Impact of Inorganic Salts on Rheology, Strength, and Microstructure of Excess-Sulfate Phosphogypsum Slag Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Mixture Design and Preparation Methods
2.2.1. Pretreatment of EPSC Raw Materials
2.2.2. Preparation of EPSC with Addition of Salts
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. pH Value
3.2. Rheological Properties
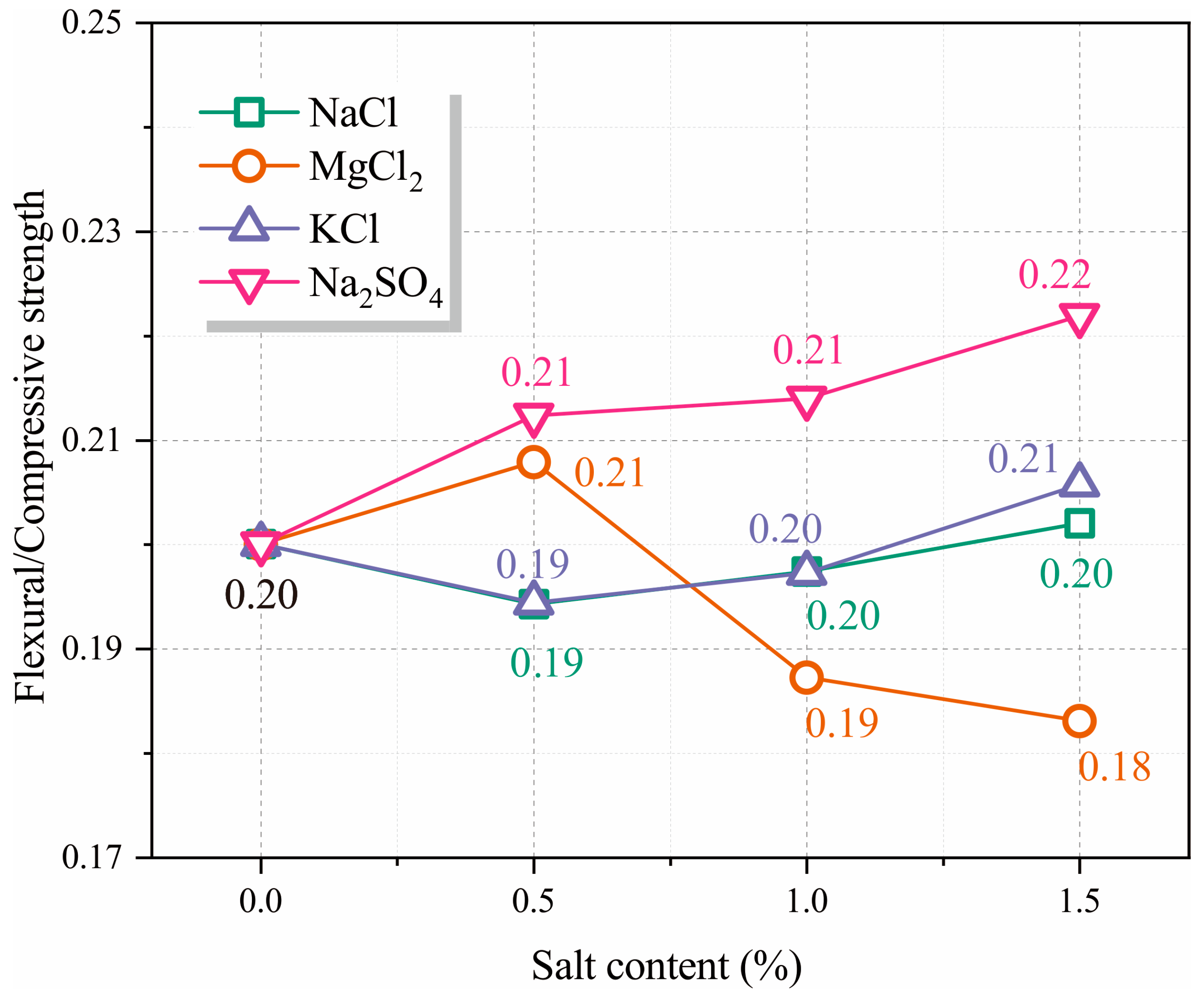
3.3. Flexural Strength and Compressive Strength
3.4. XRD Patterns
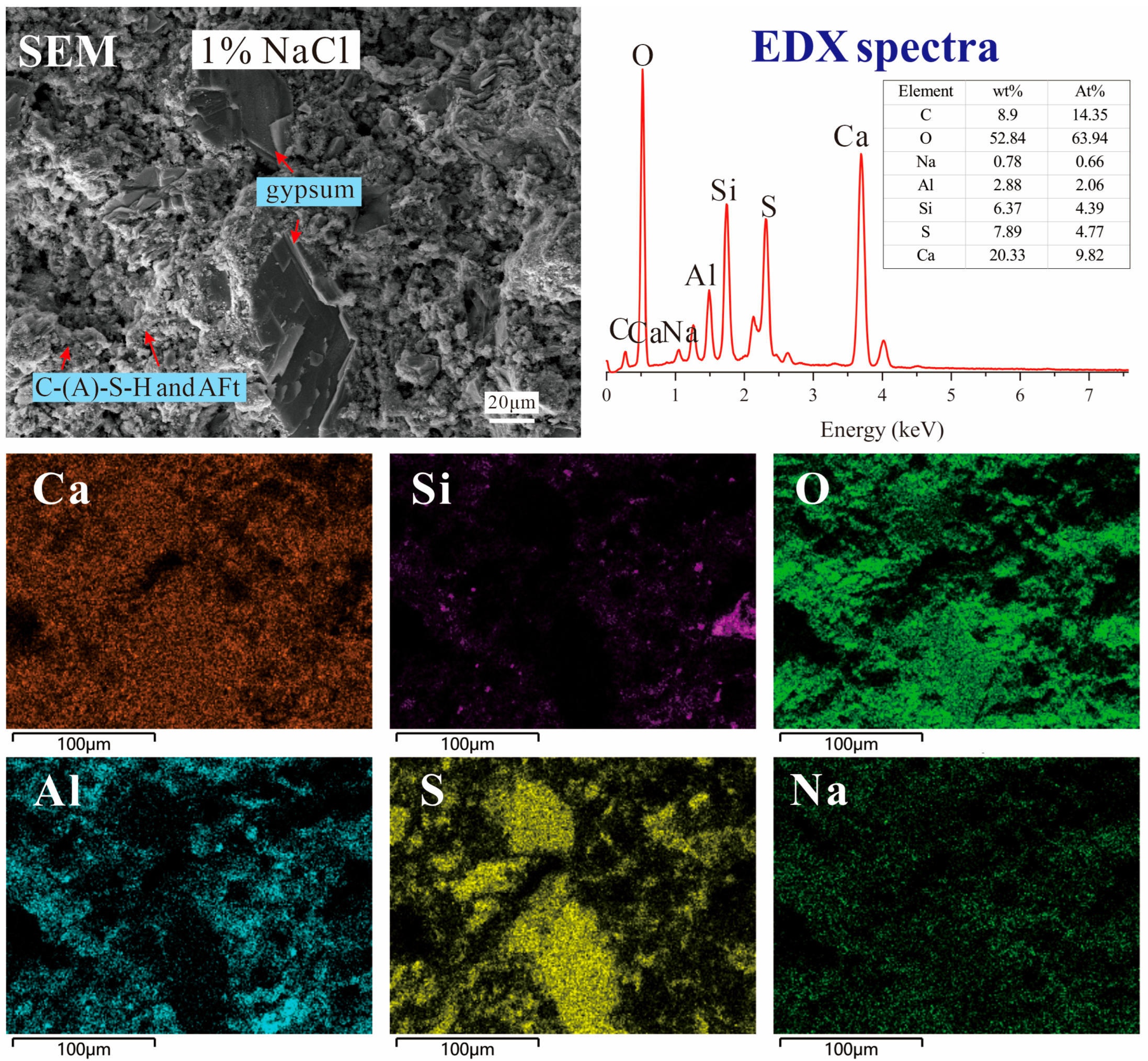
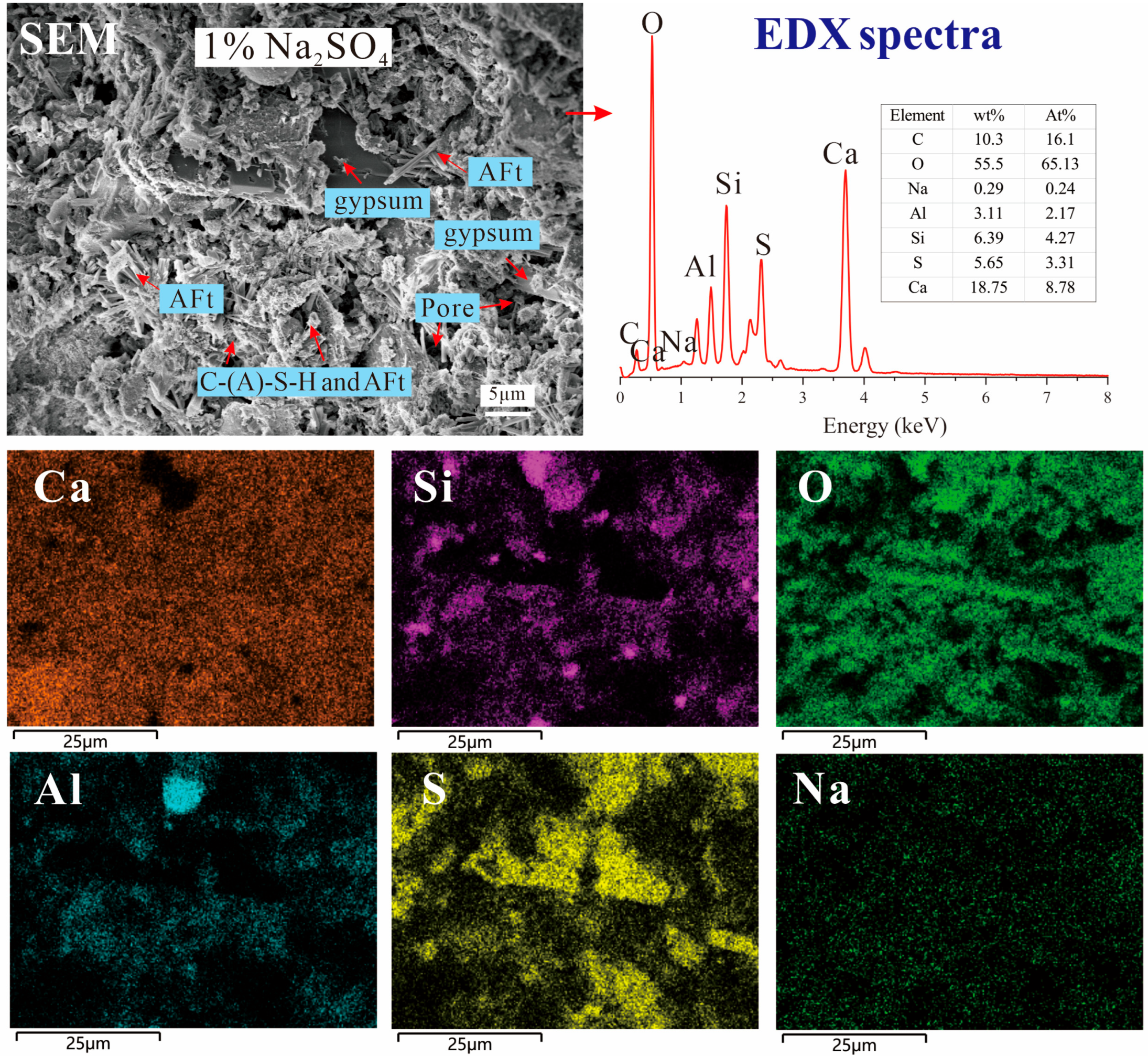
3.5. SEM Images and EDX Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPSC | excess-sulfate phosphogypsum slag cement |
| PG | phosphogypsum |
| GGBFS | ground granulated blast furnace slag |
| AFt | ettringite |
References
- Olivier, J.G.; Peters, J.A.; Janssens-Maenhout, G. Trends in Global CO2 Emissions: 2012 Report; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y. Comprehensive properties of passive film formed in simulated pore solution of alkali-activated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini, K.; Karthikeyan, J. Sustainable and greener concrete production by utilizing waste eggshell powder as cementitious material–A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 335, 127482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xie, J.; Xue, Z.; Huang, K.; Tan, J. Effects of recycled sand and nanomaterials on ultra-high performance concrete: Workability, compressive strength and microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 378, 131180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J. A state-of-the-art review on the setting behaviours of ground granulated blast furnace slag-and metakaolin-based alkali-activated materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Chen, B.; Pan, Y. Utilization of untreated-phosphogypsum as filling and binding material in preparing grouting materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masri, M.; Amin, Y.; Ibrahim, S.; Al-Bich, F. Distribution of some trace metals in Syrian phosphogypsum. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. Phosphogypsum as a construction material. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, O.; Abrantes, N.; Caetano, A.L.; Bouguerra, S.; Goncalves, F.; Römbke, J.; Pereira, R. Phosphogypsum as a soil fertilizer: Ecotoxicity of amended soil and elutriates to bacteria, invertebrates, algae and plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Gan, G.; Dong, R.; Chen, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, M. Utilization of solidified phosphogypsum as Portland cement retarder. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2012, 14, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huo, H.; Chen, B.; Cui, Q. Development and optimization of phosphogypsum-based geopolymer cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, N.; Jiang, Z. Utilization of waste phosphogypsum in high-strength geopolymer concrete: Performance optimization and mechanistic exploration. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xue, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Xie, J. Improving geopolymer concrete performance with hazardous solid waste phosphogypsum. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, B.; Xie, J.; Chen, C.; Tan, J.; Zhao, C. Effects of phosphogypsum substitution on the performance of ground granulated blast furnace slag/fly ash-based alkali-activated binders. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, F.; Li, B.; Sun, T.; Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Peng, C.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z. Investigation on mechanical properties of excess-sulfate phosphogypsum slag cement: From experiments to molecular dynamics simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Li, Z.; Sun, T.; Ye, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, W. Greener phosphogypsum-based all-solid-waste cementitious binder with steel slag activation: Hydration, mechanical properties and durability. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 140996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Deng, F.; Xu, K.; Dong, X.; Xu, D.; Liao, Y.; Tang, S. Effect of calcium sulfoaluminate cement on the hydration process and water resistance of phosphogypsum slag cement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 5375–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, T.; Yang, F.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Mechanical properties and soluble phosphorus solidification mechanism of a novel high amount phosphogypsum-based mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Shen, D.; Feng, Y.; Han, G.; An, X. Setting Time Optimization of Excessive-Sulfate Phosphogypsum Slag Cement for Self-Compacting Concrete Based on a Paste Rheological Threshold Theory. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04024285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, D.; Li, L.; Lin, M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of magnesium salt contamination on the microstructures and properties of metakaolinite-based geopolymer: The role of MgCl2 and MgSO4. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 4500–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xie, J. Seawater-mixed alkali-activated materials: A state-of-the-art review. J. Mater. Sci. 2025, 60, 2169–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jia, J.; Zhu, M. Development of admixtures on seawater sea sand concrete: A critical review on Concrete hardening, chloride ion penetration and steel corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tan, H.; Ni, J.; Ma, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Shi, T. Effect of barium ion on the stability and chloride ion binding of ettringite. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Tao, Y.; Xuan, D.; Sun, Y.; Poon, C.S. Effect of seawater on the morphology, structure, and properties of synthetic ettringite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 163, 107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.Z.Y.; Yi, Y. Durability of cementitious materials in seawater environment: A review on chemical interactions, hardened-state properties and environmental factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, V.J.; Dubberke, W.G. A different perspective for investigation of portland cement concrete pavement deterioration. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1525, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Sohn, D.; Jennings, H.; Mason, T. Hydration of alkali-activated ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.; Bai, Y.; Basheer, P.; Milestone, N.; Collier, N. Hydration and properties of sodium sulfate activated slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kroom, H.; Arif, M.A.; Saleh, A.A.; Shalaby, H.M.; Abd Elrahman, M.; Abdel-Gawwad, H.A. The role of nano magnesia in accelerating the early hydration rate of sodium sulfate activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, W.; Xue, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effects of pretreated recycled powder substitution on mechanical properties and microstructures of alkali-activated cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mu, M.; Liu, Y. Recycled cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, W.; Xu, F.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, G.; Xu, D. A new eco-friendly concrete made of high content phosphogypsum based aggregates and binder: Mechanical properties and environmental benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 7714-2015; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Z.; Sun, X.; Xing, J. Effect of sodium sulfate on the hydration and mechanical properties of lime-slag based eco-friendly binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, F.; Chidiac, S. Rheological models for predicting plastic viscosity and yield stress of fresh concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, G.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Nong, Y. Influence of flocculation structure on time-dependent fluidity and rheological property of cement paste: Analytical models based on fractal theory. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 455, 139137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, P.; Peng, H.; Fei, X. Rheology, mechanical properties, and hydration of synergistically activated coal gasification slag with three typical solid wastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 147, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, H.; Li, P. Effects of triisopropanol amine, sodium chloride and limestone on the compressive strength and hydration of Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.A.A.; Cordeiro, G.C.; Toledo Filho, R.D. Use of thermal analysis to determine the hydration products of oil well cement pastes containing NaCl and KCl. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 122, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Boul, P.; Jimenez, W.C. Isothermal calorimetry study of the effect of chloride accelerators on the hydration kinetics of oil well cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Blanco-Varela, M. Pore solution in alkali-activated slag cement pastes. Relation to the composition and structure of calcium silicate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bligh, M.W.; Shikhov, I.; Jones, A.M.; Holt, C.; Keyte, L.M.; Moghaddam, F.; Arns, C.H.; Foster, S.J.; Waite, T.D. A microstructural investigation of a Na2SO4 activated cement-slag blend. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 150, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Adesanya, E.; Ohenoja, K.; Kriskova, L.; Pontikes, Y.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Byproduct-based ettringite binder–a synergy between ladle slag and gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Tang, X.; Li, Y. Thermal activation of phosphorus slag. Cement 1991, 88, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Liu, S.; Ma, X.; Teng, Y.; Guan, X. Effect of different gypsum dosage on the chloride binding properties of C4AF hydrated paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Neubauer, J.; Schwesig, P. Mineralogical characteristics of Ettringites synthesized from solutions and suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

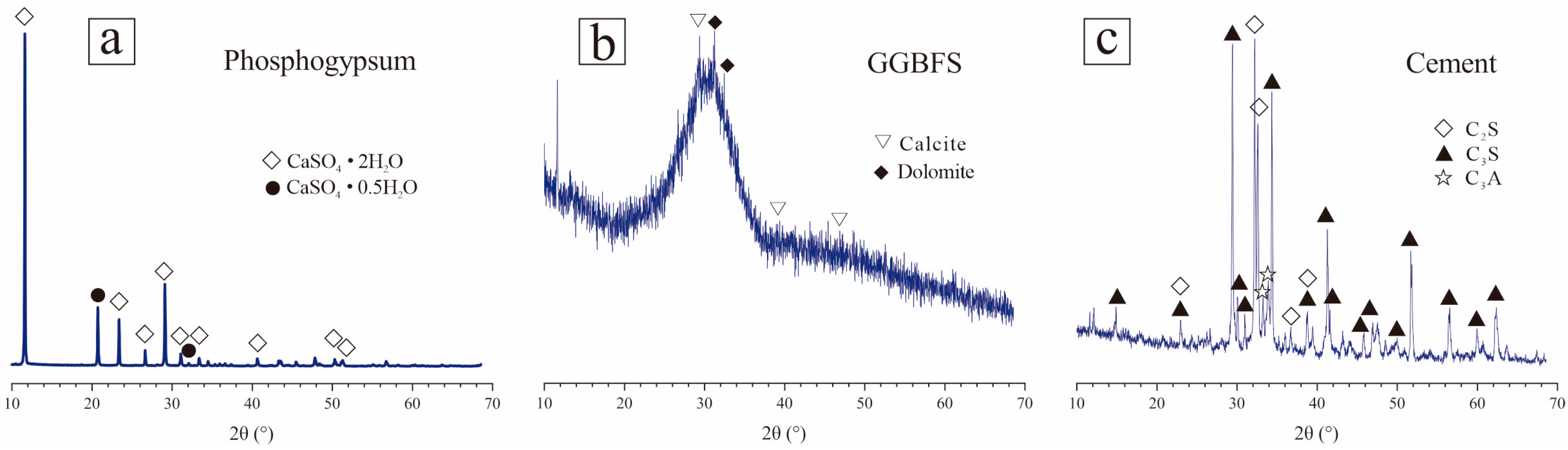


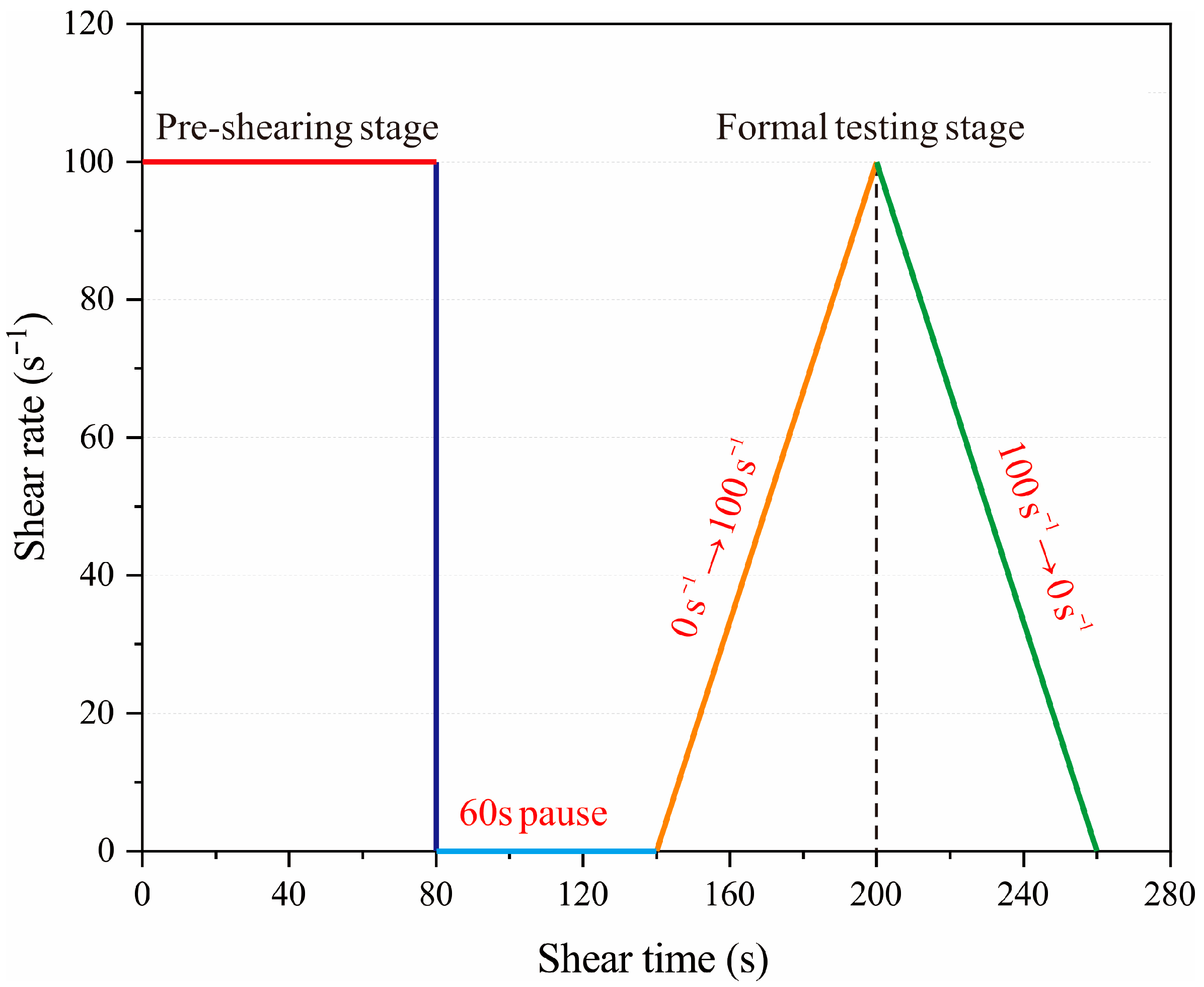
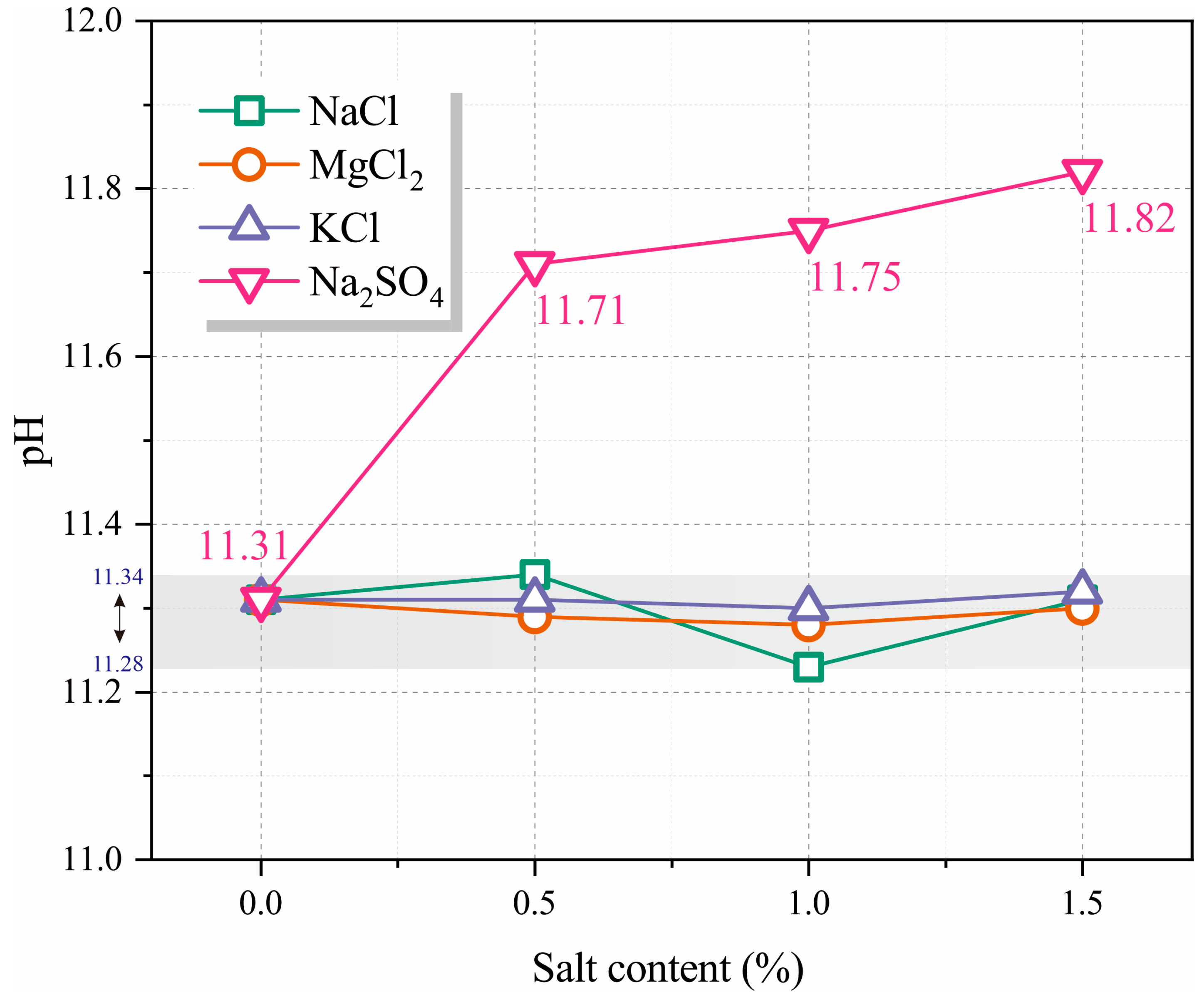

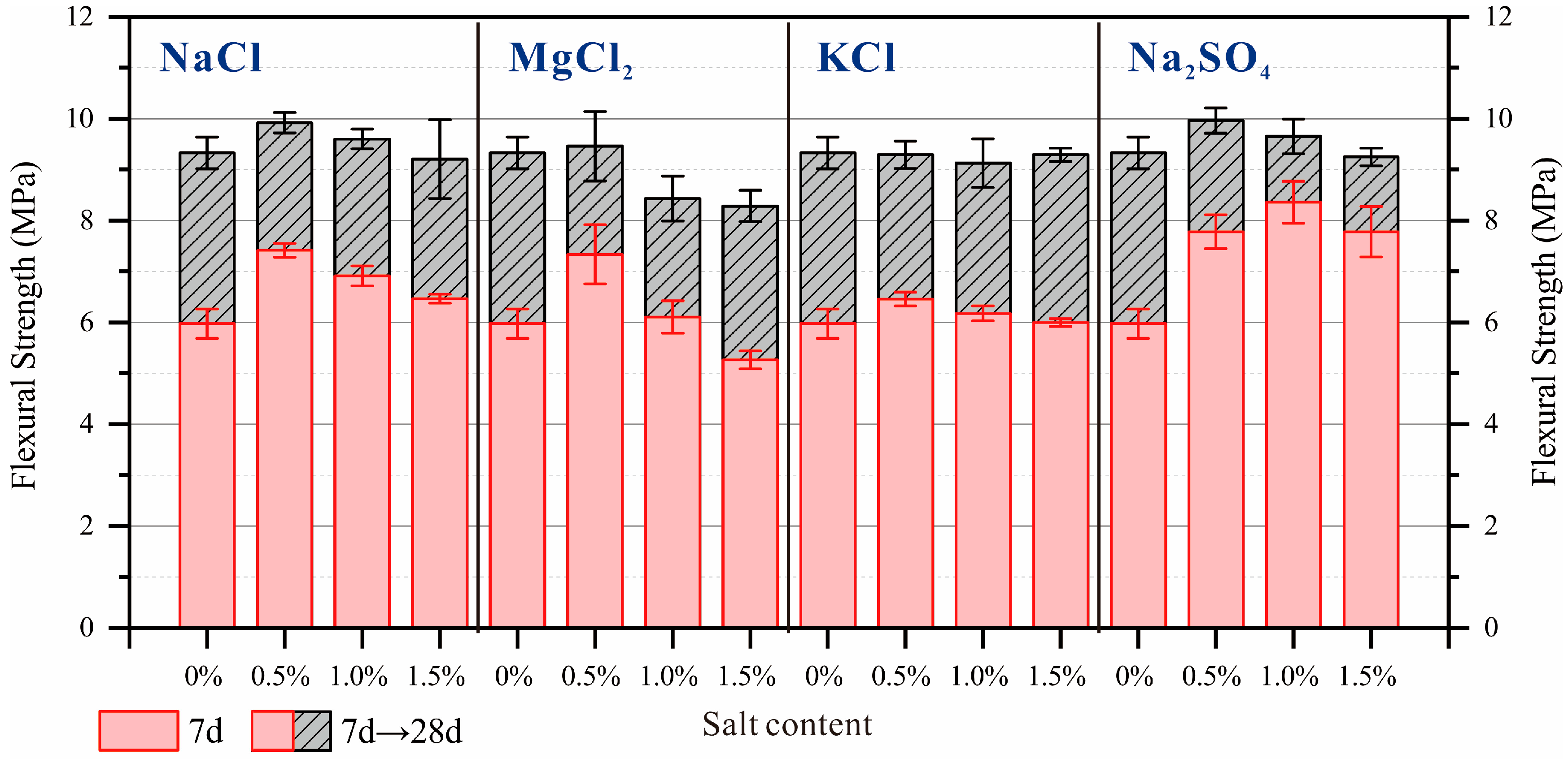



| Raw Material | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | MgO | Na2O | P2O5 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphogypsum | 42.9 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 50.5 | 0.4 | 0.04 | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| GGBFS | 42.7 | 29.6 | 13.7 | 0.6 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 7.3 | 0.02 | 2.6 |
| Cement | 76.2 | 11.5 | 2.5 | 3.9 | 3.8 | / | / | / | 2.1 |
| No. | Salt Type | Dosage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ref. | / | |
| NaCl-0.5% | NaCl | 0.5 |
| NaCl-1.0% | NaCl | 1.0 |
| NaCl-1.5% | NaCl | 1.5 |
| KCl-0.5% | KCl | 0.5 |
| KCl-1.0% | KCl | 1.0 |
| KCl-1.5% | KCl | 1.5 |
| MgCl2-0.5% | MgCl2 | 0.5 |
| MgCl2-1.0% | MgCl2 | 1.0 |
| MgCl2-1.5% | MgCl2 | 1.5 |
| Na2SO4-0.5% | Na2SO4 | 0.5 |
| Na2SO4-1.0% | Na2SO4 | 1.0 |
| Na2SO4-1.5% | Na2SO4 | 1.5 |
| No. | Time (min) | τ0 | η | c | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without salts | 0 | 28.14 | 0.045 | 0.003 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 28.80 | 0.065 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 10 | 29.46 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 15 | 29.98 | 0.081 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 20 | 30.35 | 0.091 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 25 | 30.66 | 0.105 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 30 | 30.83 | 0.114 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| NaCl-1.0% | 0 | 29.34 | 0.076 | 0.003 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 29.89 | 0.104 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 10 | 30.31 | 0.115 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 15 | 30.59 | 0.126 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 20 | 30.95 | 0.134 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 25 | 31.27 | 0.139 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| 30 | 31.32 | 0.151 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| KCl-1.0% | 0 | 29.03 | 0.077 | 0.003 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 26.93 | 0.081 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 10 | 25.64 | 0.083 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 15 | 24.94 | 0.086 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 20 | 24.45 | 0.087 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 25 | 24.14 | 0.085 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 30 | 23.91 | 0.087 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| MgCl2-1.0% | 0 | 26.59 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 25.81 | 0.033 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 10 | 25.62 | 0.031 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 15 | 25.29 | 0.048 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 20 | 25.51 | 0.036 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 25 | 25.28 | 0.046 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| 30 | 25.35 | 0.044 | 0.003 | 0.99 | |
| Na2SO4-1.0% | 0 | 31.48 | 0.120 | 0.003 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 32.13 | 0.141 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| 10 | 32.49 | 0.161 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| 15 | 32.88 | 0.177 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| 20 | 33.12 | 0.191 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| 25 | 33.40 | 0.199 | 0.002 | 0.99 | |
| 30 | 33.62 | 0.208 | 0.002 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Xue, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wu, C.; Mai, J.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J. Impact of Inorganic Salts on Rheology, Strength, and Microstructure of Excess-Sulfate Phosphogypsum Slag Cement. Buildings 2025, 15, 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132348
Chen Z, Xue Z, Xia Y, Wu C, Mai J, Liu W, Feng Y, Xie J. Impact of Inorganic Salts on Rheology, Strength, and Microstructure of Excess-Sulfate Phosphogypsum Slag Cement. Buildings. 2025; 15(13):2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132348
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhe, Zixin Xue, Yong Xia, Chunli Wu, Junming Mai, Weisen Liu, Yuan Feng, and Jianhe Xie. 2025. "Impact of Inorganic Salts on Rheology, Strength, and Microstructure of Excess-Sulfate Phosphogypsum Slag Cement" Buildings 15, no. 13: 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132348
APA StyleChen, Z., Xue, Z., Xia, Y., Wu, C., Mai, J., Liu, W., Feng, Y., & Xie, J. (2025). Impact of Inorganic Salts on Rheology, Strength, and Microstructure of Excess-Sulfate Phosphogypsum Slag Cement. Buildings, 15(13), 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132348






