Abstract
Alkali-activated fly ash and slag binders are regarded as environmentally friendly building materials. However, the creep properties of the alkali-activated materials differ from ordinary Portland cement-based materials. Currently, predicting the creep properties of alkali-activated materials is difficult. This study tested the creep properties of alkali-activated materials with various strengths and loading ages, exploring the similarities and differences in the creep properties between alkali-activated and cement-based materials. The result shows that the creep development of alkali-activated materials still conforms to the law of the hyperbolic power function commonly used to describe that of cement-based materials. Nevertheless, the proportion of the basic creep increases to about 70% of the drying creep in alkali-activated materials at 90 days. By modifying the parameters related to the relative humidity in the model of CEB-FIP MC2010, the creep behavior of alkali-activated fly ash and slag concrete could be well predicted.
1. Introduction
As environmentally friendly inorganic cementitious materials, alkali-activated materials can utilize silicon- and aluminum-rich solid waste, such as fly ash and slag, as raw materials [1,2,3]. Due to the similar mechanical properties and workability to cement-based materials, alkali-activated materials are considered one of the alternatives to ordinary Portland cement. Studies on the strength, shrinkage, and durability of alkali-activated materials have increased over the years [4,5,6]. Nevertheless, few reports have elucidated the differences in creep properties between alkali-activated concrete and cement concrete.
Generally, concrete creep leads to the redistribution of internal forces and continuous growth of deformation in a concrete structure, which must be considered in a structural design. It is known that the gel of alkali-activated fly ash pastes is N-A-S-H, and the gel of alkali-activated slag pastes is C-A-S-H, which are different from the C-S-H gel in cement-based materials [7,8]. Studies [9,10] show that the creep modulus of the C-A-S-H and N-A-S-H gels is less than that of the C-S-H gel in cement paste. Therefore, the basic creep of alkali-activated concrete is generally much higher than that of cement concrete with the same strength [11,12]. However, it is interesting that the drying creep of alkali-activated concrete is slightly lower than that of cement concrete, especially at the early stage after testing [13,14]. The creep behavior of concrete is related to the movement of pore water from high to low pressure under a sustained load [10]. The differences in the pore size distribution will inevitably result in different viscous behavior of hardened pastes with the movement of pore water. The pore size distribution of alkali-activated low-calcium fly ash pastes is similar to that of hardened cement pastes [15]. Moreover, the densification of the pore structure of alkali-activated fly ash and slag pastes with a Ca content below 20% positively correlates with the added slag [16]. For the above reasons, the creep development of alkali-activated concrete is worthy of attention.
Concrete creep is often influenced by various factors such as concrete strength, curing conditions, loading age, and section size. Hojati [17] found that the lower the compressive strength of alkali-activated fly ash and slag concrete, the more obvious its creep properties. Moreover, the curing temperature significantly affects the creep of alkali-activated concrete. The higher the curing temperature, or the longer the curing time, the smaller the corresponding creep [18]. Hence, the creep coefficient of alkali-activated low-calcium fly ash concrete that generally relies on high-temperature curing is usually lower than that of cement concrete [19]. Noushini [20] and Zhou [21,22] studied the inhibitory effect of various fibers on the creep of alkali-activated concrete and found that an appropriate fiber content can control the creep of alkali-activated concrete at a low level. Furthermore, some researchers explored the influence of the loading age [23] and stress–strength ratio [24] on the creep properties of alkali-activated concrete. The variation pattern associated with the aforementioned influencing factors has been observed to resemble that of cement concrete. However, the above research focuses on the maximum creep during the test period, and few studies pay attention to the development law of creep. There is no effective method to predict the creep of alkali-activated concrete.
The basic creep and drying creep of alkali-activated materials were tested to analyze the similarities and differences in creep development between the alkali-activated and cement-based materials. Based on this analysis, several modified parameters were proposed around the predicted method provided by CEB-FIP MC 2010. Based on the statistical results of the reported creep tests, a modified model was developed to improve the prediction accuracy of creep behavior in alkali-activated concrete.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Mixtures
As shown in Figure 1, the F-grade fly ash (Henan Yuanyuan New Materials Co., Ltd., Zhengzhou, China) and S95-grade slag (Hunan Huaxin Xianggang Cement Co., Ltd., Xiangtan, China) are selected as the precursor of the alkali-activated material. The SEM images in Figure 1 are taken by Zeiss EVO MA25 (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The specific gravity of the fly ash and slag is 2.6 g/cm3 and 2.8 g/cm3, respectively, and the corresponding XRD results are shown in Figure 2. The XRD measurement is conducted to examine the crystalline phases in the samples, with a Bruker D8 Advance powder X-ray diffractometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). Moreover, Table 1 lists the chemical composition of the fly ash and slag tested by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (Shimadzu EDX-7000, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Furthermore, the particle size of the fly ash is between 0.5 and 86.4 μm, with a d50 of 23.2 μm. Meanwhile, the particle size of the slag is between 0.6 and 111 μm, with a d50 of 24 μm.
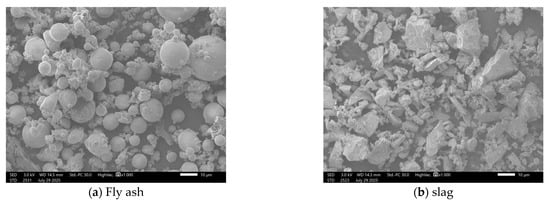
Figure 1.
SEM images of fly ash and slag.
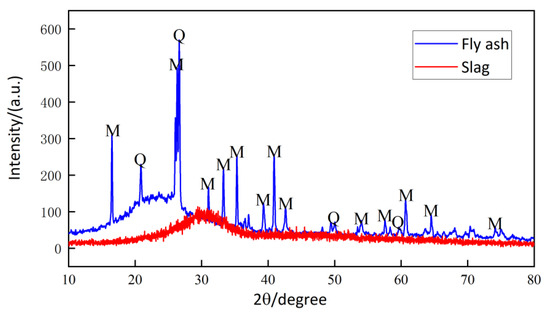
Figure 2.
XRD results of fly ash and slag (M and Q stand for mullite and quartz, respectively).

Table 1.
Chemical composition of fly ash and slag.
The mixture of the alkali-activated fly ash and slag mortars is shown in Table 2. Notably, the water glass (Hebei Litian Chemical Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang, China), powdered sodium hydroxide (Shanghai Ebei Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China, 96% purity), and deionized water are mixed for the activator. The Na2O, SiO2, and H2O content in the water glass used is 8.35%, 26.54%, and 65.11%, respectively. The purity of powdered sodium hydroxide is 98%. Moreover, the sand used in this test conforms to the Chinese ISO standard, with a particle size range of 0.08-2 mm and a density of about 1.47 g/cm3.

Table 2.
Mixture of alkali-activated mortars.
Before mixing and casting, the precursor powder and sand were dry-mixed for 3 min in advance of adding the activator. Then, we continued mixing for 3 min and then poured the sample into the corresponding molds.
2.2. Test Method
2.2.1. Test of Compressive Strength
Following the test method of Chinese standard JTG 3420-2020 [25], a 70.7 mm cube block is selected to conduct the compressive strength test of the alkali-activated fly ash and slag mortars, as shown in Table 2. The 28-day cube compressive strength of the F7S3 and F5S5 mortars was measured to be 57.75 MPa and 81.76 MPa, respectively.
2.2.2. Creep Test
The compressive strength and loading age are selected as the control variables in the creep test of mortars. The basic creep and drying creep properties of mortars with different compressive strengths were tested on the strength group containing F7S3 and F5S5 mortars. Moreover, creep tests on mortars at different loading ages were conducted only on the F7S3 mortar. Specimens with 100 mm × 100 mm × 400 mm were used to test the creep properties of alkali-activated mortars. There are seven replicate specimens for each case. Three of the seven replicate specimens were used to test the prism’s compressive strength, two for creep testing, and the other two for shrinkage testing. All specimens were placed in a room containing a constant 20 ± 3 °C, sealed with plastic wrap, and maintained for the loading ages. When the loading began, the plastic wrap around the drying creep and corresponding shrinkage specimens was removed. However, the plastic wrap around the basic creep and corresponding shrinkage specimens was still retained. It is worth noting that the basic creep and drying creep of mortars were tested separately in the above room, shown in Figure 3. A dial gauge with an accuracy of 0.001 mm was used to measure the strain at a 200 mm distance on both sides of the creep and shrinkage specimens.
Figure 3.
Creep tests of each case.
Creep testing was carried out following the methods provided by the Chinese standard GB/T 50082-2024 [26]. The stress of each creep specimen under sustained loading was controlled at 0.4 times the axial compressive strength, and the test lasted for three months. Moreover, the loading age was uniformly the 8th day in the creep test related to the strength group. Except for the loading age on the 8th day, an additional 17th and 34th days were added to the creep test of the loading age group. The creep coefficient was calculated by the ratio of the creep strain to the elastic strain. Notably, the creep strain used for analysis deducted the test strain of the shrinkage specimens with the same age. Furthermore, the elastic strain was determined by the instantaneous strain of the creep specimens during loading.
3. Test Results
3.1. Effect of Strength on Creep Coefficient
The basic creep and drying creep coefficients of the F7S3 and F5S5 mortars loaded at 8 days are shown in Figure 4a. Moreover, Figure 4b shows the slope of the curve in Figure 4a, which represents the development rate of the creep coefficient.
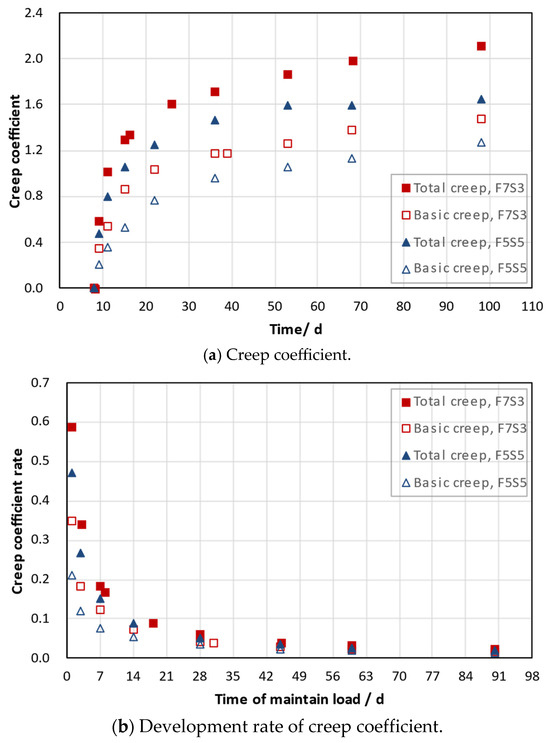
Figure 4.
Creep coefficient of mortars with various compressive strengths.
As shown in Figure 4a, the creep coefficients of each mortar gradually increase over time, with the basic creep accounting for about 70% of the drying creep. Moreover, the higher the compressive strength of the mortars, the smaller the basic creep and drying creep, which is similar to the creep law of cement-based materials. Moreover, it can be observed from Figure 4b that the creep coefficients of each mortar develop rapidly in the early stage, especially the development rate of the drying creep. Afterwards, all development rate curves rapidly decay over time and almost approach 0.02 after 3 months of loading. Correspondingly to Figure 4a, the higher the compressive strength of the mortar in Figure 4b, the smaller the change in the development rate, including the basic creep and drying creep.
3.2. Effect of Loading Age on Creep Coefficient
The creep coefficient and corresponding development rate of the F7S3 mortar with various loading ages are shown in Figure 5a and Figure 5b, respectively. As shown in Figure 5a, the later the loading age, the smaller the basic creep. According to Figure 5b, it can also be found that the earlier the mortar is loaded, the slower the decay of its creep development rate, which is consistent with the creep law of cement-based materials.
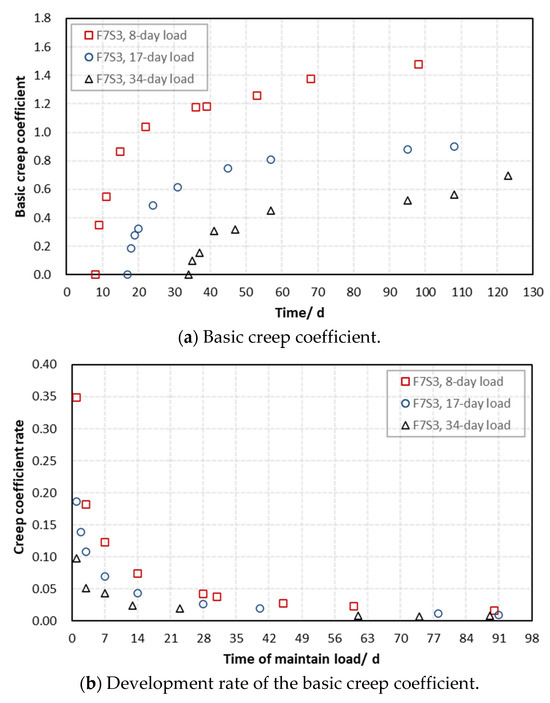
Figure 5.
Creep coefficient of mortars with various loading ages.
4. Differences in Creep Between Alkali-Activated and Cement-Based Materials
A comparison between the test results and corresponding calculations by the existing creep model of cement concrete was carried out to explore the difference in creep development law between alkali-activated and cement-based materials.
The creep coefficient defined by the creep model of CEB-FIP MC2010 [27] is
where stands for the notional creep coefficient, which is related to the relative humidity of the ambient environment (), notional size of the member (), mean compressive strength (), and the age of concrete at loading (). can be calculated from
Meanwhile, is the coefficient that describes the development of creep with time after loading and can be expressed as
where is a parameter that is related to , and .
Due to the time limitation of the test, the value of that generally corresponds to the creep coefficient after loading for 3 years could not be obtained directly. Next, the applicability of the functional form of describing the creep development law will be discussed. The measurements and calculations are normalized according to the corresponding final values, and the creep development coefficients from 0 to 1 can be obtained, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
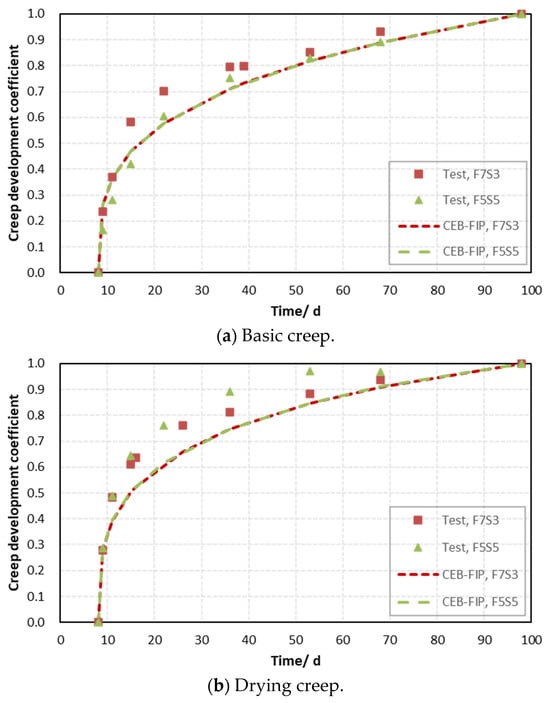
Figure 6.
Normalized creep coefficient of mortars with various strengths.
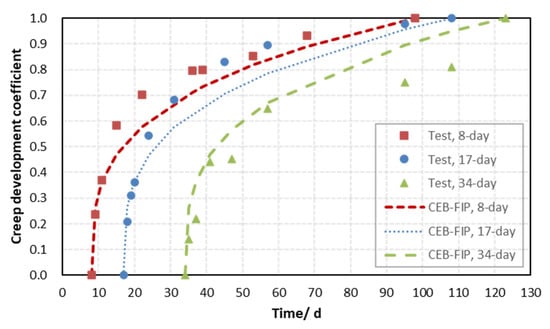
Figure 7.
Normalized creep coefficient of mortars with various loading ages.
As shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7, the development rates of the normalized creep coefficient are greater than the corresponding calculation, except for the case of the F7S3 mortar loaded after 34 days. Overall, the difference in normalized values between the test creep coefficients and the corresponding calculation obtained by the CEB-FIP MC2010 model is insignificant. It is shown that the hyperbolic power function form of in Equation (3) is also appropriate for predicting creep behavior in alkali-activated materials.
A comparison between the test creep coefficients and the corresponding calculation is shown in Table 3. The basic creep coefficients of each group at the final test period are more than two times larger than the corresponding calculation. Moreover, the drying creep coefficients of each group at the final test period are smaller than the calculated values, about 0.8 times. This difference indicates that in Equation (2) cannot be applied to describe the impact of relative humidity changes on the creep property of alkali-activated materials. This phenomenon may be attributed to the fact that the incorporation of calcium-rich slag results in a finer pore structure in alkali-activated materials compared to cement-based materials, thereby reducing the volume of macropores that are conducive to drying [18]. However, it is worth noting that the mechanism of drying creep is related to the stress redistribution of the microstructure after pore water loss. The relatively smaller volume of macropores directly leads to less drying creep of alkali-activated materials under sustained load than cement-based materials, especially in the early stage of loading. Based on the experimental results [13], as the loading duration increases, the rapid development of the basic creep of alkali-activated materials still causes their final drying creep to exceed that observed in cement-based materials.

Table 3.
Creep coefficients of each mortar during the final test.
Furthermore, as shown in Table 3, the difference between the measured and calculated creep coefficients decreases slightly with increasing loading age. This trend means that the related to loading age describes the creep behavior of alkali-activated materials correctly and only needs to be fine-tuned appropriately. In addition, the difference between the measured and calculated creep coefficients of mortar F5S5 is slightly larger than the corresponding difference for mortar F7S3, which means that the related to compressive strength can also be used for alkali-activated materials after fine-tuning appropriately.
5. Creep Correction Method Based on CEB-FIP Model
According to the above analysis, it can be found that cannot reasonably describe the effect of relative humidity changes on the creep behavior of alkali-activated materials. The expression of defined by the CEB-FIP MC2010 model is
It is known that the problem of significant differences in deviation between the basic creep and drying creep coefficient calculated by the CEB-FIP MC2010 model in the test could be solved by correcting parameters and . It is assumed that and are corrected as follows:
where is the coefficient of correction, and i = 1, 2, 3.
Moreover, coefficient describing the creep development is adjusted by correcting in Equation (3). Based on the definition in the CEB-FIP MC2010 model, can be rewritten as
where
Upon observing Equation (2), it can be found that the relationships among , and are multiplicative. The above analysis shows that and are applied to the creep calculation of alkali-activated materials, which have less effect on the accuracy of their creep results. Hence, it can be assumed that could be regarded as a combined correction coefficient of , and .
So far, the creep prediction model of alkali-activated materials can be expressed as
where , , , and , .
Taking the logarithm of both sides of Equation (8), one can obtain
As shown in Equation (9), is the logarithmic form of the creep coefficient, and (i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) are the parameters that can be calculated by the creep model of CEB-FIP MC2010. Moreover, (i = 1, 2, 3) are the constant coefficients that need to be solved. It is worth noting that this creep test involves the alkali-activated mortar, not concrete. Creep in concrete involves an additional factor known as delayed elastic response in aggregate [28,29]. Hence, the test data cannot be directly applied for fitting Equation (9). Next, existing creep test results of alkali-activated fly ash and slag concrete are statistically analyzed [11,12,17,23,24]. Then, the undetermined coefficients , , and can be obtained by fitting according to Equation (9). Figure 8 presents a comparison between the calculated results before and after the correction using the CEB-FIP MC2010 model and the experimental test results.
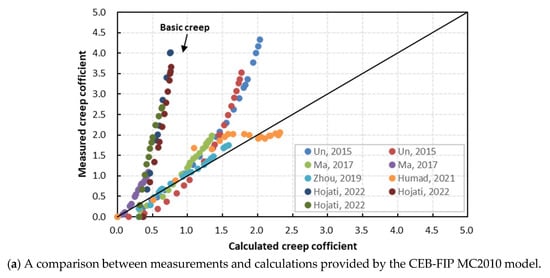
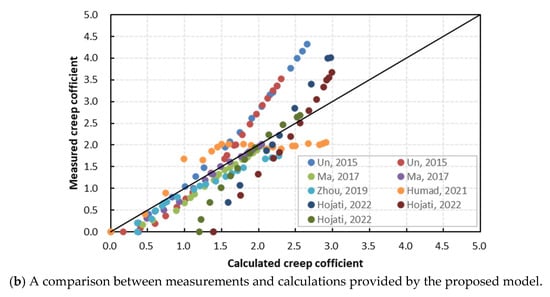
Figure 8.
Creep coefficient comparisons between calculation and measurement [11,12,17,23,24].
As shown in Figure 8, it can be seen that the proposed model fits well with the test values, with a correlation coefficient . This trend indicates that the proposed model can predict the creep behavior of alkali-activated fly ash and slag concrete more reasonably.
6. Conclusions
The creep tests of alkali-activated fly ash and slag materials with various strengths and loading ages were carried out to explore the similarities and differences in the creep properties between alkali-activated and cement-based materials. Further, a correction model based on the CEB-FIP creep model was proposed. The main research conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The basic creep of alkali-activated fly ash and slag mortars is bigger than that of cement-based mortars, accounting for approximately 70% of the drying creep when loading at 90 days. A reason for this may be that the pore size distribution of alkali-activated materials is generally finer than that of cement-based materials. Therefore, the macropore volume of alkali-activated materials prone to water loss during drying is relatively smaller, resulting in lower drying creep under sustained load, especially in the early stage of loading.
- (2)
- The creep development of alkali-activated fly ash and slag materials with time is similar to that of cement-based materials. The hyperbolic power function form commonly applied to describe the creep development of cement-based materials can be used to predict the creep of alkali-activated materials. However, the function itself needs to be modified.
- (3)
- The parameters related to the relative humidity for calculating the notional creep coefficient in the CEB-FIP MC2010 creep model must be corrected to match the significant difference in the basic creep between alkali-activated and cement-based materials. Furthermore, the time-dependent creep development coefficient in the CEB-FIP MC2010 model requires humidity-dependent modification to better reflect the creep behavior under varying relative humidity conditions.
Given the scarcity of creep test data for alkali-activated concrete, future model refinement will require extensive additional testing. Particular attention should be paid to the development of drying creep under varying environmental humidity levels. Furthermore, the disparity in nominal creep coefficients observed among alkali-activated concretes with different precursor CaO contents, even at comparable compressive strength levels, merits further investigation.
Author Contributions
Validation, Q.Y. and Y.Z.; Writing—original draft, L.X.; Writing—review & editing, D.H. (Dunwen Huang); Visualization, D.H. (Dunzhi Huang); Supervision, H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 52008036], the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 2024JJ5017], the Scientific Research Fund of the Hunan Provincial Education Department (grant number 22B0344), and the Open Fund of the Industry Key Laboratory of Traffic Infrastructure Security Risk Management (the Changsha University of Science and Technology) (grant number 22KF02). The financial support offered by these institutions is greatly appreciated.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Dunzhi Huang was employed by the company China Construction Fifth Bureau Installation Engineering Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Liao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Deng, F.; Ye, J.; Wang, K.; Tang, S. Hydration behavior and thermodynamic modelling of ferroaluminate cement blended with steel slag. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110833–110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, Y.; Ma, F.; Tang, S. Effect of ground granulated blast furnace slag on hydration characteristics of ferrite-rich calcium sulfoaluminate cement in seawater. J. Cent. South Univ. 2025, 32, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Lei, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zou, Z. Preparation and comprehensive performance optimization of green insulation building materials based on blast furnace slag. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 106, 112591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Ling, Y. Fabrication and engineering properties of concretes based on geopolymers/alkali-activated binders—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Q. Optimization of Preparation Process and Property Study of BFS-based Alkali-activated Porous Thermal Insulation Materials. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, F.; Dong, Y.; Gu, S.; Fan, X.; Xiao, W. Study on novel alkali-activated cementitious grout for scour control of offshore foundation. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2025, 42, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Chen, P.; Peng, H.; Yang, Y.W.; Yuan, Q.M.; Su, M. A Review and Comparison Study on Drying Shrinkage Prediction between Alkali-Activated Fly ash/Slag and Ordinary Portland Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Koenig, A.; Dehn, F. Structural concrete based on alkali-activated binders: Terminology, reaction mechanisms, mix designs and performance. Struct. Concr. 2018, 19, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Cao, R.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Revealing the difference between creep behavior of hydration products of Portland cement and alkali-activated slag paste at early age. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Shikhov, I.; Hamed, E.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Al-Damad, I.; Arns, C.; Foster, S.J. New insights on the basic creep mechanism of one-part alkali activated slag and fly ash paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 186, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Dehn, F. Shrinkage and creep behavior of an alkali-activated slag concrete. Struct. Concr. 2017, 18, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humad, A.M.; Provis, J.L.; Habermehl-Cwirzen, K.; Rajczakowska, M.; Cwirzen, A. Creep and long-term properties of alkali-activated swedish-slag concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04020475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, R.; Patel, R.A.; Dehn, F. Experimental study on basic and drying creep for an alkali-activated slag concrete and comparison with existing creep models. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 6405–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahban, E.; Bagheri, A.; Sanjayan, J. One-Year study of restrained shrinkage and creep behaviours of geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 376, 131057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Ye, G. The pore structure and permeability of alkali activated fly ash. Fuel 2013, 104, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Chen, P.; Peng, H.; Yuan, Q.M.; Tian, X. Drying Shrinkage Performance of Medium-Ca Alkali-Activated Fly Ash and Slag Pastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 130, 104536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, M.; Rajabipour, F.; Radlinska, A. Creep of alkali-activated cement mixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A.; Foster, S.J.; Ng, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Gilbert, R.I. Creep and drying shrinkage of a blended slag and low calcium fly ash geopolymer Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallah, S.E. Creep behaviour of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. Civ. Eng. Dimens. 2010, 12, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noushini, A.; Castel, A.; Gilbert, R.I. Creep and shrinkage of synthetic fibre-reinforced geopolymer concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 71, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, P.; Jiao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, W. Effect of fibre dosage and stress-strength ratio on creep of polypropylene fibre-reinforced alkali-activated slag concrete. Mater. Struct. 2021, 54, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, P. Effect of fiber content and stress-strength ratio on the creep of basalt fiber-reinforced alkali-activated slag concrete. Struct. Concr. 2022, 23, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, C.H.; Sanjayan, J.G.; San Nicolas, R.J.S.J.; van Deventer, C.D. Predictions of long-term deflection of geopolymer concrete beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Chen, P.; Zeng, Y. Effect of stress-strength ratio on creep property of sodium silicate-based alkali-activated slag concrete. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG 3420-2020; Test Methods of Cement and Concrete for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 50082-2024; Standard for Test Methods of Long-Term Performance and Durability of Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Fédération Internationale du Béton. Fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010; CEB-FIP MC2010; Ernst & Sohn: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Hamed, E.; Al-Damad, I.M.A.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Foster, S. Creep behaviour of alkali activated slag and fly ash concrete: Effects of hypothetical thickness, aggregates, and loading age. Mater. Struct. 2025, 58, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Q.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, T. Experimental study on basic mechanical properties of porous metal-concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).