Numerical Analysis and Resistance Design of UHPC- and UHTCC-Encased Rectangular Steel Tubular Columns Subject to Axial Compression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Constitutive Models
3. Numerical Analysis
3.1. Mesh Condition and Interaction Settings
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Mesh Size
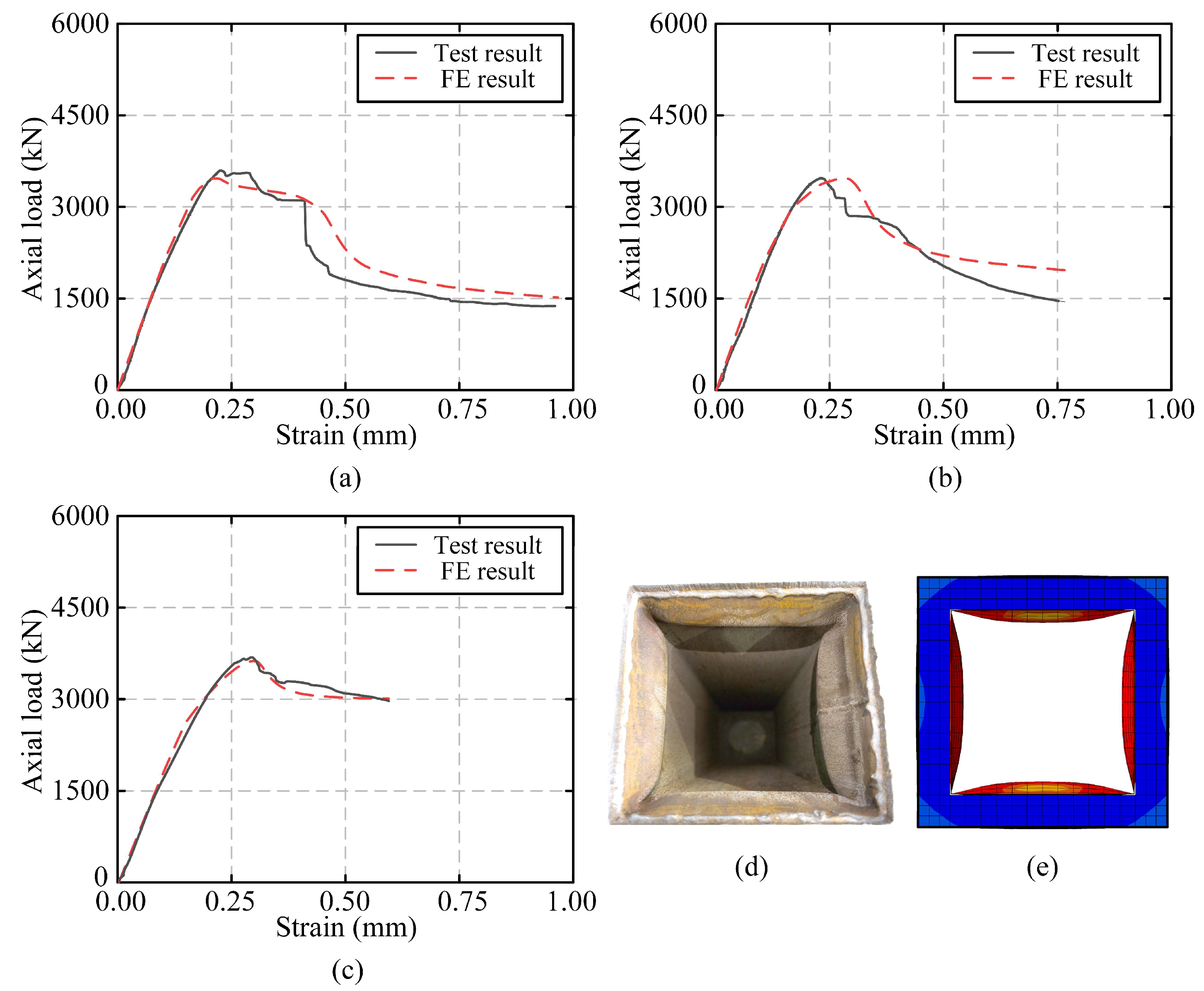
3.3. FE Model Validation
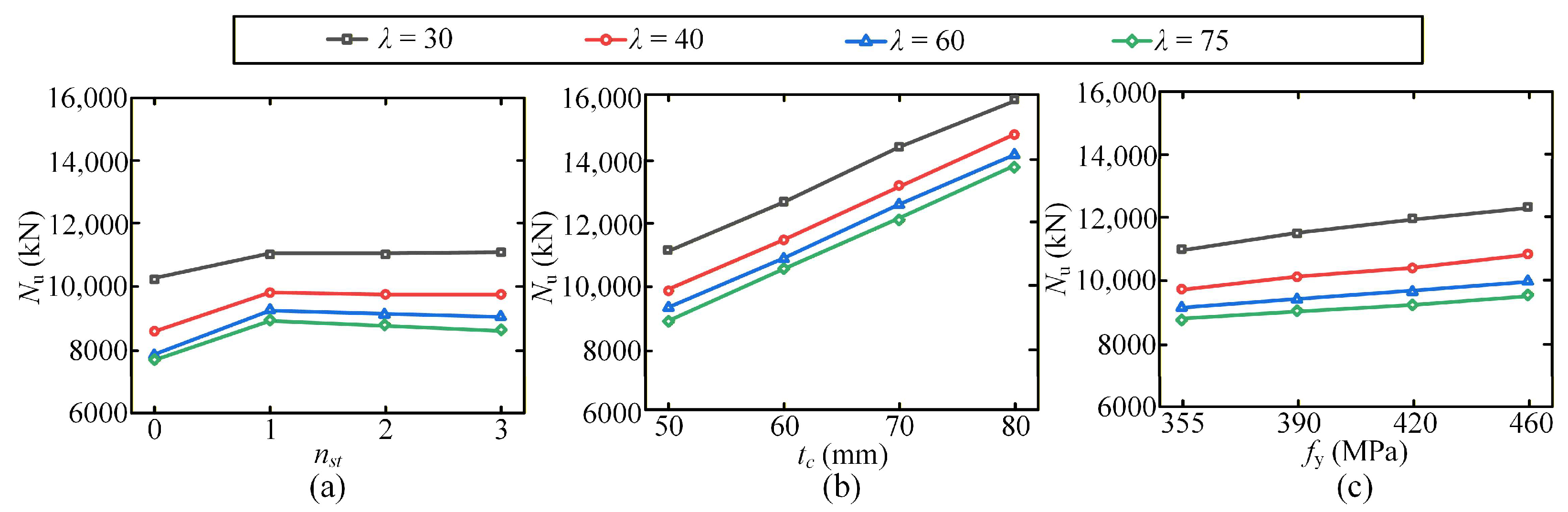
3.4. Parametric Study
4. Axial Resistance Design of UEST Columns
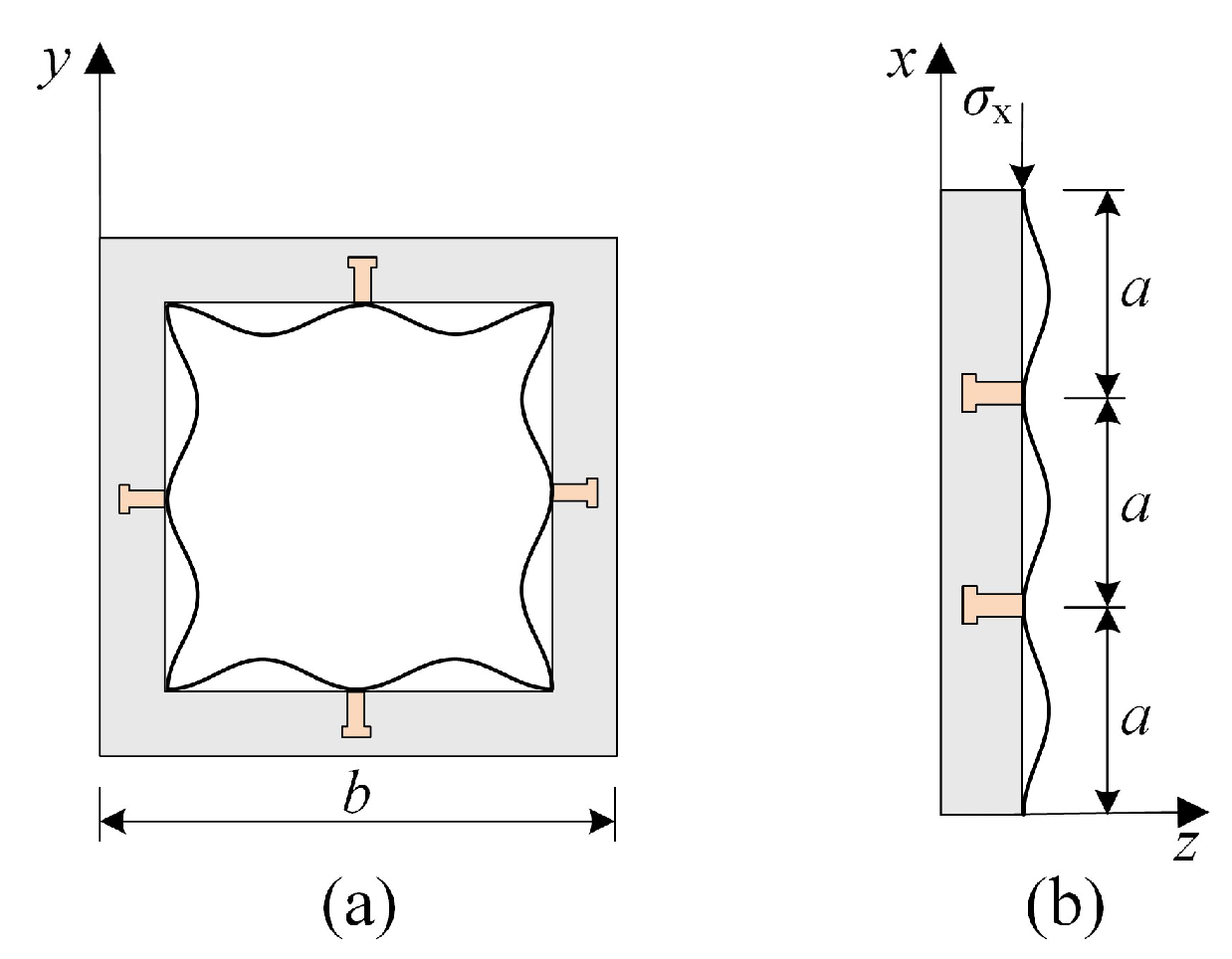
4.1. Elastic Buckling Analysis of Thin-Walled Steel Plates
- (1)
- Only in-plane stresses (σx, σy, τxy) are considered, with out-of-plane stresses neglected due to the thin-walled nature;
- (2)
- The plate undergoes elastic deformation, adhering to Hooke’s law;
- (3)
- Membrane stresses induced by minor stretching are ignored;
- (4)
- The bond stress between UHPC/UHTCC and the steel tube is negligible compared to stud-induced shear transfer.
4.2. Elastic Buckling Analysis of UEST Column
4.3. Axial Resistance of UEST Column
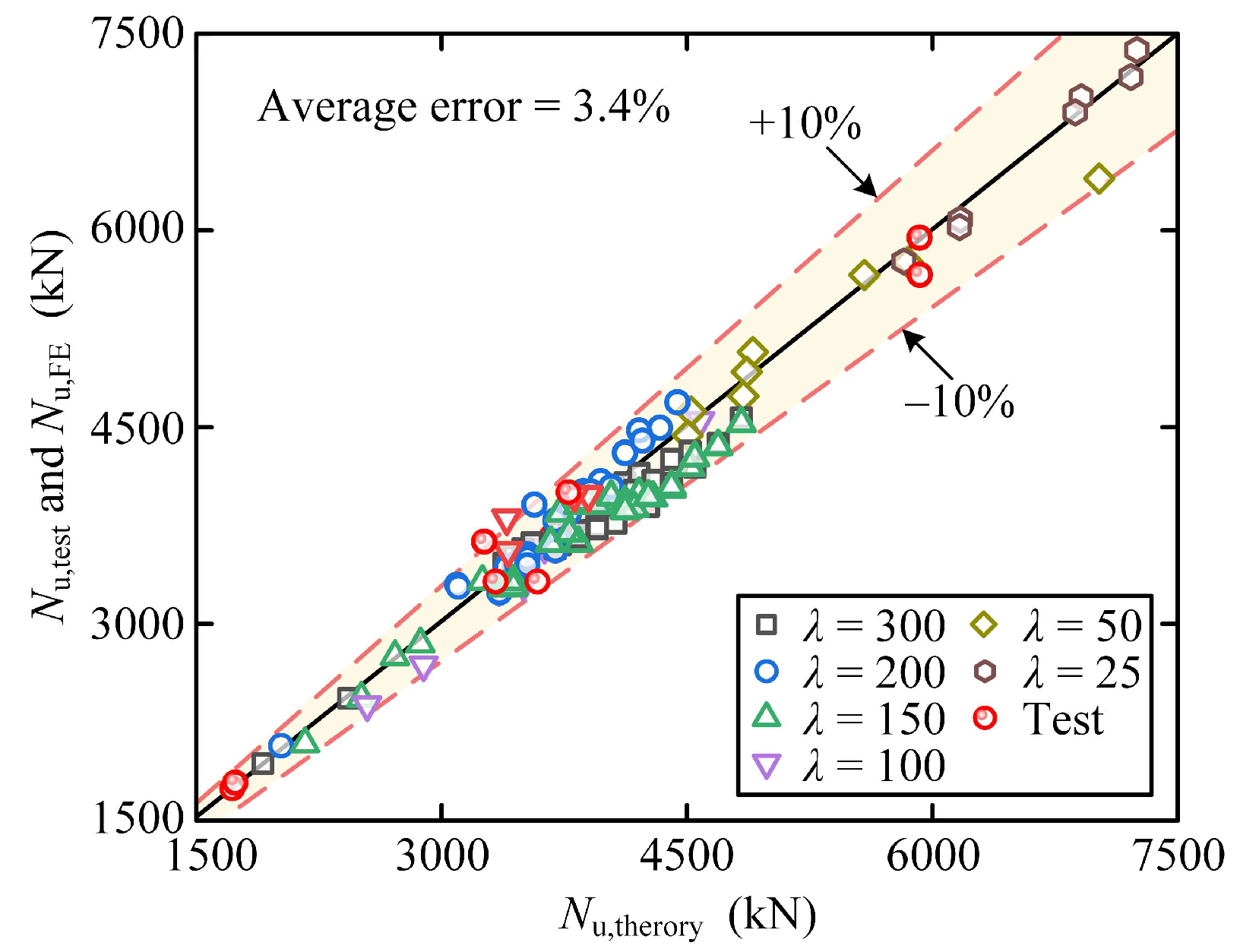
4.4. Theory Validation
5. Conclusions
- Axial resistance: UHPC-EST columns exhibit higher resistance than UHTCC-EST columns. Increasing stud number from 0 to 1 stud significantly enhances resistance due to improved interface bonding and confinement, but further increasing stud number to 2 or 3 results in marginal gains, as the steel–UHPC/UHTCC interaction reaches saturation. An increase in steel yield strength from 355 to 460 MPa linearly boosts resistance, with the effect most significant for the columns with thinner steel tube.
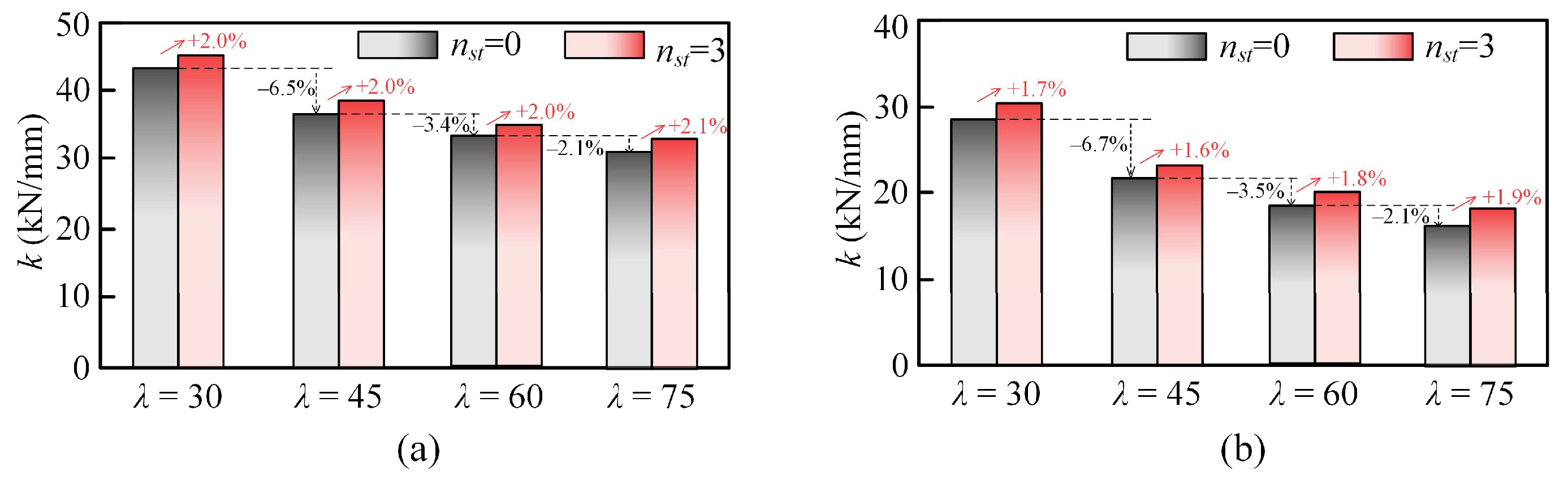
- Axial stiffness: UHPC-EST columns have higher baseline stiffness than UHTCC-EST columns. Stud number increase from 0 to 3 enhances stiffness by 2.0–2.1% for UHPC and 1.6–1.9% for UHTCC. Stiffness decreases by 2.1–6.5% as width-to thickness ratio of steel tube increases from 30 to 75 for both encasement materials.
- Proposed theory: An axial resistance design theory integrating buckling analysis and effective width method is proposed, predicting axial resistance with an average error of 3.4%, providing a reliable design method for UEST columns, particularly those with thin-walled steel tubes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UHPC | Ultra-high performance concrete |
| UHTCC | Ultra-high toughness cementitious composite |
| UEST | UHPC/UHTCC-encased steel tube |
| UHPC-EST | UHPC-encased steel tube |
| UHTCC-EST | UHTCC-encased steel tube |
| CFST | Concrete-filled steel tubular |
| CEST | Concrete-encased steel tubular |
| NC | Normal concrete |
| FE | Finite element |
| CDP | Concrete damaged plasticity |
References
- Song, W.; Yu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.H.; He, Z.Y.; Tian, W.R. Compression behavior of CFST columns under combined influence of gap and freeze-thaw. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 214, 108452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H.; Li, W.; Bjorhovde, R. Developments and advanced applications of concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) structures: Members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2014, 100, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, T.; Huang, W.J.; Yuan, H.X.; Ye, J.Q. Fire resistance of concrete-filled steel tube columns with preload. Part I: Experimental investigation. Compos. Struct. 2019, 223, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Briseghella, B.; Zordan, T.; Wu, Q.X.; Chen, B.C. Shaking table tests for the evaluation of the seismic performance of an innovative lightweight bridge with CFST composite truss girder and lattice pier. Eng. Struct. 2014, 75, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Fu, F.; Liu, M. Cyclic behavior of four-limbed circular CFST latticed beam-columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2024, 150, 4024006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Shen, S.Y.; Chen, G.X.; Pang, R.; Mao, M. Experimental and numerical study on axial compressive behaviors of reinforced UHPC-CFST composite columns. Eng. Struct. 2023, 278, 115315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayough, P.; Wang, Y.H.; Zeng, W.Y.; Liang, Q.Q.; Elchalakani, M.; Zou, C.L. Numerical investigation and design of UHPC-encased CFST stub columns under axial compression. Eng. Struct. 2024, 302, 117387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.Y.; Han, L.H.; Li, W.; Hou, C.; Mu, T.M. Behaviour of concrete-encased CFST stub columns subjected to long-term sustained loading. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 151, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.C.; Han, L.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Hou, C. Flexural behavior of circular concrete filled steel tubes (CFST) under sustained load and chloride corrosion. Thin Wall. Struct. 2016, 107, 182–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Su, R.K.; Ma, J.J.; Ni, Y.J. Experimental case study on the fatigue behavior of steel–concrete composite beams after chloride-induced corrosion and cyclic freeze–thaw. J. Bridge Eng. 2023, 28, 5022012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Abe, H.; Hayashi, D.; Tanaka, H. Behavioral characteristics of RC beams with non-uniform corrosion along the reinforcement. J. Intel. Constr. 2023, 1, 9180019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, B.Z.; Liu, B.B.; Zhao, Z.W.; Mo, S.J. Influence of corrosion on loading capacity of circular concrete-filled steel tubular column. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 215, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H.; Song, T.Y.; Zhou, K.; Cui, Z.Q. Fire performance of CFST triple-limb laced columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, L.; Ramesh, S.; Grosshandler, W.; Hoehler, M.; Seif, M.; Gross, J.; Bundy, M. Behavior and limit states of long-span composite floor beams with simple shear connections subject to compartment fires: Experimental evaluation. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tong, J.Z.; Li, Q.H.; Shen, L.; Xu, S.L. Axial compressive tests and resistance prediction of UHTCC-encased circular steel tubular columns. Eng. Struct. 2025, 338, 120626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tong, J.Z.; Li, Q.H.; Xu, S.L.; Gao, W.; Liu, X. Flexural behavior of novel profiled steel-UHTCC assembled composite bridge decks. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 212, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Teng, L.; Tang, F.J.; Khayat, K.H.; Chen, G.D.; Meng, W.N. Corrosion of steel rebar embedded in UHPC beams with cracked matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Lin, L.Q.; Peng, Z.X.; Xu, R.Q.; Wang, G.N. Cracking performance in the hogging-moment regions of natural curing steel-UHPC and steel-UHTCC continuous composite beams. J. Bridge Eng. 2022, 27, 4021106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, S.M.; Peng, Y.T.; Li, Y. Effects of FRP fiber orientations on four-point bending behaviour of FRP-concrete-steel tubular beams: Experimental study and modeling. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Corrosion of steel rebars across UHPC joint interface under chloride attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 387, 131591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, X.C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.M.; Jiang, Y.X. Novel FRP-UHPC-steel double-tube columns subjected to monotonic axial load: Compressive behavior and analytical model. Eng. Struct. 2025, 328, 119746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.D.; Shao, X.D.; Cao, J.H.; Fu, Y.G. Numerical and theoretical studies on the shear behavior of composite beams with a steel-UHPC composite web. Eng. Struct. 2025, 329, 119815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Liao, F.Y.; Ye, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Lin, K.H. Compressive behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) encased concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) stub columns under eccentric loading. Structures 2025, 78, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Zhu, R.X.; Xiang, Z. A review on behavior and fatigue performance of orthotropic steel–UHPC composite deck. Buildings 2023, 13, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zheng, L.Y.; Pei, B.D.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.F.; Zhao, J. Key design parameters analysis and calculation theory research on bending performance of steel–UHPC lightweight composite deck structure. Buildings 2023, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Wu, J.J.; Sun, R.J.; Ge, Z.; Bi, Y.F.; Zhu, D.Y. Shear behavior of short headed studs in Steel-ECC composite structure. Eng. Struct. 2022, 250, 113423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.H.; Bao, Y.; Bu, Y.Z. Static and fatigue push-out tests of short headed shear studs embedded in Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC). Eng. Struct. 2019, 182, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1994-1-1 (2004); Eurocode 4: Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings [Authority: The European Union Per Regulation 305/2011, Directive 98/34/EC, Directive 2004/18/EC]. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- AISC 360-16; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Code; American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 2016.
- Zhang, E.Y. Seismic Performance of Prefabricated Joints for High-Toughness Concrete-Encased Steel Tube Composite Members. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2025; pp. 101–111. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Maalej, M.; Li, V.C. Flexural/tensile-strength ratio in engineered cementitious composites. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 1994, 6, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Pan, J.L.; Leung, C.K.Y. Mechanical behavior of fiber-reinforced engineered cementitious composites in uniaxial compression. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2015, 27, 4014111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsimpini, P. On the seismic response of composite structures equipped with wall dampers under multiple earthquakes. Modelling 2025, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.Y.; Sun, X.J.; Takahashi, Y.Y.; Maekawa, K.; Jin, W.L. Computational modeling of combined frost damage and alkali–silica reaction on the durability and fatigue life of RC bridge decks. J. Intel. Constr. 2023, 1, 9180001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Wang, J.F.; Guo, L. Mechanical behavior analysis of LEM-infilled cold-formed steel walls. Sustain. Struct. 2022, 2, 000013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Liu, Y.K.; Chen, X.S.; Li, C.H. Axial compression behavior of prefabricated cruciform-section thin-concrete-encased steel short column. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 217, 108640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tong, J.Z.; Li, Q.H.; Peng, W.B.; Zhang, E.Y.; Gao, W.; Xu, S.L. Axial Compressive Tests and Resistance Design of UHTCC-Encased Rectangular Steel Tubular Bridge Columns. J. Bridge Eng. 2025, 30, 4025033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tong, J.Z.; Li, Q.H.; Jin, H.; Xu, S.L. Axial compressive performance of UHTCC-encased circular steel tubular columns with different PBL connection details. Compos. Struct. 2025, 371, 119528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.D. Local stability of filled and encased steel sections. J. Struct. Eng. 1995, 121, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Karman, T.; Tsein, H.S. The buckling of thin cylindrical shells under axial compression. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2003, 40, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G. Strength of thin steel compression flanges. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1947, 112, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
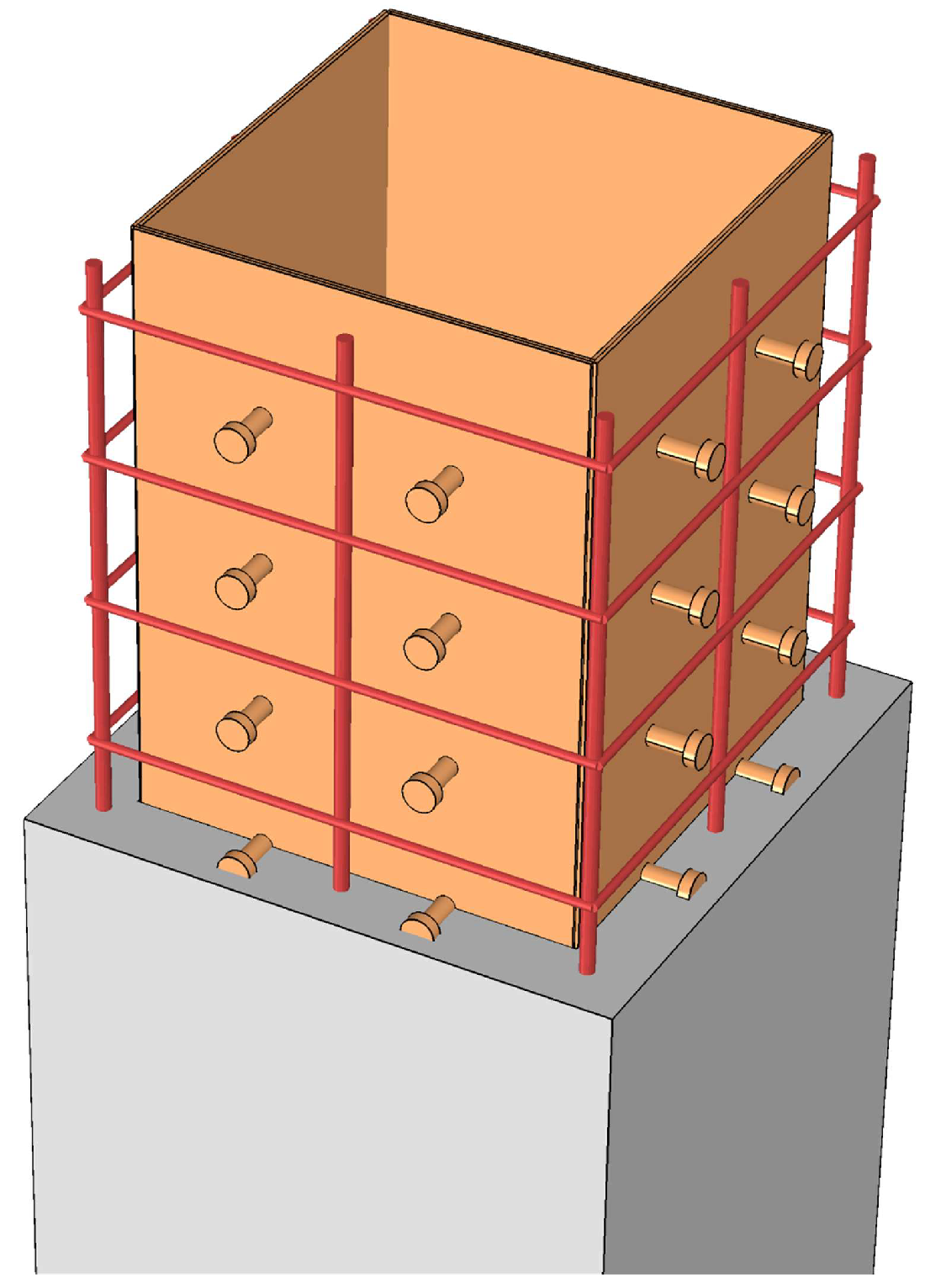
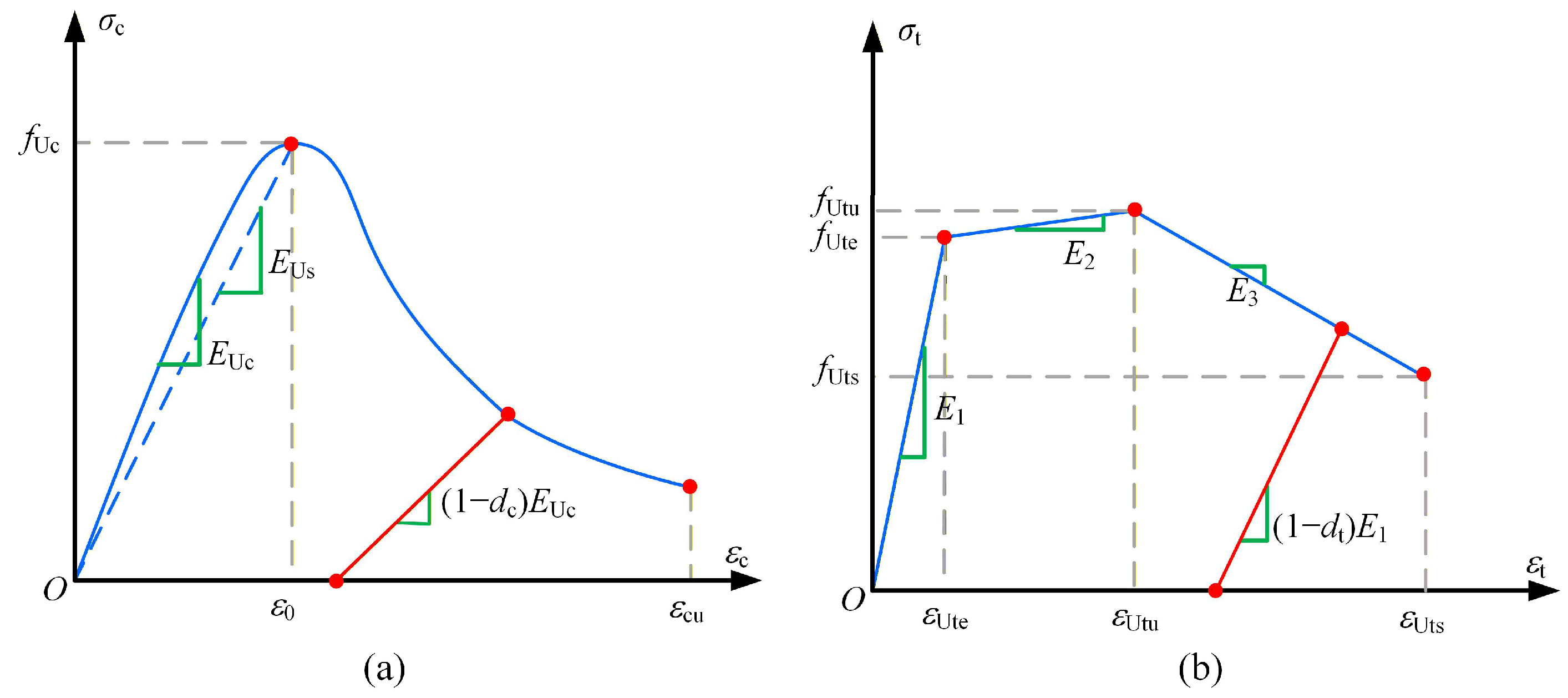
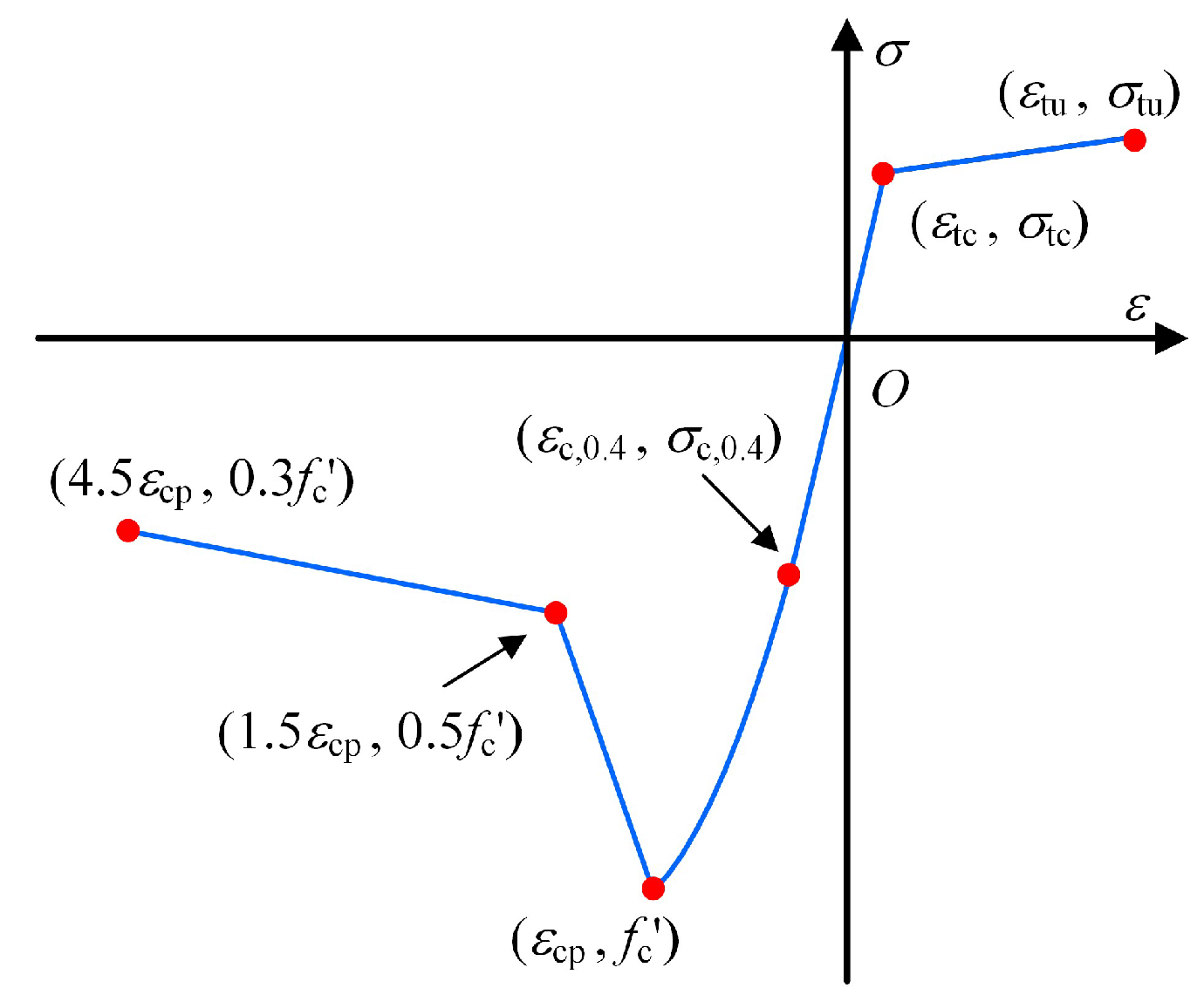
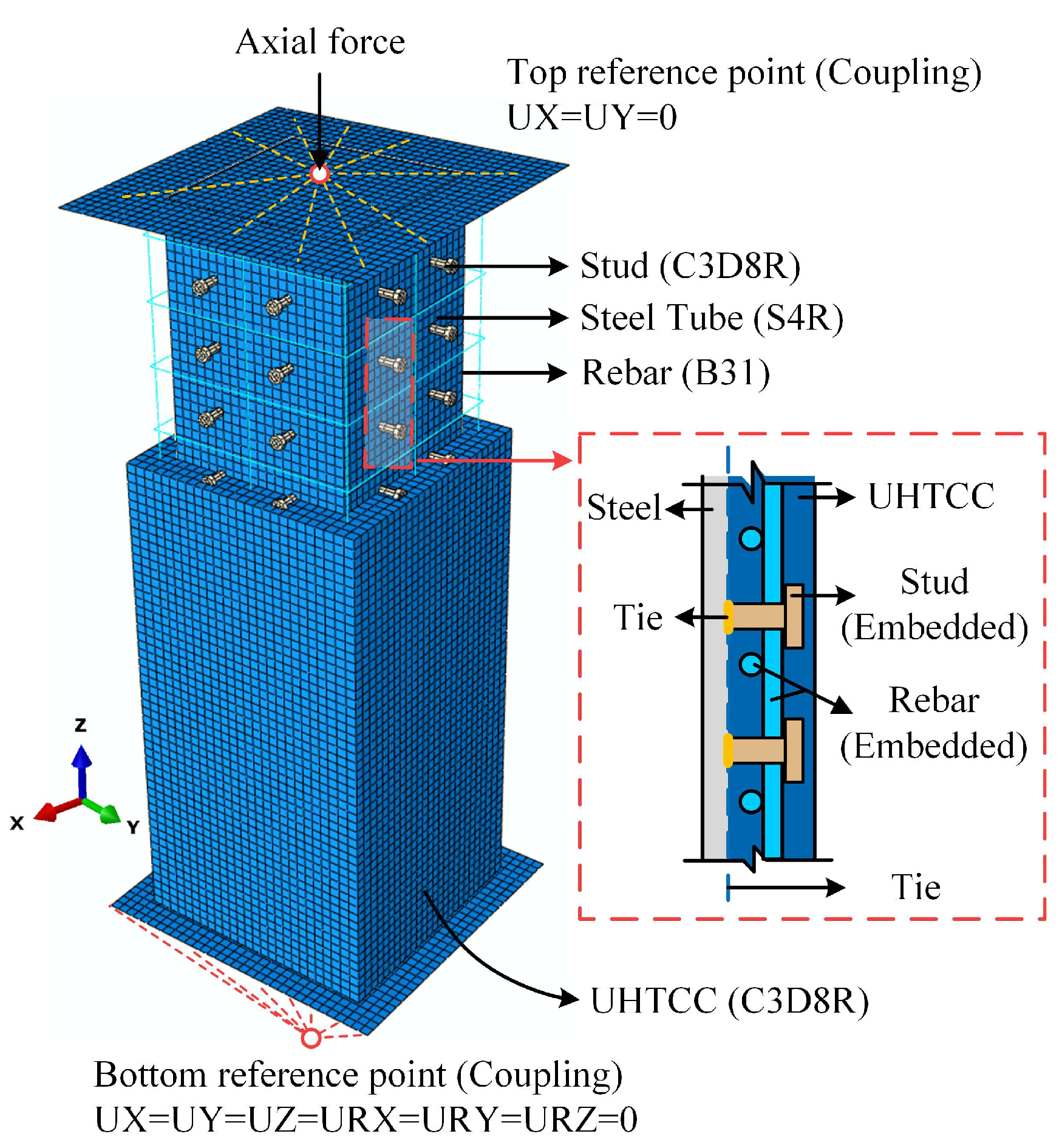




| Material | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Compressive Strength (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Peak Tensile Strain | Peak Compressive Strain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1–3 | 20–50 | 28–34.5 | 0.01% | 0.2% |
| UHPC | 6–8 | 120–160 | 40–50 | 0.15% | 0.2–0.6% |
| UHTCC | 4.5–6 | 30–60 | 15–20 | 3–6% | 0.5–0.6% |
| Specimen | Type of Result | Ultimate State | RMSE 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load (kN) | Error | |||
| Laminated column | Test | 3595 | −3.6% | 270.3 |
| FE | 3464 | |||
| Rectangular UEST columns | Test | 3461 | 0.1% | 287.3 |
| FE | 3463 | |||
| Circular UEST columns | Test | 3331 | 1.3% | 81.0 |
| FE | 3373 | |||
| Group № | Key Design Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Layer Material | nst | tc (mm) | fy | λ | |
| 1 | UHPC | 0–3 | 50 | 355 | 30–75 |
| 2 | UHPC | 2 | 50–80 | 355 | 30–75 |
| 3 | UHPC | 2 | 50 | 355–460 | 30–75 |
| 4 | UHTCC | 2 | 50 | 355 | 30–75 |
| 5 | UHTCC | 2 | 50–80 | 355 | 30–75 |
| 6 | UHTCC | 2 | 50 | 355–460 | 30–75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, X.-Y.; Tan, L.; Li, D.-F.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chai, J.-L.; Tong, J.-Z. Numerical Analysis and Resistance Design of UHPC- and UHTCC-Encased Rectangular Steel Tubular Columns Subject to Axial Compression. Buildings 2025, 15, 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203735
Min X-Y, Tan L, Li D-F, Chen Y-L, Chai J-L, Tong J-Z. Numerical Analysis and Resistance Design of UHPC- and UHTCC-Encased Rectangular Steel Tubular Columns Subject to Axial Compression. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203735
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Xiao-Yang, Lin Tan, Deng-Feng Li, Yun-Long Chen, Ji-Long Chai, and Jing-Zhong Tong. 2025. "Numerical Analysis and Resistance Design of UHPC- and UHTCC-Encased Rectangular Steel Tubular Columns Subject to Axial Compression" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203735
APA StyleMin, X.-Y., Tan, L., Li, D.-F., Chen, Y.-L., Chai, J.-L., & Tong, J.-Z. (2025). Numerical Analysis and Resistance Design of UHPC- and UHTCC-Encased Rectangular Steel Tubular Columns Subject to Axial Compression. Buildings, 15(20), 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203735








