | Date | Record Name | Comp. | Station Name | PGA (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | NS | NST | 0.388 |
| 2 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | EW | NST | 0.309 |
| 3 | 2 May 1983 | Coalinga | EW | 36227 Parkfield | 0.147 |
| 4 | 2 May 1983 | Coalinga | NS | 36227 Parkfield | 0.131 |
| 5 | 12 November 1999 | Duzce, Turkey | NS | Bolu | 0.728 |
| 6 | 12 November 1999 | Duzce, Turkey | EW | Bolu | 0.822 |
| 7 | 15 October 1979 | Imperial Valley | N015 | 6622 Computertas | 0.186 |
| 8 | 15 October 1979 | Imperial Valley | N285 | 6622 Computertas | 0.147 |
| 9 | 15 October 1979 | Imperial Valley | N012 | 6621 Chihuahua | 0.27 |
| 10 | 15 October 1979 | Imperial Valley | N282 | 6621 Chihuahua | 0.284 |
| 11 | 17 August 1999 | Kocaeli, Turkey | NS | Atakoy | 0.105 |
| 12 | 17 August 1999 | Kocaeli, Turkey | EW | Atakoy | 0.164 |
| 13 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | NS | 1028 Hollister City Hall | 0.247 |
| 14 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | EW | 1028 Hollister City Hall | 0.215 |
| 15 | 24 April 1984 | Morgan Hill | NS | 57382 Gilroy Array #4 | 0.224 |
| 16 | 24 April 1984 | Morgan Hill | EW | 57382 Gilroy Array #4 | 0.348 |
| 17 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | NS | 90057 Canyon Country | 0.482 |
| 18 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | EW | 90057 Canyon Country | 0.41 |
| 19 | 9 February 1971 | San Fernando | EW | 135 LA-Hollywood | 0.21 |
| 20 | 9 February 1971 | San Fernando | NS | 135 LA-Hollywood | 0.174 |
| 21 | 26 April 1981 | Westmorland | NS | 5169 Westmorland Fire Sta | 0.368 |
| 22 | 26 April 1981 | Westmorland | EW | 5169 Westmorland Fire Sta | 0.496 |
| 23 | 24 November 1987 | Superstition Hills(B) | NS | 01335 El Centro Imp. Co. Cent | 0.258 |
| 24 | 24 November 1987 | Superstition Hills(B) | EW | 01335 El Centro Imp. Co. Cent | 0.358 |
| 25 | 27 January 1980 | Livermore | EW | 57187 San Ramon | 0.301 |
| № | Date | Record Name | Comp. | Station Name | PGA (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 April 1981 | Westmorland | N045 | 5062 Salton Sea Wildlife Ref. | 0.199 |
| 2 | 26 April 1981 | Westmorland | N135 | 5062 Salton Sea Wildlife Ref. | 0.176 |
| 3 | 24 November 1987 | Superstitn Hills | N045 | 5062 Salton Sea Wildlife Refuge | 0.119 |
| 4 | 24 November 1987 | Superstitn Hills | N135 | 5062 Salton Sea Wildlife Refuge | 0.167 |
| 5 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | N064 | 90011 Montebello-Bluff Rd. | 0.128 |
| 6 | 17 January 1994 | Northridge | N154 | 90011 Montebello-Bluff Rd. | 0.179 |
| 7 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | NS | 58117 Treasure Island | 0.159 |
| 8 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | EW | 58117 Treasure Island | 0.1 |
| 9 | 17 August 1999 | Kocaeli, Turkey | NS | Ambarl | 0.184 |
| 10 | 17 August 1999 | Kocaeli, Turkey | EW | Ambarl | 0.249 |
| 11 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | N043 | 1002 APEEL 2-Redwood City | 0.274 |
| 12 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | N133 | 1002 APEEL 2-Redwood City | 0.22 |
| 13 | 15 October 1979 | Imperial Valley | N040 | 5057 El Centro Array 3 | 0.112 |
| 14 | 15 October 1979 | Imperial Valley | N130 | 5057 El Centro Array 3 | 0.179 |
| 15 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | N041 | CHY041 | 0.639 |
| 16 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | N131 | CHY041 | 0.302 |
| 17 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | N047 | 1002 APEEL 2-Redwood City | 0.274 |
| 18 | 18 October 1989 | Loma Prieta | N137 | 1002 APEEL 2-Redwood City | 0.22 |
| 19 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | EW | TAP003 | 0.126 |
| 20 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | NS | TAP003 | 0.106 |
| 21 | 16 January 1995 | Kobe | NS | Nishi-Akashi | 0.503 |
| 22 | 16 January 1995 | Kobe | EW | Nishi-Akashi | 0.509 |
| 23 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | N040 | TCU040 | 0.123 |
| 24 | 20 September 1999 | Chi-Chi, Taiwan | N130 | TCU040 | 0.149 |
| 25 | 16 January 1995 | Kobe | NS | Kakogawa | 0.345 |
| Type | Variable | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Features | Frame_Storeys | – | Total number of stories in the frame |
| Storey_Number | – | Story index for floor-level features | |
| ColDuct | – | Column ductility | |
| MaxColDuct | – | Maximum column ductility | |
| BeamDuct | – | Beam ductility | |
| MaxBeamDuct | – | Maximum beam ductility | |
| ColCurv | rad/m | Column curvature | |
| BeamCurv | rad/m | Beam curvature | |
| ColRot | rad | Column rotation | |
| BeamRot | rad | Beam rotation | |
| Dynamic Responses | Period | s | First natural period (T) |
| SPi | – | Target performance level | |
| Damp | % | Damping ratio | |
| MassPF | % | Mass participation factor | |
| ModPF | – | Modal participation factor | |
| Categorical Variables | Soil_Type | – | EC8 soil class (A–D) |
| SSI | – | Foundation condition: 0 = fixed base, 1 = SSI | |
| Engineering Variables | BeamDuct/MaxBeamDuct | – | Normalized beam ductility |
| ColDuct/MaxColDuct | – | Normalized column ductility | |
| SPi Period | – | Interaction term between performance level and period | |
| Damp Period | – | Interaction term between damping and period | |
| Output Variables | IDR | – | Inter-story drift ratio (IDR) |
| Base Shear | kN | Base shear force | |
| q_Factor | – | Behavior factor (q) |
| Output Variable | Without SSI | With SSI |
|---|---|---|
| IDR | 0.992 | 0.986 |
| Base Shear | 0.948 | 0.947 |
| Behavior Factor | 0.944 | 0.952 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalapodis, N.A.; Muho, E.V.; Shadabfar, M.; Kamaris, G.S. Quantifying the Impact of Soil–Structure Interaction on Performance-Based Seismic Design of Steel Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings. Buildings 2025, 15, 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203741
Kalapodis NA, Muho EV, Shadabfar M, Kamaris GS. Quantifying the Impact of Soil–Structure Interaction on Performance-Based Seismic Design of Steel Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203741
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalapodis, Nicos A., Edmond V. Muho, Mahdi Shadabfar, and George S. Kamaris. 2025. "Quantifying the Impact of Soil–Structure Interaction on Performance-Based Seismic Design of Steel Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203741
APA StyleKalapodis, N. A., Muho, E. V., Shadabfar, M., & Kamaris, G. S. (2025). Quantifying the Impact of Soil–Structure Interaction on Performance-Based Seismic Design of Steel Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings. Buildings, 15(20), 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203741







