Analytical Study on the Transverse Stress Model and Its Influencing Factors on Moso Bamboo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
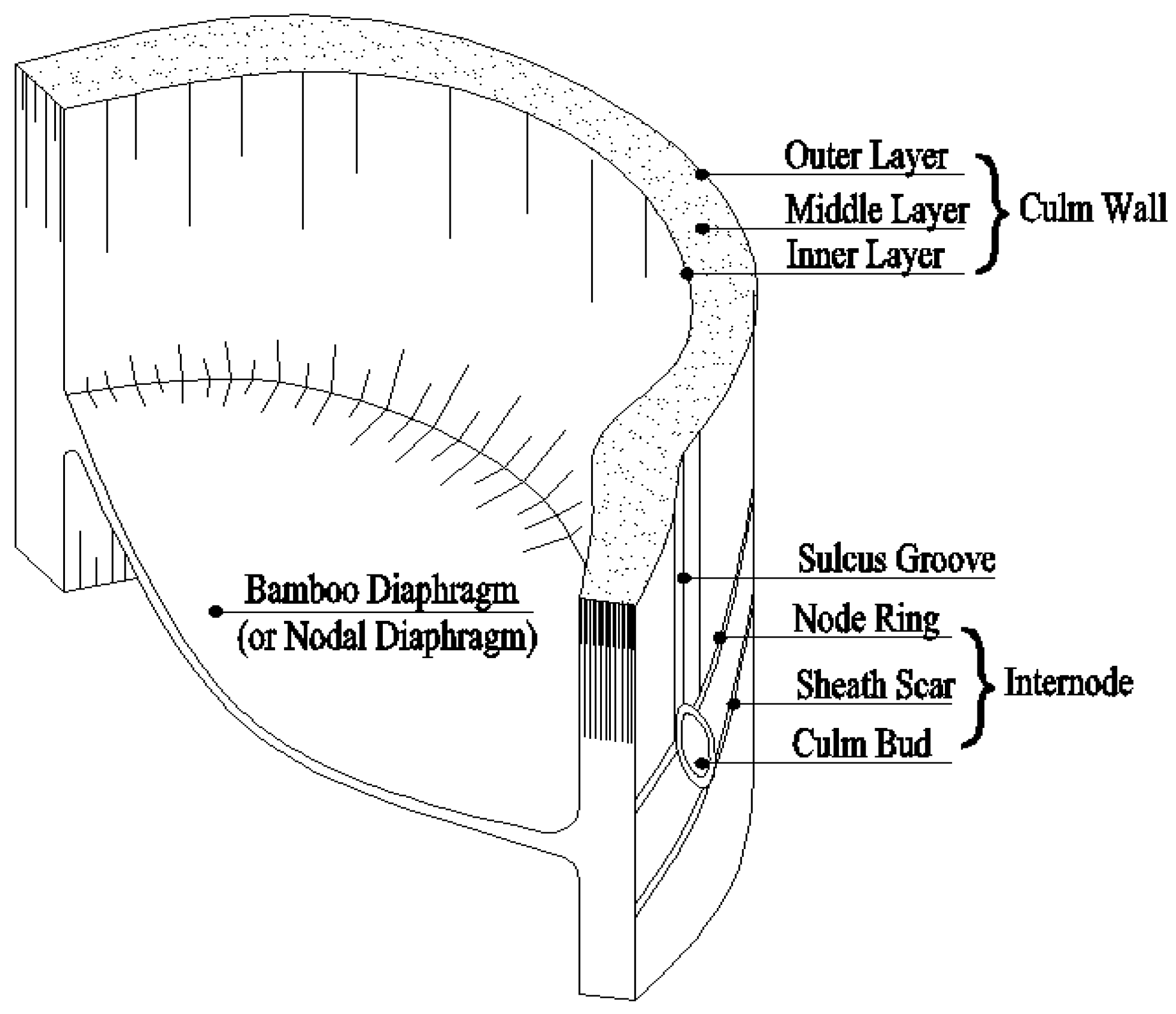
2.1.1. Moso Bamboo
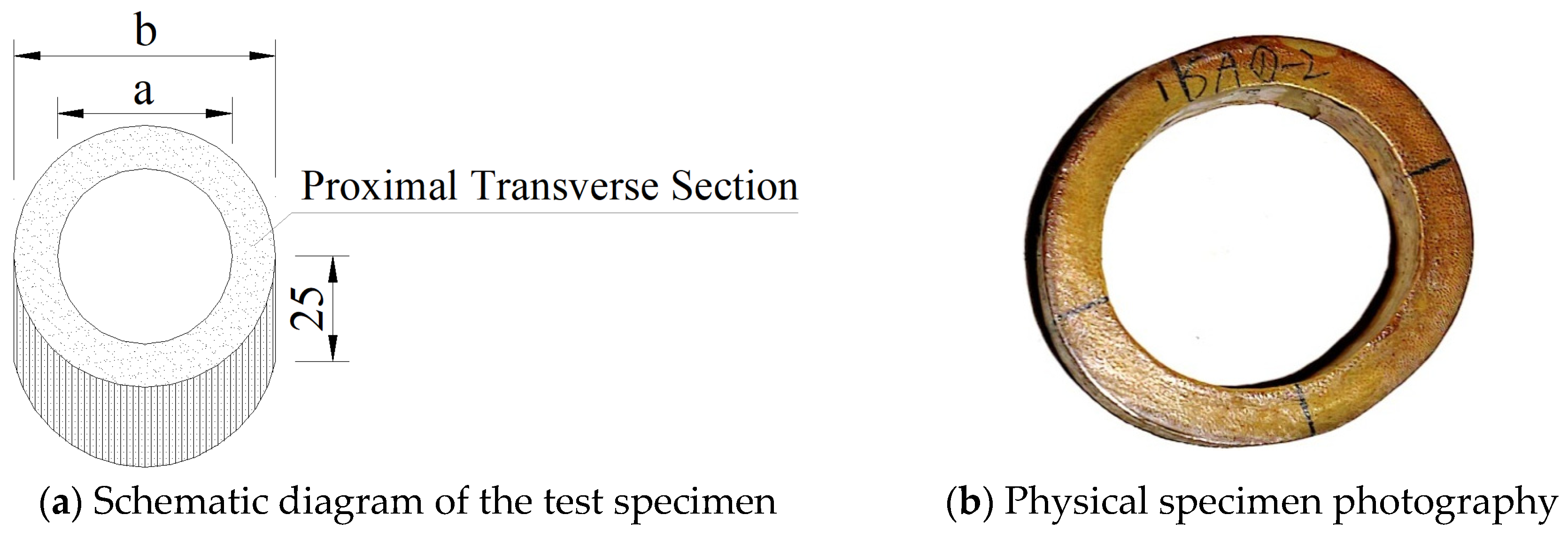
2.1.2. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Transverse Stress Model for Moso Bamboo
Adjustment of Tangential Stress Model for Moso Bamboo
- (1)
- Correction Factors for Aspect Ratio and Radial Material Heterogeneity
- (2)
- Adjustment Factor for Buttress Groove
2.3. Test Methods
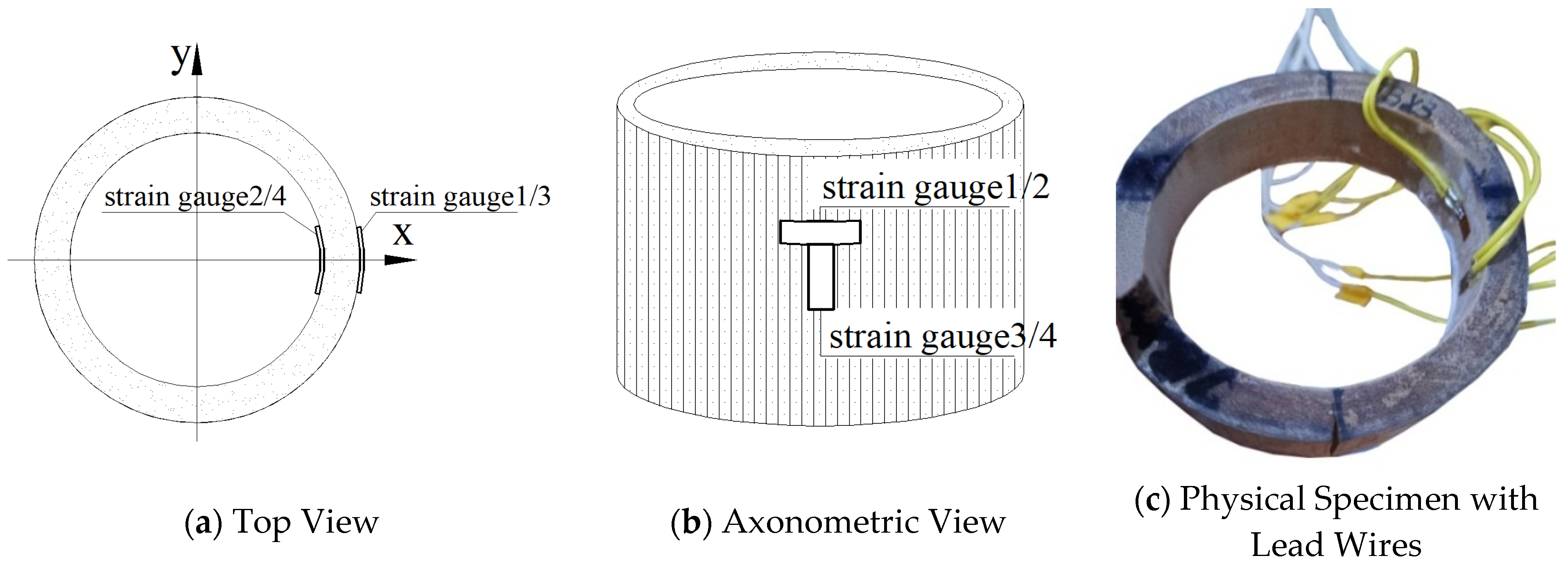
2.3.1. Test Apparatus
2.3.2. Test Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Different Factors on MDA
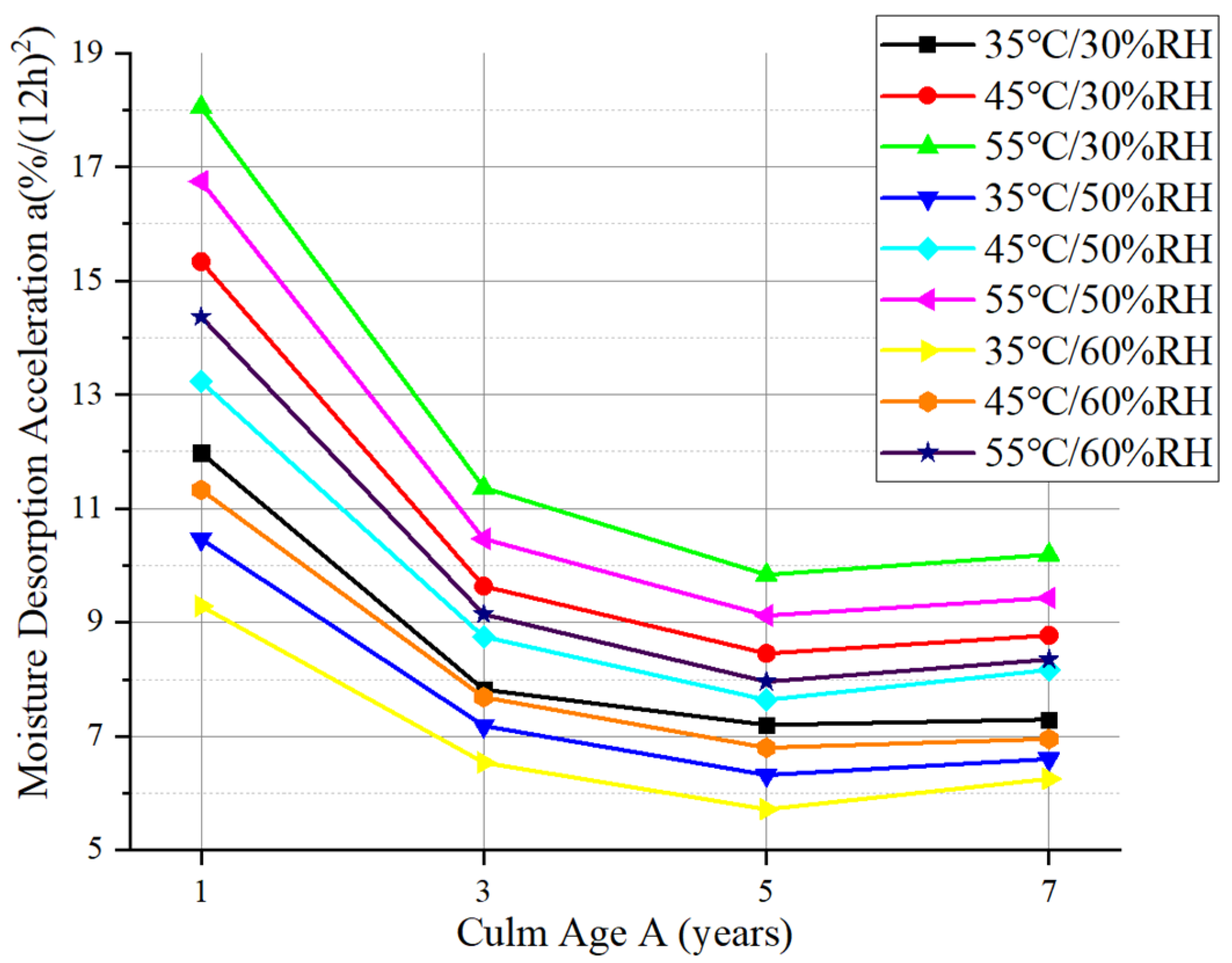
3.1.1. Culm Age
3.1.2. Annular Geometry
3.1.3. Temperature
3.1.4. Relative Humidity
3.2. Functional Relationship Between Desorption Acceleration and Influence Factors
3.3. Functional Formulation for External and Internal Surface Strain
3.4. Influence of Non-Circular Cross-Sections and Buttress Grooves on Tangential Stress
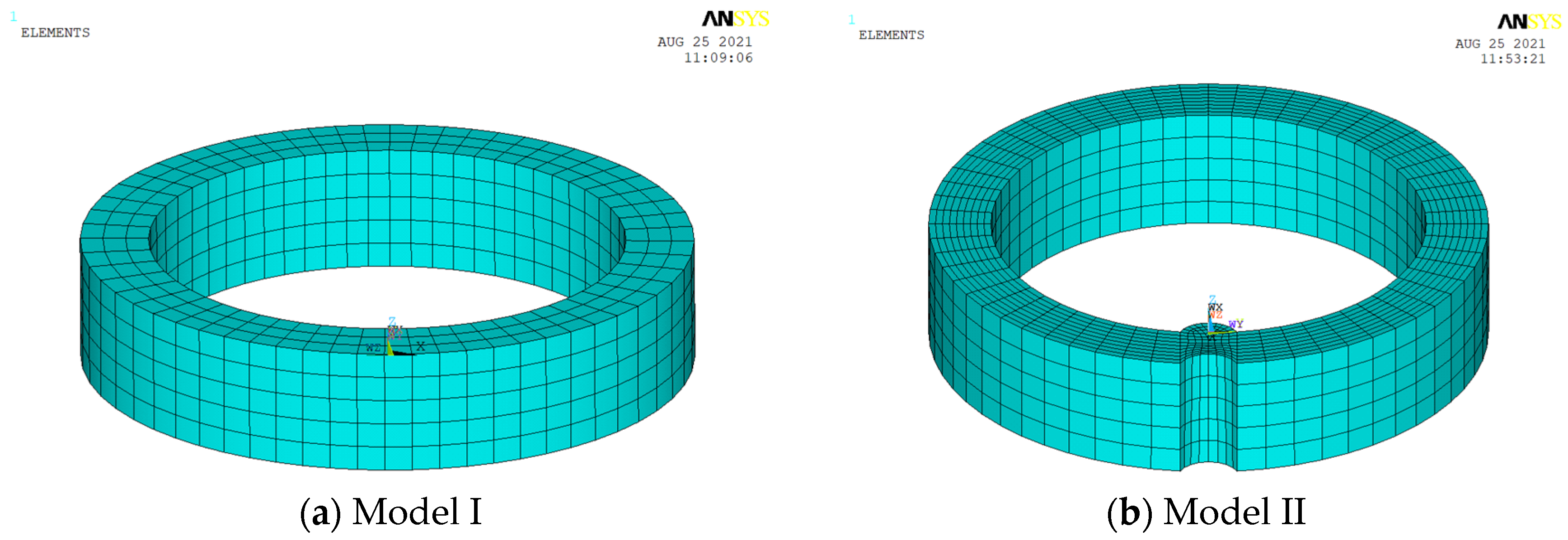
3.4.1. Finite Element Model Establishment
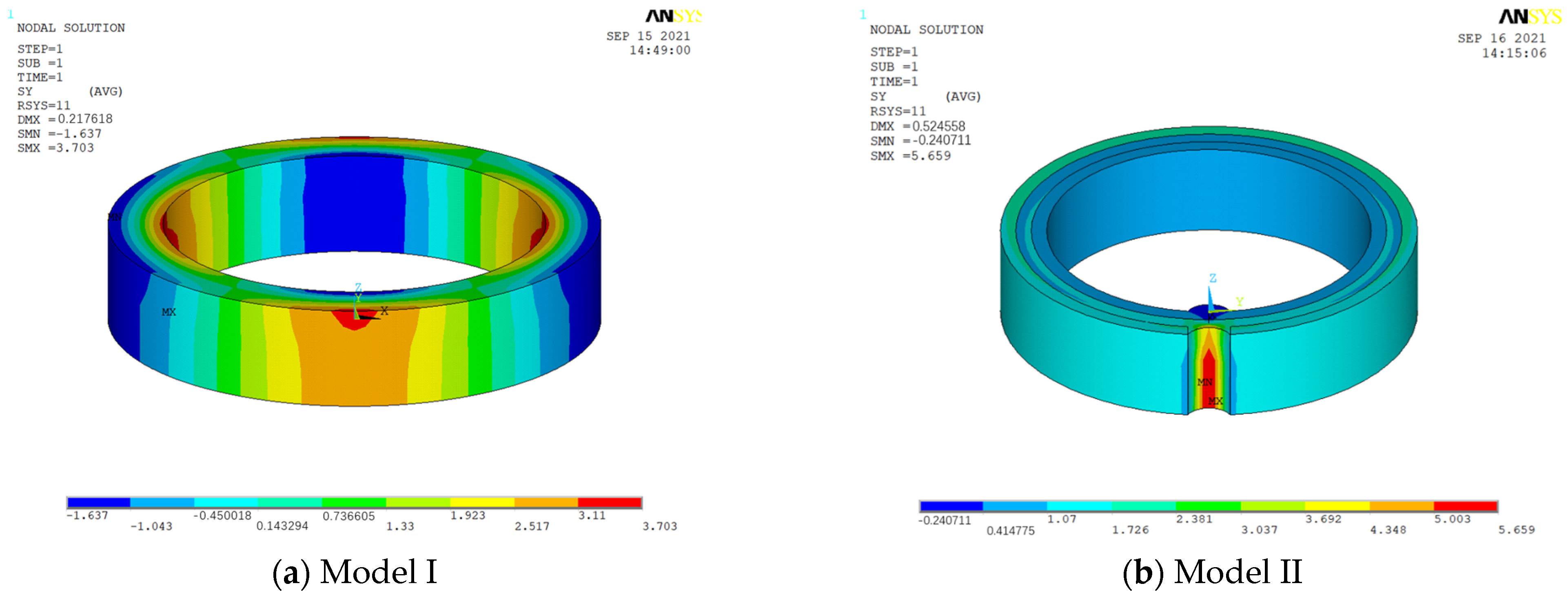
3.4.2. Results of FE Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, B.; Ren, Q.; He, Q.; Ju, Z.; Zhan, T.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X. Study on Mixed Biomass Binderless Composite Based on Simulated Wood. Wood Res. 2019, 64, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Ou, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Zuo, T. Experimental and numerical study on timber-to-bamboo scrimber connection with self-tapping screws. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Xiao, Z.; Hong, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Fu, N.; Lu, X. Review on the application of bamboo-based materials in construction engineering. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 1215–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Shang, L.; Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Fei, B.; Liu, H.; Fang, C. A straightforward and efficient gradient pressure method for bamboo flattening: Strain and multi-scale deformation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 272, 111232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Ren, Q.; Hong, L.; Xiao, Z.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Fu, N.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, J. Effect of steam explosion technology main parameters on Moso bamboo and poplar fiber. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, K. Seismic demand prediction in laminated bamboo frame structures: A comparative study of intensity measures for performance-based design. Buildings 2024, 15, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.A.G.; Orejudos, J.N.; Aniñon, M.J.C. A compendium of research, tools, structural analysis, and design for bamboo structures. Buildings 2024, 14, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniñon, M.J.C.; Garciano, L.E.O. Advances in connection techniques for raw bamboo structures-A review. Buildings 2024, 14, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Chew, Y.; Chang, W.; Ansell, M.P.; Lawrence, M.; Latif, E.; Shea, A.; Ormondroyd, G.; Du, H. Heat and moisture transfer behaviour in Phyllostachys edulis (Moso bamboo) based panels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Fei, B. The vacuum-assisted microwave drying of round bamboos: Drying kinetics, color and mechanical property. Mater. Lett. 2018, 223, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, W. Protection of bamboo in service. J. Bamboo Ratt. 2003, 1, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, S.; Chen, H.; Wu, A. Effect of bamboo unit morphology on the preparation of bamboo fibers by steam explosion. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 202, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z. Mechanical behavior of bamboo with large deformation I: The relationship between stress and strain. China Wood Ind. 2003, 17, 12–14, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z. Mechanical behavior of bamboo with large deformation II: The characteristics of microcosmic deformation. China Wood Ind. 2008, 18, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z. Interlaminar facture properties of biomaterials bamboo. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2008, 44, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Shao, Z. Fracture toughness on bamboo III mode interlaminar. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2017, 45, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F. Physical model and energy absorption mechanism of bamboo transverse fracture: The cracking of parenchyma tissue and layering of interface. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2012, 48, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, M.N.; Langrish, T.; Keep, L.B.; Keey, R.B. Model fitting for visco-elastic creep of Pinus radiata during kiln drying. Wood Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fei, B.; Liu, S. The relationship between moisture content and shrinkage strain in the process of bamboo air seasoning and cracking. Dry Technol. 2020, 40, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S. Preliminary Study on Principle and Protection of Moso Bamboo Tubes’ Splitting. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Dauletbek, A. Effects of natural weathering on the mechanical properties of Moso bamboo internodes and nodes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15780; Testing Methods for Physical and Mechanical Properties of Bamboos. State Bureau of Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1995.
- ISO 1101; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)-Geometrical Tolerancing-Tolerances of Form, Orientation, Location and Run-Out. International organization for standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ASTM D1030; Standard Test Method for Fiber Analysis of Paper and Paperboard. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995.
- Lekhnitskii, S.G. Anisotropic Plates; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1963; Volume 88. [Google Scholar]
- BS ISO 19624; Bamboo Structures-Grading of Bamboo Culms-Basic Principles and Procedures. International organization for standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 22156; Bamboo Structures-Bamboo Culms-Structural Design. International organization for standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Trujillo, D.J.A.; Jangra, S. Grading of Bamboo; International Network for Bamboo and Rattan: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Fang, Z. Wind load assembly type close packed column from light wood frame structure finite element analysis. Archit. Technol. 2016, 47, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, B.; Hong, L.; Li, S.; Tao, Y.; Cui, J.; Fu, N.; Yu, J.; Li, C.; Lu, X. Study on the tangential tensile mechanical properties of Moso bamboo. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 2203–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarinejad, S.; Kotowski, P.; Shalchy, F.; Rahbar, N. Effects of humidity on shear behavior of bamboo. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2015, 5, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

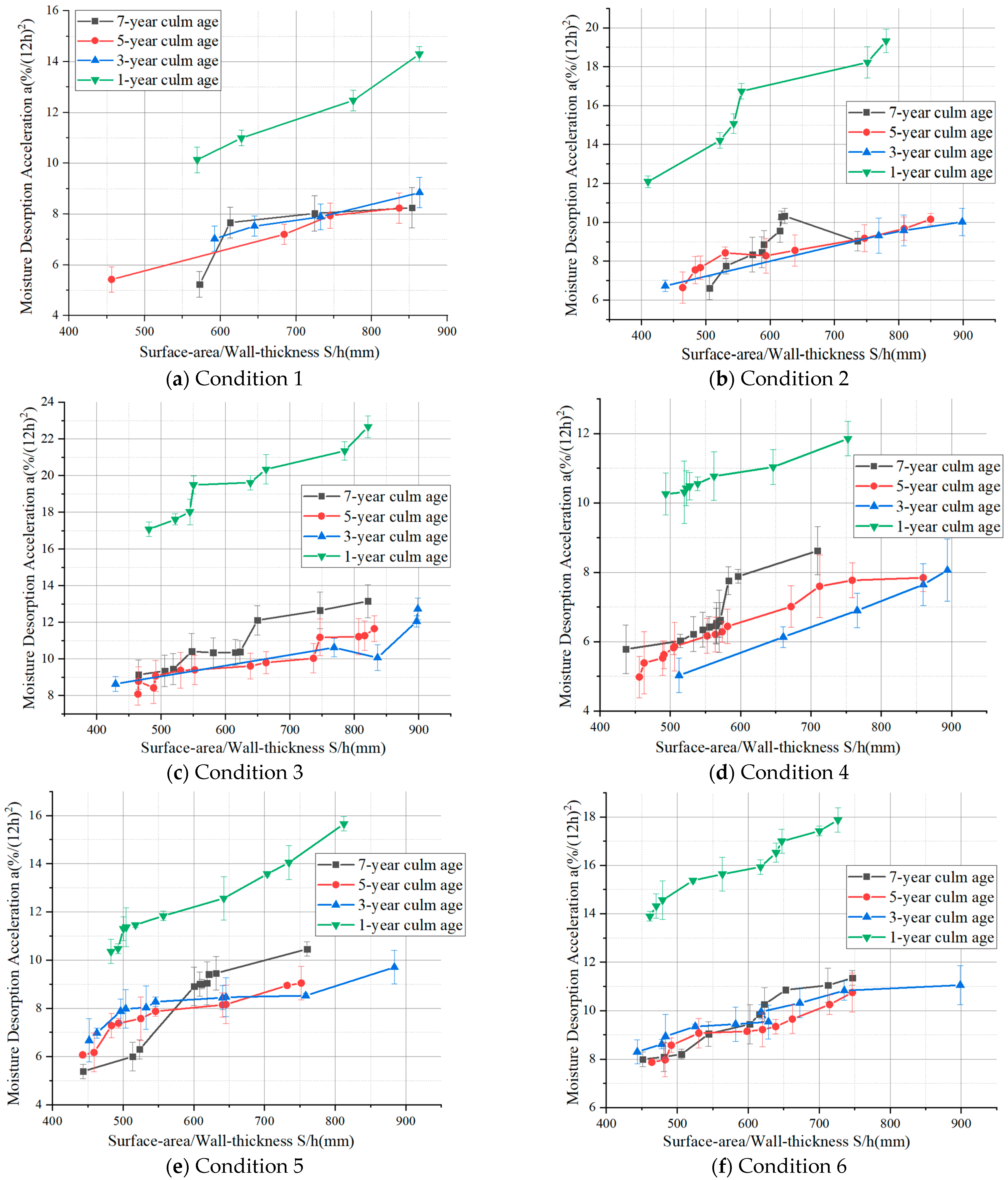
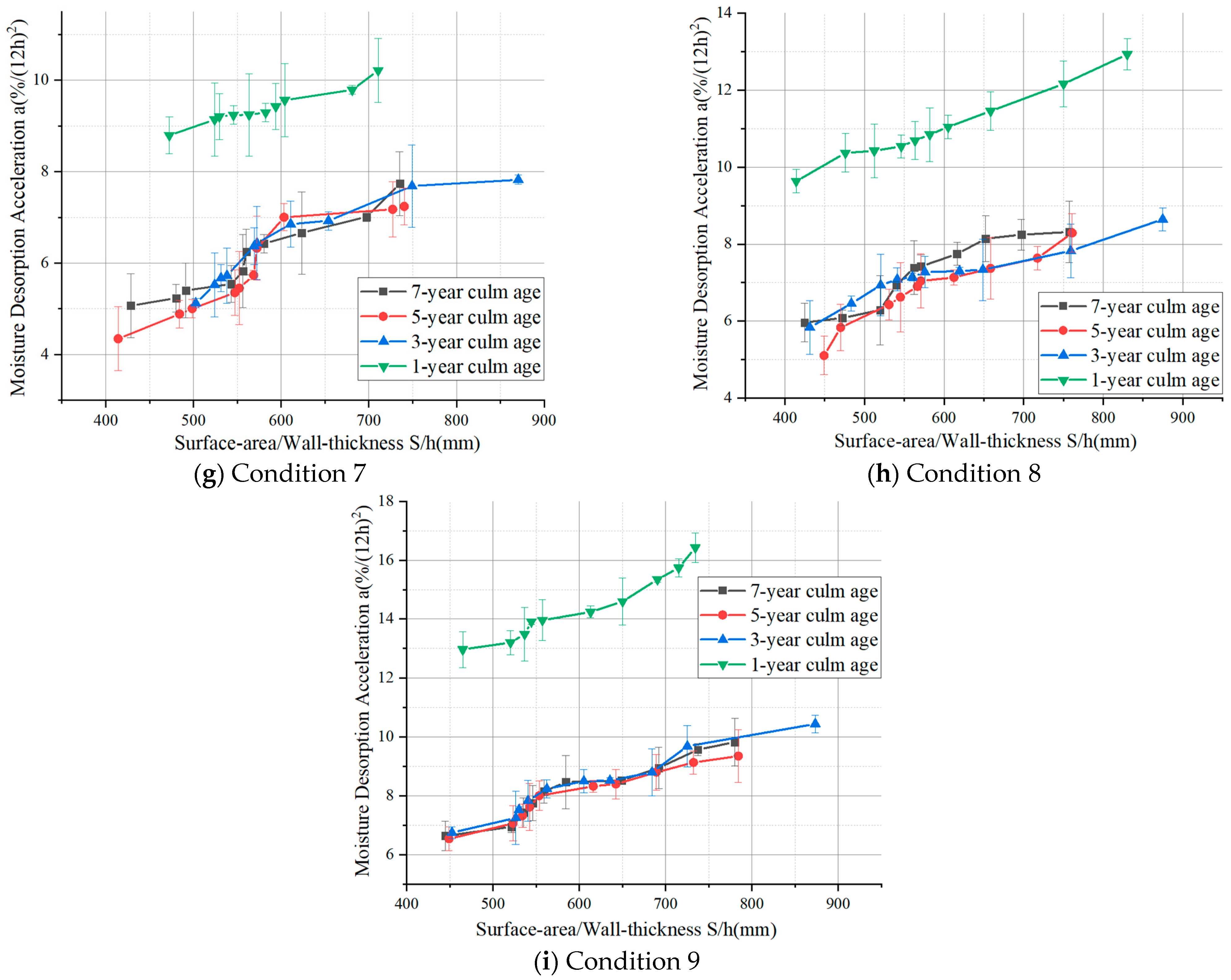
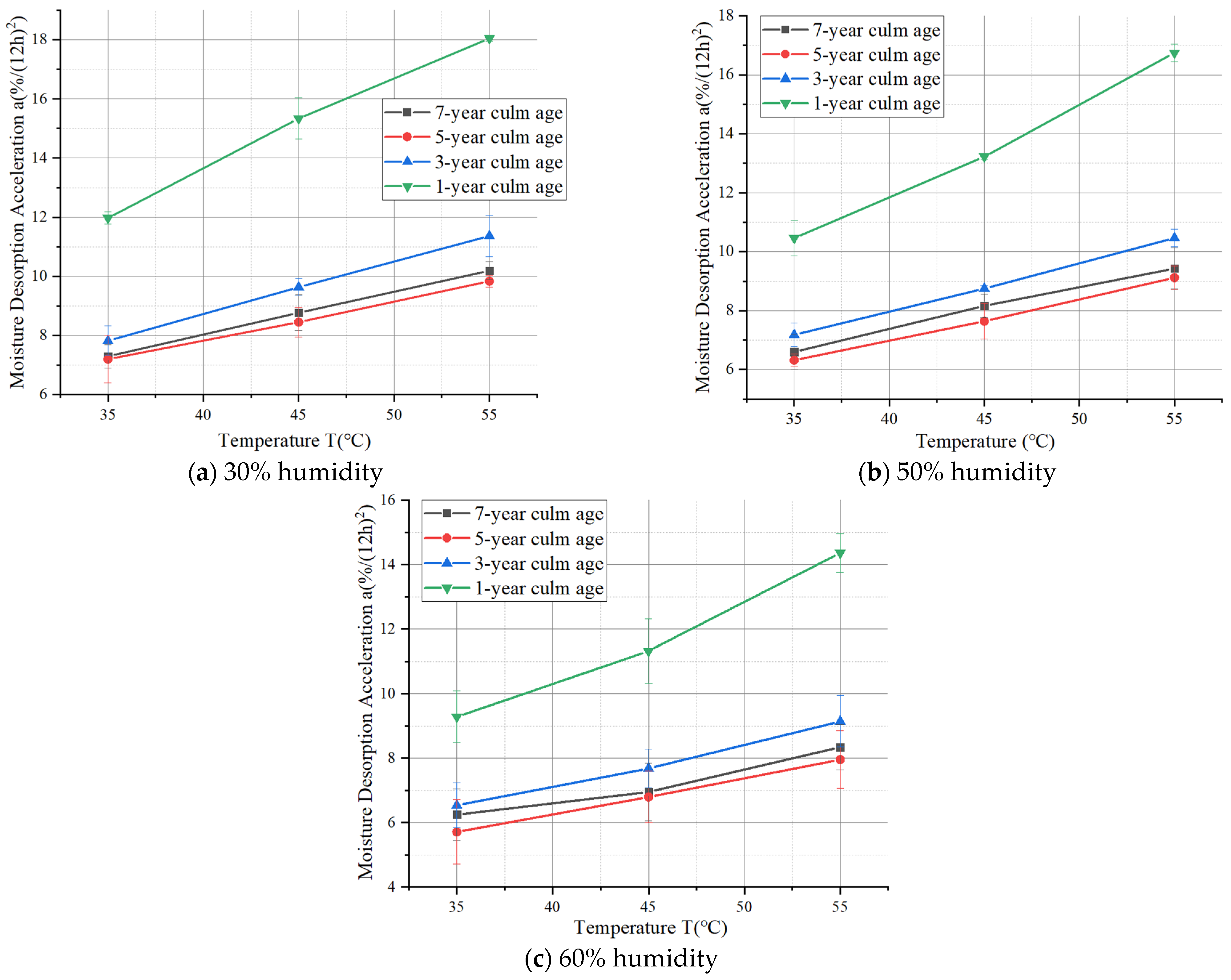
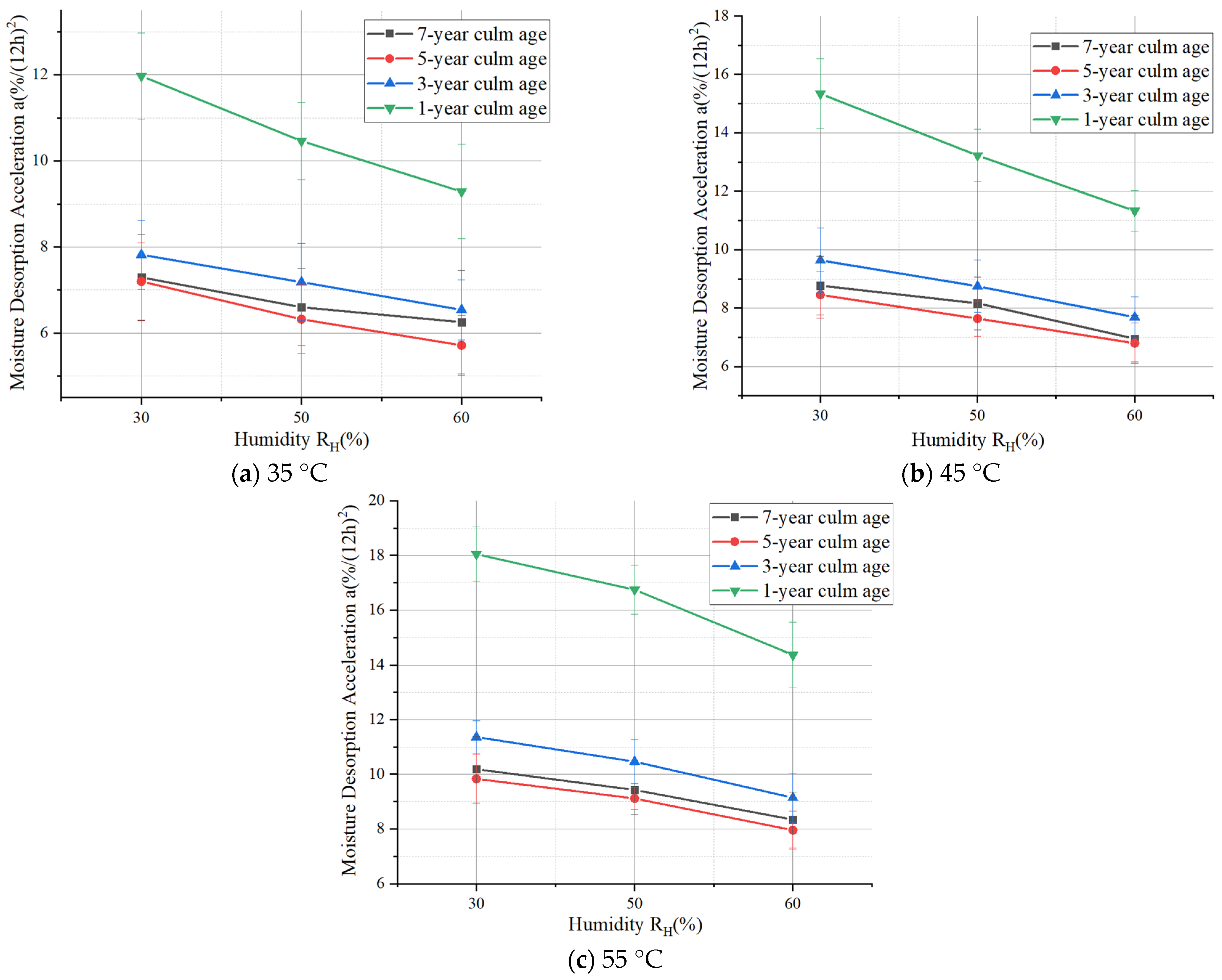
| Test Condition | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Culm Age (Years) | Replicates (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35 | 30 | 1, 3, 5, 7 | 20 per cohort |
| 2 | 45 | |||
| 3 | 55 | |||
| 4 | 35 | 50 | ||
| 5 | 45 | |||
| 6 | 55 | |||
| 7 | 35 | 60 | ||
| 8 | 45 | |||
| 9 | 55 |
| Variable Name | Coefficient | Standard Deviation | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface-area/wall-thickness ratio S/h | 0.005164 | 0.000668 | 7.732043 | 0.0000 |
| Temperature T | 0.162745 | 0.009533 | 17.07171 | 0.0000 |
| Relative humidity RH | −0.055189 | 0.006516 | −8.470331 | 0.0000 |
| Culm age N | −3.476263 | 0.168796 | −20.59447 | 0.0000 |
| Culm age squared N2 | 0.336122 | 0.020609 | 16.30975 | 0.0000 |
| Constant C | 8.338502 | 0.761463 | 10.95064 | 0.0000 |
| R-squared | 0.868355 | Dependent variable mean | 9.070804 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.864551 | Dependent variable variance | 2.863219 | |
| Standard deviation of regression | 1.053763 | Akaike criterion | 2.975557 | |
| Residual sum of squares | 192.1021 | Schwarz criterion | 3.082397 | |
| Likelihood ratio | −260.3124 | Critical value | 3.018880 | |
| F-Test | 228.2289 | Durbin–Watson test | 1.076068 | |
| F-test p-value | 0.000000 | |||
| Variable Name | Coefficient | Standard Deviation | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA a | 0.000121 | 9.66 × 10−6 | 12.55455 | 0.0000 |
| Culm Age N | 4.19 × 10−5 | 1.27 × 10−5 | 3.294407 | 0.0024 |
| Constant C | 0.000261 | 0.000132 | 1.971673 | 0.0571 |
| R-Squared | 0.859072 | Dependent Variable Mean | 0.001576 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.850531 | Dependent Variable Variance | 0.000332 | |
| Standard Deviation of Regression | 0.000128 | Akaike Criterion | −15.00241 | |
| Residual Sum of Squares | 5.44 × 10−7 | Schwarz Criterion | −14.87045 | |
| Likelihood Ratio | 273.0435 | Critical Value | −14.95636 | |
| F-Test | 100.5812 | Durbin–Watson Test | 0.479206 | |
| F-Test p-Value | 0.000000 | |||
| Variable Name | Coefficient | Standard Deviation | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA a | 0.000114 | 5.97 × 10−6 | 19.12875 | 0.0000 |
| Culm Age N | 4.80 × 10−5 | 7.86 × 10−6 | 6.110210 | 0.0000 |
| Constant C | −1.09 × 10−5 | 8.18 × 10−5 | −0.133760 | 0.8944 |
| R-Squared | 0.930228 | Dependent Variable Mean | 0.001261 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.925999 | Dependent Variable Variance | 0.000292 | |
| Standard Deviation of Regression | 7.94 × 10−5 | Akaike Criterion | −15.96547 | |
| Residual Sum of Squares | 2.08 × 10−7 | Schwarz Criterion | −15.83351 | |
| Likelihood Ratio | 290.3784 | Critical Value | −15.91941 | |
| F-Test | 219.9843 | Durbin–Watson Test | 0.492848 | |
| F-Test p-Value | 0.000000 | |||
| Parameter | External Surface (MPa) | Internal Surface (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Stress | Defect-Free Theoretical Value | Amplification Factor | Maximum Stress | Defect-Free Theoretical Value | Amplification Factor | ||
| Minor-to-major axis ratio | 0.70 | 3.70 | 2.31 | 1.60 | 3.69 | 2.62 | 1.41 |
| 0.80 | 3.49 | 2.31 | 1.51 | 3.33 | 2.62 | 1.27 | |
| 0.85 | 3.28 | 2.31 | 1.42 | 3.01 | 2.62 | 1.15 | |
| 0.90 | 3.12 | 2.31 | 1.35 | 2.80 | 2.62 | 1.07 | |
| 0.95 | 2.84 | 2.31 | 1.23 | 2.46 | 2.62 | 0.94 | |
| 1.00 (Annulus) | 2.56 | 2.31 | 1.11 | 2.17 | 2.62 | 0.83 | |
| Buttress groove depth | 0 (no groove) | 2.56 | 2.56 | 1.00 | 2.17 | 2.17 | 1.00 |
| h/5 | 3.76 | 2.56 | 1.47 | 2.52 | 2.17 | 1.16 | |
| h/4 | 4.68 | 2.56 | 1.83 | 3.02 | 2.17 | 1.39 | |
| h/3 | 5.66 | 2.56 | 2.21 | 3.80 | 2.17 | 1.75 | |
| h/2 | 6.76 | 2.56 | 2.64 | 4.36 | 2.17 | 2.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, B.; Yu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, J.; Ju, Z.; Yin, T.; Wang, Z. Analytical Study on the Transverse Stress Model and Its Influencing Factors on Moso Bamboo. Buildings 2025, 15, 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203740
Shu B, Yu J, Li C, Shen J, Ju Z, Yin T, Wang Z. Analytical Study on the Transverse Stress Model and Its Influencing Factors on Moso Bamboo. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203740
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Biqing, Junbao Yu, Chen Li, Jie Shen, Zehui Ju, Tianxiao Yin, and Zhiqiang Wang. 2025. "Analytical Study on the Transverse Stress Model and Its Influencing Factors on Moso Bamboo" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203740
APA StyleShu, B., Yu, J., Li, C., Shen, J., Ju, Z., Yin, T., & Wang, Z. (2025). Analytical Study on the Transverse Stress Model and Its Influencing Factors on Moso Bamboo. Buildings, 15(20), 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203740






