Large AI Models for Building Material Counting Task: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Survey of Large AI Models
2.1. Multimodal Large Models
2.2. Purely Visual Large Models
2.3. Large Model Platforms
3. Performance Evaluation
3.1. Multimodal Large Models
3.2. Purely Visual Large Models
4. Secondary Model Developed Based on EasyDL
4.1. Brief Introduction of EasyDL
4.2. Development Workflow of Secondary Model Based on EasyDL
4.3. Performance Comparison for Rebar Detection
4.4. Performance Comparison for Other Building Materials
4.5. Discussion
4.5.1. Advantages and Practical Significance of the Research
4.5.2. Limitations and Future Directions
- Data Augmentation and Quality Improvement: Increase the diversity of samples to cover different types of building materials and ensure sufficient sample sizes for each category. Additionally, data preprocessing techniques, such as applying data augmentation, could be improved to enhance the model’s robustness in diverse conditions.
- Model Architecture Innovation: Explore new network architectures better suited for the task of counting building materials. For instance, incorporating attention mechanisms and other advanced feature extraction techniques could improve the accuracy of key region identification.
- Automatic Online Updates: Utilize new data collected from the deployed models to continuously update and refine the existing model, thereby gradually improving its prediction accuracy.
4.5.3. Ethical and Operational Risks Reminders
- Data leakage risks: Original images uploaded to cloud platforms may contain project-sensitive information. It is recommended to blur or crop QR codes, project nameplates, background buildings, etc., in the images before uploading.
- Over-reliance risks: Large models still have missed detections and misjudgments in counting regular materials such as steel bars and wooden beams. Therefore, the model output results must undergo manual spot checks and reviews by on-site material staff. Especially in key business links involving settlement and payment, a “model initial counting, manual verification, difference tracing” closed-loop process should be established to ensure the accuracy of quantities.
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, Z. Intelligent construction: Unlocking opportunities for the digital transformation of China’s construction industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2024, 31, 1429–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduge, S.K.; Thilakarathna, S.; Perera, J.S.; Arashpour, M.; Sharafi, P.; Teodosio, B.; Shringi, A.; Mendis, P. Artificial intelligence and smart vision for building and construction 4.0: Machine and deep learning methods and applications. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, K.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D. Lightweight convolutional neural network for counting densely piled steel bars. Autom. Constr. 2023, 146, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Heo, S.; Han, S.; Kim, J.; Na, S. An image-based steel rebar size estimation and counting method using a convolutional neural network combined with homography. Buildings 2021, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.L.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.02155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Floridi, L.; Chiriatti, M. GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenduri, G.; Ramalingam, M.; Selvi, G.C.; Supriya, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Raj, G.D.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Prabadevi, B.; Wang, W.; et al. GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer)—A comprehensive review on enabling technologies, potential applications, emerging challenges, and future directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 54608–54649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, K.; Han, Q.-L.; Tang, Y. A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, X.; Clifton, D.A. Multimodal learning with transformers: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 12113–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Tian, H.; Ye, S.; Gao, Z.; Cui, E.; Tong, W.; Hu, K.; Luo, J.; Ma, Z.; et al. How far are we to GPT-4V? Closing the gap to commercial multimodal models with open-source suites. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2024, 67, 220101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xu, R.; Yao, Y.; Cui, J.; Ni, Z.; Ge, C.; Chua, T.-S.; Liu, Z.; Huang, G. LLaVA-UHD: An LMM Perceiving Any Aspect Ratio and High-Resolution Images. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15141, pp. 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; et al. GPT-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Bai, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Tan, S.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J. Qwen-VL: A versatile vision-language model for understanding, localization, text reading, and beyond. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12966. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, B.; Yin, W.; Sun, Y.; Tian, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. ERNIE-ViL 2.0: Multi-view contrastive learning for image-text pre-training. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.15270. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lv, Q.; Yu, W.; Hong, W.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xuan, S. CogVLM: Visual expert for pretrained language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 121475–121499. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.00020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bai, X. Monkey: Image resolution and text label are important things for large multi-modal models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.06607. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, R.; El-Nouby, A.; Liu, Z.; Singh, M.; Alwala, K.V.; Joulin, A.; Misra, I. Imagebind: One embedding space to bind them all. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.05665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemini Team Google. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI. Yi: Open foundation models by 01.AI. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.04652.
- Hu, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Large multilingual models pivot zero-shot multimodal learning across languages. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12038. [Google Scholar]
- XVERSE-V-13B. Available online: https://github.com/xverse-ai/XVERSE-V-13B (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. BLIP-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12597. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Lu, H.; Gao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wen, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Zheng, W.; et al. WenLan: Bridging vision and language by large-scale multi-modal pre-training. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.06561. [Google Scholar]
- Hunyuan AI. Available online: https://hunyuan.tencent.com (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. EVA-CLIP-18B: Scaling CLIP to 18 billion parameters. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.04252. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Xu, H.; Ye, J.; Yan, M.; Hu, A.; Liu, H.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J. mPLUG-Owl2: Revolutionizing multi-modal large language model with modality collaboration. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.04257. [Google Scholar]
- Xinghuo AI. Available online: https://xinghuo.xfyun.cn (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- The Claude 3 Model Family: Opus, Sonnet, Haiku. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-3-haiku?ref=ai-recon.ghost.io (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Z.; Ma, C.; Yu, S.; Dai, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Review of large vision models and visual prompt engineering. Meta-Radiology 2023, 1, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment anything (SA) project: A new task, model, and dataset for image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02643. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, L.; Ye, M.; Danelljan, M.; Liu, Y.; Tai, Y.-W.; Tang, C.-K.; Yu, F. Segment anything in high quality. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.01567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ding, W.; An, Y.; Du, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, M.; Tang, M.; Wang, J. Fast segment anything. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Shen, C.; Huang, T. SegGPT: Segmenting everything in context. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Lee, Y.J. Segment everything everywhere all at once. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.06718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Cloud Vertex AI. Available online: https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Baidu AI EasyDL. Available online: https://ai.baidu.com/easydl (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard. Available online: https://huggingface.co/spaces/open-llm-leaderboard/open_llm_leaderboard (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Shanghai AI Laboratory OpenCompass Leaderboard. Available online: https://rank.opencompass.org.cn/home (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Dong, J.; Li, C.; Su, D.; Chu, C.; Yu, D. MM-LLMs: Recent advances in multimodal large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.13601. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Ichter, B.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.; Le, Q.; Zhou, D. Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.11903. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. PM2: A new prompting multi-modal model paradigm for few-shot medical image classification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.08915. [Google Scholar]
- Automatically Generate First Draft Prompt Templates Anthropic. Available online: https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/build-with-claude/prompt-engineering/prompt-generator (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J. A deep learning approach for real-time rebar counting on the construction site based on YOLOv3 detector. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Li, Y. Intelligent real-time counting of construction materials based on object detection. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 51, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Automated counting of steel construction materials: Model, methodology, and online deployment. Buildings 2024, 14, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
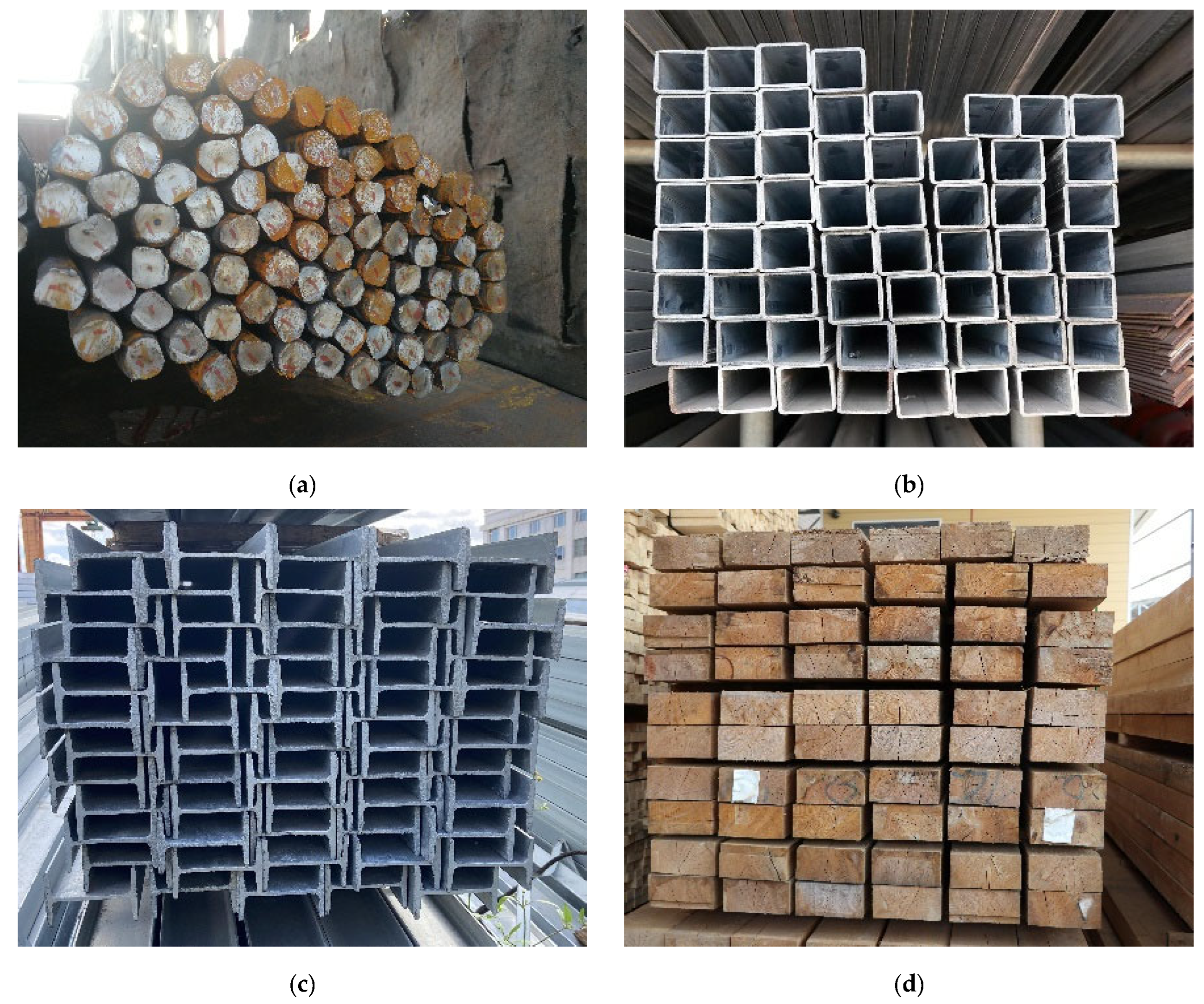

| Model Name | Developer | Release Date | Training Dataset | Number of Parameters (Billion) | Main Architecture | Implementation Strategy | Open Source Status | Application Fields | URL(Uniform Resource Locator) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InternVL-Chat-V1.5 [12] | Shanghai AI Laboratory | 2024.04 | High-quality bilingual dataset covering common scenes and document images | 25.5 | InternViT-6B-448 px-V1-5 + MLP + InternLM2-Chat-20B | Pretraining stage: ViT + MLP and Supervised fine-tuning stage: ViT + MLP + LLM | Open Source | Visual question answering, Character recognition, Real-world understanding | https://huggingface.co/OpenGVLab/InternVL-Chat-V1-5, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| LLaVA-UHD [13] | Tsinghua University | 2024.03 | CC-595 K and 656 K mixture dataset | N/A | CLIP-ViT-L/14 + Perceiver Resampler + Vicuna-13B | Modularized Visual Encoding + Compression of Visual Tokens + Spatial Schema | Open Source | Visual question answering, Optical character recognition, Vision-language understanding tasks | https://github.com/thunlp/LLaVA-UHD, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| GPT-4 [14] | OpenAI | 2023.03 | Web pages, books, articles, and conversations | Exceeds GPT-3′s 175 | Transformer + Mixture of Experts (MoE) + Self-Attention | Large-scale pre-training + Fine-tuning | Closed Source | Natural language processing, Dialogue systems, Content generation | https://chatgpt.com, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Qwen-VL [15] | Alibaba Cloud | 2023.08 | Multilingual multimodal cleaned corpus | 9.6 | ViT + Qwen-7B + Vision-Language Adapter | Multi-task Pretraining + Supervised Fine-tuning | Open Source | Image captioning, Visual question answering, Grounding | https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| ERNIE-ViL 2.0 [16] | Baidu | 2022.09 | 29 M public datasets (English), 1.5B Chinese image-text pairs | N/A | EfficientNet-L2 + BERT-large + ViT + ERNIE | Multi-View Contrastive Learning Framework | Open Source | Cross-modal retrieval, Visual question answering, Multimodal representation learning | https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/ERNIE, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| CogVLM [17] | Tsinghua University, Zhipu AI | 2024.01 | LAION-2B, COYO-700 M, and a visual grounding dataset of 40 M images | 17 | ViT + MLP + GPT + Visual Expert Module | Trainable visual expert module to deeply fuse vision and language features | Open Source | Image captioning, Visual question answering, Visual grounding | https://github.com/THUDM/CogVLM, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| CLIP [18] | OpenAI | 2021.01 | 400 million (image, text) pairs collected from the internet | N/A | ViT + ResNet + Transformer | Contrastive Learning + Pre-training | Open Source | Zero-shot transfer to various computer vision tasks | https://github.com/OpenAI/CLIP, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Monkey [19] | Huazhong University, Kingsoft | 2023.11 | 19 different datasets, including 1.44 million samples | 9.8 | ViT-BigG + Qwen-VL + LoRA | Multi-level description generation method + sliding window method | Open Source | Image Captioning, Visual question answering, Document-oriented visual question answering | https://github.com/Yuliang-Liu/Monkey, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| IMAGEBIND [20] | Meta AI | 2023.05 | Image-text, video-audio, image-depth, image-thermal, video-IMU | N/A | All modality encoders based on Transformer | Leverages image-paired data for joint embedding across six modalities | Open Source | Cross-modal retrieval, Zero-shot recognition, Few-shot recognition | https://facebookresearch.github.io/ImageBind, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro [21] | 2024.02 | Multimodal and multilingual data | N/A | Sparse mixture-of-expert (MoE) Transformer | JAX + ML Pathways + TPUv4 Distributed Training | Closed Source | Multilingual translation, Multimodal long-context understanding | https://gemini.google.com/app, accessed on 12 August 2025. | |
| Yi-VL [22] | 01.AI | 2023.11 | 3.1 T tokens of English and Chinese corpora | 6/34 | Transformer + Grouped-Query Attention + SwiGLU + RoPE | Train ViT and projection + Train higher resolution image + Joint train all modules | Open Source | Language modeling, vision-language tasks, long-context retrieval, chat models | https://huggingface.co/01-ai, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| MiniCPM-V-2_5 [23] | OpenBMB | 2024.05 | SigLip-400 M | 8 | Improved version based on Llama3-8B-Instruct | LoRA fine-tuning + GGUF format + quantization + NPU optimization | Open Source | Multilingual support, Mobile deployment, Multimodal tasks | https://github.com/OpenBMB/MiniCPM-V, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| XVERSE-V-13B [24] | Shenzhen Yuanxiang | 2024.04 | 2.1 billion pairs of images-text and 8.2 million instruction data points | 13 | Clip-vit-large-patch14-224 + MLP + XVERSE-13B-Chat | A large-scale multimodal pre-training + Fine-tuning | Open Source | Visual question answering, Character recognition, Real-world understanding | https://www.modelscope.cn/models/xverse/XVERSE-V-13B, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| BLIP-2 [25] | Salesforce Research | 2023.01 | Large dataset of 129 M images | 0.188 (Q-Former) | Q-Former + Frozen Image Encoder + Frozen LLMs | Vision-language representation learning and generative learning | Open Source | Visual question answering, Image captioning, Image-Text retrieval | https://github.com/salesforce/LAVIS/tree/main/projects/blip2, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| BriVL [26] | Renmin University of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences | 2021.07 | 30 million image-text pairs | 1 | Two-tower architecture, including text encoder and image encoder | Contrastive learning enhanced with MoCo for managing large negative sample sets efficiently | Open Source | Image-text retrieval, Captioning, Visual understanding | https://github.com/BAAI-WuDao/BriVL, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Hunyuan [27] | Tencent | 2023.09 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Closed Source | Content creation, Logical reasoning, Multimodal interaction | https://hunyuan.tencent.com, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| EVA-CLIP-18B [28] | Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence | 2024.02 | Merged-2B, LAION-2B, COYO-700 M, LAION-COCO, Merged-video | 18 | Based on CLIP, utilizing both vision and language components. | Weak-to-strong vision scaling + RMSNorm and LAMB optimizer | Open Source | Image classification, Video classification, Image-text retrieval | https://github.com/baaivision/EVA/tree/master/EVA-CLIP-18B, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| mPLUG-Owl2 [29] | Alibaba | 2023.11 | 400 M image-text pairs | 8.2 | ViT-L + LLaMA-2-7B | Modality-adaptive modular network + Pre-trained with joint tuning | Open Source | Multi-modal tasks, Vision-language tasks, Pure-text tasks | https://github.com/X-PLUG/mPLUG-Owl/tree/main/mPLUG-Owl2, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| IFlytek Spark V3.5 [30] | iFLYTEK | 2024.01 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Closed Source | Multilingual capability, Knowledge-based question answering, Text generation | https://xinghuo.xfyun.cn, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Claude 3 Family [31] | Anthropic | 2024.03 | Proprietary mix of public and non-public data as of Aug 2023 | N/A | N/A | Utilizes various training methods including unsupervised learning and Constitutional AI | Closed Source | Reasoning, Coding, Multi-lingual Understanding | https://docs.anthropic.com, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Model Name | Developer | Release Date | Number of Parameters (Million) | URL (Uniform Resource Locator) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAM [33] | Meta AI | 2023.04 | 68 | https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| HQ-SAM [34] | ETH Zürich, HKUST | 2023.10 | Slight increase over SAM | https://github.com/SysCV/SAM-HQ, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| FastSAM [35] | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 2023.06 | 68 | https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| SegGPT [36] | Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence | 2023.04 | 150 | https://github.com/baaivision/Painter, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| SEEM [37] | Microsoft research | 2023.12 | N/A | https://github.com/UX-Decoder/Segment-Everything-Everywhere-All-At-Once, accessed on 12 August 2025. |
| Model Name | Rebars Counting Test Results (Real number: 85) | Square Steel Pipes Counting Test Results (Real number: 60) | I-beams Counting Test Results (Real number: 60) | Wooden Beams Counting Test Results (Real number: 60) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 |  |  |  |  |
| ERNIE Bot |  |  |  |  |
| Qwen |  |  |  |  |
| GLM-4 |  |  |  |  |
| mPLUG |  |  |  |  |
| Spark Desk |  |  |  |  |
| Gemini |  |  |  |  |
| Hunyuan |  |  |  |  |
| Claude3 |  |  |  |  |
| MiniCPM |  |  |  |  |
| Interaction Strategy | Rebars Bars | Circular Steel Tubes | Square Steel Pipes | I-beams | Wooden Beams | Wheel Fasteners |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
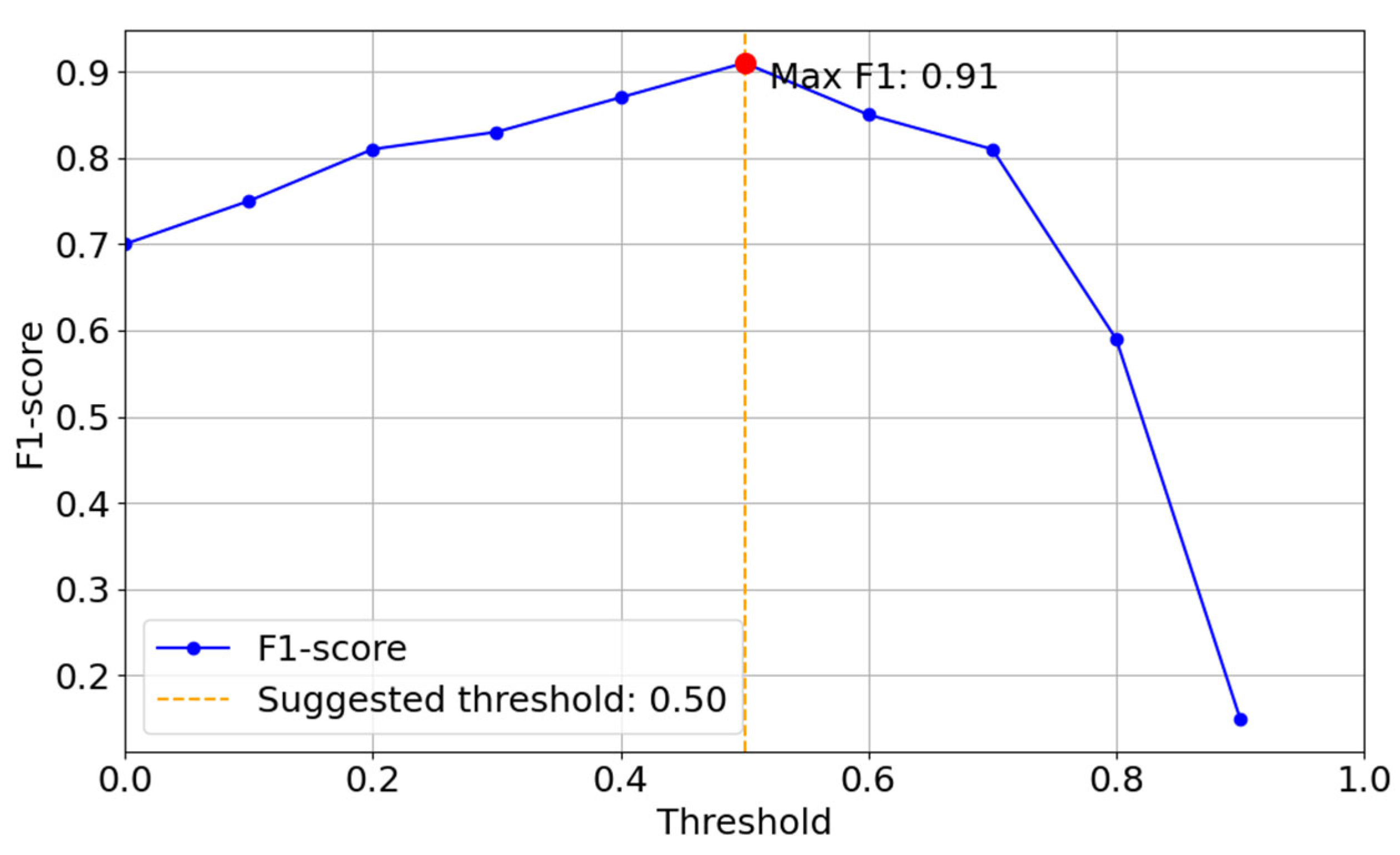
| Interactive point selection |  |  | 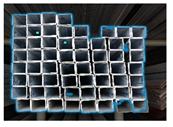 |  |  |  |
| Interactive box selection |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Automatic segmentation |  | 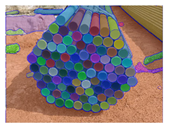 |  |  |  |  |
| Sample Image | EasyDL Model | Li’s Model |
|---|---|---|
 (Real number: 164) |  (False: 4, Missed: 10) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) |
 (Real number: 63) |  (False: 3, Missed: 0) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) |
 (Real number: 189) |  (False: 5, Missed: 2) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) |
 (Real number: 243) |  (False: 1, Missed: 13) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) |
| No. | Affected Metric | Impact Level | Root Cause Analysis | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | High | Color bias has a significant impact on accuracy, with a variance of 0.0127 across different feature ranges. | Configure “Color, Posterize” in [Add Data] → [Data Augmentation Strategy] for enhancement. |
| 2 | Accuracy | High | Color bias has a significant impact on miss rate, with a variance of 0.0127 across different feature ranges. | Configure “Color, Posterize” in [Add Data] → [Data Augmentation Strategy] for enhancement. |
| 3 | Accuracy | High | Saturation has a significant impact on accuracy, with a variance of 0.0123 across different feature ranges. | Configure “Color” in [Add Data] → [Data Augmentation Strategy] for enhancement. |
| 4 | Accuracy | High | Saturation has a significant impact on miss rate, with a variance of 0.0123 across different feature ranges. | Configure “Color” in [Add Data] → [Data Augmentation Strategy] for enhancement. |
| 5 | Accuracy | High | Target box size has a significant impact on accuracy, with a variance of 0.0116 across different feature ranges. | Try higher-precision models, or try small object detection or more optimization strategies in Baidu Machine Learning (BML). |
| Sample Image | EasyDL Model | Other’s Model |
|---|---|---|
 (Real number: 98) |  (False: 1, Missed: 12) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) |
 (Real number: 130) | (AP50: 86.85%) (False: 4, Missed: 8) (AP50: 90.54%) | (AP50: 93.01%) (False: 0, Missed: 0) (AP50: 91.41%) |
 (Real number: 55) |  (False: 4, Missed: 0) (AP50: 97.68%) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) (AP50: 99.48%) |
 (Real number: 99) |  (False: 8, Missed: 2) (AP50: 96.63%) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) (AP50: 97.06%) |
 (Real number: 36) |  (False: 1, Missed: 1) (AP50: 98.81%) |  (False: 0, Missed: 0) (AP50: 99.40%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, Q.; Fan, Z.; Chen, J. Large AI Models for Building Material Counting Task: A Comparative Study. Buildings 2025, 15, 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162900
Chen Y, Li Y, Liu S, Huang Q, Fan Z, Chen J. Large AI Models for Building Material Counting Task: A Comparative Study. Buildings. 2025; 15(16):2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162900
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yutao, Yang Li, Siyuan Liu, Qian Huang, Zekai Fan, and Jun Chen. 2025. "Large AI Models for Building Material Counting Task: A Comparative Study" Buildings 15, no. 16: 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162900
APA StyleChen, Y., Li, Y., Liu, S., Huang, Q., Fan, Z., & Chen, J. (2025). Large AI Models for Building Material Counting Task: A Comparative Study. Buildings, 15(16), 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162900







