Influence of Size and Content of Recycled Aggregate on Mechanical Properties of Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.1.1. Raw Material
2.1.2. Mix Proportion Design and Specimen Grouping
2.2. Test Scheme and Test Method
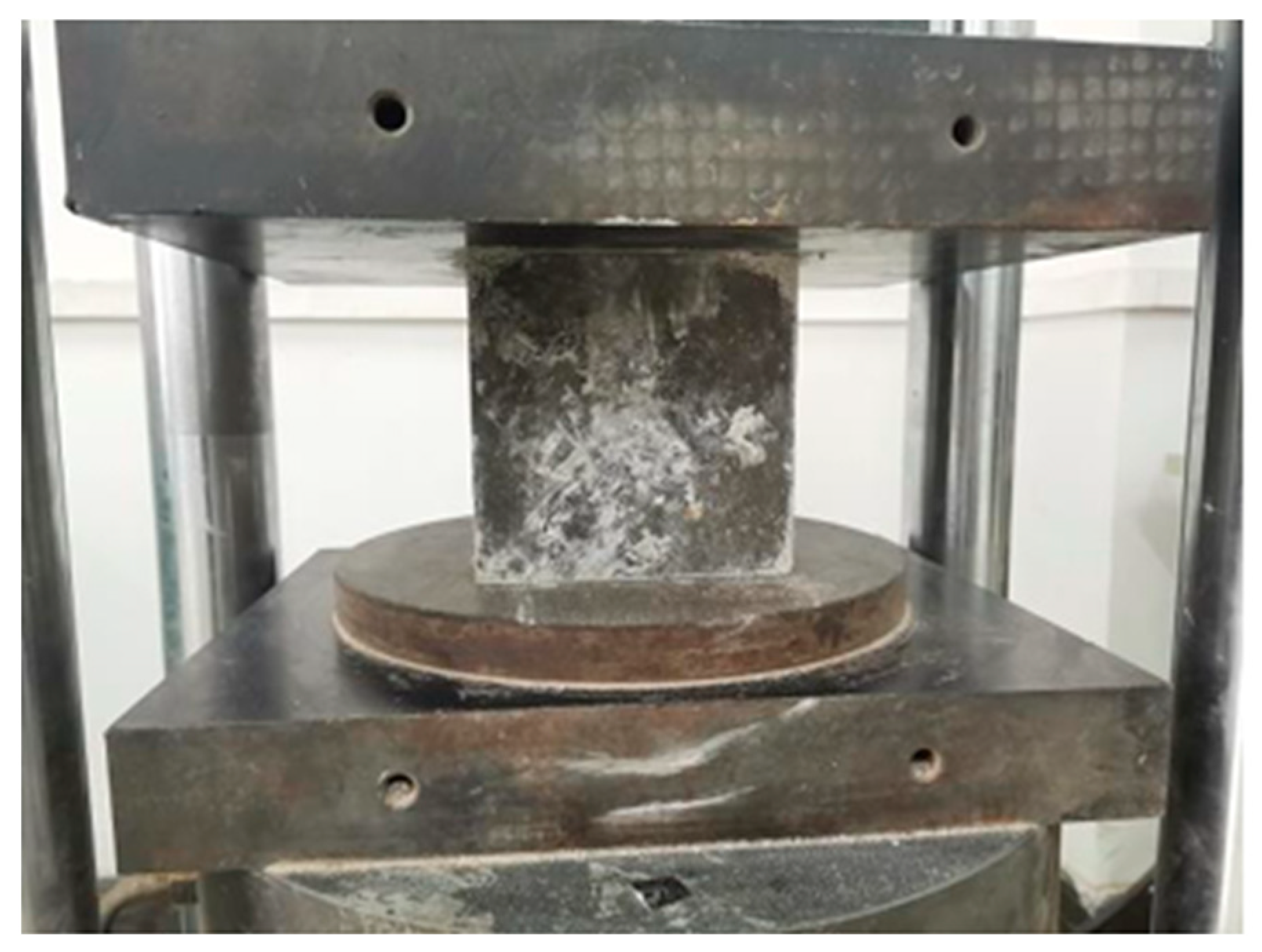
2.2.1. Compressive Strength Tests
2.2.2. Splitting Tensile Strength Test
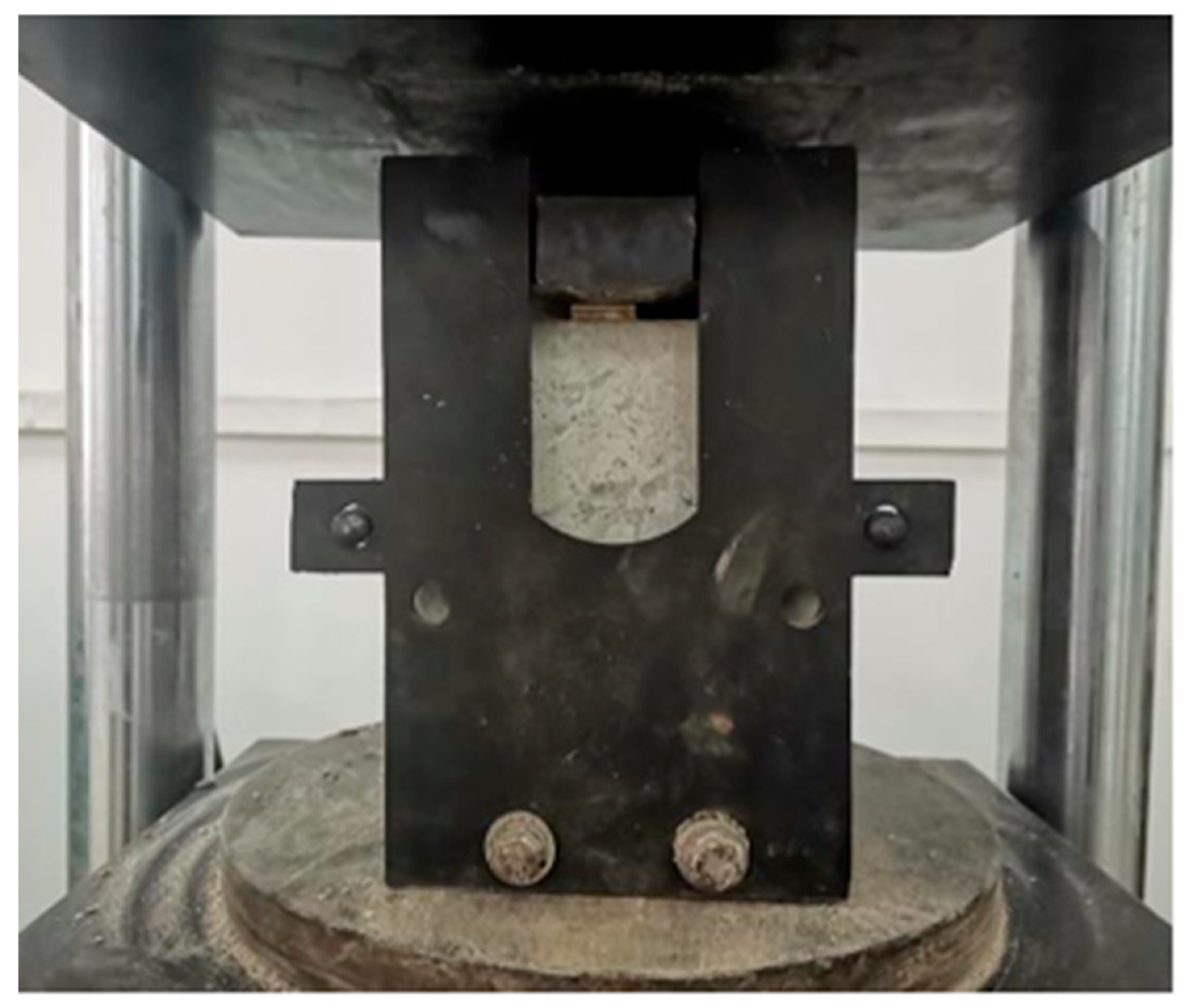
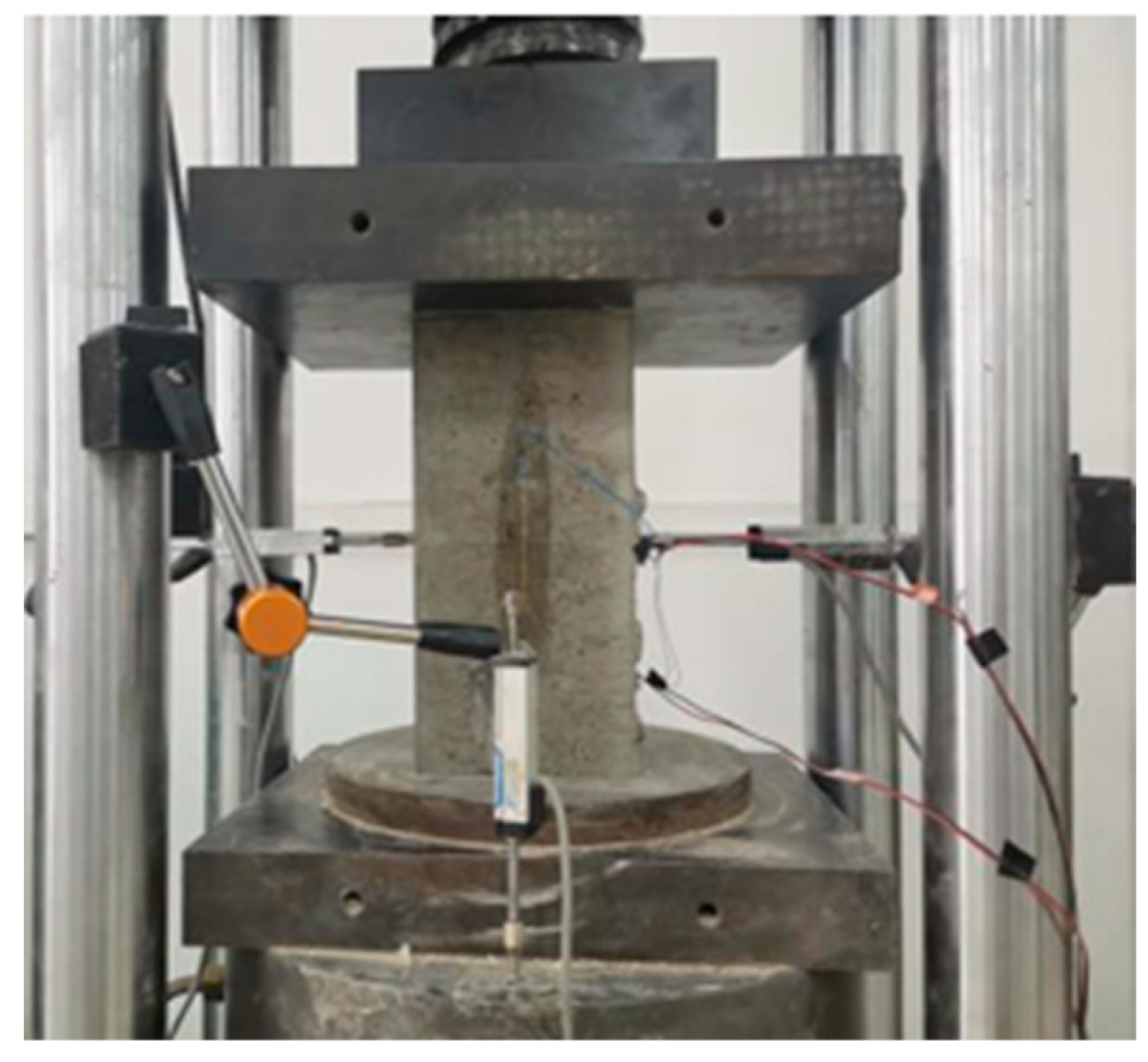
2.2.3. Axial Compressive Strength Test
2.2.4. Elastic Modulus Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
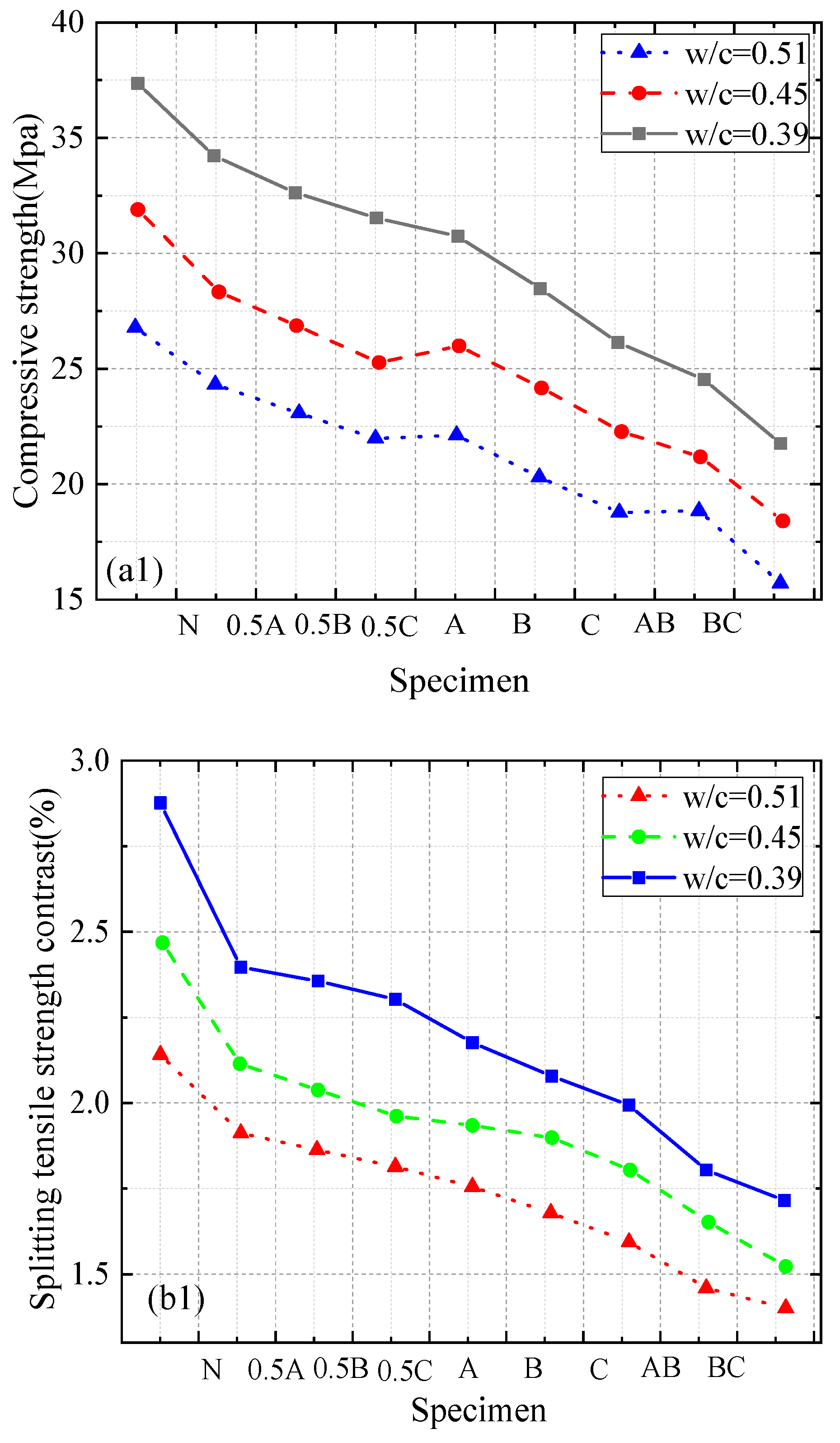
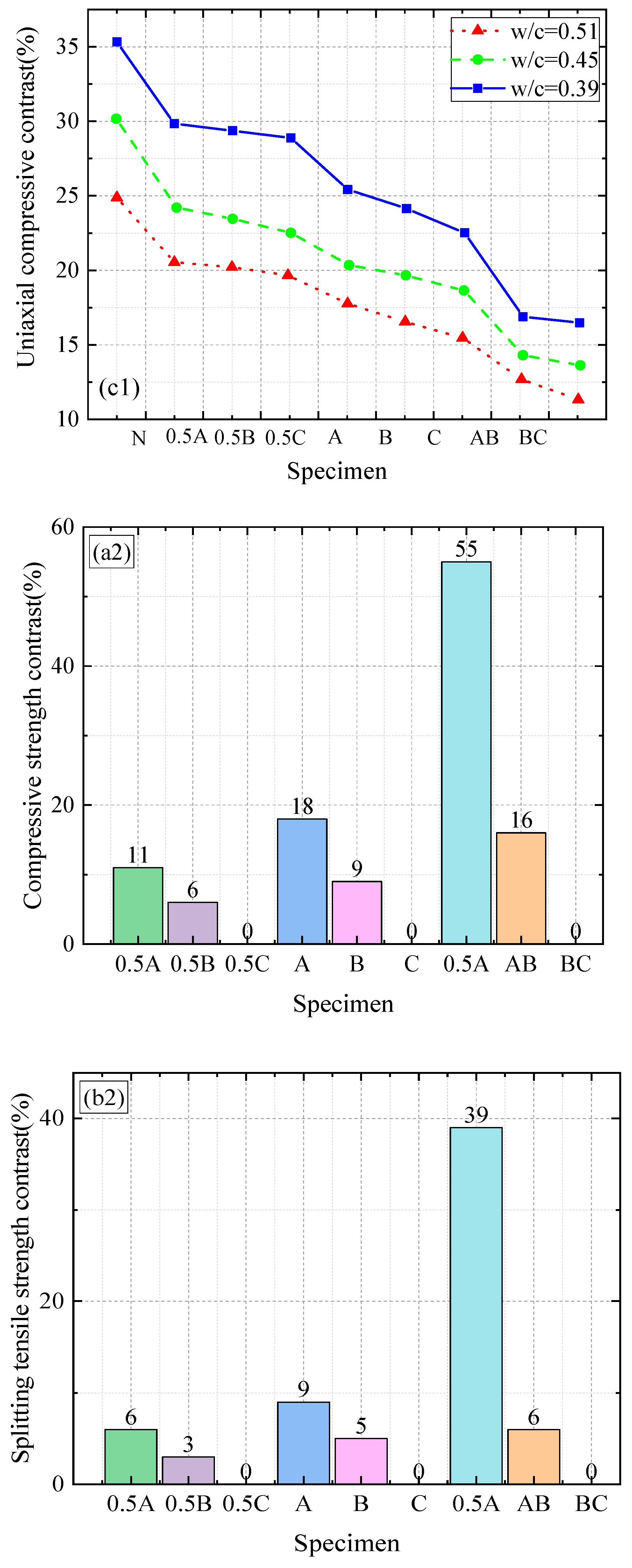
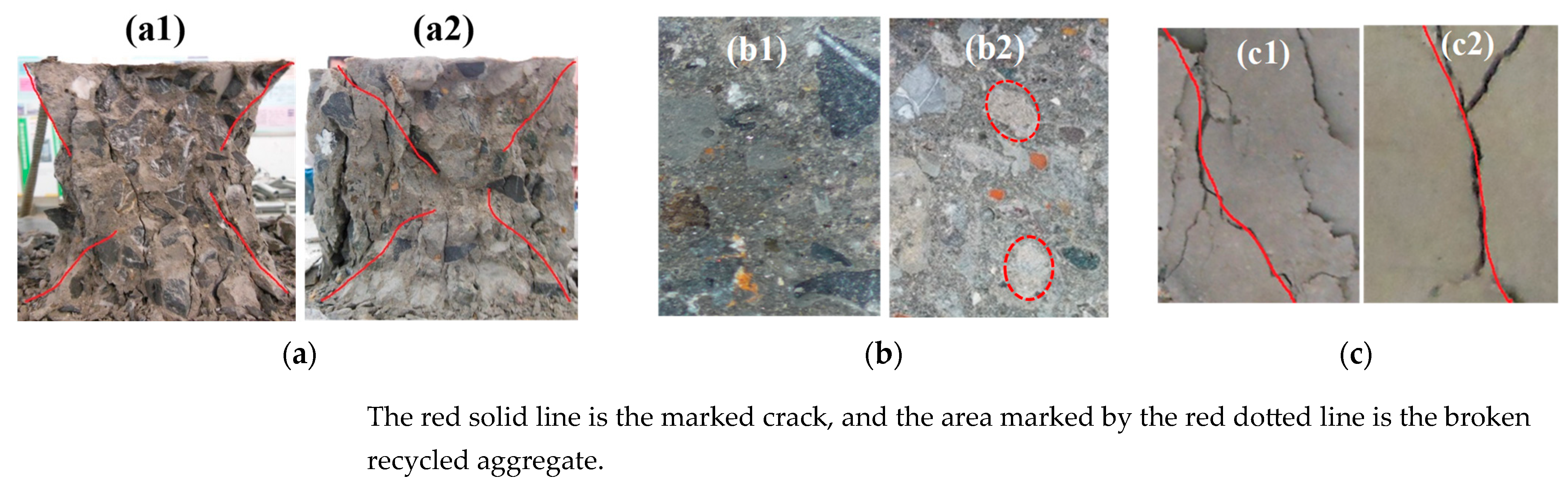
3.1. Mechanical Properties and Failure Modes of RAC
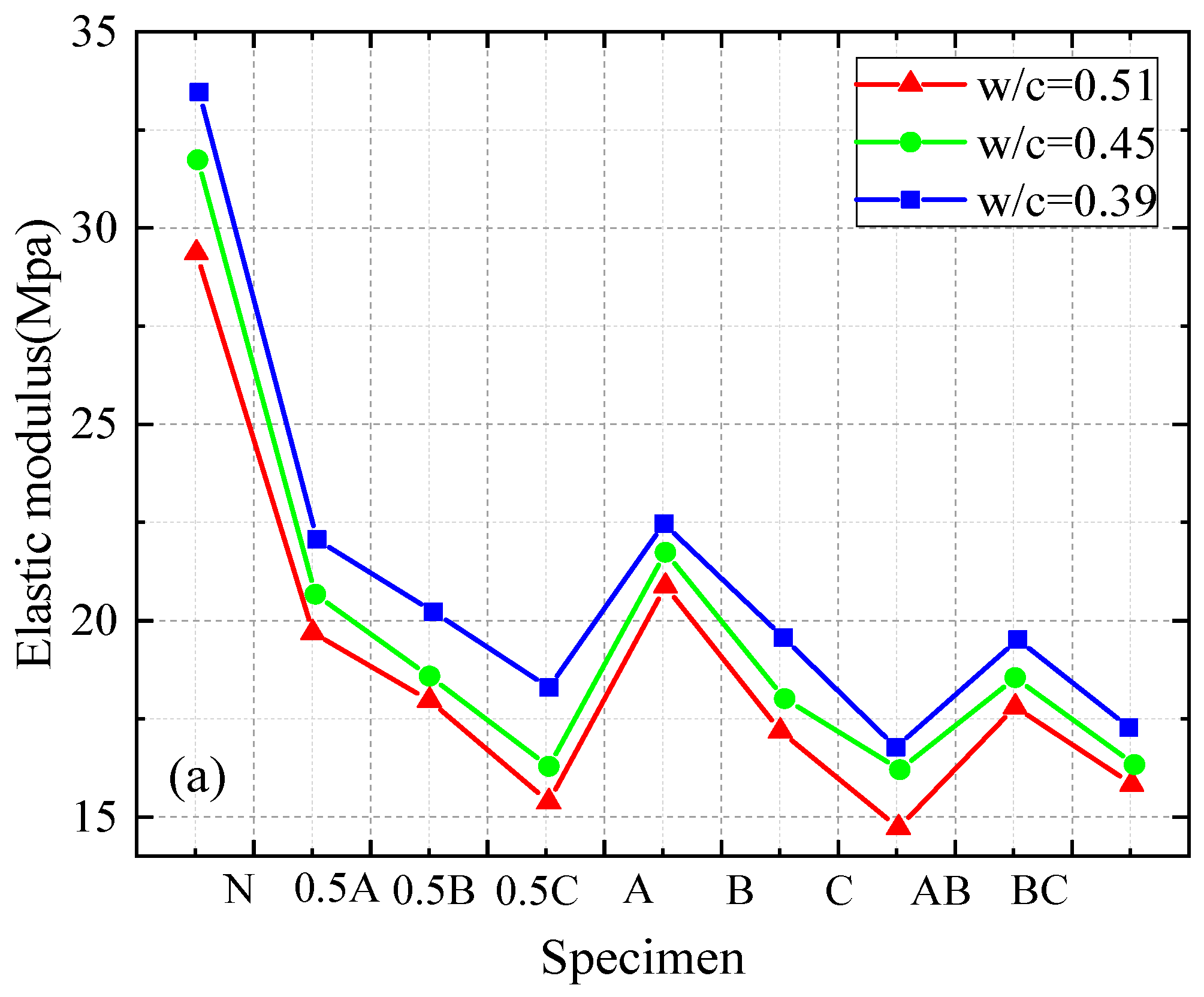
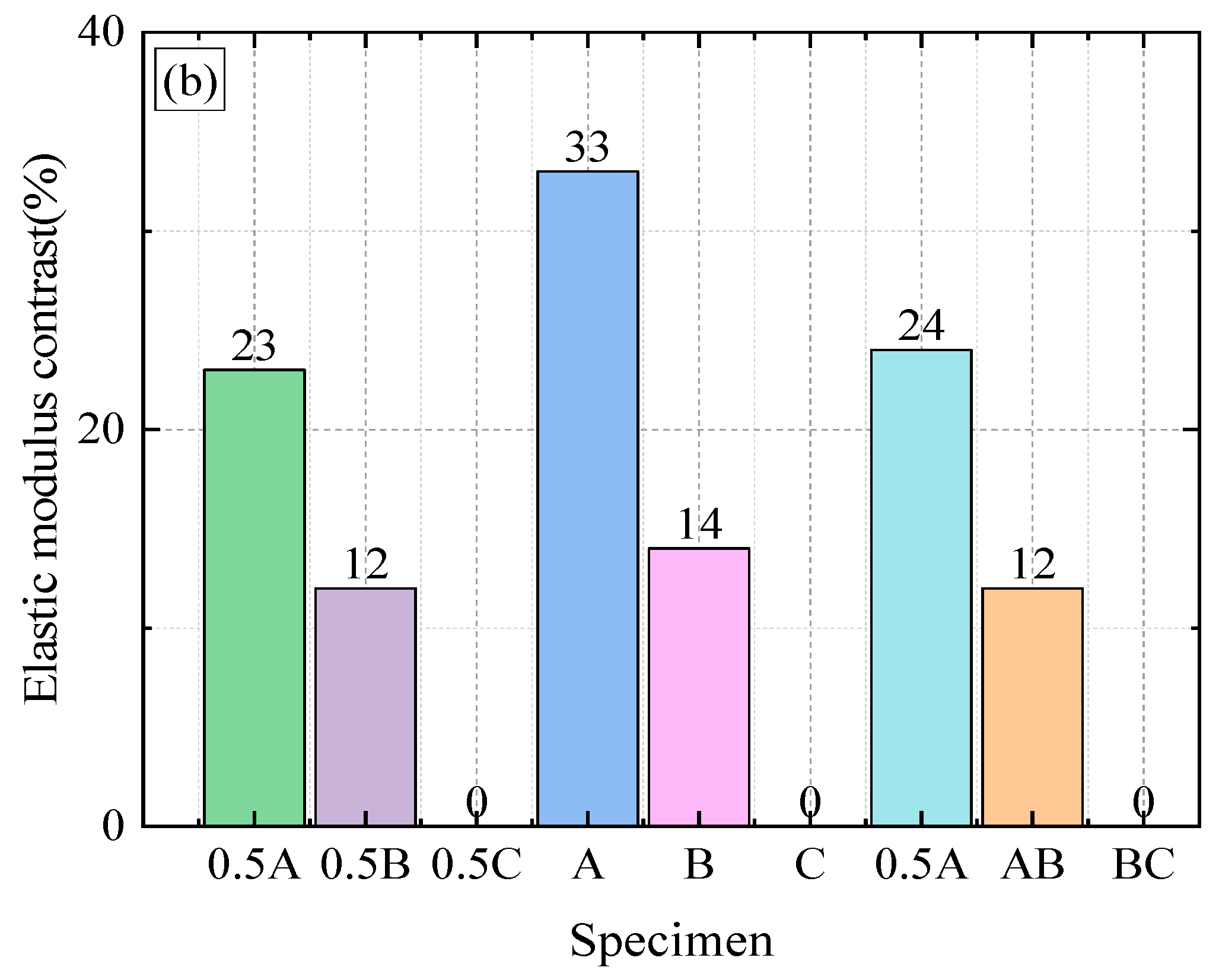
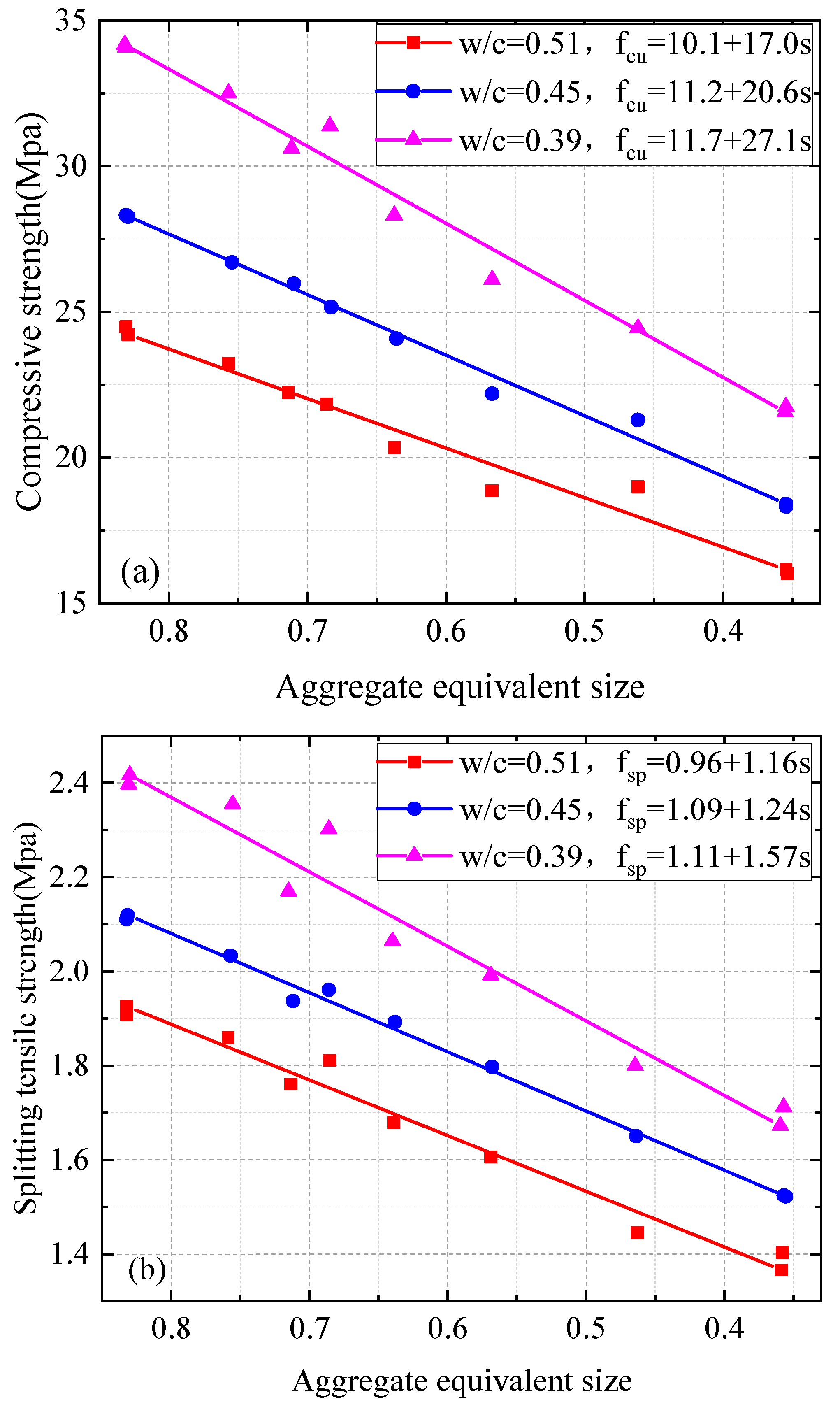
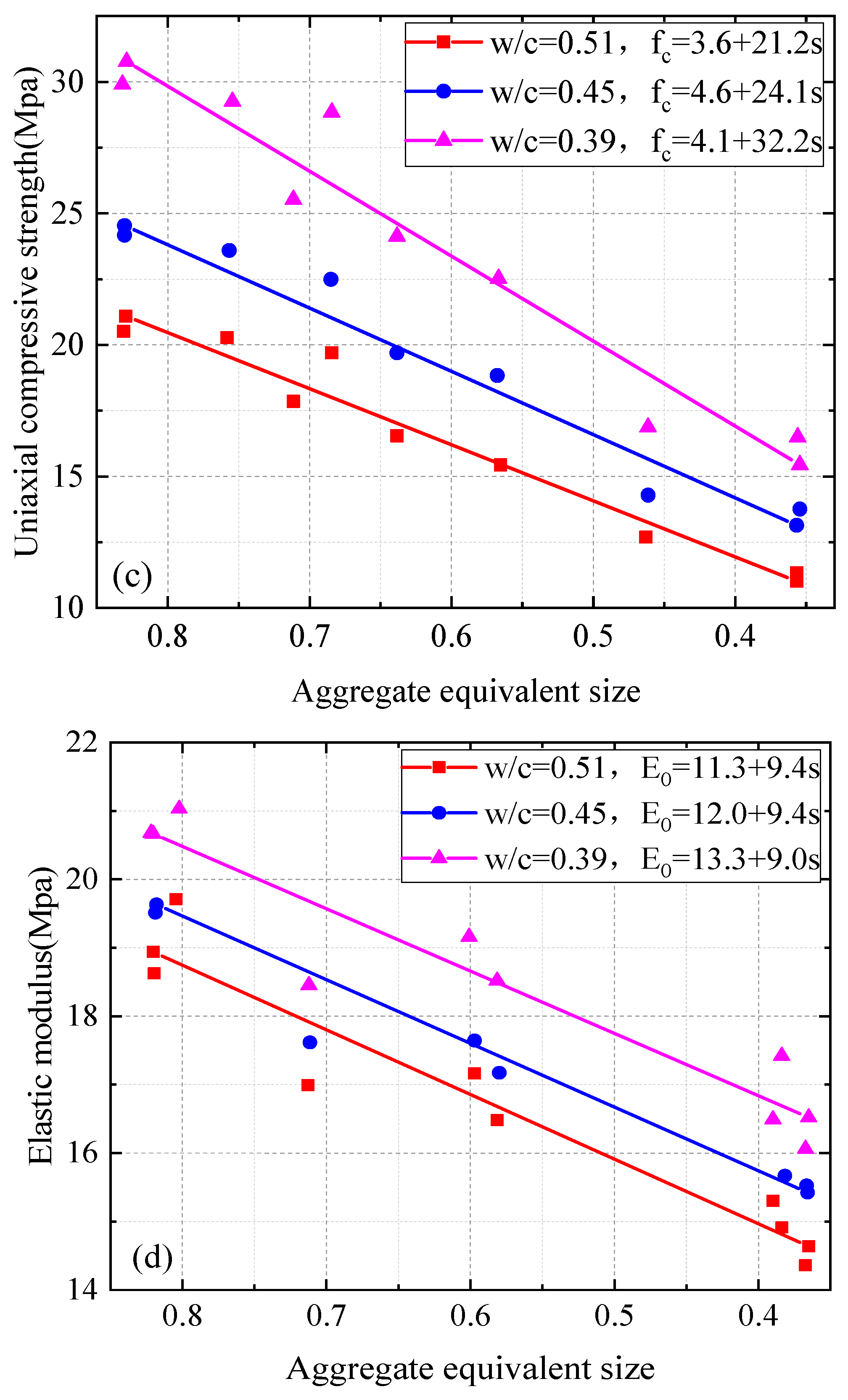
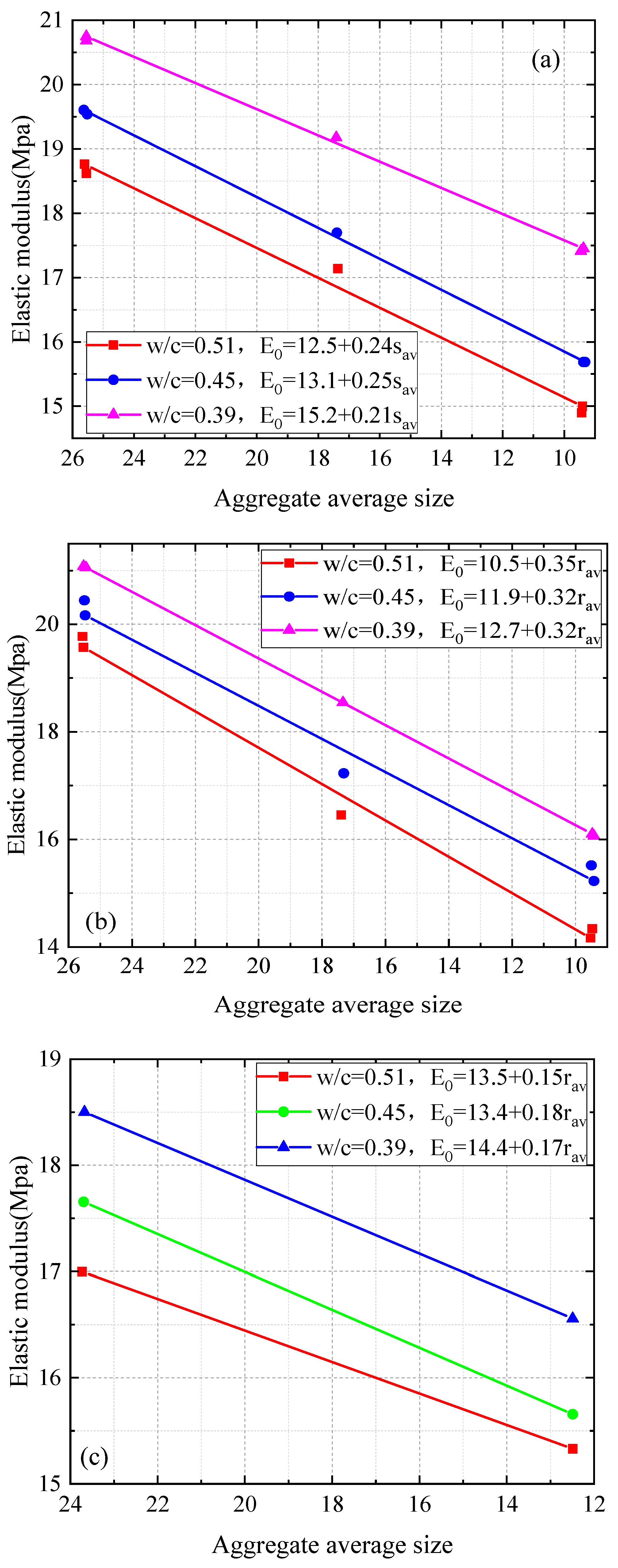
3.2. Influence of Size and Content of RA on Mechanical Properties of Concrete
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Consistent with previous research results, the compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, and axial compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) decreased with an increase in recycled aggregate (RA) content. In addition, the mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete are typically lower than those of natural aggregate concrete (NAC). The elastic modulus of recycled aggregate concrete is affected by the characteristics of recycled aggregate. Larger recycled aggregate particles can alleviate the decrease in the elastic modulus compared to smaller particles.
- (2)
- The compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, and axial compressive strength of RAC containing large-size RA were greater than those of RAC containing small-size RA for any given RA content and coarse aggregate grading curves. There was a uniform decrease in the mechanical strength of RAC as the proportion of large-size RA decreased and the proportion of small-size RA increased. The combined effect of the RA size and RA content on the mechanical strength of RAC exhibited a certain regularity.
- (3)
- The elastic modulus in the axial compression test is mainly affected by the RA size. Crushing plants that produce RA should process waste concrete into large-sized RA to obtain higher-strength concrete. When greater amounts of fine aggregates are used in an RAC mixture, the composition or percentage of other materials must be adjusted to increase the strength of the RAC.
- (4)
- A novel equivalent particle size parameter (λeq) for RA facilitates the development of simple linear regressions that can describe the mechanical strength of RAC indicators (compressive, splitting tensile, and uniaxial compressive strengths) as a function of RA content and RA size. The elastic modulus of RAC can be described by linear regression as a function of mean RA size. For practical applications similar to those investigated in this study, the regressions can provide estimates of the compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, axial compressive strength, and elastic modulus of RAC for a given combination of RA size and RA content. The regressions provide a scientific basis for determining the content and size of RA required to achieve the desired mechanical properties of RAC. As such, the regressions have a useful application value and practical significance in engineering.
- (5)
- The proposed equivalent parameter λeq and regression equation can be used to quickly predict the performance of concrete under different RA content and particle size combinations. This study provides direct support for the optimization of the recycled aggregate crushing process, the mix design of recycled aggregate concrete, and the rapid evaluation of mechanical properties in practical engineering.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padmini, A.K.; Ramamurthy, K.; Mathews, M.S. Influence of parent concrete on the properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, K. Mechanical properties of concrete with recycled coarse aggregate. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbachiya, M.C.; Marrocchino, E.; Koulouris, A. Chemical-mineralogical characterisation of coarse recycled concrete aggregate. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Wang, K.; Tam, C.M. Assessing relationships among properties of demolished concrete, recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete using regression analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabsh, S.W.; Abdelfatah, A.S. Influence of recycled concrete aggregates on strength properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, M.L. Properties of sustainable concrete containing fly ash, slag and recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.S.D.; Gutiérrez, P.A. Study on the influence of attached mortar content on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, L. Long-term performance of recycled aggregate concrete beams exposed to 10 years of loading and chloride environments. Eng. Struct. 2025, 333, 120140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chi, S.P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, T.; Duan, Z.; Peng, L. Fundamental behavior of recycled aggregate concrete—overview II: Durability and enhancement. Mag. Concr. Res. 2022, 74, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, W.H.; Ramli, M.; Kam, K.J.; Sulieman, M.Z. Influence of the amount of recycled coarse aggregate in concrete design and durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçu, İ.B.; Şengel, S. Properties of concretes produced with waste concrete aggregate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; de Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Thermal Performance of Concrete with Recycled Aggregates from CDW Plants. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, J.; Garcia, S.L.; Torres, H. Shear Strength of Concrete with Recycled Aggregates Reinforced with Steel Fibers. ACI Mater. J. 2021, 118, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjalal, M.; Islam, K.; Tiznobaik, M.; Alam, M.S.; Ahsan, R. Uniaxial Compressive Behavior of Fiber-Reinforced Rubberized Recycled Concrete Column. ACI Struct. J. 2024, 121, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, N.S.C. High-Strength Structural Concrete with Recycled Aggregates. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba, Australia, November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gandel, R.; Jerabek, J.; Peknikova, A.; Topolář, L.; Sucharda, O. Towards Sustainable Building Materials: An Experimental Investigation into the Effect of Recycled Construction Waste Aggregate on the Properties of High-Performance Concrete. Buildings 2025, 15, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, A. Some studies on durability of recycled aggregate concrete. Indian Concr. J. 2002, 76, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindrarajah, R.S.; Tam, C.T. Properties of concrete made with crushed concrete as coarse aggregate. Mag. Concr. Res. 1985, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.C.; Boegh, E. Elasticity and drying shrinkage of recycled-aggregate concrete. J. Am. Concr. Inst. 1985, 82, 648–652. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, A. Properties of concrete made with recycled aggregate from partially hydrated old concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y. Tests and analysis of the compressive performance of an integrated masonry structure of a brick-stem-insulating layer. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmoorian, F.; Samali, B.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Yeaman, J. Evaluation of mechanical properties of recycled material for utilization in asphalt mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; Brito, J.D.; Dhir, R.K. The influence of the use of recycled aggregates on the compressive strength of concrete: A review. Eur. J. Environ. Civil Eng. 2014, 19, 825–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dang, F.; An, X. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete containing brick particles. Mag. Concr. Res. 2024, 76, 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.W.; Uhlmeyer, J.S.; Russell, M. Use of recycled concrete aggregate in PCCP. Mech. Prop. 2009, 726.1, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, A.E.B.; Schalch, V.; Molin, D.C.C.D.; Ribeiro, J.L.D. Mechanical properties modeling of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A. Treatments for the Improvement of Recycled Aggregate. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2004, 16, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Gholampour, A.; Xie, T. Mechanical and Durability Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Effect of Recycled Aggregate Properties and Content. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2018, 30, 04017275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Wang, X.; Lv, C.; Wang, D.; Geng, H. Investigation of Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Incorporating Basalt Fiber, Copper Slag, and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Buildings 2025, 15, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E30-2005; The Methods of Cement and Concrete for Highway Engineering. People’s Transportation Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 14685-2022; Pebble and Gravel for Construction. China Standard Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2022.
- JGJ 55-2011; Specification for Mix Proportion Design of Ordinary Concrete. China Academy of Building Research: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Gao, X.F.; Tam, C.M. Microstructural analysis of recycled aggregate concrete produced from two-stage mixing approach. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50081-2002; Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete. State Administration of Quality Supervision: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Safiuddin, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Salam, M.A.; Jumaat, M.Z. Use of recycled concrete aggregate in concrete: A review. J. Civil. Eng. Manag. 2013, 19, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.C. Recycling of Demolished Concrete and Masonry; Report L; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
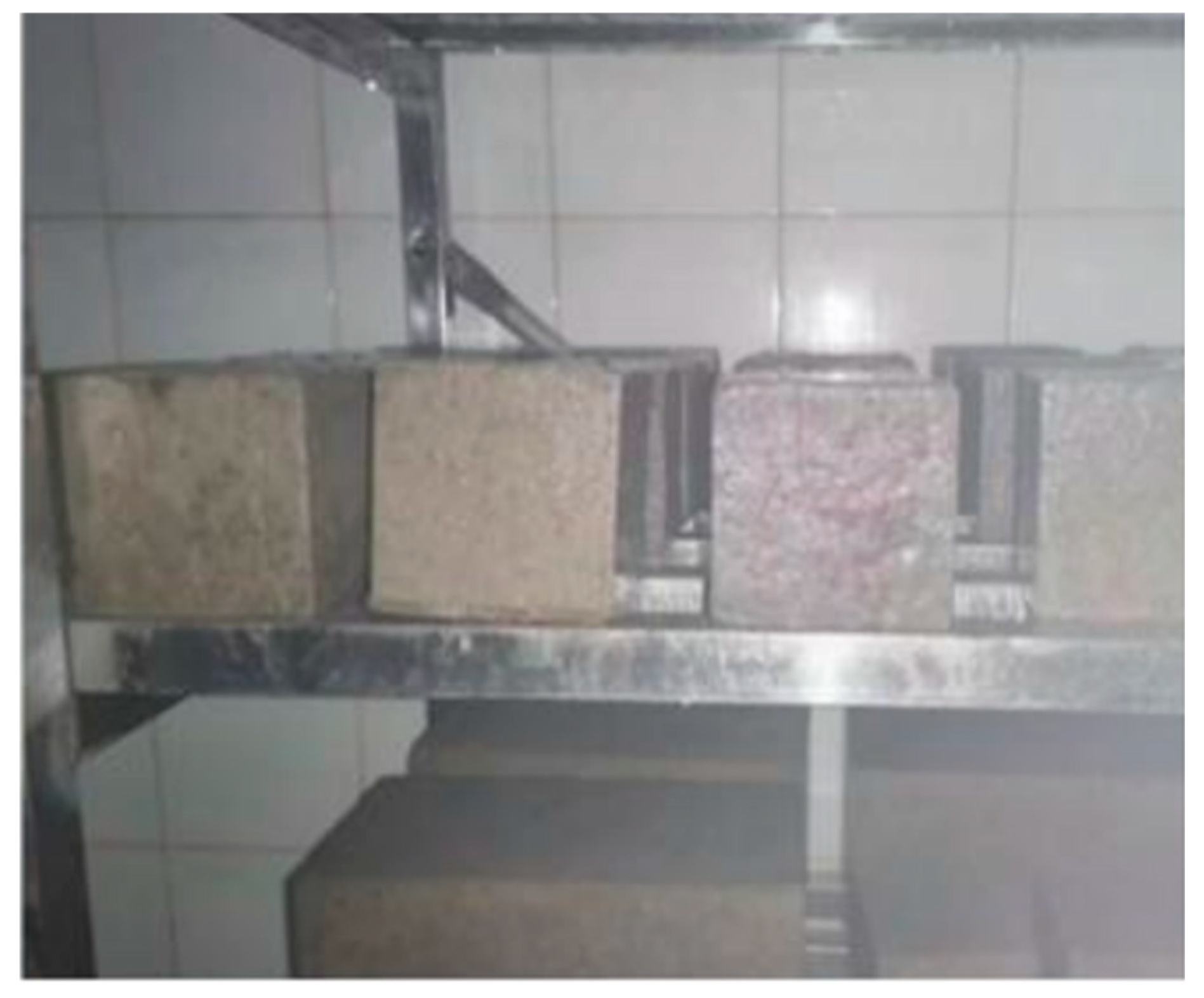
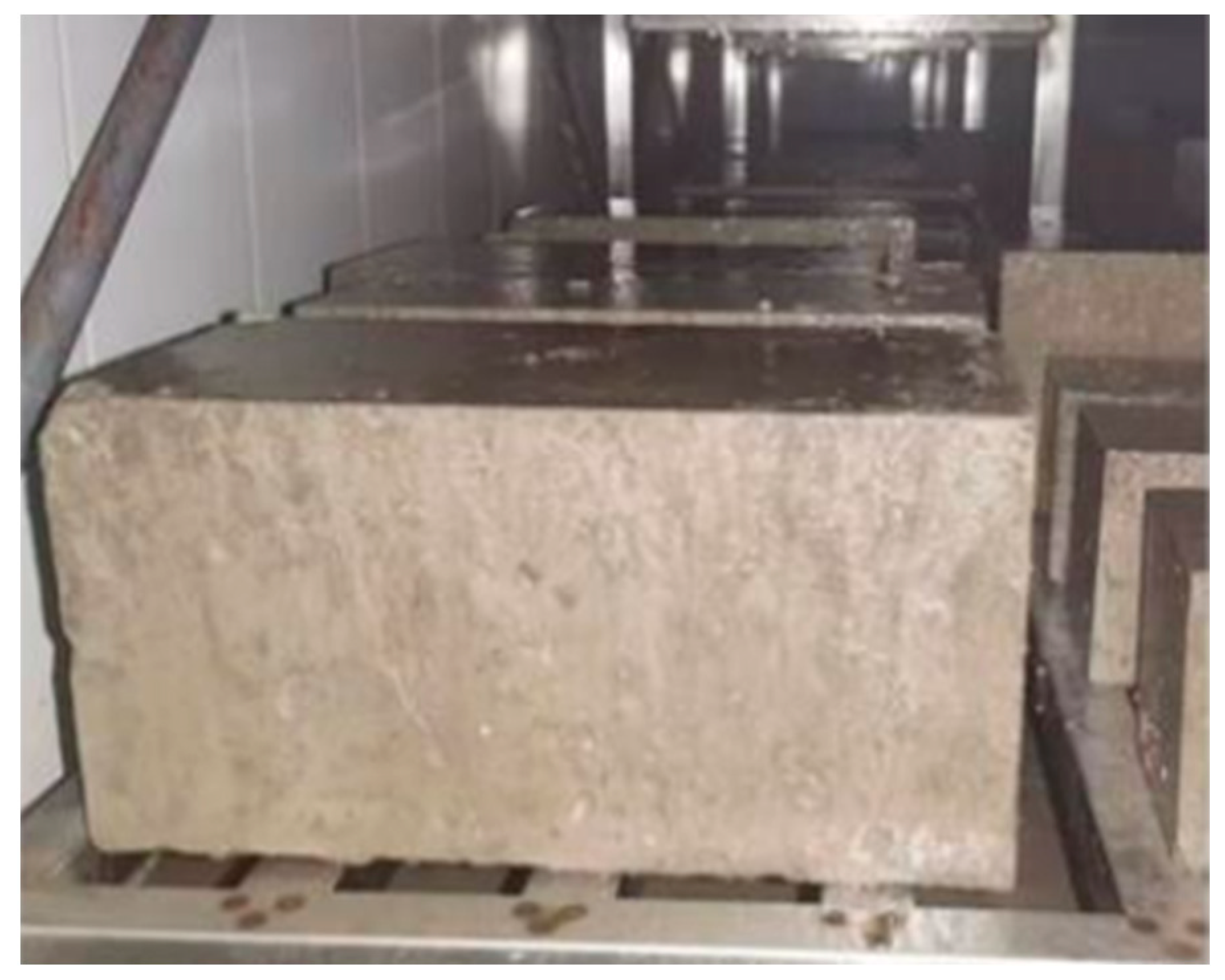
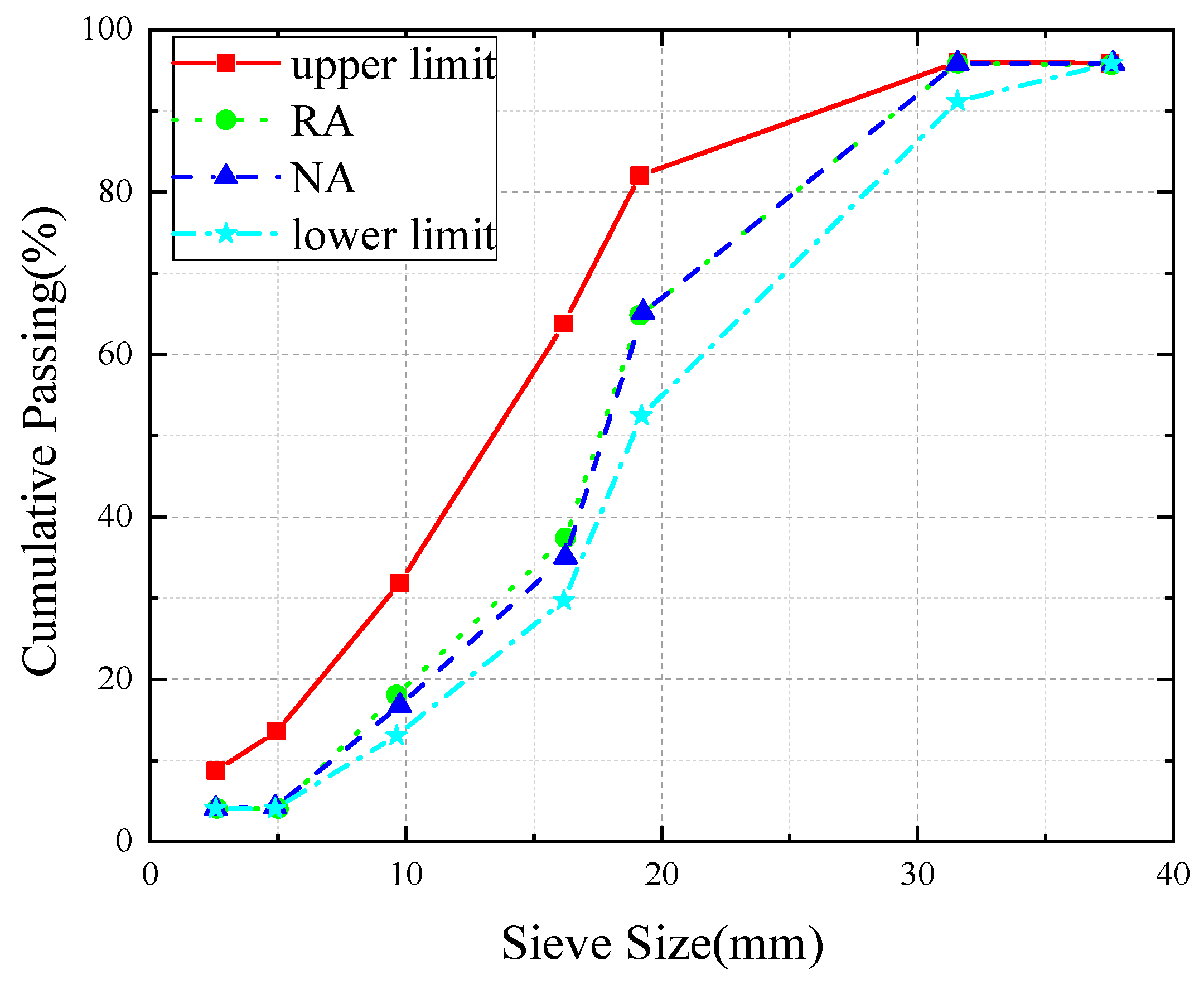
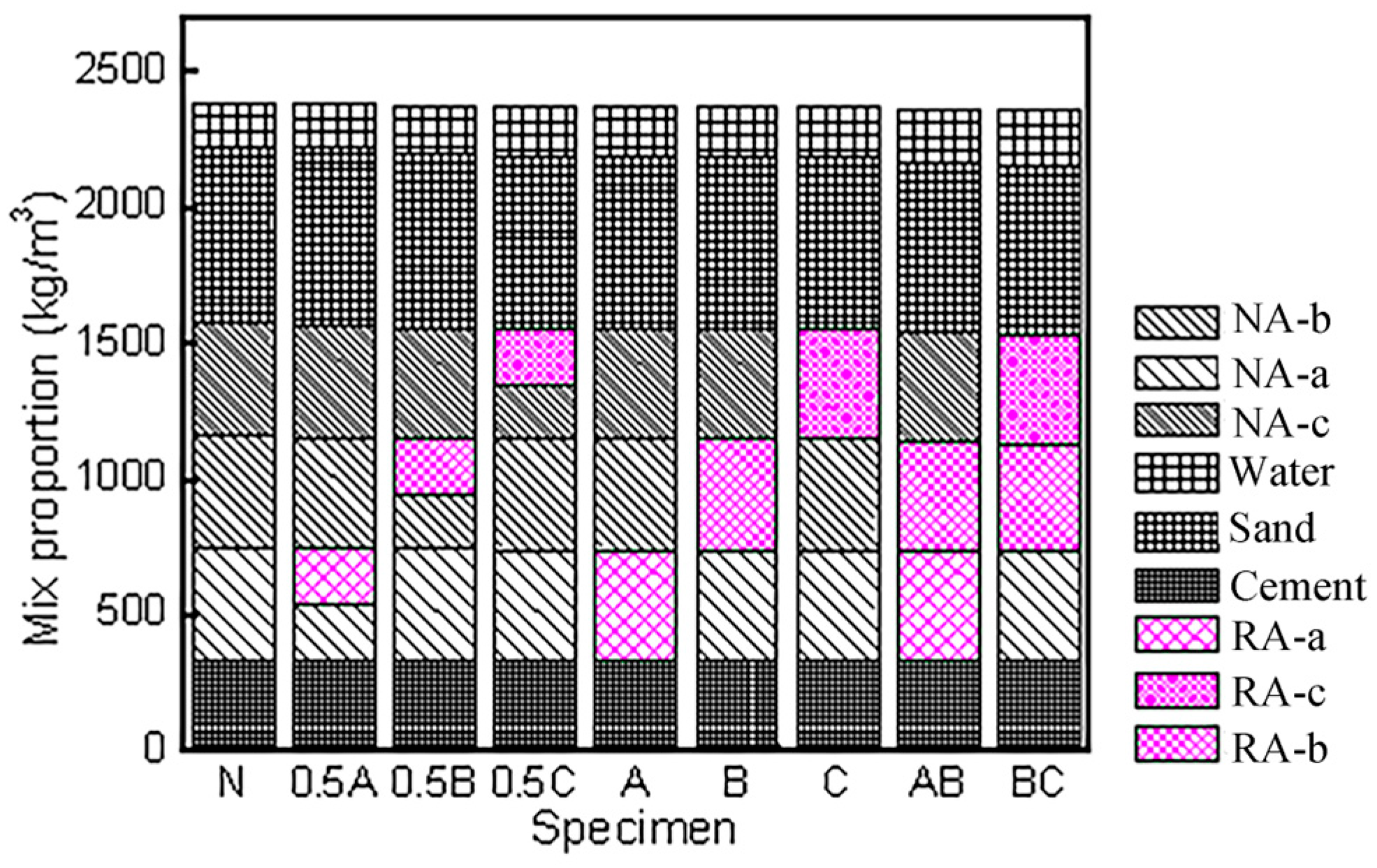








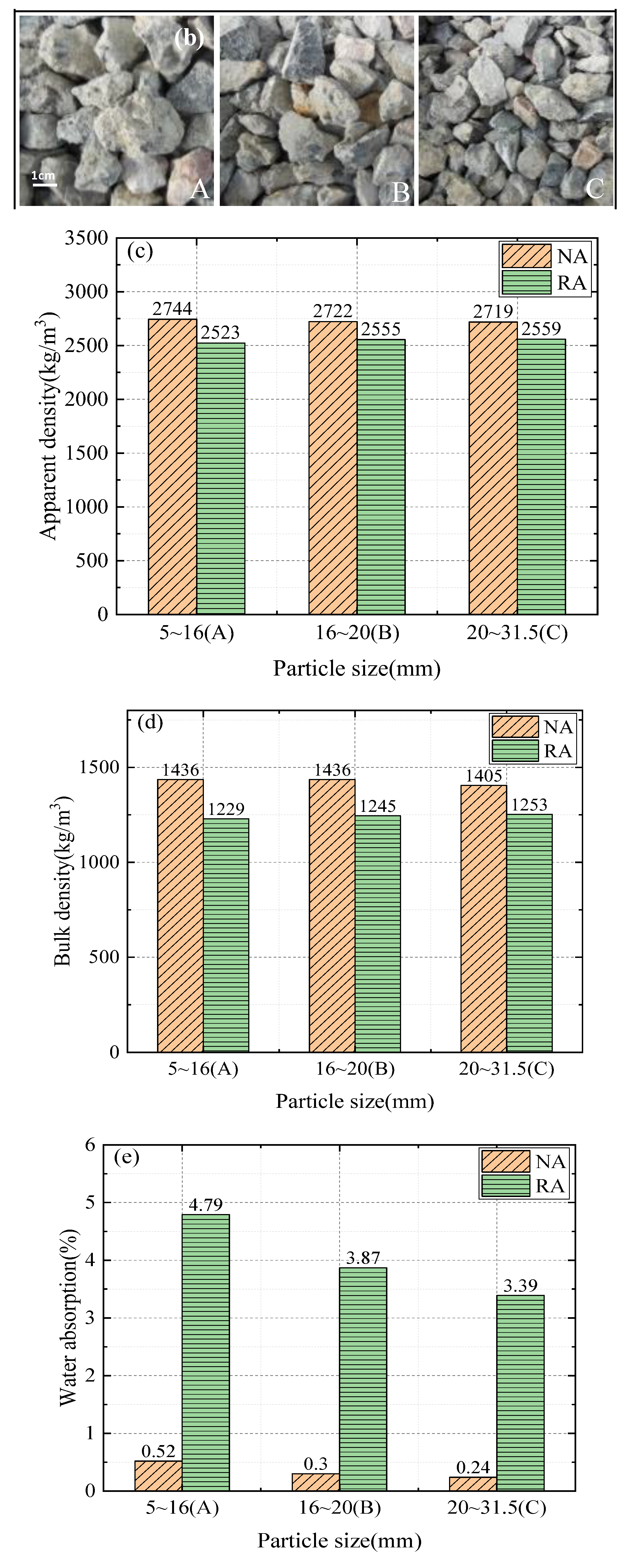
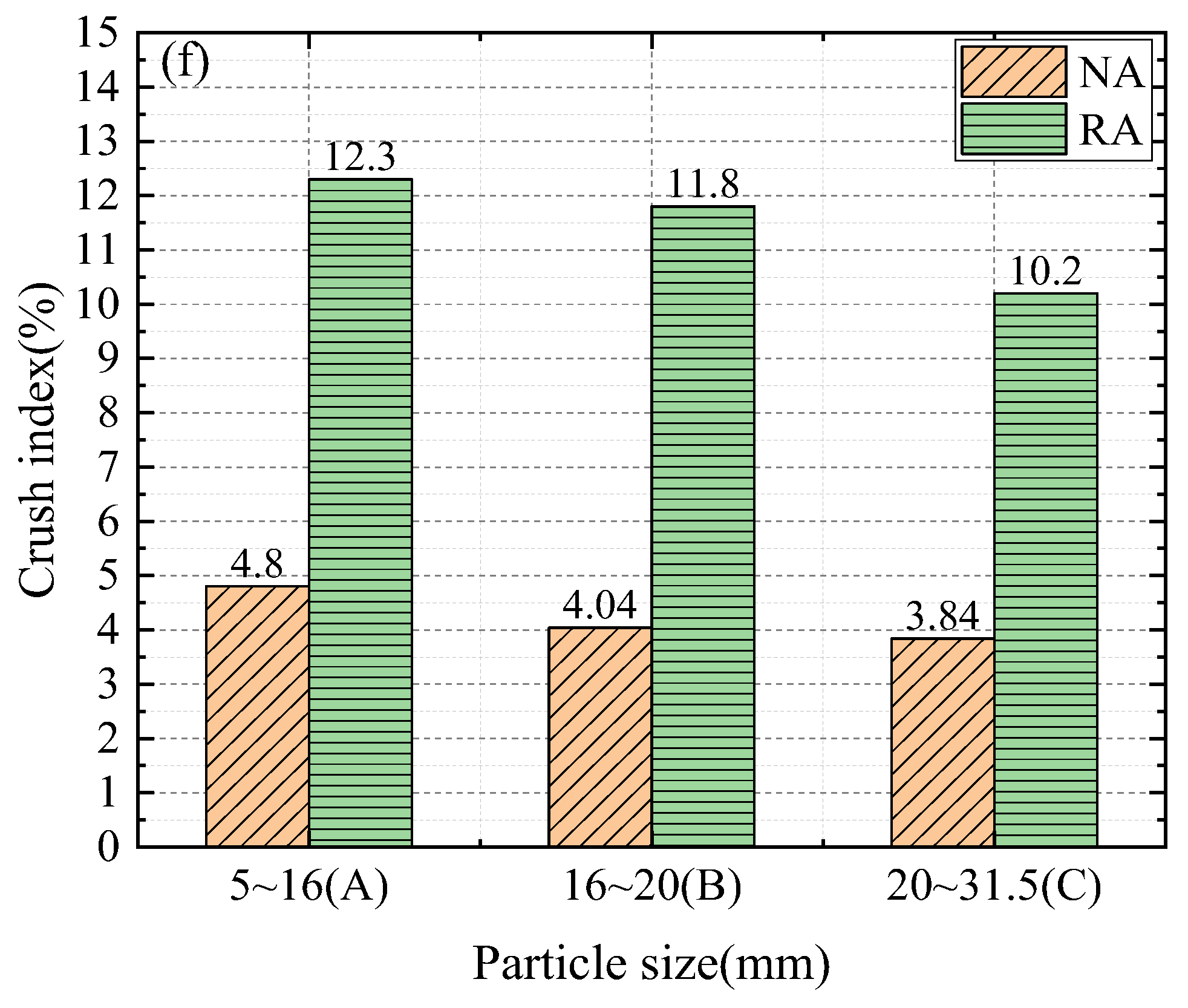
| Group | a | b | c |
| Particle size range | 20–31.5 mm | 16–20 mm | 5–16 mm |
| Group | Types in Aggregate | The Proportion of a Aggregate % | The Proportion of b Aggregate % | The Proportion of c Aggregate % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | NA | 100 | 100 | 00 |
| RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.5A | NA | 50 | 100 | 100 |
| RA | 50 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.5B | NA | 100 | 50 | 100 |
| RA | 0 | 50 | 0 | |
| 0.5C | NA | 100 | 100 | 50 |
| RA | 0 | 0 | 50 | |
| A | NA | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| RA | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| B | NA | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| RA | 0 | 100 | 0 | |
| C | NA | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| RA | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| AB | NA | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| RA | 50 | 50 | 0 | |
| BC | NA | 100 | 50 | 50 |
| RA | 0 | 50 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Shi, N.; Yu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Y. Influence of Size and Content of Recycled Aggregate on Mechanical Properties of Concrete. Buildings 2025, 15, 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173009
Liu H, Shi N, Yu Z, Liu B, Zhu Y. Influence of Size and Content of Recycled Aggregate on Mechanical Properties of Concrete. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huanqin, Nuoqi Shi, Zhifa Yu, Bin Liu, and Yonglin Zhu. 2025. "Influence of Size and Content of Recycled Aggregate on Mechanical Properties of Concrete" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173009
APA StyleLiu, H., Shi, N., Yu, Z., Liu, B., & Zhu, Y. (2025). Influence of Size and Content of Recycled Aggregate on Mechanical Properties of Concrete. Buildings, 15(17), 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173009






